Tocotrienol-Rich Vitamin E (Tocovid) Improved Nerve Conduction Velocity in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients in a Phase II Double-Blind, Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants
2.2.1. Inclusion Criteria
2.2.2. Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Randomization and Blinding
2.4. Procedures
2.4.1. Screening Visit
2.4.2. Randomization Visit
2.4.3. Follow-Up Visits
2.4.4. End-of-Study Visit
2.4.5. Washout Visit
2.5. Outcomes
2.6. Nerve Conduction Study
2.7. Serum VEGF-A and TGF-β1
2.8. Adherence and Vitamin E Levels
2.9. Renal Profile, Lipid Profile, and Liver Function Tests
2.10. HbA1c Assessment
2.11. Sample Size
2.12. Statistical Analysis
2.13. Ethics
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Effects Observed during the Intervention Trial
3.2.1. Two Months of Intervention
3.2.2. Six Months of Intervention
3.2.3. Twelve Months of Intervention (End of Treatment)
3.2.4. Changes in Time within the Intervention Group
3.2.5. Adherence and Vitamin E Levels
3.2.6. Neuropathic Pain Questionnaire (NPQ)
3.2.7. Adverse Events (AEs)
3.3. Subgroup Analysis
3.3.1. Effects of Baseline Conduction Velocity
3.3.2. Effects of Duration of Diabetes and HbA1c
3.4. Six-Month Washout
3.5. Overall Variation in Nerve Conduction Velocities
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tesfaye, S.; Boulton, A.J.M.; Dyck, P.J.; Freeman, R.; Horowitz, M.; Kempler, P.; Lauria, G.; Malik, R.; Spallone, V.; Vinik, A.; et al. Diabetic Neuropathies: Update on Definitions, Diagnostic Criteria, Estimation of Severity, and Treatments. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 2285–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiber, G.E.; Vileikyte, L.; Boyko, E.; Del Aguila, M.; Smith, D.G.; Lavery, L.A.; Boulton, A.J. Causal pathways for incident lower-extremity ulcers in patients with diabetes from two settings. Diabetes Care 1999, 22, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amour, A.A.; Chamba, N.; Kayandabila, J.; Lyaruu, I.A.; Marieke, D.; Shao, E.R.; Howlett, W. Prevalence, Patterns, and Factors Associated with Peripheral Neuropathies among Diabetic Patients at Tertiary Hospital in the Kilimanjaro Region: Descriptive Cross-Sectional Study from North-Eastern Tanzania. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2019, 2019, 5404781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadosky, A.; Mardekian, J.; Parsons, B.; Hopps, M.; Bienen, E.J.; Markman, J. Healthcare utilization and costs in diabetes relative to the clinical spectrum of painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy. J. Diabetes Its Complicat. 2015, 29, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Lamer, T.J.; Rho, R.H.; Marshall, K.A.; Sitzman, B.T.; Ghazi, S.M.; Brewer, R.P. Contemporary Management of Neuropathic Pain for the Primary Care Physician. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2004, 79, 1533–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namaka, M.; Gramlich, C.R.; Ruhlen, D.; Melanson, M.; Sutton, I.; Major, J. A treatment algorithm for neuropathic pain. Clin. Ther. 2004, 26, 951–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop-Busui, R.; Boulton, A.J.; Feldman, E.; Bril, V.; Freeman, R.; Malik, R.; Sosenko, J.M.; Ziegler, D. Diabetic Neuropathy: A Position Statement by the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 136–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, T. Amplitude of sensory nerve action potential in early stage diabetic peripheral neuropathy: An analysis of 500 cases. Neural Regen. Res. 2014, 9, 1389–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galiero, R.; Ricciardi, D.; Pafundi, P.C.; Todisco, V.; Tedeschi, G.; Cirillo, G.; Sasso, F.C. Whole plantar nerve conduction study: A new tool for early diagnosis of peripheral diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2021, 176, 108856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, K.-L.; Chin, K.-Y. The Role of Tocotrienol in Protecting against Metabolic Diseases. Molecules 2019, 24, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.J.; Tsuchiya, M.; Wassall, S.R.; Choo, Y.M.; Govil, G.; Kagan, V.E.; Packer, L. Structural and dynamic membrane properties of .alpha.-tocopherol and .alpha.