Detecting Impending Malnutrition of (Pre-) Frail Older Adults in Domestic Smart Home Environments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. State of the Art
2.1. Nutritional Intake and Body Weight
2.2. Activities of Daily Living
3. Materials and Methods
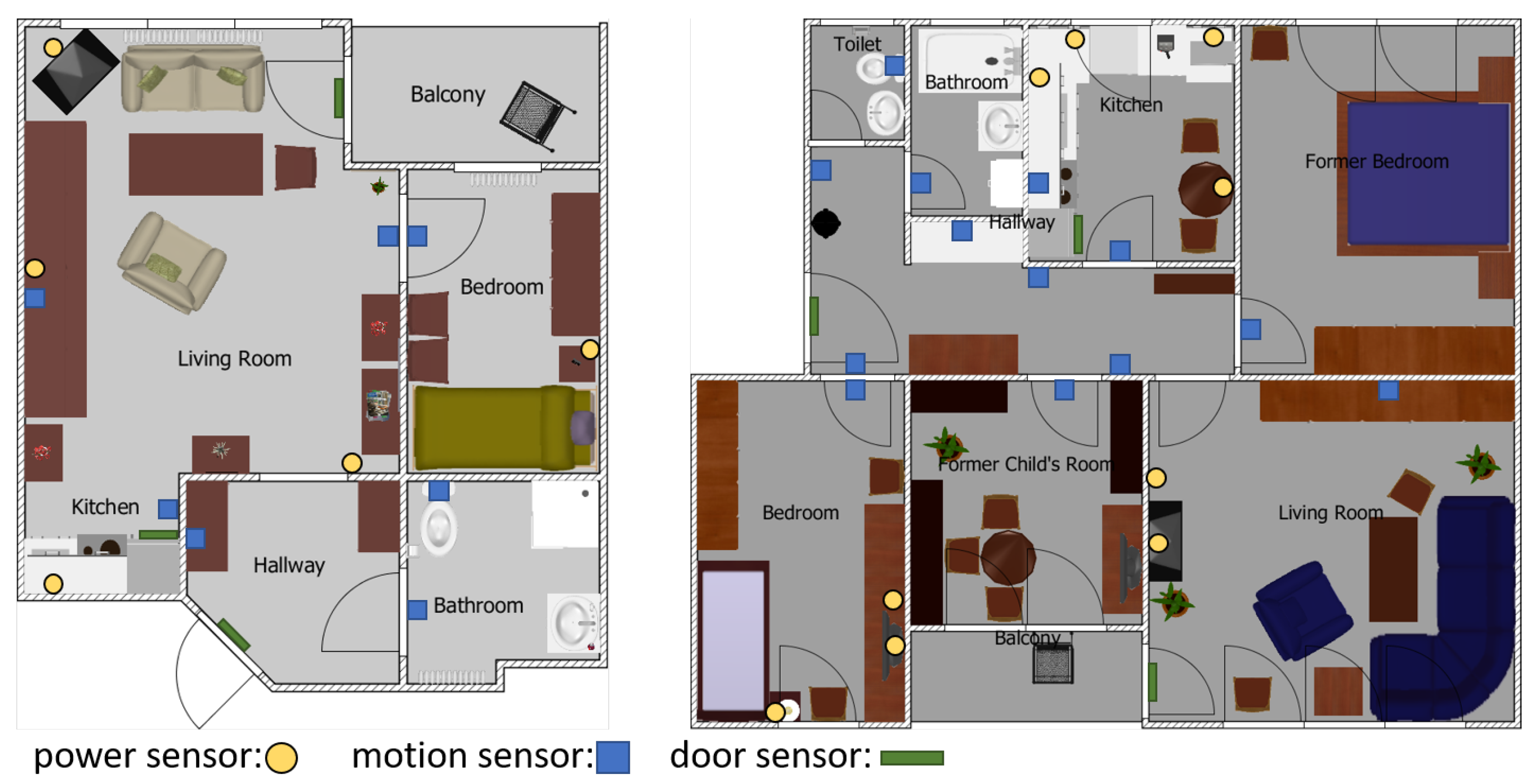
3.1. Data Acquisition
3.2. Data Preprocessing
3.3. Meal Preparation Time Estimation
3.4. Minimal Clinically Important Difference
3.5. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| (i)ADL | (instrumental) Activities of Daily Living |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| BW | Body Weight |
| ESPEN | European Society for Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism |
| HGS | Hand Grip Strength |
| KPI | Key Performance Indicator |
| MCID | Minimal Clinically Important Difference |
| N/A | Not Applicable |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| SPPB | Short Physical Performance Battery |
| TUG | Timed Up & Go |
Appendix A
| ID | Power Sensors | Motion Sensors | Door Sensor |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Kettle, Radio, Microwave, Lamp | Kitchen, Stove | Fridge |
| 2 | Kettle, Microwave, Extractor Hood | Kitchen | Fridge |
| 3 | Kettle, Microwave, Toaster, Various | Kitchen | Fridge |
| 4 | Kettle, Coffeemaker | Kitchen | N/A |
| 5 | Kettle, Coffeemaker, Espresso-maker | Kitchen | Fridge |
| 6 | Coffeemaker, Microwave, Lamp | Kitchen | Fridge |
| 7 | Kettle, Coffeemaker | Kitchen | Fridge |
| 8 | Various, Lamp | Kitchen | Fridge |
| 9 | Kettle, Toaster, Lamp, Various | Kitchen | Fridge |
| 10 | Kettle, Microwave | Kitchen | Fridge |
References
- Rolland, Y.; Czerwinski, S.; van Kan, G.A.; Morley, J.E.; Cesari, M.; Onder, G.; Woo, J.; Baumgartner, R.; Pillard, F.; Boirie, Y.; et al. Sarcopenia: Its assessment, etiology, pathogenesis, consequences and future perspectives. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2008, 12, 433–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norman, K.; Stobäus, N.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Schulzke, J.D.; Pirlich, M. Hand grip strength: Outcome predictor and marker of nutritional status. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 30, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaiser, M.J.; Bauer, J.M.; Rämsch, C.; Uter, W.; Guigoz, Y.; Cederholm, T.; Thomas, D.R.; Anthony, P.S.; Charlton, K.E.; Maggio, M.; et al. Frequency of Malnutrition in Older Adults: A Multinational Perspective Using the Mini Nutritional Assessment. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2010, 58, 1734–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkert, D.; Berner, Y.N.; Berry, E.; Cederholm, T.; Coti Bertrand, P.; Milne, A.; Palmblad, J.; Schneider, S.; Sobotka, L.; Stanga, Z.; et al. ESPEN Guidelines on Enteral Nutrition: Geriatrics. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 25, 330–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rantanen, T.; Avlund, K.; Suominen, H.; Schroll, M.; Frändin, K.; Pertti, E. Muscle strength as a predictor of onset of ADL dependence in people aged 75 years. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2002, 14, 10–15. [Google Scholar]
- Kuczmarski, M.F.; Kuczmarski, R.J.; Najjar, M. Effects of Age on Validity of Self-Reported Height, Weight, and Body Mass Index: Findings from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1988–1994. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2001, 101, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marschollek, M.; Becker, M.; Bauer, J.M.; Bente, P.; Dasenbrock, L.; Elbers, K.; Hein, A.; Kolb, G.; Künemund, H.; Lammel-Polchau, C.; et al. Multimodal activity monitoring for home rehabilitation of geriatric fracture patients–feasibility and acceptance of sensor systems in the GAL-NATARS study. Inform. Health Soc. Care 2014, 39, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hein, A.; Winkelbach, S.; Martens, B.; Wilken, O.; Eichelberg, M.; Spehr, J.; Gietzelt, M.; Wolf, K.H.; Büsching, F.; Hülsken-Giesler, M.; et al. Monitoring systems for the support of home care. Inform. Health Soc. Care 2010, 35, 157–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, P.Y.; Chen, J.H.; Chu, H.H.; Chen, B.Y. Enabling Nutrition-Aware Cooking in a Smart Kitchen. In CHI ’07 Extended Abstracts on Human Factors in Computing Systems; CHI EA ’07; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 2333–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Li, J.S. A smart fridge with an ability to enhance health and enable better nutrition. Int. J. Multimed. Ubiquitous Eng. 2009, 4, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Xia, H.; Gao, Y.; Jin, J.S.; Athauda, R. Smart Fridges with Multimedia Capability for Better Nutrition and Health. In Proceedings of the 2008 International Symposium on Ubiquitous Multimedia Computing, Hobart, Australia, 13–15 October 2008; pp. 