Highly Active Cranberry’s Polyphenolic Fraction: New Advances in Processing and Clinical Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Phytochemical Composition of Cranberry
2.2. Extraction Methods
2.3. Unconventional Extraction Techniques
2.4. Clinical Applications
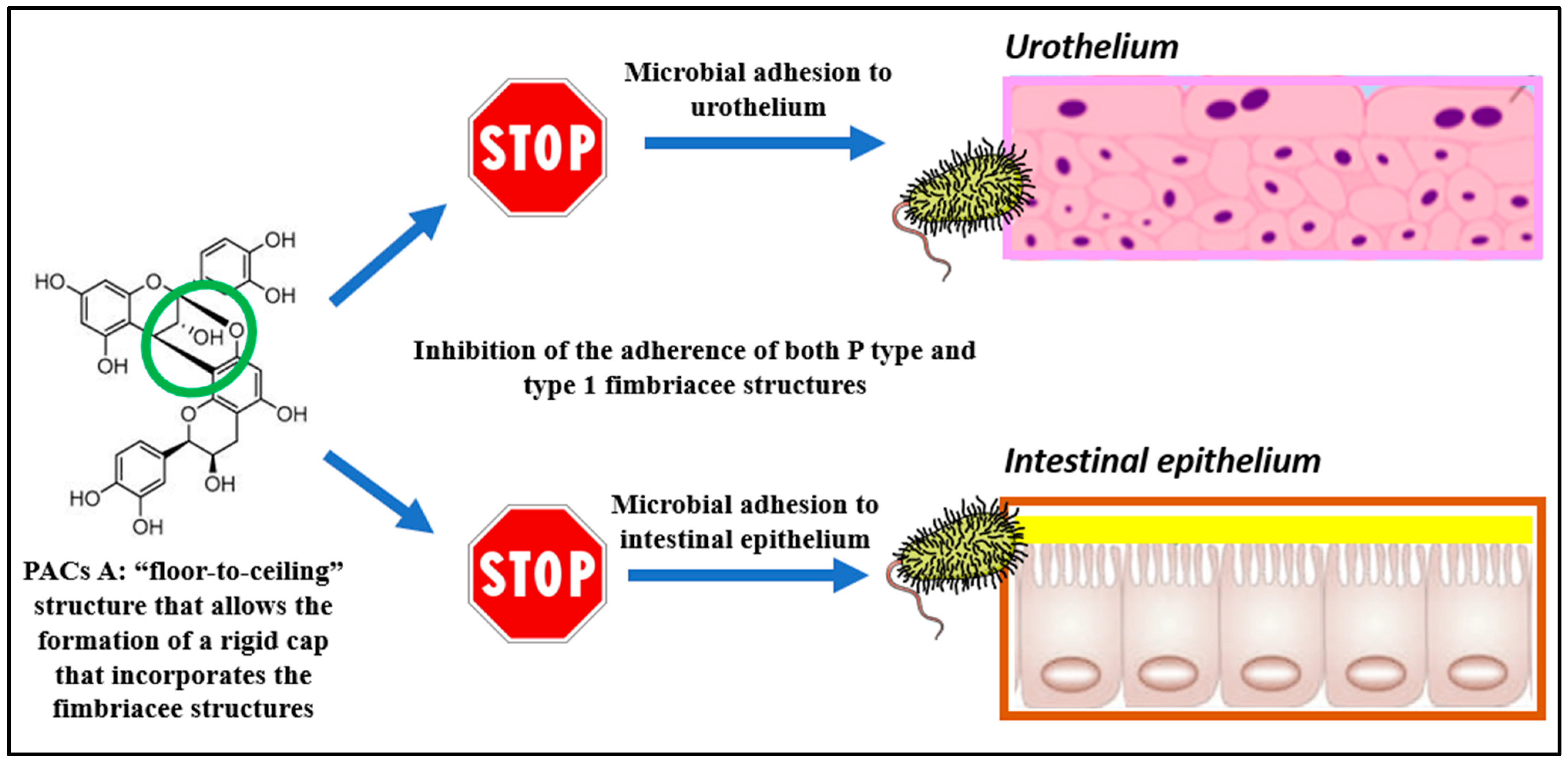
2.4.1. Urinary Tract Infections
2.4.2. Oral, Gastric and Intestinal Health
2.4.3. Cardiometabolic Effects
3. Discussion and Future Perspectives
4. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAOSTAT. Cranberry Statistics for 2020; FAOSTAT Database; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- United State Department of Agriculture, National Agriculture Statistics Service (USDA NASS). National Statistics for Cranberry. 2017. Available online: https://www.nass.usda.gov/Publications/Todays_Reports/reports/ncit0617.pdf (accessed on 23 July 2021).
