The Impact of the COVID-19 Lockdown on Weight Loss and Body Composition in Subjects with Overweight and Obesity Participating in a Nationwide Weight-Loss Program: Impact of a Remote Consultation Follow-Up—The CO-RNPC Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Remote Consultations
2.3. Data Collection and Measures
2.4. Population
2.5. Outcomes and Definitions
2.6. Statistical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
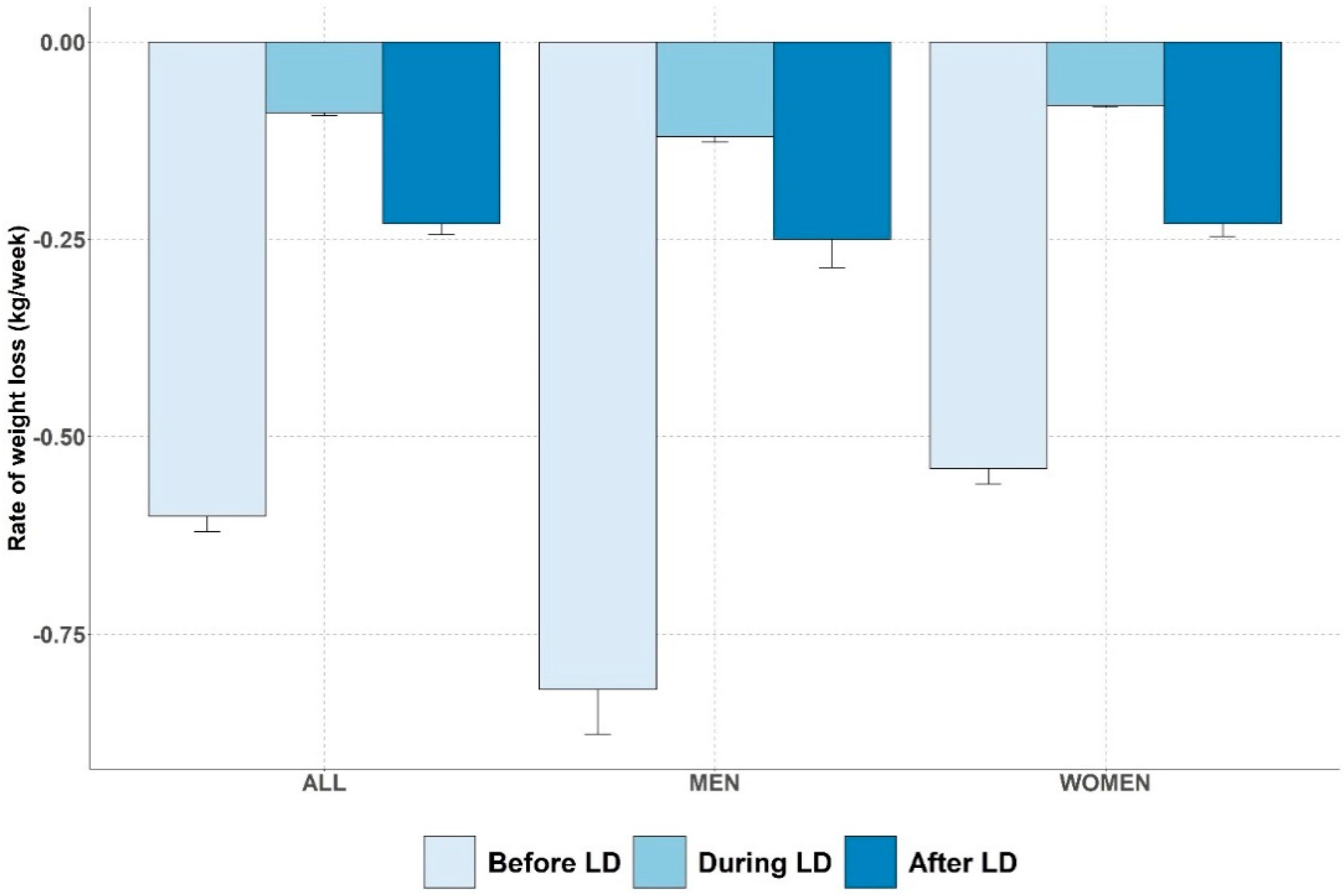
3.2. Changes in Rate of Weight Loss during COVID-19 Total Lockdown
Primary Outcome: Rate of Weight Loss (dWL)
3.3. Rate of Change in Body Composition during COVID-19 Total Lockdown
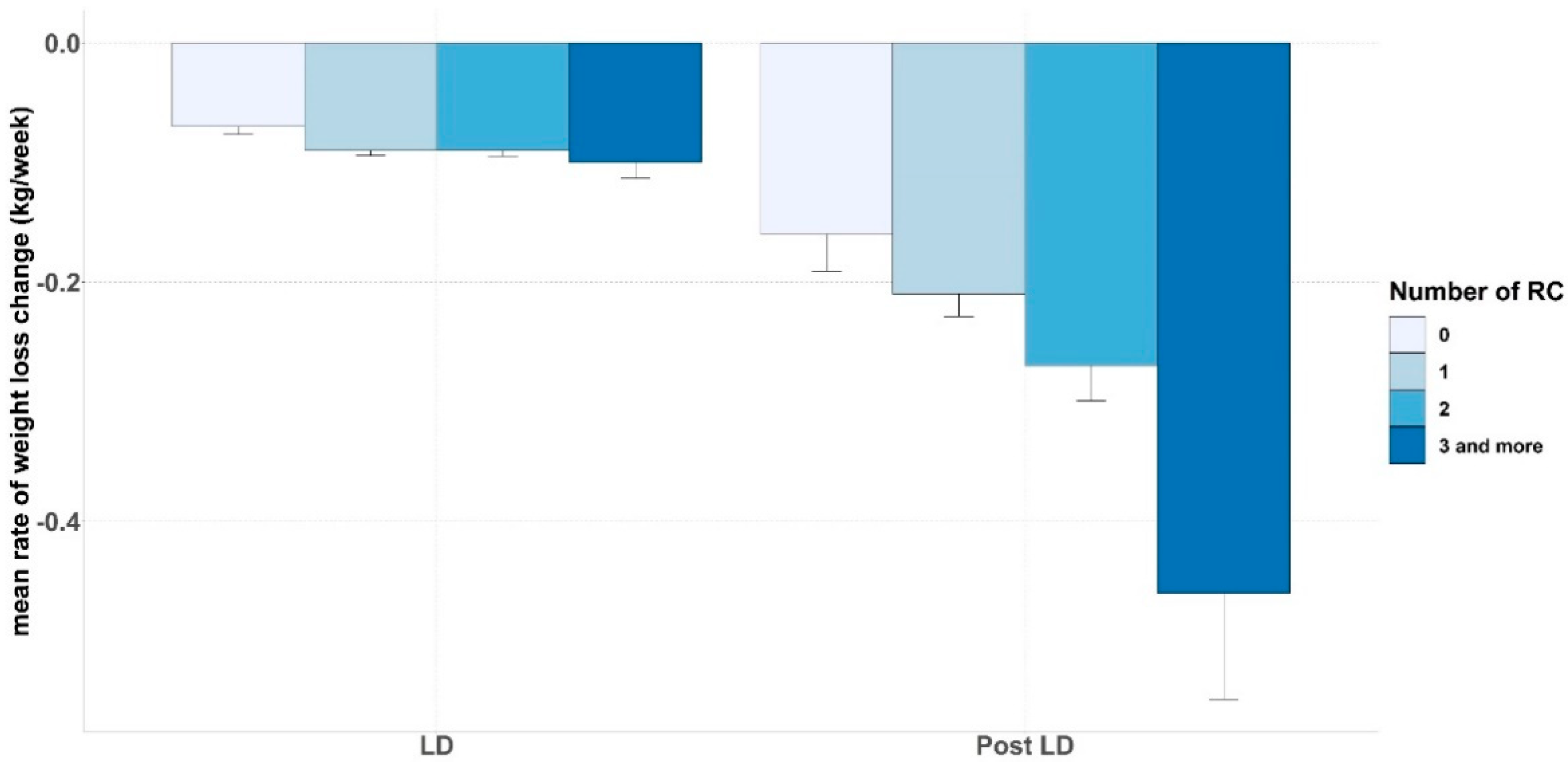
3.4. Impact of Remote Consultation Follow-up
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cauchemez, S.; Kiem, C.T.; Paireau, J.; Rolland, P.; Fontanet, A. Lockdown impact on covid-19 epidemics in regions across metropolitan france. Lancet 2020, 396, 1068–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salje, H.; Tran Kiem, C.; Lefrancq, N.; Courtejoie, N.; Bosetti, P.; Paireau, J.; Andronico, A.; Hoze, N.; Richet, J.; Dubost, C.L.; et al. Estimating the burden of sars-cov-2 in france. Science 2020, 369, 208–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepin, J.L.; Bruno, R.M.; Yang, R.Y.; Vercamer, V.; Jouhaud, P.; Escourrou, P.; Boutouyrie, P. Wearable activity trackers for monitoring adherence to home confinement during the covid-19 pandemic worldwide: Data aggregation and analysis. J. Med. Internet Res. 2020, 22, e19787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammar, A.; Brach, M.; Trabelsi, K.; Chtourou, H.; Boukhris, O.; Masmoudi, L.; Bouaziz, B.; Bentlage, E.; How, D.; Ahmed, M.; et al. Effects of covid-19 home confinement on eating behaviour and physical activity: Results of the eclb-covid19 international online survey. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sher, L. Covid-19, anxiety, sleep disturbances and suicide. Sleep Med. 2020, 70, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhao, N. Generalized anxiety disorder, depressive symptoms and sleep quality during covid-19 outbreak in china: A web-based cross-sectional survey. Psychiatry Res. 2020, 288, 112954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voitsidis, P.; Gliatas, I.; Bairachtari, V.; Papadopoulou, K.; Papageorgiou, G.; Parlapani, E.; Syngelakis, M.; Holeva, V.; Diakogiannis, I. Insomnia during the covid-19 pandemic in a greek population. Psychiatry Res. 2020, 289, 113076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balanza-Martinez, V.; Atienza-Carbonell, B.; Kapczinski, F.; De Boni, R.B. Lifestyle behaviours during the covid-19-time to connect. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2020, 141, 399–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flanagan, E.W.; Beyl, R.A.; Fearnbach, S.N.; Altazan, A.D.; Martin, C.K.; Redman, L.M. The impact of covid-19 stay-at-home orders on health behaviors in adults. Obesity 2021, 29, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini, M.; Ponzo, V.; Rosato, R.; Scumaci, E.; Goitre, I.; Benso, A.; Belcastro, S.; Crespi, C.; De Michieli, F.; Ghigo, E.; et al. Changes in weight and nutritional habits in adults with obesity during the “lockdown” period caused by the covid-19 virus emergency. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OCDE. The Heavy Burden of Obesity; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Falagas, M.E.; Kompoti, M. Obesity and infection. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2006, 6, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calle, E.E.; Thun, M.J.; Petrelli, J.M.; Rodriguez, C.; Heath, C.W., Jr. Body-mass index and mortality in a prospective cohort of U.S. Adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.H.; Chou, C.C.; Chang, L.Y. Effect of obesity and body mass index on coronavirus disease 2019 severity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2020, 21, e13089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonnet, A.; Chetboun, M.; Poissy, J.; Raverdy, V.; Noulette, J.; Duhamel, A.; Labreuche, J.; Mathieu, D.; Pattou, F.; Jourdain, M.; et al. High prevalence of obesity in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (sars-cov-2) requiring invasive mechanical ventilation. Obesity 2020, 28, 1195–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousquet, J.; Anto, J.M.; Iaccarino, G.; Czarlewski, W.; Haahtela, T.; Anto, A.; Akdis, C.A.; Blain, H.; Canonica, G.W.; Cardona, V.; et al. Is diet partly responsible for differences in covid-19 death rates between and within countries? Clin. Transl. Allergy 2020, 10, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Moverley Smith, J.E. “Covibesity”, a new pandemic. Obes. Med. 2020, 19, 100282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorning, T.K.; Fabre, O.; Legrand, R.; Astrup, A.; Hjorth, M.F. Weight loss and weight loss maintenance efficacy of a novel weight loss program: The retrospective rnpc® cohort. OBMED Obes. Med. 2018, 10, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Silent Pandemic: How Lockdown is Affecting Future Health. Available online: https://covid.joinzoe.com/post/lockdown-weight-gain (accessed on 22 June 2021).
