Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass and Caloric Restriction but Not Gut Hormone-Based Treatments Profoundly Impact the Hypothalamic Transcriptome in Obese Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Drugs
2.3. Surgeries
2.4. Extraction of mRNA
2.5. RNA Sequencing
2.6. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.7. Blood Sampling and Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
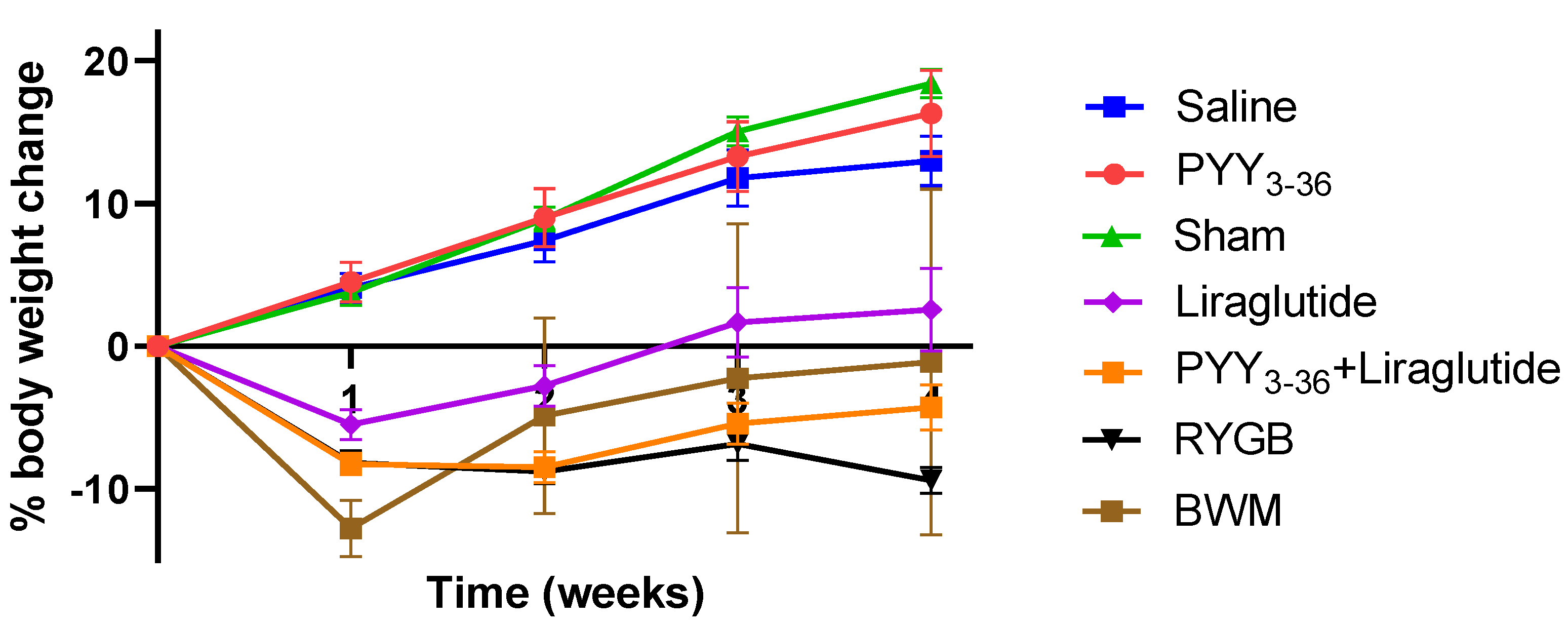
3.1. RYGB and PYY3-36 + Liraglutide Lead to Similar Changes in Body Weight
3.2. RYGB and PYY3-36 + Liraglutide Lower Overall Food Intake and Preference for High Fat Diet
3.3. RYGB and PYY3-36 + Liraglutide Increase Plasma Levels of GLP-1
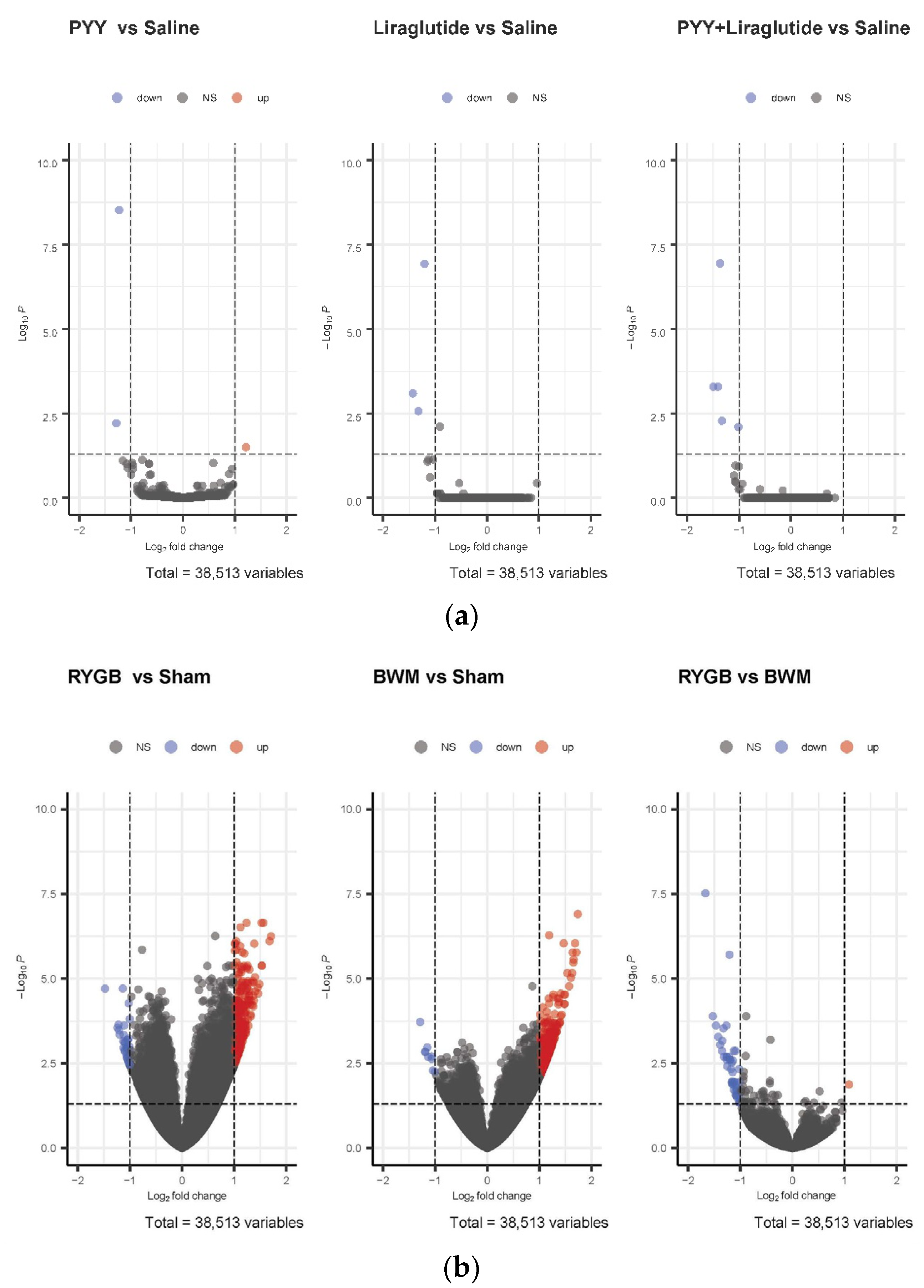
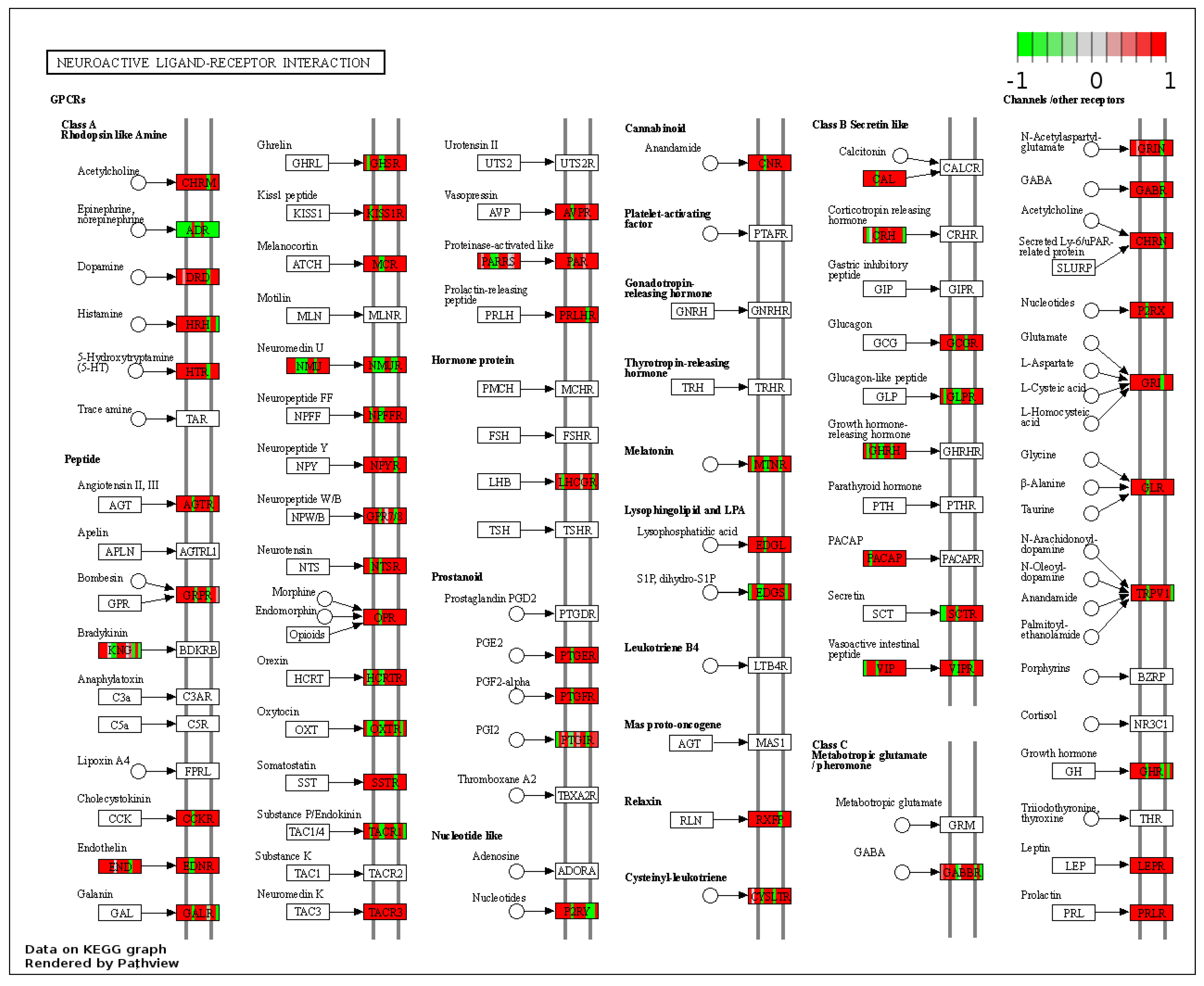
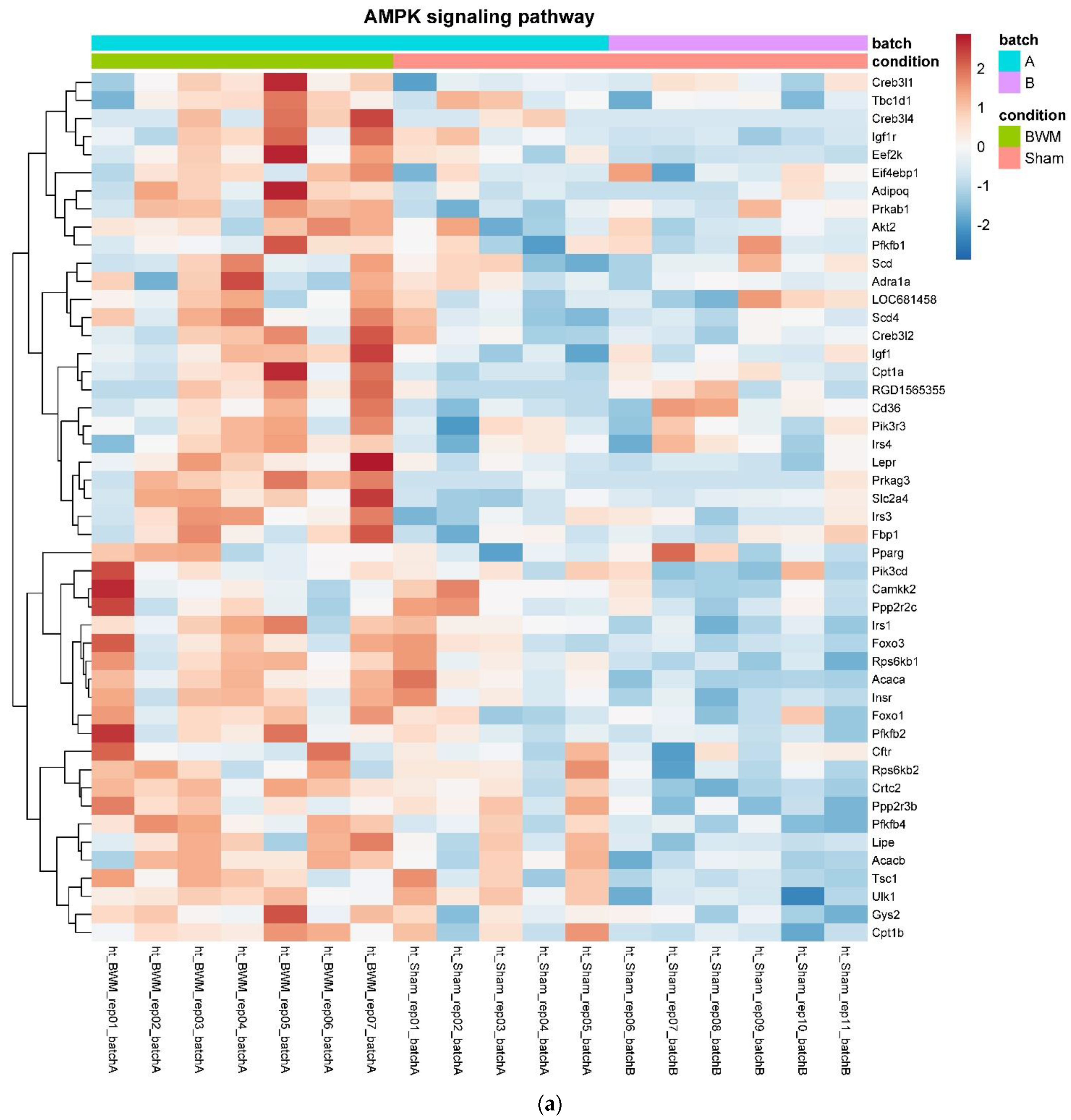
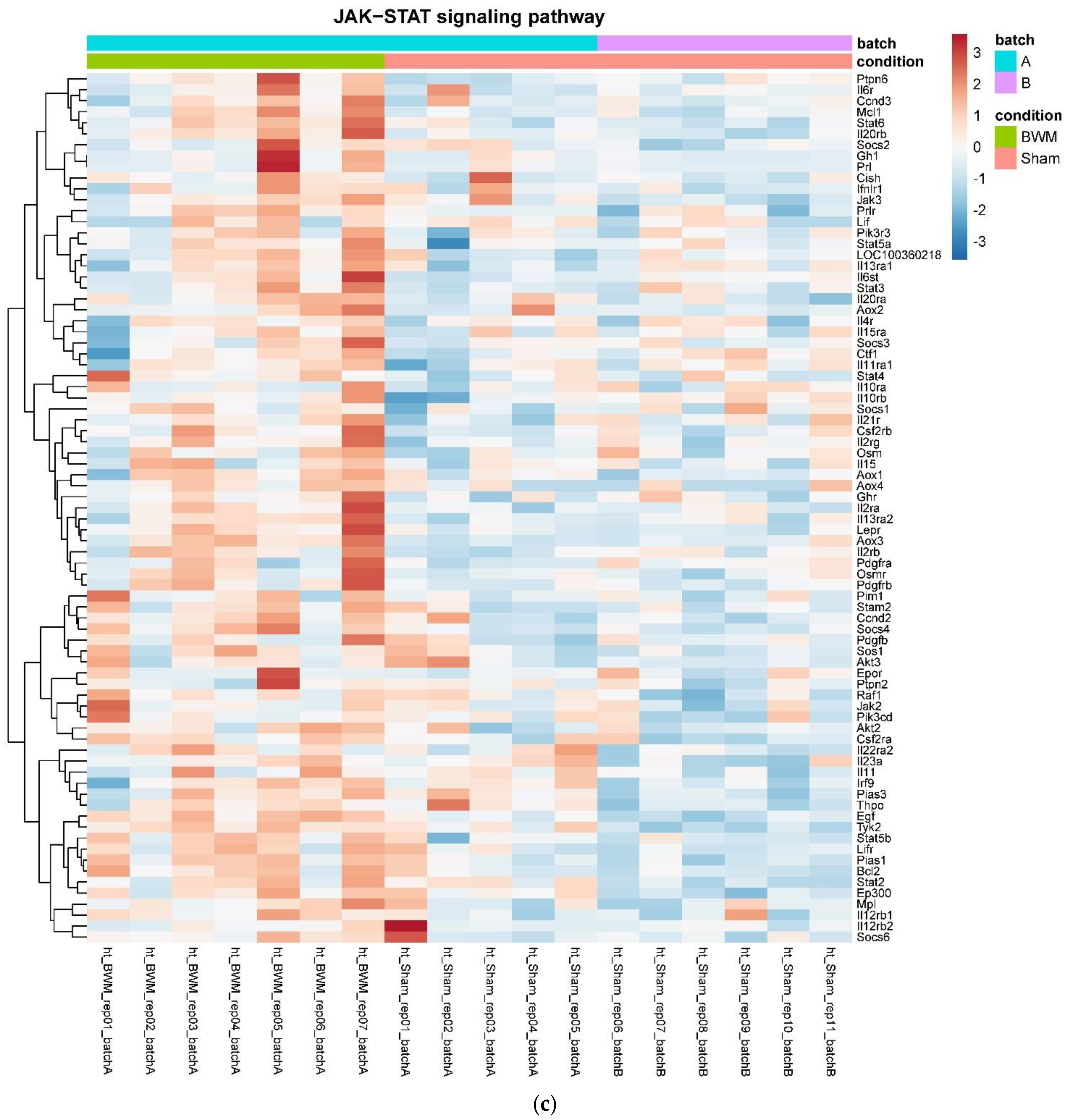
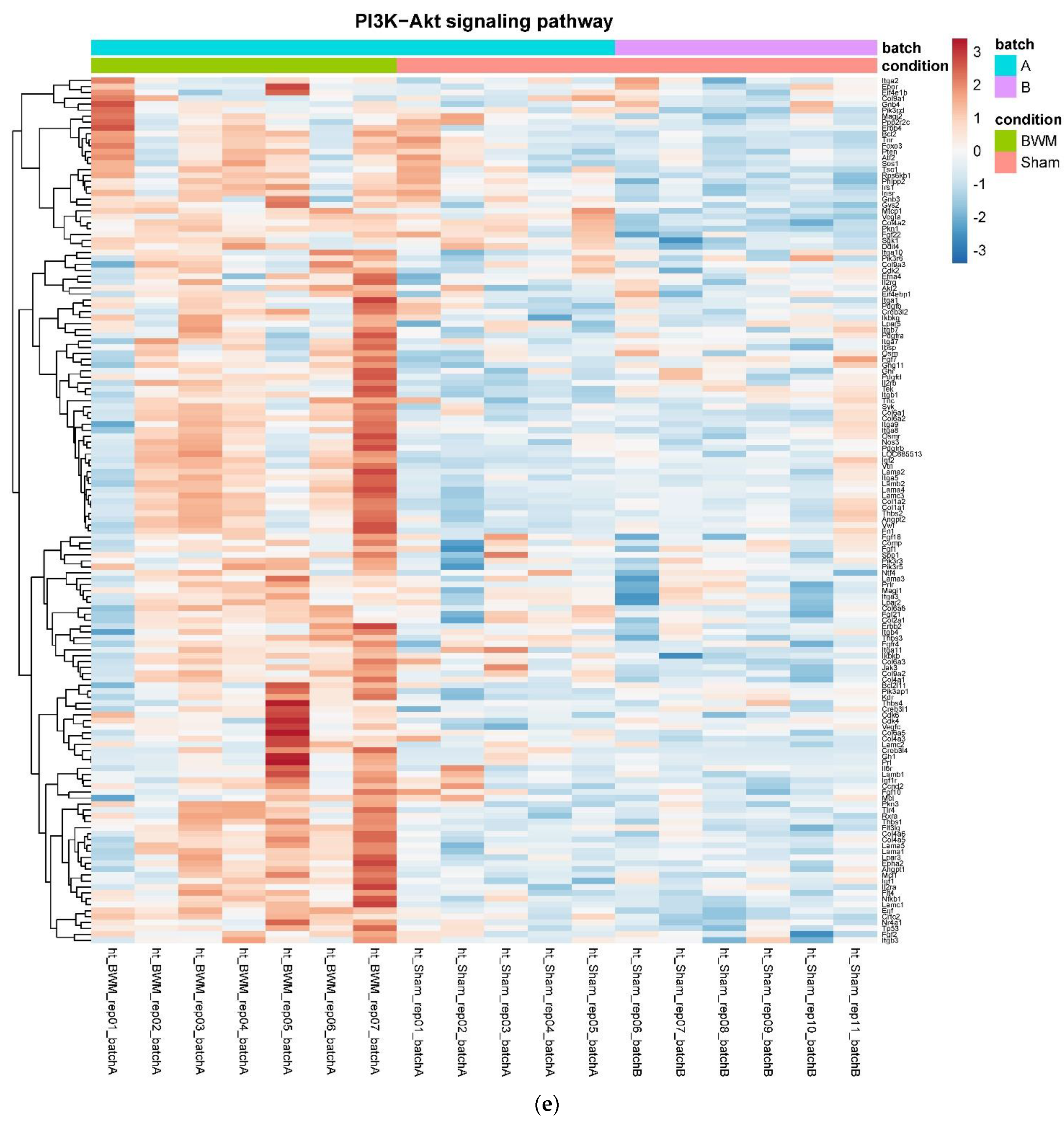
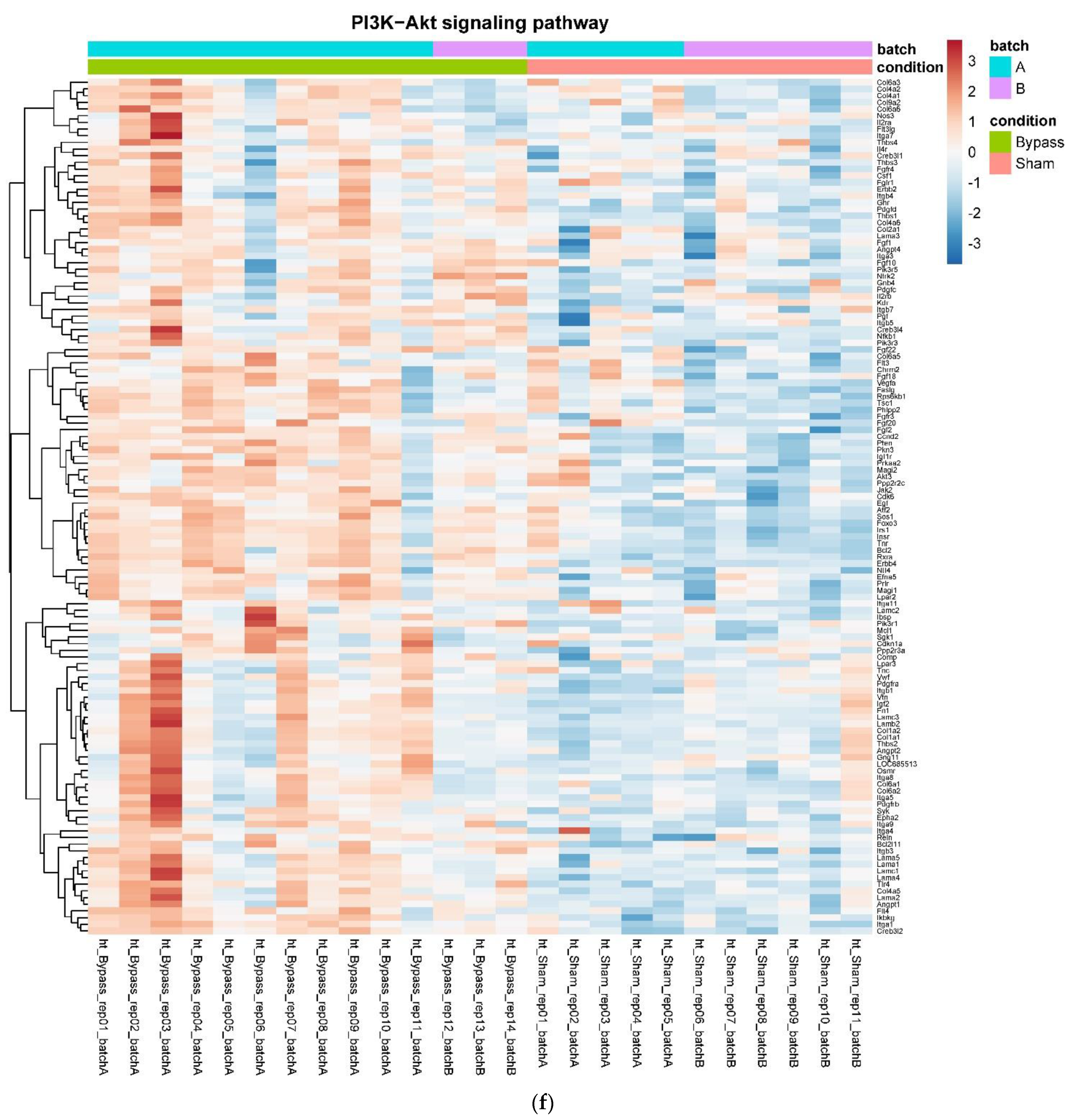
3.4. Only RYGB and Food Restriction Impact Hypothalamic mRNA Expression
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, D.D.; Basu, A. Estimating the Medical Care Costs of Obesity in the United States: Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Empirical Analysis. Value Health 2016, 19, 602–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GBD 2015 Obesity Collaborators; Afshin, A.; Forouzanfar, M.H.; Reitsma, M.B.; Sur, P.; Estep, K.; Lee, A.; Marczak, L.; Mokdad, A.H.; Moradi-Lakeh, M.; et al. Health Effects of Overweight and Obesity in 195 Countries over 25 Years. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, Z.J.; Bleich, S.N.; Cradock, A.L.; Barrett, J.L.; Giles, C.M.; Flax, C.; Long, M.W.; Gortmaker, S.L.; Projected, U.S. State-Level Prevalence of Adult Obesity and Severe Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 2440–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, E.P.; Mesidor, M.; Winters, K.; Dubbert, P.M.; Wyatt, S.B. Overweight and Obesity: Prevalence, Consequences, and Causes of a Growing Public Health Problem. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2015, 4, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schauer, P.R.; Bhatt, D.L.; Kirwan, J.P.; Wolski, K.; Aminian, A.; Brethauer, S.A.; Navaneethan, S.D.; Singh, R.P.; Pothier, C.E.; Nissen, S.E.; et al. Bariatric Surgery versus Intensive Medical Therapy for Diabetes—5-Year Outcomes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingrone, G.; Panunzi, S.; De Gaetano, A.; Guidone, C.; Iaconelli, A.; Nanni, G.; Castagneto, M.; Bornstein, S.; Rubino, F. Bariatric-metabolic surgery versus conventional medical treatment in obese patients with type 2 diabetes: 5 year follow-up of an open-label, single-centre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2015, 386, 964–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, D.E.; Arterburn, D.E.; Westbrook, E.O.; Kuzma, J.N.; Stewart, S.D.; Chan, C.P.; Bock, S.N.; Landers, J.T.; Kratz, M.; Foster-Schubert, K.E.; et al. Gastric bypass surgery vs intensive lifestyle and medical intervention for type 2 diabetes: The CROSSROADS randomised controlled trial. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjostrom, L.; Peltonen, M.; Jacobson, P.; Sjostrom, C.D.; Karason, K.; Wedel, H.; Ahlin, S.; Anveden, A.; Bengtsson, C.; Bergmark, G.; et al. Bariatric surgery and long-term cardiovascular events. JAMA 2012, 307, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olbers, T.; Bjorkman, S.; Lindroos, A.; Maleckas, A.; Lonn, L.; Sjostrom, L.; Lönroth, H. Body composition, dietary intake, and energy expenditure after laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and laparoscopic vertical banded gastroplasty: A randomized clinical trial. Ann. Surg. 2006, 244, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coluzzi, I.; Raparelli, L.; Guarnacci, L.; Paone, E.; Del Genio, G.; le Roux, C.W.; Silecchia, G. Food Intake and Changes in Eating Behavior After Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy. Obes. Surg. 2016, 26, 2059–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, E.K.; Settle, E.A.; Van Rij, A.M. Food intake patterns of gastric bypass patients. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 1982, 80, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurenius, A.; Larsson, I.; Melanson, K.J.; Lindroos, A.K.; Lonroth, H.; Bosaeus, I.; Olbers, T. Decreased energy density and changes in food selection following Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 67, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenler, H.A.; Brolin, R.E.; Cody, R.P. Changes in eating behavior after horizontal gastroplasty and Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1990, 52, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavaresco, M.; Paganini, S.; Lima, T.P.; Salgado, W.; Ceneviva, R., Jr.; Dos Santos, J.E.; Nonino-Borges, C.B. Nutritional course of patients submitted to bariatric surgery. Obes. Surg. 2010, 20, 716–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coughlin, K.; Bell, R.M.; Bivins, B.A.; Wrobel, S.; Griffen, W.O., Jr. Preoperative and postoperative assessment of nutrient intakes in patients who have undergone gastric bypass surgery. Arch. Surg. 1983, 118, 813–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giusti, V.; Theytaz, F.; Di Vetta, V.; Clarisse, M.; Suter, M.; Tappy, L. Energy and macronutrient intake after gastric bypass for morbid obesity: A 3-y observational study focused on protein consumption. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruseman, M.; Leimgruber, A.; Zumbach, F.; Golay, A. Dietary, weight, and psychological changes among patients with obesity, 8 years after gastric bypass. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2010, 110, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurenius, A.; Larsson, I.; Bueter, M.; Melanson, K.J.; Bosaeus, I.; Forslund, H.B.; Lönroth, H.; Fändriks, L.; Olbers, T. Changes in eating behaviour and meal pattern following Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Int. J. Obes. 2012, 36, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, G.D.; Norris, A.; Fernandez, A. Changes in nutrients and food groups intake following laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB). Obes. Surg. 2014, 24, 1926–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MolinNetto, B.D.; Earthman, C.P.; Farias, G.; LandiMasquio, D.C.; Grotti Clemente, A.P.; Peixoto, P.; Cravo Bettini, S.; von Der Heyde, M.E.; Damaso, A.R. Eating patterns and food choice as determinant of weight loss and improvement of metabolic profile after RYGB. Nutrition 2017, 33, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjostrom, L.; Lindroos, A.K.; Peltonen, M.; Torgerson, J.; Bouchard, C.; Carlsson, B.; Dahlgren, S.; Larsson, B.; Narbo, K.; Sjöström, C.D.; et al. Lifestyle, diabetes, and cardiovascular risk factors 10 years after bariatric surgery. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 2683–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brolin, R.E.; Robertson, L.B.; Kenler, H.A.; Cody, R.P. Weight loss and dietary intake after vertical banded gastroplasty and Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Ann. Surg. 1994, 220, 782–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- le Roux, C.W.; Bueter, M.; Theis, N.; Werling, M.; Ashrafian, H.; Lowenstein, C.; Athanasiou, T.; Bloom, S.R.; Spector, A.C.; Olbers, T.; et al. Gastric bypass reduces fat intake and preference. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2011, 301, R1057–R1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trostler, N.; Mann, A.; Zilberbush, N.; Avinoach, E.; Charuzi, I. Weight Loss and Food Intake 18 Months following Vertical Banded Gastroplasty or Gastric Bypass for Severe Obesity. Obes. Surg. 1995, 5, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korner, J.; Bessler, M.; Cirilo, L.J.; Conwell, I.M.; Daud, A.; Restuccia, N.L.; Wardlaw, S.L. Effects of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery on fasting and postprandial concentrations of plasma ghrelin, peptide YY, and insulin. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, J.L.; Mun, E.C.; Stoyneva, V.; Mantzoros, C.S.; Goldfine, A.B. Peptide YY levels are elevated after gastric bypass surgery. Obesity 2006, 14, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korner, J.; Inabnet, W.; Conwell, I.M.; Taveras, C.; Daud, A.; Olivero-Rivera, L.; Restuccia, N.L.; Bessler, M. Differential effects of gastric bypass and banding on circulating gut hormone and leptin levels. Obesity 