The Edible Insect Gryllus bimaculatus Protects against Gut-Derived Inflammatory Responses and Liver Damage in Mice after Acute Alcohol Exposure
Abstract
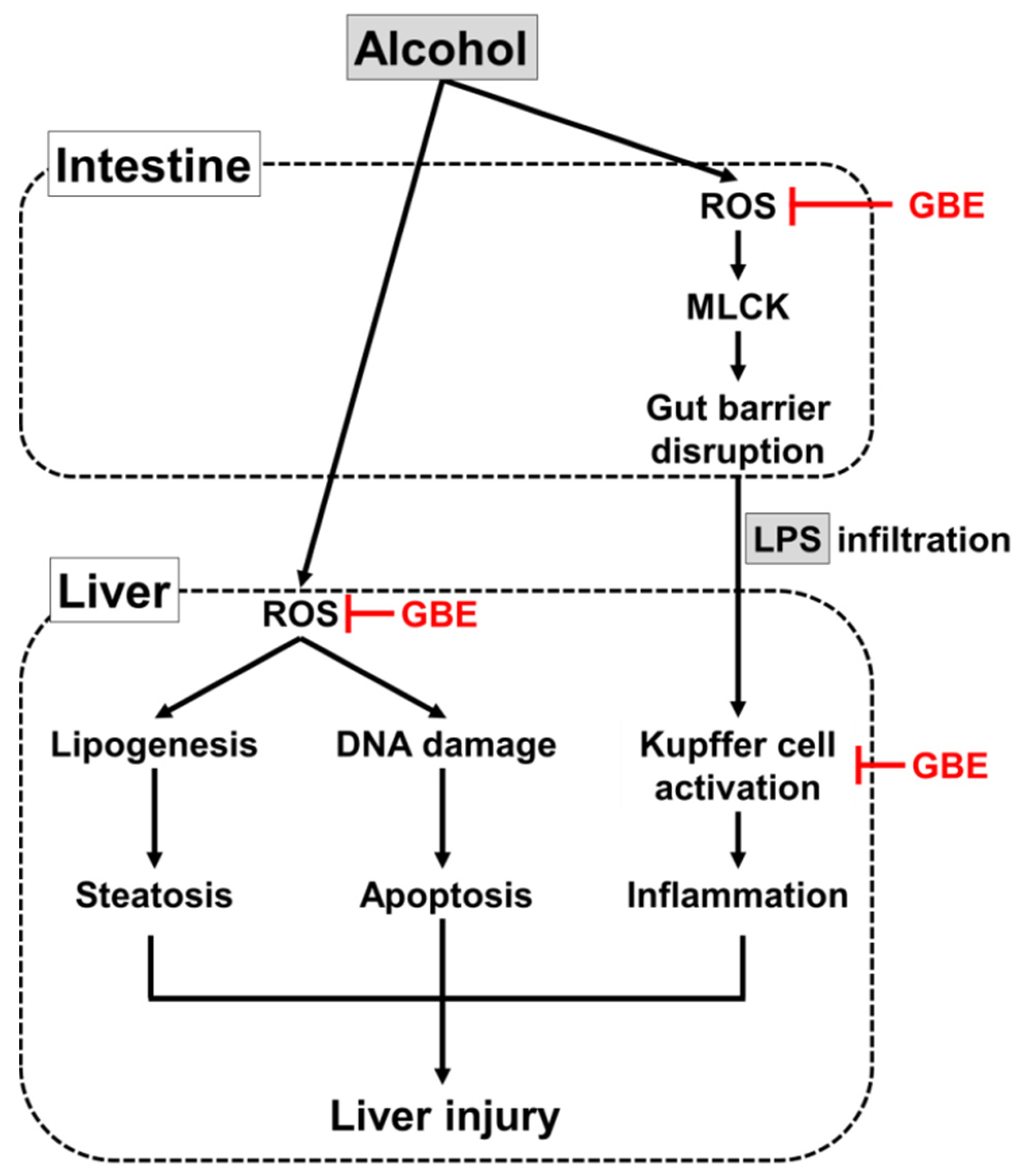
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Edible Insect Extracts
2.2. ABTS and DPPH Radical Scavenging Assay
2.3. Animal Study
2.4. Histological Analysis
2.5. Western Blot Analysis
2.6. Cell Culture
2.7. Biochemical Assays
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
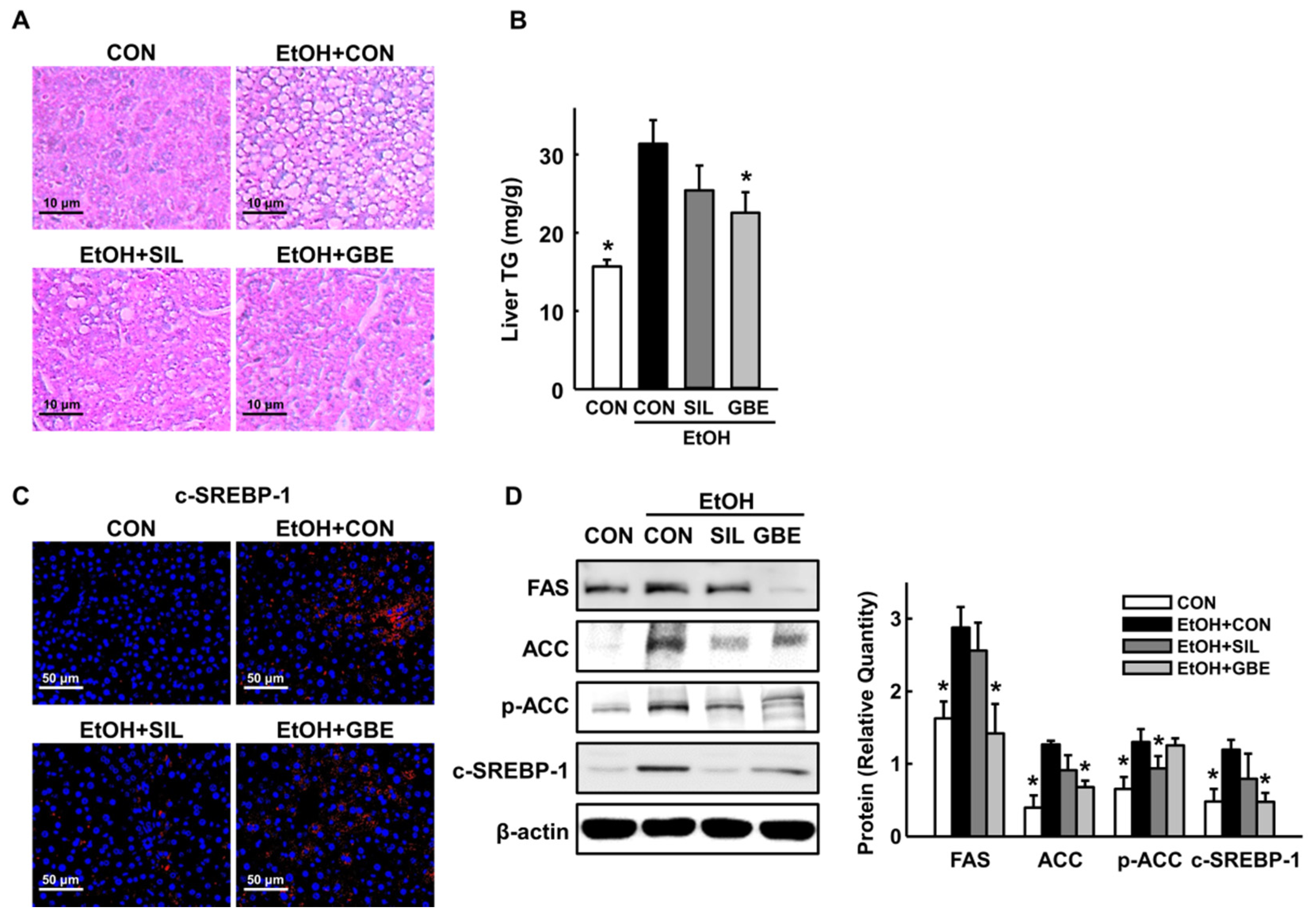
3.1. GBE Restrains Alcohol-Induced Hepatic Steatosis
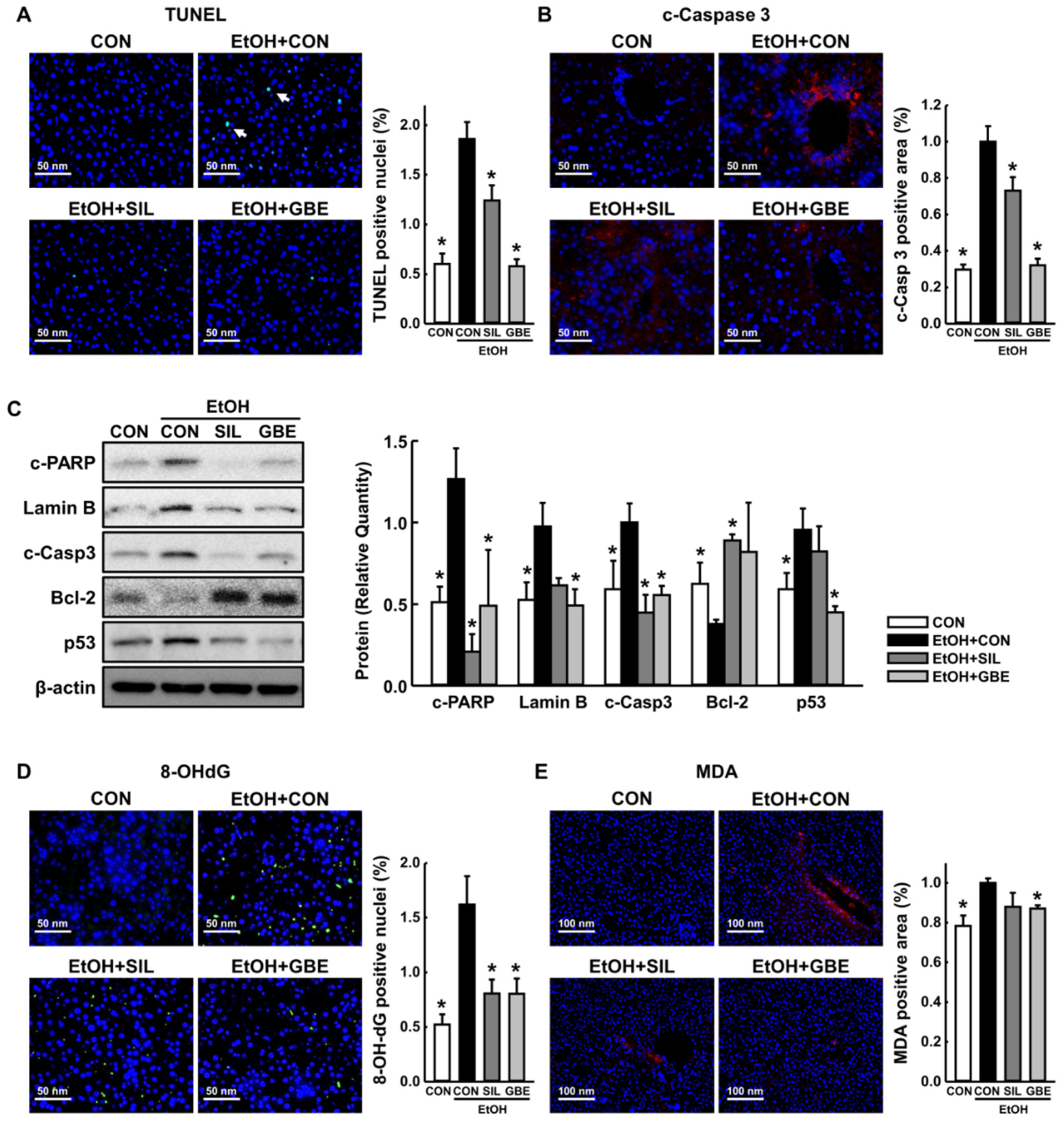
3.2. GBE Attenuates Alcohol-Induced Hepatic Apoptosis by Suppressing Oxidative Stress
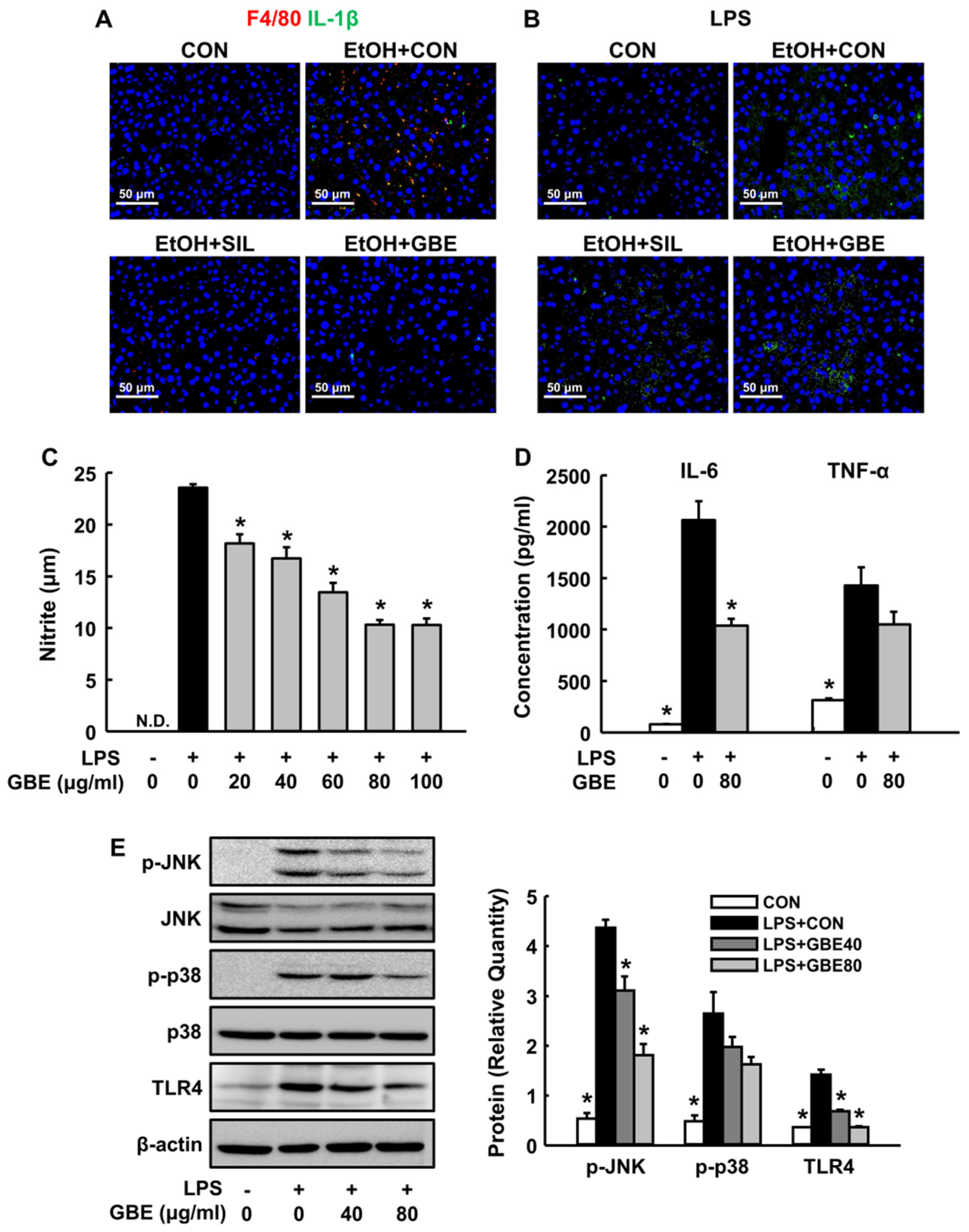
3.3. GBE Inhibits Kupffer Cell Activation In Vivo and Modulates Inflammatory Response in Macrophages
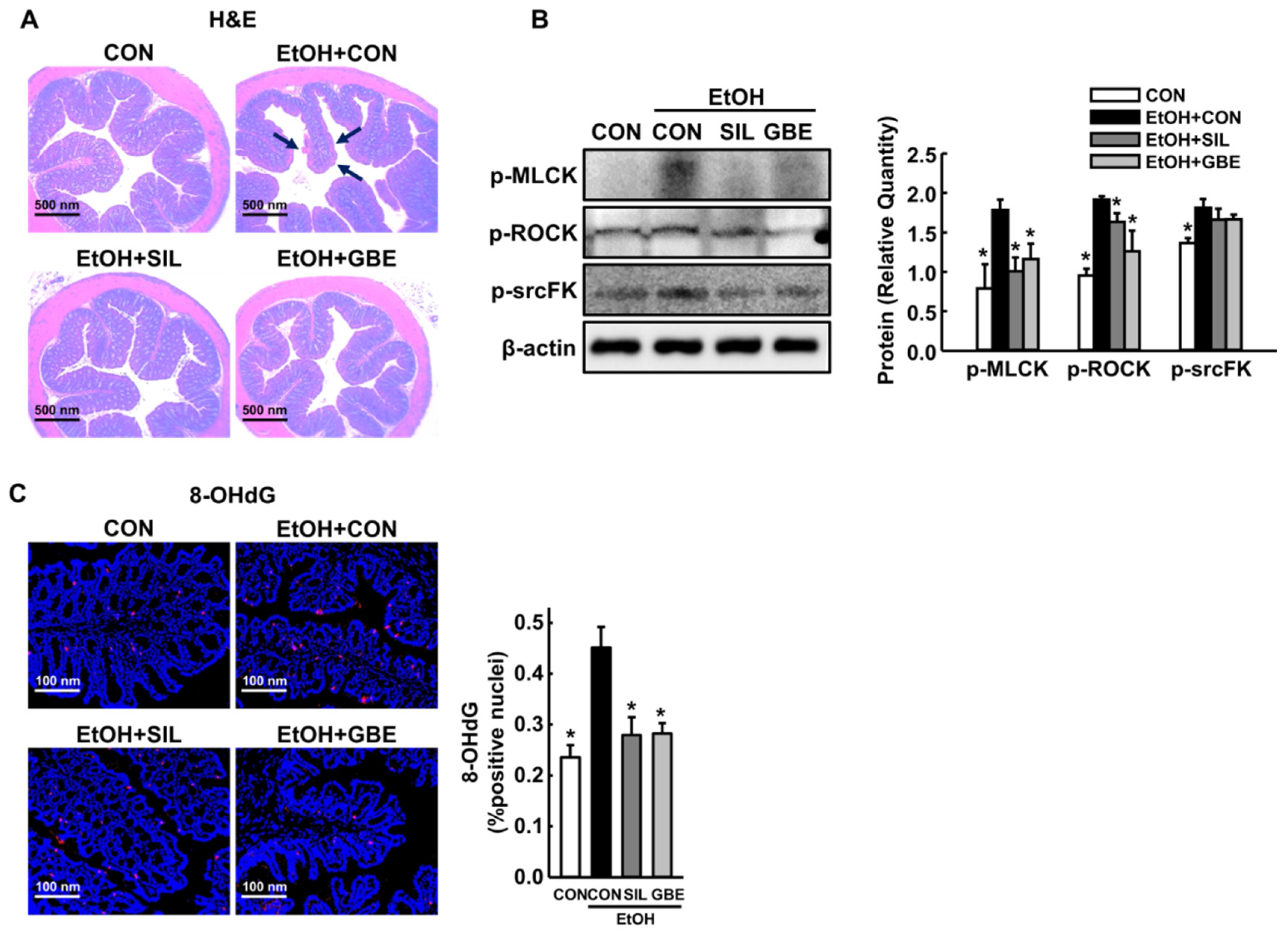
3.4. GBE Protects the Intestine against Alcohol-Induced Hyperpermeability and Oxidative Stress
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Huis, A.; Van Itterbeeck, J.; Klunder, H.; Mertens, E.; Halloran, A.; Muir, G.; Vantomme, P. Edible insects: Future Prospects for Food and Feed Security; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Belluco, S.; Losasso, C.; Maggioletti, M.; Alonzi, C.C.; Paoletti, M.G.; Ricci, A. Edible insects in a food safety and nutritional perspective: A critical review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2013, 12, 296–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobermann, D.; Swift, J.A.; Field, L.M. Opportunities and hurdles of edible insects for food and feed. Nutr. Bull. 2017, 42, 293–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, M.Y.; Hwang, J.S.; Yun, E.Y.; Kim, M.