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Wang, D. A Content-aware Fridge based on RFID in smart home for home-healthcare. In Proceedings of the 2009 11th International Conference on Advanced Communication Technology, Gangwon-Do, Korea, 15–18 February 2009; Volume 2, pp. 987–990. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Hathaipontaluk, P.; Luo, S. Intelligent stove in Smart Home Environment. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Research Challenges in Computer Science, Shanghai, China, 28–29 December 2009; pp. 247–250. [Google Scholar]
- Sundaravadivel, P.; Kesavan, K.; Kesavan, L.; Mohanty, S.P.; Kougianos, E. Smart-Log: A Deep-Learning Based Automated Nutrition Monitoring System in the IoT. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2018, 64, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mankoff, J.; Hsieh, G.; Hung, H.C.; Lee, S.; Nitao, E. Using Low-Cost Sensing to Support Nutritional Awareness. In UbiComp 2002: Ubiquitous Computing; Borriello, G., Holmquist, L.E., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002; pp. 371–378. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, K.M.; Wing, R.R. Concordance of in-home ‘smart’ scale measurement with body weight measured in-person. Obes. Sci. Pract. 2016, 2, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grace, S.L.; Taherzadeh, G.; Jae Chang, I.S.; Boger, J.; Arcelus, A.; Mak, S.; Chessex, C.; Mihailidis, A. Perceptions of seniors with heart failure regarding autonomous zero-effort monitoring of physiological parameters in the smart-home environment. Heart Lung J. Cardiopulm. Acute Care 2017, 46, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, S.; Ford, A.B.; Moskowitz, R.W.; Jackson, B.A.; Jaffe, M.W. Studies of Illness in the Aged: The Index of ADL: A Standardized Measure of Biological and Psychosocial Function. JAMA 1963, 185, 914–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Staff of the