Eating Fast Has a Significant Impact on Glycemic Excursion in Healthy Women: Randomized Controlled Cross-Over Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
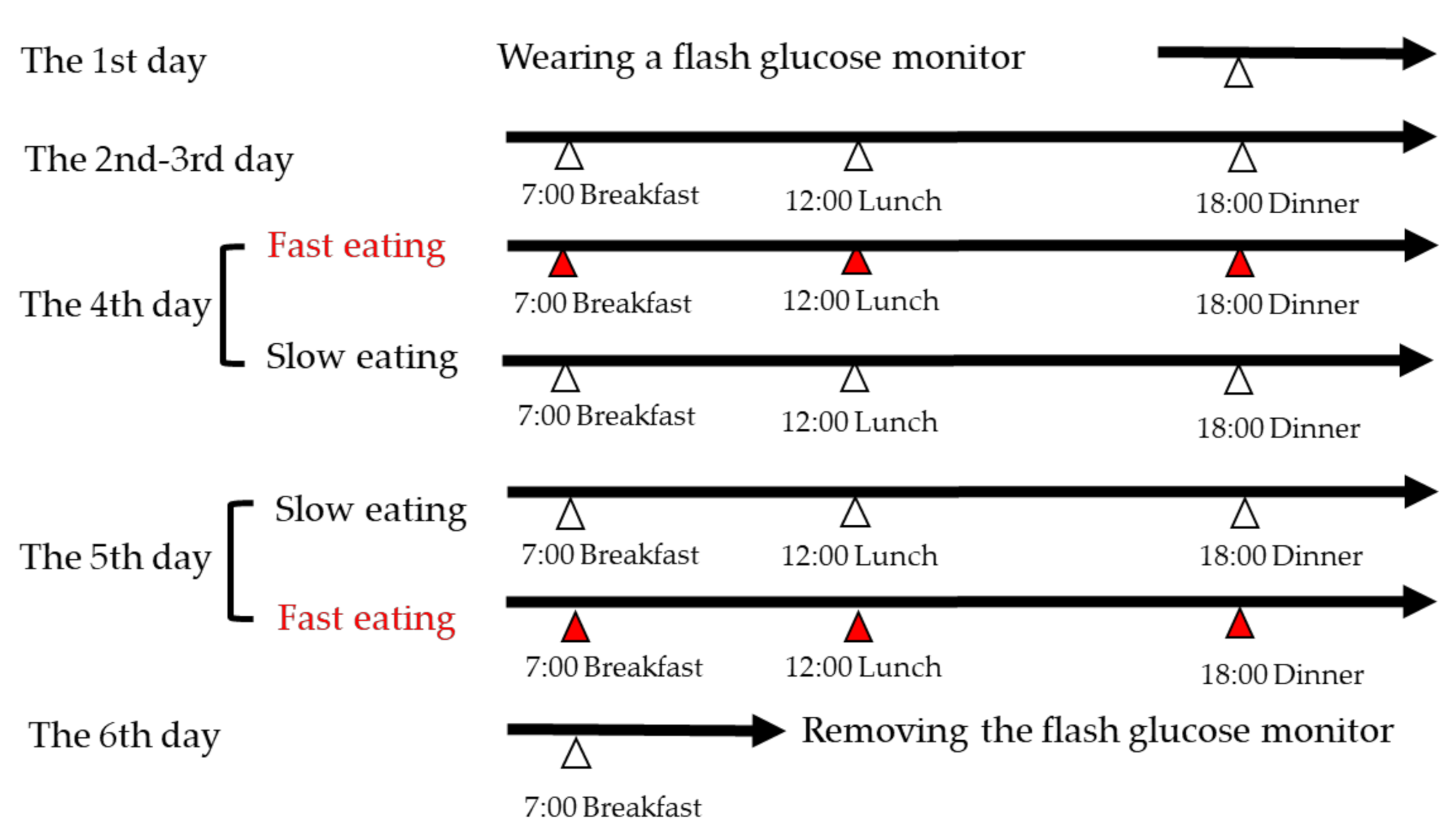
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Test Meals
2.4. Measurements
2.5. Sample Size and Statistical Analysis
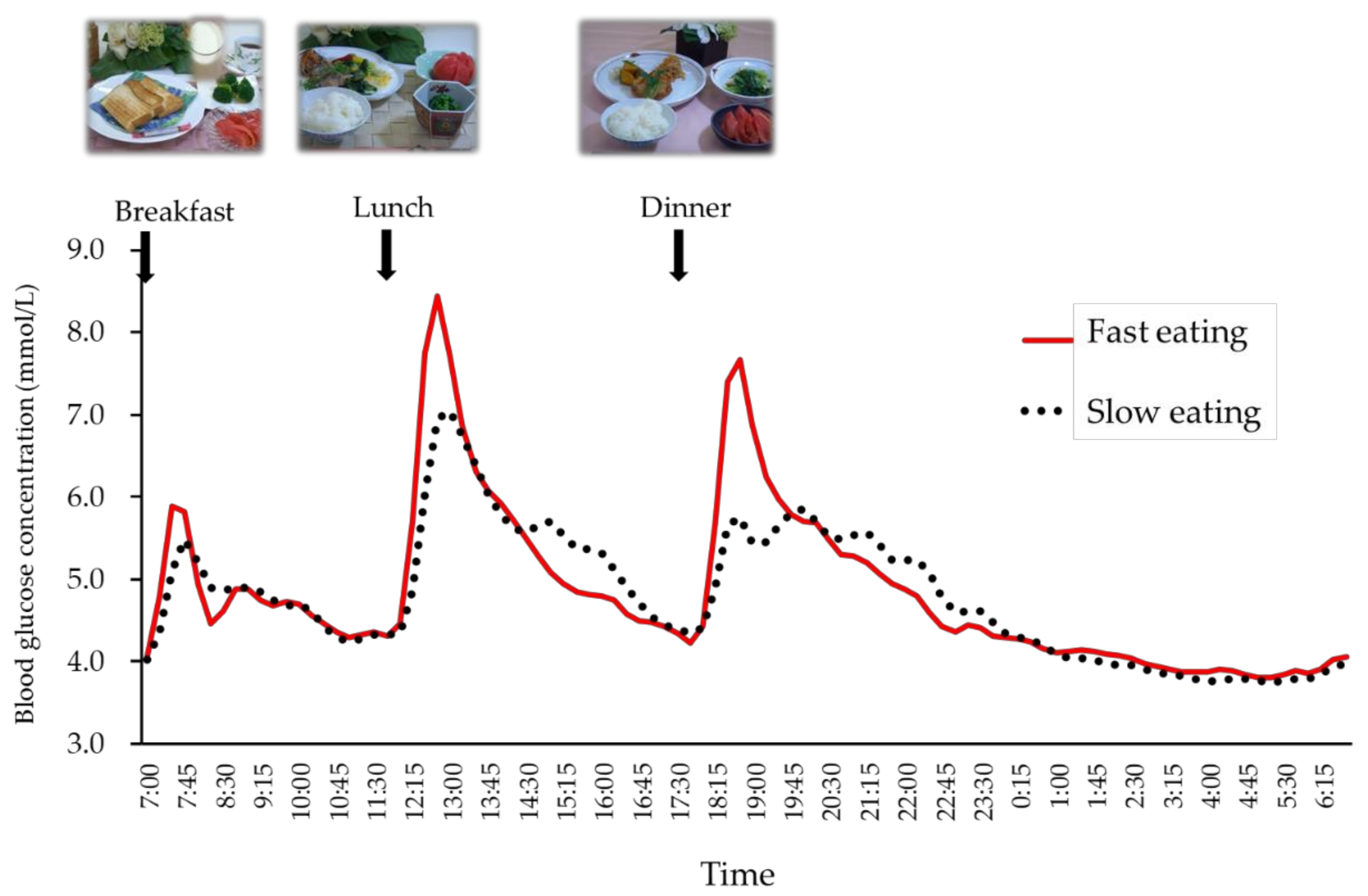
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tanihara, S.; Imatoh, T.; Miyazaki, M.; Babazono, A.; Momose, Y.; Baba, M.; Uryu, Y.; Une, H. Retrospective longitudinal study on the relationship between 8-year weight change and current eating speed. Appetite 2011, 57, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, Y.; Fukuda, H. Effects of changes in eating speed on obesity in patients with diabetes: A secondary analysis of longitudinal health check-up data. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e019589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakurai, M.; Nakamura, K.; Miura, K.; Takamura, T.; Yoshita, K.; Nagasawa, S.-Y.; Morikawa, Y.; Ishizaki, M.; Kido, T.; Naruse, Y.; et al. Self-reported speed of eating and 7-year risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in middle-aged Japanese men. Metabolism 2012, 61, 1566–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otsuka, R.; Tamakoshi, K.; Yatsuya, H.; Wada, K.; Matsushita, K.; Ouyang, P.; Hotta, Y.; Takefuji, S.; Mitsuhashi, H.; Sugiura, K.; et al. Eating fast leads to insulin resistance: Findings in middle-aged Japanese men and women. Prev. Med. 2008, 46, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Totsuka, K.; Maeno, T.; Saito, K.; Kodama, S.; Asumi, M.; Yachi, Y.; Hiranuma, Y.; Shimano, H.; Yamada, N.; Ono, Y.; et al. Self-reported fast eating is a potent predictor of development of impaired glucose tolerance in Japanese men and women: Tsukuba medical center study. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2011, 94, e72–e74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, S.L.; Madden, C.; Gray, A.; Waters, D.; Horwath, C.C. Faster self-reported speed of eating is related to higher body mass index in a nationwide survey of middle-aged women. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2011, 111, 1192–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, R.; Tamakoshi, K.; Yatsuya, H.; Murata, C.; Sekiya, A.; Wada, K.; Zhang, H.M.; Matsushita, K.; Sugiura, K.; Takefuji, S.; et al. Eating fast leads to obesity: Findings based on self-administered questionnaires among middle-aged japanese men and women. J. Epidemiol. 