- Alston, J.M.; Medellin-Azuara, J.; Saitone, T.L. Economic Impact of the North American Cranberry Industry; University de Californie à Davis: Davia, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Dugoua, J.J.; Seely, D.; Perri, D.; Mills, E.; Koren, G. Safety and efficacy of cranberry (Vaccinium macrocarpon) during pregnancy and lactation. Can. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2008, 15, e80–e86. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thimóteo, N.S.B.; Scavuzzi, B.M.; Simão, A.N.C.; Dichi, I. The impact of cranberry (Vaccinium macrocarpon) and cranberry products on each component of the metabolic syndrome: A review. Nutrire 2017, 42, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paquette, M.; Larque, A.S.M.; Weisnagel, S.J.; Desjardins, Y.; Marois, J.; Pilon, G.; Dudonné, S.; Marette, A.; Jacques, H. Strawberry and cranberry polyphenols improve insulin sensitivity in insulin-resistant, non-diabetic adults: A parallel, double-blind, controlled and randomised clinical trial. Br. J. Nutr. 2017, 117, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleman, C.M.; Ferreira, D. Oligosaccharides and Complex Carbohydrates: A New Paradigm for Cranberry Bioactivity. Molecules 2020, 25, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantzorou, M.; Zarros, A.; Vasios, G.; Theocharis, S.; Pavlidou, E.; Giaginis, C. Cranberry: A Promising Natural Source of Potential Nutraceuticals with Anticancer Activity. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2019, 19, 1672–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierre, J.F.; Heneghan, A.F.; Feliciano, R.P.; Shanmuganayagam, D.; Krueger, C.G.; Reed, J.D.; Kudsk, K.A. Cranberry proanthocyanidins improve intestinal sIgA during elemental enteral nutrition. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. (JPEN) 2014, 38, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ma, J.L.; Pan, K.F.; Go, V.L.W.; Chen, J.S.; You, W.C. Efficacy of cranberry juice on Helicobacter pylori infection: A double-blind, randomized placebo-controlled trial. Helicobacter 2005, 10, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Kelm, M.A.; Hammerstone, J.F.; Beecher, G.; Holden, J.; Haytowitz, D.; Gebhardt, S.; Prior, R.L. Concentrations of proanthocyanidins in common foods and estimations of normal consumption. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 613–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, A.B.; Reed, J.D.; Krueger, C.G.; Winterbottom, R.; Cunningham, D.G.; Leahy, M. A-type cranberry proanthocyanidins and uropathogenic bacterial anti-adhesion activity. Phytochemistry 2005, 66, 2281–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prior, R.L.; Lazarus, S.A.; Cao, G.; Muccitelli, H.; Hammerstone, J.F. Identification of procyanidins and anthocyanins in blueberries and cranberries (Vaccinium spp.) using high-performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 1270–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumberg, J.B.; Camesano, T.A.; Cassidy, A.; Kris-Etherton, P.; Howell, A.; Manach, C.; Ostertag, L.M.; Sies, H.; Skulas-Ray, A.; Vita, J.A. Cranberries and their bioactive constituents in human health. Adv. Nutr. 2013, 4, 618–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zuo, Y. Ultrasound-assisted hydrolysis and gas chromatography-mass spectrometric determination of phenolic compounds in cranberry products. Food Chem. 2011, 128, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, M.H.; Massey, A.R.; Mbeunkui, F.; Yousef, G.G.; Lila, M.A. Comparison of health-relevant flavonoids in commonly consumed cranberry products. J. Food Sci. 2012, 77, H176–H183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappas, E.; Schaich, K.M. Phytochemicals of cranberries and cranberry products: Characterization, potential health effects, and processing stability. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2009, 49, 741–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Zuo, Y. GC-MS determination of flavonoids and phenolic and benzoic acids in human plasma after consumption of cranberry juice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, M.; MacKinnon, S.L.; Craft, C.C.; Matchett, M.D.; Hurta, R.A.; Neto, C.C. Ursolic acid and its esters: Occurrence in cranberries and other Vaccinium fruit and effects on matrix metalloproteinase activity in DU145 prostate tumor cells. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2011, 91, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhan, J. Separation, characterization, and quantitation of benzoic and phenolic antioxidants in American cranberry fruit by GC-MS. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 3789–3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, Y.; Murakami, A.; Ohigashi, H. Ursolic acid: An anti- and proinflammatory triterpenoid. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2008, 52, 26–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.; Chen, S.N.; Nikolic, D.; van Breemen, R.; Farnsworth, N.R.; Pauli, G.F. Coumaroyl iridoids and a depside from cranberry (Vaccinium macrocarpon). J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, B.L.; Howard, L.R.; Prior, R.L. Impact of different stages of juice processing on the anthocyanin, flavonol, and procyanidin contents of cranberries. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 4692–4698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, B.L.; Howard, L.R.; Prior, R.L. Proximate and polyphenolic characterization of cranberry pomace. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 4030–4036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roopchand, D.E.; Krueger, C.G.; Moskal, K.; Fridlender, B.; Lila, M.A.; Raskin, I. Food-compatible method for the efficient extraction and stabilization of cranberry pomace polyphenols. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 3664–3669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mildner-Szkudlarz, S.; Bajerska, J.; Gornas, P.; Seglina, D.; Pilarska, A.; Jesionowski, T. Physical and bioactive properties of muffins enriched with raspberry and cranberry pomace powder: A promising application of fruit by-products rich in biocompounds. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2016, 71, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, B.L. Characterization of Polyphenolics in Cranberry Juice and Co-Products. Available online: https://scholarworks.uark.edu/etd/201 (accessed on 23 July 2021).
- Murayama, H.; Katsumata, T.; Endou, H.; Fukushima, T.; Sakurai, N. Effect of storage period on the molecular-mass distribution profile of pectic and hemicellulosic polysaccharides in pears. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2006, 40, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN Food and Agriculture Organization. Codex Standard 247-2005 General Standard for Fruit Juices and Nectars. Available online: www.fao.org/input/download/standards/10154/CXS_247e.pdf (accessed on 23 July 2021).
