Effectively Prescribing Oral Magnesium Therapy for Hypertension: A Categorized Systematic Review of 49 Clinical Trials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
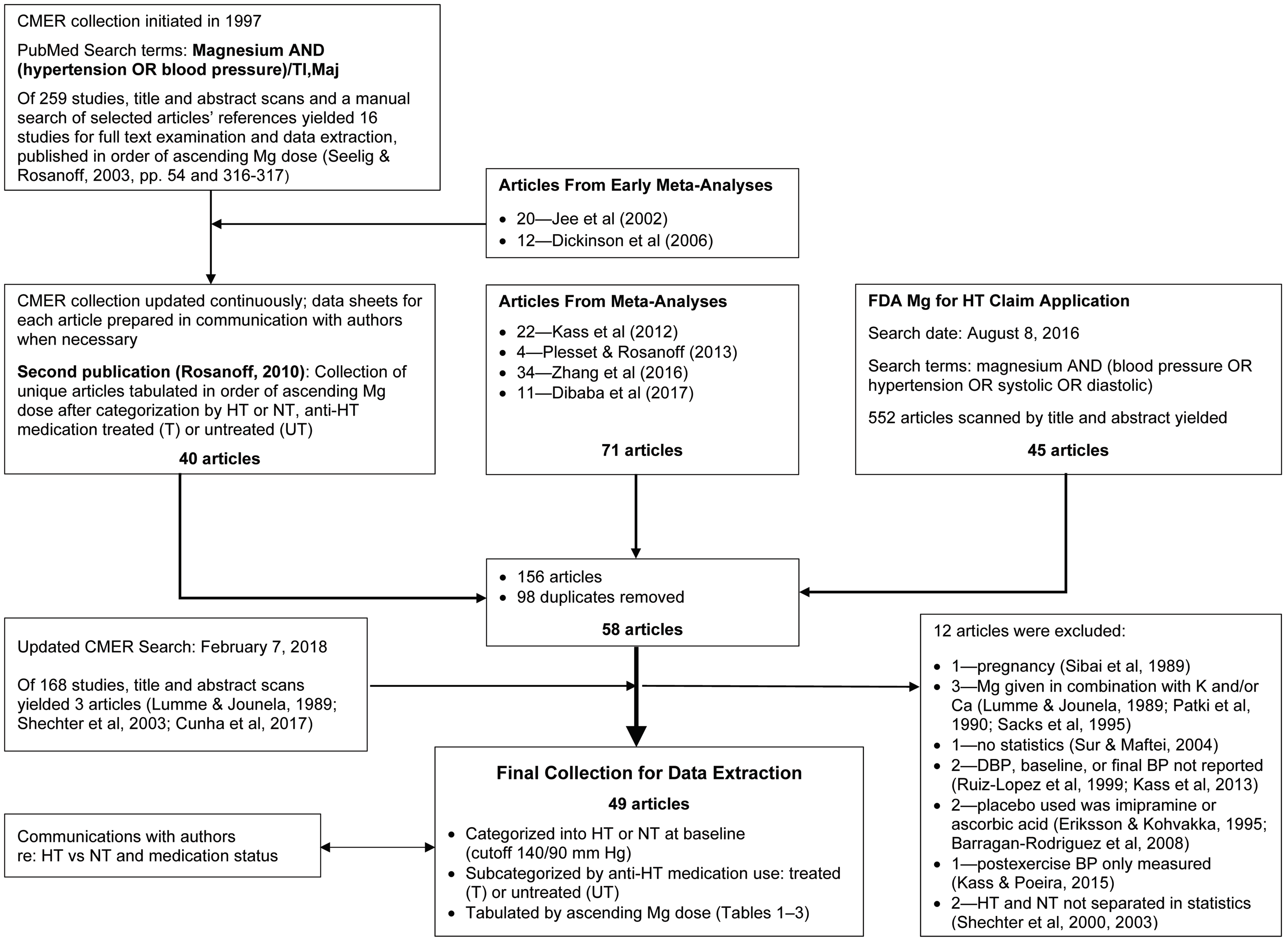
2.1. Data Sources and Searches
2.2. Study Selection
2.3. Data Extraction and Quality Assessment
2.4. Data Synthesis and Analysis
- Untreated Hypertensive, i.e., subjects were treatment naive or not using antihypertensive medications before or during the study and were hypertensive at baseline.
- Uncontrolled Hypertensive, i.e., subjects were using antihypertensive medications during and previous to the study but were still hypertensive at baseline.
- Controlled Hypertensive, i.e., subjects were using antihypertensive medications during and previous to the study and were normotensive at baseline.