-tocotrienol: Implication to the molecular mechanism of their antioxidant potency. Biochemistry 1993, 32, 10692–10699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhad, A.; Chopra, K. Tocotrienol attenuates oxidative–nitrosative stress and inflammatory cascade in experimental model of diabetic neuropathy. Neuropharmacology 2009, 57, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, Y.T.; Phang, S.C.W.; Tan, G.C.J.; Ng, E.Y.; Henien, N.P.B.; Palanisamy, U.D.M.; Ahmad, B.; Kadir, K.A. The Effects of Tocotrienol-Rich Vitamin E (Tocovid) on Diabetic Neuropathy: A Phase II Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Andary, M.; Buschbacher, R.; Del Toro, D.; Smith, B.; So, Y.; Do, K.Z.; Dillingham, T.R. Electrodiagnostic reference values for upper and lower limb nerve conduction studies in adult populations. Muscle Nerve 2016, 54, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrante, M.A.; Teresa Spiegelberg, B.; Tsao, B. Principles of Nerve Conduction Studies and Needle EMG; American Association of Neuromuscular & Electrodiagnostic Medicine: Rochester, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Che, H.-L.; Tan, D.M.-Y.; Meganathan, P.; Gan, Y.-L.; Razak, G.A.; Fu, J.-Y. Validation of a HPLC/FLD Method for Quantification of Tocotrienols in Human Plasma. Int. J. Anal. Chem. 2015, 2015, 357609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, P.; Brubacher, D.; Moser, U.; Stähelin, H.B.; Gey, K.F. Vitamin E and vitamin A concentrations in plasma adjusted for cholesterol and triglycerides by multiple regression. Clin. Chem. 1995, 41, 924–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunnigan, S.K.; Ebadi, H.; Breiner, A.; Katzberg, H.D.; Lovblom, L.E.; Perkins, B.A.; Bril, V. Conduction Slowing in Diabetic Sensorimotor Polyneuropathy. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 3684–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallik, A.; Weir, A. Nerve conduction studies: Essentials and pitfalls in practice. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2005, 76, ii23–ii31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutuncu, N.B.; Bayraktar, M.; Varli, K. Reversal of defective nerve conduction with vitamin E supplementation in type 2 diabetes: A preliminary study. Diabetes Care 1998, 21, 1915–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajanandh, M.G.; Kosey, S.; Prathiksha, G. Assessment of antioxidant supplementation on the neuropathic pain score and quality of life in diabetic neuropathy patients—A randomized controlled study. Pharmacol. Rep. 2014, 66, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogbera, A.O.; Oshinaike, O.; Ezeobi, E.; Unachukwu, C. Treatment of diabetes mellitus-associated neuropathy with vitamin E and Eve primrose. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 18, 846–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peh, H.Y.; Tan, W.S.D.; Liao, W.; Wong, W.F. Vitamin E therapy beyond cancer: Tocopherol versus tocotrienol. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 162, 152–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesfaye, S.; Selvarajah, D. Advances in the epidemiology, pathogenesis and management of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Diabetes/Metab. Res. Rev. 2012, 28, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hor, C.P.; Fung, W.Y.; Ang, H.A.; Lim, S.C.; Kam, L.Y.; Sim, S.-W.; Lim, L.H.; Choon, W.Y.; Wong, J.W.; Ch’ng, A.S.H.; et al. Efficacy of oral mixed tocotrienols in diabetic peripheral neuropathy: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Neurol. 2018, 75, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, J.; Zimmet, P. The epidemiology of diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes Rev. 1999, 7, 245–252. [Google Scholar]
- Barghash, Z.; Larsen, J.; Al-Bishri, A.; Kahnberg, K.-E. Degeneration and regeneration of motor and sensory nerves: A stereological study of crush lesions in rat facial and mental nerves. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2013, 42, 1566–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Nisar, M.U.; Asad, A.; Waqas, A.; Ali, N.A.M.; Nisar, A.; Qayyum, M.A.; Maryam, H.; Javaid, M.; Jamil, M. Association of Diabetic Neuropathy with Duration of Type 2 Diabetes and Glycemic Control. Cureus 2015, 7, e302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baderca, F.; Timar, B.; Popescu, S.; Simu, M.; Diaconu, L.; Velea, I.; Timar, R. Age as an independent factor for the development of neuropathy in diabetic patients. Clin. Interv. Aging 2016, 11, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Booya, F.; Bandarian, F.; Larijani, B.; Pajouhi, M.; Nooraei, M.; Lotfi, J. Potential risk factors for diabetic neuropathy: A case control study. BMC Neurol. 