- Zielinska, M.; Zielinska, D. Effects of freezing, convective and microwave-vacuum drying on the content of bioactive compounds and color of cranberries. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 104, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lager, B.G. Activated Cranberry Powder. U.S. Patent 2008/0020094 A1, 24 January 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Mantius, H.L. Juice Enriched in Beneficial Compounds. WO 01/03520 A1, 18 January 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Mantius, H.L.; Rose, L. Process for Producing Sugars and Acids-Rich Juice and Phytochemical-Rich Juice. U.S. Patent 2006/0177560 A1, 10 August 2006. [Google Scholar]
- O’May, C.; Amzallag, O.; Bechir, K.; Tufenkji, N. Cranberry derivatives enhance biofilm formation and transiently impair swarming motility of the uropathogen Proteus mirabilis HI4320. Can. J. Microbiol. 2016, 62, 464–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strobel, R.G.K.; Tarr, R.E. Process for Making Concentrated Low Calorie Fruit Juice. U.S. Patent 4,971,813, 20 November 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Bromberger Soquetta, M.; Schmaltz, S.; Wesz Righes, F.; Salvalaggio, R.; de Marsillac Terra, L. Effects of pretreatment ultrasound bath and ultrasonic probe, in osmotic dehydration, in the kinetics of oven drying and the physicochemical properties of beet snacks. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2018, 42, e13393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowacka, M.; Wiktor, A.; Anuszewska, A.; Dadan, M.; Rybak, K.; Witrowa-Rajchert, D. The application of unconventional technologies as pulsed electric field, ultrasound and microwave-vacuum drying in the production of dried cranberry snacks. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 56, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano-Navarro, J.I.; Díaz-Zavala, N.P.; Velasco-Santos, C.; Martínez-Hernández, A.L.; Tijerina-Ramos, B.I.; García-Hernández, M.; Reyes-de la Torre, A.I. Antimicrobial, Optical and Mechanical Properties of Chitosan–Starch Films with Natural Extracts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Chen, G.; Zhang, B.; Fu, X. Current applications and new opportunities for the thermal and non-thermal processing technologies to generate berry product or extracts with high nutraceutical contents. Food Res. Int. 2017, 100, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trost, K.; Golc-Wondra, A.; Prosek, M.; Milivojevic, L. Anthocyanin degradation of blueberry-aronia nectar in glass compared with carton during storage. J. Food Sci. 2008, 73, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichiyanagi, T.; Oikawa, K.; Tateyama, C.; Konishi, T. Acid mediated hydrolysis of blueberry anthocyanins. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2001, 49, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eker, M.E.; Aaby, K.; Budic-Leto, I.; Brnčić, S.R.; El, S.N.; Karakaya, S.; Simsek, S.; Manach, C.; Wiczkowski, W.; Pascual-Teresa, S. A Review of Factors Affecting Anthocyanin Bioavailability: Possible Implications for the Inter-Individual Variability. Foods 2019, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chughtai, B.; Howell, A. Variability of commercial cranberry dietary supplements for the prevention or uropathogenic bacterial adhesion. Am. J. Obs. Gynecol. 2016, 7, 122–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, S.; Pardo-Mates, N.; Hidalgo-Serrano, M.; Saurina, J.; Puignou, L.; Nunez, O. UHPLC-HRMS (Orbitrap) fingerprinting in classification and authentication of cranberry-based natural products and pharmaceuticals using multivariate calibration methods. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 3341–3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klavins, L.; Kviesis, J.; Nakurte, I.; Klavins, M. Berry press residues as a valuable source of polyphenolics: Extraction optimisation and analysis. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 93, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldaña, D.A.; Valdivieso-Ramírez, S.C. Pressurized fluid systems: Phytochemical production from biomass. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2015, 96, 228–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergara-Salinas, J.R.; Bulnes, P.; Zúñiga, M.C.; Pérez-Jiménez, J.; Torres, J.L.; Mateos-Martín, M.L.; Agosin, E.; Pérez-Correa, J.R. Effect of pressurized hot water extraction on antioxidants from grape pomace before and after enological fermentation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 6929–6936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babova, O.; Occhipinti, A.; Capuzzo, A.; Maffei, M.E. Extraction of bilberry (Vaccinium myrtillus) antioxidants using supercritical/subcritical CO2 and ethanol as co-solvent. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2016, 107, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swieca, M.; Gawlik-Dziki, U.; Dziki, D.; Baraniak, B.; Czyż, J. The influence of protein-flavonoid interactions on protein digestibility in vitro and the antioxidant quality of breads enriched with onion skin. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, G.; Liao, X.; Hu, X.; Wu, J.; Wang, Z. Optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction of anthocyanins in red raspberries and identification of anthocyanins in extract using high-performance liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2007, 14, 767–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latti, A.K.; Riihinen, K.R.; Kainulainen, P.S. Analysis of anthocyanin variation in wild populations of bilberry (Vaccinium myrtillus L.) in Finland. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 56, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ćujić, N.; Šavikin, K.; Janković, T.; Pljevljakušić, D.; Zdunić, G.; Ibrić, S. Optimization of polyphenols extraction from dried chokeberry using maceration as traditional technique. Food Chem. 2016, 194, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denev, P.; Ciz, M.; Ambrozova, G.; Lojek, A.; Yanakieva, I.; Kratchanova, M. Solid-phase extraction of berries’ anthocyanins and evaluation of their antioxidative properties. Food Chem. 2010, 123, 1055–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klavins, L.; Kviesis, J.; Klavins, M. Comparison of methods of extraction of phenolic compounds from American cranberry (Vaccinium macrocarpon L.) press residues. Agron. Res. 2017, 15, 1316–1329. [Google Scholar]
- Spadoni Andreani, E.; Karboune, S. Comparison of enzymatic and microwave-assisted alkaline extraction approaches for the generation of oligosaccharides from American Cranberry (Vaccinium macrocarpon) Pomace. J. Food Sci. 2020, 85, 2443–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamkutė, L.; Liepuoniūtė, R.; Pukalskienė, M.; Venskutonis, R. Recovery of valuable lipophilic and polyphenolic fractions from cranberry pomace by consecutive supercritical CO2 and pressurized liquid extraction. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2020, 159, 104755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foxman, B. Urinary tract infection syndromes. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2014, 28, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suskind, A.M.; Salgal, C.S.; Hanley, J.M.; Lai, J.; Setodjl, C.M.; Clemens, J.Q. Incidence and management of uncomplicated recurrent urinary tract infections in a national sample of women in the United States. Urology 2016, 90, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Mireles, A.L.; Walker, J.N.; Caparon, M.; Hultgren, S.J. Urinary tract infections: Epidemiology, mechanisms of infection and treatment options. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. Complicated Urinary Tract Infections: Developing Drugs for Treatment—Guidance for Industry [Internet]. 2015. Available online: http://www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/.../Guidances/ucm070981.pdf (accessed on 23 July 2021).