- Normotensive subjects, untreated with antihypertensive medications plus normotensive at baseline.
2.5. Role of the Funding Source
3. Results
3.1. Blood Pressure Outcomes with Oral Mg Therapy
3.2. Other Cardiovascular Risk Factors
3.3. Form of Magnesium
3.4. Magnesium-Replete Subjects
3.5. Treated or Untreated Normotensive Subjects
3.6. Side Effects of Oral Magnesium Therapy in These Studies
3.7. Safety of Magnesium Doses in Effective Range
3.8. How Does This Analysis Build Upon Existing Meta-analyses?
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lim, S.S.; Vos, T.; Flaxman, A.D.; Danaei, G.; Shibuya, K.; Adair-Rohani, H.; AlMazroa, M.A.; Amann, M.; Anderson, H.R.; Andrews, K.G.; et al. A comparative risk assessment of burden of disease and injury attributable to 67 risk factors and risk factor clusters in 21 regions, 1990–2010: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012, 380, 2224–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forouzanfar, M.H.; Liu, P.; Roth, G.A.; Ng, M.; Biryukov, S.; Marczak, L.; Alexander, L.; Estep, K.; Abate, K.H.; Akinyemiju, T.F.; et al. Global Burden of Hypertension and Systolic Blood Pressure of at Least 110 to 115 mm Hg, 1990–2015. JAMA 2017, 317, 165–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danaei, G.; Ding, E.L.; Mozaffarian, D.; Taylor, B.; Rehm, J.; Murray, C.J.L.; Ezzati, M. The Preventable Causes of Death in the United States: Comparative Risk Assessment of Dietary, Lifestyle, and Metabolic Risk Factors. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilt, T.J.; Kansagara, D.; Qaseem, A.; Clinical Guidelines Committee of the American College of Physicians. Hypertension Limbo: Balancing Benefits, Harms, and Patient Preferences Before We Lower the Bar on Blood Pressure. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 168, 369–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whelton, P.K.; Carey, R.M.; Aronow, W.S.; Casey, D.E., Jr.; Collins, K.J.; Dennison Himmelfarb, C.; DePalma, S.M.; Gidding, S.; Jamerson, K.A.; Jones, D.W.; et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA Guideline for the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults: Executive Summary: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Hypertension 2018, 71, 1269–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioannidis, J.P.A. Diagnosis and Treatment of Hypertension in the 2017 ACC/AHA Guidelines and in the Real World. JAMA 2018, 319, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muntner, P.; Carey, R.M.; Gidding, S.; Jones, D.W.; Taler, S.J.; Wright, J.T.; Whelton, P.K. Potential US Population Impact of the 2017 ACC/AHA High Blood Pressure Guideline. Circulation 2018, 137, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carey, R.M.; Whelton, P.K. Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults: Synopsis of the 2017 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Hypertension Guideline. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 168, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosanoff, A.; Plesset, M.R. Oral magnesium supplements decrease high blood pressure (SBP > 155mmHg) in hypertensive subjects on anti-hypertensive medications: A targeted meta-analysis. Magnes. Res. 2013, 26, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibaba, D.T.; Xun, P.; Song, Y.; Rosanoff, A.; Shechter, M.; He, K. The effect of magnesium supplementation on blood pressure in individuals with insulin resistance, prediabetes, or noncommunicable chronic diseases: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 106, 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, H.O.; Nicolson, D.; Campbell, F.; Cook, J.V.; Beyer, F.R.; A Ford, G.; Mason, J. Magnesium supplementation for the management of primary hypertension in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2006, 3, CD004640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jee, S.H.; Miller, E.R.; Guallar, E.; Singh, V.K.; Appel, L.J.; Klag, M.J. The effect of magnesium supplementation on blood pressure: A meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Am. J. Hypertens. 2002, 15, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kass, L.S.; Weekes, J.; Carpenter, L.W. Effect of magnesium supplementation on blood pressure: A meta-analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 66, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Del Gobbo, L.C.; Rosanoff, A.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W.; Song, Y. Effects of Magnesium Supplementation on Blood Pressure. Hypertension 2016, 68, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costello, R.B.; Rosanoff, A. Magnesium. In Present Knowledge in Nutrition, 11th ed.; Basic Nutrition and Metabolism; Marriott, B., Birt, D.F., Stalling, V., Yates, A., Eds.; ILSI-Academic Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2020; pp. 349–373. [Google Scholar]
- Rosique-Esteban, N.; Guasch-Ferré, M.; Hernandez-Alonso, P.; Salas-Salvadó, J. Dietary Magnesium and Cardiovascular Disease: A Review with Emphasis in Epidemiological Studies. Nutrients 2018, 10, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champagne, C. Magnesium in Hypertension, Cardiovascular Disease, Metabolic Syndrome, and Other Conditions: A Review. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2008, 23, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Center for Magnesium Education and Research LLC. Petition for the Authorization of a Qualified Health Claim for Magne-sium and Reduced Risk of High Blood Pressure (Hypertension) (FDA Docket ID FDA-2016-Q-3770). Available online: https://www.noticeandcomment.com/FDA-2016-Q-3770-fdt-138630.aspx (accessed on 30 March 2018).