Benjamin Rose Hospital. Multidisciplinary studies of illness in aged persons: II. A new classification of functional status in activities of daily living. J. Chronic Dis. 1959, 9, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, S. Assessing self-maintenance: Activities of daily living, mobility, and instrumental activities of daily living. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 1983, 31, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nef, T.; Urwyler, P.; Büchler, M.; Tarnanas, I.; Stucki, R.; Cazzoli, D.; Müri, R.; Mosimann, U. Evaluation of Three State-of-the-Art Classifiers for Recognition of Activities of Daily Living from Smart Home Ambient Data. Sensors 2015, 15, 11725–11740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, N.C.; Cook, D.J. Activity Recognition on Streaming Sensor Data. Pervasive Mob. Comput. 2014, 10, 138–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, N.; Misra, A.; Cook, D. Ambient and smartphone sensor assisted ADL recognition in multi-inhabitant smart environments. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2016, 7, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Wang, H.; Black, N. Human Activity Detection in Smart Home Environment with Self-Adaptive Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Conference on Networking, Sensing and Control, Hainan, China, 6–8 April 2008; pp. 1505–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, S.; Kim, M.; Song, S.k.; Park, S.J. Toward real time detection of the basic living activity in home using a wearable sensor and smart home sensors. In Proceedings of the 2008 30th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 21–24 August 2008; pp. 5200–5203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belley, C.; Gaboury, S.; Bouchard, B.; Bouzouane, A. Activity Recognition in Smart Homes Based on Electrical Devices Identification. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on PErvasive Technologies Related to Assistive Environments; PETRA ’13; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avgerinakis, K.; Briassouli, A.; Kompatsiaris, I. Recognition of Activities of Daily Living for Smart Home Environments. In Proceedings of the 2013 9th International Conference on Intelligent Environments, Athens, Greece, 16–17 July 2013; pp. 