Energy Expenditure, Protein Oxidation and Body Composition in a Cohort of Very Low Birth Weight Infants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
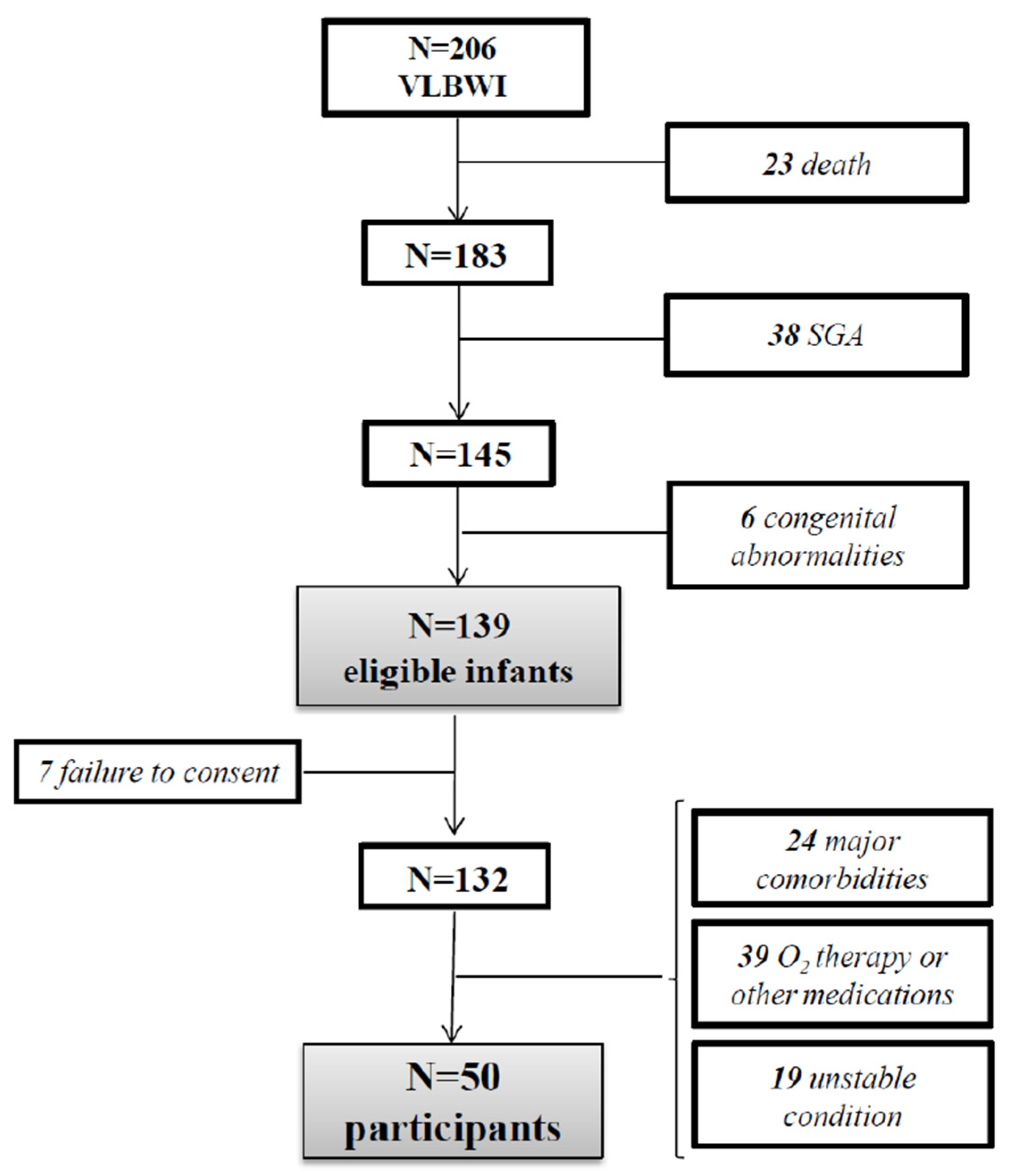
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Nutritional Practice
2.4. Clinical Data Collection
2.5. Anthropometric Measurements
2.6. Indirect Calorimetry
2.7. Substrate Oxidation
2.8. Body Composition
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clement, I. Nutritional Needs of Infants. Textb. Nutr. Diet. Post Basic BSc Nurs. Stud. 2015, 60, 395. [Google Scholar]
- Villar, J.; Giuliani, F.; Barros, F.; Roggero, P.; Zarco, C.I.A.; Rego, S.M.A.; Ochieng, R.; Gianni, M.L.; Rao, S.; Lambert, A.; et al. Monitoring the postnatal growth of preterm infants: A paradigm change. Pediatrics 2018, 141, e20172467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villar, J.; Knight, H.E.; De Onis, M.; Bertino, E.; Gilli, G.; Papageorghiou, A.T.; Ismail, L.C.; Barros, F.C.; Bhutta, Z.A. Conceptual issues related to the construction of prescriptive standards for the evaluation of postnatal growth of preterm infants. Arch. Dis. Child. 2010, 95, 1034–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.B.C.; Boskovic, D.S.; Angeles, D.M. The energy costs of prematurity and the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) experience. Antioxidants 2018, 7, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peila, C.; Spada, E.; Giuliani, F.; Maiocco, G.; Raia, M.; Cresi, F.; Bertino, E.; Coscia, A. Extrauterine growth restriction: Definitions and predictability of outcomes in a cohort of very low birth weight infants or preterm neonates. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horbar, J.D.; Ehrenkranz, R.A.; Badger, G.J.; Edwards, E.M.; Morrow, K.A.; Soll, R.F.; Buzas, J.S.; Bertino, E.; Gagliardi, L.; Bellu’, R. Weight growth velocity and postnatal growth failure in infants 501 to 1500 Grams: 2000–2013. Pediatrics 2015, 136, e84–e92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, W.W.; Ziegler, E.E. Growth failure among preterm infants due to insufficient protein is not innocuous and must be prevented. J. Perinatol. 2016, 36, 500–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carriere, D.; Kantor, E.; Torchin, H.; Le Ray, C.; Jarreau, P.H.; Zana-Taieb, E. Mortality and morbidity of preterm neonates weighing less than 750 g: A 2-year retrospective cohort study. Arch. Pediatr. 2020, 27, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brune, K.D.; Donn, S.M. Enteral feeding of the preterm infant. Neoreviews 2018, 19, e645–e653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueras-Aloy, J.; Palet-Trujols, C.; Matas-Barceló, I.; Botet-Mussons, F.; Carbonell-Estrany, X. Extrauterine growth restriction in very preterm infant: Etiology, diagnosis, and 2-year follow-up. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2020, 179, 1469–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramel, S.E.; Gray, H.L.; Christiansen, E.; Boys, C.; Georgieff, M.K.; Demerath, E.W. Greater early gains in fat-free mass, but not fat mass, are associated with improved neurodevelopment at 1 year corrected age for prematurity in very low birth weight preterm infants. J. Pediatr. 2016, 173, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cormack, B.E.; Harding, J.E.; Miller, S.P.; Bloomfield, F.H. The influence of early nutrition on brain growth and neurodevelopment in extremely preterm babies: A narrative review. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barouki, R.; Gluckman, P.D.; Grandjean, P.; Hanson, M.; Heindel, J.J. Developmental origins of non-communicable disease: Implications for research and public health. Environ. Health 2012, 11, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morlacchi, L.; Roggero, P.; Giannì, M.L.; Bracco, B.; Porri, D.; Battiato, E.; Menis, C.; Liotto, N.; Mallardi, D.; Mosca, F. Protein use and weight-gain quality in very-low-birth-weight preterm infants fed human milk or formula. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 107, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannì, M.L.; Consonni, D.; Liotto, N.; Roggero, P.; Morlacchi, L.; Piemontese, P.; Menis, C.; Mosca, F. Does human milk modulate body composition in late preterm infants at term-corrected age? Nutrients 2016, 8, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coss-Bu, J.A.; Jefferson, L.S.; Walding, D.; David, Y.; O’Brian Smith, E.; Klish, W.J. Resting energy expenditure in children in a pediatric intensive care unit: Comparison of Harris-Benedict and Talbot predictions with indirect calorimetry values. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1998, 67, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agostoni, C.; Edefonti, A.; Calderini, E.; Fossali, E.; Colombo, C.; Battezzati, A.; Bertoli, S.; Milani, G.P.; Bisogno, A.; Perrone, M.; et al. Accuracy of prediction formulae for the assessment of resting energy expenditure in hospitalized children. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2016, 63, 708–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leitch, C.A.; Denne, S.C. Energy expenditure in the extremely low-birth weight infant. Clin. Perinatol. 