A Retrospective Analysis of the Effect of Combination of Pure Fish Oil with Third Generation Lipid Emulsion on Liver Function in Children on Long-Term Parenteral Nutrition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Duggan, P.C.; Jaksic, T. Pediatric Intestinal Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 666–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courtney, C.M.; Warner, B.W. Pediatric intestinal failure-associated liver disease. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2017, 29, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Shahwani, N.H.; Sigalet, D.L. Pathophysiology, prevention, treatment, and outcomes of intestinal failure-associated liver disease. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2017, 33, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacaille, F.; Gupte, G. Intestinal failure-associated liver disease: A position paper of the ESPGHAN Working Group of Intestinal Failure and Intestinal Transplantation. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2015, 60, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavicchi, M.; Beau, P. Prevalence of liver disease and contributing factors in patients receiving home parenteral nutrition for permanent intestinal failure. Ann. Intern. Med. 2000, 132, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauriti, G.; Zani, A. Incidence, prevention, and treatment of parenteral nutrition-associated cholestasis and intestinal failure-associated liver disease in infants and children: A systematic review. J. Parenter. Enteral. Nutr. 2014, 38, 70–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wales, P.W.; Allen, N.; Worthington, P.; George, D.; Compher, C. Clinical guidelines: Support of pediatric patients with intestinal failure at risk of parenteral nutrition-associated liver disease. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2014, 38, 538–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulet, O.; Joly, F. Some new insights in intestinal failure-associated liver disease. Curr. Opin. Organ. Transplant. 2009, 14, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.S.; Sokol, R.J. Intestinal Microbiota, Lipids and the Pathogenesis of Intestinal Failure-Associated Liver Disease. J. Pediatr. 2015, 167, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurvinen, A.; Nissinen, M.J. Effects of long-term parenteral nutrition on serum lipids, plant sterols, cholesterol metabolism, and liver histology in pediatric intestinal failure. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2011, 53, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hukkinen, M.; Mutanen, A. Parenteral Plant Sterols Accumulate in the Liver Reflecting Their Increased Serum Levels and Portal Inflammation in Children with Intestinal Failure. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2017, 41, 1014–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutanen, A.; Nissinen, M.J. Serum plant sterols, cholestanol, and cholesterol precursors associate with histological liver injury in pediatric onset intestinal failure. Am. J. Clin Nutr. 2014, 100, 1085–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orso, G.; Mandato, C. Pediatric parenteral nutrition-associated liver disease and cholestasis: Novel advances in pathomechanisms-based prevention and treatment. Dig. Liver Dis. 2016, 48, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira-Fantini, P.M.; Lapthorne, S.; Altered, F.X.R. Signalling is associated with bile acid dysmetabolism in short bowel syndrome-associated liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, 1115–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.-T.; Cao, Y. Altered systemic bile acid homeostasis contributes to liver disease in pediatric patients with intestinal failure. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutanen, A.; Lohi, J. Loss of ileum decreases serum fibroblast growth factor 19 in relation to liver inflammation and fibrosis in pediatric onset intestinal failure. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 1391–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Erpecum, K.J.; Schaap, F.G. Intestinal failure to produce FGF19: A culprit in intestinal failure-associated liver disease? J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 1231–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burghardt, K.M.; Avinashi, V. A CARD9 Polymorphism Is Associated with Decreased Likelihood of Persistent Conjugated Hyperbilirubinemia in Intestinal Failure. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Contreras, J.; Villalobos Gámez, J.L. Cholestasis induced by total parenteral nutrition; effects of the addition of Taurine (Tauramin®®) on hepatic function parameters; possible synergistic action of structured lipids (SMOFlipid®®). Nutr. Hosp. 2012, 27, 1900–1907. [Google Scholar]
- Raphael, B.P.; Duggan, C. Prevention and Treatment of Intestinal Failure-Associated Liver Disease in Children. Semin. Liver Dis. 2012, 32, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cober, M.P.; Teitelbaum, D.H. Prevention of parenteral nutrition-associated liver disease: Lipid minimization. Curr. Opin. Organ. Transplant. 2010, 15, 330–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gura, K.M.; Parsons, S.K. Use of a fish oil-based lipid emulsion to treat essential fatty acid deficiency in a soy allergic patient receiving parenteral nutrition. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 24, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gura, K.M.; Duggan, C.P. Reversal of parenteral nutrition-associated liver disease in two infants with short bowel syndrome using parenteral fish oil: Implications for future management. Pediatrics 2006, 118, e197–e201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandivada, P.; Fell, G.L. Long-Term Fish Oil Lipid Emulsion Use in Children with Intestinal Failure–Associated Liver Disease. J. Parenter. Enteral. Nutr. 2017, 41, 930–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gura, K.M.; Lee, S. Safety