The Effect of Nutritional Interventions on Long-Term Patient Survival in Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Participants
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Nutrition Education Program
2.4. Laboratory Parameters
2.5. Anthropometrics and Body Composition
2.6. Dietary Intake
2.7. Nutritional Assessment
- Biochemical category: albumin <3.8 g/dL; prealbumin <30 mg/dL body mass; cholesterol <100 mg/dL without lipid-lowering medication (in our case, this criterion was not employed, given that 147 patients consumed such medication).
- Body mass category: BMI <23 kg/m2; unintentional 5% weight loss over the last 3 months or 10% weight loss over the last 6 months.
- Muscle mass category: loss of 10% of MAMC in relation to the 50th percentile.
- Intake category: protein catabolism rate (normalized protein nitrogen) <0.6 g/kg/day; energy intake <25 kcal/kg adjusted to weight/day.
2.8. Number of Hospital Admissions
2.9. Mortality
2.10. Statistical Analysis
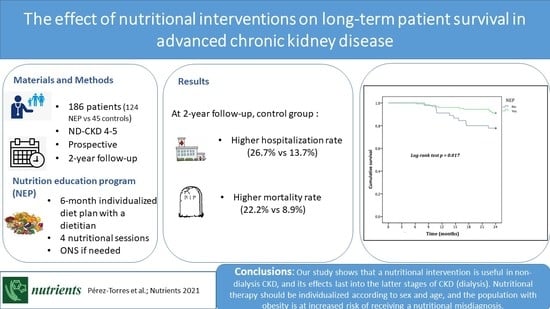
3. Results
3.1. General Characteristics of the Population
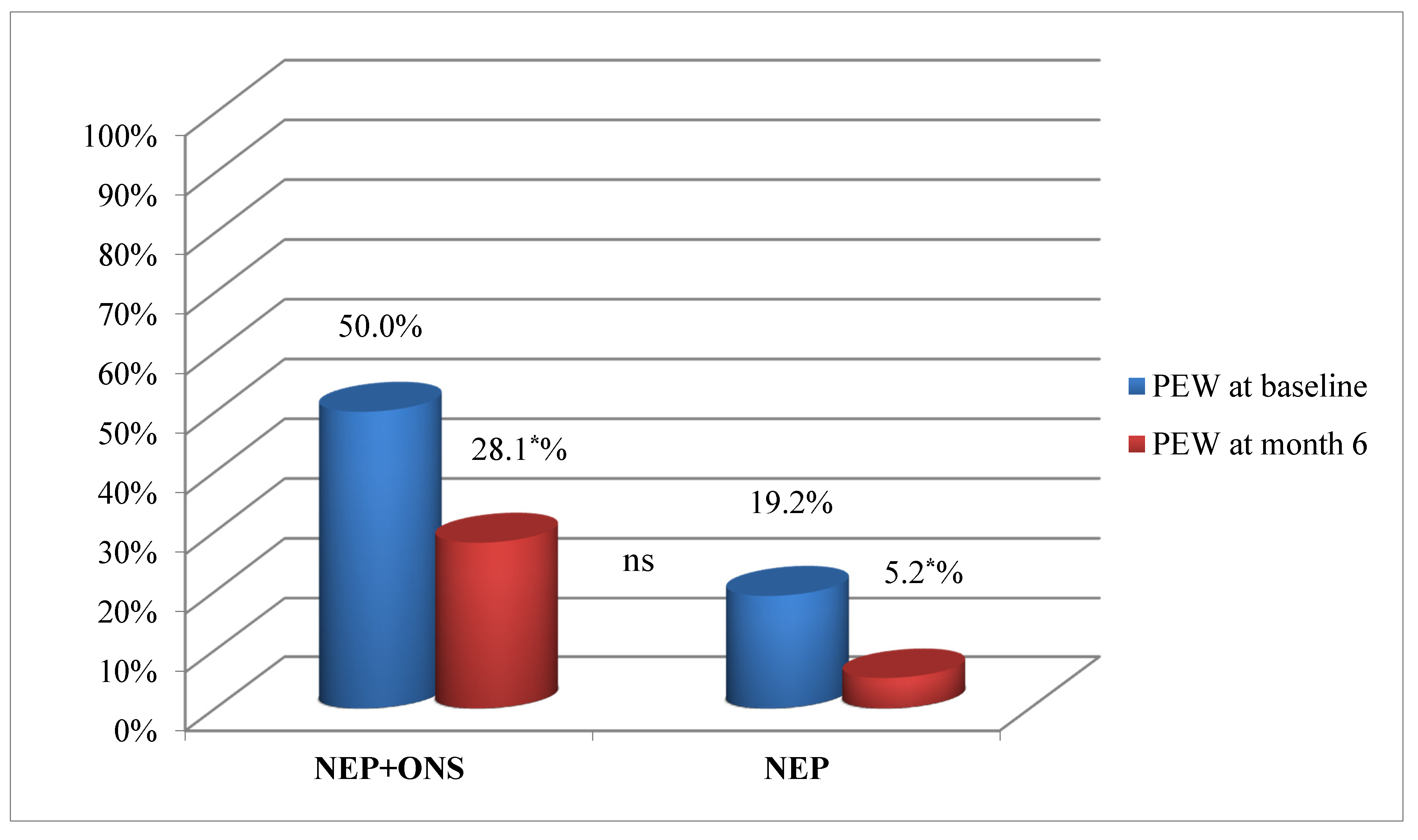
3.2. Results of the Nutritional Education Program at 6 Months
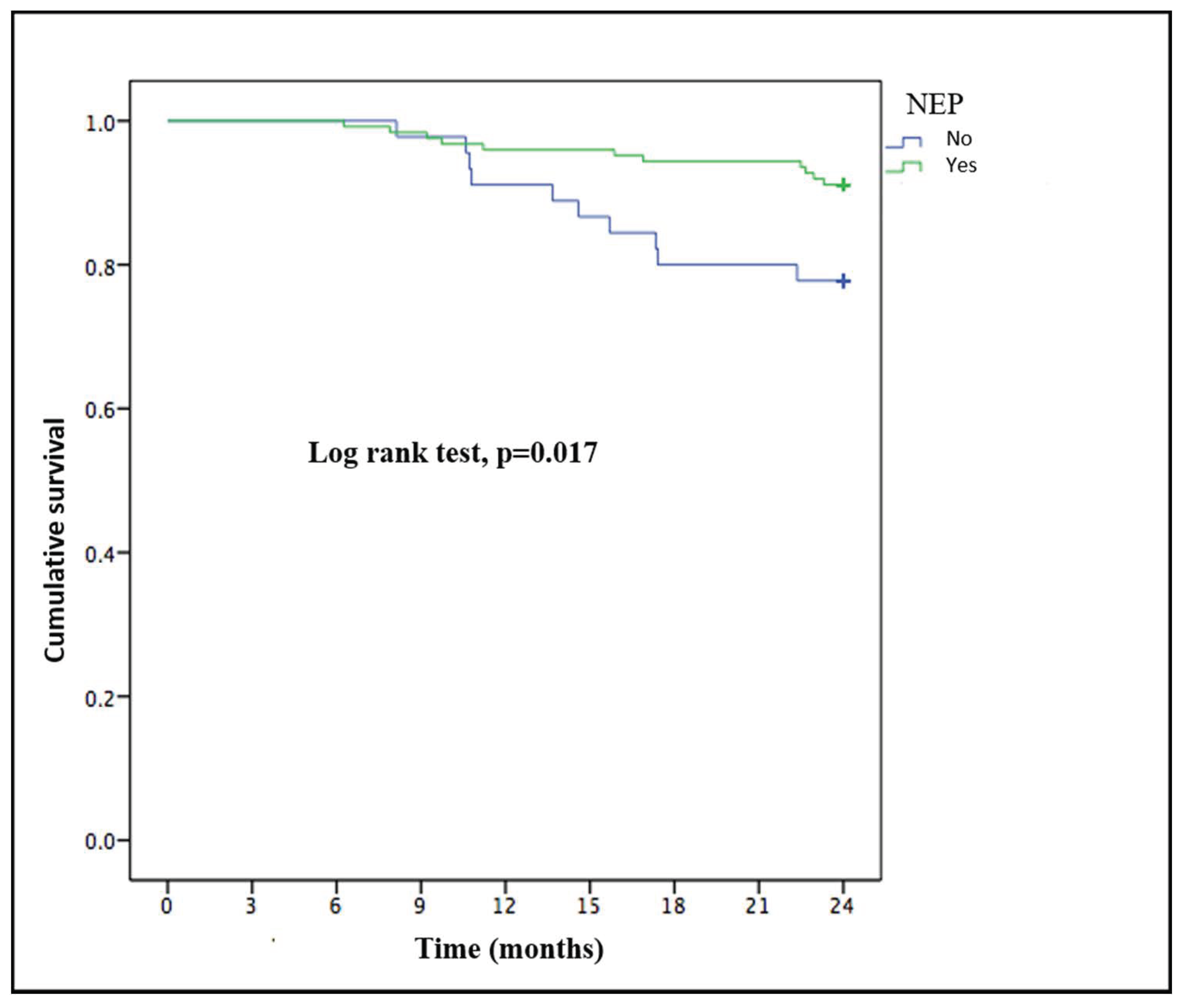
3.3. Comorbidities and Survival at the 2-Year Follow-Up
4. Discussion
4.1. Nutritional Education Program Efficacy at 6 Months
4.2. Long-Term Effects of Nutritional Education Programs on Health Outcomes
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fouque, D.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Kopple, J.; Cano, N.; Chauveau, P.; Cuppari, L.; Franch, H.; Guarnieri, G.; Ikizler, T.A.; Kaysen, G.; et al. A proposed nomenclature and diagnostic criteria for protein-energy wasting in acute and chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2008, 73, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrero, J.J.; Thomas, F.; Nagy, K.; Arogundade, F.; Avesani, C.M.; Chan, M.; Chmielewski, M.; Cordeiro, A.C.; Espinosa-Cuevas, A.; Fiaccadori, E.; et al. Prevalence of Protein-Energy Wasting in Kidney Disease: A Meta-analysis of Contemporary Observational Studies From the International Society of Renal Nutrition and Metabolism. J. Ren. Nutr. 2018, 286, 380–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovesdy, C.P.; Kopple, D.J.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Management of proteinenergy wasting in non-dialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease: Reconciling low protein intake with nutritional therapy. Am. J. Clinnutr. 2013, 97, 1163–1177. [Google Scholar]
