Association of Vitamin D Receptor and Vitamin D-Binding Protein Polymorphisms with Familial Breast Cancer Prognosis in a Mono-Institutional Cohort
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Participants
2.2. Genotype Analysis
2.3. Statistical Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Muscogiuri, G. Vitamin D: Past, present and future perspectives in the prevention of chronic diseases. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 72, 1221–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estébanez, N.; Gòmez-Acebo, I.; Palazuelos, C.; Llorca, J.; Dierssen-Sotos, T. Vitamin D exposure and Risk of Breast Cancer: A meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, J. Targets of vitamin D receptor signaling in the mammary gland. J. Bone Miner Res. 2007, 22 (Suppl. 2), V86–V90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artaza, J.N.; Sirad, F.; Ferrini, M.G.; Norris, K.C. 1, 25(OH)2vitamin D3 inhibits cell proliferation by promoting cell cycle arrest without inducing apoptosis and modifies cell morphology of mesenchymal multipotent cells. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 119, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delanghe, J.R.; Speeckaert, R.; Speeckaert, M.M. Behind the scenes of vitamin D binding protein: More than vitamin D binding. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 29, 773–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garland, C.F.; Gorham, E.D.; Mohr, S.B.; Grant, W.B.; Giovannucci, E.L.; Lipkin, M. Vitamin D and prevention of breast cancer: Pooled analysis. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2007, 103, 708–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, S.; Linseisen, J.; Slanger, T.; Kropp, S.; Mutschelknauss, E.J.; Flesch-Janys, D.; Chang-Claude, J. Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and risk of post-menopausal breast cancer—results of a large case-control study. Carcinogenesis 2008, 29, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, P.J.; Ennis, M.; Pritchard, K.I.; Koo, J.; Hood, N. Prognostic effects of 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels in early breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 3757–3763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villaseñor, A.; Ballard-Barbash, R.; Ambs, A.; Bernstein, L.; Baumgartner, K.; Baumgartner, R. Associations of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D with overall and breast cancer-specific mortality in a multiethnic cohort of breast cancer survivors. Cancer Causes Control 2013, 24, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, S.; Kwan, M.L.; Ergas, I.J.; Roh, J.M.; Cheng, T.Y.D.; Hong, C.C. Association of Serum Level of Vitamin D at Diagnosis With Breast Cancer Survival: A Case-Cohort Analysis in the Pathways Study. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keum, N.; Lee, D.H.; Greenwood, D.C.; Manson, J.E.; Giovannucci, E. Vitamin D supplementation and total cancer incidence and mortality: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uitterlinden, A.G.; Fang, Y.; van Meurs, J.B.; Pols, H.A.; van Leeuwen, J.P. Genetics and biology of vitamin D receptor polymorphisms. Gene 2004, 338, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durrin, L.K.; Haile, R.W.; Ingles, S.A.; Coetzee, G.A. Vitamin D receptor 3’-untranslated region polymorphisms: Lack of effect on mRNA stability. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1999, 1453, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield, G.K.; Remus, L.S.; Jurutka, P.W.; Zitzer, H.; Oza, A.K.; Dang, H.T. Functionally relevant polymorphisms in the human nuclear vitamin D receptor gene. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2001, 177, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guy, M.; Lowe, L.C.; Bretherton-Watt, D.; Mansi, J.L.; Peckitt, C.; Bliss, J. Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms and breast cancer risk. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 5472–5481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostner, K.; Denzer, N.; Muller, C.S.; Klein, R.; Tilgen, W.; Reichrath, J. The relevance of vitamin D receptor (VDR) gene polymorphisms for cancer: A review of the literature. Anticancer Res. 2009, 29, 3511–3536. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Easton, D.F. How many more breast cancer predisposition genes are there? Breast Cancer Res. 1999, 1, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campeau, P.M.; Foulkes, W.D.; Tischkowitz, M.D. Hereditary breast cancer: New genetic developments, new therapeutic avenues. Hum. Genet. 2008, 124, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniou, A.; Pharoah, P.D.; Narod, S. Average risks of breast and ovarian cancer associated with BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations detected in case Series unselected for family history: A combined analysis of 22 studies. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2003, 72, 1117–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domchek, S.M.; Gaudet, M.M.; Stopfer, J.E.; Fleischaut, M.H.; Powers, J.; Kauff, N. Breast cancer risks in individuals testing negative for a known family mutation in BRCA1 or BRCA2. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2010, 119, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldhirsch, A.; Wood, W.C.; Coates, A.S.; Gelber, R.D.; Thurlimann, B.; Senn, H.J. Strategies for subtypes--dealing with the diversity of breast cancer: Highlights of the St. Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2011. Ann. Oncol. 2011, 22, 1736–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan-Shaw, P.G.; O’sullivan, F.; Farrington, S.; Theodoratou, E.; Campbell, H.; Dunlop, M.G.; Zgaga, L. The impact of vitamin D pathway genetic variation and circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D on cancer outcome: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 116, 1092–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, A.V.; Swami, S.; Peng, L.; Wang, J.; Moreno, J.; Feldman, D. Tissue-selective regulation of aromatase expression by calcitriol: Implications for breast cancer therapy. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, A.V.; Swami, S.; Feldman, D. Vitamin D and breast cancer: Inhibition of estrogen synthesis and signaling. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 121, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swami, S.; Krishnan, A.V.; Peng, L.; Lundqvist, J.; Feldman, D. Transrepression of the estrogen receptor promoter by calcitriol in human breast cancer cells via two negative vitamin D response elements. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2013, 20, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.J.; Zhang, F.; Richards, J.B.; Kestenbaum, B.; Van Meurs, J.B.; Berry, D. Common genetic determinants of vitamin D insufficiency: A genome-wide association study. Lancet 2010, 376, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, B.R.; Mascarenhas, L.P.; Boguszewski, M.C.; Spritzer, P.M. Variations in the vitamin D-binding protein (DBP) gene are related to lower 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels in healthy girls: A cross-sectional study. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2013, 79, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ahearn, T.U.; Lecarpentier, J.; Barnes, D.; Beesley, J.; Qi, G. Genome-wide association study identifies 32 novel breast cancer susceptibility loci from overall and subtype-specific analyses. Nat. Genet 2020, 52, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, A.; Schwartz, Z.; Boyan, B.D. 24R, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D(3) modulates tumorigenicity in breast cancer in an estrogen receptor-dependent manner. Steroids 2019, 150, 108447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemian, E.; Akbari, M.E.; Moradi, N.; Gharibzadeh, S.; Mondul, A.M.; Jamshidi-Naeini, Y.; Khademolmele, M.; Zarins, K.R.; Ghodoosi, N.; Amouzegar, A.; et al. Vitamin D Receptor Genetic Variation and Cancer Biomarkers among Breast Cancer Patients Supplemented with Vitamin D3: A Single-Arm Non-Randomized Before and After Trial. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnagnarella, P.; Raimondi, S.; Aristarco, V. Vitamin D Receptor Polymorphisms and Cancer. Sunlight, Vitamin D and Skin Cancer, 3rd ed.; Springer Nature: Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 53–114. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.; Ge, T.; Chen, C.Y. The causal role of circulating vitamin D concentrations in human complex traits and diseases: A large-scale Mendelian randomization study. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huss, L.; Butt, S.T.; Borgquist, S. Vitamin D receptor expression in invasive breast tumors and breast cancer survival. Breast Cancer Res. 2019, 21, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perna, L.; Butterbach, K.; Haug, U.; Schöttker, B.; Müller, H.; Arndt, V. Vitamin D receptor genotype rs731236 (Taq1) and breast cancer prognosis. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2013, 22, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, M.U.; Muzaffar, M.; Khan, F.A.; Kabisch, M.; Muhammad, N.; Faiz, S. Association between the BsmI Polymorphism in the Vitamin D Receptor Gene and Breast Cancer Risk: Results from a Pakistani Case-Control Study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahabi, A.; Alipour, M.; Safiri, H.; Tavakol, P.; Alizadeh, M.; Hashemi, S.M.; Shahabi, M.; Halimi, M. Vitamin D Receptor Gene Polymorphism: Association with Susceptibility to Early-Onset Breast Cancer in Iranian, BRCA1/2-Mutation Carrier and non-carrier Patients. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2017, 24, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
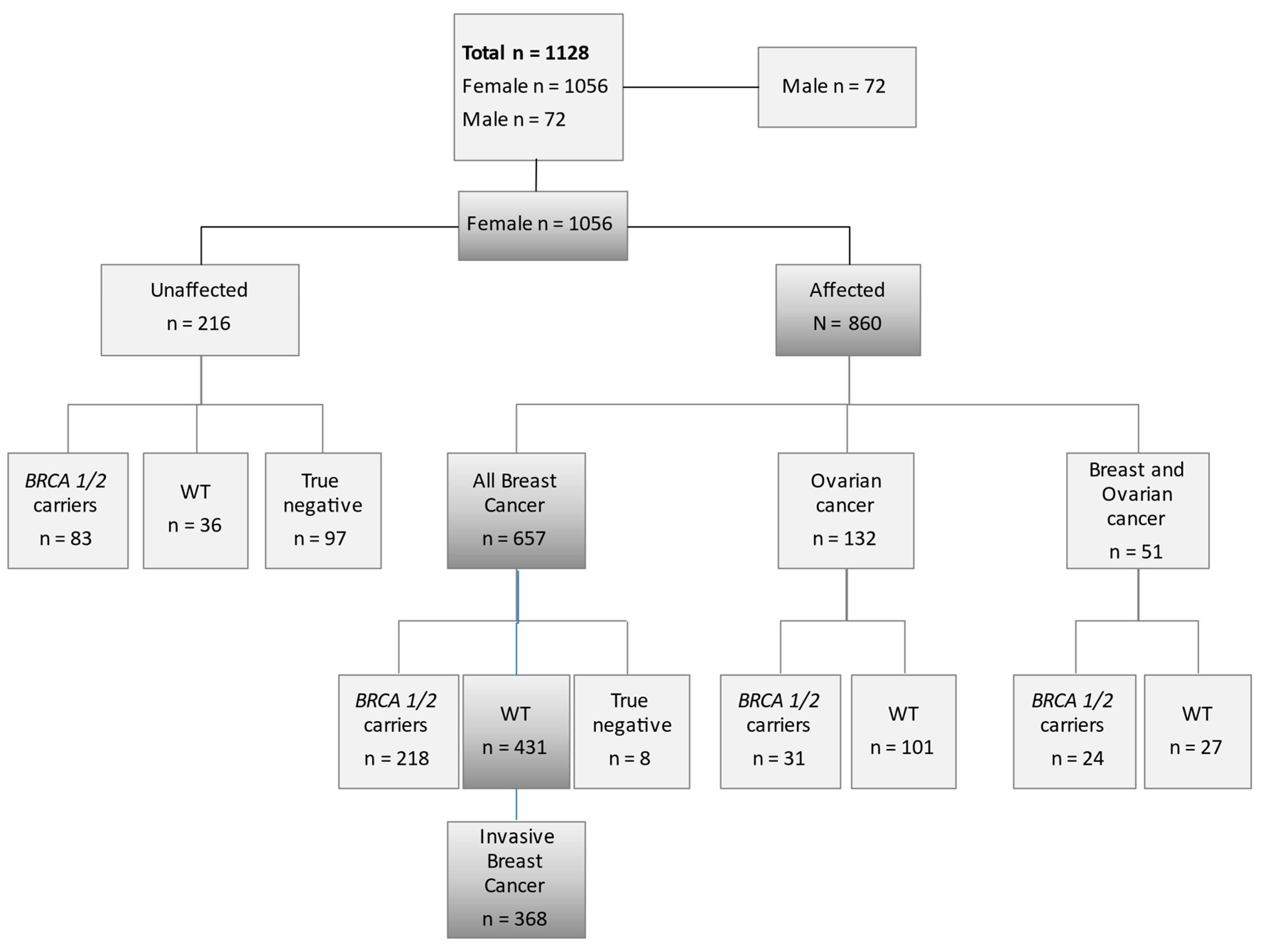
| Patients Characteristics | n | % | |
