Effects of Bacterial CLPB Protein Fragments on Food Intake and PYY Secretion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Diets
2.2. Bacterial Culture
2.3. Bacterial Proteins Extraction
2.4. Proteins Fragmentation
2.5. CLPB96 and CLPB25 Production
2.6. CLPB Fragments Identification by Western Blot
2.7. Rat Intestinal Cells Primary Culture and Gut Hormone Secretion
2.8. CLPB25 Purification
2.9. Intraperitoneal Injections of CLPB96 and CLPB25 in Mice
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
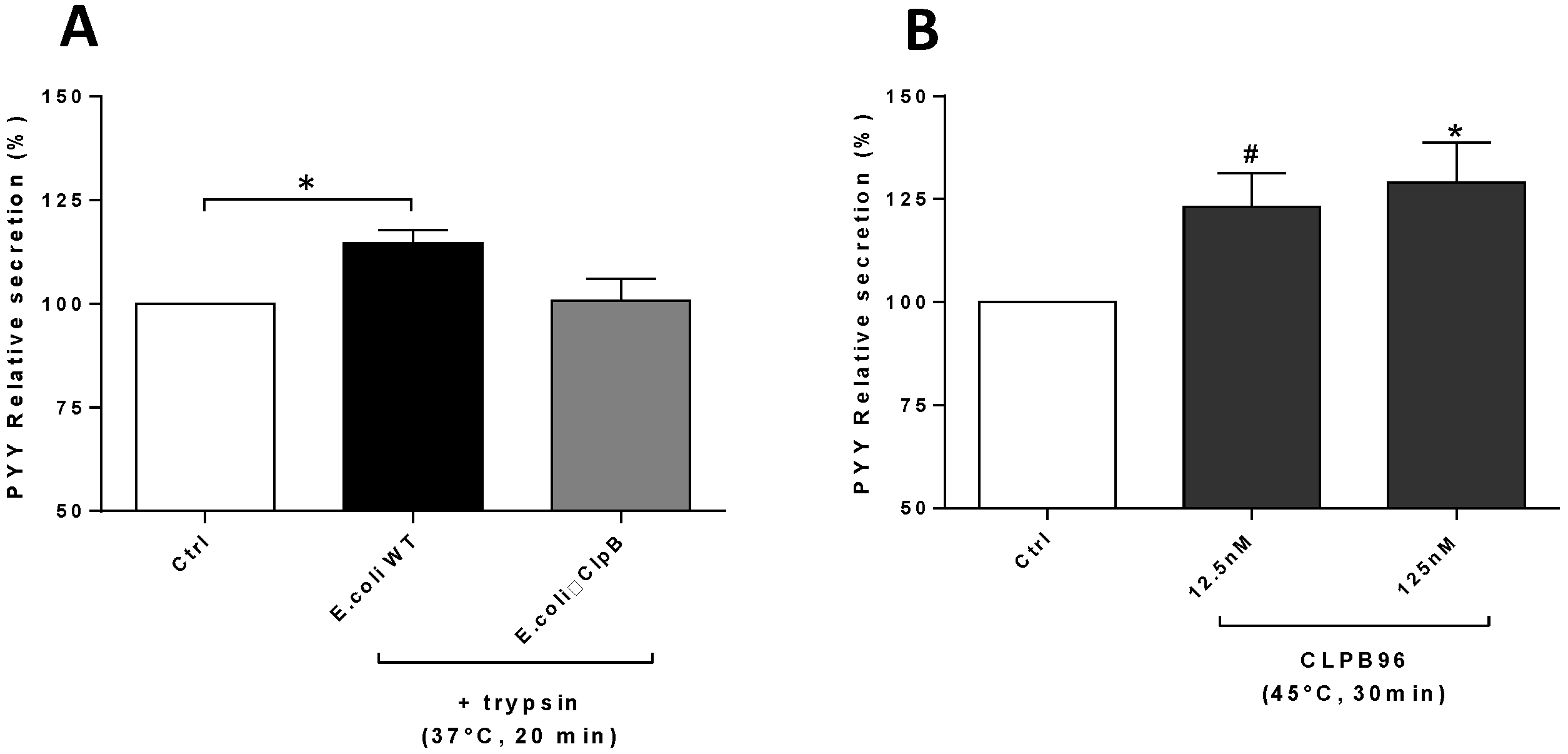