- Seelig, M.S.; Rosanoff, A. The Magnesium Factor; Avery Penguin Group: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Rosanoff, A. Magnesium supplements may enhance the effect of antihypertensive medications in stage 1 hypertensive subjects. Magnes. Res. 2010, 23, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patki, P.S.; Singh, J.; Gokhale, S.V.; Bulakh, P.M.; Shrotri, D.S.; Patwardhan, B. Efficacy of potassium and magnesium in essential hypertension: A double-blind, placebo controlled, crossover study. BMJ 1990, 301, 521–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibai, B.M.; A Villar, M.; Bray, E.; L, M.A.V. Magnesium supplementation during pregnancy: A double-blind randomized controlled clinical trial. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1989, 161, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacks, F.M.; Brown, L.E.; Appel, L.; Borhani, N.O.; Evans, D.; Whelton, P. Combinations of Potassium, Calcium, and Magnesium Supplements in Hypertension. Hypertension 1995, 26, 950–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumme, J.A.; Jounela, A.J. The effect of potassium and potassium plus magnesium supplementation on ventricular extrasystoles in mild hypertensives treated with hydrochlorothiazide. Int. J. Cardiol. 1989, 25, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sur, G.; Maftei, O. Role of magnesium in essential hypertension in teenagers. In Advances in Magnesium Research—New Data; Porr, P.J., Nechifor, M., Durlack, J., Eds.; John Libbey Eurotext: Montrouge, France, 2006; pp. 55–60. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-López, M.; Gil-Extremera, B.; Maldonado-Martín, A.; Huertas-Hernández, F.; Ceballos-Atienza, R.; Muñoz-Parra, F.; Cruz-Benayas, M.; León-Espinosa-Monteros, M.; Cobo-Martínez, F.; Soto-Mas, J. Blood pressure and metabolic syndrome in essential hypertensive patients treated with losartan or verapamil after oral magnesium supplement. Am. J. Hypertens. 1999, 4, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, J.; Kohvakka, A. Magnesium and Ascorbic Acid Supplementation in Diabetes mellitus. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 1995, 39, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barragán-Rodríguez, L.; Rodríguez-Morán, M.; Guerrero-Romero, F. Efficacy and safety of oral magnesium supplementation in the treatment of depression in the elderly with type 2 diabetes: A randomized, equivalent trial. Magnes. Res. 2008, 21, 218–223. [Google Scholar]
- Kass, L.S.; Poeira, F. The effect of acute vs chronic magnesium supplementation on exercise and recovery on resistance exercise, blood pressure and total peripheral resistance on normotensive adults. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2015, 12, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kass, L.S.; Skinner, P.; Poeira, F. A Pilot Study on the Effects of Magnesium Supplementation with High and Low Habitual Dietary Magnesium Intake on Resting and Recovery from Aerobic and Resistance Exercise and Systolic Blood Pressure. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2013, 12, 144–150. [Google Scholar]
- Shechter, M.; Sharir, M.; Labrador, M.J.P.; Forrester, J.; Silver, B.; Merz, C.N.B. Oral Magnesium Therapy Improves Endothelial Function in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease. Circulation 2000, 102, 2353–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shechter, M.; Merz, C.B.; Stuehlinger, H.-G.; Slany, J.; Pachinger, O.; Rabinowitz, B. Effects of Oral Magnesium Therapy on Exercise Tolerance, Exercise-Induced Chest Pain, and Quality of Life in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease. Am. J. Cardiol. 2003, 91, 517–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Del Gobbo, L.C.; Hruby, A.; Rosanoff, A.; He, K.; Dai, Q.; Costello, R.B.; Zhang, W.; Song, Y. The Circulating Concentration and 24-h Urine Excretion of Magnesium Dose- and Time-Dependently Respond to Oral Magnesium Supplementation in a Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Nutr. 2016, 146, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosanoff, A. Importance of magnesium dose in the treatment of hypertension. In Advances in Magnesium Research: New Data; Porr, P., Nechifor, M., Durlach, J., Eds.; Libbey Eurotext: Montrouge, France, 2006; pp. 97–104. [Google Scholar]
- Rosanoff, A. Magnesium and hypertension. Clin. Calcium 2005, 15, 255–260. [Google Scholar]
- Rosanoff, A. Importance of dosage and experimental design in trials testing the effect of magnesium supplementation on hypertension. In Proceedings of the European Magnesium Congress, Cluj-Napoca, Romania, 25–28 May 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Seelig, M.S.; Rosanoff, A. High blood pressure, salt and magnesium. In The Magnesium Factor; Avery Penguin Group: New York, NY, USA, 2003; pp. 50–84, 315–324. [Google Scholar]
