Diet Diversity and Micronutrient Adequacy among Filipino School-Age Children
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Diet Diversity Score (DDS)
2.4. Probability of Adequacy (PA) of Micronutrients
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Statistics
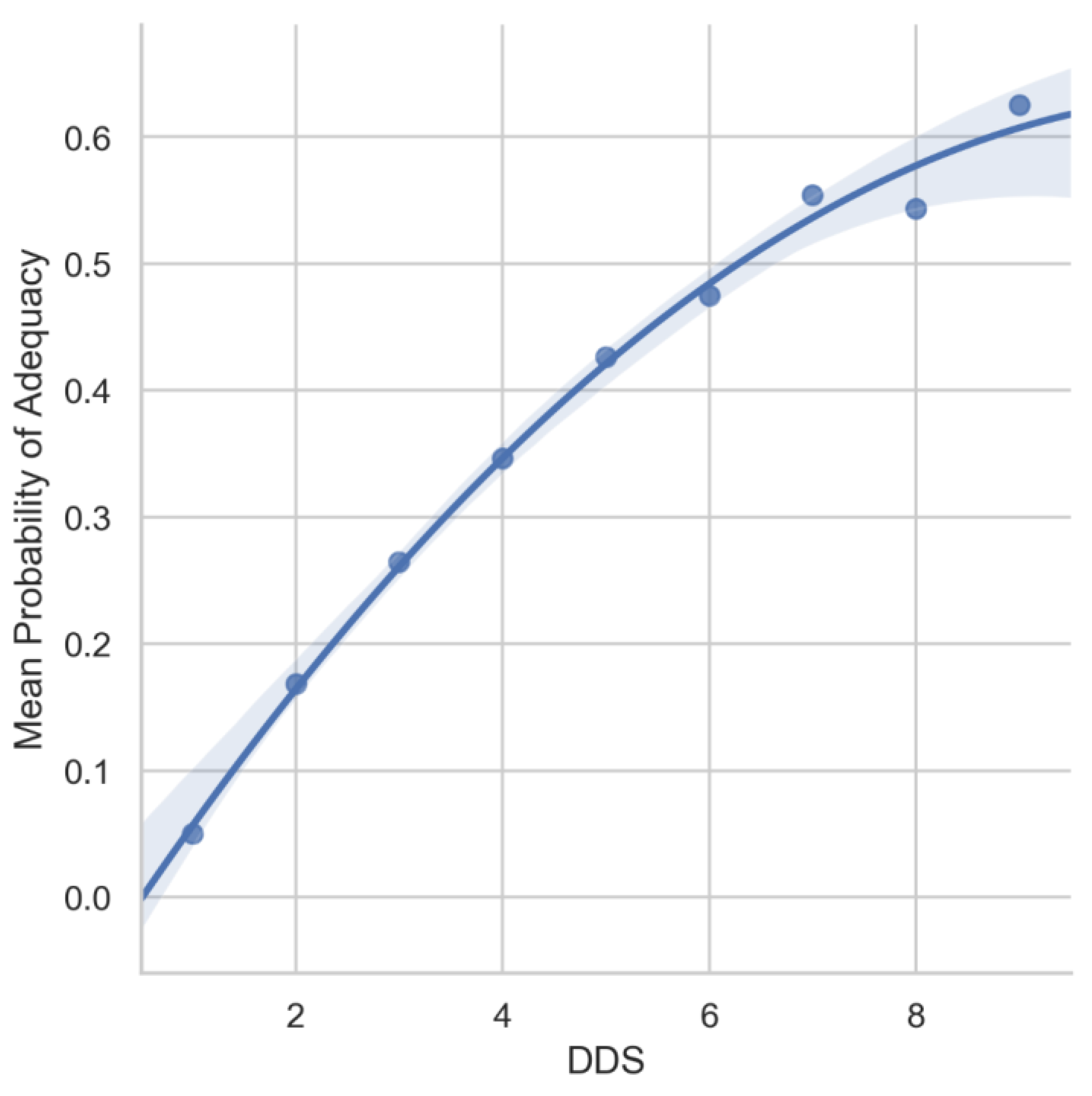
3.2. DDS and PA
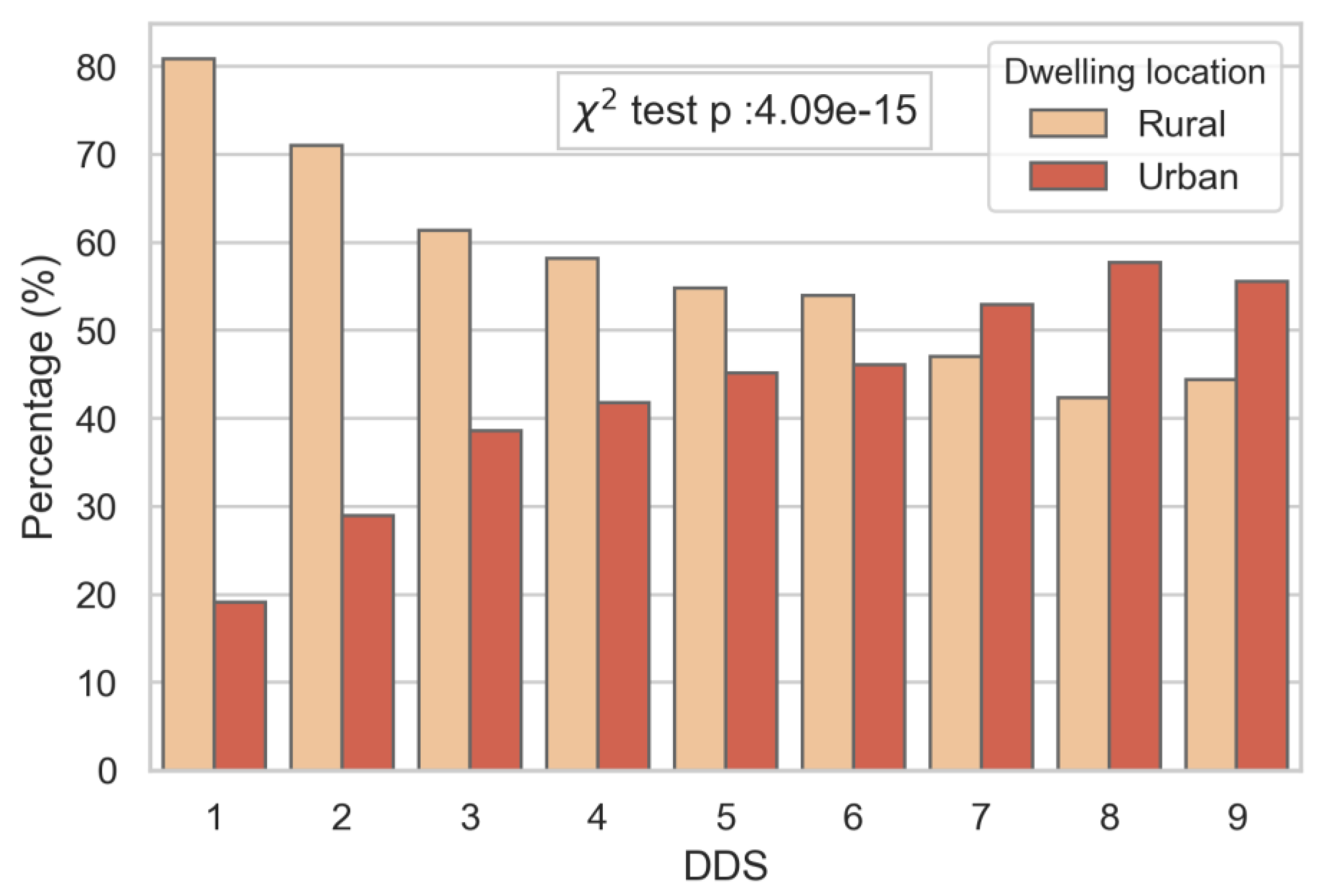
3.3. DDS, PA, and Dwelling Locations
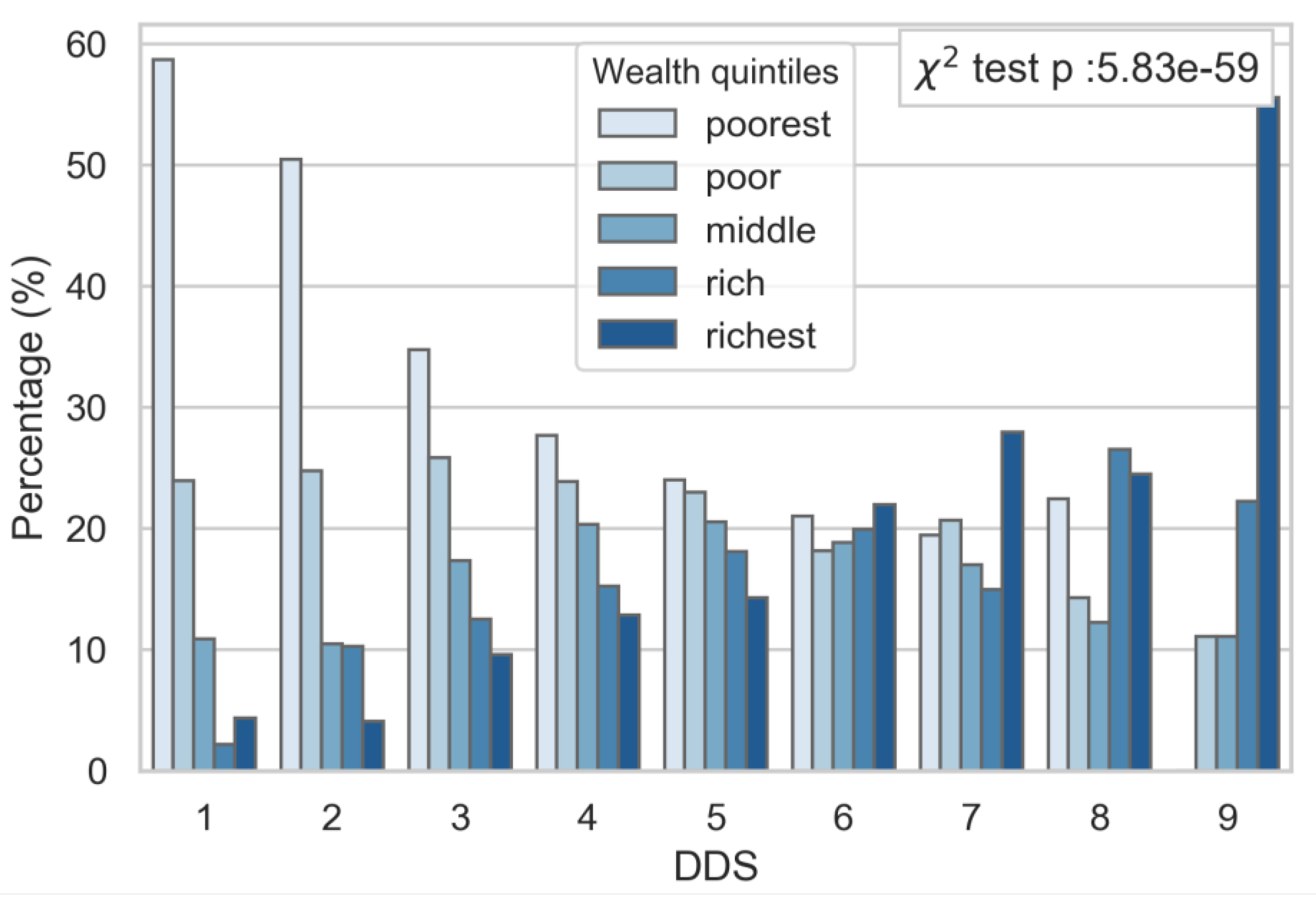
3.4. DDS, PA, and SES
4. Discussion
4.1. Diet Diversity among Filipino Children
4.2. Socio-Economic Status and Urban versus Rural Children
4.3. Calcium, Folate, Iron, Vitamin A and Vitamin C Adequacies are Difficult to Meet
4.4. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Food and Nutrition Research Institute. Philippine Nutrition Facts and Figures 2013. 8th National Nutrition Survey Overview; Department of Science and Technology-Food and Nutrition Research Institute (DOST-FNRI): Manila, Philippines, 2015.
- Food and Nutrition Research Institute. 2015 Updating of the Nutritional Status of Filipino Children and Other Population Group: Food Security Survey; Department of Science and Technology -Food and Nutrition Research Institute (DOST-FNRI): Manila, Philippines, 2016.
- Angeles-Agdeppa, I.; Denney, L.; Toledo, M.B.; Obligar, V.A.; Jacquier, E.F.; Carriquiry, A.L.; Capanzana, M.V. Inadequate nutrient intakes in filipino schoolchildren and adolescents are common among those from rural areas and poor families. Food Nutri Res. 2019, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Early Child Development—Nutrition and the Early Years. Available online: https://www.who.int/topics/early-child-development/child-nutrition/en/ (accessed on 11 September 2019).