- Sondage Ifop Pour Darwin Nutrition: L’impact du Confinement sur l’alimentation des Français.Es. Available online: https://www.darwin-nutrition.fr/actualites/alimentation-francais/ (accessed on 22 June 2021).
- Tronieri, J.S.; Wadden, T.A.; Chao, A.M.; Tsai, A.G. Primary care interventions for obesity: Review of the evidence. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2019, 8, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byaruhanga, J.; Atorkey, P.; McLaughlin, M.; Brown, A.; Byrnes, E.; Paul, C.; Wiggers, J.; Tzelepis, F. Effectiveness of individual real-time video counseling on smoking, nutrition, alcohol, physical activity, and obesity health risks: Systematic review. J. Med. Internet Res. 2020, 22, e18621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchesson, M.J.; Rollo, M.E.; Krukowski, R.; Ells, L.; Harvey, J.; Morgan, P.J.; Callister, R.; Plotnikoff, R.; Collins, C.E. Ehealth interventions for the prevention and treatment of overweight and obesity in adults: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2015, 16, 376–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.W.; Lin, Y.Y.; Wu, N.Y. The effectiveness of telemedicine on body mass index: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Telemed. Telecare 2019, 25, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varkevisser, R.D.M.; van Stralen, M.M.; Kroeze, W.; Ket, J.C.F.; Steenhuis, I.H.M. Determinants of weight loss maintenance: A systematic review. Obes. Rev. 2019, 20, 171–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Car, J.; Koh, G.C.; Foong, P.S.; Wang, C.J. Video consultations in primary and specialist care during the covid-19 pandemic and beyond. BMJ 2020, 371, m3945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhutani, S.; Cooper, J.A. Covid-19-related home confinement in adults: Weight gain risks and opportunities. Obesity 2020, 28, 1576–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Renzo, L.; Gualtieri, P.; Pivari, F.; Soldati, L.; Attina, A.; Cinelli, G.; Leggeri, C.; Caparello, G.; Barrea, L.; Scerbo, F.; et al. Eating habits and lifestyle changes during covid-19 lockdown: An italian survey. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Period | Initial Weight | Final Weight | Delta Weight (kg) | Delta Weight (%) | p-Value * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All (n = 1550) | Before Lockdown | 87.1 [77.0; 100.2] | 86.2 [76.0; 98.7] | −1.1 [−2.0; −0.3] | −1.3 [−2.2; −0.3] | <0.01 |
| Lockdown | 86.2 [76.0; 98.7] | 83.3 [73.5; 95.1] | −2.4 [−6.4; 0.5] | −2.9 [−7.2; 0.6] | <0.01 | |
| After lockdown | 83.3 [73.5; 95.1] | 82.9 [72.9; 94.7] | −0.5 [−1.2; 0.2] | −0.6 [−1.5; 0.3] | <0.01 | |
| Women (n = 1246) | Before Lockdown | 105.9 [96.0; 114.6] | 104.0 [95.2; 113.0] | −1.5 [−2.8; −0.3] | −1.4 [−2.6; −0.3] | <0.01 |
| Lockdown | 104.0 [95.2; 113.0] | 99.1 [91.6; 108.3] | −3.2 [−8.4; 0.4] | −3.2 [−7.7; 0.3] | <0.01 | |
| After lockdown | 99.1 [91.6; 108.3] | 98.6 [91.1; 107.2] | −0.5 [−1.6; 0.3] | −0.5 [−1.5; 0.3] | <0.01 | |
| Men (n = 304) | Before Lockdown | 83.5 [75.2; 94.3] | 82.5 [74.2; 92.7] | −1.1 [−1.9; −0.3] | −1.3 [−2.2; −0.4] | <0.01 |
