Analysis and Evaluation of Nutritional Intake and Nutrition Quotient of Korean Athletes with Disabilities in the Tokyo Paralympic Games
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Dietary Intake Survey
2.3. Nutrition Quotient for Adults (NQ-A)
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Comparison of the Average Dietary Intake and %RDA of Korean Nationals with Disabilities
3.2. Comparison of Nutrition Quotient for Adults (NQ-A) and Scores by Detailed Factors of Korean Nationals with Disabilities
3.3. Comparative Analysis of %RDA According to Nutrition Quotient for Adults (NQ-A) Score Groups of National Athletes with Disabilities
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shaw, K.A.; Zello, G.A.; Bandy, B.; Ko, J.; Bertrand, L.; Chilibeck, P.D. Dietary Supplementation for Para-Athletes: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tweedy, S.; Bourke, J. IPC Athletics Classification Project for Physical Impairments: Final Report—Stage 1; IPC Athletics: Bonn, Germany, 2009; p. 104. [Google Scholar]
- Kreider, R.B.; Wilborn, C.D.; Taylor, L.; Campbell, B.; Almada, A.L.; Collins, R.; Cooke, M.; Earnest, C.P.; Greenwood, M.; Kalman, D.S.; et al. ISSN exercise & sport nutrition review: Research & recommendations. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2010, 7, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Guest, N.S.; Horne, J.; Vanderhout, S.M.; El-Sohemy, A. Sport Nutrigenomics: Personalized Nutrition for Athletic Performance. Front. Nutr. 2019, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, F.E.; Landreth, A.; Beam, S.; Jones, T.; Norton, L.; Cholewa, J.M. The effects of a sports nutrition education intervention on nutritional status, sport nutrition knowledge, body composition, and performance during off season training in NCAA Division I baseball players. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2017, 16, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.S.; Lee, M.C. A research on the actual condition of nutritional status, eating habit, food and food preference of shot put and javelin players in Korean national team. J. Korean Soc. Aerob. Exerc. 2001, 5, 101–111. [Google Scholar]
- Azhari, N.A.M.; Nor, N.M.; Manaf, H. A conceptual model for developing questionnaire on nutritional knowledge and supplement habits among disabled athletes in Malaysia. Adv. Sci. Lett. 2018, 24, 2404–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, L.M.; Hawley, J.A.; Wong, S.H.; Jeukendrup, A.E. Carbohydrates for training and competition. J. Sports Sci. 2011, 29, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S.; Kim, H.Y.; Hwang, J.Y.; Kwon, S.; Chung, H.R.; Kwak, T.K.; Kang, M.H.; Choi, Y.S. Development of nutrition quotient for Korean adults: Item selection and validation of factor structure. J. Nutr. Health 2018, 51, 340–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, K.L.; Thomson, J.S.; Swift, R.J.; von Hurst, P.R. Role of nutrition in performance enhancement and postexercise recovery. J. Sports Med. 2015, 6, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- An, Y.H.; Lee, G.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, K.T.; Lee, J.Y.; Baek, N.H.; Choi, I.S.; Kim, S.H.; Bae, H.S. Attitudes and Dispositions about Doping of the Korean National Team Who Participated in the Incheon Asian Para Games. Korean J. Sports Med. 2019, 37, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Vliet, P.V.; Broad, E.; Strupler, M. Nutrition, Body Composition and Pharmacology. In The Paralympic Athlete: Handbook of Sports Medicine and Science; Thompson, Y.V.A.W., Ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Korean Ministry of Health and Welfare. Dietary Reference Intakes for Koreans: Energy and Macronutrients. 2020. Available online: http://www.mohw.go.kr/upload/viewer/skin/doc.html?fn=1608684513122_20201223092638.pdf&rs=/upload/viewer/result/202108/ (accessed on 8 April 2021).
