Effects of Soy Isoflavones on Glycemic Control and Lipid Profile in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy and Study Selection
2.2. Data Extraction
2.3. Quality Assessment and Bias Risk of the Trials
2.4. Statistical Analysis and Meta-Analysis
2.5. Subgroup Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Included Trials
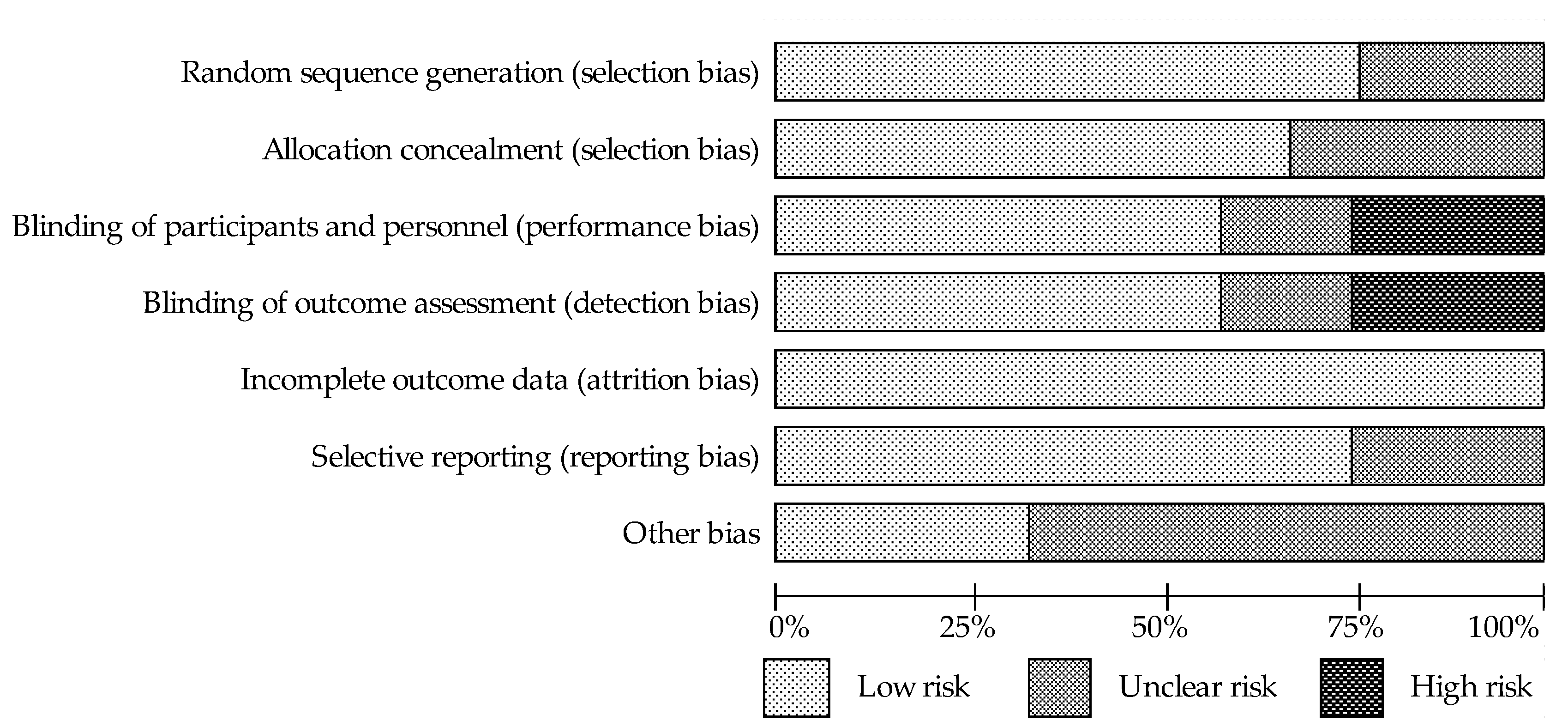
3.2. Assessment of the Methodological Quality of Trials
3.3. The Effect of Soy Isoflavones on Metabolism Glucose in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
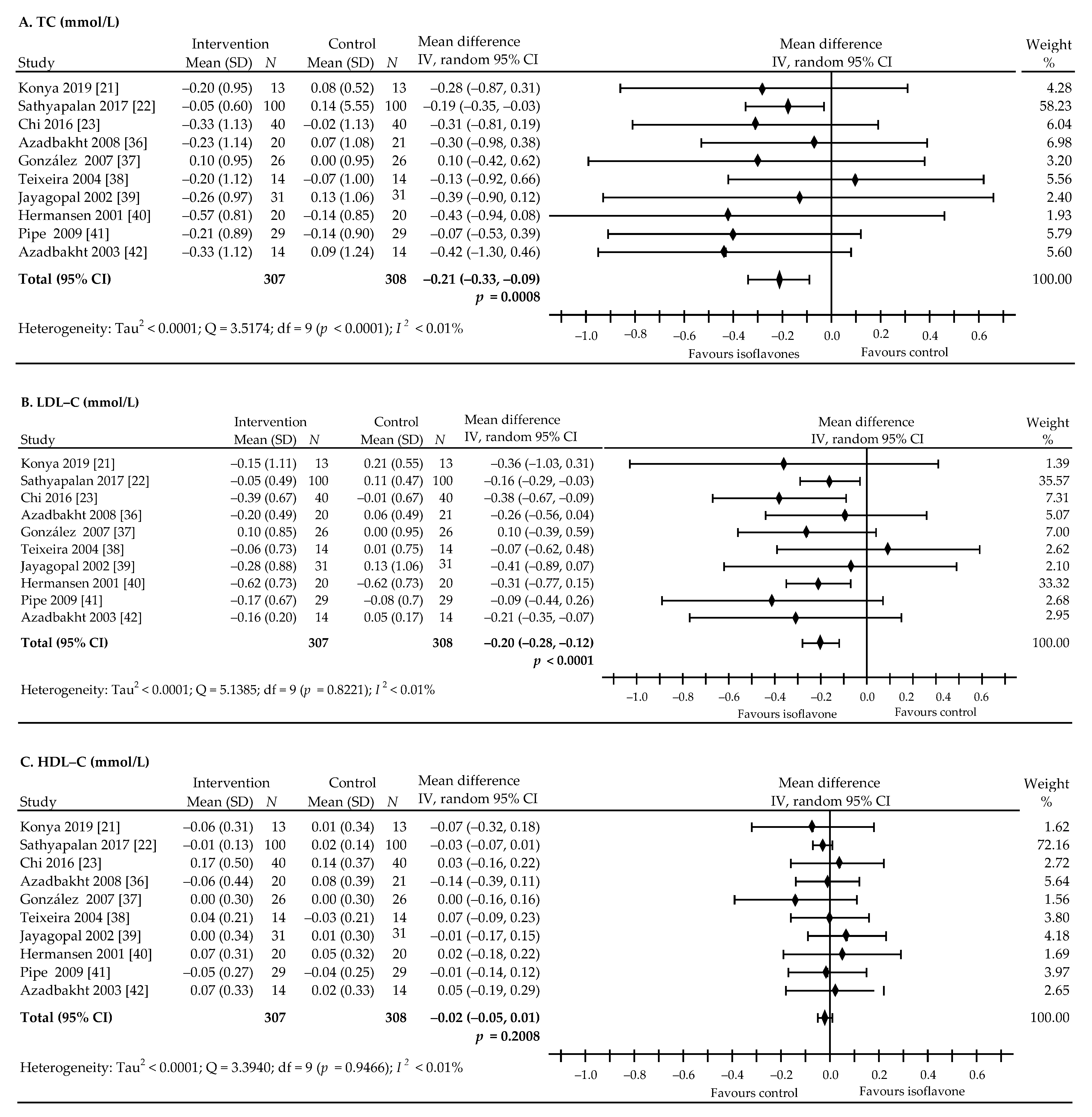
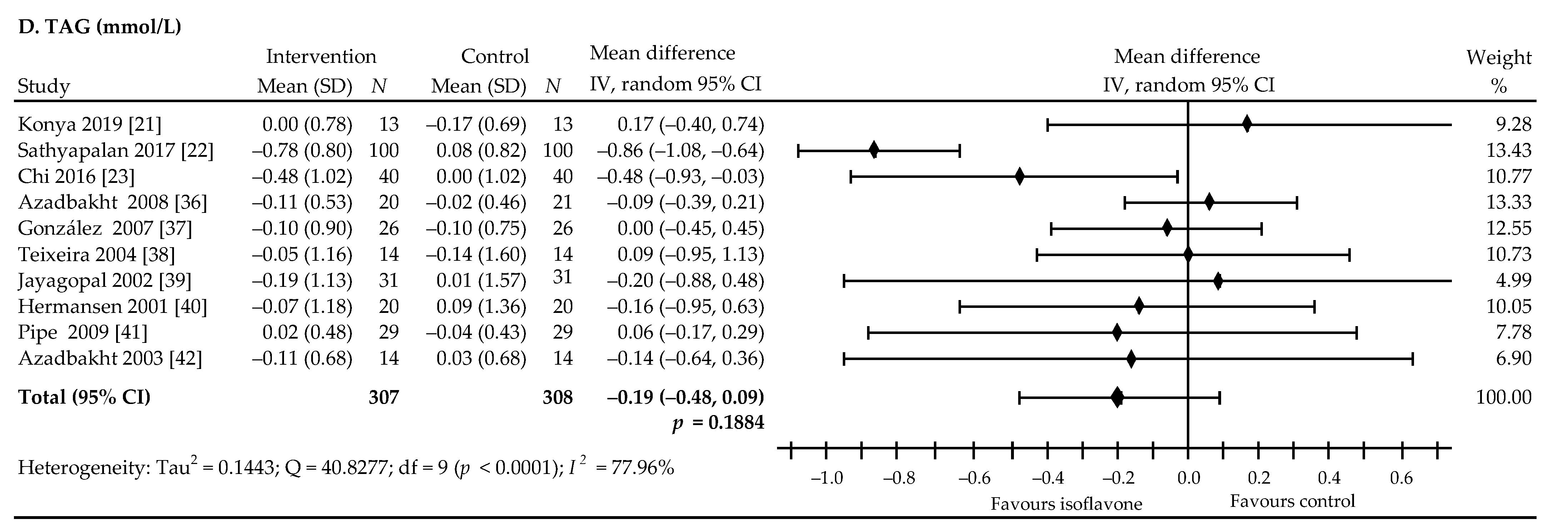
3.4. The Effect of Soy Isoflavones on Lipid Levels in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
4. Discussion
Limitations of This Study
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Ethics Statements
References
- Shaw, J.E.; Sicree, R.A.; Zimmet, P.Z. Global estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2010 and 2030. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2010, 87, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prevention CFDCa; National Diabetes Statistics Report. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2018. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/data/statistics/statistics-report.html (accessed on 6 July 2020).