- Beerepoot, M.; Geerlings, S. Non-antibiotic prophylaxis for urinary. Pathogens 2016, 5, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talan, D.A.; Takhar, S.S.; Krishnadasan, A.; Abrahamian, F.M.; Mower, W.R.; Moran, G.J. Fluoroquinolone-resistant and extended-spectrum b-lactamase producing Escherichia coli infections in patients with pyelonephritis, United States. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2016, 22, 1594–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Drug Administration. FDA Drug Safety Communication: FDA Advises Restricting Fluoroquinolone Antibiotic Use for Certain Uncomplicated Infections; Warns about Disabling Side Effects that can Occur Together [Internet]. Available online: http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DrugSafety/ucm500143.htm (accessed on 23 July 2021).
- Tamadonfar, K.O.; Omattage, N.S.; Spaulding, C.N.; Hultgren, S.J. Reaching the end of the line: Urinary tract infections. Microbiol. Spectr. 2019, 7, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodel, P.T.; Cotran, R.; Kass, E.H. Cranberry juice and the antibacterial action of hippuric acid. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1959, 54, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stang, E.J. The North American Cranberry industry. Acta Hortic. 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.D. Cranberry Harvest: A History of Cranberry Growing in Massachusetts; Spinner: New Bedford, MA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, E.B.; Barney, D.P.; Mickelsen, J.N.; Walton, R.J.; Mickelsen, R.A., Jr. Cranberry concentrate: UTI prophylaxis. J. Fam. Pract. 1997, 45, 167–168. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wawrysiuk, S.; Naber, K.; Rechberger, T.; Miotla, P. Prevention and treatment of uncomplicated lower urinary tract infections in the era of increasing antimicrobial resistance-non-antibiotic approaches: A systemic review. Arch. Gynecol. Obs. 2019, 300, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gbinigie, O.A.; Spencer, E.A.; Heneghan, C.J.; Lee, J.J.; Butler, C.C. Cranberry Extract for Symptoms of Acute, Uncomplicated Urinary Tract Infection: A Systematic Review. Antibiotics (Basel) 2020, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.H.; Fang, C.C.; Chen, N.C.; Liu, S.S.; Yu, P.H.; Wu, T.Y.; Chen, W.T.; Lee, C.C.; Chen, S.C. Cranberry-containing products for prevention of urinary tract infections in susceptible populations—A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Arch. Intern. Med. 2012, 172, 988–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyson, D.A. A review and critical analysis of the scientific literature related to 100% fruit juice and human health. Adv. Nutr. 2015, 6, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guay, D.R.P. Cranberry and urinary tract infections. Drugs 2009, 69, 775–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Liska, D.; Talan, D.; Chung, M. Cranberry reduces the risk of urinary tract infection recurrence in otherwise healthy women: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Nutr. 2017, 147, 2282–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prior, R.L.; Gu, L. Occurrence and biological significance of proanthocyanidins in the American diet. Phytochemistry 2005, 66, 2264–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Howell, A.B.; Zhang, D.J.; Khoo, C. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study to assess bacterial anti-adhesive activity in human urine following consumption of a cranberry supplement. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 7645–7652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron, G.; Altomare, A.; Regazzoni, L.; Fumagalli, L.; Artasensi, A.; Borghi, E.; Ottaviano, E.; Del Bo, C.; Riso, P.; Allegrini, P.; et al. Profiling vaccinium macrocarpon components and metabolites in human urine and the urine ex-vivo effect on Candida albicans adhesion and biofilm-formation. Biochem. Pharm. 2020, 173, 113726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domenici, L.; Monti, M.; Bracchi, C.; Giorgini, M.; Colagiovanni, V.; Muzii, L.; Benedetti Panici, P. D-mannose: A promising support for acute urinary tract infections in women. A pilot study. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 20, 2920–2925. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, H.D.; Struve, C.; Christensen, S.B.; Krogfelt, K.A. Cranberry juice and combinations of its organic acids are effective against experimental urinary tract infection. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Marais, J.P.; Khoo, C.; LaPlante, K.; Vejborg, R.M.; Givskov, M.; Nielsen, T.; Seeram, N.P.; Cranberry, D.C.R. (Vaccinium macrocarpon) oligosaccharides decrease biofilm formation by uropathogenic Escherichia coli. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 17, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luís, Â.; Domingues, F.; Pereira, L. Can Cranberries Contribute to Reduce the Incidence of Urinary Tract Infections? A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis and Trial Sequential Analysis of Clinical Trials. J. Urol. 2017, 198, 614–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jepson, R.G.; Williams, G.; Craig, J.C. Cranberries for preventing urinary tract infections. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 10, CD001321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beerepoot, M.A.; Geerlings, S.E.; van Haarst, E.P.; van Charante, N.M.; ter Riet, G. Nonantibiotic prophylaxis for recurrent urinary tract infections: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Urol. 2013, 190, 1981–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health. Cranberry Products or Topical Estrogen-Based Therapy for the Prevention of Urinary Tract Infections: A Review of Clinical Effectiveness and Guidelines; Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Feliciano, R.P.; Meudt, J.J.; Shanmuganayagam, D.; Krueger, C.G.; Reed, J.D. Ratio of “a-type” to “b-type” proanthocyanidin interflavan bonds affects extra-intestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli invasion of gut epithelial cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 3919–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Duynhoven, J.; van der Hooft, J.J.J.; van Dorsten, F.A.; Peters, S.; Foltz, M.; Gomez-Roldan, V.; Vervoort, J.; de Vos, R.C.H.; Jacobs, D.M. Rapid and sustained systemic circulation of conjugated gut microbial catabolites after single-dose black tea extract consumption. J. Proteome Res. 2014, 2, 2668–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mena, P.; González de Llano, D.; Brindani, N.; Esteban-Fernández, A.; Curti, C.; Moreno-Arribas, M.V.; Del Rio, D.; Bartolomé, B. 5-(3′,4′-Dihydroxyphenyl)-γ-valerolactone and its sulphate conjugates, representative circulating metabolites of flavan-3-ols, exhibit anti-adhesive activity against uropathogenic Escherichia coli in bladder epithelial cells. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 29, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, G. The development of probiotics for women’s health. Can. J. Microbiol. 2017, 63, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadieux, P.A.; Burton, J.; Devillard, E.; Reid, G. Lactobacillus by-products inhibit the growth and virulence of uropathogenic Escherichia coli. J. Physiol. Pharm. 2009, 60, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Beerepoot, M.A.J. Lactobacilli vs. antibiotics to prevent urinary tract infections. Arch. Intern. Med. 2012, 172, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montorsi, F.; Gandaglia, G.; Salonia, A.; Briganti, A.; Mirone, V. Effectiveness of a combination of cranberries, lactobacillus rhamnosus, and Vitamin C for the management of recurrent urinary tract infections in women: Results of a pilot study. Eur. Urol. 2016, 70, 912–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stapleton, A.E.; Au-Yeung, M.; Hooton, T.M.; Fredricks, D.N.; Roberts, P.L.; Czaja, C.A.; Yarova-Yarovaya, Y.; Fiedler, T.; Cox, M.; Stamm, W.E. Randomized, placebo-controlled phase 2 trial of a lactobacillus crispatus probiotic given intravaginally for prevention of recurrent urinary tract infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 52, 1212–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, E.I.; Houri-Haddad, Y.; Greenbaum, E.; Hochman, N.; Ofek, I.; Zakay-Rones, Z. Cranberry juice constituents affect influenza virus adhesion and infectivity. Antiviral Res. 2005, 66, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straub, T.J.; Chou, W.C.; Manson, A.L.; Schreiber, H.L.; Walker, B.J.; Desjardins, C.A.; Chapman, S.B.; Kaspar, K.L.; Kahsai, O.J.; Traylor, E.; et al. Limited effects of long-term daily cranberry consumption on the gut microbiome in a placebo-controlled study of women with recurrent urinary tract infections. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Ohn, J.; Kim, J.H.; Kwak, H.K. Effects of freeze-dried cranberry powder on serum lipids and inflammatory markers in lipopolysaccharide treated rats fed an atherogenic diet. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2011, 5, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madrigal-Carballo, S.; Rodriguez, G.; Sibaja, M.; Reed, J.D.; Vila, A.O.; Molina, F. Chitosomes loaded with cranberry proanthocyanidins attenuate the bacterial lipopolysaccharide-induced expression of iNOS and COX-2 in raw 264.7 macrophages. J. Liposome Res. 2009, 19, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anhe, F.F.; Roy, D.; Pilon, G.; Dudonne, S.; Matamoros, S.; Varin, T.V.; Garofalo, C.; Moine, Q.; Desjardins, Y.; Levy, E.; et al. A polyphenol-rich cranberry extract protects from diet-induced obesity, insulin resistance and intestinal inflammation in association with increased Akkermansia spp. population in the gut microbiota of mice. Gut 2015, 64, 872–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekiares, N.; Krueger, C.G.; Meudt, J.J.; Shanmuganayagam, D.; Reed, J.D. Effect of sweetened dried cranberry consumption on urinary proteome and fecal microbiome in healthy human subjects. OMICS J. Integr. Biol. 2017, 21, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-morató, J.; Matthan, N.R.; Liu, J.; De, R.; Chen, C.O. ScienceDirect cranberries attenuate animal-based diet-induced changes in microbiota composition and functionality: A randomized crossover controlled feeding trial. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2018, 62, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piscione, M.; Mazzone, M.; Di Marcantonio, M.C.; Muraro, R.; Mincione, G. Eradication of Helicobacter pylori and Gastric Cancer: A Controversial Relationship. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 630852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gotteland, M.; Brunser, O.; Cruchet, S. Systematic review: Are probiotics useful in controlling gastric colonization by Helicobacter pylori? Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 23, 1077–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.X.; Ma, J.L.; Guo, Y.; Liu, W.D.; Li, M.; Zhang, L.F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, J.Y.; Gao, H.E.; et al. Suppression of Helicobacter pylori infection by daily cranberry intake: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 36, 927–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyyedmajidi, M.; Ahmadi, A.; Hajiebrahimi, S.; Seyedmajidi, S.; Rajabikashani, M.; Firoozabadi, M.; Vafaeimanesh, J. Addition of cranberry to proton pump inhibitor-based triple therapy for Helicobacter pylori eradication. J. Res. Pharm. Pract. 2016, 5, 248–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shmuely, H.; Yahav, J.; Samra, Z.; Chodick, G.; Koren, R.; Niv, Y.; Ofek, I. Effect of cranberry juice on eradication of Helicobacter pylori in patients treated with antibiotics and a proton pump inhibitor. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2007, 51, 746–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotteland, M.; Andrews, M.; Toledo, M.; Muñoz, L.; Caceres, P.; Anziani, A.; Wittig, E.; Speisky, H.; Salazar, G. Modulation of Helicobacter pylori colonization with cranberry juice and Lactobacillus johnsonii La1 in children. Nutrition 2008, 24, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare Javid, A.; Maghsoumi-Norouzabad, L.; Bazyar, H.; Aghamohammadi, V.; Alavinejad, P. Effects of Concurrent Omega-3 and Cranberry Juice Consumption Along with Standard Antibiotic Therapy on the Eradication of Helicobacter pylori, Gastrointestinal Symptoms, Some Serum Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress Markers in Adults with Helicobacter pylori Infection: A Study Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 3179–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feghalvi, K.; Feldman, M.; La, V.D.; Santos, J. Grenier, D. Cranberry proanthocyanidins: Natural weopons against periodontal diseases. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 13, 5728–5735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodet, C.; Piche, M.; Chardad, F.; Grenier, D. Inhibition of periodontopathogen-derived proteolytic enzymes by a high molecular weight fraction isolated from cranberry. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2006, 57, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodet, C.; Chandad, F.; Grenier, F. Anti-inflammatory Activity of a High-molecular weight Cranberry Fraction on Macrophages Stimulated by Lipopolysaccarides from Periodontopathogens. J. Dent. Res. 2006, 85, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La, V.D.; Howell, A.B.; Grenier, D. Cranberry Proanthrocyanidins Inhibit MMP Production and Activity. J. Dent. Res. 2009, 88, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodet, C.; Grenier, D.; Chandad, F.; Ofek, I.; Steinberg, D.; Weissy, E.I. Potential Oral Health Benefits of Cranberry. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2008, 48, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, H.; Nino de Guzman, P.; Schobel, B.D.; Smith, A.V.V.; Bowen, W.H. Influenze of cranberry juice on glucan-mediated processes involved in Streptococcus mutans biofilm devolepment. Caries Res. 2006, 40, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamanaka, O.A.; Sato, E.; Kouchi, T.; Kimizuka, R.; Kato, T.; Okuda, K. Inhibitory effect of cranberry Polyphenol on Cariogenic bacteria. Bull. Tokyo Dent. Coll. 2008, 119, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durate, S.; Gregorie, S.; Singh, A.; Vorsa, N.; Schiah, K.; Bowen, W.; Koo, H. Inhibitory effects of polyphenols on formation and acidogenicity of streptococcus mutans biofilms. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2006, 257, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, E.I.; Kozlovsky, A.; Steinberg, D. A high molecular mass cranberry constituent reduces mutans streptococci level in saliva and inhibits in vitro adhesion to hydroxyapatite. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2004, 232, 8–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, G.A.; Johnson, C.; Abajobir, A.; Abd-Allah, F.; Aberam, S.F.; Abyu, G.; Ahmed, M.; Aksut, B.; Alam, T.; Alam, K.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases for 10 Causes, 1990 to 2015. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 70, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloom, D.E.; Cafiero, E.T.; Jané-Llopis, E.; Abrahams-Gessel, S.; Bloom, L.R.; Fathima, S.; Feigl, A.B.; Gaziano, T.; Hamandi, A.; Mowafi, M.; et al. The Global Economic Burden of Noncommunicable Diseases; Report No.: 080911; World Economic Forum: Geneva, Switzerland, September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Chew, B.; Mathison, B.; Kimble, L.; McKay, D.; Kaspar, K.; Khoo, C.; Chen, C.-Y.O.; Blumberg, J. Chronic consumption of a low calorie, high polyphenol cranberry beverage attenuates inflammation and improves glucoregulation and HDL cholesterol in healthy overweight humans: A randomized controlled trial. Eur. J. Nutr. 2019, 58, 1223–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novotny, J.A.; Baer, D.J.; Khoo, C.; Gebauer, S.K.; Charron, C.S. Cranberry juice consumption lowers markers of cardiometabolic risk, including blood pressure and circulating C-reactive protein, triglyceride, and glucose concentrations in adults. J. Nutr. 2015, 145, 1185–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shidfar, F.; Heydari, I.; Hajimiresmaiel, S.J.; Hosseini, S.; Shidfar, S.; Amiri, F. The effects of cranberry juice on serum glucose, apoB, apoA-I, Lp(a), and Paraoxonase-1 activity in type 2 diabetic male patients. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2012, 17, 355–360. [Google Scholar]
