A Natural Dietary Supplement with a Combination of Nutrients Prevents Neurodegeneration Induced by a High Fat Diet in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Plasma Level of Lipids and Glucose
2.3. Total Protein Extraction and Western Blot
2.4. Tissue Cholesterol Assay
2.5. Analysis of Nitrogens Level, Griess Assay
2.6. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.7. Detection of Oxidative Levels: DCFH-DA Assay
2.8. Lipid Peroxidation Assay
2.9. Nile Red Staining
2.10. Immunofluorescence
2.11. Immunohistochemistry
2.12. Nuclear Staining
2.13. Tunel Assay
2.14. ELISA Assay
2.15. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
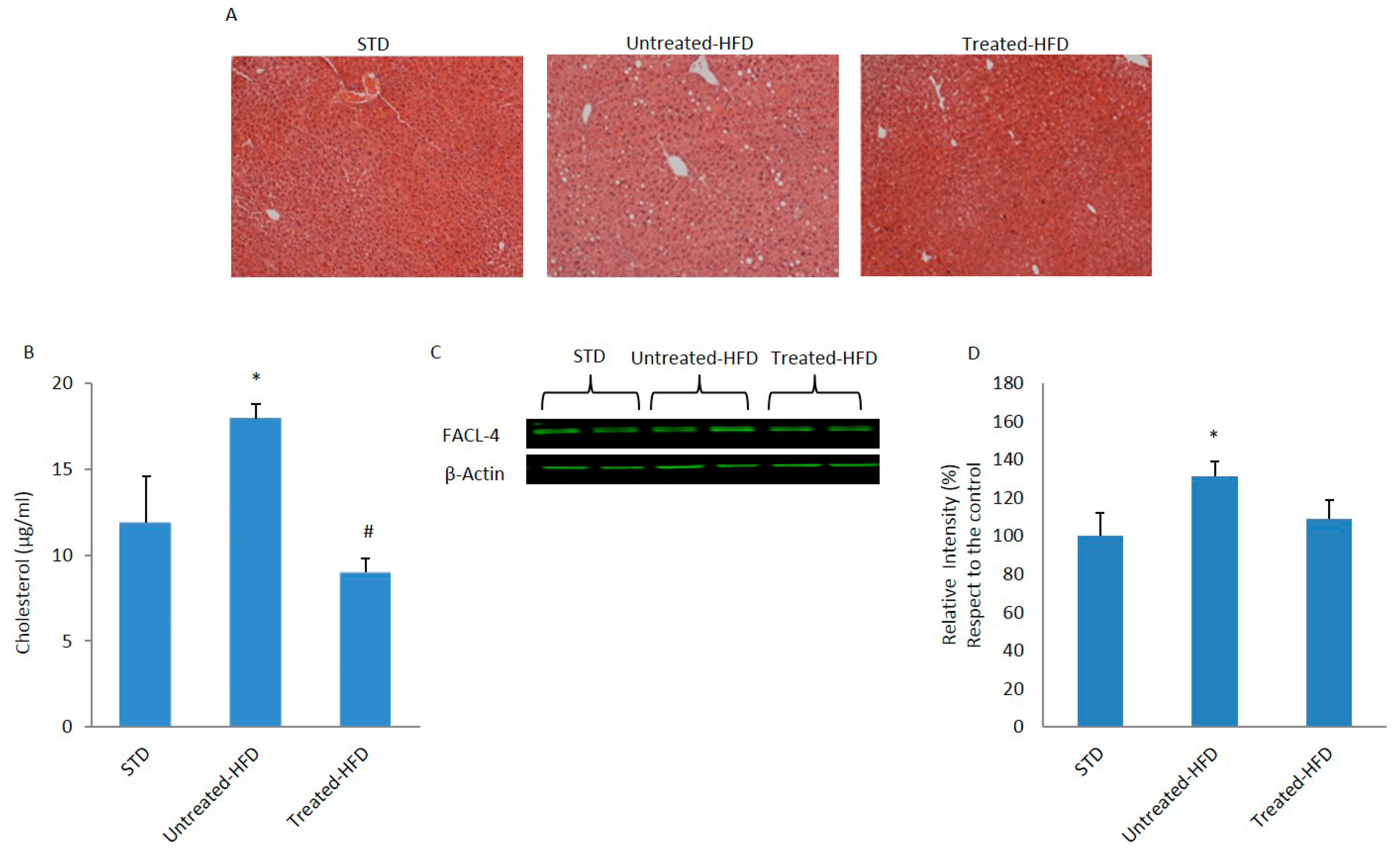
3.1. NDS Prevents HFD-Induced Dysmetabolism
3.2. Brain Lipid Accumulation is Prevented by NDS
3.3. NDS Decreases Insulin Signaling Alteration
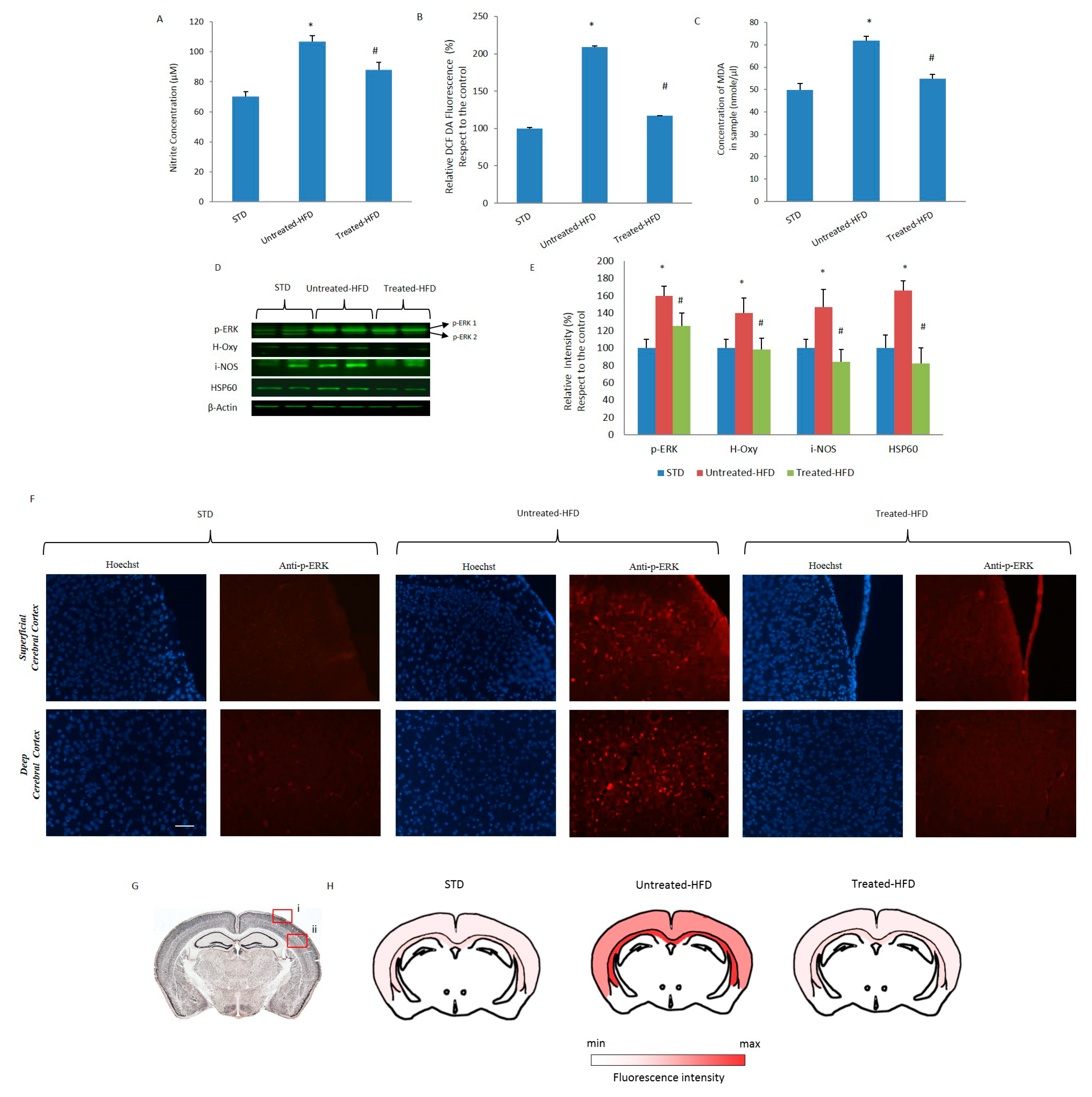
3.4. NDS Prevents Oxidative Stress and Lipid Peroxidation
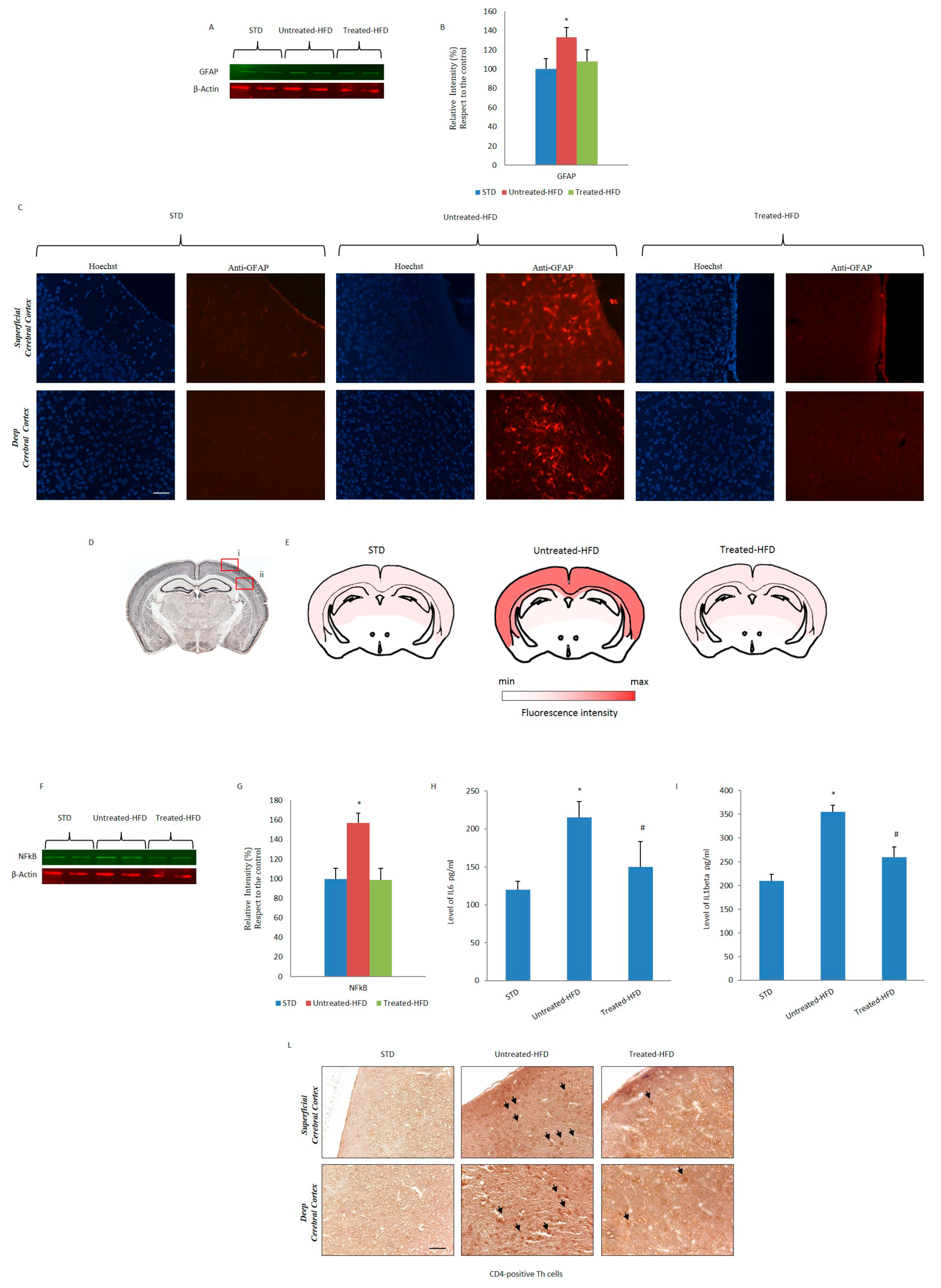
3.5. NDS Decreases the Hdf-Induced Brain Inflammation Profile
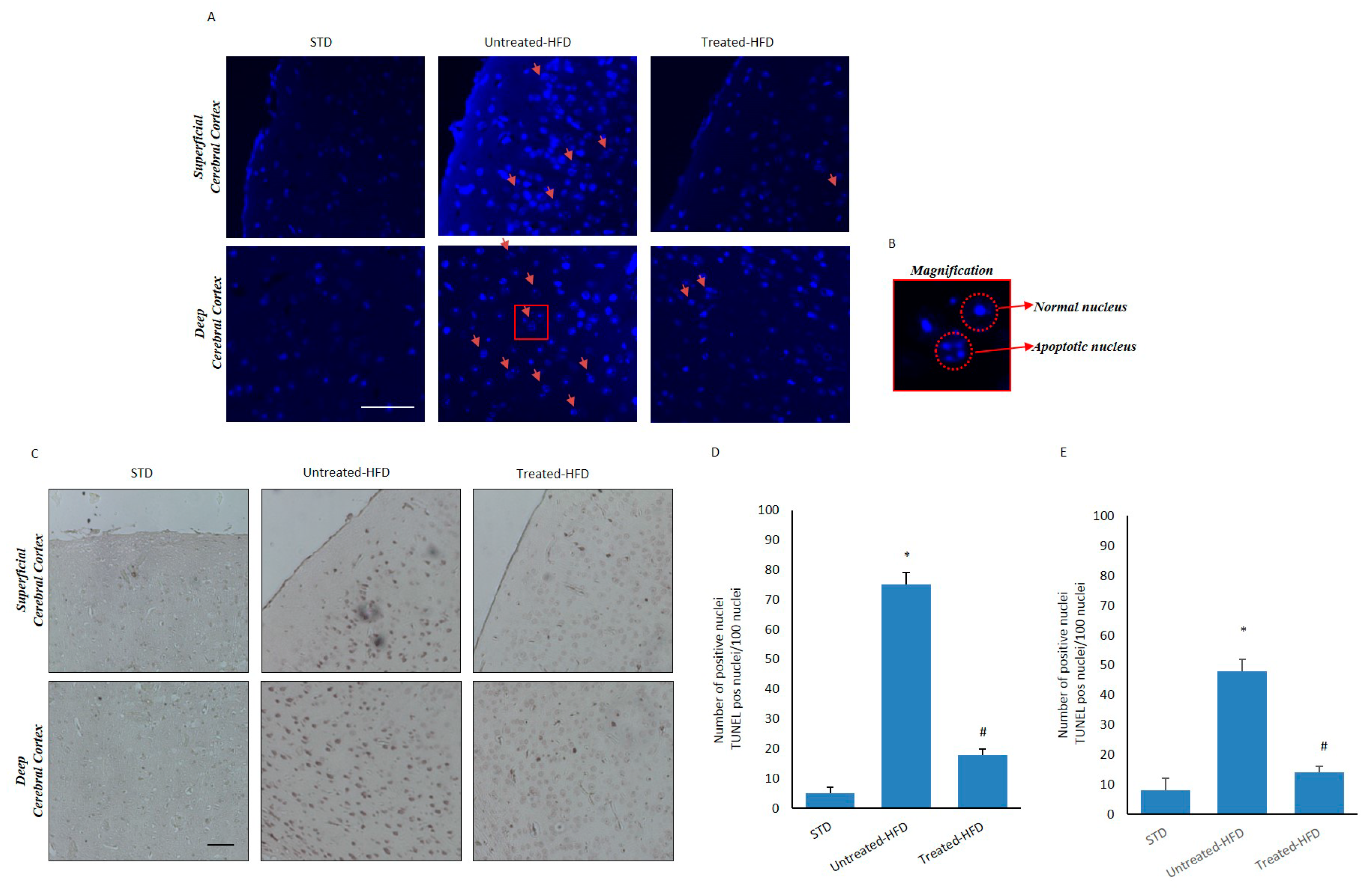
3.6. NDS Counteracts Hfd-Induced Neurodegeneration
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Castelli, V.; Grassi, D.; Bocale, R.; D’Angelo, M.; Antonosante, A.; Cimini, A.; Ferri, C.; Desideri, G. Diet and brain health: Which role for polyphenols? Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 24, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- S Roriz-Filho, J.; Sá-Roriz, T.M.; Rosset, I.; Camozzato, A.L.; Santos, A.C.; Chaves, M.L.; Moriguti, J.C.; Roriz-Cruz, M. (Pre)Diabetes, Brain, Aging and Cognition. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1792, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayarama, A.; Pike, C.J. Alzheimer’s Disease and Type 2 Diabetes: Multiple Mechanisms Contribute to Interactions. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2014, 14, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.B. Obesity, leptin, and Alzheimer’s disease. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1243, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghareeb, D.A.; Hafez, H.S.; Hussien, H.M.; Kabapy, N.F. Non-alcoholic fatty liver induces insulin resistance and metabolic disorders with development of brain damage and dysfunction. Metab. Brain Dis. 2011, 26, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bynoe, M.S. NAFLD induces neuroinflammation and accelerates Alzheimer’s disease. J. Immunol. 2016, 196 (Suppl. 1), 188. Available online: http://www.jimmunol.org/content/196/1_Supplement/188.4.short (accessed on 1 May 2016).