2005, 5, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, G.; Rizvi, S.A.A.; Singhal, S.; Zubair, M.; Ahmad, J. Serum levels of TGF-β1 in patients of diabetic peripheral neuropathy and its correlation with nerve conduction velocity in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2016, 10, S135–S139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ybarra, J.; Pou, J.M.; Romeo, J.H.; Merce, J.; Jurado, J.; Jurado, J. Transforming growth factor beta 1 as a biomarker of diabetic peripheral neuropathy: Cross-sectional study. J. Diabetes Its Complicat. 2010, 24, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, S.; Dent, C.; Duran-Jimenez, B.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Rebar, E.J.; Case, C.C.; Gregory, P.D.; Martin, T.J.; Spratt, S.K.; et al. Gene Transfer of an Engineered Transcription Factor Promoting Expression of VEGF-A Protects against Experimental Diabetic Neuropathy. Diabetes 2006, 55, 1847–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Oosthuyse, B.; Moons, L.; Storkebaum, E.; Beck, H.; Nuyens, D.; Brusselmans, K.; Van Dorpe, J.; Hellings, P.; Gorselink, M.; Heymans, S.; et al. Deletion of the hypoxia-response element in the vascular endothelial growth factor promoter causes motor neuron degeneration. Nat. Genet. 2001, 28, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, K.L.; Mao, X.O.; Greenberg, D.A. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Rescues HN33 Neural Cells from Death Induced by Serum Withdrawal. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2000, 14, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, K.L.; Mao, X.O.; Greenberg, D.A. Vascular endothelial growth factor: Direct neuroprotective effect in in vitro ischemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 10242–10247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sondell, M.; Lundborg, G.; Kanje, M. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Has Neurotrophic Activity and Stimulates Axonal Outgrowth, Enhancing Cell Survival and Schwann Cell Proliferation in the Peripheral Nervous System. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 5731–5740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondell, M.; Lundborg, G.; Kanje, M. Vascular endothelial growth factor stimulates Schwann cell invasion and neovascularization of acellular nerve grafts. Brain Res. 1999, 846, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sondell, M.; Sundler, F.; Kanje, M. Vascular endothelial growth factor is a neurotrophic factor which stimulates axonal outgrowth through the flk-1 receptor. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2000, 12, 4243–4254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simovic, D.; Isner, J.M.; Ropper, A.H.; Pieczek, A.; Weinberg, D.H. Improvement in chronic ischemic neuropathy after intramuscular phVEGF165 gene transfer in patients with critical limb ischemia. Arch. Neurol. 2001, 58, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deguchi, T.; Hashiguchi, T.; Horinouchi, S.; Uto, T.; Oku, H.; Kimura, K.; Makisumi, K.; Arimura, K. Serum VEGF increases in diabetic polyneuropathy, particularly in the neurologically active symptomatic stage. Diabet. Med. 2009, 26, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Amici, D.; Klersy, C.; Ramajoli, F.; Brustia, L.; Politi, P. Impact of the Hawthorne Effect in a Longitudinal Clinical Study: The Case of Anesthesia. Control. Clin. Trials 2000, 21, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, R.; Leonard, S.; Park, S.-I.; Zhao, Y.; Traber, M.G. Human vitamin E requirements assessed with the use of apples fortified with deuterium-labeled α-tocopheryl acetate. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 83, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.E.; Ferruzzi, M.G.; Campbell, W.W. Egg Consumption Increases Vitamin E Absorption from Co-Consumed Raw Mixed Vegetables in Healthy Young Men. J. Nutr. 2016, 146, 2199–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeanes, Y.M.; Hall, W.L.; Ellard, S.; Lee, E.; Lodge, J.K. The absorption of vitamin E is influenced by the amount of fat in a meal and the food matrix. Br. J. Nutr. 2004, 92, 575–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, S.; Patel, V.; Rink, C.; Roy, S.; Sen, C.K. Delivery of orally supplemented α-tocotrienol to vital organs of rats and tocopherol-transport protein deficient mice. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2005, 39, 1310–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-B.; Cheng, Y.-Z.; Shi, M.; Zhang, H.-M.; Dai, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.-J.; Chen, J.-W.; Wang, H.-X.; Chen, J.-W. The relationship between plasma homocysteine levels and diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi 2011, 50, 14–17. [Google Scholar]
