Telehealth: A Useful Tool for the Management of Nutrition and Exercise Programs in Pediatric Obesity in the COVID-19 Era
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
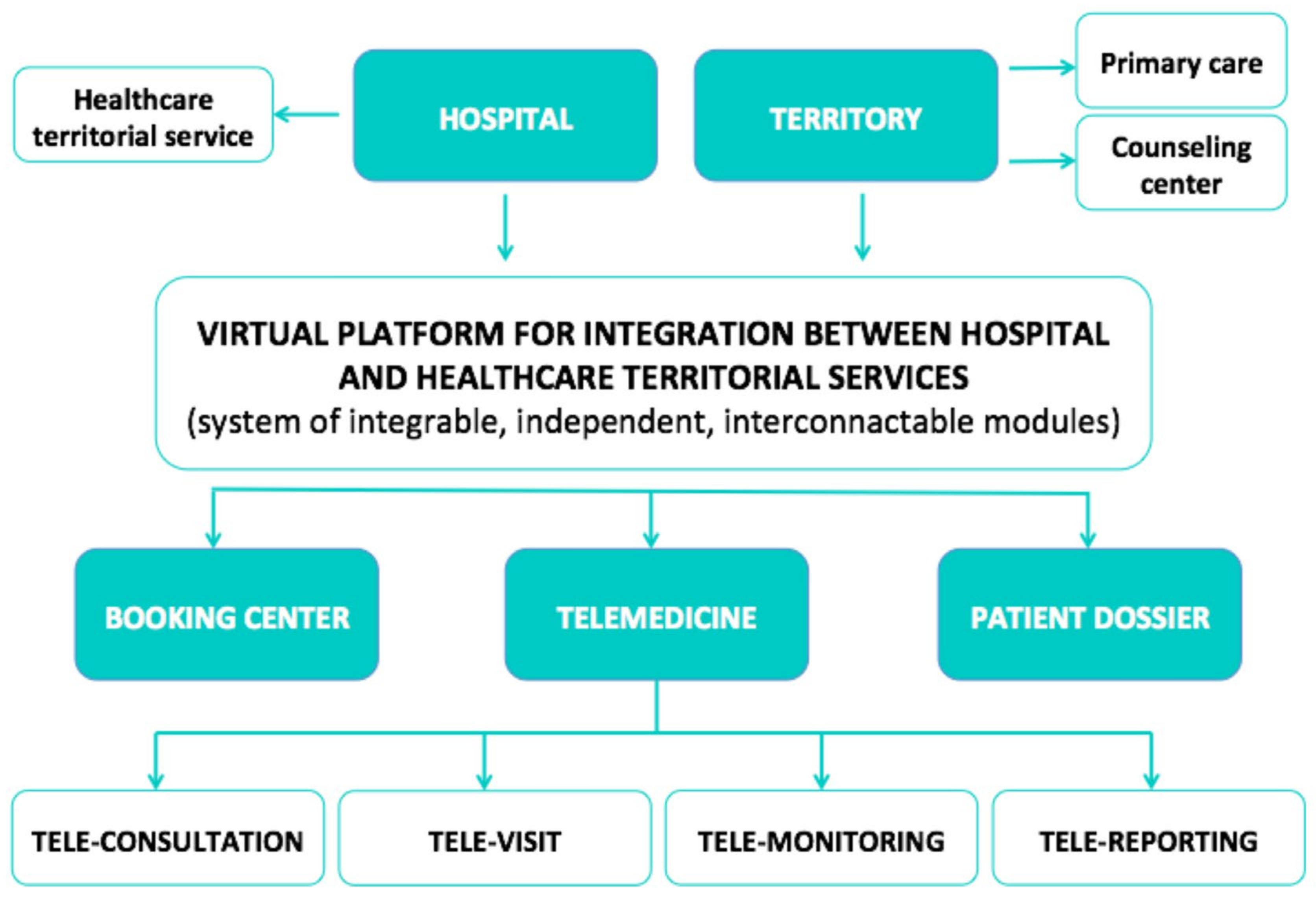
3. Telehealth and the COVID-19 Era
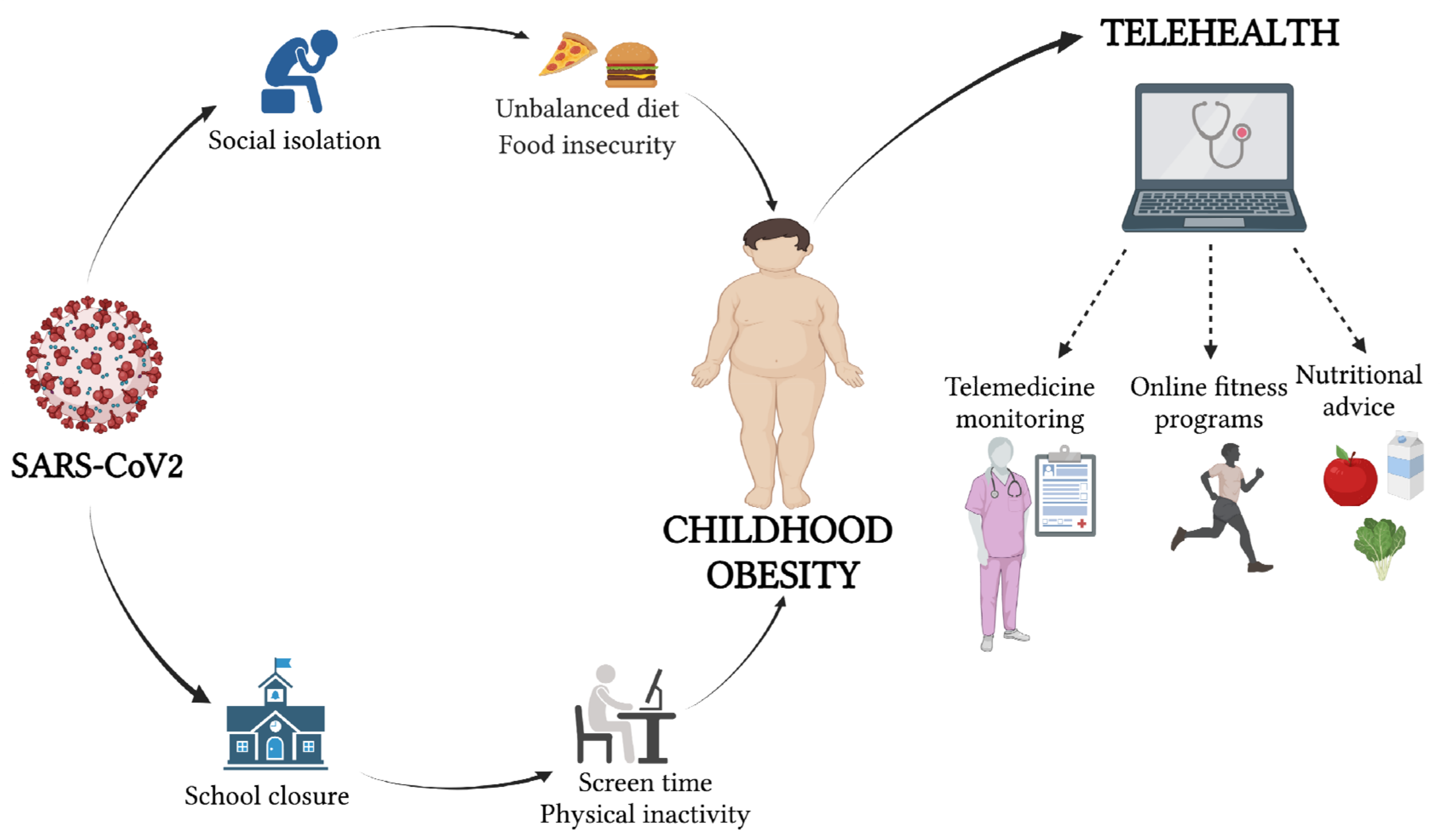
4. Pediatric Obesity during the COVID-19 Era
5. Tele-Nutrition in Pediatric Obesity
5.1. Before the COVID-19 Pandemic
5.2. During the COVID-19 Pandemic
6. Tele-Exercise in Pediatric Obesity
6.1. Before the COVID-19 Pandemic
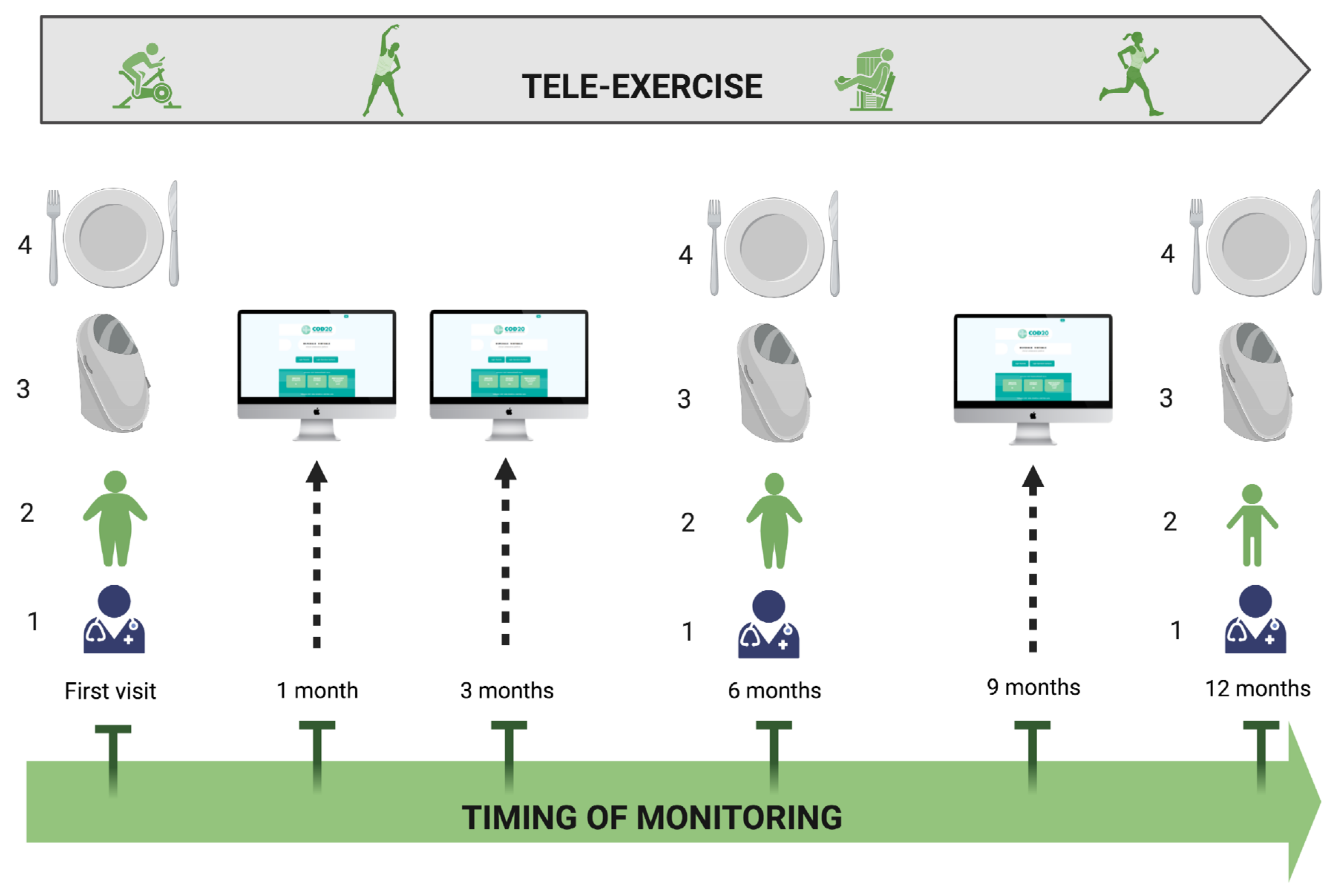
6.2. During the COVID-19 Pandemic
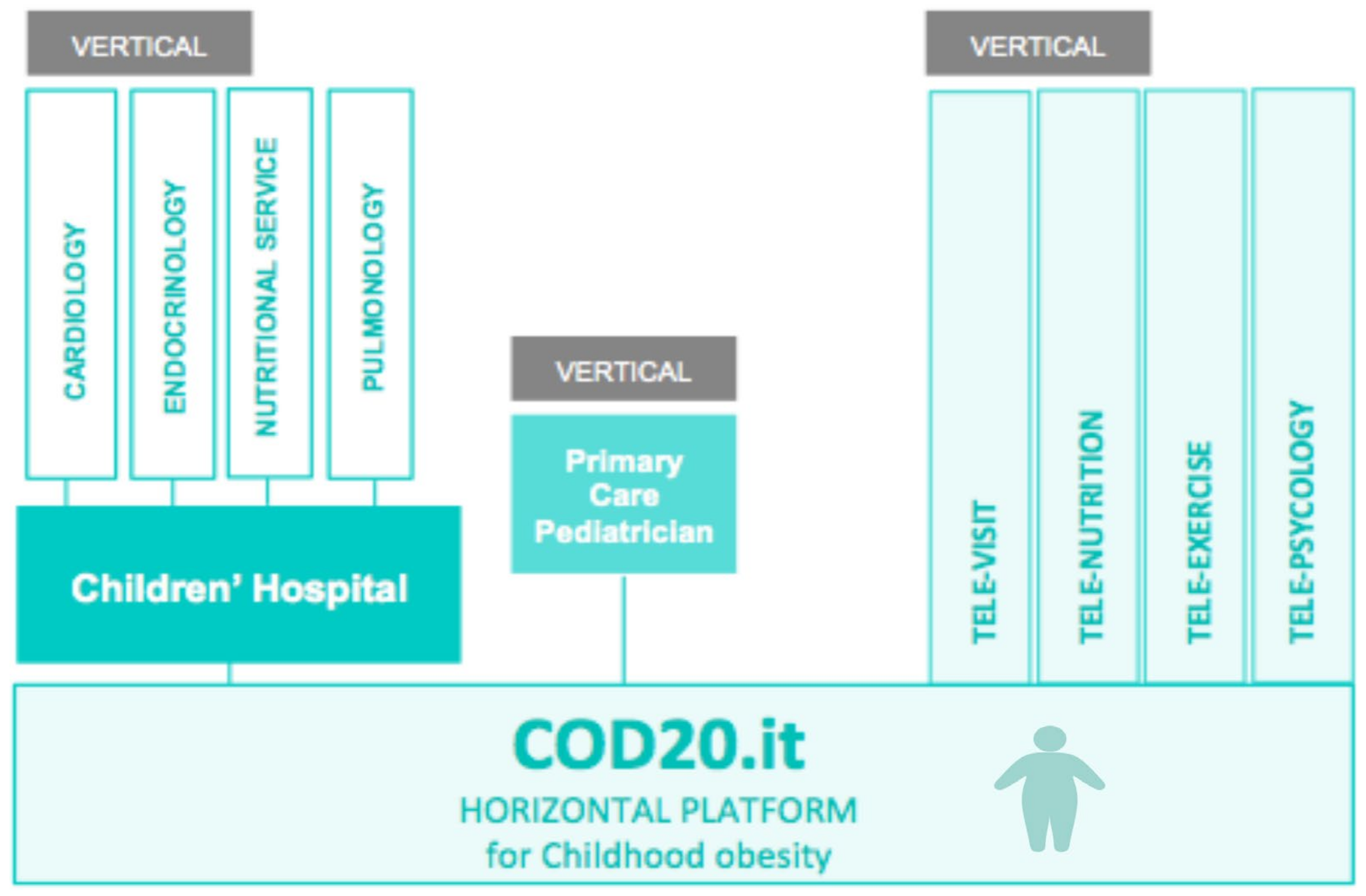
7. Future Prospective after the COVID-19 Pandemic
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gontariuk, M.; Krafft, T.; Rehbock, C.; Townend, D.; Van der Auwermeulen, L.; Pilot, E. The European Union and Public Health Emergencies: Expert Opinions on the Management of the First Wave of the COVID-19 Pandemic and Suggestions for Future Emergencies. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 698995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tornaghi, M.; Lovecchio, N.; Vandoni, M.; Chirico, A.; Codella, R. Physical Activity Levels across COVID-19 Outbreak in Youngsters of Northwestern Lombardy. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fitness 2021, 61, 971–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Renzo, L.; Gualtieri, P.; Pivari, F.; Soldati, L.; Attinà, A.; Cinelli, G.; Leggeri, C.; Caparello, G.; Barrea, L.; Scerbo, F.; et al. Eating Habits and Lifestyle Changes during COVID-19 Lockdown: An Italian Survey. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vancini, R.L.; Andrade, M.S.; Viana, R.B.; Nikolaidis, P.T.; Knechtle, B.; Campanharo, C.R.V.; de Almeida, A.A.; Gentil, P.; de Lira, C.A.B. Physical Exercise and COVID-19 Pandemic in PubMed: Two Months of Dynamics and One Year of Original Scientific Production. Sports Med. Health Sci. 2021, 3, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szcześniak, D.; Gładka, A.; Misiak, B.; Cyran, A.; Rymaszewska, J. The SARS-CoV-2 and Mental Health: From Biological Mechanisms to Social Consequences. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 104, 110046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bull, F.C.; Al-Ansari, S.S.; Biddle, S.; Borodulin, K.; Buman, M.P.; Cardon, G.; Carty, C.; Chaput, J.-P.; Chastin, S.; Chou, R.; et al. World Health Organization 2020 Guidelines on Physical Activity and Sedentary Behaviour. Br. J. Sports Med. 2020, 54, 1451–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Global Observatory for eHealth Telemedicine: Opportunities and Developments in Member States: Report on the Second Global Survey on EHealth. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/44497 (accessed on 16 October 2021).