- Kahn, S.E. The relative contributions of insulin resistance and beta-cell dysfunction to the pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2003, 46, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, S.E.; Hull, R.L.; Utzschneider, K.M. Mechanisms linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nature 2006, 444, 840–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taskinen, M.R. Controlling lipid levels in diabetes. Acta Diabetol. 2002, 39, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGill, J.B. Improving microvascular outcomes in patients with diabetes through management of hypertension. Postgrad. Med. 2009, 121, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maggio, C.A.; Pi-Sunyer, F.X. Obesity and type 2 diabetes. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2003, 32, 805–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guariguata, L.; Whiting, D.; Weil, C.; Unwin, N. The International Diabetes Federation diabetes atlas methodology for estimating global and national prevalence of diabetes in adults. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2011, 94, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krook, A.; Holm, I.; Pettersson, S.; Wallberg-Henriksson, H. Reduction of risk factors following lifestyle modification programme in subjects with type 2 (non-insulin dependent) diabetes mellitus. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging. 2003, 23, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Jung, T.S.; Jung, J.H.; Kim, S.K.; Lee, S.M.; Kim, K.Y.; Kim, D.R.; Seo, Y.M.; Hahm, J.R. Improvement of glycemic control after re-emphasis of lifestyle modification in type 2 diabetic patients reluctant to additional medication. Yonsei Med. J. 2013, 54, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brekke, H.K.; Lenner, R.A.; Taskinen, M.R.; Månsson, J.E.; Funahashi, T.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Jansson, P.A. Lifestyle modification improves risk factors in type 2 diabetes relatives. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2005, 68, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dailey, G. Early and intensive therapy for management of hyperglycemia and cardiovascular risk factors in patients with type 2 diabetes. Clin. Ther. 2011, 33, 665–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartke, A.; Peluso, M.R.; Moretz, N.; Wright, C.; Bonkowski, M.T.A.; Winters, T.A.; Shanahan, M.F.; Kopchick, J.J.; Banz, W.J. Effects of soy-derived diets on plasma and liver lipids, glucose tolerance, and longevity in normal, long-lived and short-lived mice. Horm. Metab. Res. 2004, 36, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.P.; Wang, R.; Song, X.; Chibbar, R.; Wang, X.; Wu, L.; Meng, Q.H. Dietary soy isoflavones increase insulin secretion and prevent the development of diabetic cataracts in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Nutr. Res. 2008, 28, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordentoft, I.; Jeppesen, P.B.; Hong, J.; Abudula, R.; Hermansen, K. Increased insulin sensitivity and changes in the expression profile of key insulin regulatory genes and beta cell transcription factors in diabetic KKAy-mice after feeding with a soy bean protein rich diet high in isoflavone content. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 4377–4385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbazian, H.; Reza, A.; Javad, S.; Heshmatollah, S.; Mahmood, L.; Ali, A.; Hosain, H.M. Beneficial effects of soy protein isoflavones on lipid and blood glucose concentrations in type 2 diabetic subjects. Saudi Med. J. 2007, 28, 652–654. [Google Scholar]
- Vaisman, N.; Lansink, M.; Rouws, C.H.; van Laere, K.M.; Segal, R.; Niv, E.; Bowling, T.E.; Waitzberg, D.L.; Morley, J.E. Tube feeding with a diabetes-specific feed for 12 weeks improves glycaemic control in type 2 diabetes patients. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 28, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clerici, C.; Nardi, E.; Battezzati, P.M.; Asciutti, S.; Castellani, D.; Corazzi, N.; Giuliano, V.; Gizzi, S.; Perriello, G.; Di Matteo, G.; et al. Novel soy germ pasta improves endothelial function, blood pressure, and oxidative stress in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 1946–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urita, Y.; Noda, T.; Watanabe, D.; Iwashita, S.; Hamada, K.; Sugimoto, M. Effects of a soybean nutrition bar on the postprandial blood glucose and lipid levels in patients with diabetes mellitus. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2012, 63, 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setchell, K.D.; Nardi, E.; Battezzati, P.M.; Asciutti, S.; Castellani, D.; Perriello, G.; Clerici, C. Novel soy germ pasta enriched in isoflavones ameliorates gastroparesis in type 2 diabetes: A pilot study. Diabetes Care. 2013, 36, 3495–3497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konya, J.; Sathyapalan, T.; Kilpatrick, E.S.; Atkin, S.L. The effects of soy protein and cocoa with or without isoflavones on glycemic control in type 2 diabetes. A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathyapalan, T.; Rigby, A.S.; Bhasin, S.; Thatcher, N.J.; Kilpatrick, E.S.; Atkin, S.L. Effect of soy in men with type 2 diabetes mellitus and subclinical hypogonadism: A randomized controlled study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 102, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, X.X.