- González, R.; Pedro, T.; Martinez-Hervas, S.; Civera, M.; Priego, M.A.; Catalá, M.; Chaves, F.J.; Ascaso, J.F.; Carmena, R.; Real, J.T. Plasma homocysteine levels are independently associated with the severity of peripheral polyneuropathy in type 2 diabetic subjects. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2012, 17, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Sivaraaman, K.; Nouh, A.; Dun, N. Elevated Plasma Level of Homocysteine is an Independent Risk Factor for Peripheral Neuropathy. Br. J. Med. Med. Res. 2014, 4, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohara, N.; Kimura, J.; Kaji, R.; Goto, Y.; Ishii, J.; Takiguchi, M.; Nakai, M. F-wave latency serves as the most reproducible measure in nerve conduction studies of diabetic polyneuropathy: Multicentre analysis in healthy subjects and patients with diabetic polyneuropathy. Diabetologia 2000, 43, 915–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, J. Long and short of nerve conduction measures: Reproducibility for sequential assessments. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2001, 71, 427–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jerath, N.U.; Aul, E.; Reddy, C.G.; Azadeh, H.; Swenson, A.; Kimura, J. Prolongation of F-wave minimal latency: A Sensitive Predictor of Polyneuropathy. Int. J. Neurosci. 2016, 126, 520–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
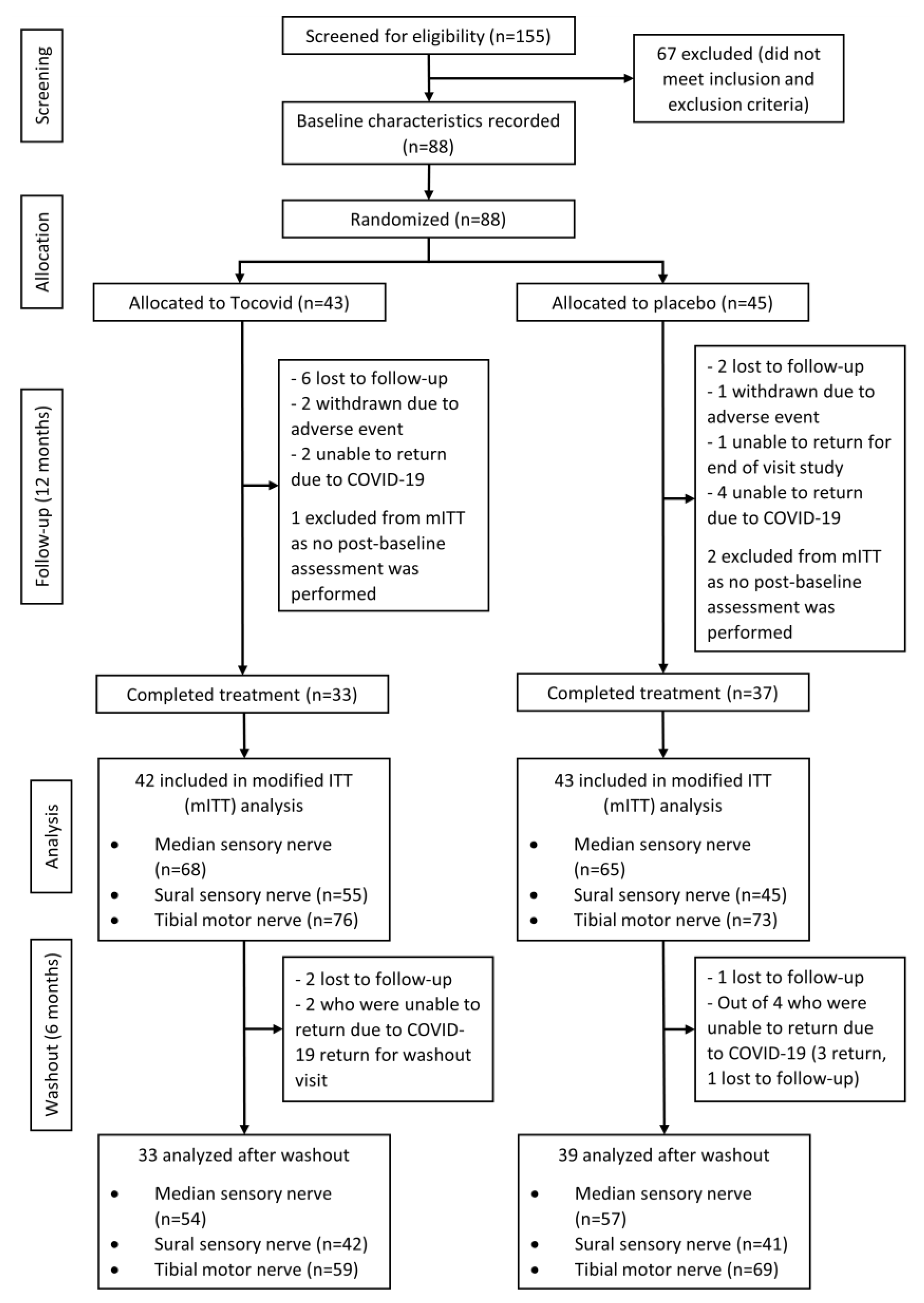

| Baseline Characteristics | Total (n = 88) | Tocovid (n = 43) | Placebo (n = 45) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender, n (%) | ||||
| Male | 58 (65.9) | 29 (67.4) | 29 (64.4) | 0.943 † |
| Female | 30 (34.1) | 14 (32.6) | 16 (35.6) | |
| Race, n (%) | ||||
| Malay | 44 (50) | 23 (53.5) | 21 (46.7) | 0.834 ‡ |
| Chinese | 22 (25) | 10 (23.3) | 12 (26.7) | |
| Indian | 18 (20.5) | 9 (20.9) | 9 (20) | |
| Others | 4 (4.5) | 1 (2.3) | 3 (6.7) | |
| Age (years) ¶ | 64 (13) | 63 (11.5) | 64 (13) | 0.997 |
| Duration of DM (years) § | 15.9 ± 8.8 | 15.5 ± 8.57 | 16.2 ± 9.06 | 0.720 |
| HbA1c (%) § | 7.6 ± 1.1 | 7.56 ± 1.00 | 7.7 ± 1.2 | 0.546 |
| SBP (mmHg) § | 131.4 ± 12.9 | 134.7 ± 12.9 | 129.2 ± 12.6 | 0.101 |
| DBP (mmHg) § | 77.8 ± 8.69 | 78.0 ± 8.45 | 77.5 ± 9.01 | 0.775 |
| BMI (kg/m2) § | 28.2 ± 4.64 | 28.0 ± 4.13 | 28.3 ± 5.11 | 0.811 |
| Serum Biomarkers | ||||
| TGFβ-1 (ng/mL) | 33.1 (31.1) | 33.6 (16.7) | 32.1 (37.4) | 0.887 |
| VEGF-A (pg/mL) | 707 (600) | 762 (478) | 655 (582) | 0.231 |
| Plasma Vitamin E | ||||
| α-Tocotrienol (pg/mL) ¶ | 37.3 (55.5) | 36.7 (53.8) | 37.5 (56.4) | 0.729 |
| γ-Tocotrienol (pg/mL) ¶ | 24.3 (29.4) | 19.6 (30.8) | 42.7 (29.5) | 0.815 |
| δ-Tocotrienol (pg/mL) ¶ | 12.5 (13.6) | 12.4 (16.2) | 12.7 (13.2) | 0.784 |
| α-Tocopherol (ng/mL) ¶ | 1.69 (1.46) | 1.63 (1.20) | 2.02 (1.58) | 0.698 |
| Safety Tests | ||||
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) ¶ | 66.3 (36.9) | 64.5 (35.2) | 69 (37.5) | 0.848 |
| Serum Creatinine (µmol/L) ¶ | 99.5 (43.2) | 95.1 (46.6) | 100.5 (38.5) | 0.710 |
| Urea (mmol/L) ¶ | 5.9 (3.3) | 5.7 (3.6) | 6.1 (3.2) | 0.844 |
| AST (U/L) ¶ | 10 (11) | 10 (11.5) | 11 (9) | 0.391 |
| ALT (U/L) ¶ | 14 (14.3) | 12 (15.5) | 14 (12) | 0.358 |
| TC (mmol/L) § | 34.1 ± 18.4 | 37 ± 19.1 | 31.3 ± 17.5 | 0.146 |
| HDL-C (mmol/L) § | 12.8 ± 4.9 | 12.9 ± 5.0 | 12.8 ± 4.9 | 0.920 |
| Baseline Characteristics | Pearson’s Correlation (r) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median | Sural | Tibial | |||||||||
| NPA | PPA | CV | PV | NPA | PPA | CV | PV | CV | AA | KA | |
| Age (years) | −0.25 ** | −0.22 ** | −0.15 | −0.17 * | −0.11 | −0.14 | −0.06 | −0.11 | 0.06 | −0.25 ** | −0.21 * |
| DM duration (years) | −0.27 ** | −0.28 ** | −0.16 | −0.14 | −0.51 *** | −0.42 *** | −0.39 *** | −0.32 ** | −0.05 | −0.15 | −0.12 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | −0.17 | −0.17 * | −0.10 | −0.07 | −0.01 | −0.17 | 0 | −0.01 | 0.08 | −0.10 | −0.13 |
| HbA1c (%) | −0.26 ** | −0.29 *** | −0.27 ** | −0.28 ** | −0.23 * | −0.22 * | −0.33 *** | −0.33 *** | −0.47 *** | −0.14 | −0.24 ** |
| SBP (mmHg) | −0.12 | −0.11 | −0.08 | −0.10 | −0.03 | −0.06 | −0.01 | −0.04 | −0.14 | −0.28 *** | −0.20 * |
| DBP (mmHg) | 0.03 | −0.01 | 0.02 | 0.02 | −0.08 | −0.11 | −0.05 | −0.05 | −0.10 | −0.09 | −0.05 |
| TGFβ-1 (ng/mL) | −0.17 * | −0.18 * | −0.03 | −0.01 | −0.16 * | −0.18 * | −0.21 * | −0.14 | 0.02 | −0.11 | −0.11 |
| VEGF-A (pg/mL) | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.04 | −0.06 | −0.06 | −0.34 *** | −0.29 ** | −0.09 | 0.10 | 0.06 |
| Median Sensory Nerve | Sural Sensory Nerve | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tocovid (n = 68) † | Placebo (n = 65) † | Treatment Effect (95% CI) | p-Value ‡ | Tocovid (n = 55) † | Placebo (n = 45) † | Treatment Effect (95% CI) | p-Value ‡ | |