- Staiano, A.E.; Beyl, R.A.; Guan, W.; Hendrick, C.A.; Hsia, D.S.; Newton, R.L. Home-Based Exergaming among Children with Overweight and Obesity: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Pediatr Obes. 2018, 13, 724–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Infection Prevention and Control during Health Care When Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Is Suspected or Confirmed. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-2019-nCoV-IPC-2021.1 (accessed on 16 October 2021).
- WHO. WHO/Europe Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Outbreak—WHO Announces COVID-19 Outbreak a Pandemic. Available online: https://www.euro.who.int/en/health-topics/health-emergencies/coronavirus-covid-19 (accessed on 16 October 2021).
- WHO Responding to Community Spread of COVID-19: Interim Guidance. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/331421 (accessed on 16 October 2021).
- Zhu, N.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B.; Shi, W.; Lu, R.; et al. A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; McGoogan, J.M. Characteristics of and Important Lessons From the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Outbreak in China: Summary of a Report of 72 314 Cases From the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA 2020, 323, 1239–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.T.; Leung, K.; Leung, G.M. Nowcasting and Forecasting the Potential Domestic and International Spread of the 2019-NCoV Outbreak Originating in Wuhan, China: A Modelling Study. Lancet 2020, 395, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johns Hopkins Coronavirus Resource Center COVID-19 Dashboard. Available online: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html (accessed on 16 October 2021).
- Guo, G.; Ye, L.; Pan, K.; Chen, Y.; Xing, D.; Yan, K.; Chen, Z.; Ding, N.; Li, W.; Huang, H.; et al. New Insights of Emerging SARS-CoV-2: Epidemiology, Etiology, Clinical Features, Clinical Treatment, and Prevention. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, S.M.; Radovic, A. Digital Approaches to Remote Pediatric Health Care Delivery During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Existing Evidence and a Call for Further Research. JMIR Pediatr. Parent 2020, 3, e20049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, S.M.; Thompson, A.A.; Liem, R.I. Technology Access and Smartphone App Preferences for Medication Adherence in Adolescents and Young Adults With Sickle Cell Disease. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2016, 63, 848–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.-T.; Chen, L.; Yue, W.-W.; Xu, H.-X. Digital Technology-Based Telemedicine for the COVID-19 Pandemic. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 646506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, D.U.; Belcher, H.M.E. COVID-19 Pandemic Health Disparities and Pediatric Health Care-The Promise of Telehealth. JAMA Pediatr. 2021, 175, 345–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lurie, N.; Carr, B.G. The Role of Telehealth in the Medical Response to Disasters. JAMA Intern. Med. 2018, 178, 745–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollander, J.E.; Carr, B.G. Virtually Perfect? Telemedicine for Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1679–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, A.U.; Randolph, F.T.; Chang, A.M.; Slovis, B.H.; Rising, K.L.; Sabonjian, M.; Sites, F.D.; Hollander, J.E. Impact of Emergency Department Tele-Intake on Left Without Being Seen and Throughput Metrics. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2020, 27, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portnoy, J.; Waller, M.; Elliott, T. Telemedicine in the Era of COVID-19. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2020, 8, 1489–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuccotti, G.V.; Bertoli, S.; Foppiani, A.; Verduci, E.; Battezzati, A. COD19 and COD20: An Italian Experience of Active Home Surveillance in COVID-19 Patients. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NEJM Catalyst What Is Telehealth? Available online: https://catalyst.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/CAT.18.0268 (accessed on 16 October 2021).
- Kichloo, A.; Albosta, M.; Dettloff, K.; Wani, F.; El-Amir, Z.; Singh, J.; Aljadah, M.; Chakinala, R.C.; Kanugula, A.K.; Solanki, S.; et al. Telemedicine, the Current COVID-19 Pandemic and the Future: A Narrative Review and Perspectives Moving Forward in the USA. Fam. Med. Community Health 2020, 8, e000530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waller, M.; Stotler, C. Telemedicine: A Primer. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2018, 18, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medicaid.gov Telemedicine. Available online: https://www.medicaid.gov/medicaid/benefits/telemedicine/index.html (accessed on 16 October 2021).