- Rosanoff, A. Changing crop magnesium concentrations: Impact on human health. Plant Soil 2013, 368, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosanoff, A.; Weaver, C.M.; Rude, R.K. Suboptimal magnesium status in the United States: Are the health consequences underestimated? Nutr. Rev. 2012, 70, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrello, G.; Mastroroberto, P.; Curcio, F.; Chello, M.; Zofrea, S.; Mazza, M.L. The effects of magnesium oxide on mild essential hypertension and quality of life. Curr. Ther. Res. 1996, 57, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowson, C.; Morgan, T.O. Magnesium supplementation in mild hypertensive patients on a moderately low sodium diet. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 1989, 16, 299–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, L.A.; Iannuzzi, R.; Castaldo, A.; Iannuzzi, A.; Russo, A.D.; Mancini, M. Long-Term Magnesium Supplementation in Essential Hypertension. Cardiology 1992, 81, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lind, L.; Lithell, H.; Pollare, T.; Ljunghall, S. Blood Pressure Response During Long-Term Treatment With Magnesium Is Dependent on Magnesium Status. Am. J. Hypertens. 1991, 4, 674–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Valk, H.W.; Verkaaik, R.; van Rijn, H.J.; Geerdink, R.A.; Struyvenberg, A. Oral magnesium supplementation in insu-lin-requiring type 2 diabetic patients. Diabet. Med. 1998, 15, 503–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plum-Wirell, M.; Stegmayr, B.G.; O Wester, P. Nutritional magnesium supplementation does not change blood pressure nor serum or muscle potassium and magnesium in untreated hypertension. A double-blind crossover study. Magnes. Res. 1994, 7, 277–283. [Google Scholar]
- Wirell, M.M.; Wester, P.O.; Stegmayr, B.G. Nutritional dose of magnesium given to short-term thiazide treated hypertensive patients does not alter the blood pressure or the magnesium and potassium in muscle-A double blind cross-over study. Magnes. Bull. 1993, 15, 50–54. [Google Scholar]
- Cappuccio, F.P.; Markandu, N.D.; Beynon, G.W.; Shore, A.C.; Sampson, B.; A MacGregor, G. Lack of effect of oral magnesium on high blood pressure: A double-blind study. BMJ 1985, 291, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbagallo, M.; Dominguez, L.; Galioto, A.; Pineo, A.; Belvedere, M. Oral magnesium supplementation improves vascular function in elderly diabetic patients. Magnes. Res. 2010, 23, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reyes, A.J.; Leary, W.P.; Acosta-Barrios, T.N.; Davis, W.H. Magnesium supplementation in hypertension treated with hy-drochlorothiazide. Curr. Ther. Res. 1984, 36, 332–340. [Google Scholar]
- Olhaberry, J.; Reyes, A.J.; Acosta-Barrios, T.N.; Leary, W.P.; Queiruga, G. Pilot evaluation of the putative antihypertensive effect of magnesium. Magnes. Bull. 1987, 9, 181–184. [Google Scholar]
- Purvis, J.R. Effect of oral magnesium supplementation on selected cardiovascular risk factors in non-insulin-dependent diabetics. Arch. Fam. Med. 1994, 3, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, L.; Laor, A.; Kitzes, R. Reversible retinal vasospasm in magnesium-treated hypertension despite no significant change in blood pressure. Magnesium 1984, 3, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Witteman, J.C.; E Grobbee, D.; Derkx, F.H.; Bouillon, R.; De Bruijn, A.M.; Hofman, A. Reduction of blood pressure with oral magnesium supplementation in women with mild to moderate hypertension. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1994, 60, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, A.F.; Marakis, G.; Morris, A.P.; Robinson, P.A. Promising hypotensive effect of hawthorn extract: A randomized double-blind pilot study of mild, essential hypertension. Phytother. Res. 2002, 16, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haga, H. Effects of Dietary Magnesium Supplementation on Diurnal Variations of Blood Pressure and Plasma Na+, K+-ATPase Activity in Essential Hypertension. Jpn. Heart J. 1992, 33, 785–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Motoyama, T.; Sano, H.; Fukuzaki, H. Oral magnesium supplementation in patients with essential hypertension. Hypertension 1989, 13, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjuliani, A.F.; Fagundes, V.G.D.A.; Francischetti, E.A. Effects of magnesium on blood pressure and intracellular ion levels of Brazilian hypertensive patients. Int. J. Cardiol. 1996, 56, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemel, P.C.; Zemel, M.; Urberg, M.; Douglas, F.L.; Geiser, R.; Sowers, J.R. Metabolic and hemodynamic effects of magnesium supplementation in patients with essential hypertension. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1990, 51, 665–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widman, L.; Wester, P.; Stegmayr, B.; Wirell, M. The Dose-Dependent Reduction in Blood Pressure Through Administration of Magnesium A Double Blind Placebo Controlled Cross-Over Study. Am. J. Hypertens. 1993, 6, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafique, M.; Misbah ul, A.; Ashraf, M. Role of magnesium in the management of hypertension. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 1993, 43, 77–78. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sebeková, K.; Revúsová, V.; Polakovicová, D.; Drahosová, J.; Zverková, D.; Dzúrik, R. Anti-hypertensive treatment with magnesium-aspartate-dichloride and its influence on peripheral serotonin metabolism in man: A subacute study. Cor et Vasa 1992, 34, 390–401. [Google Scholar]