- Kovesdy, C.P.; George, S.M.; Anderson, J.E.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Outcome predictability of biomarkers of protein-energy wasting and inflammation in moderate and advanced chronic kidney disease. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 90, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, K.L.; Ash, S.; Davies, P.S.; Bauer, J.D. Randomized controlled trial of nutritional counselling on body composition and dietary intake in severe CKD. Am. J. Kidney. Dis. 2008, 51, 748–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cliffe, M.; Bloodworth, L.L.; Jibani, M.M. Can malnutrition in predialysis patients be prevented by dietetic intervention? J. Ren. Nutr. 2001, 11, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, S.; Molfino, A.; Coppola, B.; Deleo, S.; Tommasi, V.; Galani, A.; Migliaccio, S.; Greco, E.A.; Gnerremusto, T.; Muscaritoli, M. Effect of personalized dietary intervention on nutritional, metabolic and vascular indices in patients with chronic kidney disease. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 19, 3351–3359. [Google Scholar]
- Kopple, J.D. National kidney foundation K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for nutrition in chronic renal failure. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2001, 37 (Suppl 2), S66–S70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikizler, T.A.; Burrowes, J.D.; Byham-Gray, L.D.; Campbell, K.L.; Carrero, J.J.; Chan, W.; Fouque, D.; Friedman, A.N.; Ghaddar, S.; Goldstein-Fuchs, D.J.; et al. KDOQI Clinical Practice Guideline for Nutrition in CKD: 2020 Update. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 76 (Suppl 1), S1–S107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikizler, T.A.; Cano, N.J.; Franch, H.; Fouque, D.; Himmelfarb, J.