2000, 27, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrone, M.; Mallardi, D.; Tabasso, C.; Bracco, B.; Menis, C.; Piemontese, P.; Amato, O.; Liotto, N.; Roggero, P.; Mosca, F. The indirect calorimetry in very low birth weight preterm infants: An easier and reliable procedure. Nutrition 2021, 86, 111180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frayn, K.N. Calculation of substrate oxidation rates in vivo from gaseous exchange. J. Appl. Physiol. 2016, 121, 628–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askanazi, J.; Carpentier, Y.A.; Elwyn, D.H.; Nördenström, J.; Jeevanandam, M.; Rosenbaum, S.H.; Gump, F.E.; Kinney, J.M. Influence of total parenteral nutrition on fuel utilization in injury and sepsis. Ann. Surg. 1980, 191, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoner, H.B.; Little, R.A.; Frayn, K.N.; Elebute, A.E.; Tresadern, J.; Gross, E. The effect of sepsis on the oxidation of carbohydrate and fat. Br. J. Surg. 1983, 70, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freymond, D.; Schutz, Y.; Decombaz, J.; Micheli, J.L.; Jéquier, E. Energy balance, physical activity, and thermogenic effect of feeding in premature infants. Pediatr. Res. 1986, 20, 638–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roggero, P.; Giannì, M.L.; Orsi, A.; Amato, O.; Piemontese, P.; Liotto, N.; Morlacchi, L.; Taroni, F.; Garavaglia, E.; Bracco, B.; et al. Implementation of Nutritional Strategies Decreases Postnatal Growth Restriction in Preterm Infants. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agostoni, C.; Buonocore, G.; Carnielli, V.P.; De Curtis, M.; Darmaun, D.; Decsi, T.; Domellof, M.; Embleton, N.D.; Fusch, C.; Genzel-Boroviczeny, O.; et al. Enteral nutrient supply for preterm infants: Commentary from the european society of paediatric gastroenterology, hepatology and nutrition committee on nutrition. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2010, 50, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morlacchi, L.; Mallardi, D.; Giannì, M.L.; Roggero, P.; Amato, O.; Piemontese, P.; Consonni, D.; Mosca, F. Is targeted fortification of human breast milk an optimal nutrition strategy for preterm infants? An interventional study. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villar, J.; Giuliani, F.; Figueras-Aloy, J.; Barros, F.; Bertino, E.; A Bhutta, Z.; Kennedy, S.H. Growth of preterm infants at the time of global obesity. Arch. Dis. Child. 2019, 104, 725–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The International Fetal and Newborn Growth Consortium. International Fetal and Newborn Growth Standards for the 21st Century Anthropometry Handbook; The International Fetal and Newborn Growth Consortium: Oxford, UK, 2012; pp. 1–59. [Google Scholar]
- The INTERGROWTH-21st Project. Available online: http://intergrowth21.ndog.ox.ac.uk (accessed on 21 September 2021).