| 368 | 100 | ||
| Age at diagnosis, y: Median (Q1–Q3) | 41 (36–47) | ||
| BMI, kg/m2: Median (Q1–Q3) | 22.3 (20.5–24.9) | ||
| Age at menarche, y: Median (Q1–Q3) | 12 (11–13) | ||
| Oral contraceptive | No | 139 | 36.8 |
| Yes | 225 | 59.5 | |
| Missing | 14 | 3.7 | |
| Parity | No | 99 | 26.9 |
| Yes | 269 | 73.1 | |
| Family history | Breast | 335 | 91.1 |
| Breast and ovary | 33 | 8.9 | |
| Personal history of other cancer | No | 355 | 96.5 |
| Yes | 13 | 3.5 | |
| Smoking | Former | 98 | 26.6 |
| No | 231 | 62.8 | |
| Current | 39 | 10.6 | |
| Molecular subtype | Luminal A | 75 | 20.4 |
| Luminal B | 141 | 38.3 | |
| Luminal B-Her2+ | 36 | 9.8 | |
| HER2+ | 25 | 6.8 | |
| Triple negative | 22 | 6.0 | |
| Missing | 69 | 18.8 | |
| pT | I | 246 | 66.9 |
| II | 86 | 23.4 | |
| III | 18 | 4.9 | |
| IV | 1 | 0.3 | |
| Missing | 18 | 4.6 | |
| pN | Negative | 246 | 66.8 |
| Positive | 86 | 28.3 | |
| Missing | 18 | 4.9 |
| Gene | SNP | n | MAF | Genotype, n % | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Major/Major | Major/Minor | Minor/Minor | HWE p Value | ||||
| VDR | rs1544410 BsmI (C > T) | 368 | 0.45 (T) | 113 (31) | 185 (50) | 70 (19) | 0.85 |
| VDR | rs2228570 FokI (A > G) | 368 | 0.40 (A) | 147 (40) | 179 (49) | 42 (11) | 0.76 |
| VDR | rs731236 TaqI (A > G) | 368 | 0.45 (G) | 119 (32) | 184 (50) | 65 (18) | 0.88 |
| VDR | rs7975232 ApaI (A > C) | 368 | 0.42 (C) | 132(36) | 176 (48) | 60 (16) | 0.08 |
| GC | rs2282679 (T > G) | 368 | 0.26 (G) | 182 (49) | 155 (42) | 31 (8) | 0.97 |
| GC | rs4588 (G > T) | 368 | 0.26 (T) | 158 (43) | 157 (43) | 53 (14) | 0.87 |
| GC | rs7041 (A > C) | 368 | 0.59 (C) | 71 (20) | 180 (49) | 117 (32) | 0.38 |
| SNP | Major/Major | Major/Minor | Minor/Minor | Total | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Histotype | Total | n = 182 | n = 155 | n = 31 | n = 368 | ||
| GC rs228679 | Luminal A or B | n. | 115 | 117 | 20 | 252 | |
| % | 63.19 | 75.48 | 64.5 | 83.43 | |||
| HER2+ or TN | n. | 33 | 13 | 1 | 47 | 0.007 | |
| % | 18.13 | 8.39 | 3.23 | 12.77 | |||
| Missing | n. | 34 | 25 | 10 | 69 | ||
| % | 18.68 | 16.13 | 32.26 | 18.75 | |||
| Total | n = 158 | n = 157 | n = 53 | n = 368 | |||
| GC rs4588 | Luminal A or B | n. | 37 | 34 | 12 | 83 | |
| % | 23.42 | 21.66 | 22.64 | 22.55 | |||
| HER2+ or TN | n. | 87 | 98 | 31 | 216 | 0.766 | |
| % | 55.06 | 62.42 | 58.49 | 58.70 | |||
| Missing | n. | 34 | 25 | 10 | 69 | ||
| % | 21.52 | 15.92 | 18.87 | 18.75 | |||
