Ginsenoside Rh2 Ameliorates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury by Regulating the TLR4/PI3K/Akt/mTOR, Raf-1/MEK/ERK, and Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathways in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Animals
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid (BALF) Collection and Cell Count
2.5. Nitrites Assay
2.6. Histopathological Analysis
2.7. Cytokine Assay
2.8. Lung Wet to Dry (W/D) Weight Ratio
2.9. Myeloperoxidase Activity
2.10. Western Blot Analysis
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
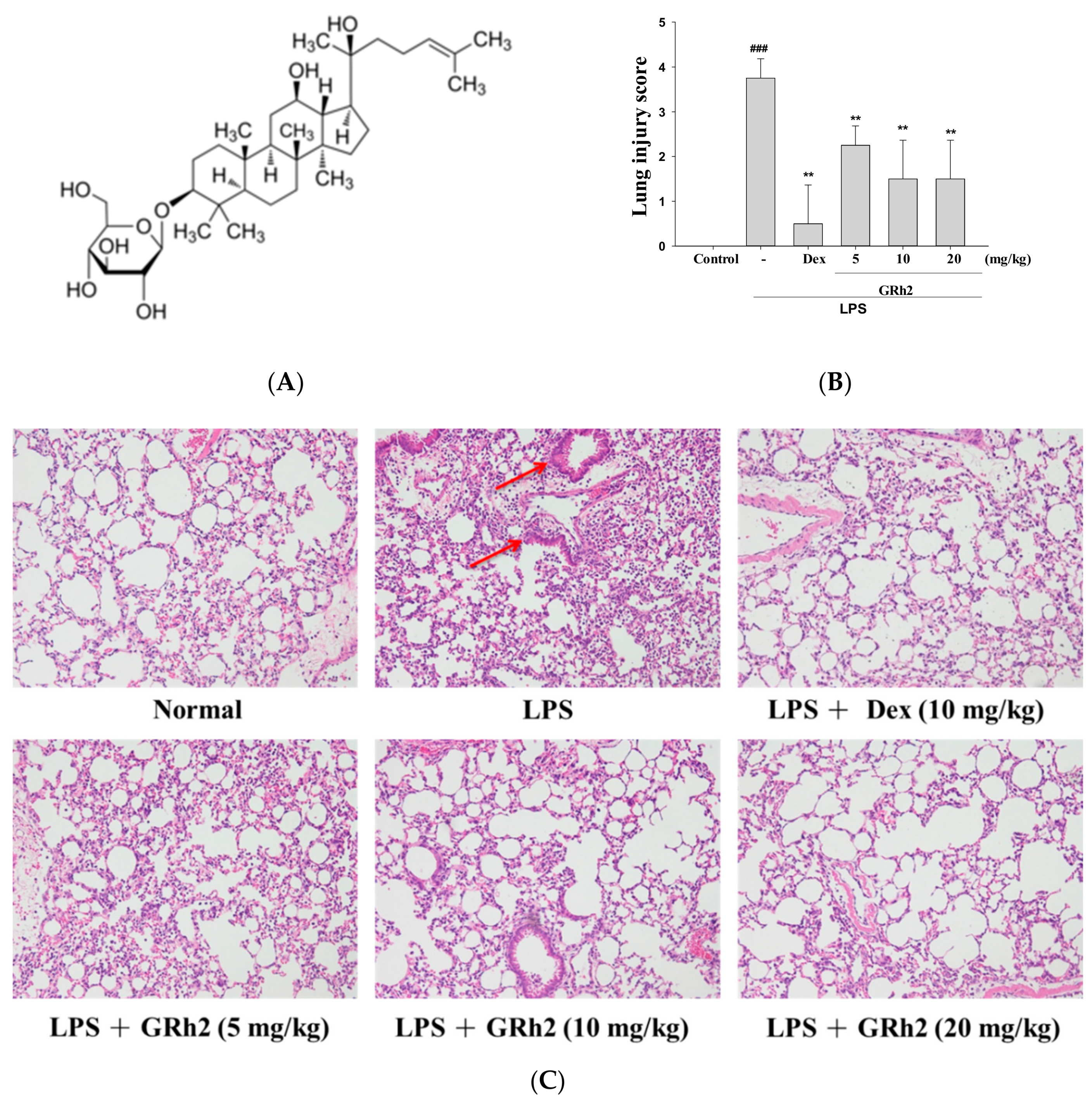
3.1. GRh2 Reduces LPS-Induced Histopathology Changes in Mice Lungs
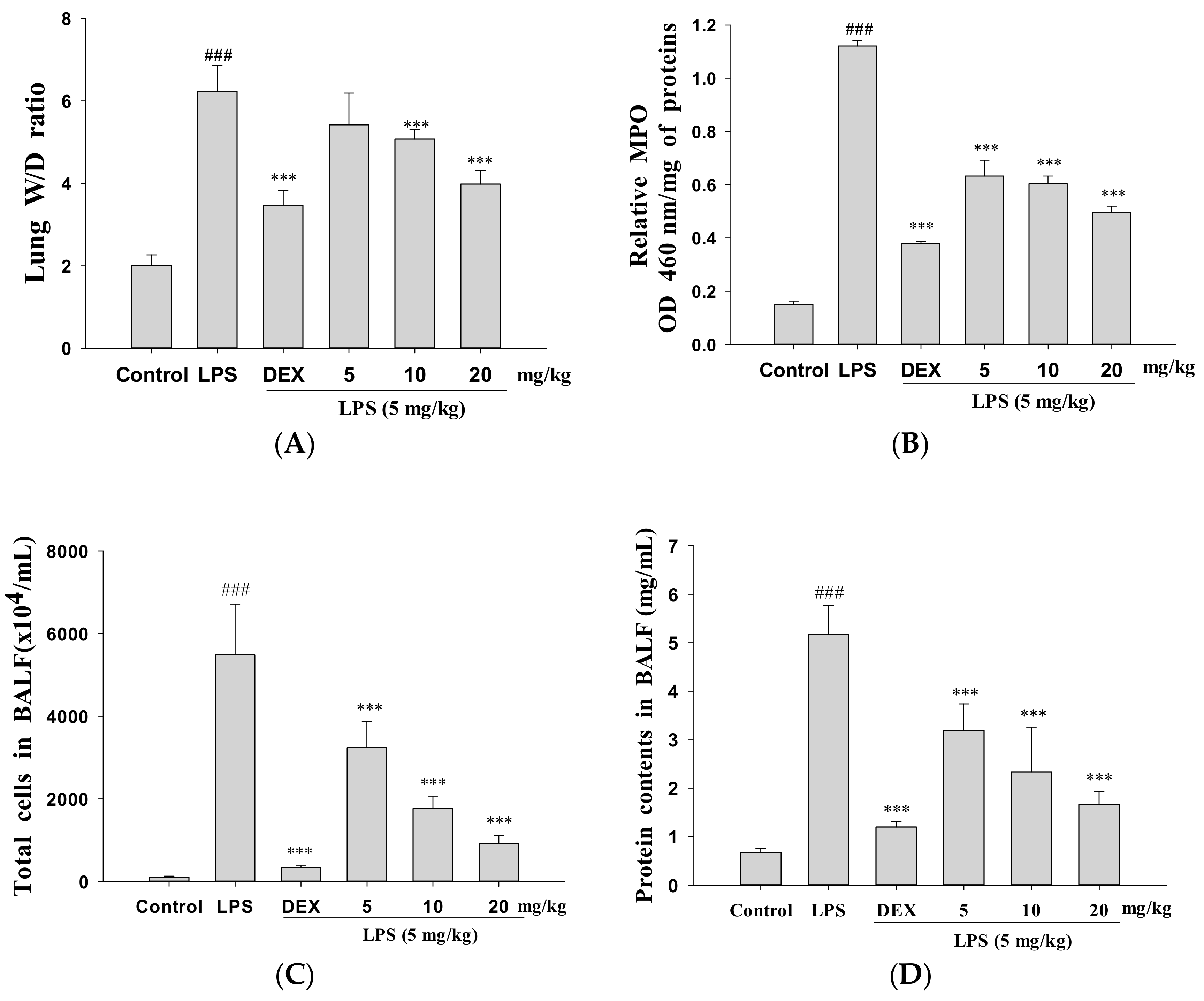
3.2. Decreased Pulmonary Wet/Dry Weight Ratio and MPO Activity
3.3. Decreased Total Cell Count and Protein Concentration
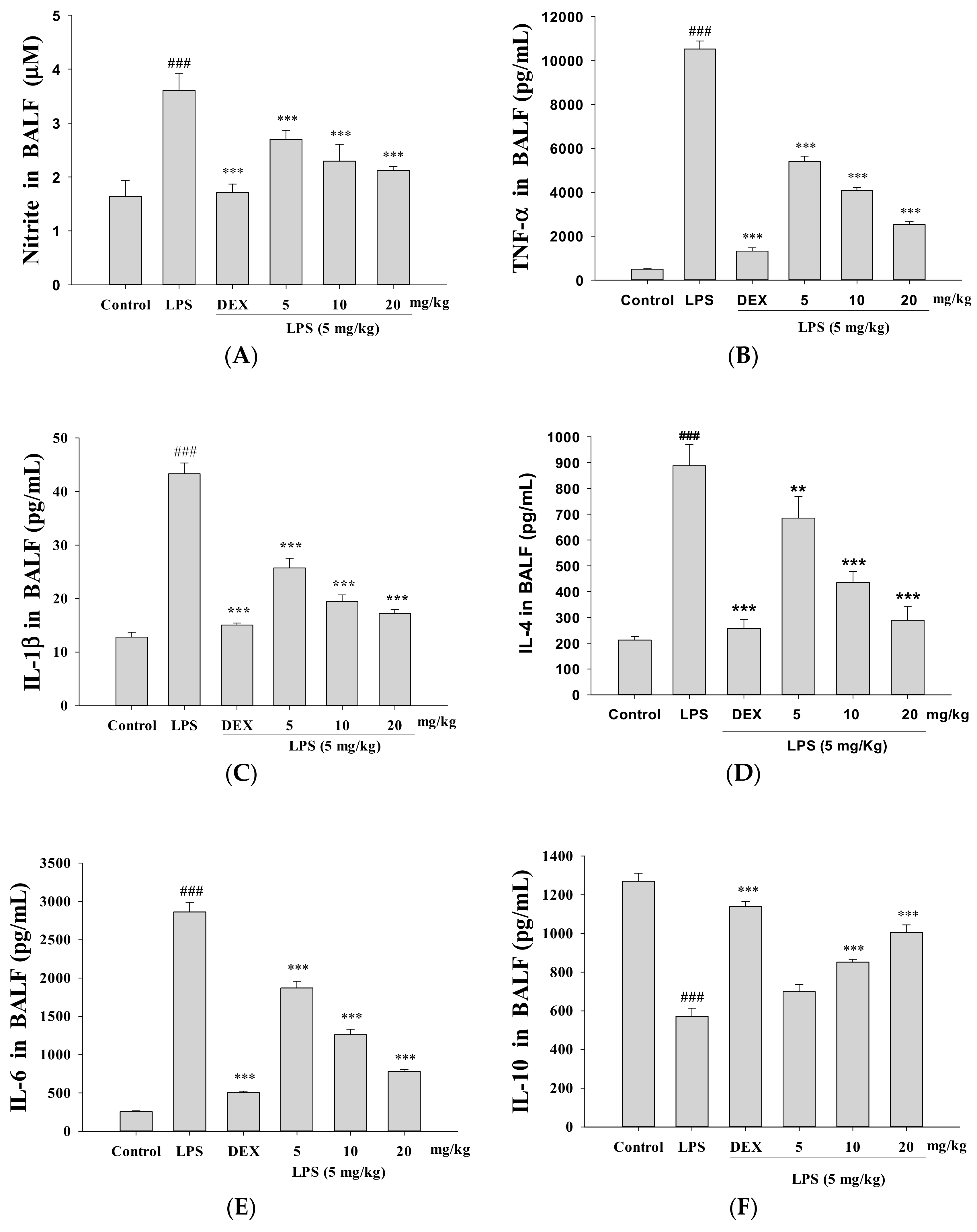
3.4. Decreased Proinflammatory Cytokine Levels
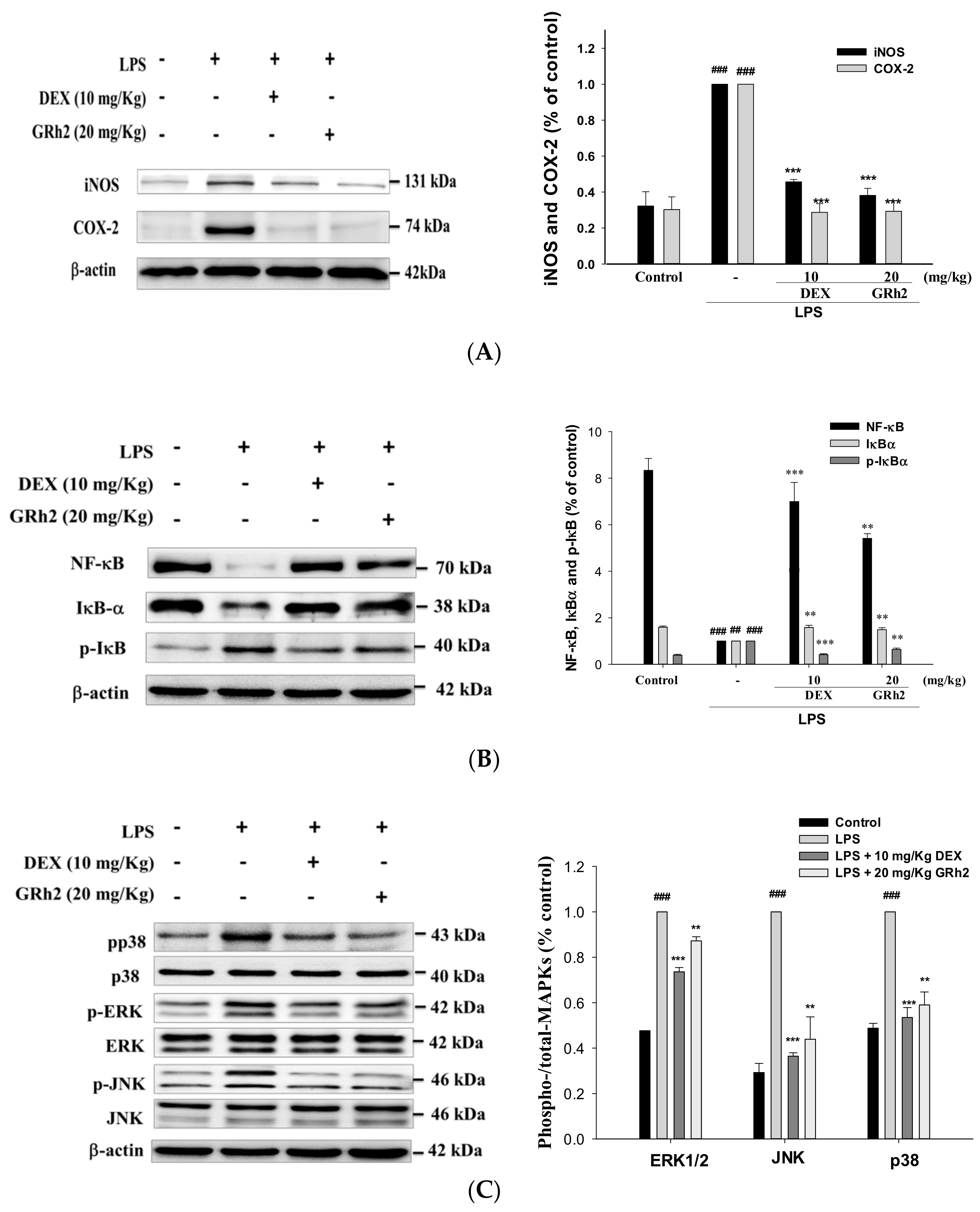
3.5. Inhibition of LPS-Induced ALI iNOS and COX-2 and Inactivation of NF-κB and IκBα Protein Expressions
3.6. Suppression of the MAPK Pathway Activation
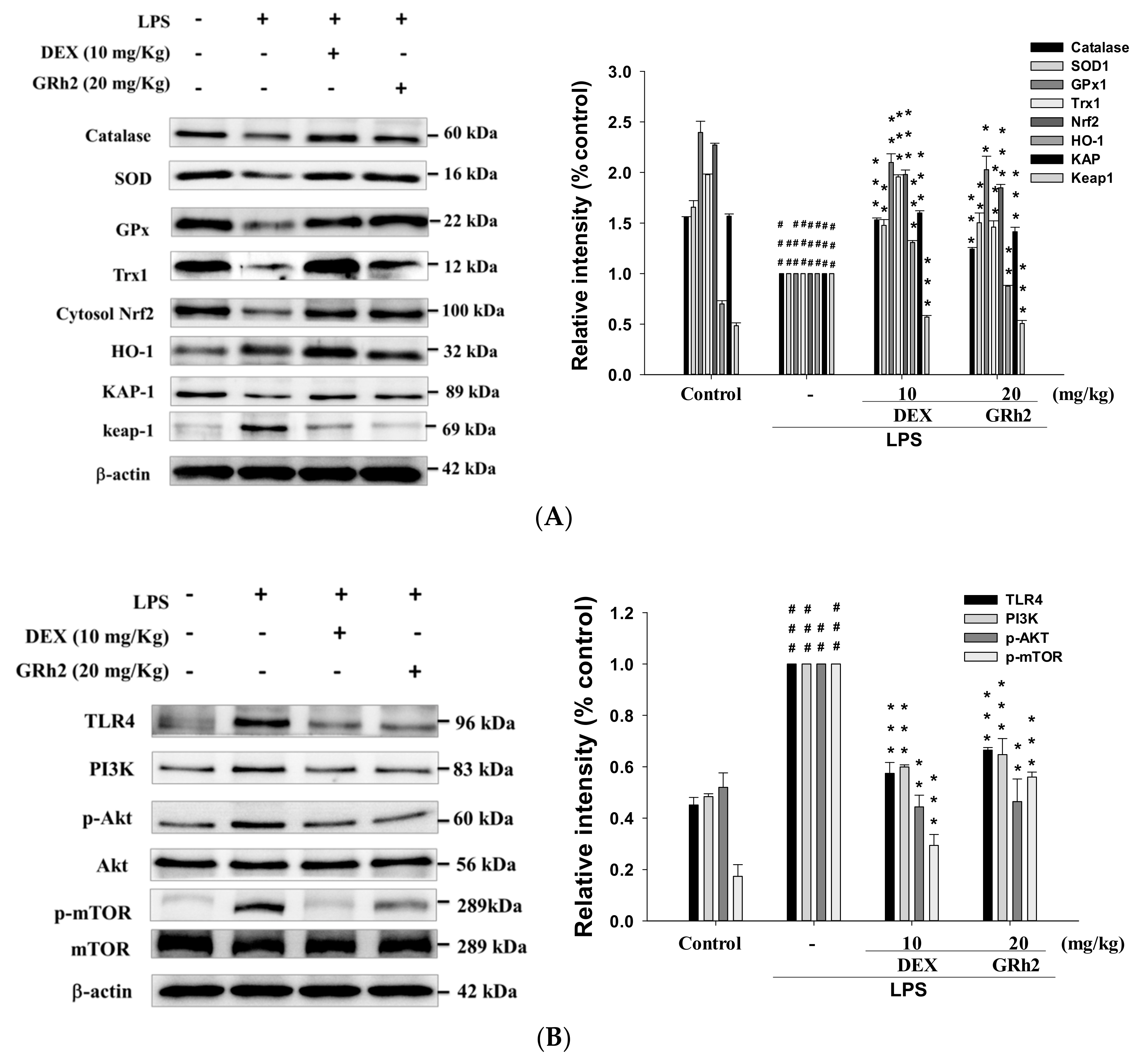
3.7. Decreased LPS-Induced Oxidative Stress and HO-1/Trx-1/KAP-1/Nrf2 Signaling Pathway
3.8. Decreased TLR4/PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling
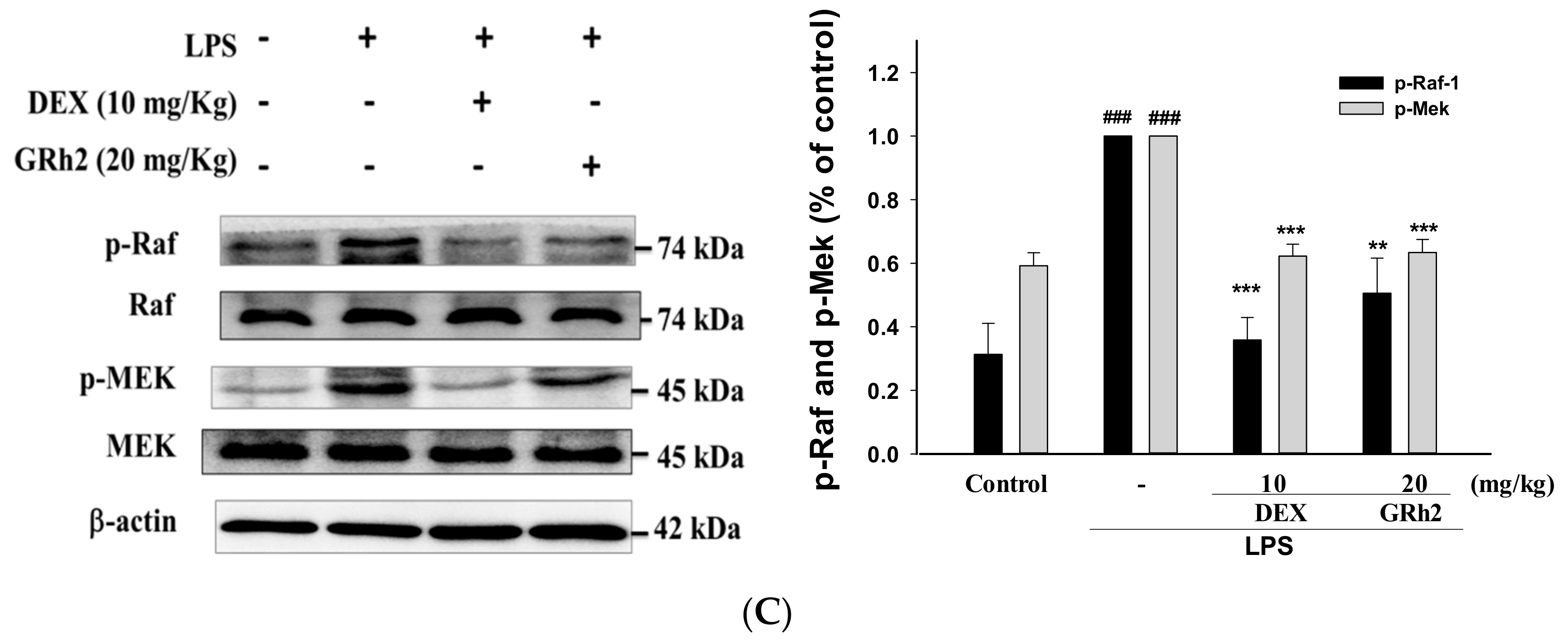
3.9. Activation of the RAF/MEK Pathway
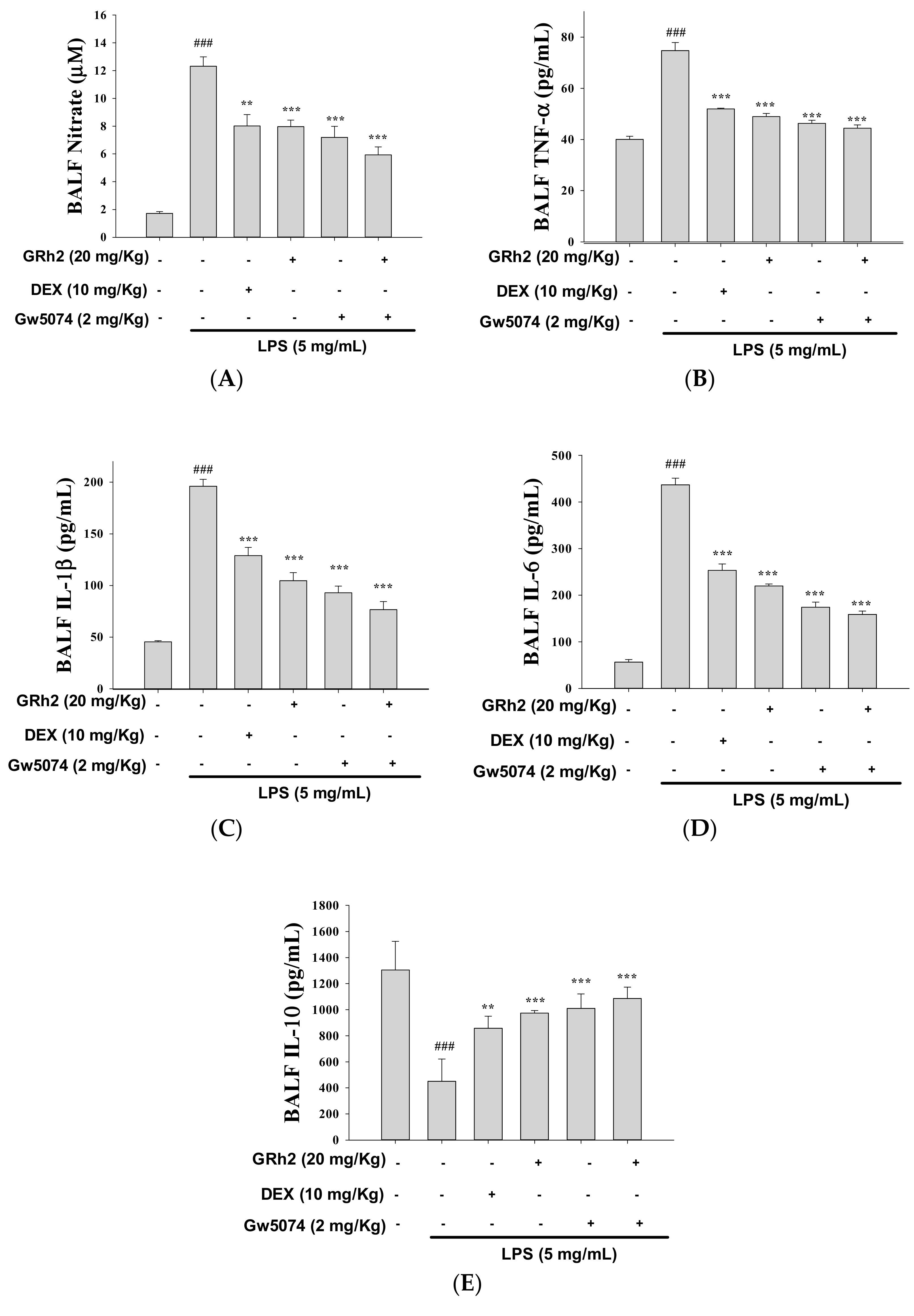
3.10. Blocking RAF Synergy with GW-5074 to Increase Anti-Inflammatory Capacity of GRh2
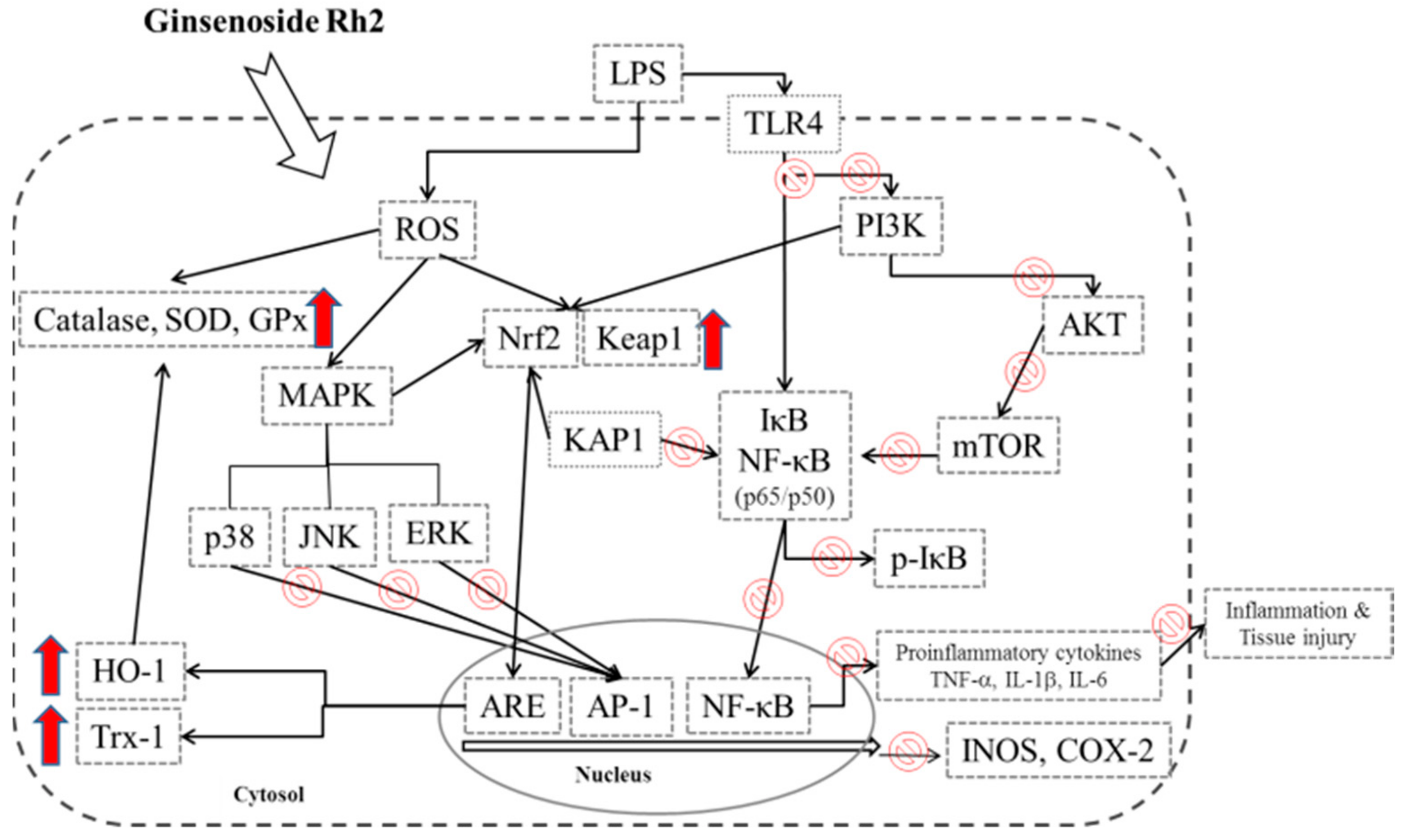