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Kuhlmann, M.K.; Stenvinkel, P.; TerWee, P.; Teta, D.; et al. Prevention and treatment of protein energy wasting in chronic kidney disease patients: A consensus statement by the International Society of Renal Nutrition and Metabolism. Kidney Int. 2013, 846, 1096–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Methodology of Nutritinal Surveillance; Report of Ajoint FAO/UNICEF/WHO Expert Consultation; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Jagadeswaran, D.; Indhumathi, E.; Hemamalini, A.J.; Sivakumar, V.; Soundararajan, P.; Jayakumar, M. Inflammation and nutritional status assessment by malnutrition inflammation score and its outcome in pre-dialysis chronic kidney disease patients. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 381, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeloka, T.K.; Dharmatti, G.; Jamdade, T.; Pandit, M. Are oral protein supplements helpful in the management of malnutrition in dialysis patients? Indian J. Nephrol. 2013, 231, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Cano, N.J.; Budde, K.; Chazot, C.; Kovesdy, C.P.; Mak, R.H.; Mehrotra, R.; Raj, D.S.; Sehgal, A.R.; Stenvinkel, P.; et al. Diets and enteral supplements for improving outcomes in chronic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2011, 77, 369–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabatino, A.; Piotti, G.; Cosola, C.; Gandolfini, I.; Kooman, J.P.; Fiaccadori, E. Dietary protein and nutritional supplements in conventional hemodialysis. Semin. Dial. 2018, 316, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezer, S.; Bal, Z.; Tutal, E.; Uyar, M.E.; Acar, N.O. Long-term oral nutrition supplementation improves outcomes in malnourished patients with chronic kidney disease on hemodialysis. JPEN J. Parenter. Enteral Nutr. 2014, 388, 960–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández Morante, J.J.; Sánchez-Villazala, A.; Cutillas, R.C.; Fuentes, M.C. Effectiveness of a nutrition education program for the prevention and treatment of malnutrition in end-stage renal disease. J. Ren. Nutr. 2014, 241, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obi, Y.; Qader, H.; Kovesdy, C.P.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Latest consensus and update on protein-energy wasting in chronic kidney disease. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2015, 183, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, A.J.; Buitrago, G.; Rodríguez, N.; Gómez, G.; Sulo, S.; Gómez, C.; Partridge, J.; Misas, J.; Dennis, R.; Alba, M.J.; et al. Clinical and economic outcomes associated with malnutrition in hospitalized patients. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 383, 1310–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yárnoz-Esquíroz, P.; Lacasa, C.; Riestra, M.; Silva, C.; Frühbeck, G. Clinical and financial implications of hospital malnutrition in Spain. Eur. Eat. Disord. Rev. 2019, 276, 581–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano, N.J.M.; Fouque, D.; Roth, H.; Aparicio, M.; Azar, R.; Canaud, B.; Chauveau, P.; Combe, C.; Laville, M.; Leverve, X.M. Intradialytic Parenteral Nutrition Does Not Improve Survival in Malnourished Hemodialysis Patients: A 2-Year Multicenter, Prospective, Randomized Study. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 18, 2583–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazairac, A.H.; de Wit, G.A.; Grooteman, M.P.; Penne, E.L.; van der Weerd, N.C.; van den Dorpel, M.A.; Nubé, M.J.; Lévesque, R.; Ter Wee, P.M.; Bots, M.L.; et al. A composite score of protein-energy nutritional status predicts mortality in haemodialysis patients no better than its individual components. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 266, 1962–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Mehrotra, R.; Chiu, Y.W.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Bargman, J.; Vonesh, E. Similar outcomes with hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis in patients with end-stage renal disease. Arch. Intern. Med. 2011, 1712, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaar, B.G.; Plantinga, L.C.; Crews, D.C.; Fink, N.E.; Hebah, N.; Coresh, J.; Kliger, A.S.; Powe, N.R. Timing, causes, predictors and prognosis of switching from peritoneal dialysis to hemodialysis: A prospective study. BMC Nephrol. 2009, 10, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sladoje-Martinovic, B.; Mikolasevic, I.; Bubic, I.; Racki, S.; Orlic, L. Survival of chronic hemodialysis patients over 80 years of age. Clin. Interv. Aging 2014, 9, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Brar, A.; Markell, M. Impact of gender and gender disparities in patients with kidney disease. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2019, 282, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrero, J.J.; Hecking, M.; Chesnaye, N.C.; Jager, K.J. Sex and gender disparities in the epidemiology and outcomes of chronic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2018, 143, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| NEP+ONS | NEP | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month 0 | Month 6 | p | Month 0 | Month 6 | p | |