2006, 16, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagahama, S.; Kurotani, K.; Pham, N.M.; Nanri, A.; Kuwahara, K.; Dan, M.; Nishiwaki, Y.; Mizoue, T. Self-reported eating rate and metabolic syndrome in Japanese people: Cross-sectional study. BMJ Open 2014, 4, e005241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.S.; Kim, D.; Jang, J.; Nam, G.; Shin, Y.; Bok, A.; Kim, M.; Cho, K. Eating rate is associated with cardiometabolic risk factors in Korean adults. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2013, 23, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.-X.; Yang, K.; Huang, F.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Luo, Y.; Wu, L.; Guo, X. Association between self-reported eating speed and metabolic syndrome in a Beijing adult population: A cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health 2018, 18, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, K.; Sato, S.; Ohira, T.; Maeda, K.; Noda, H.; Kubota, Y.; Nishimura, S.; Kitamura, A.; Kiyama, M.; Okada, T.; et al. The joint impact on being overweight of self reported behaviours of eating quickly and eating until full: Cross sectional survey. BMJ 2008, 337, a2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, E.; Almiron-Roig, E.; Rutters, F.; De Graaf, C.; Forde, C.; Smith, C.T.; Nevitt, S.J.; Jebb, S.A. A systematic review and meta-analysis examining the effect of eating rate on energy intake and hunger. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 100, 123–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, A.M.; Greene, G.W.; Melanson, K.J. Eating slowly led to decreases in energy intake within meals in healthy women. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2008, 108, 1186–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolinder, J.; Antuna, R.; Geelhoed-Duijvestijn, P.; Kröger, J.; Weitgasser, R. Novel glucose-sensing technology and hypoglycaemia in type 1 diabetes: A multicentre, non-masked, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2016, 388, 2254–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haak, T.; Hanaire, H.; Ajjan, R.; Hermanns, N.; Riveline, J.-P.; Rayman, G. Use of flash glucose-sensing technology for 12 months as a replacement for blood glucose monitoring in insulin-treated type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Ther. 2017, 8, 573–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oskarsson, P.; Antuna, R.; Geelhoed-Duijvestijn, P.; Kröger, J.; Weitgasser, R.; Bolinder, J. Impact of flash glucose monitoring on hypoglycaemia in adults with type 1 diabetes managed with multiple daily injection therapy: A pre-specified subgroup analysis of the IMPACT randomised controlled trial. Diabetologia 2017, 61, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, S.; Fukui, M.; Kajiyama, S. Effect of eating vegetables before carbohydrates on glucose excursions in patients with type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2014, 54, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Baghurst, P.A. Calculating the mean amplitude of glycemic excursion from continuous glucose monitoring data: An automated algorithm. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2011, 13, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, S.; Fukui, M.; Ozasa, N.; Ozeki, T.; Kurokawa, M.; Komatsu, T.; Kajiyama, S. Eating vegetables before carbohydrates improves postprandial glucose excursions. Diabet. Med. 2013, 30, 370–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Mishra, G.; Hayashi, K.; Watanabe, E.; Mori, K.; Kawakubo, K. Combined eating behaviors and overweight: Eating quickly, late evening meals, and skipping breakfast. Eat. Behav. 2016, 21, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Haruyama, Y.; Muto, T.; Yamazaki, T. Association between eating speed and metabolic syndrome in a three-year population-based cohort study. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 25, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, N.L.; Peng, C.; Carreira, M.C.; Halder, L.; Hattersley, J.; Piya, M.K.; Tripathi, G.; Randeva, H.S.; Casanueva, F.F.; McTernan, P.G.; et al. Enhanced thermic effect of food, postprandial NEFA suppression and raised adiponectin in obese women who eat slowly. Clin. Endocrinol. 2015, 82, 831–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochizuki, K.; Misaki, Y.; Miyauchi, R.; Takabe, S.; Shimada, M.; Kuriki, K.; Ichikawa, Y.; Goda, T. A higher rate of eating is associated with higher circulating interluekin-1β concentrations in Japanese men not being treated for metabolic diseases. Nutrition 2012, 28, 978–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuki, T.; Horai, R.; Sudo, K.; Iwakura, Y. IL-1 plays an important role in lipid metabolism by regulating insulin levels under physiological conditions. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 198, 877–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galhardo, J.; Hunt, L.P.; Lightman, S.L.; Sabin, M.; Bergh, C.; Sodersten, P.; Shield, J.P.H. Normalizing eating behavior reduces body weight and improves gastrointestinal hormonal secretion in obese adolescents. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, M.; Crisp, K.; Adams-Huet, B.; Dart, L.; Bouza, B.; Franklin, B.; Phillips, M. The effect of eating speed at breakfast on appetite hormone responses and daily food consumption. J. Investig. Med. 2015, 63, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torimoto, K.; Okada, Y.; Mori, H.; Tanaka, Y. Relationship between fluctuations in glucose levels measured by continuous glucose monitoring and vascular endothelial dysfunction in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2013, 12, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cederberg, H.; Saukkonen, T.; Laakso, M.; Jokelainen, J.; Härkönen, P.; Timonen, M.; Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi, S.; Rajala, U. Postchallenge glucose, A1C, and fasting glucose as predictors of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 2077–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tominaga, M.; Eguchi, H.; Manaka, H.; Igarashi, K.; Kato, T.; Sekikawa, A. Impaired glucose tolerance is a risk factor for cardiovascular disease, but not impaired fasting glucose. The funagata diabetes study. Diabetes Care 1999, 22, 920–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, K.; Nappo, F.; Marfella, R.; Giugliano, G.; Giugliano, F.; Ciotola, M.; Quagliaro, L.; Ceriello, A.; Giugliano, D. Inflammatory cytokine concentrations are acutely increased by hyperglycemia in humans. Circulation 2002, 106, 2067–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, T.; Ogawa, H.; Kawano, H.; Hirai, N.; Miyamoto, S.; Takazoe, K.; Soejima, H.; Kugiyama, K.; Yoshimura, M.; Yasue, H. Rapid change of platelet aggregability in acute hyperglycemia. Detection by a novel laser-light scattering method. Thromb. Haemost. 2000, 83, 475–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawano, H.; Motoyama, T.; Hirashima, O.; Hirai, N.; Miyao, Y.; Sakamoto, T.; Kugiyama, K.; Ogawa, H.; Yasue, H. Hyperglycemia rapidly suppresses flow-mediated endothelium-dependent vasodilation of brachial artery. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1999, 34, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, A.L.; Bergh, C.; Sodersten, P.; Sabin, M.; Hollinghurst, S.; Hunt, L.P.; Shield, J.P.H. Treatment of childhood obesity by retraining eating behaviour: Randomised controlled trial. BMJ 2009, 340, b5388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazquez, B.Y.S.; Gutiérrez, G.L.; Rosales, K.A.; Cabrales, P.; Vadillo-Ortega, F.; Intaglietta, M.; Tamayo, R.P.; Schmid-Schönbein, G.W.; Vázquez, M.A.S. Control of overweight and obesity in childhood through education in meal time habits. The “good manners for a healthy future” programme. Pediatr. Obes. 2015, 11, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Meal | Energy | Protein | Fat | Carbohydrate | Fiber | Detail Content |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (kcal) | (g) | (g) | (g) | (g) | ||