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleury, A.; Vacher, M.; Noury, N. SVM-Based Multimodal Classification of Activities of Daily Living in Health Smart Homes: Sensors, Algorithms, and First Experimental Results. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2010, 14, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guralnik, J.M.; Simonsick, E.M.; Ferrucci, L.; Glynn, R.J.; Berkman, L.F.; Blazer, D.G.; Scherr, P.A.; Wallace, R.B. A Short Physical Performance Battery Assessing Lower Extremity Function: Association With Self-Reported Disability and Prediction of Mortality and Nursing Home Admission. J. Gerontol. 1994, 49, M85–M94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podsiadlo, D.; Richardson, S. The Timed “Up & Go”: A Test of Basic Functional Mobility for Frail Elderly Persons. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 1991, 39, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fried, L.P.; Tangen, C.M.; Walston, J.; Newman, A.B.; Hirsch, C.; Gottdiener, J.; Seeman, T.; Tracy, R.; Kop, W.J.; Burke, G.; et al. Frailty in Older Adults: Evidence for a Phenotype. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2001, 56, M146–M157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawton, M.P.; Brody, E.M. Assessment of Older People: Self-Maintaining and Instrumental Activities of Daily Living1. Gerontologist 1969, 9, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2008, 61, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schünemann, H.J.; Guyatt, G.H. Commentary—Goodbye M(C)ID! Hello MID, where do you come from? Health Serv. Res. 2005, 40, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, A.; Hannon, J.; Hegedus, E.J.; Kavchak, A.E. Clinimetrics corner: A closer look at the minimal clinically important difference (MCID). J. Man. Manip. Ther. 2012, 20, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virtanen, P.; Gommers, R.; Oliphant, T.E.; Haberland, M.; Reddy, T.; Cournapeau, D.; Burovski, E.; Peterson, P.; Weckesser, W.; Bright, J.; et al. SciPy 1.0: Fundamental Algorithms for Scientific Computing in Python. Nat. Methods 2020, 17, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
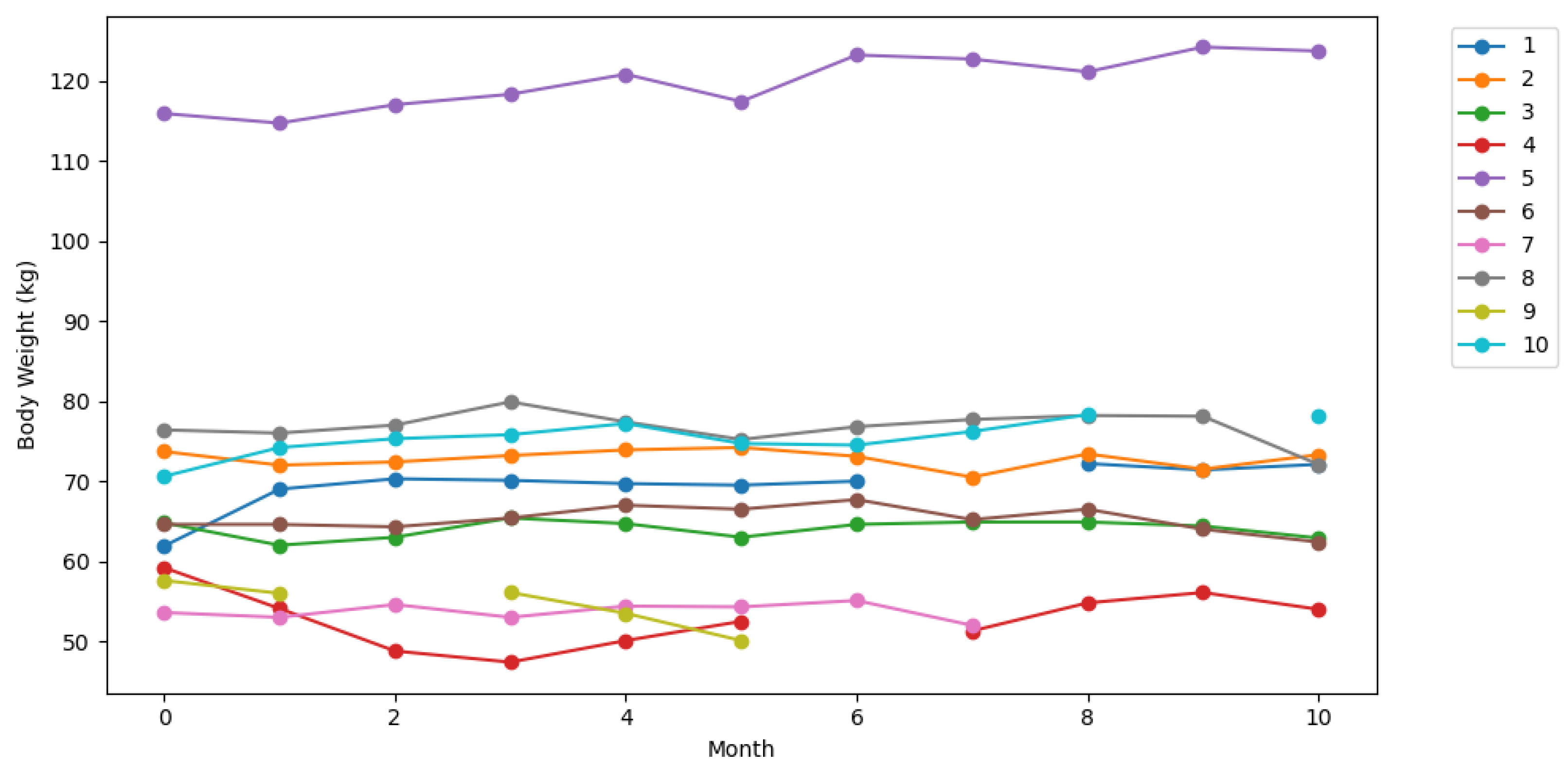
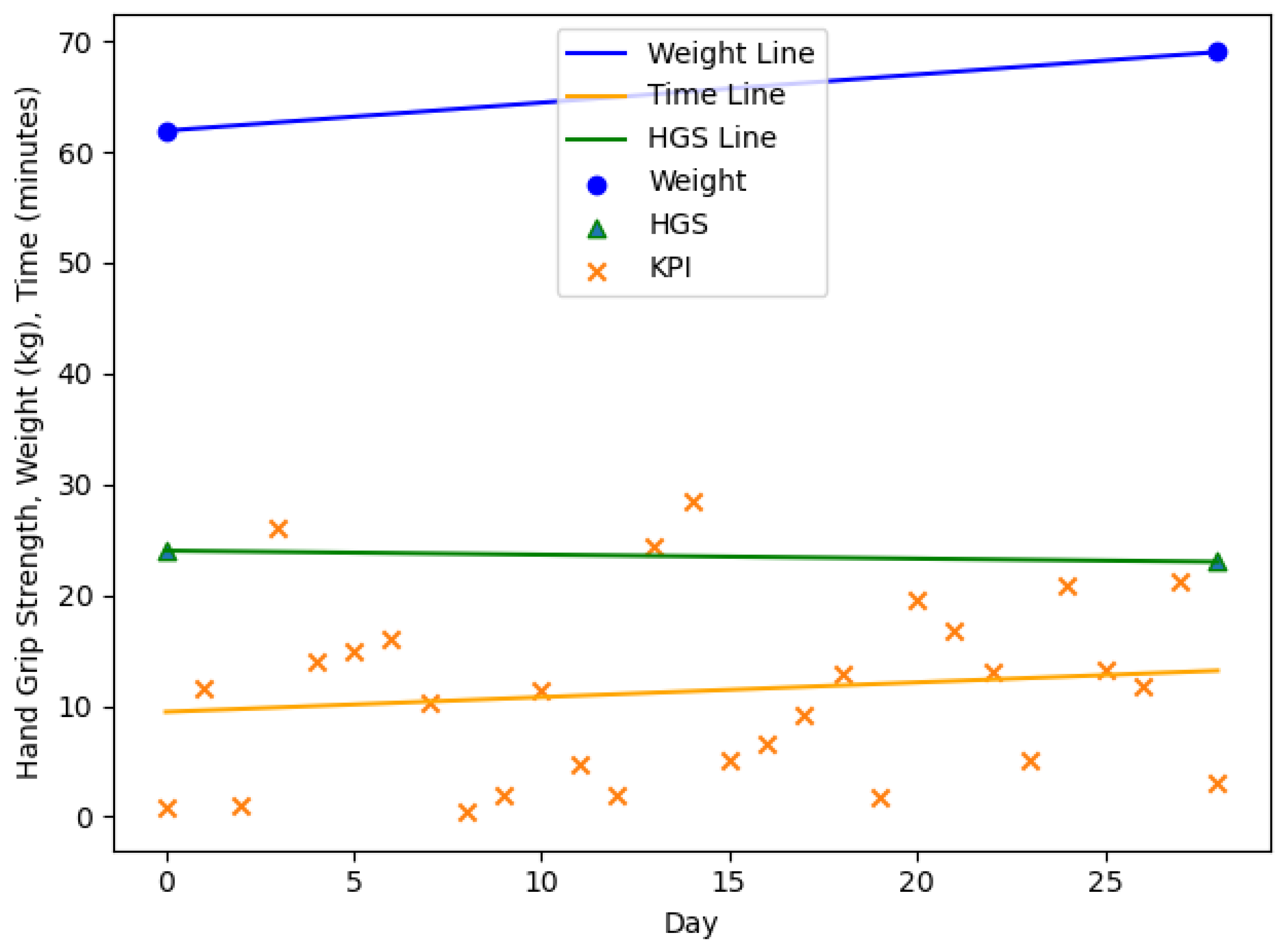