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, K.C.; Ho, Y.L.; Hsieh, W.T.; Huang, S.S.; Chang, Y.S.; Huang, G.J. Apigenin-7-glycoside prevents LPS-induced acute lung injury via downregulation of oxidative enzyme expression and protein activation through inhibition of MAPK phosphorylation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 1736–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.C.; Ho, Y.L.; Chen, C.Y.; Hsieh, W.T.; Chang, Y.S.; Huang, G.J. Lobeline improve acute lung injury via nuclear factor-kB-signaling pathway and oxidative stress. Respirator. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2016, 225, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.J.; Deng, J.S.; Chen, C.C.; Huang, C.J.; Sung, P.J.; Huang, S.S.; Kuo, Y.H. Methanol extract of Antrodia camphorata protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by suppressing NF-κB and MAPK pathways in mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 5321–5329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.S.; Lin, H.J.; Deng, J.S.; Wu, W.T.; Huang, S.S.; Huang, G.J. Preventive effects of Velvet Antler (Cervus elaphus) against lipopolysaccharide induced acute lung injury in mice by inhibiting MAPK/NF-κB activation and inducing AMPK/Nrf2 pathways. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2018, 2018, 2870503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, Y.H.; Deng, J.S.; Pan, H.P.; Liao, J.C.; Huang, S.S.; Huang, G.J. Sclareol ameliorate lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury through inhibition of MAPK and induction of HO-1 signaling. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 44, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.C.; Deng, J.S.; Huang, S.S.; Wu, S.H.; Chen, C.C.; Lin, W.R.; Lin, H.Y.; Huang, G.J. Anti-inflammatory activity of Sanghuangporus sanghuang mycelium. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.C.; Huang, S.S.; Kuo, Y.H.; Ho, Y.L.; Yang, C.S.; Chang, Y.S.; Huang, G.J. Ugonin M, a Helminthostachys zeylanica constituent, prevents LPS-induced acute lung injury through TLR4-mediated MAPK and NF-kB signaling pathways. Molecules 2017, 22, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Lan, S.J.; Liu, Q.R.; Liu, J.M.; Chen, X.Q. Neuroglobin, a novel intracellular hexa-coordinated globin, functions as a tumor suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma via Raf/MAPK/Erk. Mol. Pharmacol. 2013, 83, 1109–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.; Im, K.; Kim, G.; Min, H. Antiviral activity of 20(R)-ginsenoside Rh2 against murine gammaherpesvirus. J. Ginseng. Res. 2017, 41, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, J.; Yin, J.; Xu, C.; Mu, Y.; Lv, S. 20(S)-ginsenoside Rh2 induce the apoptosis and autophagy in U937 and K562 Cells. Nutrients 2018, 10, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Choi, J.S. Effect of ginsenoside Rh-2 via activation of caspase-3 and Bcl-2-insensitive pathway in ovarian cancer cells. Physiol. Res. 2016, 65, 1031–1037. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Dai, C.; Shang, Y.; Xie, J. Ginsenoside Rh2 alleviates tumor-associated depression in a mouse model of colorectal carcinoma. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2016, 8, 2189–2195. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Zhao, T.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L. Ginsenoside Rh2 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma through β-catenin and autophagy. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinoth, K.R.; Oh, T.W.; Park, Y.K. Anti-inflammatory effects of ginsenoside-Rh2 inhibits LPS-induced activation of microglia and overproduction of inflammatory mediators via modulation of TGF-β1/Smad pathway. Neurochem. Res. 2016, 41, 951–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, H.S.; Ku, J.M.; Choi, H.S.; Woo, J.K.; Jang, B.H.; Shin, Y.C.; Ko, S.G. Induction of caspase-dependent apoptosis by apigenin by inhibiting STAT3 signaling in HER2-overexpressing MDA-MB-453 breast cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 2014, 34, 2869–2882. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.Y.; Chen, Y.C.; Lin, J.G.; Lin, I.H.; Huang, H.F.; Yeh, C.C.; Chen, J.J.; Huang, G.J. Asatone prevents acute lung injury by reducing expressions of NF-κB, MAPK and inflammatory cytokines. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2018, 46, 651–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeung, Y.G.; Stanley, E.R. A solution for stripping antibodies from polyvinylidene fluoride immunoblots for multiple reprobing. Anal. Biochem. 2009, 389, 89–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.C.; Deng, J.S.; Huang, S.S.; Wu, S.H.; Lin, H.Y.; Huang, G.J. Anti-inflammatory activity of Sanghuangporus sanghuang by suppressing TLR4-mediated PI3K/AKT/mTOR/IKKß signaling pathway. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 21234–21251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthay, M.A.; Zimmerman, G.A. Acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome: Four decades of inquiry into pathogenesis and rational management. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2005, 33, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, C.L.; Lin, Y.C.; Wang, H.M.; Chou, T.C. Baicalein, an active component of Scutellaria baicalensis, protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 153, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.C.; Lai, Y.S.; Chou, T.C. The protective effect of alpha-lipoic acid in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury is mediated by heme oxygenase-1. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2013, 2013, 590363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, M.; Zhu, T.; Zhang, W.; Wang, T.; Shen, Y.C.; Wan, Q.F.; Wen, F.Q. Emodin ameliorates LPS-induced acute lung injury, involving the inactivation of NF-κB in mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 19355–19368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.; Zhu, L.; Wang, J.; He, H.; Chang, X.; Gao, J.; Shumin, W.; Yan, T. Anti-inflammatory effects of water extract of Taraxacum mongolicum hand.-Mazz on lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in acute lung injury by suppressing PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 168, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, J.; Pan, D.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, L.; Sun, J.; Wang, Y.; You, Q.D.; Xi, T.; Guo, Q.L.; Lu, N. Wogonin prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury and inflammation in mice via peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma-mediated attenuation of the nuclear factor-kappaB pathway. Immunology 2014, 143, 241–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Du, L.; Zhao, L.; Shang, R.; Liu, D.; Jing, Q.; Liang, J.; Ren, Y. The total alkaloids of Aconitum tanguticum protect against lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 155, 1483–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Y.T.; Xiao, L.; Zhu, L.; Wan, Q.G.; Yan, T. Anti-inflammatory effects of apigenin in lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory in acute lung injury by suppressing COX-2 and NF-kB pathway. Inflammation 2014, 37, 2085–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.Y.; Yang, J.J.; Lee, S.S.; Chen, C.J.; Huang, Y.C.; Huang, K.H.; Kuan, Y.H. Protective effect of Ginkgo biloba leaves extract, EGb761, on endotoxin-induced