- Figel, K.; Pritchett, K.; Pritchett, R.; Broad, E. Energy and nutrient issues in athletes with spinal cord injury: Are they at risk for low energy availability? Nutrients 2018, 10, 1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grams, L.; Garrido, G.; Villacieros, J.; Ferro, A. Marginal micronutrient intake in high-performance male wheelchair basketball players: A dietary evaluation and the effects of nutritional advice. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krempien, J.L.; Barr, S.I. Risk of nutrient inadequacies in elite Canadian athletes with spinal cord injury. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2011, 21, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özdemir, G.; Ersoy, G. Interaction of nutrition, health and performance in disabled athletes. Turk. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2009, 55, 116–121. [Google Scholar]
- Farkas, G.J.; Pitot, M.A.; Berg, A.S.; Gater, D.R. Nutritional Status in Chronic Spinal Cord Injury: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Spinal Cord 2019, 57, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goosey-Tolfrey, V.L.; Crosland, J. Nutritional practices of competitive British wheelchair games players. Adapt. Phys. Act. Q. 2010, 27, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruettimann, B.; Perret, C.; Parnell, J.A.; Flueck, J.L. Carbohydrate Considerations for Athletes with a Spinal Cord Injury. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, S.M.; Van Loon, L.J.C. Dietary Protein for Athletes: From Requirements to Optimum Adaptation. J. Sports Sci. 2011, 29, S29–S38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islamoglu, A.H.; Kenger, E.B. Nutrition Considerations for Athletes with Physical Disabilities. Curr. Sports Med. Rep. 2019, 18, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madden, R.F.; Shearer, J.; Parnell, J.A. Evaluation of Dietary Intakes and Supplement Use in Paralympic Athletes. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flueck, J.L.; Parnell, J.A. Protein Considerations for Athletes with a Spinal Cord Injury. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 652441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, D.T.; Erdman, K.A.; Burke, L.M. Position of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, Dietitians of Canada and the American College of Sports Medicine: Nutrition and athletic performance. J. Acad. Nutr. 2016, 116, 501–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eskici, G.; Ersoy, G. An evaluation of wheelchair basketball players’ nutritional status and nutritional knowledge levels. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2016, 56, 259–268. [Google Scholar]