-J.; Park, K.-K. Anti-aging effect and gene expression profiling of aged rats treated with G. bimaculatus extract. Toxicol. Res. 2015, 31, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, M.Y.; Kim, M.-J.; Kwon, R.H.; Hwang, J.S.; Park, K.-K. Gene expression profiling and inhibition of adipose tissue accumulation of G. bimaculatus extract in rats on high fat diet. Lipids Health Dis. 2015, 14, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong-Hwan, S.; Hwang, S.Y.; Han, J.; Koh, S.K.; Kim, I.; Ryu, K.S.; Yun, C.Y. Immune-Enhancing Activity Screening on Extracts from Two Crickets, Gryllus bimaculatus and Teleogryllus emma. Entomol. Res. 2004, 34, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, A.-R.; Yang, W.-K.; Park, Y.-C.; Kim, S.H.; Chae, S. Hepatoprotective Effects of Insect Extracts in an Animal Model of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Nutrients 2018, 10, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, M.Y.; Han, J.W.; Hwang, J.S.; Yun, E.Y.; Lee, B.M. Anti-inflammatory effect of glycosaminoglycan derived from Gryllus bimaculatus (a type of cricket, insect) on adjuvant-treated chronic arthritis rat model. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2014, 77, 1332–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, M.Y.; Hwang, J.S.; Kim, M.-J.; Park, K.-K. Antilipidemic effects and gene expression profiling of the glycosaminoglycans from cricket in rats on a high fat diet. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2016, 39, 926–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcellin, P.; Kutala, B.K. Liver diseases: A major, neglected global public health problem requiring urgent actions and large-scale screening. Liver Int. 2018, 38, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakhuja, P. Pathology of alcoholic liver disease, can it be differentiated from nonalcoholic steatohepatitis? World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2014, 20, 16474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambade, A.; Mandrekar, P. Oxidative stress and inflammation: Essential partners in alcoholic liver disease. Int. J. Hepatol. 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louvet, A.; Mathurin, P. Alcoholic liver disease: Mechanisms of injury and targeted treatment. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 12, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceni, E.; Mello, T.; Galli, A. Pathogenesis of alcoholic liver disease: Role of oxidative metabolism. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2014, 20, 17756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.-H.; Hashimoto, N.; Fukushima, M. Relationships among alcoholic liver disease, antioxidants, and antioxidant enzymes. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Tan, H.-Y.; Wang, N.; Zhang, Z.-J.; Lao, L.; Wong, C.-W.; Feng, Y. The role of oxidative stress and antioxidants in liver diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 26087–26124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, U.; Deis, A.; Sørensen, T.I.; Grønbaek, M.; Borch-Johnsen, K.; Müller, C.F.; Schnohr, P.; Jensen, G. Prediction of risk of liver disease by alcohol intake, sex, and age: A prospective population study. Hepatology 1996, 23, 1025–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, N.; Lindros, K.O.; Baraona, E.; Ikejima, K.; Mezey, E.; Järveläinen, H.A.; Ramchandani, V.A. Sex difference in alcohol-related organ injury. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2001, 25, 40S–45S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh Dastidar, S.; Warner, J.B.; Warner, D.R.; McClain, C.J.; Kirpich, I.A. Rodent Models of Alcoholic Liver Disease: Role of Binge Ethanol Administration. Biomolecules 2018, 8, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, A.W.; Chen, L.; Fisher, S.J.; Szanto, I.; Ristow, M.; Jozsi, A.C.; Hirshman, M.F.; Rosen, E.D.; Goodyear, L.J.; Gonzalez, F.J. Muscle-specific PPARγ-deficient mice develop increased adiposity and insulin resistance but respond to thiazolidinediones. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 608–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luedde, T.; Kaplowitz, N.; Schwabe, R.F. Cell death and cell death responses in liver disease: Mechanisms and clinical relevance. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 765–783.e764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haupt, S.; Berger, M.; Goldberg, Z.; Haupt, Y. Apoptosis-the p53 network. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116, 4077–4085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K. Molecular mechanisms of hepatic apoptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 5, e996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, T.; Zhang, C.-L.; Xiao, M.; Yang, R.; Xie, K.-Q. Critical roles of Kupffer cells in the pathogenesis of alcoholic liver disease: From basic science to clinical trials. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, T.H.; Tam, K.; Chen, S.F.; Liou, J.Y.; Tsai, Y.C.; Lee, Y.M.; Huang, T.Y.; Shyue, S.K. Deletion of caveolin-1 attenuates LPS/GalN-induced acute liver injury in mice. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 5573–5582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bala, S.; Marcos, M.; Kodys, K.; Csak, T.; Catalano, D.; Mandrekar, P.; Szabo, G. Up-regulation of microRNA-155 in macrophages contributes to increased tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα) production via increased mRNA half-life in alcoholic liver disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 1436–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purohit, V.; Bode, J.C.; Bode, C.; Brenner, D.A.; Choudhry, M.A.; Hamilton, F.; Kang, Y.J.; Keshavarzian, A.; Rao, R.; Sartor, R.B. Alcohol, intestinal bacterial growth, intestinal permeability to endotoxin, and medical consequences: Summary of a symposium. Alcohol 2008, 42, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Black, E.D.; Witkowski, E.D.; Lencer, W.I.; Guerriero, V.; Schneeberger, E.E.; Turner, J.R. Myosin light chain phosphorylation regulates barrier function by remodeling tight junction structure. J. Cell Sci. 2006, 119, 2095–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacKay, C.E.; Shaifta, Y.; Snetkov, V.V.; Francois, A.A.; Ward, J.P.; Knock, G.A. ROS-dependent activation of RhoA/Rho-kinase in pulmonary artery: Role of Src-family kinases and ARHGEF1. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 110, 316–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saller, R.; Meier, R.; Brignoli, R. The use of silymarin in the treatment of liver diseases. Drugs 2001, 61, 2035–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McVicker, B.L.; Tuma, D.J.; Casey, C.A. Effect of ethanol on pro-apoptotic mechanisms in polarized hepatic cells. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2007, 13, 4960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, G. Gut–liver axis in alcoholic liver disease. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forsyth, C.B.; Voigt, R.M.; Keshavarzian, A. Intestinal CYP2E1: A mediator of alcohol-induced gut leakiness. Redox Biol. 2014, 3, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keshavarzian, A.; Farhadi, A.; Forsyth, C.B.; Rangan, J.; Jakate, S.; Shaikh, M.; Banan, A.; Fields, J.Z. Evidence that chronic alcohol exposure promotes intestinal oxidative stress, intestinal hyperpermeability and endotoxemia prior to development of alcoholic steatohepatitis in rats. J. Hepatol. 2009, 50, 538–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo, G.M.; Avenoso, A.; Campo, S.; D’Ascola, A.; Ferlazzo, A.M.; Calatroni, A. The antioxidant and antifibrogenic effects of the glycosaminoglycans hyaluronic acid and chondroitin-4-sulphate in a subchronic rat model of carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrogenesis. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2004, 148, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bramley, P.; Rathbone, B.; Forbes, M.; Cooper, E.; Losowsky, M. Serum hyaluronate as a marker of hepatic derangement in acute liver damage. J. Hepatol. 