2006, 14, 1553–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- le Roux, C.W.; Aylwin, S.J.; Batterham, R.L.; Borg, C.M.; Coyle, F.; Prasad, V.; Shurey, S.; Ghatei, M.A.; Patel, A.G.; Bloom, S.R. Gut hormone profiles following bariatric surgery favor an anorectic state, facilitate weight loss, and improve metabolic parameters. Ann. Surg. 2006, 243, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morinigo, R.; Moize, V.; Musri, M.; Lacy, A.M.; Navarro, S.; Marin, J.L.; Delgado, S.; Casamitjana, R.; Vidal, J. Glucagon-like peptide-1, peptide YY, hunger, and satiety after gastric bypass surgery in morbidly obese subjects. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 1735–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morinigo, R.; Vidal, J.; Lacy, A.M.; Delgado, S.; Casamitjana, R.; Gomis, R. Circulating peptide YY, weight loss, and glucose homeostasis after gastric bypass surgery in morbidly obese subjects. Ann. Surg. 2008, 247, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivan, B.; Teixeira, J.; Bose, M.; Bawa, B.; Chang, T.; Summe, H.; Lee, H.; Laferrere, B. Effect of weight loss by diet or gastric bypass surgery on peptide YY3-36 levels. Ann. Surg. 2009, 249, 948–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bose, M.; Machineni, S.; Olivan, B.; Teixeira, J.; McGinty, J.J.; Bawa, B.; Koshy, N.; Colarusso, A.; Laferrere, B. Superior appetite hormone profile after equivalent weight loss by gastric bypass compared to gastric banding. Obesity 2010, 18, 1085–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, S.H.; Olesen, S.C.; Dirksen, C.; Jorgensen, N.B.; Bojsen-Moller, K.N.; Kielgast, U.; Worm, D.; Aldmal, T.; Naver, L.S.; Hvolris, L.E.; et al. Changes in gastrointestinal hormone responses, insulin sensitivity, and beta-cell function within 2 weeks after gastric bypass in non-diabetic subjects. Obes. Surg. 2012, 22, 1084–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousseif, A.; Emmanuel, J.; Karra, E.; Millet, Q.; Elkalaawy, M.; Jenkinson, A.D.; Hashemi, M.; Adamo, M.; Finer, N.; Fiennes, A.G.; et al. Differential effects of laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy and laparoscopic gastric bypass on appetite, circulating acyl-ghrelin, peptide YY3-36 and active GLP-1 levels in non-diabetic humans. Obes. Surg. 2014, 24, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dischinger, U.; Hasinger, J.; Konigsrainer, M.; Corteville, C.; Otto, C.; Fassnacht, M.; Hankir, M.; Seyfried, F.J.D. Toward a Medical Gastric Bypass: Chronic Feeding Studies with Liraglutide + PYY3-36 Combination Therapy in Diet-Induced Obese Rats. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 598843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dischinger, U.; Corteville, C.; Otto, C.; Fassnacht, M.; Seyfried, F.; Hankir, M.K. GLP-1 and PYY3-36 reduce high-fat food preference additively after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass in diet-induced obese rats. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2019, 15, 1483–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Hao, Z.; Mumphrey, M.B.; Townsend, R.L.; Patterson, L.M.; Stylopoulos, N.; Münzberg, H.; Morrison, C.D.; Drucker, D.J.; Berthoud, H.-R. GLP-1 receptor signaling is not required for reduced body weight after RYGB in rodents. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2014, 306, R352–R362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmody, J.S.; Munoz, R.; Yin, H.; Kaplan, L.M. Peripheral, but not central, GLP-1 receptor signaling is required for improvement in glucose tolerance after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 310, E855–E861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokadem, M.; Zechner, J.F.; Margolskee, R.F.; Drucker, D.J.; Aguirre, V. Effects of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass on energy and glucose homeostasis are preserved in two mouse models of functional glucagon-like peptide-1 deficiency. Mol. Metab. 2014, 3, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boland, B.; Mumphrey, M.B.; Hao, Z.; Gill, B.; Townsend, R.L.; Yu, S.; Münzberg, H.; Morrison, D.C.; Trevaskis, J.L.; Berthoud, H.-R. The PYY/Y2R-Deficient Mouse Responds Normally to High-Fat Diet and Gastric Bypass Surgery. Nutrients 2019, 11, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svane, M.S.; Jorgensen, N.B.; Bojsen-Moller, K.N.; Dirksen, C.; Nielsen, S.; Kristiansen, V.B.; Toräng, S.; Wewer Albrechtsen, N.J.; Rehfeld, J.F.; Hartmann, B.; et al. Peptide YY and glucagon-like peptide-1 contribute to decreased food intake after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery. Int. J. Obes. 2016, 40, 1699–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behary, P.; Tharakan, G.; Alexiadou, K.; Johnson, N.; WewerAlbrechtsen, N.J.; Kenkre, J.; Cuenco, J.; Hope, D.; Anyiam, O.; Chodhury, S.; et al. Combined GLP-1, Oxyntomodulin, and Peptide YY Improves Body Weight and Glycemia in Obesity and Prediabetes/Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized, Single-Blinded, Placebo-Controlled Study. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 1446–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perakakis, N.; Kokkinos, A.; Peradze, N.; Tentolouris, N.; Ghaly, W.; Pilitsi, E.; Upadhyay, J.; Alexandrou, A.; Mantzoros, C.S. Circulating levels of gastrointestinal hormones in response to the most common types of bariatric surgery and predictive value for weight loss over one year: Evidence from two independent trials. Metabolism 2019, 101, 153997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holdstock, C.; Zethelius, B.; Sundbom, M.; Karlsson, F.A.; Eden Engstrom, B. Postprandial changes in gut regulatory peptides in gastric bypass patients. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32, 1640–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Christ-Crain, M.; Stoeckli, R.; Ernst, A.; Morgenthaler, N.G.; Bilz, S.; Korbonits, M.; Struck, J.; Bergmann, A.; Müller, B.; Keller, U. Effect of gastric bypass and gastric banding on proneurotensin levels in morbidly obese patients. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 3544–3547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratner, C.; He, Z.; Grunddal, K.V.; Skov, L.J.; Hartmann, B.; Zhang, F.; Feuchtinger, A.; Bjerregaard, A.; Christoffersen, C.; Tschöp, M.H.; et al. Long-Acting Neurotensin Synergizes with Liraglutide to Reverse Obesity Through a Melanocortin-Dependent Pathway. Diabetes 2019, 68, 1329–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, O.; Kim, K.W.; Kim, M.S. Leptin signalling pathways in hypothalamic neurons. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 1457–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, C.F.; Aschkenasi, C.; Lee, C.; Kelly, J.; Ahima, R.S.; Bjorbaek, C.; Flier, J.S.; Saper, C.B.; Elmquist, J.K. Leptin differentially regulates NPY and POMC neurons projecting to the lateral hypothalamic area. Neuron 1999, 23, 775–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkholt, P.; Rigbolt, K.T.G.; Falkenhahn, M.; Hubschle, T.; Schwahn, U.; Fernandez-Cachon, M.L.; Schmidt, T.; Theis, S.; Hansen, H.H.; Hay-Schmidt, A.; et al. Global transcriptome analysis of rat hypothalamic arcuate nucleus demonstrates reversal of hypothalamic gliosis following surgically and diet induced weight loss. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diane, A.; Pierce, W.D.; Mangat, R.; Borthwick, F.; Nelson, R.; Russell, J.C.; Heth, C.D.; Jacobs, R.L.; Vine, D.F.; Proctor, S.D. Differential expression of hypothalamic, metabolic and inflammatory genes in response to short-term calorie restriction in juvenile obese- and lean-prone JCR rats. Nutr. Diabetes 2015, 5, e178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Barkholt, P.; Pedersen, P.J.; Hay-Schmidt, A.; Jelsing, J.; Hansen, H.H.; Vrang, N. Alterations in hypothalamic gene expression following Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Mol. Metab. 2016, 5, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Secher, A.; Jelsing, J.; Baquero, A.F.; Hecksher-Sorensen, J.; Cowley, M.A.; Dalboge, L.S.; Hansen, G.; Grove, K.L.; Pyke, C.; Raun, K.; et al. The arcuate nucleus mediates GLP-1 receptor agonist liraglutide-dependent weight loss. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 4473–4488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalboge, L.S.; Pedersen, P.J.; Hansen, G.; Fabricius, K.; Hansen, H.B.; Jelsing, J.; Vrang, N. A Hamster Model of Diet-Induced Obesity for Preclinical Evaluation of Anti-Obesity, Anti-Diabetic and Lipid Modulating Agents. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, A.A.; Milardo, L.F.; DeCarr, L.B.; Buckholz, T.M.; Mays, M.R.; Claus, T.H.; Livingston, J.N.; Mahle, C.D.; Lumb, K.J. A novel long-acting selective neuropeptide Y2 receptor polyethylene glycol-conjugated peptide agonist reduces food intake and body weight and improves glucose metabolism in rodents. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2007, 323, 692–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyfried, F.; Bueter, M.; Spliethoff, K.; Miras, A.D.; Abegg, K.; Lutz, T.A.; le Roux, C.W. Roux-en Y gastric bypass is superior to duodeno-jejunal bypass in improving glycaemic control in Zucker diabetic fatty rats. Obes. Surg. 2014, 24, 1888–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte, A.; Bieniussa, L.; Gupta, R.; Samtleben, S.; Bischler, T.; Doering, K.; Sodmann, P.; Rittner, H.; Blum, R. Homeostatic calcium fluxes, ER calcium release, SOCE, and calcium oscillations in cultured astrocytes are interlinked by a small calcium toolkit. Cell Calcium 2021, 101, 102515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: Ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. featureCounts: An efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.G.; Han, Y.; He, Q.Y. clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. Omics 2012, 16, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, Z.; Lu, D.; Li, T.; Ding, Y.; Ruan, Y.; Xu, A. The Neuroprotection of Liraglutide Against Ischaemia-induced Apoptosis through the Activation of the PI3K/AKT and MAPK Pathways. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.; Sands, C.; Alexiadou, K.; Minnion, J.; Tharakan, G.; Behary, P.; Ahmed, A.R.; Purkayastha, S.; Lewis, M.R.; Bloom, S.; et al. The metabolomic effects of tripeptide gut hormone infusion compared to Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and caloric restriction. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyfried, F.; Phetcharaburanin, J.; Glymenaki, M.; Nordbeck, A.; Hankir, M.; Nicholson, J.K.; Holmes, E.; Marchesi, J.R.; Li, J.V. Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery in Zucker rats induces bacterial and systemic metabolic changes independent of caloric restriction-induced weight loss. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1875108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obradovic, M.; Sudar-Milovanovic, E.; Soskic, S.; Essack, M.; Arya, S.; Stewart, A.J.; Gojobori, T.; Isenovic, E.R. Leptin and Obesity: Role and Clinical Implication. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 585887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Haase, N.; Haange, S.B.; Sucher, R.; Munzker, J.; Jager, E.; Schischke, K.; Seyfried, F.; von Bergen, M.; Hankir, M.K.; et al. Roux-en-Y gastric bypass contributes to weight loss-independent improvement in hypothalamic inflammation and leptin sensitivity through gut-microglia-neuron-crosstalk. Mol. Metab. 