- Lukaski, H.C. Vitamin and mineral status: Effects on physical performance. Nutrition 2004, 20, 632–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrokhyar, F.; Sivakumar, G.; Savage, K.; Koziarz, A.; Jamshidi, S.; Ayeni, O.R.; Peterson, D.; Bhandari, M. Effects of vitamin D supplementation on serum 25-hydroxy vitamin D concentrations and physical performance in athletes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Sports Med. 2017, 47, 2323–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Quan, M.; Cao, Z.-B. Effect of vitamin D supplementation on upper and lower limb muscle strength and muscle power in athletes: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maroon, J.C.; Mathyssek, C.M.; Bost, J.W.; Amos, A.; Winkelman, R.; Yates, A.P.; Duca, M.A.; Norwig, J.A. Vitamin D profile in national football league players. Am. J. Sports Med. 2015, 43, 1241–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchett, K.; Pritchett, R.; Ogan, D.; Bishop, P.; Broad, E.; Lacroix, M. 25(OH)D Status of Elite Athletes with Spinal Cord Injury Relative to Lifestyle Factors. Nutrients 2016, 8, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sacheck, J.M.; Blumberg, B.B. Role of vitamin E and oxidative stress in exercise. Nutrition 2001, 17, 809–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohlmeier, H.; Salomon, A.; Saupe, J.; Shearer, M.J. Transport of vitamin K to bone in humans. J. Nutr. 1996, 126, 1192S–1196S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolinsky, I.; Driskell, J.A. Sports Nutrition: Vitamins and Trace Elements; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1997; p. 47. [Google Scholar]
- Teucher, B.; Dainty, J.R.; Spinks, C.A.; Majsak-Newman, G.; Berry, D.J.; Hoogewerff, J.A. Sodium and bone health: Impact of moderately high and low salt intakes on calcium metabolism in postmenopausal women. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2008, 23, 1477–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beard, J.L. Iron biology in immune function, muscle metabolism and neuronal functioning. J. Nutr. 2001, 131, 568S–579S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, M.; Garvican-Lewis, L.A.; Cox, G.R.; Govus, A.; McKay, A.K.A.; Stellingwerff, T.; Peeling, P. Iron considerations for the athlete: A narrative review. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2019, 119, 1463–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil, Á.; Victoria, E.M.d.; Olza, J. Indicators for the evaluation of diet quality. Nutr. Hosp. 2015, 31, 128–144. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.Y.; Lee, J.S.; Hwang, J.Y.; Kwon, S.; Chung, H.R.; Kwak, T.K.; Kang, M.H.; Choi, Y.S. Development of NQ-A, nutrition quotient for korean adolescents, to assess dietary quality and food behavior. J. Nutr. Health 2017, 50, 142–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.S.; Kang, M.H.; Kwak, T.K.; Chung, H.R.; Kwon, S.; Kim, H.Y.; Hwang, J.Y.; Choi, Y.S. Development of nutrition quotient for Korean preschoolers (NQ-P): Item selection and validation of factor structure. J. Nutr. Health 2016, 49, 378–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.; Je, Y. Dietary fibre intake and mortality from cardiovascular disease and all cancers: A meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Arch. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2016, 109, 39–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chung, M.J.; Kwak, T.K.; Kim, H.Y.; Kang, M.H.; Lee, J.S.; Chung, H.R.; Kwon, S.; Hwang, J.Y.; Choi, Y.S. Development of NQ-E, Nutrition Quotient for Korean elderly: Item selection and validation of factor structure. J. Nutr. Health 2018, 51, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yim, J.S.; Heo, Y.R. Factors associated with the dietary quality and nutrition status using the Nutrition Quotient for adults focusing on workers in the manufacturing industry. J. Nutr. Health 2020, 53, 488–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, N.Y.; Kwon, T.Y. Effects of self-management on the Nutrition Quotient (NQ) of college athletes. Korean J. Community Living Sci. 2020, 31, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, R.; Mainous, A.; King, D.; Simpson, K. Dietary fiber for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis. J. Am. Board Fam. Med. 2012, 25, 6–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anderson, J.J.B.; Klemmer, P.J.; Watts, M.L.S.; Garner, S.C.; MS, C. Phosphorus. In Present Knowledge in Nutrition; Barbara, A., Bowman, R., Russell, M., Eds.; Intl. Life Sciences Inst. (ILSI): Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Swaminathan, R. Magnesium metabolism and its disorders. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2003, 24, 47–66. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Coudray, C.; Demigne, C.; Rayssiguier, Y. Effects of dietary fibers on magnesium absorption in animals and humans. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| n = 21 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Gender | Males | 16 |
| Females | 5 | |
| Age | 19–29 | 3 |
| 30–49 | 12 | |
| 50–64 | 6 | |
| Sport | Shooting | 3 |
| Archery | 4 | |
| Boccia | 3 | |
| Table tennis | 2 | |
| Athletics | 2 | |
| Swimming | 1 | |
| Judo | 2 | |
| Track cycling | 2 | |
| Badminton | 3 | |
| National Team career | Less than 5 years | 6 |
| More than 5 years | 15 | |
| Type of disability | Visual impairments | 2 |
| Spinal cord disorder | 16 | |
| Cerebral palsy | 3 | |
| Total energy intake ratio | Carbohydrate | 58.97% |
| Protein | 15.74% | |
| Fat | 25.29% | |
| Variables | Males (n = 16) | Females (n = 5) | Total Mean Intakes | Total Mean %RDA | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Intakes | RDA | %RDA, %AI | Mean Intakes | RDA | %RDA, %AI | |||||
| Macronutrient intakes | ||||||||||
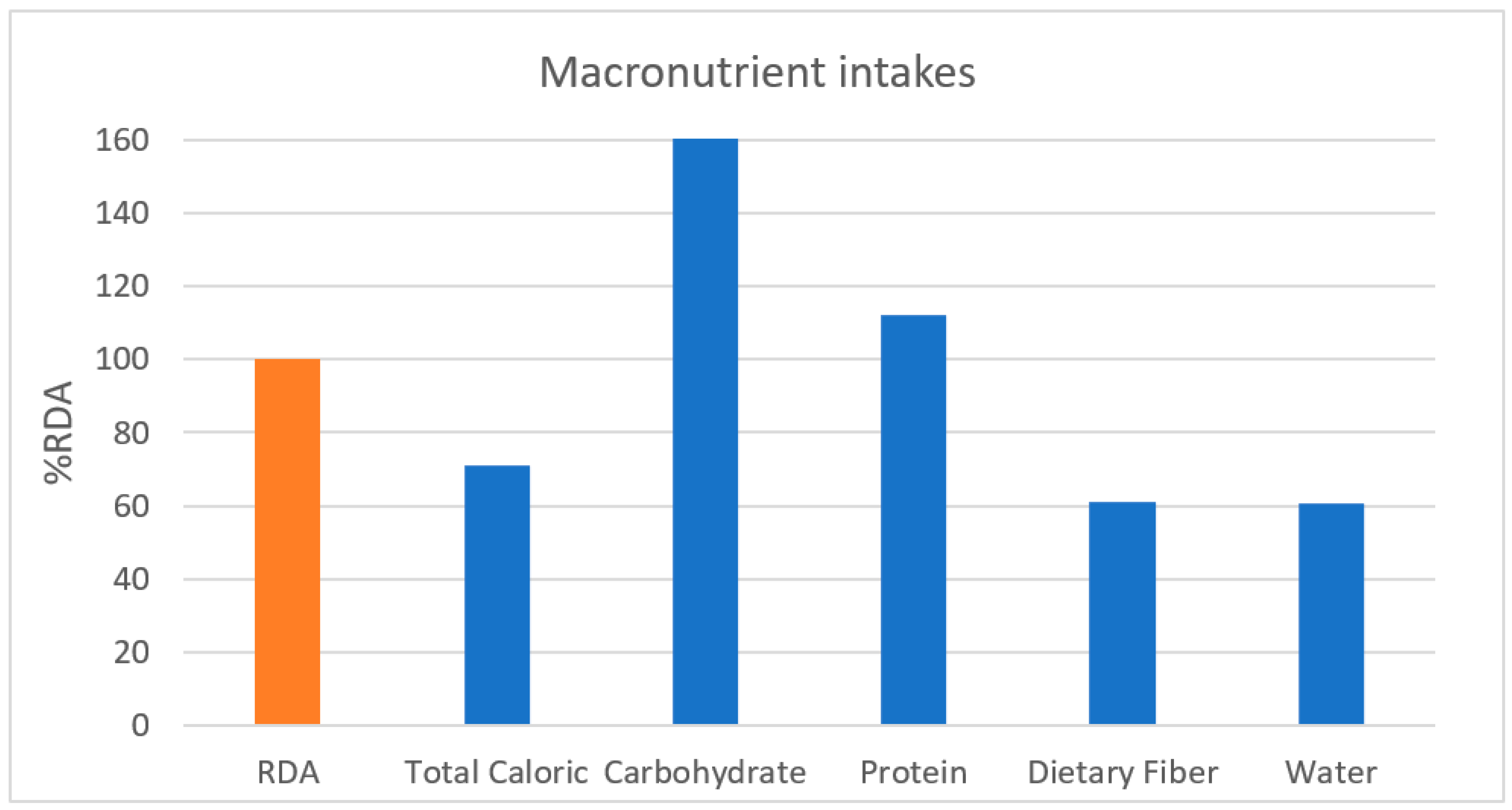
| Total calories (kcal) | 19–29 | 1448.75 | 2600 | 56% | - | - | - | 1622.59 | 70.9% | |
| 30–49 | 1806.86 | 2500 | 72% | 1346.25 | 1900 | 74% | ||||
| 50–64 | 1833.54 | 2200 | 83% | 1155.51 | 1700 | 68% | ||||
| Carbohydrate (g) | 233.48 | 130 | 180% | 164.32 | 130 | 126% | 217.01 | 166.9% | ||
| Protein (g) | 19–49 | 70.04 | 65 | 108% | 56.45 | 50 | 113% | 67.94 | 112.3% | |
| 50–64 | 72.97 | 60 | 122% | 61.52 | 50 | 123% | ||||
| Dietary fiber (g) | 17.67 | 30 | 59% | 13.65 | 20 | 68% | 16.71 | 61.1% | ||
| Water (g) | 19–29 | 423.85 | 1400 | 30% | - | - | - | 725.84 | 60.6% | |
| 30–49 | 863.16 | 1300 | 66% | 732.02 | 1000 | 73% | ||||
| 50–64 | 862.75 | 1200 | 72% | 595.82 | 900 | 66% | ||||
| Vitamins | ||||||||||
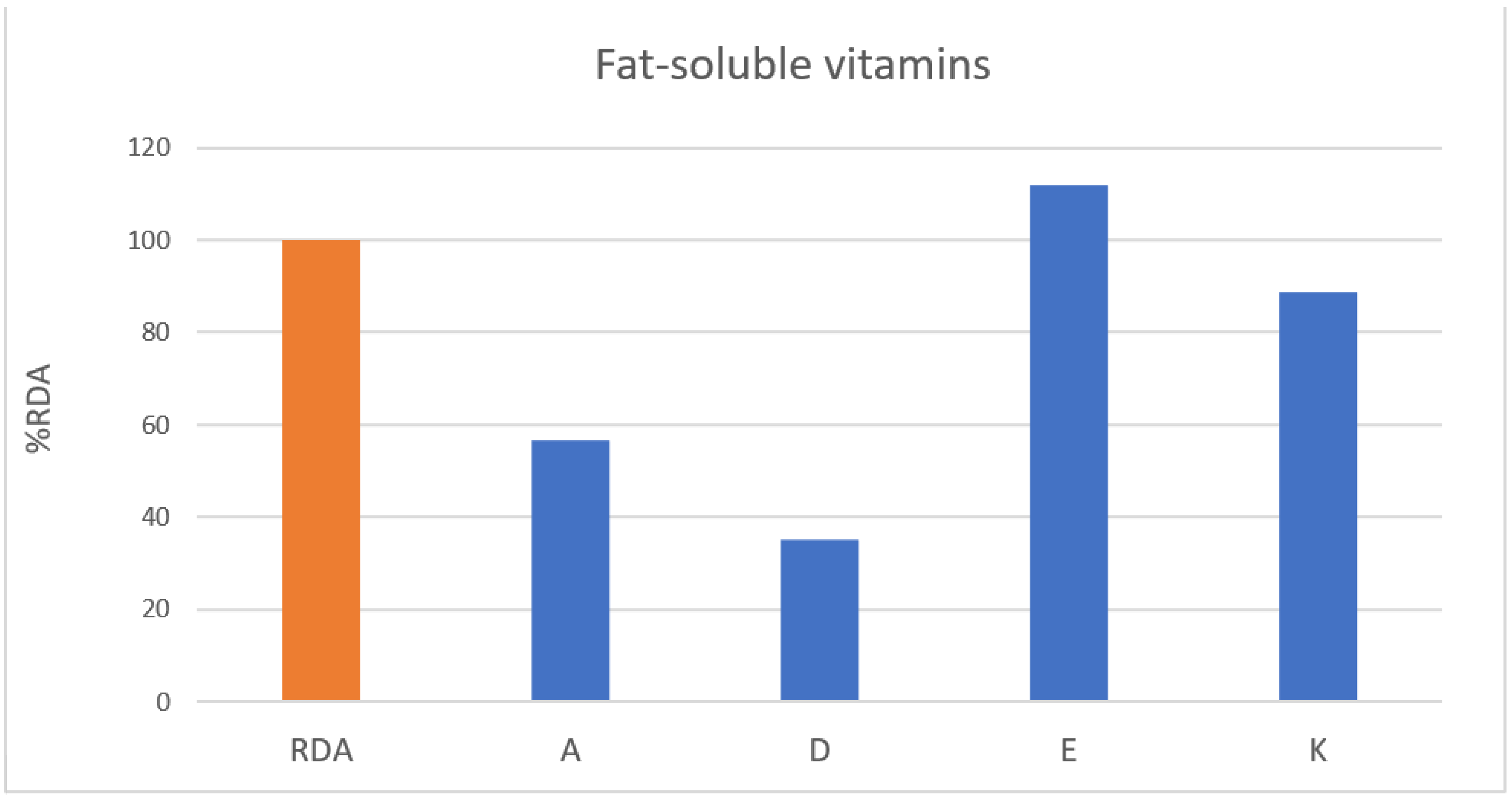
| Fat-soluble vitamins | A (µg) | 19–49 | 409.03 | 800 | 51% | 324.80 | 650 | 50% | 424.91 | 56.5% |
| 50–64 | 702.18 | 750 | 94% | 283.24 | 600 | 47% | ||||
| D (µg) | 3.81 | 10 | 38% | 2.56 | 10 | 26% | 3.51 | 35.1% | ||