| Age | 70.5 ± 14.5 | 66.0 ± 14.8 | ||||
| Albumin, g/dL | 3.3 ± 0.5 * | 3.5 ± 0.5 | 0.106 | 3.6 ± 0.4 | 3.8 ± 0.3 | <0.05 |
| Prealbumin, mg/dL | 26.0 ± 5.6 * | 30.0 ± 4.4 b | <0.05 | 31.1 ± 6.4 | 32.1 ± 6.2 b | 0.480 |
| CrCl, ml/min | 16.8 ± 4.1 | 18.9 ± 6.2 | <0.05 | 17.6 ± 3.8 | 19.5 ± 6.5 | <0.05 |
| Creatinine, mg/dL | 3.4 ± 1.1 | 3.3 ± 1.0 | 0.252 | 3,8 ± 1,2 | 3.6 ± 1.3 | 0.400 |
| Proteinuria, g/24 | 2.0 ± 3.1 | 1.8 ± 2.8 | 0.086 | 1.7 ± 1.6 | 1.6 ± 1.7 | 0.176 |
| Potassium, meq/L | 4.8 ± 0.6 | 4.6 ± 0.5 | 0.105 | 4.8 ± 0.6 | 4.6 ± 0.5 | <0.05 |
| Phosphorous, mg/dL | 3.8 ± 0.9 | 3.8 ± 0.6 | 0.592 | 4.1 ± 0.9 | 3.9 ± 0.7 | <0.05 |
| LDL, mg/dL | 109.1 ± 29.2 | 106 ± 30.3 | 0.411 | 114.0 ± 35.2 | 104.9 ± 28.1 | <0.05 |
| Triglycerides, mg/dL | 125.3 ± 53.7 | 120.2 ± 48.4 | 0.362 | 141.5 ± 61.6 | 125.6 ± 38.8 | <0.05 |
| Weight, kg | 61.5 ± 13.1 * | 62.2 ± 11.3 b | 0.590 | 73.9 ± 12.4 | 72.2 ± 11.3 b | <0.001 |
| Height, m | 160.7 ± 9.8 | 159.1 ± 8.9 | ||||
| BMI, kg/m2 | 24.5 ± 5.4 * | 24.7 ± 4.6 b | <0.05 | 28.8 ± 4.4 | 28.0 ± 4.0 b | <0.001 |
| TSF, mm | 15.3 ± 7.1 * | 15.5 ± 7.1 b | 0.091 | 20.1 ± 7.1 | 19.7 ± 7.0 b | <0.001 |
| MAMC, mm2 | 20.5 ± 3.5 * | 21.0 ± 3.4 | <0.05 | 23.9 ± 3.9 | 23.9 ± 3.6 | 0.956 |
| Resistance, ohms | 550.4 ± 99.9 | 535.3 ± 96.9 b | 0.061 | 507.3 ± 74.7 | 506.4 ± 79.9 b | 0.073 |
| Reactance, ohms | 33.4 ± 7.7 | 41.7 ± 8.5 b | 0.053 | 44.8 ± 10.9 | 46.3 ± 10.7 b | 0.073 |
| Phase angle, degrees | 3.9 ± 0.9 | 4.5 ± 0.8 b | 0.051 | 5.2 ± 1.2 | 5.21 ± 0.6 b | 0.540 |
| Na/K Exchange | 1.6 ± 0.5 | 1.4 ± 0.5 b | 0.059 | 1.0 ± 0.2 | 1.0 ± 0.5 b | 0.974 |
| TBW, % | 57.7 ± 6.0 | 54.6 ± 9.6 b | 0.054 | 52.5 ± 6.1 | 52.6 ± 6.0 b | 0.608 |
| ECW, % | 58.7 ± 6.2 | 53.6 ± 4.4 b | <0.05 | 50.5 ± 5.8 | 49.5 ± 5.5 b | <0.05 |
| ICW, % | 41.1 ± 6.2 | 46.4 ± 4.4 b | <0.05 | 49.4 ± 5.8 | 50.6 ± 5.5 b | 0.070 |
| Fat mass, % | 27.7 ± 12.5 | 30.8 ± 11.9 b | <0.05 | 33.4 ± 8.4 | 32.7 ± 8.8 b | 0.634 |
| Muscle mass, % | 39 ± 13.6 | 40.2 ± 12.7 | 0.084 | 38.5 ± 7.6 | 40.4 ± 7.5 | <0.05 |
| Body cellular mass index | 7.0 ± 2.6 | 7.7 ± 2.7 | <0.05 | 8.2 ± 2.1 | 8.5 ± 1.8 | <0.05 |
| NEP group N = 124 (73.4%) | Control Group N = 45 (26.6%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month 0 | 2 Years | Month 0 | 2 Years | |||