2021, 48, 101214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, T.; Seyfried, F.; Docherty, N.G.; Tremaroli, V.; le Roux, C.W.; Perkins, R.; Bäckhed, F. Diabetes-associated microbiota in fa/fa rats is modified by Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. ISME J. 2017, 11, 2035–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hankir, M.K.; Seyfried, F.; Hintschich, C.A.; Diep, T.A.; Kleberg, K.; Kranz, M.; Deuther-Conrad, W.; Tellez, L.A.; Rullmann, M.; Patt, M.; et al. Gastric Bypass Surgery Recruits a Gut PPAR-alpha-Striatal D1R Pathway to Reduce Fat Appetite in Obese Rats. Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyfried, F.; Miras, A.D.; Rotzinger, L.; Nordbeck, A.; Corteville, C.; Li, J.V.; Schlegel, N.; Hankir, M.; Fenske, W.; Otto, C.; et al. Gastric Bypass-Related Effects on Glucose Control, beta Cell Function and Morphology in the Obese Zucker Rat. Obes. Surg. 2016, 26, 1228–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dischinger, U.; Heckel, T.; Bischler, T.; Hasinger, J.; Königsrainer, M.; Schmitt-Böhrer, A.; Otto, C.; Fassnacht, M.; Seyfried, F.; Hankir, M.K. Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass and Caloric Restriction but Not Gut Hormone-Based Treatments Profoundly Impact the Hypothalamic Transcriptome in Obese Rats. Nutrients 2022, 14, 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14010116
Dischinger U, Heckel T, Bischler T, Hasinger J, Königsrainer M, Schmitt-Böhrer A, Otto C, Fassnacht M, Seyfried F, Hankir MK. Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass and Caloric Restriction but Not Gut Hormone-Based Treatments Profoundly Impact the Hypothalamic Transcriptome in Obese Rats. Nutrients. 2022; 14(1):116. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14010116
Chicago/Turabian StyleDischinger, Ulrich, Tobias Heckel, Thorsten Bischler, Julia Hasinger, Malina Königsrainer, Angelika Schmitt-Böhrer, Christoph Otto, Martin Fassnacht, Florian Seyfried, and Mohammed Khair Hankir. 2022. "Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass and Caloric Restriction but Not Gut Hormone-Based Treatments Profoundly Impact the Hypothalamic Transcriptome in Obese Rats" Nutrients 14, no. 1: 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14010116
APA StyleDischinger, U., Heckel, T., Bischler, T., Hasinger, J., Königsrainer, M., Schmitt-Böhrer, A., Otto, C., Fassnacht, M., Seyfried, F., & Hankir, M. K. (2022). Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass and Caloric Restriction but Not Gut Hormone-Based Treatments Profoundly Impact the Hypothalamic Transcriptome in Obese Rats. Nutrients, 14(1), 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14010116