| E (mg) | 14.57 | 12 | 121% | 9.83 | 12 | 82% | 13.44 | 112.0% | ||
| K (µg) | 72.50 | 75 | 97% | 41.52 | 65 | 64% | 65.12 | 88.8% | ||
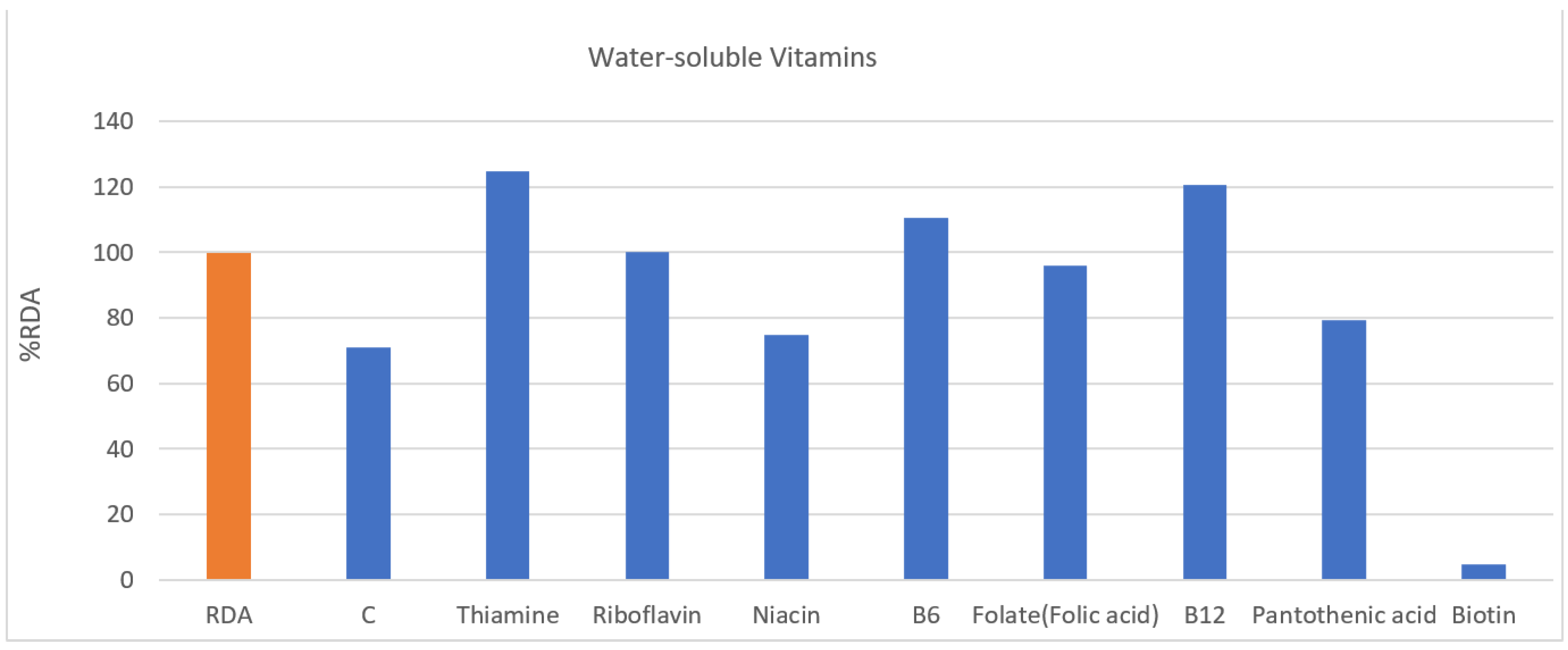
| Water-soluble vitamins | C (mg) | 81.14 | 100 | 81% | 38.48 | 100 | 38% | 70.98 | 70.9% | |
| Thiamine (mg) | 1.63 | 1.2 | 136% | 0.99 | 1.1 | 90% | 1.47 | 124.6% | ||
| Riboflavin (mg) | 1.54 | 1.5 | 103% | 1.10 | 1.2 | 92% | 1.43 | 100.2% | ||
| Niacin (mg) | 12.98 | 16 | 81% | 7.59 | 14 | 54% | 11.69 | 74.8% | ||
| B6 (mg) | 1.76 | 1.5 | 118% | 1.25 | 1.4 | 89% | 1.63 | 110.6% | ||
| Folate (folic acid) (µg) | 413.65 | 400 | 103% | 289.77 | 400 | 72% | 384.15 | 96.0% | ||
| B12 (µg) | 2.94 | 2.4 | 122% | 2.77 | 2.4 | 116% | 3.51 | 120.7% | ||
| Pantothenic acid (mg) | 4.20 | 5 | 84% | 3.22 | 5 | 64% | 3.95 | 79.2% | ||
| Biotin (µg) | 1.59 | 30 | 5% | 1.17 | 30 | 4% | 1.48 | 4.9% | ||
| Minerals | ||||||||||
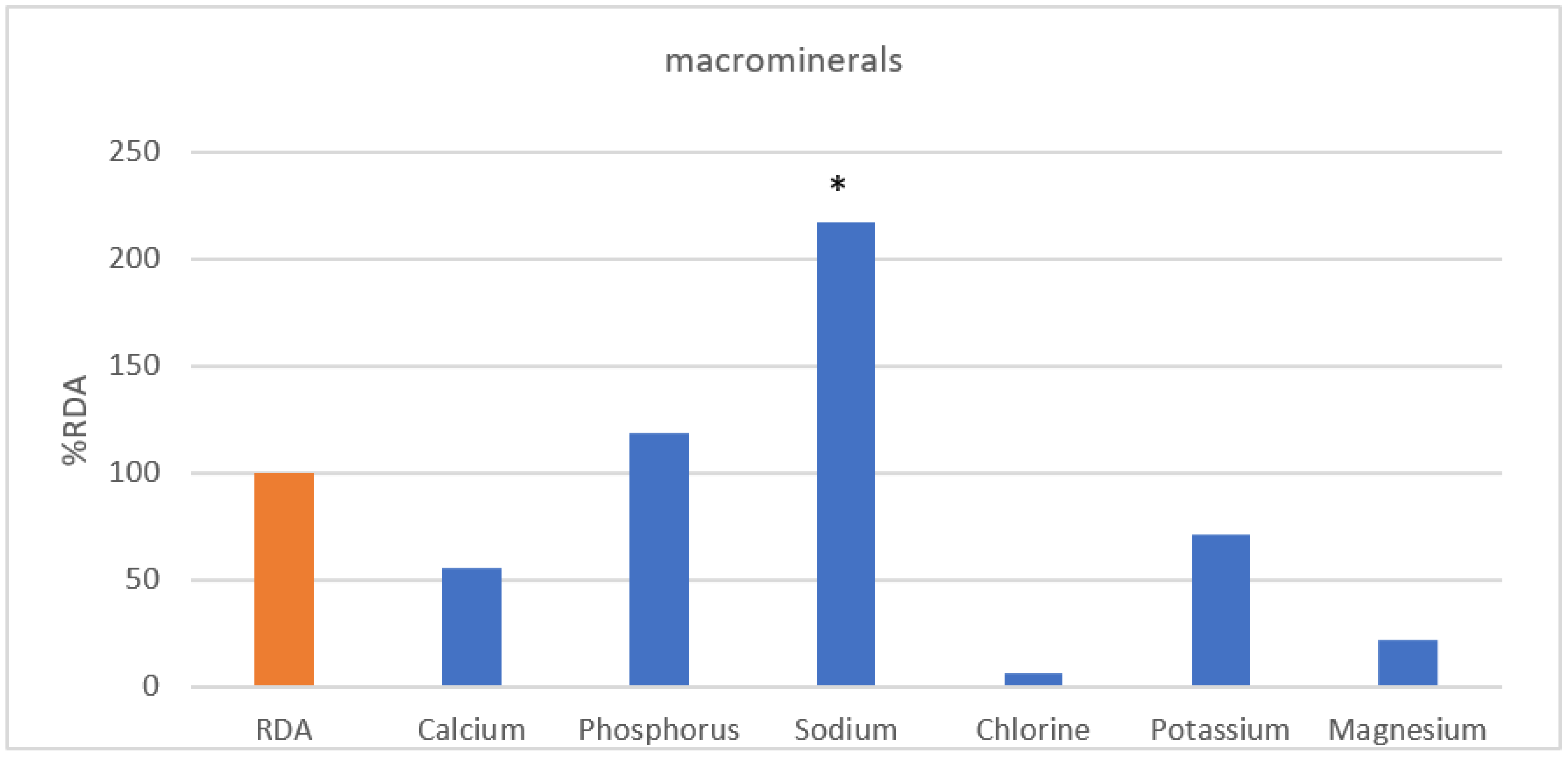
| Macrominerals | Calcium (mg) | 19–49 | 367.13 | 800 | 46% | 608.16 | 700 | 87% | 432.25 | 55.74% |
| 50–64 | 702.48 | 750 | 94% | 393.62 | 800 | 49% | ||||
| Phosphorus (mg) | 1019.19 | 700 | 146% | 701.56 | 700 | 100% | 829.27 | 118.3% | ||
| Sodium (mg) | 3439.03 | 1500 | 229% | 2643.89 | 1500 | 176% | 3249.71 | 216.6% | ||
| Chlorine (mg) | 90.78 | 2300 | 4% | 320.08 | 2300 | 14% | 145.37 | 6.3% | ||
| Potassium (mg) | 19–49 | 2321.87 | 3500 | 66% | 1776.74 | 3500 | 51% | 2297.16 | 71.3% | |
| 50–64 | 3057.48 | 2400 | 127% | |||||||
| Magnesium (mg) | 19–29 | 42.40 | 360 | 12% | 44.47 | 280 | 16% | 78.08 | 22.0% | |
| 30–64 | 99.25 | 370 | 27% | |||||||
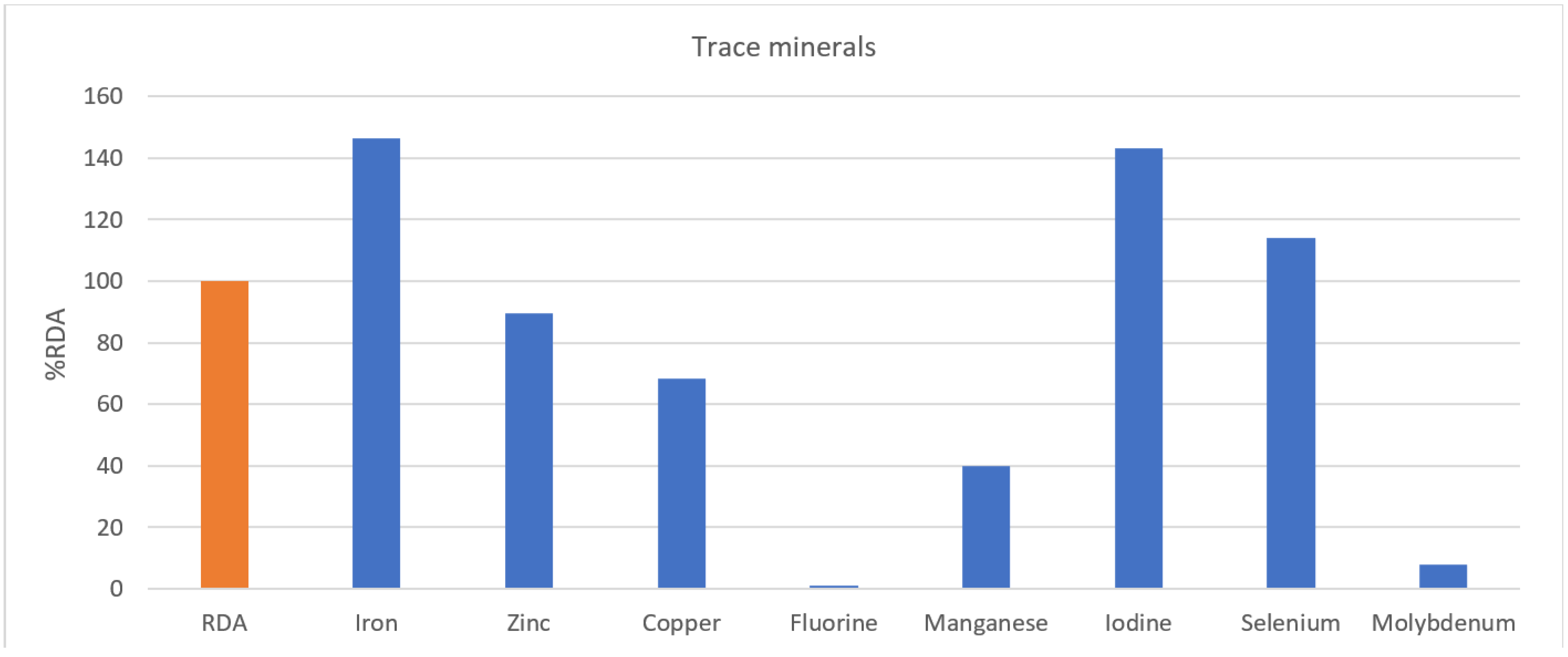
| Trace Minerals | Iron (mg) | 19–49 | 14.00 | 10 | 140% | 7.79 | 14 | 56% | 14.17 | 146.5% |
| 50–64 | 19.37 | 8 | 242% | |||||||
| Zinc (mg) | 9.34 | 10 | 93% | 6.23 | 8 | 78% | 8.59 | 89.6% | ||
| Copper (mg) | 563.04 | 850 | 66% | 484.58 | 650 | 75% | 544.36 | 68.3% | ||
| Fluorine (mg) | 19–49 | 0.06 | 3.4 | 2% | 0.01 | 2.7 | 0% | 0.04 | 1.2% | |
| 50–64 | 0.01 | 3.2 | 0% | 0.01 | 2.6 | 0% | ||||
| Manganese (µg) | 1.58 | 4 | 39% | 1.45 | 3.5 | 41% | 1.54 | 39.9% | ||
| Iodine (µg) | 238.65 | 150 | 159% | 138.46 | 150 | 92% | 214.79 | 143.2% | ||
| Selenium (µg) | 72.61 | 60 | 121% | 55.57 | 60 | 93% | 68.54 | 114.2% | ||
| Molybdenum (µg) | 19–49 | 2.23 | 30 | 7% | 3.00 | 25 | 12% | 2.13 | 7.8% | |
| 50–64 | 1.07 | 14 | 8% | |||||||