3.1. Bacteria and CLPB96 Effects on PYY Secretion
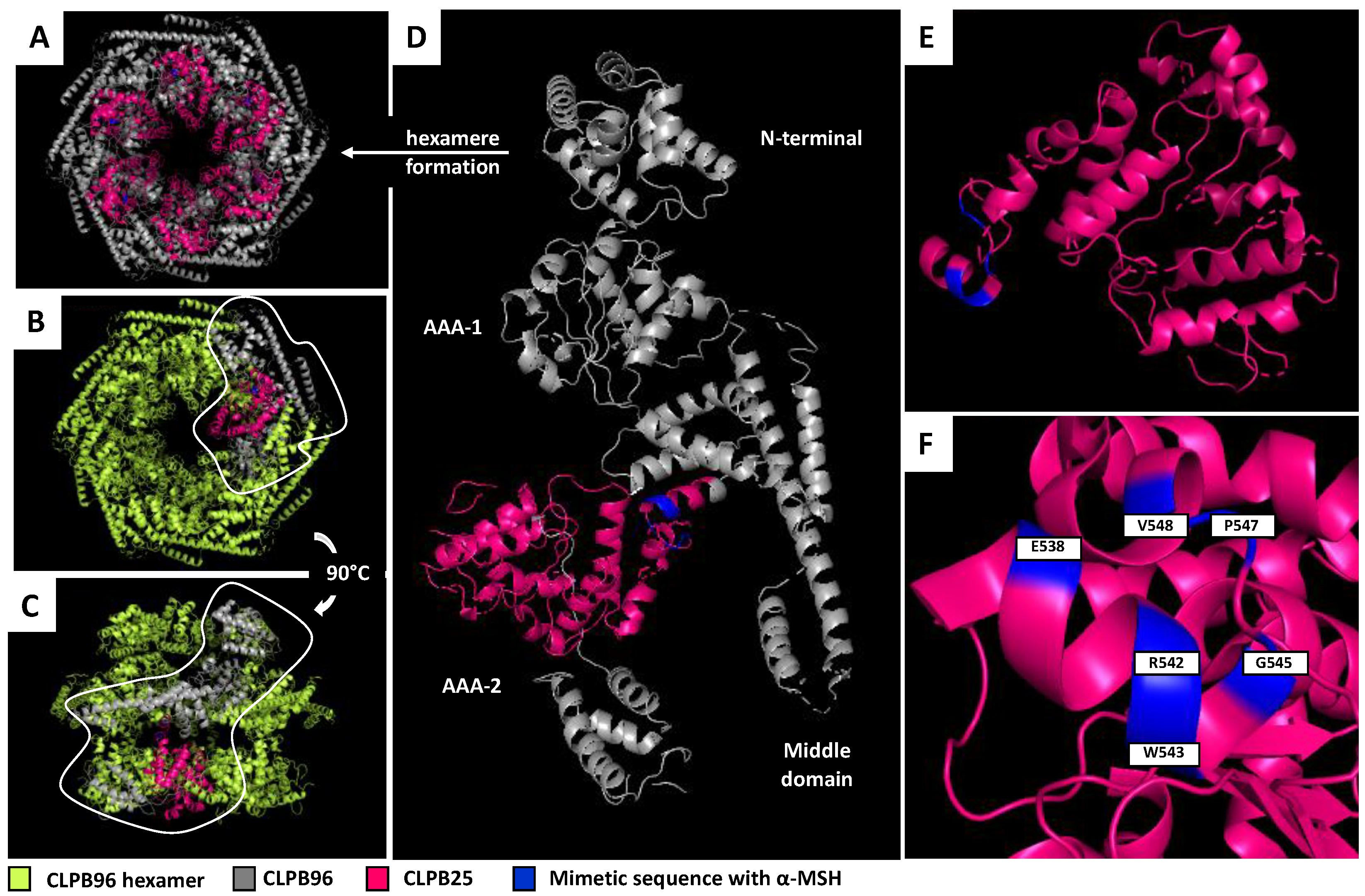
3.2. CLPB25 Identification
3.3. Localization of CLPB25
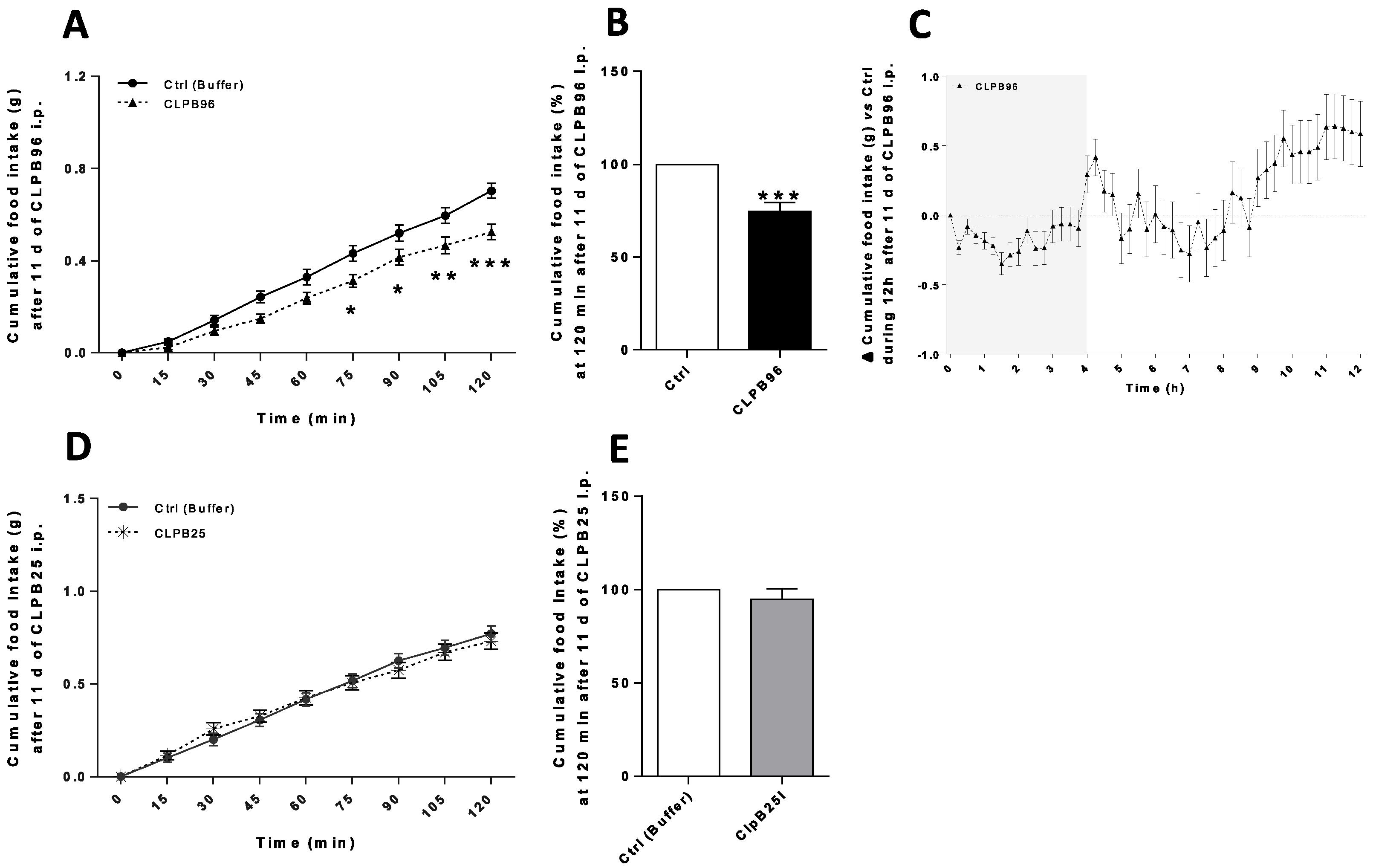
3.4. In Vivo Effects of CLPB96 and CLPB25 in C57Bl/6 Mice
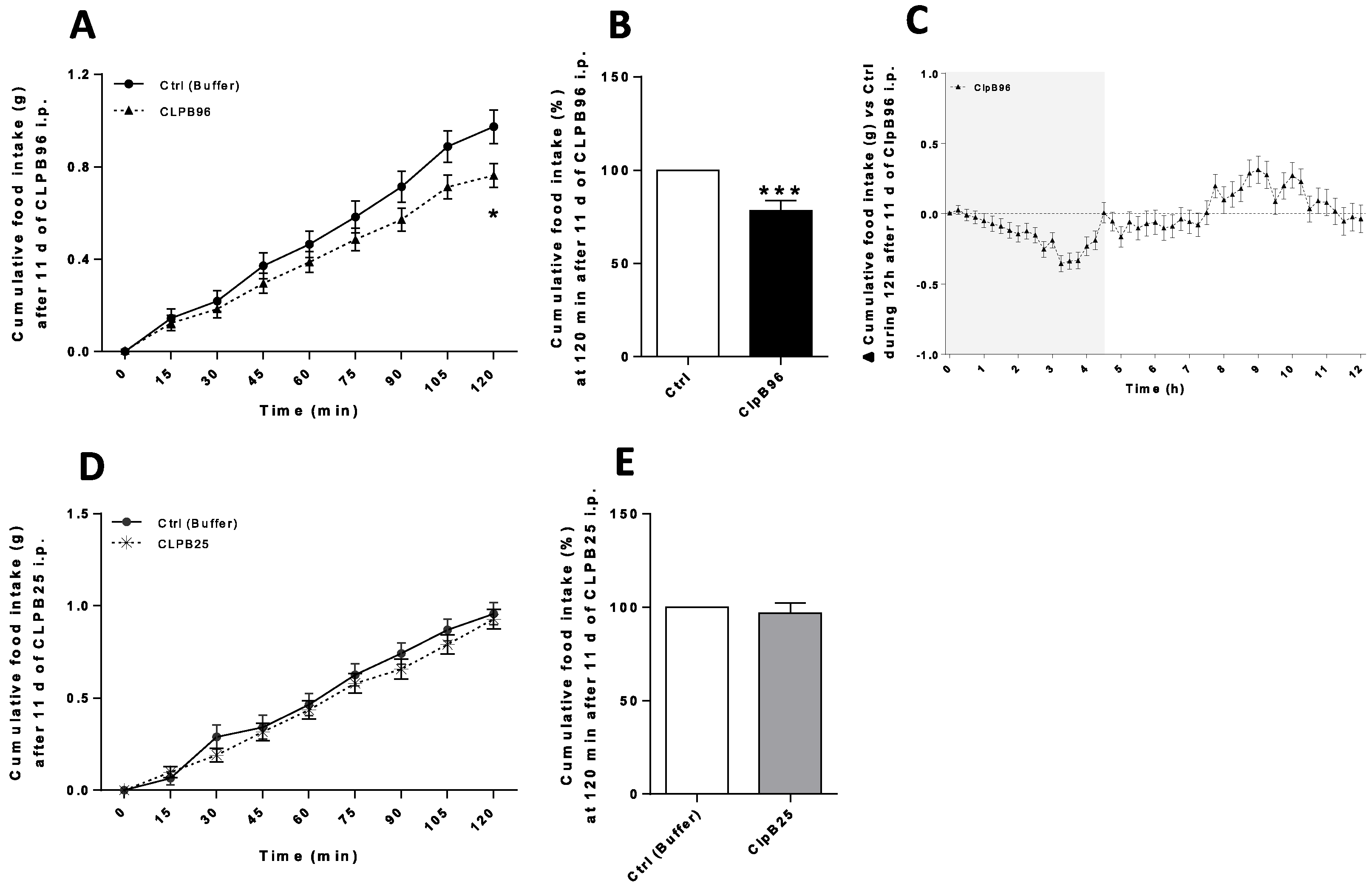
3.5. In Vivo Effects of CLPB96 and CLPB25 in ob/ob Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization (WHO). Obesity and Overweight, Févr. 16. Available online: https://www.who.int/fr/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 16 February 2019).