| NP Amplitude (µV) | ||||||||
| At baseline | 19.5 (14.0) | 17.5 (12.0) | 2.3 (−1.1, 5.7) | 0.200 | 9.7 (8.00) | 10.1 (4.9) | 0.20 (−1.80, 2.30) | 0.843 |
| 2-month changes | 1.25 ± 5.98 | 0.79 ± 4.87 | 0.45 (−1.42, 2.33) | 0.632 § | 0.2 (4.45) | −0.4 (1.9) | 0.60 (−0.70, 1.80) | 0.362 |
| 6-month changes | 0.8 (6.35) | 0.5 (6.20) | 0.5 (−1.1, 2.1) | 0.539 | 0.7 (4.35) | −1.2 (3.70) | 1.40 (−0.10, 2.70) | 0.075 |
| 12-month changes | 0.25 (5.72) | 0.6 (5.9) | −0.2 (−2.0, 1.7) | 0.843 | −0.6 (5.15) | −0.3 (4.50) | 0.50 (−1.60, 2.10) | 0.635 |
| PP Amplitude (µV) | ||||||||
| At baseline | 31.9 (22.7) | 27.3 (14.7) | 3.5 (−2.0, 8.8) | 0.213 | 6.6 (8.3) | 8.7 (7.8) | −1.40 (−3.50, 0.90) | 0.244 |
| 2-month changes | 3.15 (10.6) | 0.9 (6.9) | 2.0 (−0.8, 5.0) | 0.137 | 1.11 ± 2.48 | 0.43 ± 2.99 | 0.68 (−0.41, 1.76) | 0.218 § |
| 6-month changes | 3.45 (14.1) | 0.6 (7.20) | 2.1 (−1.1, 5.7) | 0.193 | 1.70 (5.13) | 0.40 (5.30) | 1.70 (0.10, 3.20) | 0.040 * |
| 12-month changes | 3.60 (15.4) | 2.60 (13.8) | 2.0 (−1.6, 6.2) | 0.320 | 2.10 (5.35) | 1.70 (4.56) | 1.00 (−0.74, 2.80) | 0.257 |
| Conduction Velocity (m/s) | ||||||||
| At baseline | 44.0 ± 6.79 | 43.2 ± 7.10 | 0.88 (−1.51, 3.26) | 0.469 § | 43.8 (7.8) | 43.1 (6.7) | 0 (−2.40, 2.60) | 0.906 |
| 2-month changes | 1.25 (2.85) | 0 (1.5) | 1.80 (1.10, 2.70) | <0.001 *** | 1.4 (1.60) | −0.6 (1.7) | 2.20 (1.60, 2.90) | <0.001 *** |
| 6-month changes | 1.10 (2.73) | −0.6 (2.6) | 1.60 (0.70, 2.40) | <0.001 *** | 1.2 (2.1) | −0.6 (1.5) | 2.10 (1.50, 2.90) | <0.001 *** |
| 12-month changes | 1.97 (4.28) | 0 (4.1) | 1.60 (0.50, 2.60) | 0.007 ** | 1.80 (2.05) | 0.6 (2.90) | 1.97 (1.10, 3.45) | 0.036 * |
| Peak Velocity (m/s) | ||||||||
| At baseline | 35.2 ± 4.80 | 34.7 ± 5.06 | 0.47 (−1.22, 2.16) | 0.582 § | 34.1 ± 4.32 | 34.4 ± 3.73 | −0.23 (−1.85, 1.40) | 0.783 § |
| 2-month changes | 1.03 ± 1.75 | −0.35 ± 1.92 | 1.38 (0.75, 2.01) | <0.001 ***,§ | 1.1 ± 1.57 | −0.54 ± 1.62 | 1.64 (1.00, 2.27) | <0.001 ***,§ |
| 6-month changes | 0.70 (2.62) | −0.5 (2.10) | 1.30 (0.70, 2.00) | <0.001 ** | 1.36 ± 1.97 | −0.04 ± 1.68 | 1.41 (0.67, 2.14) | <0.001 ***,§ |
| 12-month changes | 0.75 (3.90) | 0 (2.10) | 0.30 (−0.60, 1.10) | 0.484 | 2.5 (3.6) | 0.20 (3.1) | 2.10 (1.00, 3.20) | <0.001 *** |
| Tibial Motor Nerve | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tocovid (n = 76) † | Placebo (n = 73) † | Treatment Effect (95% CI) | p-Value ‡ | |
| Conduction Velocity (m/s) | ||||
| At baseline | 41.5 ± 5.54 | 39.9 ± 6.15 | 1.60 (−0.30, 3.49) | 0.097 § |
| 2-month changes | 0.6 (1.88) | −1 (3.2) | 1.80 (1.10, 2.60) | <0.001 *** |
| 6-month changes | 0.45 (2.38) | −0.6 (3.50) | 1.30 (0.60, 2.20) | <0.001 *** |
| 12-month changes | −0.5 (5.35) | −1.5 (4.70) | 1.20 (−9.71 × 10−6, 2.46) | 0.055 |
| Distal Amplitude at Ankle (mV) | ||||
| At baseline | 7.25 (5.75) | 7.6 (7.2) | 0.6 (−0.90, 2.10) | 0.387 |
| 2-month changes | 0.8 (1.85) | 0.6 (1.80) | 0.20 (−0.20, 0.70) | 0.295 |
| 6-month changes | 0.35 (2.62) | 0.6 (1.7) | −0.30 (−0.90, 0.30) | 0.359 |
| 12-month changes | 1.60 (3.25) | 0.5 (1.70) | 0.60 (−0.20, 1.34) | 0.122 |
| Proximal Amplitude at Knee (mV) | ||||
| At baseline | 5.20 (3.98) | 5.5 (5.90) | 0.40 (−0.70, 1.60) | 0.475 |
| 2-month changes | 0.60 (1.25) | 0.5 (1.40) | 0.10 (−0.30, 0.40) | 0.653 |
| 6-month changes | 0.5 (1.52) | 0.5 (1.5) | −0.10 (−0.50, 0.30) | 0.779 |
| 12-month changes | 0.3 (2) | 0.2 (1.6) | 0.19 (−0.34, 0.70) | 0.555 |
| Analytes | Tocovid (n = 42) | Placebo (n = 43) | Mean/Median Difference (95% CI) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HbA1c (%) ‡ | 7.34 (1.20) | 8 (1.91) | −0.50 (−1.00, 4.47 × 10−5) | 0.058 |
| SBP (mmHg) † | 135.97 ± 11.91 | 132.70 ± 13.14 | 3.27 (−2.15, 8.68) | 0.233 |
| DBP (mmHg) † | 74.39 ± 8.10 | 74.93 ± 7.73 | −0.54 (−3.96, 2.87) | 0.752 |
| Serum Biomarkers | ||||
| TGFβ-1 (ng/mL) ‡ | 22.0 (11.5) | 17.8 (13.3) | 2.81 (−0.99, 6.36) | 0.115 |
| VEGF-A (pg/mL) ‡ | 745.1 (505.3) | 726.1 (715.9) | 10.4 (−177.2, 207.9) | 0.916 |
| Safety Tests | ||||
| eGFR † | 65.9 ± 18.7 | 64.0 ± 21.2 | 1.89 (−6.74, 10.52) | 0.664 |
| Serum Creatinine ‡ | 95.9 (38.7) | 100.8 (33.7) | −2.85 (−15.0, 9.73) | 0.613 |
| Urea ‡ | 6.18 (2.98) | 6.35 (3.04) | −0.50 (−1.34, 0.39) | 0.287 |
| Tocovid (n = 43) | Placebo (n = 45) | p-Value † | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neuropathic pain | 8 | 7 | 0.923 |
| Non-neuropathic pain | 35 | 38 |
| Component | Tocovid (n = 8) | Placebo (n = 7) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD/ Median (IQR) | p-Value (within Group) † | Mean ± SD/ Median (IQR) | p-Value (within Group) † | p-Value (between Group) ‡ | |