| Variables | High-Score Group (n = 10) (a) | Middle-Score Group (n = 6) (b) | Low-Score Group (n = 5) (c) | F | p | Scheffe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall NQ-A | 66.73 ± 3.40 | 51.18 ± 3.48 | 42.22 ± 1.07 | 118.399 | 0.001 ** | c < b < a |
| NQ-A components | ||||||
| Balance | 44.95 ± 15.58 | 34.91 ± 14.85 | 25.62 ± 12.66 | 2.977 | 0.076 | |
| Diversity | 66.24 ± 9.35 | 53.45 ± 10.83 | 28.82 ± 11.34 | 22.228 | 0.001 ** | c < ab |
| Moderation | 82.26 ± 9.35 | 66.01 ± 11.70 | 72.72 ± 4.31 | 5.415 | 0.014 * | b < a |
| Dietary behavior | 71.46 ± 5.97 | 46.46 ± 10.83 | 34.06 ± 8.73 | 39.573 | 0.001 ** | bc > a |
| Variables | Quotient-Adults (NQ-A) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High-Score Group (n = 10) (a) | Middle-Score Group (n = 6) (b) | Low-Score Group (n = 5) (c) | F | p | Scheffe | ||
| Macronutrient intakes (%RDA) | |||||||
| Total calories | 79.97 ± 11.85 | 62.33 ± 13.49 | 63.16 ± 13.15 | 4.908 | 0.020 * | b < a | |
| Carbohydrate | 187.30 ± 54.37 | 155.67 ± 27.33 | 139.79 ± 29.99 | 2.279 | 0.131 | ||
| Protein | 126.75 ± 45.57 | 101.00 ± 21.28 | 97.08 ± 19.32 | 1.608 | 0.228 | ||
| Dietary fiber | 78.92 ± 32.08 | 44.33 ± 12.06 | 45.72 ± 15.99 | 4.941 | 0.019 * | b < a | |
| Water | 67.00 ± 13.26 | 56.00 ± 19.62 | 53.68 ± 21.50 | 1.302 | 0.296 | ||
| Vitamins (%RDA, %AI) | |||||||
| Fat-soluble vitamins | A | 74.64 ± 54.78 | 41.67 ± 22.13 | 38.30 ± 18.54 | 1.829 | 0.189 | |
| D | 42.30 ± 28.33 | 35.00 ± 17.45 | 21.17 ± 17.24 | 1.348 | 0.285 | ||
| E | 142.35 ± 56.19 | 99.00 ± 25.63 | 67.07 ± 26.14 | 5.311 | 0.015 * | c < a | |
| K | 107.37 ± 77.47 | 84.33 ± 61.38 | 57.22 ± 42.35 | 0.962 | 0.401 | ||
| Water-soluble vitamins | C | 114.68 ± 76.64 | 35.33 ± 13.66 | 26.28 ± 14.19 | 6.050 | 0.010 ** | bc < a |
| Thiamine | 158.26 ± 57.69 | 103.83 ± 22.12 | 82.59 ± 27.77 | 5.768 | 0.012 * | c < a | |
| Riboflavin | 110.73 ± 46.61 | 92.17 ± 34.23 | 89.07 ± 11.08 | 0.735 | 0.493 | ||
| Niacin | 83.98 ± 37.65 | 77.17 ± 17.95 | 53.72 ± 22.78 | 1.696 | 0.211 | ||
| B6 | 118.16 ± 43.68 | 118.67 ± 60.16 | 86.01 ± 32.06 | 0.911 | 0.420 | ||
| Folate (folic acid) | 110.94 ± 54.85 | 97.67 ± 38.70 | 64.36 ± 24.30 | 1.768 | 0.199 | ||
| B12 | 120.50 ± 35.53 | 128.00 ± 41.78 | 120.76 ± 35.75 | 0.234 | 0.794 | ||
| Pantothenic acid | 88.83 ± 23.79 | 75.33 ± 27.26 | 64.88 ± 8.96 | 2.012 | 0.163 | ||