- Dohadwala, M.M.; Holbrook, M.; Hamburg, N.M.; Shenouda, S.M.; Chung, W.B.; Titas, M.; Kluge, M.A.; Wang, N.; Palmisano, J.; Milbury, P.E.; et al. Effects of cranberry juice consumption on vascular function in patients with coronary artery disease. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 93, 934–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basu, A.; Betts, N.M.; Ortiz, J.; Simmons, B.; Wu, M.; Lyons, T.J. Low-energy cranberry juice decreases lipid oxidation and increases plasma antioxidant capacity in women with metabolic syndrome. Nutr. Res. 2011, 31, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Sun, R.; Xia, M. Purified anthocyanin supplementation reduces dyslipidemia, enhances antioxidant capacity, and prevents insulin resistance in diabetic patients. J. Nutr. 2015, 145, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsia, D.S.; Zhang, D.J.; Beyl, R.S.; Greenway, F.L.; Khoo, C. Effect of daily consumption of cranberry beverage on insulin sensitivity and modification of cardiovascular risk factors in adults with obesity: A pilot, randomised, placebo-controlled study. Br. J. Nutr. 2020, 124, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hormoznejad, R.; Mohammad Shahi, M.; Rahim, F.; Helli, B.; Alavinejad, P.; Sharhani, A. Combined cranberry supplementation and weight loss diet in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A double-blind placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 71, 991–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruel, G.; Lapointe, A.; Pomerleau, S.; Couture, P.; Lemieux, S.; Lamarche, B.; Couillard, C. Evidence that cranberry juice may improve augmentation index in overweight men. Nutr. Res. 2013, 33, 414–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duthie, S.J.; Jenkinson, A.M.; Crozier, A.; Mullen, W.; Pirie, L.; Kyle, J.; Yap, L.S.; Christen, P.; Duthie, G.G. The effects of cranberry juice consumption on antioxidant status and biomarkers relating to heart disease and cancer in healthy human volunteers. Eur. J. Nutr. 2006, 45, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruel, G.; Pomerleau, S.; Couture, P.; Lamarche, B.; Couillard, C. Changes in plasma antioxidant capacity and oxidized low-density lipoprotein levels in men after short-term cranberry juice consumption. Metabolism 2005, 54, 856–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caton, P.W.; Pothecary, M.R.; Lees, D.M.; Khan, N.Q.; Wood, E.G.; Shoji, T.; Kanda, T.; Rull, G.; Corder, R. Regulation of vascular endothelial function by procyanidin-rich foods and beverages. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 4008–4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yung, L.M.; Tian, X.Y.; Wong, W.T.; Leung, F.P.; Yung, L.H.; Chen, Z.Y.; Lau, C.W.; Vanhoutte, P.M.; Yao, X.; Huang, Y. Chronic cranberry juice consumption restores cholesterol profiles and improves endothelial function in ovariectomized rats. Eur. J. Nutr. 2013, 52, 1145–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmering, J.E.; Tang, F.; Cavanaugh, J.E.; Polgreen, L.A.; Polgreen, P.M. The Increase in Hospitalizations for Urinary Tract Infections and the Associated Costs in the United States, 1998–2011. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2017, 4, ofw281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wing, D.A.; Rumney, P.J.; Hindra, S.; Guzman, L.; Le, J.; Nageotte, M. Pilot Study to Evaluate Compliance and Tolerability of Cranberry Capsules in Pregnancy for the Prevention of Asymptomatic Bacteriuria. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2015, 21, 700–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stothers, L. A randomized trial to evaluate effectiveness and cost effectiveness of naturopathic cranberry products as prophylaxis against urinary tract infection in women. Can. J. Urol. 2002, 9, 1558–1562. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- van den Hout, W.B.; Caljouw, M.A.; Putter, H.; Cools, H.J.; Gussekloo, J. Cost-effectiveness of cranberry capsules to prevent urinary tract infection in long-term care facilities: Economic evaluation with a randomized controlled trial. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2014, 62, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Harrington, P.B.; Chen, P. Analysis of Phenolic Compositions in Cranberry Dietary Supplements using UHPLC-HRMS. J. Food Compost. Anal. 2020, 86, 103362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannino, G.; Di Stefano, V.; Lauria, A.; Pitonzo, R.; Gentile, C. Vaccinium macrocarpon (Cranberry)-Based Dietary Supplements: Variation in Mass Uniformity, Proanthocyanidin Dosage and Anthocyanin Profile Demonstrates Quality Control Standard Needed. Nutrients 2020, 12, 992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Kong, X.; Yao, B.; He, Q.; Hao, K. Determination of 88 pesticide residues in cranberry plant extract by gas chromatography-triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometry. Se Pu 2011, 29, 974–982. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (EFSA NDA Panel). Scientific Opinion on the safety of cranberry extract powder as a novel food ingredient pursuant to Regulation (EC) No 258/97. EFSA J. 2017, 15, 4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Food Source | Flavan-3-ol Monomers and Dimers [11,15] | Proanthocyanidins [11,16] | Anthocyanins [17,16] | Hydroxybenzoic Acids [15,18] | Hydroxycinnamic Acids [15,18] | Terpenes [19] | Flavonols [18] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cranberry fruit | mg/100 g | 7–33 | 133–367 | 13–171 | 503–602 | 73–82 | 65–125 | 20–40 |