- Weir, J.B.V. New methods for calculating metabolic rate with special reference to protein metabolism. J. Physiol. 1949, 109, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClave, S.A.; Lowen, C.C.; Kleber, M.J.; McConnell, J.W.; Jung, L.Y.; Goldsmith, L.J. Clinical use of the respiratory quotient obtained from indirect calorimetry. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2003, 27, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fell, J.M.E.; Thakkar, H.; Newman, D.J.; Price, C.P. Measurement of albumin and low molecular weight proteins in the urine of newborn infants using a cotton wool ball collection method. Acta Paediatr. Int. J. Paediatr. 1997, 86, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roggero, P.; Giannì, M.L.; Amato, O.; Price, C. Evaluation of air-displacement plethysmography for body composition assessment in preterm infants. Pediatr. Res. 2012, 72, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urlando, A.; Dempster, P.; Aitkens, S. A new air displacement plethysmograph for the measurement of body composition in infants. Pediatr. Res. 2003, 53, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fomon, S.J.; Haschke, F.; Ziegler, E.E.; Nelson, S.E. Body composition of reference children from birth to age 10 years. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1982, 35, 1169–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubetzky, R.; Vaisman, N.; Mimouni, F.B.; Dollberg, S. Energy expenditure in human milk- versus formula-fed preterm infants. J. Pediatr. 2003, 143, 750–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larcade, J.; Pradat, P.; Buffin, R.; Leick-Courtois, C.; Jourdes, E.; Picaud, J.C. Estimation of fat-free mass at discharge in preterm infants fed with optimized feeding regimen. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2017, 64, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.; Zhou, J.; Yin, Y.; Jing, W.; Luo, B.; Wang, J. Effects of breast-feeding compared with formula-feeding on preterm infant body composition: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 116, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lönnerdal, B.; Erdmann, P.; Thakkar, S.K.; Sauser, J.; Destaillats, F. Longitudinal evolution of true protein, amino acids and bioactive proteins in breast milk: A developmental perspective. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2017, 41, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, F.V.M.; Abranches, A.D.; Méio, M.D.B.B.; Gomes, S.C.; Villela, L.D.; Moreira, M.E.L. Differences in energy expenditure in human donor milk versus formula milk in preterm newborns: A crossover study. Nutrition 2019, 66, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putet, G.; Senterre, J.; Rigo, J.; Salle, B. Nutrient balance, energy utilization, and composition of weight gain in very-low-birth-weight infants fed pooled human milk or a preterm formula. J. Pediatr. 1984, 105, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whyte, R.K.; Haslam, R.; Vlainic, C.; Shannon, S.; Samulski, K.; Campbell, D.; Bayley, H.S.; Sinclair, J.C. Energy balance and nitrogen balance in growing low birthweight infants fed human milk or formula. Pediatr. Res. 1983, 17, 891–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Brooke, O.G.; Wood, C.; Barley, J. Energy balance, nitrogen balance, and growth in preterm infants fed expressed breast milk, a premature infant formula, and two low-solute adapted formulae. Arch. Dis. Child. 1982, 57, 898–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| HMF (23) | PFF (27) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Range | Mean | SD | Range | p | |