- Pedro, M.R.A.; Benavides, R.C.; Barba, C.V.C. Dietary Changes and Their Health Implications in the Philippines, in The Double Burden of Malnutrition: Case Studies from Six Developing Countries; FAO Food and Nutrition Paper: Rome, Italy, 2006; pp. 205–258. [Google Scholar]
- Rah, J.H.; Akhter, N.; Semba, R.D.; De Pee, S.; Bloem, M.W.; Campbell, A.A.; Kraemer, K. Low dietary diversity is a predictor of child stunting in rural Bangladesh. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 64, 1393–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, G.L.; Pedro, M.R.; Seghieri, C.; Nantel, G.; Brouwer, I. Dietary diversity score is a useful indicator of micronutrient intake in non-breast-feeding Filipino children. J. Nutr. 2007, 137, 472–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arimond, M.; Ruel, M.T. Dietary diversity is associated with child. Nutritional status: Evidence from 11 demographic and health surveys. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 2579–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nti, C. Dietary diversity is associated with nutrient intakes and nutritional status of children in Ghana. Asian J. Med Sci. 2011, 2, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsenault, J.E.; Yakes, E.A.; Islam, M.M.; Hossain, M.B.; Ahmed, T.; Hotz, C.; Brown, K.H. Very low adequacy of micronutrient intakes by young children and women in rural Bangladesh is primarily explained by low food intake and limited diversity. J. Nutr. 2013, 143, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Olmedo, N.; Carriquiry, A.L.; Rodríguez-Ramírez, S.; Ramírez-Silva, I.; Espinosa-Montero, J.; Hernández-Barrera, L.; Rivera, J. A usual intake of added sugars and saturated fats is high while dietary fiber is low in the Mexican population. J. Nutr. 2016, 146, 1856s–1865s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- USDA. What We Eat in America Food Categories. Available online: https://www.ars.usda.gov/ARSUserFiles/80400530/pdf/1314/food_category_list.pdf (accessed on 11 September 2019).
- Denney, L.; Angeles-Agdeppa, I.; Capanzana, M.; Toledo, M.; Donohue, J.; Carriquiry, A. Nutrient intakes and food sources of Filipino infants, toddlers and young children are inadequate: Findings from the national nutrition survey 2013. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, G.L.; Nantel, G. Basic Guidelines for Validation of a Simple Dietary Diversity Score as an Indicator of Dietary Nutrient Adequacy for Non-Breastfeeding Children 2–6 Years; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Daniels, M.C.; Adair, L.S.; Popkin, B.M.; Truong, Y.K. Dietary diversity scores can be improved through the use of portion requirements: An analysis in young Filipino children. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 63, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foote, J.A.; Murphy, S.P.; Wilkens, L.R.; Basiotis, P.P.; Carlson, A. Dietary variety increases the probability of nutrient adequacy among adults. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 1779–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Institute of Medicine. Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin A, Vitamin K, Arsenic, Boron, Chromium, Copper, Iodine, Iron, Manganese, Molybdenum, Nickel, Silicon, Vanadium and Zinc; National Academy Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Vanderplas, J. Scikit-learn: Machine learning in python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, E.; Travis, E.; Peterson, P. SciPy: Open Source Scientific Tools for Python; 2001. Available online: http://www.scipy.org/ (accessed on 11 September 2019).
- Santos, L.P.; Assunção, M.C.F.; Matijasevich, A.; Santos, I.S.; Barros, A.J. Dietary intake patterns of children aged 6 years and their association with socioeconomic and demographic characteristics, early feeding practices and body mass index. BMC Public Health 2016, 16, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angeles-Agdeppa, I.G.G.; Constantino, M. Evaluation of calcium intakes of young children in the Philippines as a result of the 2008 national nutrition survey. Philipp. J. Sci. 2016, 145, 165–174. [Google Scholar]
- Vega, M.L.A. Fortification Efforts in the Philippines: Successes and Challenges; National Nutrition Council: Taguig, Philippines, 2000.