- Michoń, P. Level of total and ionized magnesium fraction based on biochemical analysis of blood and hair and effect of supplemented magnesium (Slow Mag B6) on selected parameters in hypertension of patients treated with various groups of drugs. Ann. Acad. Med. Stetin. 2002, 48, 85–97. [Google Scholar]
- Wirell, M.P.; Wester, P.O.; Stegmayr, B. Nutritional dose of magnesium in hypertensive patients on beta blockers lowers systolic blood pressure: A double-blind, cross-over study. J. Intern. Med. 1994, 236, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyckner, T.; O Wester, P. Effect of magnesium on blood pressure. BMJ 1983, 286, 1847–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolisso, G.; Di Maro, G.; Cozzolino, D.; Salvatore, T.; D’Amore, A.; Lama, D.; Varricchio, M.; D’Onofrio, F. Chronic Maenesium Administration Enhances Oxidative Glucose Metabolism in Thiazide Treated Hypertensive Patients. Am. J. Hypertens. 1992, 5, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Romero, F.; Rodriguez-Moran, M. The effect of lowering blood pressure by magnesium supplementation in diabetic hy-pertensive adults with low serum magnesium levels: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2009, 23, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawano, Y.; Matsuoka, H.; Takishita, S.; Omae, T. Effects of Magnesium Supplementation in Hypertensive Patients. Hypertension 1998, 32, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, A.R.; D’El-Rei, J.; Medeiros, F.; Umbelino, B.; Oigman, W.; Touyz, R.M.; Neves, M.F. Oral magnesium supplementation improves endothelial function and attenuates subclinical atherosclerosis in thiazide-treated hypertensive women. J. Hypertens. 2017, 35, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattori, K.; Saito, K.; Sano, H.; Fukuzaki, H. Intracellular magnesium deficiency and effect of oral magnesium on blood pressure and red cell sodium transport in diuretic-treated hypertensive patients. Jpn. Circ. J. 1988, 52, 1249–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, D.G.; Schierup, J.; Schodt, T. Effect of magnesium supplementation on blood pressure and electrolyte concentrations in hypertensive patients receiving long term diuretic treatment. BMJ 1986, 293, 664–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Itoh, K.; Kawasaki, T.; Nakamura, M. The effects of high oral magnesium supplementation on blood pressure, serum lipids and related variables in apparently healthy Japanese subjects. Br. J. Nutr. 1997, 78, 737–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doyle, L.; Flynn, A.; Cashman, K. The effect of magnesium supplementation on biochemical markers of bone metabolism or blood pressure in healthy young adult females. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 53, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Park, H.; Son, S.; Lee, C.W.; Kim, I.; Kim, H. Effects of oral magnesium supplementation on insulin sensitivity and blood pressure in normo-magnesemic nondiabetic overweight Korean adults. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2009, 19, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrero-Romero, F.; E Tamez-Perez, H.; González-González, G.; Salinas-Martínez, A.M.; Montes-Villarreal, J.; Treviño-Ortiz, J.H.; Rodríguez-Morán, M. Oral Magnesium supplementation improves insulin sensitivity in non-diabetic subjects with insulin resistance. A double-blind placebo-controlled randomized trial. Diabetes Metab. 