and efficacy of a fish-oil-based fat emulsion in the treatment of parenteral nutrition-associated liver disease. Pediatrics 2008, 121, e678–e686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Meijer, V.E.; Gura, K.M. Parenteral fish oil monotherapy in the management of patients with parenteral nutrition-associated liver disease. Arch. Surg. 2010, 145, 547–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandivada, P.; Fell, G.L. Lipid emulsions in the treatment and prevention of parenteral nutrition-associated liver disease in infants and children. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 629S–634S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandivada, P.; Cowan, E. Mechanisms for the effects of fish oil lipid emulsions in the management of parenteral nutrition-associated liver disease. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids 2013, 89, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puder, M.; Valim, C. Parenteral fish oil improves outcomes in patients with parenteral nutrition associated liver injury. Ann. Surg. 2009, 250, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premkumar, M.H.; Carter, B.A. High rates of resolution of cholestasis in parenteral nutrition-associated liver disease with fish oil-based lipid emulsion monotherapy. J. Pediatr. 2013, 162, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillman, E.M.; Helms, R.A. ω-3 long chain polyunsaturated Fatty acids for treatment of parenteral nutrition-associated liver disease: A review of the literature. J. Pediatr. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 16, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fallon, E.M.; Le, H.D. Prevention of parenteral nutrition-associated liver disease: Role of v-3 fish oil. Curr. Opin. Organ. Transplant. 2010, 15, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshpande, G.; Simmer, K. Fish Oil (SMOFlipid) and olive oil lipid (Clinoleic) in very preterm neonates. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2014, 58, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Park, H.J. Reversal of Intestinal Failure-Associated Liver Disease by Switching from a Combination Lipid Emulsion Containing Fish Oil to Fish Oil Monotherapy. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2016, 40, 437–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomsits, E.; Pataki, M. Safety and Efficacy of a Lipid Emulsion Containing a Mixture of Soybean Oil, Medium-chain Triglycerides, Olive Oil, and Fish Oil: A Randomised, Double-blind Clinical Trial in Premature Infants Requiring Parenteral Nutrition. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2010, 51, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goulet, O.; Antébi, H. A new intravenous fat emulsion containing soybean oil, medium-chain triglycerides, olive oil, and fish oil: A single-center, double-blind randomized study on efficacy and safety in pediatric patients receiving home parenteral nutrition. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2010, 34, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrin, D.G.; Ng, K. Impact of new-generation lipid emulsions on cellular mechanisms of parenteral nutrition-associated liver disease. Adv. Nutr. 2014, 5, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seida, J.C.; Mager, D.R. Parenteral ω-3 Fatty Acid Lipid Emulsions for Children with Intestinal Failure and Other Conditions. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2013, 37, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, V.; Malviya, M.N. Lipid emulsions for parenterally fed preterm infants. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, V.; Malviya, M.N. Lipid emulsions for parenterally fed term and late preterm infants. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilja, H.E.; Finkel, Y. Prevention and reversal of intestinal failure-associated liver disease in premature infants with short bowel syndrome using intravenous fish oil in combination with omega-6/9 lipid emulsions. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2011, 46, 1361–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, I.R.; Sterescu, A. Changing the Paradigm: Omegaven for the Treatment of Liver Failure in Pediatric Short Bowel Syndrome. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2009, 48, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandivada, P.; Baker, M.A. Predictors of failure of fish-oil therapy for intestinal failure–associated liver disease in children. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 104, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonucci, A.; Fronzoni, L. Chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 21, 2953–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercer, D.F.; Hobson, B.D. Hepatic Fibrosis Persists and Progresses Despite Biochemical Improvement in Children Treated with Intravenous Fish Oil Emulsion. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2013, 56, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, C.S.; Kaufman, S.S. Hepatic explant pathology of pediatric intestinal transplant recipients previously treated with ω-3 fatty acid lipid emulsion. J. Pediatr. 2014, 165, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandivada, P.; Chang, M.I. The Natural History of Cirrhosis from Parenteral Nutrition-Associated Liver Disease After Resolution of Cholestasis with Parenteral Fish Oil Therapy. Ann. Surg. 2015, 261, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.A.; Fisher, J.G. Preservation of Biochemical Liver Function with Low-Dose Soy-Based Lipids in Children with Intestinal Failure Associated Liver Disease. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2015, 60, 375–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Venick, R.S. Long-Term Outcomes in Children with Intestinal Failure-Associated Liver Disease Treated With 6 Months of Intravenous Fish Oil Followed by Resumption of Intravenous Soybean Oil. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2019, 43, 708–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumbo, C.; Martinez, M.I. Utility of Aminotransferase/Platelet Ratio Index to Predict Liver Fibrosis in Intestinal Failure-Associated Liver Disease in Pediatric Patients. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2017, 41, 884–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