- Smith, A.C.; Thomas, E.; Snoswell, C.L.; Haydon, H.; Mehrotra, A.; Clemensen, J.; Caffery, L.J. Telehealth for Global Emergencies: Implications for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). J. Telemed Telecare 2020, 26, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcin, J.P.; Shaikh, U.; Steinhorn, R.H. Addressing Health Disparities in Rural Communities Using Telehealth. Pediatr. Res. 2016, 79, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katzow, M.W.; Steinway, C.; Jan, S. Telemedicine and Health Disparities During COVID-19. Pediatrics 2020, 146, e20201586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Pazi, H.; Browne, P.; Chan, P.; Cubo, E.; Guttman, M.; Hassan, A.; Hatcher-Martin, J.; Mari, Z.; Moukheiber, E.; Okubadejo, N.U.; et al. The Promise of Telemedicine for Movement Disorders: An Interdisciplinary Approach. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2018, 18, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brophy, P.D. Overview on the Challenges and Benefits of Using Telehealth Tools in a Pediatric Population. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2017, 24, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, B.L.; Hall, R.W. SECTION ON TELEHEALTH CARE Telemedicine: Pediatric Applications. Pediatrics 2015, 136, e293–e308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Combi, C.; Pozzani, G.; Pozzi, G. Telemedicine for Developing Countries. A Survey and Some Design Issues. Appl. Clin. Inform. 2016, 7, 1025–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.-T.; Li, J.-M.; Zhu, C.-R.; Hong, Z.; An, D.-M.; Yang, H.-Y.; Ren, J.-C.; Zou, X.-M.; Huang, C.; Chi, X.-S.; et al. Assessment of Utilization and Cost-Effectiveness of Telemedicine Program in Western Regions of China: A 12-Year Study of 249 Hospitals Across 112 Cities. Telemed. J. E Health 2016, 22, 909–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wosik, J.; Fudim, M.; Cameron, B.; Gellad, Z.F.; Cho, A.; Phinney, D.; Curtis, S.; Roman, M.; Poon, E.G.; Ferranti, J.; et al. Telehealth Transformation: COVID-19 and the Rise of Virtual Care. J. Am. Med. Inform Assoc. 2020, 27, 957–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal-Alaball, J.; Acosta-Roja, R.; Pastor Hernández, N.; Sanchez Luque, U.; Morrison, D.; Narejos Pérez, S.; Perez-Llano, J.; Salvador Vèrges, A.; López Seguí, F. Telemedicine in the Face of the COVID-19 Pandemic. Aten Primaria 2020, 52, 418–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.C.; Badawy, S.M. Telemedicine in Pediatrics: Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. JMIR Pediatr. Parent 2021, 4, e22696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Hara, V.M.; Johnston, S.V.; Browne, N.T. The Paediatric Weight Management Office Visit via Telemedicine: Pre- to Post-COVID-19 Pandemic. Pediatr. Obes. 2020, 15, e12694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walters, J.; Johnson, T.; DeBlasio, D.; Klein, M.; Sikora, K.; Reilly, K.; Hutzel-Dunham, E.; White, C.; Xu, Y.; Burkhardt, M.C. Integration and Impact of Telemedicine in Underserved Pediatric Primary Care. Clin. Pediatr. 2021, 60, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veinot, T.C.; Mitchell, H.; Ancker, J.S. Good Intentions Are Not Enough: How Informatics Interventions Can Worsen Inequality. J. Am. Med. Inform Assoc. 2018, 25, 1080–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodie, G.D.; Dutta, M.J. Understanding Health Literacy for Strategic Health Marketing: EHealth Literacy, Health Disparities, and the Digital Divide. Health Mark Q 2008, 25, 175–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capusan, K.Y.; Fenster, T. Patient Satisfaction with Telehealth During the COVID-19 Pandemic in a Pediatric Pulmonary Clinic. J. Pediatr. Health Care 2021, S0891-5245(21)00187-5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donskoy, I.; Loghmanee, D.; Fields, B.G.; Troester, M.; Martin, W. Telemedicine-Based Sleep Services for a Complex Child: Optimizing Care during a Pandemic and Beyond. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Preventive Services Task Force; Grossman, D.C.; Bibbins-Domingo, K.; Curry, S.J.; Barry, M.J.; Davidson, K.W.; Doubeni, C.A.; Epling, J.W.; Kemper, A.R.; Krist, A.H.; et al. Screening for Obesity in Children and Adolescents: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. JAMA 2017, 317, 2417–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlow, S.E. Expert Committee Expert Committee Recommendations Regarding the Prevention, Assessment, and Treatment of Child and Adolescent Overweight and Obesity: Summary Report. Pediatrics 2007, 120 (Suppl. 4), S164–S192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute for Healthy Childhood Weight Algorithm for the Assessment and Management of Childhood1Obesity in Patients 2 Years and Older 2015. Available online: https://ihcw.aap.org/Documents/Assessment%20%20and%20Management%20of%20Childhood%20Obesity%20Algorithm_FINAL.pdf (accessed on 16 October 2021).
- Dietz, W.; Santos-Burgoa, C. Obesity and Its Implications for COVID-19 Mortality. Obesity 2020, 28, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleischman, A.; Hourigan, S.E.; Lyon, H.N.; Landry, M.G.; Reynolds, J.; Steltz, S.K.; Robinson, L.; Keating, S.; Feldman, H.A.; Antonelli, R.C.; et al. Creating an Integrated Care Model for Childhood Obesity: A Randomized Pilot Study Utilizing Telehealth in a Community Primary Care Setting. Clin. Obes. 2016, 6, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, E.T.; Vernacchio, L.; Mitchell, A.A.; Fischer, C.; Giacalone, P.; Ludwig, D.S.; Ebbeling, C.B. A Telephone Intervention to Achieve Differentiation in Dietary Intake: A Randomized Trial in Paediatric Primary Care. Pediatr. Obes. 2017, 12, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.M.; Sampilo, M.; Gallagher, K.S.; Dean, K.; Saroja, M.B.; Yu, Q.; He, J.; Sporn, N. Treating Rural Paediatric Obesity through Telemedicine vs. Telephone: Outcomes from a Cluster Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Telemed Telecare 2016, 22, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferro, F.; Tozzi, A.E.; Erba, I.; Dall’Oglio, I.; Campana, A.; Cecchetti, C.; Geremia, C.; Rega, M.L.; Tontini, G.; Tiozzo, E.; et al. Impact of Telemedicine on Health Outcomes in Children with Medical Complexity: An Integrative Review. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2021, 180, 2389–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.A.; Ming, D.; Maslow, G.; Gifford, E.J. Mitigating the Impacts of the COVID-19 Pandemic Response on At-Risk Children. Pediatrics 2020, 146, e20200973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Well Telehealth Index: 2019 Consumer Survey. Available online: https://static.americanwell.com/app/uploads/2019/07/American-Well-Telehealth-Index-2019-Consumer-Survey-eBook2.pdf (accessed on 16 October 2021).