| Age, years | 67.2 ± 14.9 | 63.2±18.3 | 0.036 | |||
| Male sex, n (%) | 57 (46%) | 32 (71.1%) | 0.050 | |||
| Albumin, g/dL | 3.5 ± 0.4 | 3.8 ± 0.5 | <0.001 | 3.6±0.4 | 3.4 ± 0.5 | 0.027 |
| nPNA, g/kg/day | 1.18 ± 0.35 | 1.30 ± 0.27 | 0.020 | 1.2±0.35 | 1.3 ± 0.34 | 0.617 |
| Weight, kg | 70.5 ± 13.3 * | 70.1 ± 11.6 | 0.084 | 74.0±18.2* | 75.0 ± 20.6 | 0.635 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 27.55 ± 4.9 | 27.5 ± 4.4 | 0.110 | 27.0±5.3 | 27.1 ± 6.18 | 0.635 |
| Multivariate Model | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | OR | 95% CI | p | ||
| Age | 169 | 1.094 | 1.035–1.157 | 0.001 | |
| Sex | Male | 80 | |||
| Female | 89 | 3.332 | 1.054–10.535 | 0.040 | |
| NEP | Yes | 124 | |||
| No | 45 | 2.883 | 0.993–8.365 | 0.051 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pérez-Torres, A.; González García, M.E.; Ossorio-González, M.; Álvarez García, L.; Bajo, M.A.; del Peso, G.; Castillo Plaza, A.; Selgas, R. The Effect of Nutritional Interventions on Long-Term Patient Survival in Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease. Nutrients 2021, 13, 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13020621
Pérez-Torres A, González García ME, Ossorio-González M, Álvarez García L, Bajo MA, del Peso G, Castillo Plaza A, Selgas R. The Effect of Nutritional Interventions on Long-Term Patient Survival in Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease. Nutrients. 2021; 13(2):621. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13020621
Chicago/Turabian StylePérez-Torres, Almudena, M. Elena González García, Marta Ossorio-González, Laura Álvarez García, M. Auxiliadora Bajo, Gloria del Peso, Ana Castillo Plaza, and Rafael Selgas. 2021. "The Effect of Nutritional Interventions on Long-Term Patient Survival in Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease" Nutrients 13, no. 2: 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13020621
APA StylePérez-Torres, A., González García, M. E., Ossorio-González, M., Álvarez García, L., Bajo, M. A., del Peso, G., Castillo Plaza, A., & Selgas, R. (2021). The Effect of Nutritional Interventions on Long-Term Patient Survival in Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease. Nutrients, 13(2), 621. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13020621