1991, 13, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadanaka, S.; Kitagawa, H. EXTL2 controls liver regeneration and aortic calcification through xylose kinase-dependent regulation of glycosaminoglycan biosynthesis. Matrix Biol. 2014, 35, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hwang, B.B.; Chang, M.H.; Lee, J.H.; Heo, W.; Kim, J.K.; Pan, J.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, J.H. The Edible Insect Gryllus bimaculatus Protects against Gut-Derived Inflammatory Responses and Liver Damage in Mice after Acute Alcohol Exposure. Nutrients 2019, 11, 857. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11040857
Hwang BB, Chang MH, Lee JH, Heo W, Kim JK, Pan JH, Kim YJ, Kim JH. The Edible Insect Gryllus bimaculatus Protects against Gut-Derived Inflammatory Responses and Liver Damage in Mice after Acute Alcohol Exposure. Nutrients. 2019; 11(4):857. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11040857
Chicago/Turabian StyleHwang, Bo Byeol, Moon Han Chang, Jin Hyup Lee, Wan Heo, Jae Kyeom Kim, Jeong Hoon Pan, Young Jun Kim, and Jun Ho Kim. 2019. "The Edible Insect Gryllus bimaculatus Protects against Gut-Derived Inflammatory Responses and Liver Damage in Mice after Acute Alcohol Exposure" Nutrients 11, no. 4: 857. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11040857
APA StyleHwang, B. B., Chang, M. H., Lee, J. H., Heo, W., Kim, J. K., Pan, J. H., Kim, Y. J., & Kim, J. H. (2019). The Edible Insect Gryllus bimaculatus Protects against Gut-Derived Inflammatory Responses and Liver Damage in Mice after Acute Alcohol Exposure. Nutrients, 11(4), 857. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11040857