| Breakfast | 437 | 18.2 | 12 | 70.1 | 5.8 | White bread 90 g, tomato 100 g, broccoli 60 g, milk 200 g, strawberry jam (sugar free) 13 g |
| Lunch | 624 | 25.1 | 11.5 | 104 | 8.1 | Boiled white rice 200 g, frozen lunch box of fried fish with vegetable, tomato 100 g, spinach 80 g |
| Dinner | 689 | 23.6 | 17.4 | 107.6 | 7.8 | Boiled white rice 200 g, tomato 100 g, frozen lunch box of gluten-meat steak with vegetable, spinach 80 g with fried tofu 15 g |
| Total | 1750 | 66.9 | 40.9 | 281.7 | 21.7 |
| Glycemic Parameters | Fast Eating (10 min) | Slow Eating (20 min) |
|---|---|---|
| Mean plasma glucose concentration (mmol/L) | 4.76 ± 0.11 | 4.79 ± 0.12 |
| SD of plasma glucose concentration (mmol/L) | 1.18 ± 0.10 * | 0.92 ± 0.06 |
| MAGE (mmol/L) | 3.67 ± 0.31 ** | 2.67 ± 0.20 |
| IGP after breakfast (mmol/L) | 2.30 ± 0.19 ** | 1.71 ± 0.12 |
| IGP after lunch (mmol/L) | 4.06 ± 0.33 ** | 3.13 ± 0.28 |
| IGP after dinner (mmol/L) | 3.87 ± 0.38 *** | 2.27 ± 0.27 |
| IAUC for glucose of breakfast 0–120 min (mmol/L × min) | 111 ± 10 | 107 ± 8 |
| IAUC for glucose of lunch 0–120 min (mmol/L × min) | 265 ± 28 | 216 ± 21 |
| IAUC for glucose of dinner 0–120 min (mmol/L × min) | 256 ± 30 *** | 128 ± 18 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saito, Y.; Kajiyama, S.; Nitta, A.; Miyawaki, T.; Matsumoto, S.; Ozasa, N.; Kajiyama, S.; Hashimoto, Y.; Fukui, M.; Imai, S. Eating Fast Has a Significant Impact on Glycemic Excursion in Healthy Women: Randomized Controlled Cross-Over Trial. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2767. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12092767
Saito Y, Kajiyama S, Nitta A, Miyawaki T, Matsumoto S, Ozasa N, Kajiyama S, Hashimoto Y, Fukui M, Imai S. Eating Fast Has a Significant Impact on Glycemic Excursion in Healthy Women: Randomized Controlled Cross-Over Trial. Nutrients. 2020; 12(9):2767. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12092767
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaito, Yuuki, Shizuo Kajiyama, Ayasa Nitta, Takashi Miyawaki, Shinya Matsumoto, Neiko Ozasa, Shintaro Kajiyama, Yoshitaka Hashimoto, Michiaki Fukui, and Saeko Imai. 2020. "Eating Fast Has a Significant Impact on Glycemic Excursion in Healthy Women: Randomized Controlled Cross-Over Trial" Nutrients 12, no. 9: 2767. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12092767
APA StyleSaito, Y., Kajiyama, S., Nitta, A., Miyawaki, T., Matsumoto, S., Ozasa, N., Kajiyama, S., Hashimoto, Y., Fukui, M., & Imai, S. (2020). Eating Fast Has a Significant Impact on Glycemic Excursion in Healthy Women: Randomized Controlled Cross-Over Trial. Nutrients, 12(9), 2767. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12092767