2004, 30, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacks, F.M.; Willett, W.C.; Smith, A.; Brown, L.E.; Rosner, B.; Moore, T.J. Effect on blood pressure of potassium, calcium, and magnesium in women with low habitual intake. Hypertension 1998, 31, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joris, P.J.; Plat, J.; Bakker, S.J.L.; Mensink, R.P. Long-term magnesium supplementation improves arterial stiffness in overweight and obese adults: Results of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled intervention trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 1260–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whelton, P.K.; Appel, L.; Charleston, J.; Dalcin, A.T.; Ewart, C.; Fried, L.; Kaidy, D.; Klag, M.J.; Kumanyika, S.; Steffen, L.; et al. The Effects of Nonpharmacologic Interventions on Blood Pressure of Persons with High Normal Levels. JAMA 1992, 267, 1213–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooren, F.C.; Krüger, K.; Völker, K.; Golf, S.W.; Wadepuhl, M.; Kraus, A. Oral magnesium supplementation reduces insulin resistance in non-diabetic subjects - a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2011, 13, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simental-Mendía, L.E.; Rodríguez-Morán, M.; Guerrero-Romero, F. Oral Magnesium Supplementation Decreases C-reactive Protein Levels in Subjects with Prediabetes and Hypomagnesemia: A Clinical Randomized Double-blind Placebo-controlled Trial. Arch. Med. Res. 2014, 45, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simental-Mendía, L.E.; Rodríguez-Morán, M.; Reyes-Romero, M.A.; Guerrero-Romero, F. No positive effect of oral magnesium supplementation in the decreases of inflammation in subjects with prediabetes: A pilot study. Magnes. Res. 2012, 25, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Moran, M.; Guerrero-Romero, F. Oral Magnesium Supplementation Improves the Metabolic Profile of Metabolically Obese, Normal-weight Individuals: A Randomized Double-blind Placebo-controlled Trial. Arch. Med. Res. 2014, 45, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosaro, E.; Bonafini, S.; Montagnana, M.; Danese, E.; Trettene, M.; Minuz, P.; Delva, P.; Fava, C. Effects of magnesium supplements on blood pressure, endothelial function and metabolic parameters in healthy young men with a family history of metabolic syndrome. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2014, 24, 1213–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Morán, M.; Guerrero-Romero, F. Oral Magnesium Supplementation Improves Insulin Sensitivity and Metabolic Control in Type 2 Diabetic Subjects: A randomized double-blind controlled trial. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 1147–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Hernandez, H.; Cervantes-Huerta, M.; Rodríguez-Morán, M.; Guerrero-Romero, F. Oral magnesium supplementation decreases alanine aminotransferase levels in obese women. Magnes. Res. 2010, 23, 90–96. [Google Scholar]
- Daly, N.M.; Allen, K.G.D.; Harris, M. Magnesium supplementation and blood pressure in borderline hypertensive subjects: A double blind study. Magnes. Bull. 1990, 12, 149–154. [Google Scholar]
- Kisters, K.; Spieker, C.; Tepel, M.; Zidek, W. New data about the effects of oral physiological magnesium supplementation on several cardiovascular risk factors (lipids and blood pressure). Magnes. Res. 1993, 6, 355–360. [Google Scholar]
- Wary, C.; Brillault-Salvat, C.; Bloch, G.; Leroy-Willig, A.; Roumenov, D.; Grognet, J.M.; Leclerc, J.H.; Carlier, P.G. Effect of chronic magnesium supplementation on magnesium distribution in healthy volunteers evaluated by 31 P-NMRS and ion selective electrodes. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1999, 48, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Romero, F.; Rodríguez-Morán, M. Magnesium improves the beta-cell function to compensate variation of insulin sensitivity: Double-blind, randomized clinical trial. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 41, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Institute of Medicine (US) Standing Committee on the Scientific Evaluation of Dietary Reference Intakes. Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium, Phosphorus, Magnesium, Vitamin D, and Fluoride; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1997.
- Rosanoff, A. Perspective: US adult magnesium requirements need updating: Impacts of rising body weights and data-derived variance. Adv. Nutr. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turlapaty, P.; Altura, B. Magnesium deficiency produces spasms of coronary arteries: Relationship to etiology of sudden death ischemic heart disease. Science 1980, 208, 198–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolte, D.; Vijayaraghavan, K.; Khera, S.; Sica, D.A.; Frishman, W.H. Role of Magnesium in Cardiovascular Diseases. Cardiol. Rev. 2014, 22, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touyz, R.M. Transient receptor potential melastatin 6 and 7 channels, magnesium transport, and vascular biology: Implications in hypertension. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2008, 294, H1103–H1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kass, L.; Sullivan, K.R. Low Dietary Magnesium Intake and Hypertension. World J. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2016, 6, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute of Medicine (US) Food Forum. Providing Healthy and Safe Foods as We Age; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21391340/ (accessed on 15 May 2020).