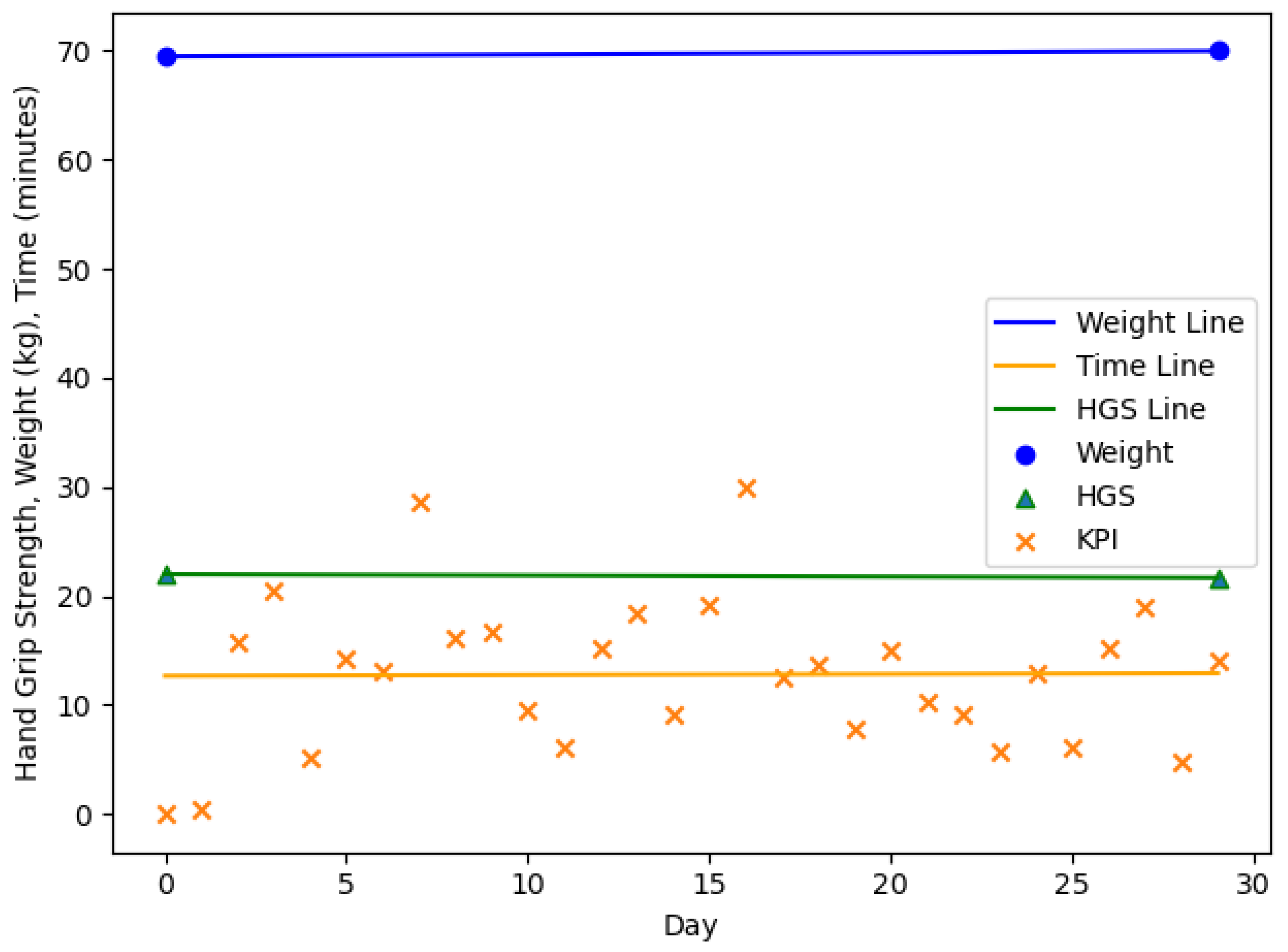
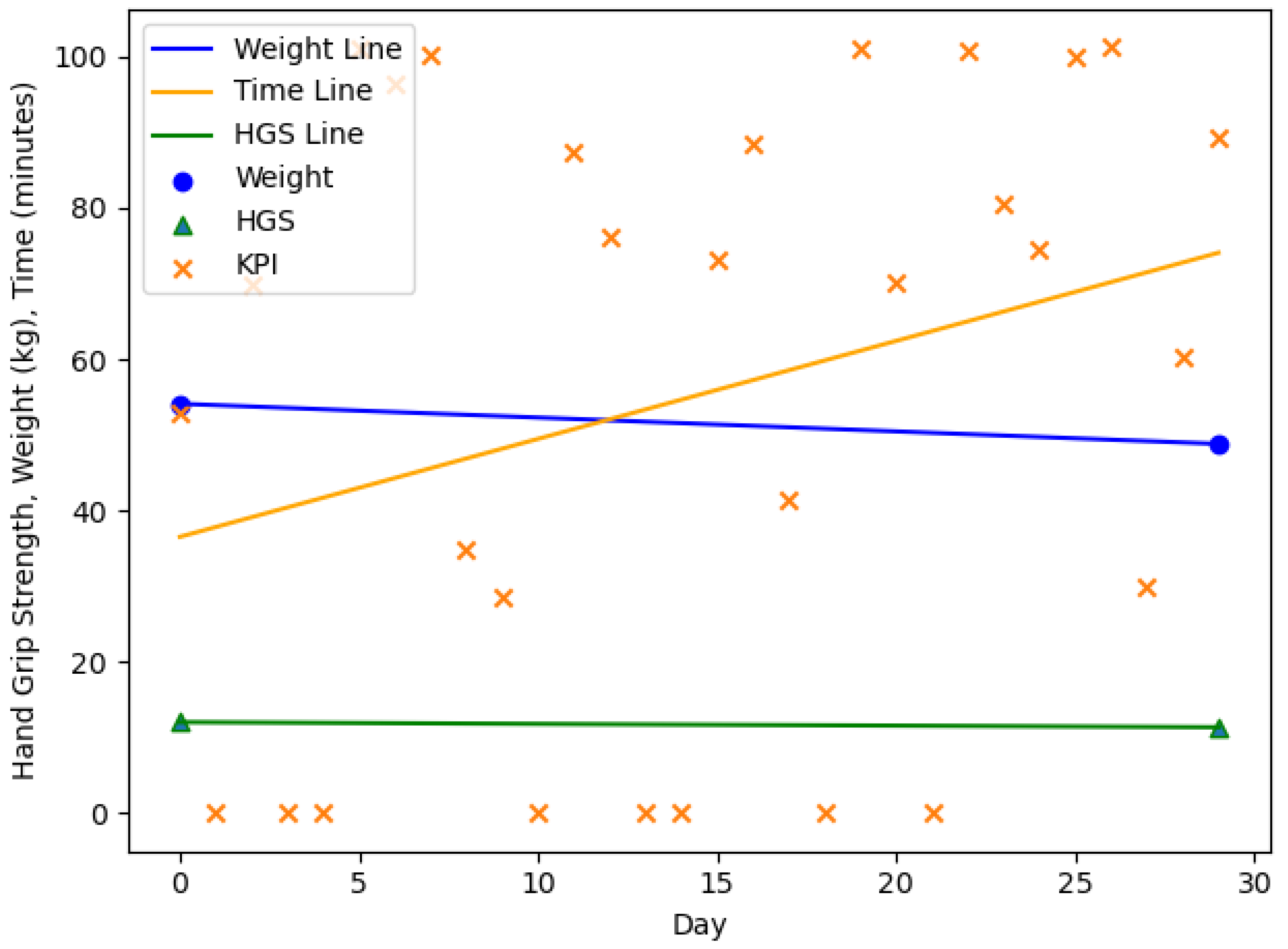
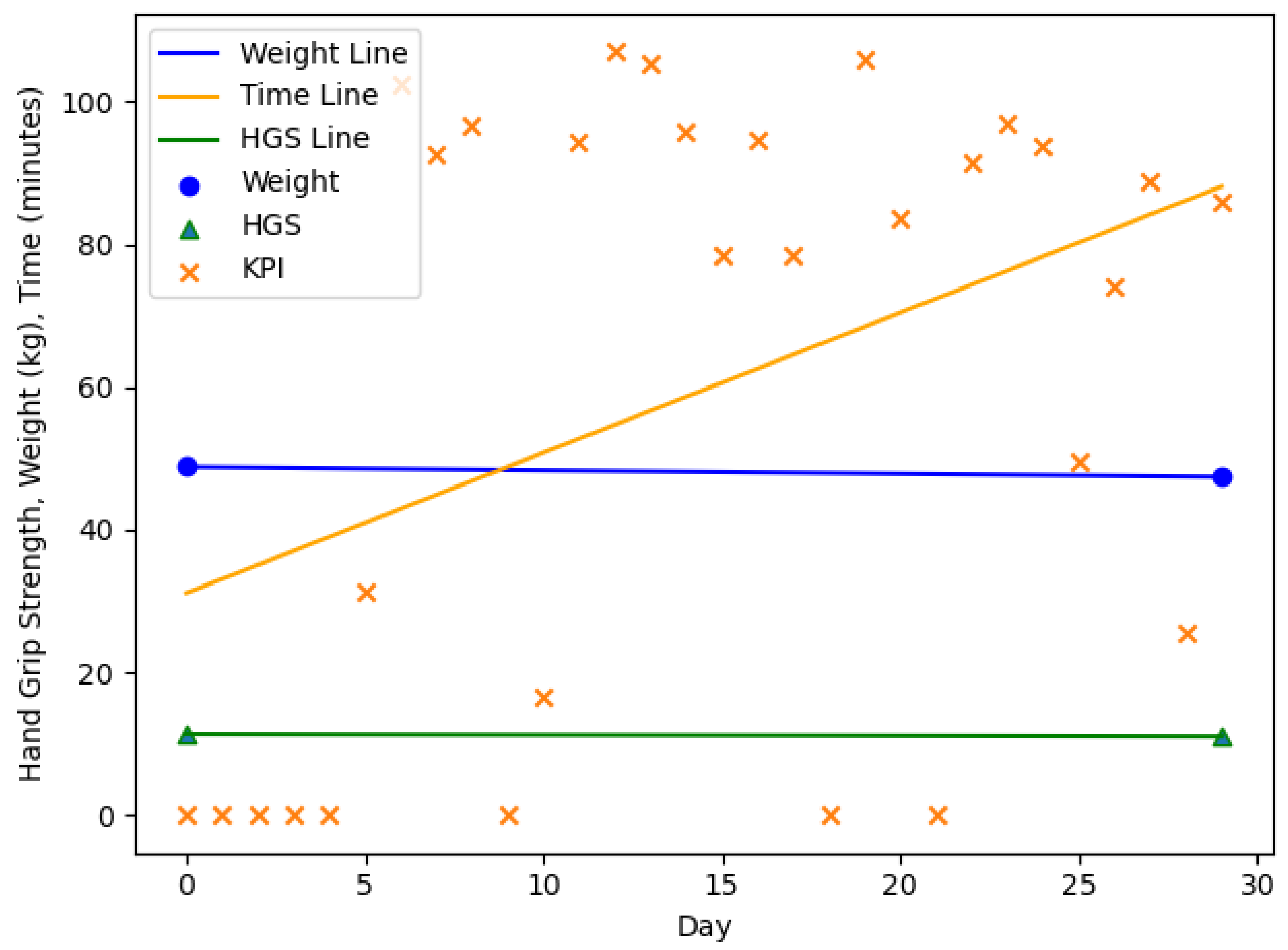
| n = 20, m = 3, f = 17 | Age (y) | Body Weight (kg) m/f | HGS (kg) m/f | |
| Mean | 84.8 | 66.2/69.2 | 17.1/14.1 | |
| SD (±) | 5.2 | 3.6/17.3 | 5.1/7.0 | |
| Range (min–max) | 76.0–92.0 | 61.9/43.8–70.8/115.9 | 11.7/3.7–24.0/33.0 | |
| n = 20, m = 3, f = 17 | Frailty Index (pts.) | SPPB (pts.) | TUG (s) | iADL (pts.) |
| Mean | 1.9 | 6.0 | 17.9 | 7.3 |
| SD (±) | 0.7 | 2.3 | 5.3 | 1.4 |
| Range (min–max) | 1.0–3.0 | 3.0–11.0 | 11.2–31.6 | 3.0–8.0 |
| n = 18, m = 3, f = 15 | Age (y) | Body Weight (kg) m/f | HGS (kg) m/f | |
| Mean | 84.5 | 66.1/71.0 | 16.8/12.2 | |
| SD (±) | 4.9 | 5.4/19.1 | 4.2/3.7 | |
| Range (min–max) | 77.0–93.0 | 59.1/42.7–72.1/123.7 | 13.3/5.0–22.7/18.0 | |
| n = 18, m = 3, f = 15 | Frailty Index (pts.) | SPPB (pts.) | TUG (s) | iADL (pts.) |
| Mean | 2.0 | 6.6 | 16.4 | 6.1 |
| SD (±) | 1.0 | 2.9 | 6.0 | 2.3 |
| Range (min–max) | 0.0–4.0 | 2.0–12.0 | 8.5–30.06 | 1.0–8.0 |
| n = 10, m = 1, f = 9 | Age (y) | Body Weight (kg) m/f | HGS (kg) m/f | |
| Mean | 85.1 | 61.9/70.7 | 24.0/15.4 | |
| SD (±) | 4.6 | 0.0/18.6 | 0.0/6.1 | |
| Range (min–max) | 77.0–91.0 | 61.9/53.6–61.9/115.9 | 24.0/7.3–24.0/23.7 | |
| n = 10, m = 1, f = 9 | Frailty Index (pts.) | SPPB (pts.) | TUG (s) | iADL (pts.) |
| Mean | 1.8 | 5.7 | 18.3 | 7.8 |
| SD (±) | 1.0 | 2.1 | 6.1 | 0.6 |
| Range (min–max) | 1.0–3.0 | 3.0–9.1 | 12.0–31.6 | 6.0–8.0 |
| n = 10, m = 1, f = 9 | Age (y) | Body Weight (kg) m/f | HGS (kg) m/f | |
| Mean | 85.1 | 72.1/74.8 | 22.7/14.5 | |
| SD (±) | 4.5 | 0.0/21.2 | 0.0/5.0 | |
| Range (min–max) | 77.0–91.0 | 72.1/54.0–72.1/123.7 | 22.7/8.0–22.7/22.7 | |
| n = 10, m = 1, f = 9 | Frailty Index (pts.) | SPPB (pts.) | TUG (s) | iADL (pts.) |
| Mean | 2.3 | 5.9 | 15.5 | 7.1 |
| SD (±) | 1.1 | 2.5 | 5.3 | 1.6 |
| Range (min–max) | 1.0–4.0 | 3.0–10.0 | 8.5–22.3 | 4.0–8.0 |
| ID | MCID | BW Change | HGS Change | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.99 | no | gain | −0.99 | decrease |
| −1.00 | no | gain | 1.00 | decrease | |
| N/A | no | no change | N/A | N/A | |
| N/A | no | no change | N/A | N/A | |
| N/A | no | no change | N/A | N/A | |
| N/A | no | no change | N/A | N/A | |