- Guh, D.P.; Zhang, W.; Bansback, N.; Amarsi, Z.; Birmingham, C.L.; Anis, A.H. The incidence of co-morbidities related to obesity and overweight: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Public Health 2009, 9, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hartemink, N.; Boshuizen, H.C.; Nagelkerke, N.J.D.; Jacobs, M.A.M.; van Houwelingen, H.C. Combining Risk Estimates from Observational Studies with Different Exposure Cutpoints: A Meta-analysis on Body Mass Index and Diabetes Type. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2006, 163, 1042–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bergström, A.; Pisani, P.; Tenet, V.; Wolk, A.; Adami, H. Overweight as an avoidable cause of cancer in Europe. Int. J. Cancer 2001, 91, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asia Pacific Cohort Studies Collaboration Body mass index and cardiovascular disease in the Asia-Pacific Region: An overview of 33 cohorts involving 310,000 participants. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2004, 33, 751–758. [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ley, R.E.; Mahowald, M.A.; Magrini, V.; Mardis, E.R.; Gordon, J.I. An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006, 444, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castaner, O.; Goday, A.; Park, Y.-M.; Lee, S.-H.; Magkos, F.; Shiow, S.-A.T.E.; Schröder, H. The Gut Microbiome Profile in Obesity: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 2018, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ley, R.E.; Bäckhed, F.; Turnbaugh, P.; Lozupone, C.A.; Knight, R.D.; Gordon, J.I. Obesity alters gut microbial ecology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 11070–11075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Million, M.; Angelakis, E.; Maraninchi, M.; Henry, M.; Giorgi, R.; Valero, R.; Vialettes, B.; Raoult, D. Correlation between body mass index and gut concentrations of Lactobacillus reuteri, Bifidobacterium animalis, Methanobrevibacter smithii and Escherichia coli. Int. J. Obes. 2013, 37, 1460–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, B.; Wu, J.; Jiang, X.; Tang, H.; Nielsen, O.H. Modulation of Gut Microbiota in Pathological States. Engineering 2017, 3, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tennoune, N.; Chan, P.; Breton, J.; Legrand, R.; Chabane, Y.N.; Akkermann, K.; Järv, A.; Ouelaa, W.; Takagi, K.; Ghouzali, I.; et al. Bacterial ClpB heat-shock protein, an antigen-mimetic of the anorexigenic peptide α-MSH, at the origin of eating disorders. Transl. Psychiatry 2014, 4, e458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, W.; Boston, B.A.; Kesterson, R.A.; Hruby, V.J.; Cone, R.D. Role of melanocortinergic neurons in feeding and the agouti obesity syndrome. Nat. Cell Biol. 1997, 385, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, S.; Batterham, R.L. Enteroendocrine MC4R and energy balance: Linking the long and the short of it. Cell Metab. 2014, 20, 929–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Panaro, B.L.; Tough, I.; Engelstoft, M.S.; Matthews, R.T.; Digby, G.J.; Møller, C.L.; Svendsen, B.; Gribble, F.; Reimann, F.; Holst, J.J.; et al. The Melanocortin-4 Receptor Is Expressed in Enteroendocrine L Cells and Regulates the Release of Peptide YY and Glucagon-like Peptide 1 In Vivo. Cell Metab. 2014, 20, 1018–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fetissov, S.O. Role of the gut microbiota in host appetite control: Bacterial growth to animal feeding behaviour. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2017, 13, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van De Wouw, M.; Schellekens, H.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis: Modulator of Host Metabolism and Appetite. J. Nutr. 2017, 147, 727–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Legrand, R.; Lucas, N.; Dominique, M.; Azhar, S.; Deroissart, C.; Le Solliec, M.-A.; Rondeaux, J.; Nobis, S.; Guérin, C.; Léon, F.; et al. Commensal Hafnia alvei strain reduces food intake and fat mass in obese mice—A new potential probiotic for appetite and body weight management. Int. J. Obes. 2020, 44, 1041–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Breton, J.; Tennoune, N.; Lucas, N.; Francois, M.; Legrand, R.; Jacquemot, J.; Goichon, A.; Guérin, C.; Peltier, J.; Pestel-Caron, M.; et al. Gut Commensal E. coli Proteins Activate Host Satiety Pathways following Nutrient-Induced Bacterial Growth. Cell Metab. 2016, 23, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dominique, M.; Breton, J.; Guérin, C.; Bole-Feysot, C.; Lambert, G.; Déchelotte, P.; Fetissov, S. Effects of Macronutrients on the In Vitro Production of ClpB, a Bacterial Mimetic Protein of α-MSH and Its Possible Role in Satiety Signaling. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Breton, J.; Legrand, R.; Akkermann, K.; Järv, A.; Harro, J.; Déchelotte, P.; Fetissov, S.O. Elevated plasma concentrations of bacterial ClpB protein in patients with eating disorders. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2016, 49, 805–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominique, M.; Legrand, R.; Galmiche, M.; Azhar, S.; Deroissart, C.; Guérin, C.; Rego, J.-L.D.; Leon, F.; Nobis, S.; Lambert, G.; et al. Changes in Microbiota and Bacterial Protein Caseinolytic Peptidase B During Food Restriction in Mice: Relevance for the Onset and Perpetuation of Anorexia Nervosa. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fetissov, S.O.; Hökfelt, T. On the origin of eating disorders: Altered signaling between gut microbiota, adaptive immunity and the brain melanocortin system regulating feeding behavior. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2019, 48, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mogk, A.; Tomoyasu, T.; Goloubinoff, P.; Rüdiger, S.; Röder, D.; Langen, H.; Bukau, B. Identification of thermolabile Escherichia coli proteins: Prevention and reversion of aggregation by DnaK and ClpB. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 6934–6949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mogk, A.; Schlieker, C.; Strub, C.; Rist, W.; Weibezahn, J.; Bukau, B. Roles of Individual Domains and Conserved Motifs of the AAA+ Chaperone ClpB in Oligomerization, ATP Hydrolysis, and Chaperone Activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 17615–17624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Psichas, A.; Sleeth, M.L.; Murphy, K.; Brooks, L.; Bewick, G.; Hanyaloglu, A.C.; Ghatei, M.A.; Bloom, S.R.; Frost, G. The short chain fatty acid propionate stimulates GLP-1 and PYY secretion via free fatty acid receptor 2 in rodents. Int. J. Obes. 2015, 39, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Horwich, A.L. Chaperoned Protein Disaggregation—The ClpB Ring Uses Its Central Channel. Cell 2004, 119, 579–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spreckley, E. The L-cell in nutritional sensing and the regulation of appetite. Front. Nutr. 2015, 2, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heyder, N.; Kleinau, G.; Szczepek, M.; Kwiatkowski, D.; Speck, D.; Soletto, L.; Cerdá-Reverter, J.M.; Krude, H.; Kühnen, P.; Biebermann, H.; et al. Signal Transduction and Pathogenic Modifications at the Melanocortin-4 Receptor: A Structural Perspective. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, J.; Gimenez, L.E.; Hernandez, C.C.; Wu, Y.; Wein, A.H.; Han, G.W.; McClary, K.; Mittal, S.R.; Burdsall, K.; Stauch, B.; et al. Determination of the melanocortin-4 receptor structure identifies Ca2+ as a cofactor for ligand binding. Science 2020, 368, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurevich, V.V.; Gurevich, E.V. GPCRs and Signal Transducers: Interaction Stoichiometry. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 39, 672–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenbaum, D.M.; Zhang, C.; Lyons, J.A.; Holl, R.; Aragao, D.; Arlow, D.H.; Rasmussen, S.G.F.; Choi, H.-J.; DeVree, B.; Sunahara, R.K.; et al. Structure and function of an irreversible agonist-β2 adrenoceptor complex. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 469, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adrian, T.; Ferri, G.-L.; Bacarese-Hamilton, A.; Fuessl, H.; Polak, J.; Bloom, S. Human distribution and release of a putative new gut hormone, peptide YY. Gastroenterology 1985, 89, 1070–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hambly, C.; Speakman, J.R. Contribution of Different Mechanisms to Compensation for Energy Restriction in the Mouse. Obes. Res. 2005, 13, 1548–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dominique, M.; Lucas, N.; Legrand, R.; Bouleté, I.-M.; Bôle-Feysot, C.; Deroissart, C.; Léon, F.; Nobis, S.; do Rego, J.-C.; Lambert, G.; et al. Effects of Bacterial CLPB Protein Fragments on Food Intake and PYY Secretion. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2223. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13072223
Dominique M, Lucas N, Legrand R, Bouleté I-M, Bôle-Feysot C, Deroissart C, Léon F, Nobis S, do Rego J-C, Lambert G, et al. Effects of Bacterial CLPB Protein Fragments on Food Intake and PYY Secretion. Nutrients. 2021; 13(7):2223. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13072223
Chicago/Turabian StyleDominique, Manon, Nicolas Lucas, Romain Legrand, Illona-Marie Bouleté, Christine Bôle-Feysot, Camille Deroissart, Fatima Léon, Séverine Nobis, Jean-Claude do Rego, Grégory Lambert, and et al. 2021. "Effects of Bacterial CLPB Protein Fragments on Food Intake and PYY Secretion" Nutrients 13, no. 7: 2223. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13072223
APA StyleDominique, M., Lucas, N., Legrand, R., Bouleté, I.-M., Bôle-Feysot, C., Deroissart, C., Léon, F., Nobis, S., do Rego, J.-C., Lambert, G., & Déchelotte, P. (2021). Effects of Bacterial CLPB Protein Fragments on Food Intake and PYY Secretion. Nutrients, 13(7), 2223. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13072223