- Blumberg, J.B.; Frei, B.; Fulgoni, V.L.; Weaver, C.; Zeisel, S.H. Contribution of Dietary Supplements to Nutritional Adequacy in Various Adult Age Groups. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Department of Agriculture; US Department of Health and Human Services. Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 2015–2020, 8th ed. Available online: https://health.gov/dietaryguidelines/2015/resources/2015-2020_Dietary_Guidelines.pdf (accessed on 7 March 2018).
- Greenland, P. Cardiovascular Guideline Skepticism vs Lifestyle Realism? JAMA 2018, 319, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez, L.J.; Veronese, N.; Barbagallo, M. Magnesium and Hypertension in Old Age. Nutrients 2020, 13, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Study Citation | Mg Dose, mg/day | Form of Mg | BP Status at Baseline, NT or HT | Medical Status at Baseline, T or UT | BP Outcome 1 | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Borrello et al. (1996) [40] | 120 | MgO | HT | UT | No change 2 | Decrease in SBP only |
| Nowson and Morgan (1989) [41] | 240 | Aspartate | HT | UT | No change | |
| Ferrara et al. (1992) [42] | 365 | Pidolate | HT | UT | No change | |
| Lind et al. (1991) [43] | 365 | Lactate and citrate | HT | UT | No change 2,3 | |
| de Valk et al. (1998) [44] | 365 | Aspartate HCl | HT | UT | No change 2 | |
| Plum-Wirell et al. (1994) [45] | 365 | Aspartate | HT | UT | No change | |
| Wirell et al. (1993) [46] | 365 | Aspartate | HT | UT | No change 2 | |
| Cappuccio et al. (1985) [47] | 365 | Aspartate | HT | UT | No change 2 | Decrease in DBP only; medication interrupted 2–3 months pre-study |
| Barbagallo et al. (2010) [48] | 368 | Pidolate | HT | UT | No change 2,4 | Baseline BP: 150/82 mm Hg; some perhaps taking medications |
| Reyes et al. (1984) [49] | 384 | MgCl2 | HT | UT | No change | Decrease in DBP only; medication interrupted 4 weeks pre-study |
| Olhaberry et al. (1987) [50] | 384 | MgCl2 | HT | UT | No change | Decrease in SBP only |
| Purvis et al. (1994) [51] | 389 | MgCl2 | HT | UT | No change | Decrease in SBP only |
| Cohen et al. (1984) [52] | 450 | MgO | HT | UT | No change 2,5,6 | |
| Witteman et al. (1994) [53] | 486 | Aspartate HCl | HT | UT | No change | Decrease in DBP only |
| Walker et al. (2002) [54] | 607 | Amino acid chelate | HT | UT | No change | Mg replete 7 |
| Haga (1992) [55] | 607 | MgO | HT | UT | Decrease 6 | MBP measured in HT vs. NT “control” 8 |
| Motoyama et al. (1989) [56] | 607 | MgO | HT | UT | Decrease 6 | No medications during study or 1 month pre-study, at least |
| Sanjuliani et al. (1996) [57] | 607 | MgO | HT | UT | Decrease | No medications 2 weeks pre-study or during study |
| Zemel et al. (1990) [58] | 972 | Aspartate | HT | UT | No change | Mg replete 9; no medications 3 mo pre-study at least |
| Widman et al. (1993) [59] | 365 | Mg(OH)2 | HT | UT | No change | Only titrated Mg dose study |
| 729 | Mg(OH)2 | HT | UT | Decrease 10 | ||
| 972 | Mg(OH)2 | HT | UT | Decrease |
| Study Citation | Mg Dose, mg/day | Form of Mg | BP Status at Baseline, NT or HT | Medical Status at Baseline, T or UT | BP Outcome 1 | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shafique et al. (1993) [60] | 240 | MgCl2 | HT | T | Decrease 2 | Diuretics >1 year |
| Sebekova et al. (1992) [61] | 255 | Aspartate HCl | HT | T | Decrease 2 | Interrupted medications |
| Michon (2002) [62] | 323 | Slow-mag/B6 | HT | T | Decrease 2 | Beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, calcium channel blockers, diuretics |
| Wirell et al. (1994) [63] | 365 | Aspartate | HT | T | Decrease | Beta-blockers |
| Dyckner and Wester (1983) [64] | 365 | Aspartate HCl | HT | T | Decrease | Beta-blockers |
| Paolisso et al. (1992) [65] | 384 | Pidolate | HT | T | Decrease 3 | Thiazide diuretics—long term |