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, D.J.; Yu, W.; Wang, Q.Y.; Zhen, J.L. Effects of isoflavones on lipid and apolipoprotein levels in patients with type 2 diabetes in Heilongjiang Province in China. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2016, 59, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Shamseer, L.; Clarke, M.; Ghersi, D.; Liberati, A.; Petticrew, M.; Shekelle, P.; Stewart, L.A. PRISMA-P Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst. Rev. 2015, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Altman, D.G.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Jüni, P.; Moher, D.; Oxman, A.D.; Savovic, J.; Schulz, K.F.; Weeks, L.; Sterne, J.A.C. Cochrane Bias Methods Group; Cochrane Statistical Methods Group. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2011, 343, d5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begg, C.B.; Mazumdar, M. Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics 1994, 50, 1088–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egger, M.; Smith, G.D.; Schneider, M.; Minder, C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 1997, 315, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thomas, J.; Chandler, J.; Cumpston, M.; Li, T.; Page, M.J.; Welch, V.A. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 6.0 (Updated July 2020); John Wiley: Hooboken, NJ, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Follmann, D.; Elliott, P.; Suh, I.; Cutler, J. Variance imputation for overviews of clinical trials with continuous response. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1992, 45, 769–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DerSimonian, R.; Laird, N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials revisited. Contemp. Clin. Trials 2015, 45, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 2002, 21, 1539–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, A.V.; Steyerberg, E.W.; Habbema, J.D. Covariate adjustment in randomized controlled trials with dichotomous outcomes increases statistical power and reduces sample size requirements. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2004, 57, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, W.J.; White, C.M.; Cappelleri, J.C.; Kluger, J.; Coleman, C.I. Health Outcomes, Policy and Economics (HOPE) Collaborative Group. Understanding heterogeneity in meta-analysis: The role of meta-regression. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2009, 63, 1426–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.M.; Chen, Y.M.; Ho, S.C.; Ho, Y.P.; Woo, J. Effects of soy protein and isoflavones on glycemic control and insulin sensitivity: A 6-mo double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial in postmenopausal Chinese women with prediabetes or untreated early diabetes. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 91, 1394–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gobert, C.P.; Pipe, E.A.; Capes, S.E.; Darlington, G.A.; Lampe, J.W.; Duncan, A.M. Soy protein does not affect glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 103, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadbakht, L.; Atabak, S.; Esmaillzadeh, A. Soy protein intake, cardiorenal indices, and C-reactive protein in type 2 diabetes with nephropathy: A longitudinal randomized clinical trial. Diabetes Care 2008, 31, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, S.; Jayagopal, V.; Kilpatrick, E.S.; Chapman, T.; Atkin, S.L. Effects of isoflavone dietary supplementation on cardiovascular risk factors in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 1871–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, S.R.; Tappenden, K.A.; Carson, L.; Jones, R.; Prabhudesai, M.; Marshall, W.P.; Erdman, J.W., Jr. Isolated soy protein consumption reduces urinary albumin excretion and improves the serum lipid profile in men with type 2 diabetes mellitus and nephropathy. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 1874–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayagopal, V.; Albertazzi, P.; Kilpatrick, E.S.; Howarth, E.M.; Jennings, P.E.; Hepburn, D.A.; Atkin, S.L. Beneficial effects of soy phytoestrogen intake in postmenopausal women with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2002, 25, 1709–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermansen, K.; Søndergaard, M.; Høie, L.; Carstensen, M.; Brock, B. Beneficial effects of a soy-based dietary supplement on lipid levels and cardiovascular risk markers in type 2 diabetic subjects. Diabetes Care 2001, 24, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pipe, E.A.; Gobert, C.P.; Capes, S.E.; Darlington, G.A.; Lampe, J.W.; Duncan, A.M. Soy protein reduces serum LDL cholesterol and the LDL cholesterol: HDL cholesterol and apolipoprotein B: Apolipoprotein A-I ratios in adults with type 2 diabetes. J. Nutr. 2009, 139, 1700–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadbakht, L.; Shakerhosseini, R.; Atabak, S.; Jamshidian, M.; Mehrabi, Y.; Esmaill-Zadeh, A. Beneficiary effect of dietary soy protein on lowering plasma levels of lipid and improving kidney function in type II diabetes with nephropathy. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 57, 1292–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.M.; Zhang, Y.B.; Chi, M.H. Soy protein supplementation reduces clinical indices in type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome. Yonsei Med. J. 2016, 57, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Chen, Y.; Xu, T.; Yu, Y.; Huang, T.; Hu, X.; Li, D. Systematic review and meta–analysis of soy products consumption in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 20, 593–602. [Google Scholar]