- Angeles-Agdeppa, I.; Magsadia, C.R.; Capanzana, M.V. Fortified juice drink improved iron and zinc status of schoolchildren. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 20, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kuriyan, R.; Thankachan, P.; Selvam, S.; Pauline, M.; Srinivasan, K.; Kamath-Jha, S.; Kurpad, A.V. The effects of regular consumption of a multiple micronutrient fortified milk beverage on the micronutrient status of school children and on their mental and physical performance. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 35, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lien, D.T.K.; Nhung, B.T.; Khan, N.C.; Hop, L.T.; Nga, N.T.Q.; Hung, N.T.; te Biesebeke, R. Impact of milk consumption on performance and health of primary school children in rural Vietnam. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 18, 326–334. [Google Scholar]
| Age | Mean: 9.6 years (SD: ±2) | ||||||||||
| Gender | Girls: 51.5%; boys: 48.5% | ||||||||||
| Dwelling Location | Urban: 41.5%, rural: 58.5% | ||||||||||
| Socio-Economic Status | Richest | Rich | Middle | Poor | Poorest | ||||||
| 12.9% | 14.8% | 17.9% | 22.8% | 28.9% | |||||||
| Diet Diversity Score | Mean: 4.1 (SD: ±1.3) | ||||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | |||
| 0.7% | 8.3% | 24.8% | 29.9% | 21.4% | 10.0% | 3.9% | 0.8% | 0.1% | |||
| DDS | Calcium | Folate | Iron | Niacin | Riboflavin | Thiamine | Vitamin B12 | Vitamin B6 | Vitamin C | Vitamin A | Zinc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| 2 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| 3 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.2500 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0020 |
| 4 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.9536 | 0.9940 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0880 |
| 5 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.6530 |
| 6 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.9389 |
| 7 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0620 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 |
| 8 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.2360 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 |
| 9 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.0060 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 |
| Dwelling | DDS | Calcium | Folate | Iron | Niacin | Riboflavin | Thiamine | Vitamin B12 | Vitamin B6 | Vitamin C | Vitamin A | Zinc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rural | 1 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| 2 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | |
| 3 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0560 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | |
| 4 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.8110 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0220 | |
| 5 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.5150 | |
| 6 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.7540 | |
| 7 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0010 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.9893 | |
| 8 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0880 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.9998 | |
| 9 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.2120 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| Urban | 1 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| 2 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0030 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | |
| 3 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.6830 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0270 | |
| 4 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.9987 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.4110 | |
| 5 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.8410 | |
| 6 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0010 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.9949 | |
| 7 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.4570 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 8 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.5410 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 9 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.3660 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 |
| SES | DDS | Calcium | Folate | Iron | Niacin | Riboflavin | Thiamine | Vitamin B12 | Vitamin B6 | Vitamin C | Vitamin A | Zinc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Poorest | 1 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| 2 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0001 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | |
| 3 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0024 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | |
| 4 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.6563 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0021 | |
| 5 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.2042 | |
| 6 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.6348 | |
| 7 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0005 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.9403 | |
| 8 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0134 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.9885 | |
| 9 | ||||||||||||
| Richest | 1 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.3470 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.5000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.2519 |
| 2 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.2193 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0125 | |
| 3 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.9897 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.3302 | |
| 4 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.8195 | |
| 5 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0001 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.9915 | |
| 6 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0093 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 7 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.2964 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 8 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.9539 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 9 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.1209 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mak, T.-N.; Angeles-Agdeppa, I.; Lenighan, Y.M.; Capanzana, M.V.; Montoliu, I. Diet Diversity and Micronutrient Adequacy among Filipino School-Age Children. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2197. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11092197
Mak T-N, Angeles-Agdeppa I, Lenighan YM, Capanzana MV, Montoliu I. Diet Diversity and Micronutrient Adequacy among Filipino School-Age Children. Nutrients. 2019; 11(9):2197. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11092197
Chicago/Turabian StyleMak, Tsz-Ning, Imelda Angeles-Agdeppa, Yvonne M. Lenighan, Mario V. Capanzana, and Ivan Montoliu. 2019. "Diet Diversity and Micronutrient Adequacy among Filipino School-Age Children" Nutrients 11, no. 9: 2197. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11092197
APA StyleMak, T.-N., Angeles-Agdeppa, I., Lenighan, Y. M., Capanzana, M. V., & Montoliu, I. (2019). Diet Diversity and Micronutrient Adequacy among Filipino School-Age Children. Nutrients, 11(9), 2197. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11092197