| Guerrero-Romero and Rodriguez-Moran (2009) [66] | 450 | MgCl2 | HT | T | Decrease | All taking medications ≥6 months pre-study, type not specified |
| Kawano et al. (1998) [67] | 486 | MgO | HT | T | Decrease | 33% untreated; 30% monotherapy; 37% combination therapy; therapy included calcium channel blockers, beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, thiazides, spironolactone, alpha-blockers |
| Cunha et al. (2017) [68] | 600 | Mg chelate | HT | T | Decrease | Hydrochlorothiazide |
| Hattori et al. (1988) [69] | 607 | MgO | HT | T | Decrease 4 | Thiazide diuretics—long term |
| NT | T | No change 4 | Thiazide diuretics—long term |
| Study Citation | Mg Dose, mg/day | Form of Mg | BP Status at Baseline, NT or HT | Medical Status at Baseline, T or UT | BP Outcome 1 | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Henderson et al. (1986) [70] | 304 | MgO | NT | T | No change | Potassium depleting diuretics ≥ 6 months |
| Itoh et al. (1997) [71] | 413–583 | Mg(OH)2 | NT | T and UT | No change 2,3 | Some subjects were borderline HT; medications kept constant “when necessary” (medications not specified) |
| Study Citation | Mg Dose, mg/day | Form of Mg | BP Status at Baseline, NT or HT | Medical Status at Baseline, T or UT | BP Outcome 1 | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Doyle et al. (1999) [72] | 250 | Mg(OH)2 | NT | UT | No change | |
| Lee et al. (2009) [73] | 300 | MgO | NT | Unknown | No change | |
| Guerrero-Romero et al. (2004) [74] | 304 | MgCl2 | NT | UT | No change | |
| Sacks et al. (1998) [75] | 340 | Lactate | NT | UT | No change | |
| Joris et al. (2016) [76] | 350 | Citrate | NT | UT | No change | Overweight, healthy |
| TOHP Study Group (1992) [77] | 365 | Diglycine | NT | UT | No change | |
| Mooren et al. (2011) [78] | 365 | Aspartate HCl | NT | Not reported | No change | |
| Simental-Mendia et al. (2014) [79] | 382 | MgCl2 | NT | UT | No change | |
| Simental-Mendia et al. (2012) [80] | 382 | MgCl2 | NT | UT | No change | |
| Rodriguez-Moran and Guerrero-Romero (2014) [81] | 381 | MgCl2 | NT | UT | No change 2 | Hyperglycemic, insulin resistant, hypertriglyceridemic, hypomagnesemic, normal weight |
| Cosaro et al. (2014) [82] | 394 | Pidolate | NT | UT | No change | |
| Rodriguez-Moran and Guerrero-Romero (2003) [83] | 450 | MgCl2 | Borderline HT/NT | UT | No change | |
| Rodriguez-Hernandez et al. (2010) [84] | 450 | MgCl2 | NT | UT | No change | |
| Daly et al. (1990) [85] | 500 | MgO | NT | UT | No change | |
| Kisters et al. (1993) [86] | 505 | Aspartate | NT | UT | No change | |
| Wary et al. (1999) [87] | 600 | Lactate + B6 | NT | UT | No change | |
| Guerrero-Romero and Rodriguez-Moran (2011) [88] | 632 | MgCl2 | NT | UT | No change 3 | Subjects had low serum Mg that normalized with Mg therapy |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rosanoff, A.; Costello, R.B.; Johnson, G.H. Effectively Prescribing Oral Magnesium Therapy for Hypertension: A Categorized Systematic Review of 49 Clinical Trials. Nutrients 2021, 13, 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13010195
Rosanoff A, Costello RB, Johnson GH. Effectively Prescribing Oral Magnesium Therapy for Hypertension: A Categorized Systematic Review of 49 Clinical Trials. Nutrients. 2021; 13(1):195. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13010195
Chicago/Turabian StyleRosanoff, Andrea, Rebecca B. Costello, and Guy H. Johnson. 2021. "Effectively Prescribing Oral Magnesium Therapy for Hypertension: A Categorized Systematic Review of 49 Clinical Trials" Nutrients 13, no. 1: 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13010195
APA StyleRosanoff, A., Costello, R. B., & Johnson, G. H. (2021). Effectively Prescribing Oral Magnesium Therapy for Hypertension: A Categorized Systematic Review of 49 Clinical Trials. Nutrients, 13(1), 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13010195