- Soltanipour, S.; Hasandokht, T.; Soleimani, R.; Mahdavi-Roshan, M.; Jalali, M.M. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the effects of soy on glucose metabolism in patients with type 2 diabetes. Rev. Diab. Stud. 2019, 15, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, E.; Dávalos, A.; Crespo, M.C.; Tomé-Carneiro, J.; Gómez-Coronado, D.; Visioli, F. Soy isoflavones in nutritionally relevant amounts have varied nutrigenomic effects on adipose tissue. Molecules 2015, 20, 2310–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.W.; Blake, J.; Turner, J.; Smith, B.M. Effects of soy protein on renal function and proteinuria in patients with type 2 diabetes. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 68, 1347–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Ahn, C.W.; Park, S.H.; Shim, S.T.; Song, Y.D.; Han, E.N.; Lee, K.H.; Chae, J.S. Black soy peptide supplementation improves glucose control in subjects with prediabetes and newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Med. Food. 2010, 13, 1307–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azadbakht, L.; Kimiagar, M.; Mehrabi, Y.; Esmaillzadeh, A.; Padyab, M.; Hu, F.B.; Willett, W.C. Soy inclusion in the diet improves features of the metabolic syndrome: Used soy protein alone a randomized crossover study in postmenopausal women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 735–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miraghajani, M.S.; Mirlohi, M.; Esmaillzadeh, A.; Azadbakht, L.; Najafbadi, M.M. Soy milk consumption, inflammation, coagulation, and oxidative stress among type 2 diabetic patients with nephropathy. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 1981–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.H.; Min Sun Kim, M.S.; Kim, T.W.; Lee, S.S. Effects of soybean supplementation on blood glucose, plasma lipid levels, and erythrocyte antioxidant enzyme activity in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2008, 2, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salari Moghaddam, A.; Hassan Entezari, M.H.; Iraj, B.; Gholam Reza Askari, G.R.; Maracy, M.R. The effects of consumption of bread fortified with soy bean flour on metabolic profile in Type 2 diabetic women: A cross-over randomized controlled clinical trial. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2014, 5, 1529–1536. [Google Scholar]
- Ble-Castillo, J.L.; Aparicio-Trápala, M.A.; Francisco-Luria, M.U.; Córdova-Uscanga, R.; Rodríguez-Hernández, A.; Méndez, J.D.; Díaz-Zagoya, J.C. Effects of native banana starch supplementation on body weight and insulin sensitivity in obese type 2 diabetics. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 1953–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, P.J.; Sampson, M.; Potter, J.; Dhatariya, K.; Kroon, P.A.; Cassidy, A. Chronic ingestion of flavan-3-ols and isoflavones improves insulin sensitivity and lipoprotein status and attenuates estimated 10-year CVD risk in medicated postmenopausal women with type 2 diabetes: A 1-year, double-blind, randomized, controlled trial. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, D.C.; Piazza, C.; Melilli, B.; Drago, F.; Salomone, S. Isoflavones: Estrogenic activity, biological effect and bioavailability. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2013, 38, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andres, S.; Hansen, U.; Niemann, B.; Palavinskas, R.; Lampen, A. Determination of the isoflavone composition and estrogenic activity of commercial dietary supplements based on soy or red clover. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 2017–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, S.; Kim, H.; Darley-Usmar, V.; Patel, R.; Xu, J.; Boersma, B.; Luo, M. Beyond ERalpha and ERbeta: Estrogen receptor binding is only part of the isoflavone story. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 656–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhen, W.; Yang, Z.; Carter, J.D.; Si, H.; Reynolds, K.A. Genistein acutely stimulates insulin secretion in pancreatic beta-cells through a cAMP-dependent protein kinase pathway. Diabetes 2006, 55, 1043–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonas, J.C.; Plant, T.D.; Gilon, P.; Detimary, P.; Nenquin, M.; Henquin, J.C. Multiple effects and stimulation of insulin secretion by the tyrosine kinase inhibitor genistein in normal mouse islets. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1995, 114, 872–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazirian, M.; Nabavi, S.M.; Jafari, S.; Manayi, A. Natural activators of adenosine 5’-monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and their pharmacological activities. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 122, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, B.G.; Nagaoka, M.; Yonezawa, T.; Tanabe, R.; Woo, J.T.; Kato, H.; Chung, U.I.; Yagasaki, K. Regulatory mechanism for the stimulatory action of genistein on glucose uptake in vitro and in vivo. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2012, 23, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.S.; Lee, S.H. Genistein, a soy isoflavone, is a potent alpha-glucosidase inhibitor. FEBS Lett. 2001, 501, 84–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhen, W.; Lum, H.; Nadler, J.; Bassaganya-Riera, J.; Jia, Z.; Wang, Y.; Misra, H.; Liu, D. Genistein induces pancreatic beta-cell proliferation through activation of multiple signaling pathways and prevents insulin-deficient diabetes in mice. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 3026–3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, E.R.; Liu, D. Anti-diabetic functions of soy isoflavone genistein: Mechanisms underlying its effects on pancreatic β-cell function. Food Funct. 2013, 4, 200–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Z.C.; Audinot, V.; Papapoulos, S.E.; Boutin, J.A.; Löwik, C.W.G.M. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) as a molecular target for the soy phytoestrogen genistein. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 962–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mezei, O.; Li, Y.; Mullen, E.; Ross-Viola, J.S.; Shay, N.F. Dietary isoflavone supplementation modulates lipid metabolism via PPARalpha-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Physiol. Genomics 2006, 26, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cederroth, C.R.; Vinciguerra, M.; Gjinovci, A.; Kühne, F.; Klein, M.; Cederroth, M.; Caille, D.; Suter, M.; Neumann, D.; James, R.W.; et al. Dietary phytoestrogens activate AMP-activated protein kinase with improvement in lipid and glucose metabolism. Diabetes 2008, 57, 1176–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullen, E.; Brown, R.M.; Osborne, T.F.; Shay, N.F. Soy isoflavones affect sterol regulatory element binding proteins (SREBPs) and SREBP-regulated genes in HepG2 cells. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 2942–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; So, J.S.; Park, J.G.; Lee, A.H. Transcriptional control of hepatic lipid metabolism by SREBP and ChREBP. Semin. Liver Dis. 2013, 33, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demonty, I.; Lamarche, B.; Deshaies, Y.; Jacques, H. Role of soy isoflavones in the hypotriglyceridemic effect of soy protein in the rat. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2002, 13, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, W.; Wen, H.; Hou, X.; Li, D.; Kou, X. Potential lipid-lowering mechanisms of biochanin A. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 3842–3850.72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaheer, K.; Humayoun Akhtar, M. An updated review of dietary isoflavones: Nutrition, processing, bioavailability and impacts on human health. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 1280–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| First Author | Study Design | Study Population | Intervention (Daily Dose) | Control (Daily Dose) | Dietary Advice during Study | Outcome Measures |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data [Reference] | (DM Duration; Diabetes Therapy) | |||||
| Country | Trial Duration | “Conditions Accompany Diabetes” | ||||
| Konya 2019 [21] Qatar | Parallel groups; 2-w run-in, 8-w follow-up. | n = 26, 8 women and 18 men; age 65.1 ± 7.3 y; BMI 30.5 ± 5.1 [4.4 ± 3.7; diet or metformin] | 16 g SP, 32 mg ISF; in form of bars | 16 g SP alone; in form of bars | Maintained current diet; avoid dietary products with a high-ISF content | TC, LDL-C, HDL-C, TAG FBG, FI, HbA1c, HOMA-IR |
| Sathyapalan 2017 [22] UK | Parallel groups, 3-mo follow-up. | n = 200 men; age 52.0 y †; BMI 31.8 †. [7.3 *; stable drugs for T2DM] “subclinical hypogonadism’ | 15 g SP, 166 mg ISF; in form of bars | 15 g SP alone: in form of bars | Avoiding soy products, nutritional, mineral and vitamin supplements | TC, LDL-C, HDL-C, TAG FBG, FI, HbA1c |
| Chi 2016 [23] China | Parallel groups, 2-mo follow-up. | n = 80 women; age 51.9 ± 11.0 y; BMI 24.1 ± 0. 8[N/A; N/A] | 435 mg IAE (52.2% Gen, 47.8% Dai) capsule | Starch; capsule | ISF intake from foods was restricted to less than 19 mg/day | TC, LDL-C, HDL-C, TAG |
| Liu 2010 [34] Hong Kong | Three-arm study, parallel groups; 2-w run-in, 24-w follow-up. | n = 180 women; age 56.1 ± 4.3 y; BMI 24.5 ± 3.7 [untreated early diabetes] | A. 15 g SP, 100 g ISF (≈25 mg Agl). B. 15 g MP, 100 mg ISF (≈25 mg Agl); powder | 15 g MP; powder | Maintained habitual diet; not to take supplements containing isoflavones or other extracts | FBG, FI, HOMA-IR |
| Gobert 2010 [35] | Cross-over trial; 4-w washout, 57-d active phase. | n = 29, 13 women and 16 men; age 60.1 ± 9.6 y; BMI 29.6 ± 4.1 | 40 g SP; 88 mg IAE (65% Gen, 31% Dai, 4% Gly powder) | 40 g MP powder | Maintained habitual diet; other phytoestrogen | FBG, FI, HbA1c, HOMA-IR |
| Azadbakht 2008 [36] Iran | Parallel groups *; 4-y follow-up. | n = 41, 23 women and 18 men; age 62.1 ± 12.1 y; 71.5 ± 8.5 kg # [10.0 ± 3.0; insulin or oral drugs] “nephropathy” | 16 ± 9 g SP, ≈43 ISF ‡ | ≈20 g AP § | Maintained current diet | TC, LDL-C, HDL-C, TAG FBG |
| González 2007 [37] UK | Cross-over trial; 4-w washout, 12-w active phase. | n = 26 women; age N/A; BMI 30.8 ± 5.9 [N/A; non medications] | 132 mg IAE (35% Gen, 37% Dai, 10% Gly); pill | Microcrystalline cellulose, pill | Diet-controlled diabetes | TC, LDL-C, HDL-C, TAG FBG, FI, HOMA-IR |
| Teixeira 2004 [38] Portugal | Cross-over trial *; 4-w washout, 8-w active phase. | n = 14 men; age 53–73 y; BMI 29.8 ± 2.3; [~14.0 y; insulin] “early stages nephropathy” | 0.5 g/kg SP isolate, 2.0 mg/g protein IAE, powder | 0.5 g/kg casein; powder | Diet excluding foods containing soy | TC, LDL-C, HDL-C, TAG HbA1C |