- Umano, G.R.; Di Sessa, A.; Guarino, S.; Gaudino, G.; Marzuillo, P.; Miraglia Del Giudice, E. Telemedicine in the COVID-19 Era: Taking Care of Children with Obesity and Diabetes Mellitus. World J. Diabetes 2021, 12, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Looman, W.S.; Antolick, M.; Cady, R.G.; Lunos, S.A.; Garwick, A.E.; Finkelstein, S.M. Effects of a Telehealth Care Coordination Intervention on Perceptions of Health Care by Caregivers of Children With Medical Complexity: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Pediatr. Health Care 2015, 29, 352–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, N.T.; Snethen, J.A.; Greenberg, C.S.; Frenn, M.; Kilanowski, J.F.; Gance-Cleveland, B.; Burke, P.J.; Lewandowski, L. When Pandemics Collide: The Impact of COVID-19 on Childhood Obesity. J. Pediatr. Nurs. 2021, 56, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Lancet Public Health, null Childhood Obesity beyond COVID-19. Lancet Public Health 2021, 6, e534. [CrossRef]
- Skinner, A.C.; Ravanbakht, S.N.; Skelton, J.A.; Perrin, E.M.; Armstrong, S.C. Prevalence of Obesity and Severe Obesity in US Children, 1999-2016. Pediatrics 2018, 141, e20173459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauria, L.; Spinelli, A.; Buoncristiano, M.; Nardone, P. Decline of Childhood Overweight and Obesity in Italy from 2008 to 2016: Results from 5 Rounds of the Population-Based Surveillance System. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Kelly, A.S. Review of Childhood Obesity: From Epidemiology, Etiology, and Comorbidities to Clinical Assessment and Treatment. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2017, 92, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucinotta, D.; Vanelli, M. WHO Declares COVID-19 a Pandemic. Acta Biomed. 2020, 91, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical Features of Patients Infected with 2019 Novel Coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Han, X.; Jiang, N.; Cao, Y.; Alwalid, O.; Gu, J.; Fan, Y.; Zheng, C. Radiological Findings from 81 Patients with COVID-19 Pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A Descriptive Study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Yu, T.; Du, R.; Fan, G.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xiang, J.; Wang, Y.; Song, B.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical Course and Risk Factors for Mortality of Adult Inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Lancet 2020, 395, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira-de-Almeida, C.A.; Del Ciampo, L.A.; Ferraz, I.S.; Del Ciampo, I.R.L.; Contini, A.A.; Ued, F.d.V. COVID-19 and Obesity in Childhood and Adolescence: A Clinical Review. J. Pediatr. 2020, 96, 546–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frühbeck, G.; Baker, J.L.; Busetto, L.; Dicker, D.; Goossens, G.H.; Halford, J.C.G.; Handjieva-Darlenska, T.; Hassapidou, M.; Holm, J.-C.; Lehtinen-Jacks, S.; et al. European Association for the Study of Obesity Position Statement on the Global COVID-19 Pandemic. Obes. Facts 2020, 13, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogueira-de-Almeida, C.A. We Need To Look At the Comorbidities of Obesity during Childhood and Adolescence. Biomed. J. Sci. Tech. Res. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Xiong, Y.; Wei, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wang, F.; Li, G.; Liu, K.; Du, R.; Wang, C.-Y.; Zhu, W. Obesity Predisposes to the Risk of Higher Mortality in Young COVID-19 Patients. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 92, 2536–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kass, D.A.; Duggal, P.; Cingolani, O. Obesity Could Shift Severe COVID-19 Disease to Younger Ages. Lancet 2020, 395, 1544–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Götzinger, F.; Santiago-García, B.; Noguera-Julián, A.; Lanaspa, M.; Lancella, L.; Calò Carducci, F.I.; Gabrovska, N.; Velizarova, S.; Prunk, P.; Osterman, V.; et al. COVID-19 in Children and Adolescents in Europe: A Multinational, Multicentre Cohort Study. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health 2020, 4, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hon, K.L.; Leung, K.K.Y.; Leung, A.K.C.; Sridhar, S.; Qian, S.; Lee, S.L.; Colin, A.A. Overview: The History and Pediatric Perspectives of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndromes: Novel or Just like SARS. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2020, 55, 1584–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Mo, X.; Hu, Y.; Qi, X.; Jiang, F.; Jiang, Z.; Tong, S. Epidemiology of COVID-19 Among Children in China. Pediatrics 2020, 145, e20200702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panahi, L.; Amiri, M.; Pouy, S. Clinical Characteristics of COVID-19 Infection in Newborns and Pediatrics: A Systematic Review. Arch. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2020, 8, e50. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiehao, C.; Jin, X.; Daojiong, L.; Zhi, Y.; Lei, X.; Zhenghai, Q.; Yuehua, Z.; Hua, Z.; Ran, J.; Pengcheng, L.; et al. A Case Series of Children With 2019 Novel Coronavirus Infection: Clinical and Epidemiological Features. Clin. Infect Dis. 2020, 71, 1547–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, P.; Curtis, N. COVID-19 in Children, Pregnancy and Neonates: A Review of Epidemiologic and Clinical Features. Pediatr. Infect Dis. J. 2020, 39, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Rinaldi, E.; Zusi, C.; Beatrice, G.; Saccomani, M.D.; Dalbeni, A. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Children and/or Adolescents: A Meta-Analysis. Pediatr. Res. 2021, 89, 733–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludvigsson, J.F. Systematic Review of COVID-19 in Children Shows Milder Cases and a Better Prognosis than Adults. Acta Paediatr. 2020, 109, 1088–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, N.; Kalra, A.; Nowacki, A.S.; Anjewierden, S.; Han, Z.; Bhat, P.; Carmona-Rubio, A.E.; Jacob, M.; Procop, G.W.; Harrington, S.; et al. Association of Use of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors and Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers With Testing Positive for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). JAMA Cardiol. 2020, 5, 1020–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Yang, J.; Zhao, F.; Zhi, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, L.; Bi, Z.; Zhao, Y. Prevalence and Impact of Cardiovascular Metabolic Diseases on COVID-19 in China. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2020, 109, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balasubramanian, S.; Rao, N.M.; Goenka, A.; Roderick, M.; Ramanan, A.V. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Children—What We Know So Far and What We Do Not. Indian Pediatr. 2020, 57, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhochak, N.; Singhal, T.; Kabra, S.K.; Lodha, R. Pathophysiology of COVID-19: Why Children Fare Better than Adults? Indian J. Pediatr. 2020, 87, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, C.; Buffa, S.; Candore, G.; Colonna-Romano, G.; Dunn-Walters, D.; Kipling, D.; Pawelec, G. Mechanisms of Immunosenescence. Immun. Ageing 2009, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.B.; Verma, A. Nasal ACE2 Levels and COVID-19 in Children. JAMA 2020, 323, 2386–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Netea, M.G.; Domínguez-Andrés, J.; Barreiro, L.B.; Chavakis, T.; Divangahi, M.; Fuchs, E.; Joosten, L.A.B.; van der Meer, J.W.M.; Mhlanga, M.M.; Mulder, W.J.M.; et al. Defining Trained Immunity and Its Role in Health and Disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teran, R.; Mitre, E.; Vaca, M.; Erazo, S.; Oviedo, G.; Hübner, M.P.; Chico, M.E.; Mattapallil, J.J.; Bickle, Q.; Rodrigues, L.C.; et al. Immune System Development during Early Childhood in Tropical Latin America: Evidence for the Age-Dependent down Regulation of the Innate Immune Response. Clin. Immunol. 2011, 138, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, A.K.; Hollander, G.A.; McMichael, A. Evolution of the Immune System in Humans from Infancy to Old Age. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2015, 282, 20143085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, A.; Reandelar, M.J.; Fasciglione, K.; Roumenova, V.; Li, Y.; Otazu, G.H. Correlation between Universal BCG Vaccination Policy and Reduced Mortality for COVID-19. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Xudong, X.; Chen, J.; Junzhu, C.; Wang, X.; Xingxiang, W.; Zhang, F.; Furong, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yanrong, L. Age- and Gender-Related Difference of ACE2 Expression in Rat Lung. Life Sci. 2006, 78, 2166–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, Y.; Kuba, K.; Rao, S.; Huan, Y.; Guo, F.; Guan, B.; Yang, P.; Sarao, R.; Wada, T.; Leong-Poi, H.; et al. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 Protects from Severe Acute Lung Failure. Nature 2005, 436, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Heialy, S.; Hachim, M.Y.; Senok, A.; Gaudet, M.; Abou Tayoun, A.; Hamoudi, R.; Alsheikh-Ali, A.; Hamid, Q. Regulation of Angiotensin- Converting Enzyme 2 in Obesity: Implications for COVID-19. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riollano-Cruz, M.; Akkoyun, E.; Briceno-Brito, E.; Kowalsky, S.; Reed, J.; Posada, R.; Sordillo, E.M.; Tosi, M.; Trachtman, R.; Paniz-Mondolfi, A. Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children Related to COVID-19: A New York City Experience. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdoni, L.; Mazza, A.; Gervasoni, A.; Martelli, L.; Ruggeri, M.; Ciuffreda, M.; Bonanomi, E.; D’Antiga, L. An Outbreak of Severe Kawasaki-like Disease at the Italian Epicentre of the SARS-CoV-2 Epidemic: An Observational Cohort Study. Lancet 2020, 395, 1771–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caussy, C.; Wallet, F.; Laville, M.; Disse, E. Obesity Is Associated with Severe Forms of COVID-19. Obesity 2020, 28, 1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Dong, X.; Zhang, J.-J.; Cao, Y.-Y.; Akdis, M.; Huang, P.-Q.; Chen, H.-W.; Li, Y.; Liu, G.-H.; Akdis, C.A.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of 182 Pediatric COVID-19 Patients with Different Severities and Allergic Status. Allergy 2021, 76, 510–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, W.-J.; Liang, W.-H.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, H.-R.; Chen, Z.-S.; Li, Y.-M.; Liu, X.-Q.; Chen, R.-C.; Tang, C.-L.; Wang, T.; et al. Comorbidity and Its Impact on 1590 Patients with COVID-19 in China: A Nationwide Analysis. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 2000547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, L.; Eagon, J.C.; Trujillo, M.E.; Scherer, P.E.; Klein, S. Visceral Fat Adipokine Secretion Is Associated with Systemic Inflammation in Obese Humans. Diabetes 2007, 56, 1010–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, F.; Huang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Yin, M.; Chen, X.; Xiao, L.; Deng, G. Association of Inflammatory Markers with the Severity of COVID-19: A Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Infect Dis. 2020, 96, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lighter, J.; Phillips, M.; Hochman, S.; Sterling, S.; Johnson, D.; Francois, F.; Stachel, A. Obesity in Patients Younger Than 60 Years Is a Risk Factor for COVID-19 Hospital Admission. Clin. Infect Dis. 2020, 71, 896–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zachariah, P.; Johnson, C.L.; Halabi, K.C.; Ahn, D.; Sen, A.I.; Fischer, A.; Banker, S.L.; Giordano, M.; Manice, C.S.; Diamond, R.; et al. Epidemiology, Clinical Features, and Disease Severity in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in a Children’s Hospital in New York City, New York. JAMA Pediatr. 2020, 174, e202430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrobelli, A.; Pecoraro, L.; Ferruzzi, A.; Heo, M.; Faith, M.; Zoller, T.; Antoniazzi, F.; Piacentini, G.; Fearnbach, S.N.; Heymsfield, S.B. Effects of COVID-19 Lockdown on Lifestyle Behaviors in Children with Obesity Living in Verona, Italy: A Longitudinal Study. Obesity 2020, 28, 1382–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.M.; Jeong, D.C.; Suh, B.K.; Ahn, M.B. The Impact of the Coronavirus Disease-2019 Pandemic on Childhood Obesity and Vitamin D Status. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2021, 36, e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parekh, N.; Ali, S.H.; O’Connor, J.; Tozan, Y.; Jones, A.M.; Capasso, A.; Foreman, J.; DiClemente, R.J. Food Insecurity among Households with Children during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Results from a Study among Social Media Users across the United States. Nutr. J. 2021, 20, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almandoz, J.P.; Xie, L.; Schellinger, J.N.; Mathew, M.S.; Gazda, C.; Ofori, A.; Kukreja, S.; Messiah, S.E. Impact of COVID-19 Stay-at-Home Orders on Weight-Related Behaviours among Patients with Obesity. Clin. Obes. 2020, 10, e12386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, R. Projecting the Impact of the Coronavirus Disease-2019 Pandemic on Childhood Obesity in the United States: A Microsimulation Model. J. Sport Health Sci. 2020, 9, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, E.; Rodríguez, A.; Martin-Loeches, I.; Lorente, L.; Del Mar Martín, M.; Pozo, J.C.; Montejo, J.C.; Estella, A.; Arenzana, Á.; Rello, J.; et al. Impact of Obesity in Patients Infected with 2009 Influenza A(H1N1). Chest 2011, 139, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, W.D.; Beck, M.A. Obesity Impairs the Adaptive Immune Response to Influenza Virus. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2017, 14, S406–S409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekerdemian, L.S.; Mahmood, N.R.; Wolfe, K.K.; Riggs, B.J.; Ross, C.E.; McKiernan, C.A.; Heidemann, S.M.; Kleinman, L.C.; Sen, A.I.; Hall, M.W.; et al. Characteristics and Outcomes of Children With Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Infection Admitted to US and Canadian Pediatric Intensive Care Units. JAMA Pediatr. 2020, 174, 868–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajifathalian, K.; Kumar, S.; Newberry, C.; Shah, S.; Fortune, B.; Krisko, T.; Ortiz-Pujols, S.; Zhou, X.K.; Dannenberg, A.J.; Kumar, R.; et al. Obesity Is Associated with Worse Outcomes in COVID-19: Analysis of Early Data from New York City. Obesity 2020, 28, 1606–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, T.; Razieh, C.; Zaccardi, F.; Davies, M.J.; Khunti, K. Obesity and Risk of COVID-19: Analysis of UK Biobank. Prim. Care Diabetes 2020, 14, 566–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo Baidal, J.A.; Chang, J.; Hulse, E.; Turetsky, R.; Parkinson, K.; Rausch, J.C. Zooming Toward a Telehealth Solution for Vulnerable Children with Obesity During Coronavirus Disease 2019. Obesity 2020, 28, 1184–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dooley, D.G.; Bandealy, A.; Tschudy, M.M. Low-Income Children and Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in the US. JAMA Pediatr. 2020, 174, 922–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fore, H.H. A Wake-up Call: COVID-19 and Its Impact on Children’s Health and Wellbeing. Lancet Glob. Health 2020, 8, e861–e862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rundle, A.G.; Park, Y.; Herbstman, J.B.; Kinsey, E.W.; Wang, Y.C. COVID-19-Related School Closings and Risk of Weight Gain Among Children. Obesity 2020, 28, 1008–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.M.; Fathy, S.K.; Fawzy, A.T.; Salem, A.S.; Shawky, M.S. The Mutual Effects of COVID-19 and Obesity. Obes. Med. 2020, 19, 100250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, D.C.; Moss, R.H.; Sykes-Muskett, B.; Conner, M.; O’Connor, D.B. Stress and Eating Behaviors in Children and Adolescents: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Appetite 2018, 123, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isasi, C.R.; Parrinello, C.M.; Jung, M.M.; Carnethon, M.R.; Birnbaum-Weitzman, O.; Espinoza, R.A.; Penedo, F.J.; Perreira, K.M.; Schneiderman, N.; Sotres-Alvarez, D.; et al. Psychosocial Stress Is Associated with Obesity and Diet Quality in Hispanic/Latino Adults. Ann. Epidemiol. 2015, 25, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte, E.M.; Avena, N.M.; Gearhardt, A.N. Which Foods May Be Addictive? The Roles of Processing, Fat Content, and Glycemic Load. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felső, R.; Lohner, S.; Hollódy, K.; Erhardt, É.; Molnár, D. Relationship between Sleep Duration and Childhood Obesity: Systematic Review Including the Potential Underlying Mechanisms. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2017, 27, 751–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenney, E.L.; Gortmaker, S.L. United States Adolescents’ Television, Computer, Videogame, Smartphone, and Tablet Use: Associations with Sugary Drinks, Sleep, Physical Activity, and Obesity. J. Pediatr. 2017, 182, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, R.J.; Campbell, J.P.; Gleeson, M.; Krüger, K.; Nieman, D.C.; Pyne, D.B.; Turner, J.E.; Walsh, N.P. Can Exercise Affect Immune Function to Increase Susceptibility to Infection? Exerc. Immunol. Rev. 2020, 26, 8–22. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Durá-Travé, T.; Gallinas-Victoriano, F.; Chueca-Guindulain, M.J.; Berrade-Zubiri, S. Prevalence of Hypovitaminosis D and Associated Factors in Obese Spanish Children. Nutr. Diabetes 2017, 7, e248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.J.; Skow, Á.; Bodurtha, J.; Kinra, S. Health Information Technology in Screening and Treatment of Child Obesity: A Systematic Review. Pediatrics 2013, 131, e894–e902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaikh, U.; Cole, S.L.; Marcin, J.P.; Nesbitt, T.S. Clinical Management and Patient Outcomes among Children and Adolescents Receiving Telemedicine Consultations for Obesity. Telemed J E Health 2008, 14, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaikh, U.; Nettiksimmons, J.; Romano, P. Pediatric Obesity Management in Rural Clinics in California and the Role of Telehealth in Distance Education. J. Rural. Health 2011, 27, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Irby, M.B.; Boles, K.A.; Jordan, C.; Skelton, J.A. TeleFIT: Adapting a Multidisciplinary, Tertiary-Care Pediatric Obesity Clinic to Rural Populations. Telemed J E Health 2012, 18, 247–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slusser, W.; Whitley, M.; Izadpanah, N.; Kim, S.L.; Ponturo, D. Multidisciplinary Pediatric Obesity Clinic via Telemedicine Within the Los Angeles Metropolitan Area: Lessons Learned. Clin. Pediatr. 2016, 55, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.M.; James, R.L.; Boles, R.E.; Goetz, J.R.; Belmont, J.; Malone, B. The Use of TeleMedicine in the Treatment of Paediatric Obesity: Feasibility and Acceptability. Matern Child Nutr. 2011, 7, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tully, L.; Burls, A.; Sorensen, J.; El-Moslemany, R.; O’Malley, G. Mobile Health for Pediatric Weight Management: Systematic Scoping Review. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth 2020, 8, e16214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garza, C.; Martinez, D.A.; Yoon, J.; Nickerson, B.S.; Park, K.-S. Effects of Telephone Aftercare Intervention for Obese Hispanic Children on Body Fat Percentage, Physical Fitness, and Blood Lipid Profiles. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 5133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitley, A.; Yahia, N. Efficacy of Clinic-Based Telehealth vs. Face-to-Face Interventions for Obesity Treatment in Children and Adolescents in the United States and Canada: A Systematic Review. Child. Obes. 2021, 17, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, L.; Hagman, E.; Danielsson, P. A Novel Interactive Mobile Health Support System for Pediatric Obesity Treatment: A Randomized Controlled Feasibility Trial. BMC Pediatr. 2020, 20, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidmar, A.P.; Pretlow, R.; Borzutzky, C.; Wee, C.P.; Fox, D.S.; Fink, C.; Mittelman, S.D. An Addiction Model-Based Mobile Health Weight Loss Intervention in Adolescents with Obesity. Pediatr. Obes. 2019, 14, e12464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, M.; Dryden, E.M.; Horan, C.M.; Price, S.; Marshall, R.; Hacker, K.; Finkelstein, J.A.; Taveras, E.M. Leveraging Text Messaging and Mobile Technology to Support Pediatric Obesity-Related Behavior Change: A Qualitative Study Using Parent Focus Groups and Interviews. J. Med. Internet Res. 2013, 15, e272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.M.; Haemer, M.; Kharofa, R.Y.; Christison, A.L.; Hampl, S.E.; Tinajero-Deck, L.; Lockhart, M.K.; Reich, S.; Pont, S.J.; Stratbucker, W.; et al. Community Healthcare and Technology to Enhance Communication in Pediatric Obesity Care. Child Obes. 2018, 14, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunton, C.; Arensberg, M.B.; Drawert, S.; Badaracco, C.; Everett, W.; McCauley, S.M. Perspectives of Registered Dietitian Nutritionists on Adoption of Telehealth for Nutrition Care during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Healthcare 2021, 9, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cueto, V.; Sanders, L.M. Telehealth Opportunities and Challenges for Managing Pediatric Obesity. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 67, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stella, A.B.; Ajčević, M.; Furlanis, G.; Cillotto, T.; Menichelli, A.; Accardo, A.; Manganotti, P. Smart Technology for Physical Activity and Health Assessment during COVID-19 Lockdown. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2021, 61, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.; Lau, P.W.C.; Jiang, Y.; Maddison, R. Getting Active with Active Video Games: A Quasi-Experimental Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, R.W.; Williams, S.A.; Gucciardi, D.F.; Bear, N.; Gibson, N. Evaluating the Effectiveness of Home Exercise Programmes Using an Online Exercise Prescription Tool in Children with Cerebral Palsy: Protocol for a Randomised Controlled Trial. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e018316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil-Cosano, J.J.; Ubago-Guisado, E.; Sánchez, M.J.; Ortega-Acosta, M.J.; Mateos, M.E.; Benito-Bernal, A.I.; Llorente-Cantarero, F.J.; Ortega, F.B.; Ruiz, J.R.; Labayen, I.; et al. The Effect of an Online Exercise Programme on Bone Health in Paediatric Cancer Survivors (IBoneFIT): Study Protocol of a Multi-Centre Randomized Controlled Trial. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.J. Tele-Exercise as a Promising Tool to Promote Exercise in Children With Cystic Fibrosis. Front. Public Health 2018, 6, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.W.; Williams, S.A.; Gucciardi, D.F.; Bear, N.; Gibson, N. Can an Online Exercise Prescription Tool Improve Adherence to Home Exercise Programmes in Children with Cerebral Palsy and Other Neurodevelopmental Disabilities? A Randomised Controlled Trial. Randomized Control. Trial 2020, 10, e040108. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Sun, H. Effects of Active Videogame and Sports, Play, and Active Recreation for Kids Physical Education on Children’s Health-Related Fitness and Enjoyment. Games Health J. 2017, 6, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosino, P.; Fuschillo, S.; Papa, A. Exergaming as a Supportive Tool for Home-Based Rehabilitation in the COVID-19 Pandemic Era. Games Health J. 2020, 9, 311–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, R.B. Exergames as Coping Strategies for Anxiety Disorders During the COVID-19 Quarantine Period. Games Health J. 2020, 9, 147–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valeriani, F.; Protano, C.; Marotta, D.; Liguori, G.; Spica, V.R.; Valerio, G.; Vitali, M.; Gallè, F. Exergames in Childhood Obesity Treatment: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Chen, S. Are Fieldbased Exergames Useful in Preventing Childhood Obesity? A Systematic Review. Obes. Rev. 2014, 15, 676–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamboglia, C.M.G.F.; da Silva, V.T.B.L.; de Vasconcelos Filho, J.E.; Pinheiro, M.H.N.P.; Munguba, M.C.d.S.; Silva Júnior, F.V.I.; de Paula, F.A.R.; da Silva, C.A.B. Exergaming as a Strategic Tool in the Fight against Childhood Obesity: A Systematic Review. J. Obes. 2013, 2013, 438364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zeng, N.; Gao, Z. Exergaming and Obesity in Youth: Current Perspectives. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2016, 9, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bethea, T.C.; Berry, D.; Maloney, A.E.; Sikich, L. Pilot Study of an Active Screen Time Game Correlates with Improved Physical Fitness in Minority Elementary School Youth. Games Health J. 2012, 1, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calcaterra, V.; Larizza, D.; Codrons, E.; De Silvestri, A.; Brambilla, P.; Abela, S.; Arpesella, M.; Vandoni, M. Improved Metabolic and Cardiorespiratory Fitness during a Recreational Training Program in Obese Children. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 26, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, M.H.; Lahart, I.; Carlin, A.; Murtagh, E. The Effects of Continuous Compared to Accumulated Exercise on Health: A Meta-Analytic Review. Sports Med. 2019, 49, 1585–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, K.A.; Yen, S.; Wlasiuk, L.; Newman, T.B.; Lustig, R. Feasibility of a Dance Videogame to Promote Weight Loss among Overweight Children and Adolescents. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2007, 161, 105–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni Mhurchu, C.; Maddison, R.; Jiang, Y.; Jull, A.; Prapavessis, H.; Rodgers, A. Couch Potatoes to Jumping Beans: A Pilot Study of the Effect of Active Video Games on Physical Activity in Children. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2008, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Training for Life: Optimizing Positive Youth Development Through Sport and Physical Activity—Oxford Handbooks; 2019; 55. Available online: https://www.oxfordhandbooks.com/view/10.1093/oxfordhb/9780199731763.001.0001/oxfordhb-9780199731763-e-24 (accessed on 16 October 2021).