| −1.00 | no | gain | −1.00 | increase | |
| 1.00 | no | gain | −1.00 | decrease | |
| −1.00 | no | loss | 1.00 | increase | |
| N/A | no | no change | N/A | N/A |
| ID | MCID | BW Change | HGS Change | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 1.00 | no | loss | 1.00 | decrease |
| N/A | no | no change | N/A | N/A | |
| −1.00 | no | gain | 1.00 | decrease | |
| N/A | no | no change | N/A | N/A | |
| N/A | no | no change | N/A | N/A | |
| 1.00 | no | loss | 1.00 | decrease | |
| −1.00 | no | loss | 1.00 | increase | |
| 1.00 | no | gain | 1.00 | increase | |
| 1.00 | no | loss | 1.00 | decrease | |
| −1.00 | no | gain | −1.00 | increase |
| ID | MCID | BW Change | HGS Change | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | −0.99 | no | loss | −0.99 | decrease |
| −1.00 | no | gain | N/A | no change | |
| 1.00 | no | gain | −1.00 | decrease | |
| −1.00 | no | loss | 1.00 | decrease | |
| 1.00 | no | loss | 1.00 | decrease | |
| 1.00 | no | gain | 1.00 | increase | |
| N/A | no | no change | N/A | N/A | |
| N/A | no | no change | N/A | N/A | |
| −1.00 | no | loss | 1.00 | increase |
| ID | MCID | BW Change | HGS Change | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 1.00 | yes | loss | 1.00 | decrease |
| −1.00 | yes | loss | −1.00 | decrease | |
| −1.00 | yes | loss | −1.00 | decrease | |
| −1.00 | yes | gain | 1.00 | decrease | |
| −1.00 | yes | gain | −1.00 | increase |
| ID | MCID | BW Change | HGS Change | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | −1.00 | no | gain | −1.00 | increase |
| 1.00 | no | gain | −1.00 | decrease | |
| N/A | no | no change | N/A | N/A | |
| −1.00 | no | loss | 1.00 | increase | |
| −1.00 | no | gain | 1.00 | decrease |
| ID | MCID | BW Change | HGS Change | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | −0.99 | no | loss | 0.99 | increase |
| −1.00 | no | gain | 1.00 | decrease | |
| −1.00 | no | gain | −1.00 | increase | |
| −1.00 | no | gain | 1.00 | decrease | |
| −1.00 | no | loss | 1.00 | increase | |
| −1.00 | no | gain | −1.00 | increase | |
| N/A | no | no change | N/A | N/A | |
| 1.00 | no | loss | −1.00 | decrease | |
| -1.00 | no | gain | 1.00 | decrease | |
| N/A | no | no change | N/A | N/A |
| ID | MCID | BW Change | HGS Change | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | 0.99 | no | loss | 0.99 | increase |