| GA (weeks) | 30.09 | 2.02 | (25–32) | 30.33 | 1.44 | (26–33) | ns |
| Birth weight (g) | 1280.22 | 252.5 | (720–1490) | 1283.67 | 159.3 | (890–1500) | ns |
| Birth weight z-score | −0.46 | 0.59 | (−1.27–0.88) | −0.45 | 0.61 | (−1.27–0.87) | ns |
| GA at IC (weeks) | 36.48 | 0.85 | (36–39) | 36.7 | 0.99 | (36–39) | ns |
| Weight at IC (g) | 2156.22 | 331.3 | (1800–3310) | 2251.26 | 292.57 | (1861–2795) | ns |
| Weight z-score at IC | −0.97 | 0.86 | (−2.29–1.47) | −0.84 | 0.88 | (−2.44–0.63) | ns |
| HMF (23) | PFF (27) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Range | Mean | SD | Range | p | |
| Volume mL/kg/day | 152.46 | 15.79 | (116.95–184) | 153.14 | 14 | (125.99–182.92) | ns |
| Energy kcal/kg/day | 126.69 | 19.33 | (100.4–166.27) | 125.55 | 12.37 | (105.4–158.75) | ns |
| Protein g/kg/day | 3.34 | 0.72 | (2.14–4.66) | 3.47 | 0.46 | (2.59–4.39) | ns |
| Carbohydrate g/kg/day | 13.18 | 1.91 | (10.22–16.55) | 13.3 | 1.74 | (9.25–15.91) | ns |
| Lipid g/kg/day | 7.08 | 1.14 | (5.57–9.52) | 7.56 | 0.73 | (6.31–9.83) | ns |
| HMF (23) | PFF (27) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Range | Mean | SD | Range | p | |
| REE kcal/kg/day | 59.69 | 9.8 | (47.01–82.71) | 59.27 | 13.15 | (45.42–105.09) | ns |
| REE kcal/FFM(kg)day | 64.18 | 1.46 | (62.28–65.65) | 73.31 | 1.87 | (71.40–75.21) | p < 0.001 |
| RQ | 0.89 | 0.04 | (0.77–0.95) | 0.85 | 0.08 | (0.69–0.97) | p < 0.05 |
| Protein ox g/kg/day | 1.7 | 0.92 | (0.41–3.66) | 2.8 | 1.65 | (0.9–6.34) | p < 0.01 |
| Carbohydrate ox g/kg/day | 7.28 | 1.36 | (5.17–9.22) | 7.01 | 1.97 | (3.62–9.71) | p = 0.56 |
| Lipid ox g/kg/day | 1.27 | 0.37 | (0.51–1.82) | 1.25 | 0.49 | (0.45–2.05) | ns |
| HMF (23) | PFF (27) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Range | Mean | SD | Range | p | |
| FFM kg | 2.05 | 0.26 | (1.68–2.55) | 1.82 | 0.35 | (1.17–2.88) | p < 0.01 |
| FFM % | 88.02 | 3.93 | (80.40–94.90) | 84.91 | 4.12 | (78.45–89.48) | p < 0.01 |
| FM kg | 0.28 | 0.12 | (0.11–0.60) | 0.34 | 0.09 | (0.11–0.42) | p < 0.05 |
| FM % | 11.97 | 3.93 | (5.1–19.6) | 15.09 | 2.87 | (7.12–21.4) | p < 0.01 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Perrone, M.; Menis, C.; Piemontese, P.; Tabasso, C.; Mallardi, D.; Orsi, A.; Amato, O.; Liotto, N.; Roggero, P.; Mosca, F. Energy Expenditure, Protein Oxidation and Body Composition in a Cohort of Very Low Birth Weight Infants. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3962. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13113962
Perrone M, Menis C, Piemontese P, Tabasso C, Mallardi D, Orsi A, Amato O, Liotto N, Roggero P, Mosca F. Energy Expenditure, Protein Oxidation and Body Composition in a Cohort of Very Low Birth Weight Infants. Nutrients. 2021; 13(11):3962. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13113962
Chicago/Turabian StylePerrone, Michela, Camilla Menis, Pasqua Piemontese, Chiara Tabasso, Domenica Mallardi, Anna Orsi, Orsola Amato, Nadia Liotto, Paola Roggero, and Fabio Mosca. 2021. "Energy Expenditure, Protein Oxidation and Body Composition in a Cohort of Very Low Birth Weight Infants" Nutrients 13, no. 11: 3962. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13113962
APA StylePerrone, M., Menis, C., Piemontese, P., Tabasso, C., Mallardi, D., Orsi, A., Amato, O., Liotto, N., Roggero, P., & Mosca, F. (2021). Energy Expenditure, Protein Oxidation and Body Composition in a Cohort of Very Low Birth Weight Infants. Nutrients, 13(11), 3962. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13113962