| Jayagopal 2002 [39] UK | Cross-over trial; 2-w washout, 12-w active phase. | n = 32 women; age 63.5 ± 12.1 y; BMI 32.2 ± 5.0 [2.6 ± 2.7; non medications] | 30 g SP isolate, 135 mg ISF (95% glucosides) | Microcrystalline cellulose 30 g | Recommended maintain a diabetes diet | TC, LDL-C, HDL-C, TAG FBG, FI, HbA1c, HOMA-IR |
| Hermansen 2001 [40] Norway | Cross-over trial; 3-w washout, 6-w active phase. | n = 20. 6 women and 14 men; age 63.6 ± 7.5 y; BMI 30.2 ± 4.2 [3.0 ± 2.7; oral drugs] | 50 g SP isolate, ≥165 mg ISF; 20 g cotyledon fiber | 50 g casein; 20 g cellulose | Diet set and controlled by a dietitians | TC, LDL-C, HDL-C, TAG FBG, FI, HbA1C |
| Pipe 2009 [41] Canada | Cross-over trial; 4-w washout, 57-d active phase. | n = 29, 13 women and 16 men; age 60.1 ± 9.6 y; BMI 29.6 ± 4.1 | 40 g SP; 88 mg IAE (65% Gen, 31% Dai, 4% Gly powder) | 40 g MP powder | intake were prohibited | TC, LDL-C, HDL-C, TAG |
| Azadbakht 2003 [42] Iran | Crossover trial *; 4-w washout, 7-w active phase. | n = 14, 4 women and 10 men; age 62.5 ± 12.1 y; 70.6 ± 10.3 kg # [N/A; N/A], ‘nephropathy’ | ≈20 g SP, ≈43 mg ISF ‡ | ≈20 g AP § | The alternate test diet | TC, LDL-C, HDL-C, TAG |
| FBG (mmol/L) | FI (pmol/L) | HbA1c (%) | HOMA-IR (%) | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | n | N | WMD (95% CI) | p | I2 (%) | n | N | WMD (95% CI) | p | I2 (%) | n | N | WMD (95% CI) | p | I2 (%) | n | N | WMD (95% CI) | p | I2 (%) |
| Overall effects | 9 | 721 | −0.30 (−0.85, 0.24) | 0.2279 | 85.66 | 8 | 680 | −3.40 (−10.77, 3.97) | 0.3661 | 37.43 | 6 | 416 | −0.80 (−1.85, 0.25) | 0.1341 | 96.25 | 6 | 440 | −0.07 (−0.54, 0.41) | 0.7857 | 22.52 |
| Study design | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Parallel groups | 5 | 507 | −0.50 (−1.34, 0.33) | 0.2379 | 92.12 | 4 | 466 | −4.54 (−12.83, 3.75) | 0.2831 | 42.98 | 2 | 226 | −2.47 (−7.07, 2.12) | 0.2916 | 99.06 | 3 | 266 | 0.04 (−0.63, 0.72) | 0.8977 | 43.73 |
| Cross-over | 4 | 214 | 0.04 (−0.36, 0.44) | 0.8527 | <0.01 | 4 | 214 | −1.46 (−17.47, 14.55) | 0.8585 | 41.47 | 4 | 190 | −0.06 (−0.27, 0.16) | 0.6126 | <0.01 | 3 | 174 | −0.26 (−1.25, 0.73) | 0.6048 | 20.04 |
| Follow-up period | ||||||||||||||||||||
| ≤8 weeks | 3 | 124 | 0.32 (−0.21, 0.85) | 0.2342 | <0.01 | 3 | 124 | 3.31 (−10.78, 17.40) | 0.6457 | <0.01 | 4 | 152 | −0.05 (−0.30, 0.20) | 0.6919 | <0.01 | 2 | 84 | 1.00 (−1.71, 3.72) | 0.4695 | 66.62 |
| >8 weeks | 6 | 597 | −0.53 (−1.21, 0.14) | 0.1222 | 89.71 | 5 | 556 | −5.33 (−13.81, 3.15) | 0.2176 | 46.62 | 2 | 264 | −2.46 (−7.08, 2.17) | 0.2981 | 99.17 | 4 | 356 | −0.14 (−0.56, 0.29) | 0.5249 | 1.08 |
| Age | ||||||||||||||||||||
| ≤60 years | 3 | 440 | −0.72 (−1.75, 0.31) | 0.1699 | 95.74 | 3 | 440 | −5.65 (−13.23, 1.92) | 0.1434 | 43.26 | 1 | 200 | −4.83 (−5.61, −4.05) | <0.0001 | N/R | 2 | 240 | −0.09 (−0.53, 0.35) | 0.6944 | <0.01 |
| >60 years | 5 | 229 | 0.09 (−0.34, 0.52) | 0.6879 | <0.01 | 4 | 188 | −2.22 (−20.43, 5.99) | 0.8112 | 42.78 | 5 | 216 | −0.07 (−0.27, 0.12) | 0.4533 | <0.01 | 3 | 148 | 0.03 (−1.74, 1.79) | 0.9763 | 65.74 |
| Body mass index | ||||||||||||||||||||
| <30 kg/m2 | 4 | 339 | 0.07 (−0.28, 0.14) | 0.4989 | <0.01 | 3 | 298 | −1.25 (−9.29, 6.79) | 0.7606 | <0.01 | 2 | 86 | 0.03 (−0.30, 0.35) | 0.8742 | <0.01 | 3 | 298 | −0.08 (−0.47, 0.32) | 0.7031 | <0.01 |
| ≥30 kg/m2 | 5 | 382 | −0.43 (−1.54, 0.69) | 0.4511 | 89.33 | 5 | 382 | −2.46 (−17.58, 12.66) | 0.7494 | 52.49 | 4 | 330 | −1.30 (−2.96, 0.37) | 0.1269 | 97.63 | 3 | 142 | 0.36 (−2.42, 3.14) | 0.1669 | 37.01 |
| Diabetes duration * | ||||||||||||||||||||
| <5 years | 6 | 428 | −0.05 (−0.25, 0.15) | 0.6238 | <0.01 | 6 | 428 | −1.41 (−9.58, 6.76) | 0.7347 | 12.76 | 4 | 188 | −0.09 (−0.28, 0.11) | 0.3682 | <0.01 | 5 | 388 | −0.10 (−0.63, 0.43) | 0.4104 | 33.93 |
| ≥5 years | 2 | 241 | −1.76 (−2.71, −0.81) | 0.0003 | 37.46 | 1 | 200 | −10.26 (−15.96, −4.56) | 0.0004 | N/R | 2 | 228 | −2.23 (−7.35, 2.90) | 0.3945 | 98.35 | |||||
| Isoflavone intake | ||||||||||||||||||||
| <100 mg/d | 3 | 125 | 0.26 (−0.34, 0.85) | 0.3961 | 11.29 | 4 | 324 | −0.59 (−8.54, 7.36) | 0.8839 | <0.01 | 3 | 112 | −0.04 (−0.29, 0.22) | 0.7820 | <0.01 | 2 | 84 | 1.00 (−1.71, 3.72) | 0.4695 | 66.62 |
| ≥100 mg/d | 6 | 596 | −0.48 (−1.15, 0.19) | 0.1618 | 89.63 | 4 | 356 | −4.85 (−19.79, 10.10) | 0.5249 | 54.10 | 3 | 304 | −1.70 (−4.56, 1.15) | 00.2426 | 98.36 | 4 | 356 | −0.14 (−0.56, 0.29) | 0.5249 | 1.08 |
| Diabetes therapy | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Non medications | 5 | 414 | −0.06 (−0.26, 0.13) | 0.5159 | <0.01 | 5 | 414 | −2.17 (−10.59, 6.24) | 0.6127 | 15.07 | 2 | 122 | −0.07 (−0.30, 0.16) | 0.5658 | <0.01 | 5 | 414 | −0.12 (−0.49, 0.26) | 0.5446 | <0.01 |
| Diet and/or drugs | 4 | 307 | −0.69 (−2.19, 0.81) | 0.3651 | 86.36 | 3 | 266 | 0.32 (−19.22, 19.87) | 0.9741 | 54.76 | 4 | 294 | −1.20 (−3.49, 1.09) | 0.3052 | 97.45 | 1 | 26 | 2.86 (−0.29, 6.01) | 0.0755 | |
| Complications | ||||||||||||||||||||
| without | 7 | 480 | −0.05 (−0.24, 0.14) | 0.6366 | <0.01 | 7 | 480 | −0.36 (−8.15, 7.44) | 0.9287 | 10.68 | 4 | 188 | −0.09 (−0.28, 0.11) | 0.3685 | <0.01 | 6 | 440 | −0.07 (−0.54, 0.41) | 0.7857 | 22.52 |
| with | 2 | 241 | −1.76 (−2.71, −0.80) | 0.0003 | 37.67 | 1 | 200 | −10.26 (−15.96, −4.56) | 0.0004 | 98.35 | 2 | 228 | −2.23 (−7.35, 2.90) | 0.3945 | 98.35 | |||||