| mg/serving (80 g whole fruit) | 5.6–26.4 | 106–293 | 10.4–136.8 | 402–482 | 57.6–65.6 | 52–100 | 16–32 | |
| Cranberry juice | mg/100 g | 6–35 | 89–230 | 27–132 | 64 | 12–19 | Trace | 11–58 |
| mg/serving (200 mL juice) | 7 | 17.8–46 | 5.4–26.4 | 12.8 | 2.4–3.8 | Trace | 2.2–11.6 | |
| Canned cranberry sauce | mg/100 g | 112.8 | 16–54.4 | 0.6–11.8 | 476 | 47.5 | 1.1–22.8 | — |
| mg/serving (70 g sauce) | 78.9 | 11.2–38 | 0.4–8.3 | 333.2 | 33.2 | 0.8–16 | — | |
| Sweetened, dried cranberries | mg/100 g | — | 64.2 | 10.3 | — | — | 98.5 | — |
| mg/serving (40 g dried fruit) | — | 25.6 | 4.1 | — | — | 39.4 | — | |
| Polyphenols | Concentration (mg/100 g dw) |
|---|---|
| Anthocyanins | |
| Cyanidin 3-arabinoside | 49.6 ± 6.8 |
| Peonidin 3-arabinoside | 26.6 ± 0.5 |
| Peonidin 3-galactoside | 20.1 ± 0.5 |
| Cyanidin 3-galactoside | 13.2 ± 0.2 |
| Peonidin 3-glucoside | 7.4 ± 0.3 |
| Cyanidin 3-glucoside | 4.5 ± 0.2 |
| Total anthocyanins | 121.4 ± 5.9 |
| Flavonols | |
| Quercetin | 146.2 ± 22.7 |
| Myricetin | 55.6 ± 2.6 |
| Quercetin 3-benzoyl galactoside | 27.5 ± 3.4 |
| Quercetin 3-rhamnoside | 18.5 ± 3.4 |
| Quercetin 3-arabinofuranoside | 16.7 ± 3.5 |
| Quercetin 3-arabinopyranoside | 15.2 ± 3.6 |
| Quercetin 3-galactoside | 12.8 ± 3.6 |
| Unidentified | 12.1 ± 3.5 |
| Methoxyquercetin 3-xyloside | 11.4 ± 3.7 |
| Quercetin 3-xyloside | 5.5 ± 0.3 |
| Quercetin 3-coumaroyl galactoside | 2.3 ± 0.3 |
| Myricetin 3-arabinoside | 1.8 ± 0.1 |
| Myricetin 3-xyloside | 1.5 ± 0.3 |
| Total flavonols | 358.4 ± 16.3 |
| Procyanidins | |
| Dimer (DP2) | 52.7 ± 1.7 |
| Trimer (DP3) | 30.7 ± 1.4 |
| Hexamer (DP6) | 25.6 ± 1.2 |
| Pentamer (DP5) | 22.7 ± 1.2 |
| Heptamer (DP7) | 16.6 ± 1.2 |
| Octamer (DP8) | 16.1 ± 2.9 |
| Tetramer (DP4) | 16.1 ± 1.3 |
| Nonomer (DP9) | 13.2 ± 1.1 |
| Monomer (DP1) | 5.12 ± 0.0 |
| Total procyanidins | 186.5 ± 8.8 |
| Processing Step | Pre-Treatment | Polymer Concentration (mg/100 g Fresh Berries) | Polymer % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fresh | - | 206.2 ± 9.3 | 81.7 |
| Blanched | Grinding + blanching | 251.8 ± 8.4 | 80.7 |
| No grinding + blanching | 245.3 ± 18.5 | 82.6 | |
| Enzyme treated mash | Grinding + blanching | 261.4 ± 20.9 | 81.2 |
| Grinding + no blanching | 319.6 ± 11.5 | 85.3 | |
| No grinding + blanching | 172.7 ± 8.6 | 76.1 | |
| Unclarified juice | Grinding + blanching | 104.2 ± 17.7 | 82.3 |
| Grinding + no blanching | 103.5 ± 8.2 | 76.0 | |
| No grinding + blanching | 100.7 ± 4.3 | 78.5 | |
| Clarified juice | Grinding + blanching | 107.7 ± 3.6 | 80.4 |
| Grinding + no blanching | 74.0 ± 10.9 | 67.5 | |
| No grinding + blanching | 86.2 ± 4.5 | 78.0 | |
| Pasteurized juice | Grinding + blanching | 76.1 ± 4.0 | 76.5 |
| Grinding + no blanching | 69.4 ± 2.7 | 68.0 | |
| No grinding + blanching | 75.3 ± 7.2 | 73.6 | |
| Pomace | Grinding + blanching | 109.7 ± 1.7 | 88.9 |
| Grinding + no blanching | 127.7 ± 3.9 | 92.5 | |
| No grinding + blanching | 130.4 ± 0.5 | 90.0 |
| Technique | Advantages | Limits | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional methods | Juice | Low costs | Food industry waste (pomace) | [24,29,30] |
| Pressing or decanting from frozen berries | Low costs | |||
| Drying process | Low costs | Exposition of cranberry fruits to high temperature and air for long time. Partial loss of nutritional value | ||
| Spray-drying evaporation | Enriched amount of poliphenols | Variable concentration of polyphenols, depending on enzymes, temperature and time conditions and the concentration and drying steps | [7] | |
| Non-conventional methods | Subcritical water extraction | Selectivity and purity of the final extract. Environmentally friendly Efficacy of extraction of other biactive molecules. Fast and low-cost. | High energy for water evaporation | [46] |
| Ultrasound-assisted extraction | Short extraction time | Scalability mainly in flow mode | [37,45] | |
| Microwave-assisted extraction | Selectivity and purity of the final extract. | Limited to MW-adsorbing mixtures | [37,55] | |
| Supercritical carbon dioxide extraction followed by pressurized fluid extraction | Environmentally friendly, easy scalability | High CAPEX | [56] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Colletti, A.; Sangiorgio, L.; Martelli, A.; Testai, L.; Cicero, A.F.G.; Cravotto, G. Highly Active Cranberry’s Polyphenolic Fraction: New Advances in Processing and Clinical Applications. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2546. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13082546
Colletti A, Sangiorgio L, Martelli A, Testai L, Cicero AFG, Cravotto G. Highly Active Cranberry’s Polyphenolic Fraction: New Advances in Processing and Clinical Applications. Nutrients. 2021; 13(8):2546. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13082546
Chicago/Turabian StyleColletti, Alessandro, Luciano Sangiorgio, Alma Martelli, Lara Testai, Arrigo F. G. Cicero, and Giancarlo Cravotto. 2021. "Highly Active Cranberry’s Polyphenolic Fraction: New Advances in Processing and Clinical Applications" Nutrients 13, no. 8: 2546. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13082546
APA StyleColletti, A., Sangiorgio, L., Martelli, A., Testai, L., Cicero, A. F. G., & Cravotto, G. (2021). Highly Active Cranberry’s Polyphenolic Fraction: New Advances in Processing and Clinical Applications. Nutrients, 13(8), 2546. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13082546