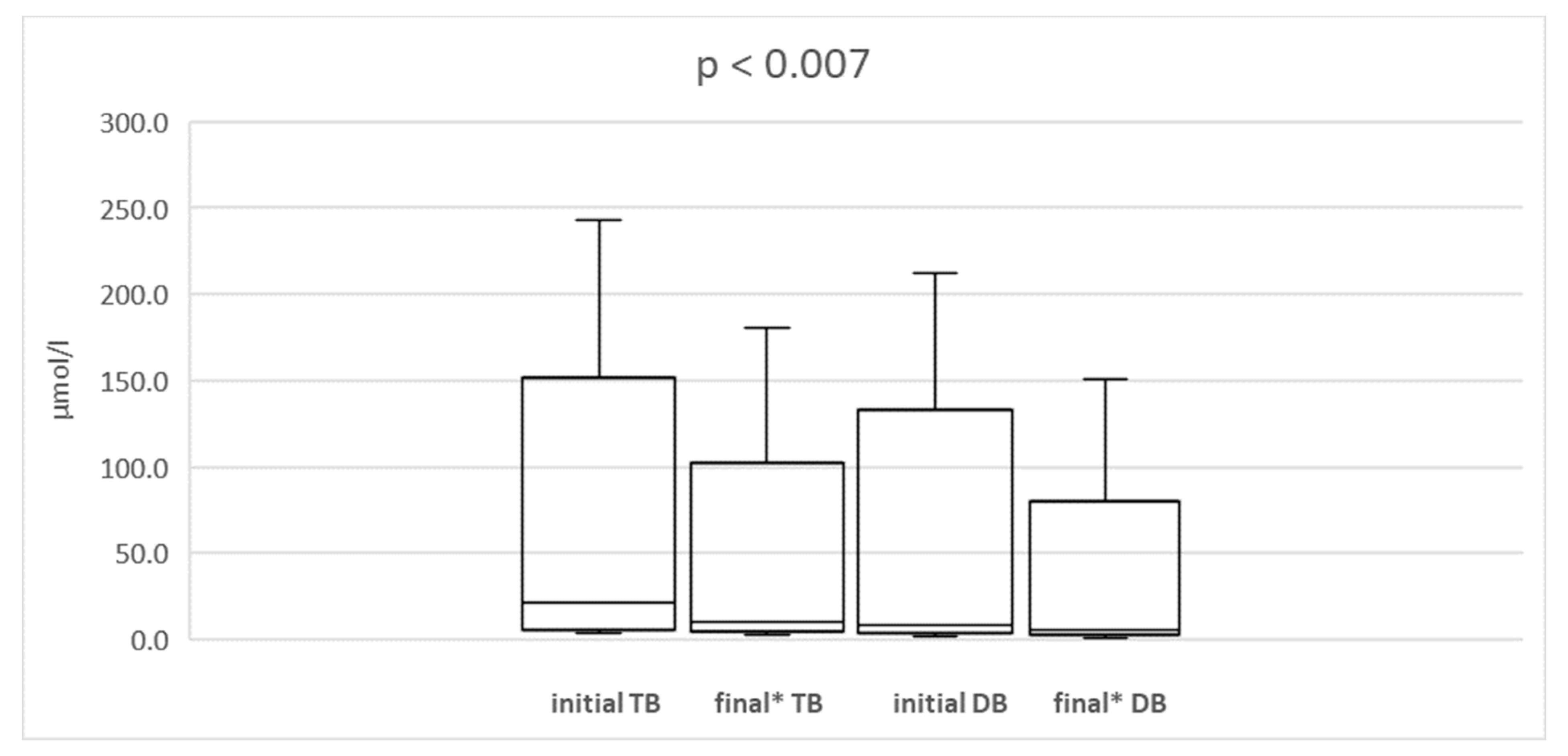
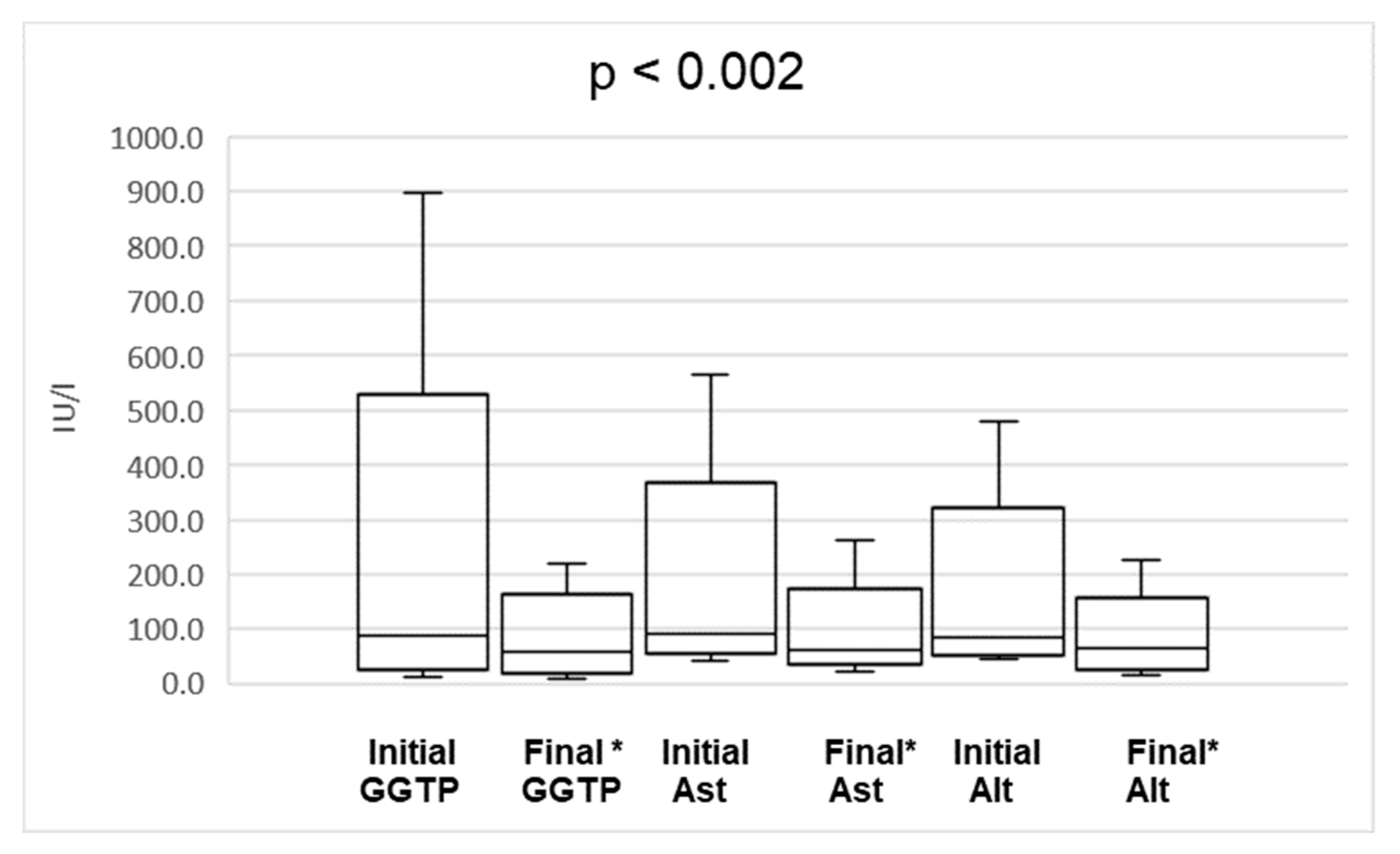

| Lipid Emulsion | 10% Omegaven (Fresenius Kabi®®) | 20% SmofLipid (Fresenius Kabi®®) | 20% Lipidem (BBraun®®) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Soybean oil | - | 30% | 40% |
| Olive oil | - | 25% | - |
| Medium chain triglycerides | - | 30% | 50% |
| Fish Oil | 100% | 15% | 10% |
| AST IU/L | ALT IU/L | GGT IU/L |
|---|---|---|
| 6 d.o.–6 m.o.: <84 7–12 m.o: <89 1–3 y.o.: <56 4–12 y.o.: <52 13–17 y.o.: <33 | 6 d.o–6 m.o.: <60 7–12 m.o: <57 1–12 y.o.: <39 13–17 y.o.: <26 | <1 y.o.: <203 1–3 y.o.: <87 4–6 y.o.: <26 7–12 y.o: <31 13–17 y.o.: <29 |
| Number of Patients: | 40 |
|---|---|
| Sex: | |
| Male: | 20 |
| Female: | 20 |
| Median age (range): | 38 m.o. (1.5–200) |
| Median time of PN before the treatment (range) | 30.5 months (0.5–166) |
| Median body weight (range): | 13.33 kg (2–40.3) |
| Diagnosis: | |
| SBS | 30 |
| Motility disorders | 9 |
| Others | 1 |
| Median days of PN/week (range): | 7 (4–7) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Danko, M.; Żyła-Pawlak, A.; Książyk, J.; Olszewska-Durkacz, K.; Sibilska, M.; Żydak, J.; Popińska, K. A Retrospective Analysis of the Effect of Combination of Pure Fish Oil with Third Generation Lipid Emulsion on Liver Function in Children on Long-Term Parenteral Nutrition. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2495. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11102495
Danko M, Żyła-Pawlak A, Książyk J, Olszewska-Durkacz K, Sibilska M, Żydak J, Popińska K. A Retrospective Analysis of the Effect of Combination of Pure Fish Oil with Third Generation Lipid Emulsion on Liver Function in Children on Long-Term Parenteral Nutrition. Nutrients. 2019; 11(10):2495. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11102495
Chicago/Turabian StyleDanko, Mikołaj, Aleksandra Żyła-Pawlak, Janusz Książyk, Katarzyna Olszewska-Durkacz, Marta Sibilska, Joanna Żydak, and Katarzyna Popińska. 2019. "A Retrospective Analysis of the Effect of Combination of Pure Fish Oil with Third Generation Lipid Emulsion on Liver Function in Children on Long-Term Parenteral Nutrition" Nutrients 11, no. 10: 2495. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11102495
APA StyleDanko, M., Żyła-Pawlak, A., Książyk, J., Olszewska-Durkacz, K., Sibilska, M., Żydak, J., & Popińska, K. (2019). A Retrospective Analysis of the Effect of Combination of Pure Fish Oil with Third Generation Lipid Emulsion on Liver Function in Children on Long-Term Parenteral Nutrition. Nutrients, 11(10), 2495. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11102495