| −1.00 | no | gain | −1.00 | increase | |
| 1.00 | no | loss | 1.00 | decrease | |
| 1.00 | no | gain | 1.00 | increase | |
| N/A | no | no change | N/A | N/A | |
| −1.00 | no | loss | 1.00 | increase |
| ID | MCID | BW Change | HGS Change | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | N/A | no | no change | N/A | N/A |
| −1.00 | no | gain | −1.00 | increase | |
| −1.00 | no | gain | −1.00 | increase | |
| −1.00 | no | loss | 1.00 | increase | |
| −1.00 | no | loss | −1.00 | decrease | |
| −1.00 | no | gain | −1.00 | increasae | |
| 1.00 | no | gain | −1.00 | decrease | |
| N/A | yes | no change | N/A | N/A | |
| N/A | yes | no change | N/A | N/A | |
| 1.00 | yes | loss | -1.00 | increase |
| ID | MCID | BW Change | HGS Change | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9 | 0.99 | N/A | loss | 0.99 | decrease |
| ID | MCID | BW Change | HGS Change | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | −1.00 | no | gain | 1.00 | decrease |
| 1.00 | no | gain | −1.00 | decrease | |
| N/A | no | no change | N/A | N/A | |
| −1.00 | no | gain | −1.00 | increase | |
| −1.00 | no | loss | −1.00 | decrease |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Friedrich, B.; Bauer, J.M.; Hein, A.; Diekmann, R. Detecting Impending Malnutrition of (Pre-) Frail Older Adults in Domestic Smart Home Environments. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1955. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13061955
Friedrich B, Bauer JM, Hein A, Diekmann R. Detecting Impending Malnutrition of (Pre-) Frail Older Adults in Domestic Smart Home Environments. Nutrients. 2021; 13(6):1955. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13061955
Chicago/Turabian StyleFriedrich, Björn, Jürgen M. Bauer, Andreas Hein, and Rebecca Diekmann. 2021. "Detecting Impending Malnutrition of (Pre-) Frail Older Adults in Domestic Smart Home Environments" Nutrients 13, no. 6: 1955. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13061955
APA StyleFriedrich, B., Bauer, J. M., Hein, A., & Diekmann, R. (2021). Detecting Impending Malnutrition of (Pre-) Frail Older Adults in Domestic Smart Home Environments. Nutrients, 13(6), 1955. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13061955