| TC (mmol/L) | LDL-C (mmol/L) | HDL-C (mmol/L) | TAG (mmol/L) | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | n | N | WMD (95% CI) | p | I2 (%) | n | N | WMD (95% CI) | p | I2 (%) | n | N | WMD (95% CI) | p | I2 (%) | n | N | WMD (95% CI) | p | I2 (%) |
| Overall effects | 10 | 615 | −0.21 (−0.33, −0.09) | 0.0008 | <0.01 | 10 | 615 | −0.20 (−0.28, −0.120 | <0.0001 | <0.01 | 10 | 615 | −0.02 (−0.05, 0.01) | 0.2008 | <0.01 | 10 | 615 | 0.19 (−0.48, 0.09) | 0.1884 | 77.96 |
| Study design | ||||||||||||||||||||
| parallel group | 4 | 347 | -0.21 (−0.35, −0.07) | 0.0041 | <0.01 | 4 | 347 | −0.21 (−0.32, −0.10) | 0.0002 | <0.01 | 4 | 347 | −0.03 (−0.07, 0.01) | 0.0922 | <0.01 | 4 | 347 | −0.34 (−0.83, 0.14) | 0.1620 | 86.50 |
| cross-over | 6 | 268 | −0.20 (−0.43, 0.03) | 0.0828 | <0.01 | 6 | 268 | −0.19 (−0.31, −0.08) | 0.0009 | <0.01 | 6 | 268 | 0.02 (−0.05, 0.08) | 0.6564 | <0.01 | 6 | 268 | −0.00 (−0.18, 0.18) | 0.9816 | <0.01 |
| Follow-up period | ||||||||||||||||||||
| ≤8 weeks | 6 | 260 | −0.26 (−0.49, −0.03) | 0.0287 | <0.01 | 6 | 260 | −0.23 (−0.34, −0.12) | 0.0001 | <0.01 | 6 | 260 | 0.02 (−0.06, 0.09) | 0.6238 | <0.01 | 6 | 260 | −0.05 (−0.24, 0.13) | 0.5689 | 5.07 |
| >8 weeks | 4 | 355 | −0.19 (−0.33, −0.05) | 0.0095 | <0.01 | 4 | 355 | −0.17 (−0.29, −0.06) | 0.0029 | <0.01 | 4 | 355 | −0.03 (−0.06, 0.01) | 0.0988 | <0.01 | 4 | 350 | −0.31 (−0.81, 0.19) | 0.2875 | 86.55 |
| Age * | ||||||||||||||||||||
| ≤60 years | 2 | 280 | −0.20 (−0.35, −0.05) | 0.0094 | <0.01 | 2 | 280 | −0.23 (−0.43, −0.03) | 0.0248 | 40.10 | 2 | 280 | −0.03 (−0.06, 0.01) | 0.1380 | <0.01 | 2 | 280 | −0.72 (−1.08, −0.36) | 0.0001 | 54.65 |
| >60 years | 7 | 283 | −0.28 (−0.50, −0.06) | 0.0134 | <0.01 | 7 | 283 | −0.22 (−0.34, −0.11) | 0.0001 | <0.01 | 7 | 283 | 0.00 (−0.07, 0.07) | 0.9924 | <0.01 | 7 | 283 | −0.01 (−0.17, 0.14) | 0.8772 | <0.01 |
| Body mass index † | ||||||||||||||||||||
| <30 kg/m2 | 3 | 166 | −0.17 (−0.48, 0.14) | 0.2730 | <0.01 | 3 | 166 | −0.23 (−0.44, −0.02) | 0.0283 | <0.01 | 3 | 166 | 0.03 (−0.06, 0.12) | 0.5802 | <0.01 | 3 | 166 | −0.13 (−0.54, 0.28) | 0.5338 | 55.42 |
| ≥30 kg/m2 | 5 | 380 | −0.21 (−0.34, −0.07) | 0.0031 | <0.01 | 5 | 380 | −0.18 (−0.29, −0.06) | 0.0035 | <0.01 | 5 | 380 | −0.03 (−0.06, 0.01) | 0.1328 | <0.01 | 5 | 380 | −0.24 (−0.74, 0.26) | 0.3456 | 81.16 |
| Diabetes duration ‡ | ||||||||||||||||||||
| <5 years | 4 | 186 | −0.28 (−0.54, −0.02) | 0.0316 | <0.01 | 4 | 186 | −0.25 (−0.47, −0.02) | 0.0349 | <0.01 | 4 | 186 | −0.01 (−0.10, 0.07) | 0.8012 | <0.01 | 4 | 186 | 0.04 (−0.16, 0.24) | 0.7179 | <0.01 |
| ≥5 years | 3 | 269 | −0.19 (−0.35, −0.04) | 0.0129 | <0.01 | 3 | 269 | −0.17 (−0.29, −0.05) | 0.0047 | <0.01 | 3 | 269 | −0.02 (−0.08, 0.03) | 0.4296 | 12.00 | 3 | 269 | −0.36 (−1.02, 0.29) | 0.2753 | 88.59 |
| Isoflavone intake | ||||||||||||||||||||
| <100 mg/d | 4 | 152 | −0.21 (−0.51, 0.09) | 0.1690 | <0.01 | 4 | 152 | −0.21 (−0.32, −0.09) | 0.0004 | <0.01 | 4 | 152 | −0.03 (−0.13, 0.07) | 0.5648 | <0.01 | 4 | 152 | −0.14 (−0.64, 0.36) | 0.5860 | <0.01 |
| ≥100 mg/d | 6 | 463 | −0.21 (−0.34, −0.07) | 0.0022 | <0.01 | 6 | 463 | −0.19 (−0.30, −0.09) | 0.0004 | <0.01 | 6 | 463 | 0.01 (−0.04, 0.06) | 0.2481 | <0.01 | 6 | 463 | −0.35 (−0.73, 0.03) | 0.0727 | 69.56 |
| Diabetes therapy # | ||||||||||||||||||||
| non medications | 3 | 172 | −0.12 (−0.40, 0.16) | 0.4085 | <0.01 | 3 | 172 | −0.13 (−0.38, 0.13) | 0.3400 | 7.72 | 3 | 172 | −0.01 (−0.11, 0.10) | 0.9093 | <0.01 | 3 | 172 | 0.03 (−0.17, 0.23) | 0.7971 | <0.01 |
| diet and/or drugs | 5 | 355 | −0.22 (−0.36, −0.07) | 0.0028 | <0.01 | 5 | 355 | −0.19 (−0.30, −0.07) | 0.0014 | <0.01 | 5 | 355 | −0.03 (−0.06, 0.01) | 0.1439 | <0.01 | 5 | 355 | −0.23 (−0.73, 0.28) | 0.3793 | 83.47 |
| Complications | ||||||||||||||||||||
| without | 6 | 318 | −0.22 (−0.43, −0.02) | 0.0347 | <0.01 | 6 | 318 | −0.25 (−0.42, −0.08) | 0.0039 | <0.01 | 6 | 318 | −0.00 (−0.07, 0.07) | 0.9233 | <0.01 | 6 | 318 | −0.05 (−0.23, 0.13) | 0.5875 | 5.68 |
| with § | 4 | 297 | −0.20 (−0.35, −0.05) | 0.0090 | <0.01 | 4 | 297 | −0.19 (−0.28, −0.10) | 0.0000 | <0.01 | 4 | 297 | −0.03 (−0.06, 0.01) | 0.1660 | <0.01 | 4 | 297 | −0.32 (−0.84, 0.20) | 0.2343 | 85.00 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barańska, A.; Błaszczuk, A.; Polz-Dacewicz, M.; Kanadys, W.; Malm, M.; Janiszewska, M.; Jędrych, M. Effects of Soy Isoflavones on Glycemic Control and Lipid Profile in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1886. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13061886
Barańska A, Błaszczuk A, Polz-Dacewicz M, Kanadys W, Malm M, Janiszewska M, Jędrych M. Effects of Soy Isoflavones on Glycemic Control and Lipid Profile in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients. 2021; 13(6):1886. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13061886
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarańska, Agnieszka, Agata Błaszczuk, Małgorzata Polz-Dacewicz, Wiesław Kanadys, Maria Malm, Mariola Janiszewska, and Marian Jędrych. 2021. "Effects of Soy Isoflavones on Glycemic Control and Lipid Profile in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials" Nutrients 13, no. 6: 1886. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13061886
APA StyleBarańska, A., Błaszczuk, A., Polz-Dacewicz, M., Kanadys, W., Malm, M., Janiszewska, M., & Jędrych, M. (2021). Effects of Soy Isoflavones on Glycemic Control and Lipid Profile in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients, 13(6), 1886. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13061886