| Total | n = 71 | n = 180 | n = 117 | n = 368 | |||
| GC rs7041 | Luminal A or B | n. | 12 | 38 | 33 | 83 | |
| % | 16.90 | 21.11 | 28.21 | 22.55 | |||
| HER2+ or TN | n. | 43 | 114 | 59 | 216 | 0.102 | |
| % | 60.56 | 63.33 | 50.43 | 58.70 | |||
| Missing | n. | 16 | 28 | 25 | 69 | ||
| % | 22.54 | 15.56 | 21.37 | 18.75 |
| HR | Low 95%CI | Up 95%CI | p-Values | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.98 | 0.96 | 1.00 | 0.08 | |
| pN+ | No vs. Yes | 0.51 | 0.36 | 0.72 | <0.001 |
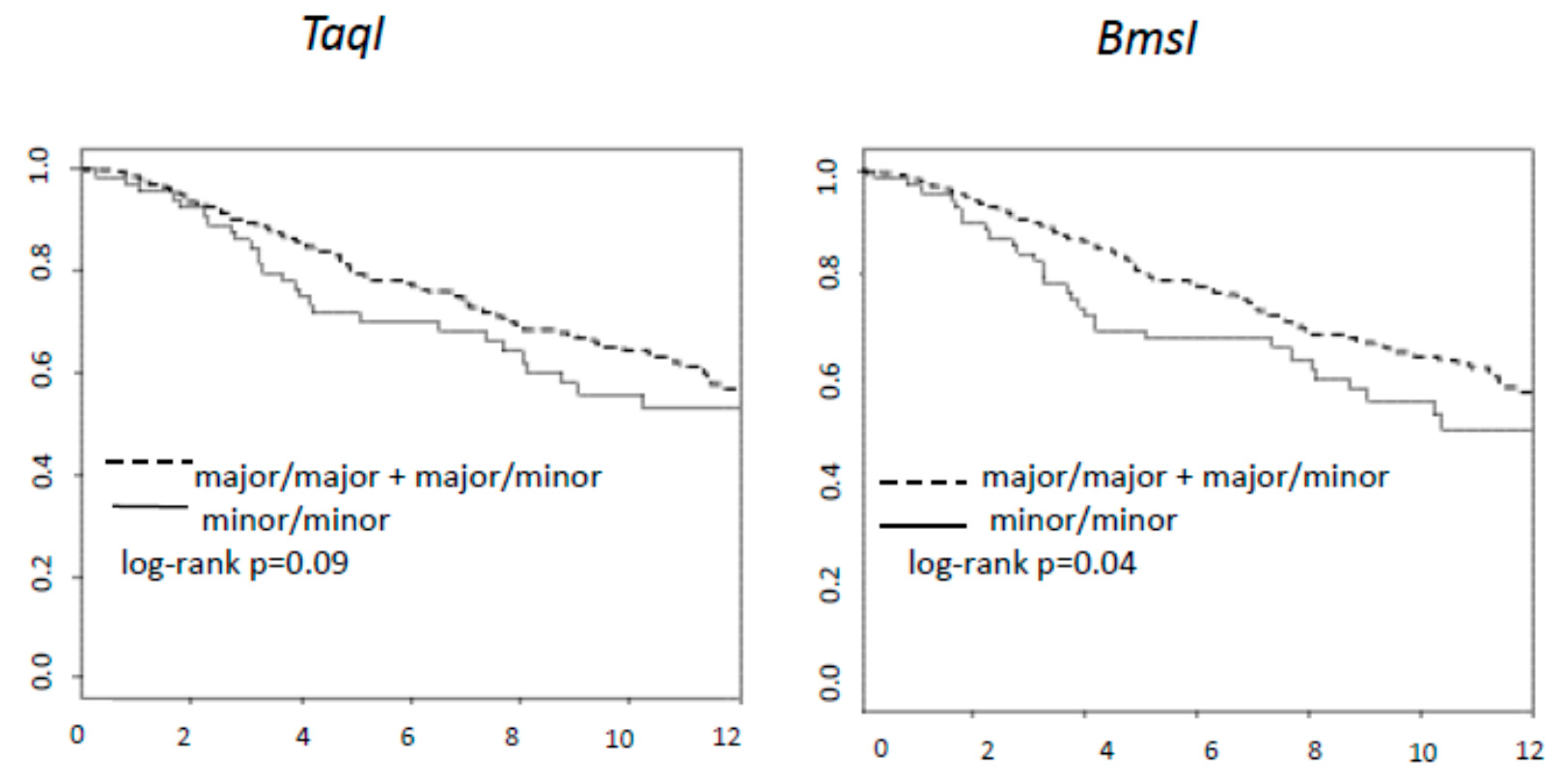
| TaqI | Major/Major Major/Minor vs Minor/Minor | 0.64 | 0.43 | 0.96 | 0.03 |
| Age | 0.98 | 0.96 | 1.00 | 0.07 | |
| pN+ | No vs Yes | 0.50 | 0.36 | 0.72 | <0.001 |
| BsmI | Major/Major Major/Minor vs Minor/Minor | 0.62 | 0.42 | 0.91 | 0.02 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aristarco, V.; Johansson, H.; Gandini, S.; Macis, D.; Zanzottera, C.; Tolva, G.; Feroce, I.; Accornero, C.; Bonanni, B.; Guerrieri-Gonzaga, A.; et al. Association of Vitamin D Receptor and Vitamin D-Binding Protein Polymorphisms with Familial Breast Cancer Prognosis in a Mono-Institutional Cohort. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1208. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13041208
Aristarco V, Johansson H, Gandini S, Macis D, Zanzottera C, Tolva G, Feroce I, Accornero C, Bonanni B, Guerrieri-Gonzaga A, et al. Association of Vitamin D Receptor and Vitamin D-Binding Protein Polymorphisms with Familial Breast Cancer Prognosis in a Mono-Institutional Cohort. Nutrients. 2021; 13(4):1208. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13041208
Chicago/Turabian StyleAristarco, Valentina, Harriet Johansson, Sara Gandini, Debora Macis, Cristina Zanzottera, Gianluca Tolva, Irene Feroce, Chiara Accornero, Bernardo Bonanni, Aliana Guerrieri-Gonzaga, and et al. 2021. "Association of Vitamin D Receptor and Vitamin D-Binding Protein Polymorphisms with Familial Breast Cancer Prognosis in a Mono-Institutional Cohort" Nutrients 13, no. 4: 1208. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13041208
APA StyleAristarco, V., Johansson, H., Gandini, S., Macis, D., Zanzottera, C., Tolva, G., Feroce, I., Accornero, C., Bonanni, B., Guerrieri-Gonzaga, A., & Serrano, D. (2021). Association of Vitamin D Receptor and Vitamin D-Binding Protein Polymorphisms with Familial Breast Cancer Prognosis in a Mono-Institutional Cohort. Nutrients, 13(4), 1208. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13041208