- Bernardi, N.F.; Codrons, E.; di Leo, R.; Vandoni, M.; Cavallaro, F.; Vita, G.; Bernardi, L. Increase in Synchronization of Autonomic Rhythms between Individuals When Listening to Music. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Füzéki, E.; Schröder, J.; Groneberg, D.A.; Banzer, W. Online Exercise Classes during the COVID-19 Related Lockdown in Germany: Use and Attitudes. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natalucci, V.; Carnevale Pellino, V.; Barbieri, E.; Vandoni, M. Is It Important to Perform Physical Activity During Coronavirus Pandemic (COVID-19)? Driving Action for a Correct Exercise Plan. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 602020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calcaterra, V.; Vandoni, M.; Pellino, V.C.; Cena, H. Special Attention to Diet and Physical Activity in Children and Adolescents With Obesity During the Coronavirus Disease-2019 Pandemic. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascarenhas, M.N.; Chan, J.M.; Vittinghoff, E.; Van Blarigan, E.L.; Hecht, F. Increasing Physical Activity in Mothers Using Video Exercise Groups and Exercise Mobile Apps: Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Med. Internet Res. 2018, 20, e179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muellmann, S.; Forberger, S.; Möllers, T.; Bröring, E.; Zeeb, H.; Pischke, C.R. Effectiveness of EHealth Interventions for the Promotion of Physical Activity in Older Adults: A Systematic Review. Prev. Med. 2018, 108, 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwan, R.Y.C.; Salihu, D.; Lee, P.H.; Tse, M.; Cheung, D.S.K.; Roopsawang, I.; Choi, K.S. The Effect of E-Health Interventions Promoting Physical Activity in Older People: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Eur. Rev. Aging Phys. Act 2020, 17, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calcaterra, V.; Iafusco, D.; Pellino, V.C.; Mameli, C.; Tornese, G.; Chianese, A.; Cascella, C.; Macedoni, M.; Redaelli, F.; Zuccotti, G.; et al. “CoVidentary”: An Online Exercise Training Program to Reduce Sedentary Behaviours in Children with Type 1 Diabetes during the COVID-19 Pandemic. J. Clin. Transl. Endocrinol. 2021, 25, 100261. [Google Scholar]
- Maddison, R.; Foley, L.; Ni Mhurchu, C.; Jiang, Y.; Jull, A.; Prapavessis, H.; Hohepa, M.; Rodgers, A. Effects of Active Video Games on Body Composition: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 94, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Agostino, E.M.; Urtel, M.; Webster, C.A.; McMullen, J.; Culp, B. Virtual Physical Education During COVID-19: Exploring Future Directions for Equitable Online Learning Tools. Front. Sports Act. Living 2021, 3, 716566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardman, K. Physical Education in Schools: A Global Perspective. Kinesiology 2008, 40, 5–28. [Google Scholar]
- Webster, C.; D’Agostino, E.; Urtel, M.; Mcmullen, J.; Culp, B.; Loiacono, C.; Killian, C. Physical Education in the COVID Era: Considerations for Online Program Delivery Using the Comprehensive School Physical Activity Program Framework. J. Teach. Phys. Educ. 2021, 40, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daum, D.N. Thinking about Hybrid or Online Learning in Physical Education? Start Here! Null 2020, 91, 42–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esentürk, O. Parents’ Perceptions on Physical Activity for Their Children with Autism Spectrum Disorders during the Novel Coronavirus Outbreak. Int. J. Dev. Disabil. 2020, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draper, C.E.; Milton, K.; Schipperijn, J. COVID-19 and Physical Activity: How Can We Build Back Better? J. Phys. Act. Health 2021, 18, 149–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Calcaterra, V.; Verduci, E.; Vandoni, M.; Rossi, V.; Di Profio, E.; Carnevale Pellino, V.; Tranfaglia, V.; Pascuzzi, M.C.; Borsani, B.; Bosetti, A.; et al. Telehealth: A Useful Tool for the Management of Nutrition and Exercise Programs in Pediatric Obesity in the COVID-19 Era. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3689. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13113689
Calcaterra V, Verduci E, Vandoni M, Rossi V, Di Profio E, Carnevale Pellino V, Tranfaglia V, Pascuzzi MC, Borsani B, Bosetti A, et al. Telehealth: A Useful Tool for the Management of Nutrition and Exercise Programs in Pediatric Obesity in the COVID-19 Era. Nutrients. 2021; 13(11):3689. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13113689
Chicago/Turabian StyleCalcaterra, Valeria, Elvira Verduci, Matteo Vandoni, Virginia Rossi, Elisabetta Di Profio, Vittoria Carnevale Pellino, Valeria Tranfaglia, Martina Chiara Pascuzzi, Barbara Borsani, Alessandra Bosetti, and et al. 2021. "Telehealth: A Useful Tool for the Management of Nutrition and Exercise Programs in Pediatric Obesity in the COVID-19 Era" Nutrients 13, no. 11: 3689. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13113689
APA StyleCalcaterra, V., Verduci, E., Vandoni, M., Rossi, V., Di Profio, E., Carnevale Pellino, V., Tranfaglia, V., Pascuzzi, M. C., Borsani, B., Bosetti, A., & Zuccotti, G. (2021). Telehealth: A Useful Tool for the Management of Nutrition and Exercise Programs in Pediatric Obesity in the COVID-19 Era. Nutrients, 13(11), 3689. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13113689