| Biotin | 7.44 ± 10.09 | 2.17 ± 4.83 | 3.43 ± 2.13 | 1.027 | 0.378 | ||
| Minerals (%RDA, %AI) | |||||||
| Macrominerals | Calcium | 65.89 ± 27.74 | 44.66 ± 14.88 | 48.75 ± 26.88 | 1.656 | 0.219 | |
| Phosphorus | 145.27 ± 40.91 | 108.66 ± 39.95 | 76.17 ± 21.79 | 6.027 | 0.010 ** | c < a | |
| Sodium | 259.86 ± 121.75 | 201.83 ± 44.27 | 147.86 ± 40.75 | 2.622 | 0.100 | ||
| Chlorine | 5.86 ± 6.18 | 2.17 ± 1.47 | 12.22 ± 25.05 | 0.880 | 0.432 | ||
| Potassium | 96.15 ± 42.60 | 53.83 ± 13.61 | 42.81 ± 9.95 | 6.152 | 0.009 ** | c < a | |
| Magnesium | 26.80 ± 8.72 | 22.50 ± 5.61 | 11.99 ± 4.64 | 7.107 | 0.005 ** | c < a | |
| Trace minerals | Iron | 184.45 ± 116.95 | 124.17 ± 28.65 | 97.63 ± 64.71 | 1.834 | 0.188 | |
| Zinc | 97.84 ± 25.67 | 93.17 ± 25.17 | 69.12 ± 9.01 | 2.724 | 0.093 | ||
| Copper | 78.42 ± 40.47 | 56.67 ± 11.71 | 62.13 ± 29.22 | 0.968 | 0.399 | ||
| Fluorine | 0.88 ± 2.18 | 2.50 ± 3.78 | 0.41 ± 0.43 | 1.113 | 0.350 | ||
| Manganese | 45.80 ± 39.39 | 33.17 ± 20.93 | 36.36 ± 35.50 | 0.290 | 0.752 | ||
| Iodine | 190.02 ± 205.89 | 89.17 ± 55.66 | 114.48 ± 202.98 | 0.698 | 0.511 | ||
| Selenium | 124.30 ± 58.32 | 104.53 ± 27.60 | 105.54 ± 29.22 | 0.457 | 0.640 | ||
| Molybdenum | 8.84 ± 5.63 | 6.83 ± 5.98 | 7.00 ± 4.84 | 0.316 | 0.733 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeoung, B.; Kim, J. Analysis and Evaluation of Nutritional Intake and Nutrition Quotient of Korean Athletes with Disabilities in the Tokyo Paralympic Games. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3631. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13103631
Jeoung B, Kim J. Analysis and Evaluation of Nutritional Intake and Nutrition Quotient of Korean Athletes with Disabilities in the Tokyo Paralympic Games. Nutrients. 2021; 13(10):3631. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13103631
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeoung, Bogja, and Jiyoun Kim. 2021. "Analysis and Evaluation of Nutritional Intake and Nutrition Quotient of Korean Athletes with Disabilities in the Tokyo Paralympic Games" Nutrients 13, no. 10: 3631. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13103631
APA StyleJeoung, B., & Kim, J. (2021). Analysis and Evaluation of Nutritional Intake and Nutrition Quotient of Korean Athletes with Disabilities in the Tokyo Paralympic Games. Nutrients, 13(10), 3631. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13103631