| Lockdown | 82.5 [74.2; 92.7] | 79.2 [71.5; 89.5] | −2.3 [−6.0; 0.5] | −2.9 [−6.9; 0.6] | <0.01 | |
| After lockdown | 79.2 [71.5; 89.5] | 78.8 [71.0; 88.7] | −0.5 [−1.2; 0.2] | −0.6 [−1.4; 0.3] | <0.01 |
| No Remote Consultation (n = 265) | Remote Consultation (n = 1285) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (female) | 220 (79.1) | 1076 (81.4) | 0.38 |
| Age (year) | 54 [46; 61] | 54 [45; 63] | 0.31 |
| Tobacco consumption | 32 (11.5) | 150 (11.3) | 0.94 |
| Menopause | 104 (37.4) | 534 (40.4) | 0.36 |
| Sleep apnea | 31 (11.2) | 240 (18.2) | <0.01 |
| Arthrosis | 87 (31.3) | 483 (36.5) | 0.10 |
| Venous disease | 38 (13.7) | 216 (16.3) | 0.27 |
| Diabetes | 8 (2.9) | 54 (4.1) | 0.34 |
| Hyper-triglyceridemia | 0 (0) | 7 (0.5) | 0.22 |
| Initial body mass index (kg/m2) | 33.2 [29.4; 36.8] | 34.2 [30.8; 38.3] | <0.01 |
| Initial fat mass (%) | 41 [36.8; 45] | 42.3 [38.9; 46.2] | <0.01 |
| Initial muscle mass (%) | 29.3 [27.4; 31.6] | 29.1 [26.9; 32.2] | 0.82 |
| Initial percentage of body water (%) | 43 [40.1; 45.9] | 42 [39.2; 44.5] | <0.01 |
| Initial waist circumference (cm) | 106 [96; 119] | 110 [100; 120] | 0.02 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bailly, S.; Fabre, O.; Legrand, R.; Pantagis, L.; Mendelson, M.; Terrail, R.; Tamisier, R.; Astrup, A.; Clément, K.; Pépin, J.-L. The Impact of the COVID-19 Lockdown on Weight Loss and Body Composition in Subjects with Overweight and Obesity Participating in a Nationwide Weight-Loss Program: Impact of a Remote Consultation Follow-Up—The CO-RNPC Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2152. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13072152
Bailly S, Fabre O, Legrand R, Pantagis L, Mendelson M, Terrail R, Tamisier R, Astrup A, Clément K, Pépin J-L. The Impact of the COVID-19 Lockdown on Weight Loss and Body Composition in Subjects with Overweight and Obesity Participating in a Nationwide Weight-Loss Program: Impact of a Remote Consultation Follow-Up—The CO-RNPC Study. Nutrients. 2021; 13(7):2152. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13072152
Chicago/Turabian StyleBailly, Sébastien, Odile Fabre, Rémy Legrand, Laurent Pantagis, Monique Mendelson, Robin Terrail, Renaud Tamisier, Arne Astrup, Karine Clément, and Jean-Louis Pépin. 2021. "The Impact of the COVID-19 Lockdown on Weight Loss and Body Composition in Subjects with Overweight and Obesity Participating in a Nationwide Weight-Loss Program: Impact of a Remote Consultation Follow-Up—The CO-RNPC Study" Nutrients 13, no. 7: 2152. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13072152
APA StyleBailly, S., Fabre, O., Legrand, R., Pantagis, L., Mendelson, M., Terrail, R., Tamisier, R., Astrup, A., Clément, K., & Pépin, J.-L. (2021). The Impact of the COVID-19 Lockdown on Weight Loss and Body Composition in Subjects with Overweight and Obesity Participating in a Nationwide Weight-Loss Program: Impact of a Remote Consultation Follow-Up—The CO-RNPC Study. Nutrients, 13(7), 2152. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13072152