| Burning pain | |||||
| At baseline | 20.5 (65.0) | 40 (55) | 0.810 | ||
| At 6 months | 18.8 (35.0) | 0.361 | 40 (45) | 0.789 | |
| At 12 months | 0 (0) | 0.058 | 0 (0) | 0.100 | |
| 6-month changes | −7.93 ± 21.74 | −3.57 ± 34.0 | 0.769 ¶ | ||
| 12-month changes | −19.5 ± 65.0 | −30 ± 45 | 0.765 ¶ | ||
| Overly sensitive to touch | |||||
| At baseline | 12.5 (48.5) | 0 (75) | 0.660 | ||
| At 6 months | 7 (21.25) | 0.174 | 30 (60) | 1.00 | |
| At 12 months | 0 (0) | 0.100 | 0 (25) | 0.462 | |
| 6-month changes | 0 (30) | 0 (0) | 0.334 | ||
| 12-month changes | −12.5 (41.0) | 0 (50) | 0.951 | ||
| Shooting pain | |||||
| At baseline | 40 ± 27.3/40 (35) | 0 (40) | 0.229 | ||
| At 6 months | 26.4 ± 24.7 | 0.199 § | 0 (0) | 1.00 | |
| At 12 months | 14 (50) | 0.107 | 0 (30) | 0.850 | |
| 6-month changes | 0 (41.5) | 0 (0) | 0.948 | ||
| 12-month changes | −14.0 ± 21.8 | −2.86 ± 61.6 | 0.663 ¶ | ||
| Numbness | |||||
| At baseline | 53.5 ± 22.1 | 52.9 ± 30.4/50 (20) | 0.963 ¶ | ||
| At 6 months | 39.5 ± 29.4 | 0.124 § | 48.6 ± 25.4 | 0.200 § | |
| At 12 months | 29.8 ± 29.3 | 0.034 *,§ | 60.0 (12.5) | 0.892 | |
| 6-month changes | −4 (15) | 0 (5) | 0.433 | ||
| 12-month changes | −23.8 ± 25.6 | −2.14 ± 17.3 | 0.082 ¶ | ||
| Electric pain | |||||
| At baseline | 9.0 (22.5) | 0 (0) | 0.168 | ||
| At 6 months | 3.0 (22.5) | 0.371 | 0 (0) | NA | |
| At 12 months | 0.0 (24.5) | 1.00 | 0 (0) | 1.00 | |
| 6-month changes | 0 (3) | 0 (0) | 0.204 | ||
| 12-month changes | 0 (19) | 5.7 (25.1) | 0.660 | ||
| Tingling pain | |||||
| At baseline | 32.1 ± 14.1/30 (5.25) | 41.4 ± 15.7/50 (20) | 0.249 ¶ | ||
| At 6 months | 28.0 ± 17.8 | 0.298 § | 44.3 ± 12.7 | 0.569 § | |
| At 12 months | 0 (23.5) | 0.313 | 0 (40) | 0.289 | |
| 6-month changes | 0 (8.5) | 0 (0) | 0.433 | ||
| 12-month changes | −14.1 ± 34.7 | −20.0 ± 35.6 | 0.749 ¶ | ||
| Squeezing pain | |||||
| At baseline | 0 (6.25) | 0 (25) | 0.710 | ||
| At 6 months | 0 (10) | 0.586 | 0 (15) | 1.00 | |
| At 12 months | 0 (0) | 0.371 | 0 (0) | 0.346 | |
| 6-month changes | 0.0 (2.5) | 0 (0) | 1.00 | ||
| 12-month changes | 0.00 (6.25) | 0 (25) | 0.71 | ||
| Freezing pain | |||||
| At baseline | 24.6 ± 24.8/20 (21) | 0 (30) | |||
| At 6 months | 17.4 ± 19.6 | 0.353 § | 0 (30) | NA | |
| At 12 months | 0 ± 0 | 0.026 *,§ | 0 (0) | 0.181 | |
| 6-month changes | 0.00 (3.75) | 0 (0) | 0.620 | ||
| 12-month changes | −20 (21) | 0 (30) | 0.546 | ||
| How unpleasant is your usual pain? | |||||
| At baseline | 38.8 ± 20.8 | 57.1 ± 30.9 | 0.195 | ||
| At 6 months | 28.1 ± 19.6 | 0.164 § | 52.9 ± 28.1 | 0.200 § | |
| At 12 months | 31.5 ± 29.6 | 0.396 § | 37.9 ± 28.0 | 0.144 § | |
| 6-month changes | 0.0 (12.5) | 0 (5) | 0.679 | ||
| 12-month changes | −9 (20) | −5 (25) | 0.954 | ||
| How overwhelming is your usual pain? | |||||
| At baseline | 43.1 ± 28.1 | 30.0 ± 31.1/20 (45) | 0.406 | ||
| At 6 months | 36.1 ± 26.2 | 0.491 § | 27.1 ± 26.3 | 0.356 § | |
| At 12 months | 29.3 ± 29.1 | 0.076 § | 0 (55) | 0.490 | |
| 6-month changes | 0.0 (2.5) | 0 (0) | 1.00 | ||
| 12-month changes | −13.9 ± 18.8 | −4.29 ± 12.7 | 0.276 ¶ | ||
| Increased pain due to touch | |||||
| At baseline | 2.5 (15.0) | 0 (0) | 0.045 * | ||
| At 6 months | 0 (10) | 0.423 | 0 (0) | NA | |
| At 12 months | 0 (0) | 0.201 | 0 (0) | 1.00 | |
| 6-month changes | 0.0 (2.5) | 0 (0) | 0.620 | ||
| 12-month changes | 0 (15) | 0 (0) | 0.191 | ||
| Increased pain due to weather changes | |||||
| At baseline | 29.4 ± 26.2/25 (45) | 0 (0) | 0.044 * | ||
| At 6 months | 14.5 ± 10.5 | 0.114 § | 0 (0) | 1.00 | |
| At 12 months | 22.1 ± 25.6 | 0.577 § | 0 (0) | 1.00 | |
| 6-month changes | 0.0 (32.5) | 0 (0) | 0.535 | ||
| 12-month changes | 0 (45) | 0 (0) | 0.951 | ||
| Baseline Characteristics | Tocovid (n) | Placebo (n) | 2-Month Changes | 6-Month Changes | 12-Month Changes | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tocovid | Placebo | p-Value † | Tocovid | Placebo | p-Value † | Tocovid | Placebo | p-Value † | ||||
| Low- baseline CV | Median CV < 43.61 m/s a | |||||||||||
| CV | 36 | 32 | 1.60 (2.25) | 0.20 (2.88) | 0.008 ** | 1.75 (2.13) | 0.20 (3.25) | 0.096 | 2.95 (4.42) | 2.55 (3.03) | 0.370 | |
| PV | 1.07 ± 1.47 | 0.32 ± 1.84 | 0.067 ‡ | 0.95 (2.20) | 0 (2.93) | 0.037 * | 0.67 ± 2.24 | 1.37 ± 2.23 | 0.203 ‡ | |||
| Sural CV < 43.16 m/s a | ||||||||||||
| NPA | 26 | 25 | 0.45 ± 2.02 | −0.62 ± 2.66 | 0.111 ‡ | 0.36 ± 2.90 | −1.58 ± 3.13 | 0.026 *,‡ | 1.82 ± 3.55 | −0.99 ± 3.83 | 0.009 **,‡ | |
| PPA | 0.79 ± 2.12 | 0.19 ± 2.65 | 0.380 ‡ | 1.70 (4.85) | −0.5 (4.5) | 0.070 | 3.74 (5.12) | 1.0 (5.5) | 0.014 * | |||