acute lung injury via a JNK- and Akt-dependent NFκB pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 6337–6344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouratis, M.A.; Magkrioti, C.; Oikonomou, N.; Katsifa, A.; Prestwich, G.D.; Kaffe, E.; Aidinis, V. Autotaxin and endotoxin-induced acute lung injury. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, L.; Cao, F.; Xu, G.; Xie, H.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, C. Mogroside IIIE attenuates LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice partly through regulation of the TLR4/MAPK/NF-κB axis via AMPK activation. Phytother. Res. 2017, 31, 1097–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shie, P.H.; Huang, S.S.; Deng, J.S.; Huang, G.J. Spiranthes sinensis suppresses production of pro-inflammatory mediators by down-regulating the NF-κB signaling pathway and up-regulating HO-1/Nrf2 anti-oxidant protein. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2015, 43, 969–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.J.; Huang, S.S.; Deng, J.S. Anti-inflammatory activities of inotilone from Phellinus linteus through the inhibition of MMP-9, NF-κB, and MAPK activation In Vitro and In Vivo. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.S.; Chiu, C.S.; Lin, T.H.; Lee, M.M.; Lee, C.Y.; Chang, S.J.; Hou, W.C.; Huang, G.J.; Deng, J.S. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of aqueous extract of Centipeda minima. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 147, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.C.; Ho, Y.L.; Huang, G.J.; Chang, Y.S. Anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory effects of Lobelia chinensis Lour In Vitro and In Vivo. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2015, 43, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.L.; Chen, C.S.; Hsu, C.W.; Li, M.H.; Chang, H.; Tsai, S.H.; Chu, S.J. Therapeutic effects of baicalin on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in rats. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2008, 36, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Wang, Y. The protective effect of cinnamaldehyde on lipopolysaccharide induced acute lung injury in mice. Cell Mol. Biol. 2017, 63, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, L.; Li, L.; Lu, S.; Li, K.; Su, Z.; Wang, Y.; Fan, X.; Li, X.; Zhao, G. The protective effect of dexmedetomidine on LPS-induced acute lung injury through the HMGB1-mediated TLR4/NF-κB and PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathways. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 94, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Gulbins, E.; Zhang, Y. Role of kinase suppressor of ras-1 in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 30, 905–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Jiang, H.; Wang, Y.; Ma, J. Pentoxifylline inhibits hepatic stellate cells proliferation via the Raf/ERK pathway. APMIS 2012, 120, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Y.; Cao, Y.X.; Xu, C.B.; Zhang, Y. The Raf-1 inhibitor GW5074 and dexamethasone suppress sidestream smoke-induced airway hyperresponsiveness in mice. Respir. Res. 2008, 9, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemmar, A.; Al-Salam, S.; Beegam, S.; Yuvaraju, P.; Hamadi, N.; Ali, B.H. In Vivo protective effects of Nootkatone against particles-induced lung injury caused by diesel exhaust is mediated via the NF-κB Pathway. Nutrients 2018, 10, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.P.; Li, Y.C.; Chen, H.Y.; Lin, R.H.; Huang, S.S.; Chen, H.L.; Kuan, P.C.; Liao, M.F.; Chen, C.J.; Kuan, Y.H. Protective effects of luteolin against lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury involves inhibition of MEK/ERK and PI3K/Akt pathways in neutrophils. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2010, 31, 831–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsieh, Y.-H.; Deng, J.-S.; Chang, Y.-S.; Huang, G.-J. Ginsenoside Rh2 Ameliorates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury by Regulating the TLR4/PI3K/Akt/mTOR, Raf-1/MEK/ERK, and Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathways in Mice. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1208. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10091208
Hsieh Y-H, Deng J-S, Chang Y-S, Huang G-J. Ginsenoside Rh2 Ameliorates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury by Regulating the TLR4/PI3K/Akt/mTOR, Raf-1/MEK/ERK, and Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathways in Mice. Nutrients. 2018; 10(9):1208. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10091208
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsieh, Yung-Hung, Jeng-Shyan Deng, Yuan-Shiun Chang, and Guan-Jhong Huang. 2018. "Ginsenoside Rh2 Ameliorates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury by Regulating the TLR4/PI3K/Akt/mTOR, Raf-1/MEK/ERK, and Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathways in Mice" Nutrients 10, no. 9: 1208. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10091208
APA StyleHsieh, Y.-H., Deng, J.-S., Chang, Y.-S., & Huang, G.-J. (2018). Ginsenoside Rh2 Ameliorates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury by Regulating the TLR4/PI3K/Akt/mTOR, Raf-1/MEK/ERK, and Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathways in Mice. Nutrients, 10(9), 1208. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10091208