| CV | 1.85 (1.28) | 0.0 (1.3) | <0.001 *** | 1.7 (2.3) | 0 (0.7) | <0.001 *** | 2.95 ± 3.23 | 1.59 ± 2.55 | 0.102 ‡ | |||
| PV | 1.35 (1.48) | 0.0 (1.5) | <0.001 *** | 2.29 ± 1.79 | 0.43 ± 1.73 | <0.001 ***,‡ | 3.20 (6.84) | 0.4 (3.4) | <0.001 *** | |||
| Tibial CV < 40.71 m/s a | ||||||||||||
| CV | 38 | 40 | 1.05 (2.50) | −0.3 (1.9) | <0.001 *** | 0.85 (3.20) | 0 (1.83) | 0.015 * | 1.78 ± 4.27 | 0.39 ± 4.21 | 0.152 ‡ | |
| AA | 0.80 (1.88) | 0.40 (1.25) | 0.276 | 0.00 (2.75) | 0.55 (1.48) | 0.291 | 1.95 (3.18) | 0.25 (1.37) | 0.016 * | |||
| High- baseline CV | Median CV ≥ 43.61 m/s a | |||||||||||
| CV | 32 | 33 | 0.95 (3.00) | −0.7 (3.10) | <0.001 *** | 0.35 (2.95) | −1.2 (2.3) | 0.008 ** | 0.9 (3.30) | −0.8 (2.3) | 0.005 ** | |
| PV | 0.80 (2.95) | −0.5 (1.4) | <0.001 *** | 0.26 ± 2.30 | −1.22 ± 1.67 | 0.004 **,‡ | 0.55 (4.20) | −0.5 (2.3) | 0.203 | |||
| Sural CV ≥ 43.16 m/s a | ||||||||||||
| NPA | 29 | 20 | 0.1 (5.7) | −0.25 (1.95) | 0.684 | 0.3 (4.8) | 0.00 (5.65) | 0.927 | −3.12 ± 6.09 | 0.18 ± 4.83 | 0.049 *,‡ | |
| CV | 1.23 ± 1.70 | −1.80 ± 1.47 | <0.001 ***,‡ | 0.91 ± 2.13 | −1.50 ± 1.53 | <0.001 ***,‡ | 1.0 (3.3) | −0.65 (2.63) | 0.065 | |||
| PV | 0.79 ± 1.59 | −1.36 ± 1.56 | <0.001 ***,‡ | 0.53 ± 1.76 | −0.64 ± 1.44 | 0.019 *,‡ | 2.12 ± 2.70 | 0.30 ± 2.64 | 0.023 *,‡ | |||
| Tibial CV ≥ 40.71 m/s a | ||||||||||||
| CV | 38 | 33 | 0.40 (1.45) | −2.5 (3.0) | <0.001 *** | −0.35 ± 2.31 | −2.21 ± 2.62 | 0.002 **,‡ | −2.00 (3.18) | −3.30 (4.18) | 0.032 * | |
| Baseline Characteristics | Total (N) | Tocovid (n) | Placebo (n) | 2-Month Changes | 6-Month Changes | 12-Month Changes | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tocovid | Placebo | p-Value † | Tocovid | Placebo | p-Value † | Tocovid | Placebo | p-Value † | ||||
| DM duration a | ||||||||||||
| Median | ||||||||||||
| <15 years | 66 | 37 | 29 | 1.87 ± 2.11 | 0.06 ± 2.08 | <0.001 ***‡ | 1.1 (3.7) | −0.6 (0.9) | 0.058 | 2.6 (4.3) | 0.0 (3.6) | 0.014 * |
| ≥15 years | 67 | 21 | 36 | 1.52 ± 2.05 | −0.79 ± 2.94 | <0.001 ***‡ | 1.27 ± 2.22 | −0.58 ± 2.85 | 0.005 **‡ | 1.2 (3.5) | 0.3 (4.8) | 0.129 |
| Sural | ||||||||||||
| <14 years | 47 | 23 | 24 | 1.20 (1.25) | −0.75 (2.10) | <0.001 *** | 1.18 ± 2.21 | −1.05 ± 1.60 | <0.001 ***‡ | 1.0 (3.5) | 0 (3.18) | 0.394 |
| ≥14 years | 53 | 32 | 21 | 1.55 ± 1.65 | −0.17 ± 1.89 | <0.001 ***‡ | 1.45 (2.40) | −0.6 (1.2) | <0.001 *** | 2.25 (1.83) | 0.7 (3.5) | 0.107 |
| Tibial | ||||||||||||
| <14 years | 67 | 33 | 34 | 1.0 (2.4) | −0.3 (3.38) | <0.001 *** | 1.1 (2.8) | −0.60 (2.95) | 0.004 ** | 0.76 (5.10) | −0.86 (4.23) | 0.153 |
| ≥14 years | 82 | 43 | 39 | 0.40 (1.65) | −1.3 (3.0) | <0.001 *** | 0.3 (2.0) | −0.70 (3.75) | 0.032 * | −1.2 (4.75) | −2.4 (5.4) | 0.118 |
| HbA1c a | ||||||||||||
| Median | ||||||||||||
| <7.55% | 65 | 39 | 26 | 0.90 (2.25) | 0 (2.03) | 0.009 ** | 0.90 (2.55) | −0.30 (2.05) | 0.030 * | 2.15 ± 3.20 | 0.75 ± 4.45 | 0.145 ‡ |
| ≥7.55% | 68 | 29 | 39 | 1.9 (2.5) | 0 (1.8) | <0.001 *** | 1.3 (3.3) | −0.60 (2.95) | <0.001 *** | 2.6 (3.6) | 0 (3.6) | 0.016 * |
| Sural | ||||||||||||
| <7.2% | 48 | 27 | 21 | 1.63 ± 1.86 | −0.95 ± 1.21 | <0.001 ***‡ | 1.87 ± 2.34 | −0.86 ± 1.33 | <0.001 ***‡ | 1.69 ± 2.07 | −0.13 ± 2.76 | 0.012 *,‡ |
| ≥7.2% | 52 | 28 | 24 | 1.30 (1.55) | −0.6 (2.6) | <0.001 *** | 1.30 (1.56) | −0.60 (1.23) | <0.001 *** | 1.91 (3.72) | 1.05 (3.83) | 0.497 |
| Tibial | ||||||||||||
| <7.55% | 74 | 43 | 31 | 0.4 (2.0) | −0.80 (3.25) | 0.007 ** | 0.3 (2.1) | −0.9 (4.7) | 0.057 | −0.34 ± 2.92 | −1.19 ± 3.71 | 0.274 |
| ≥7.55% | 75 | 33 | 42 | 0.8 (2.4) | −1.15 (3.18) | <0.001 *** | 1.0 (3.5) | −0.30 (2.88) | 0.003 ** | 0.20 (6.98) | −1.60 (4.58) | 0.147 |
| M ± SD/ MD (IQR) | Difference M/MD (95% CI) † | p-Value (within Group) † | M ± SD/ MD (IQR) | Difference M/MD (95% CI) † | p-Value (within Groups) † | p-Value (between Groups) ‡ | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median Sensory Nerve | Tocovid (n = 54) | Placebo (n = 57) | |||||
| NPA (µV) | |||||||
| At baseline (B) | 18.2 (14.4) | 17.2 (10.5) | 0.368 ¶ | ||||
| WO—B | 0.45 (5.48) | 0.85 (−0.40, 1.90) § | 0.188 § | 0.2 (4.20) | 0.10 (−0.90, 1.00) § | 0.830 § | 0.362 ¶ |
| WO—12M | −0.25 (4.68) | 0.16 (−0.95, 1.45) § | 0.750 § | −0.4 (6) | −0.50 (−2.05, 0.95) § | 0.451 § | 0.433 ¶ |
| PPA (µV) | |||||||
| At baseline (B) | 31.8 (20.8) | 27.3 (14.8) | 0.320 ¶ | ||||
| WO—B | 2.1 (11.2) | 3.21 (0.48, 5.93) | 0.022 * | 1 (6.9) | 0.65 (−1.20, 2.25) § | 0.533 § | 0.256 ¶ |
| WO—12M | 0.20 (8.38) | −0.49 (−2.64, 1.66) | 0.650 | −0.1 (8.44) | −0.20 (−2.40, 2.15) § | 0.874 § | 0.894 ¶ |
| CV (m/s) | |||||||
| At baseline (B) | 43.6 ± 6.96 | 43.4 ± 7.22 | 0.919 | ||||
| WO—B | 1.9 (3.07) | 1.75 (0.70, 2.55) § | 0.003**,§ | 0.80 (3.3) | 0.79 (0.07, 1.52) | 0.033 * | 0.141 ¶ |
| WO—12M | −0.85 (2.93) | −0.80 (−1.45, 4.78 × 10−5) § | 0.051 § | 0.6 (1.40) | 0.80 (0.05, 1.30) § | 0.034 *,§ | 0.004 **,¶ |
| PV (m/s) | |||||||
| At baseline (B) | 34.9 ± 4.97 | 34.9 ± 5.05 | 0.942 | ||||
| WO—B | 1.15 (3.47) | 0.90 (1.88 × 10−5, 1.65) § | 0.050 § | 0.5 (2.3) | 0.35 (−0.14, 0.85) | 0.161 | 0.198 ¶ |
| WO—12M | −0.35 (2.35) | −0.25 (−0.75, 0.25) § | 0.308 § | 0 (1.80) | 0.25 (−0.20, 0.70) § | 0.259 § | 0.128 ¶ |
| Sural Sensory Nerve | Tocovid (n = 42) | Placebo (n = 41) | |||||
| NPA (µV) | |||||||
| At baseline (B) | 9.35 (7.55) | 9.8 (5.4) | 0.827 ¶ | ||||
| WO—B | −1.62 ± 4.22 | −1.55 (−2.75, −0.15) § | 0.028 *,§ | −0.66 ± 3.10 | −1.00 (−2.00, 0.15) § | 0.076 § | 0.256 |
| WO—12M | −0.8 (4.37) | −1.10 (−2.60, 0.20) § | 0.088 § | −0.3 (3.8) | −0.25 (−1.25, 0.90) § | 0.669 § | 0.310 ¶ |
| PPA (µV) | |||||||
| At baseline (B) | 6.15 (7.3) | 7.4 (7.9) | 0.310 ¶ | ||||
| WO—B | 0.788 ± 3.41 | 0.75 (−0.45, 1.85) § | 0.232 § | 0.77 ± 4.21 | 0.70 (−0.65, 2.15) § | 0.279 § | 0.986 |
| WO—12M | −1.45 (3.88) | −1.65 (−2.82, −0.50) § | 0.007 **,§ | 0.2 (3.9) | 0.15 (−0.95, 1.50) § | 0.777 § | 0.027 *,¶ |
| CV (m/s) | |||||||
| At baseline (B) | 43.3 (8.42) | 41.8 (6.7) | 0.626 ¶ | ||||
| WO—B | 1.45 (3.38) | 1.15 (0.20, 2.10) § | 0.023 *,§ | 1.30 (2.8) | 1.26 (0.27, 2.25) | 0.014 * | 0.535 ¶ |
| WO—12M | −0.50 (2.93) | −1.70 (−2.50, −0.75) § | <0.001 ***,§ | 0.90 (2.20) | 0.81 (−0.27, 1.89) | 0.136 | <0.001 ***,¶ |
| PV (m/s) | |||||||
| At baseline (B) | 33.8 ± 4.39 | 34.2 ± 3.84 | 0.630 | ||||
| WO—B | 0.95 (3.12) | 1.02 (0.23, 1.82) | 0.013 * | 1.1 (1.6) | 1.42 (0.58, 2.25) | 0.001 ** | 0.802 ¶ |
| WO—12M | −1.10 (2.67) | −1.40 (−2.25, −0.65) § | <0.001 ***,§ | 0.70 (2.2) | 0.78 (0.05, 1.52) | 0.038 * | <0.001 ***,¶ |
| Tibial Motor Nerve | Tocovid (n = 59) | Placebo (n = 69) | |||||
| CV (m/s) | |||||||
| At baseline (B) | 41.7 ± 5.63 | 39.8 ± 6.32 | 0.087 | ||||
| WO—B | −1.34 ± 3.52 | −1.34 (−2.26, −0.43) | 0.005 ** | −1.53 ± 3.20 | −1.53 (−2.30, −0.76) | <0.001 *** | 0.752 |
| WO—12M | −0.5 (2.65) | −1.32 (−2.29, −0.36) | 0.008 ** | −0.3 (2.9) | −0.40 (−1.10, 0.30) § | 0.275 § | 0.368 ¶ |
| AA (mV) | |||||||
| At baseline (B) | 6.9 (5.15) | 7.2 (7.30) | 0.340 ¶ | ||||
| WO—B | 0.10 (2.25) | 0.25 (−0.30, 0.80) § | 0.384 § | 0.30 (2.10) | 0.50 (0.10, 0.95) § | 0.025 *,§ | 0.384 ¶ |
| WO—12M | −0.4 (2.1) | −0.55 (−1.05, −0.05) § | 0.028 *,§ | −0.1 (1.6) | −0.10 (−0.50, 0.25) § | 0.504 § | 0.181 ¶ |
| KA (mV) | |||||||
| At baseline (B) | 5.3 (3.9) | 5.2 (5.6) | 0.236 ¶ | ||||
| WO—B | 0.10 (1.30) | 0.10 (−0.25, 0.50) § | 0.512 § | 0.30 (1.1) | 0.45 (0.15, 0.75) § | 0.001 **,§ | 0.125 ¶ |
| WO—12M | −0.2 (1.60) | −0.30 (−0.65, 0.02) § | 0.071 § | 0 (1.20) | −0.05 (−0.35, 0.20) § | 0.700 § | 0.248 ¶ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chuar, P.F.; Ng, Y.T.; Phang, S.C.W.; Koay, Y.Y.; Ho, J.-I.; Ho, L.S.; Botross Henien, N.P.; Ahmad, B.; Abdul Kadir, K. Tocotrienol-Rich Vitamin E (Tocovid) Improved Nerve Conduction Velocity in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients in a Phase II Double-Blind, Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3770. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13113770
Chuar PF, Ng YT, Phang SCW, Koay YY, Ho J-I, Ho LS, Botross Henien NP, Ahmad B, Abdul Kadir K. Tocotrienol-Rich Vitamin E (Tocovid) Improved Nerve Conduction Velocity in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients in a Phase II Double-Blind, Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Nutrients. 2021; 13(11):3770. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13113770
Chicago/Turabian StyleChuar, Pei Fen, Yeek Tat Ng, Sonia Chew Wen Phang, Yan Yi Koay, J-Ian Ho, Loon Shin Ho, Nevein Philip Botross Henien, Badariah Ahmad, and Khalid Abdul Kadir. 2021. "Tocotrienol-Rich Vitamin E (Tocovid) Improved Nerve Conduction Velocity in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients in a Phase II Double-Blind, Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial" Nutrients 13, no. 11: 3770. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13113770
APA StyleChuar, P. F., Ng, Y. T., Phang, S. C. W., Koay, Y. Y., Ho, J.-I., Ho, L. S., Botross Henien, N. P., Ahmad, B., & Abdul Kadir, K. (2021). Tocotrienol-Rich Vitamin E (Tocovid) Improved Nerve Conduction Velocity in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients in a Phase II Double-Blind, Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Nutrients, 13(11), 3770. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13113770