- Charradi, K.; Mahmoudi, M.; Bedhiafi, T.; Kadri, S.; Elkahoui, S.; Limam, F.; Aouani, E. Dietary supplementation of grape seed and skin flour mitigates brain oxidative damage induced by a high-fat diet in rat: Gender dependency. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 87, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borg, M.L.; Omran, S.F.; Weir, J.; Meikle, P.J.; Watt, M.J. Consumption of a high-fat diet, but not regular endurance exercise training, regulates hypothalamic lipid accumulation in mice. J. Physiol. 2012, 1, 4377–4389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyn-Cook, L.E., Jr.; Lawton, M.; Tong, M.; Silbermann, E.; Longato, L.; Jiao, P.; Mark, P.; Wands, J.R.; Xu, H.; de la Monte, S.M. Hepatic ceramide may mediate brain insulin resistance and neurodegeneration in type 2 diabetes and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2009, 16, 715–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryan, J.N.; Suzanne, C. Insulin Resistance and Alzheimer’s Disease: Bioenergetic Linkages. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2017, 31, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Monte, S.M.; Wands, J.R. Review of insulin and insulin-like growth factor expression, signaling, and malfunction in the central nervous system: Relevance to Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2005, 7, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Felice, F.G.; Vieira, M.N.; Bomfim, T.R.; Decker, H.; Velasco, P.T.; Lambert, M.P.; Viola, K.L.; Zhao, W.Q.; Ferreira, S.T.; Klein, W.L. Protection of synapses against Alzheimer’s-linked toxins: Insulin signaling prevents the pathogenic binding of Abeta oligomers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 10, 1971–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picone, P.; Giacomazza, D.; Vetri, V.; Carrotta, R.; Militello, V.; San Biagio, P.L.; Di Carlo, M. Insulin activated Akt rescues Ab oxidative stress induced cell death by orchestrating molecules trafficking. Aging Cell 2011, 10, 832–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuzzo, D.; Picone, P.; Baldassano, S.; Caruana, L.; Messina, E.; Marino Gammazza, A.; Cappello, F.; Mulè, F.; Di Carlo, M. Insulin Resistance as Common Molecular Denominator Linking Obesity to Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2015, 12, 723–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Monte, S. Type 3 Diabetes is Sporadic Alzheimer’s disease: Mini-Review. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014, 24, 1954–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Monte, S.; Tong, M. Brain metabolic dysfunction at the core of Alzheimer’s disease. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2014, 15, 548–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Monte, S.; Derdak, Z.; Wands, J.R. Alcohol, insulin resistance and the liver-brain axis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 27, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Monte, S.M.; Tong, M.; Nguyen, V.; Setshedi, M.; Longato, L.; Wands, J.R. Ceramide-mediated insulin resistance and impairment of cognitive-motor functions. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2010, 21, 967–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, L.; Bhaumik, E.; Raychaudhuri, U.; Chakraborty, R. Role of nutraceuticals in human health. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 49, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willett, W.C.; Sacks, F.; Trichopoulou, A.; Drescher, G.; Ferro-Luzzi, A.; Helsing, E.; Trichopoulos, D. Mediterranean diet pyramid: A cultural model for healthy eating. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1995, 61, 1402S–1406S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solfrizzi, V.; Frisardi, V.; Seripa, D.; Logroscino, G.; Imbimbo, B.P.; D’Onofrio, G.; Addante, F.; Sancarlo, D.; Cascavilla, L.; Pilotto, A.; et al. Mediterranean diet in predementia and dementia syndromes. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2011, 8, 520–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasto, S.; Buscemi, S.; Barera, A.; Di Carlo, M.; Accardi, G.; Caruso, C. Mediterranean diet and healthy ageing: A sicilian perspective. Gerontology 2014, 60, 508–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasto, S.; Barera, A.; Rizzo, C.; Di Carlo, M.; Caruso, C.; Panotopoulos, G. Mediterranean Diet and Longevity: An Example of Nutraceuticals? Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2014, 12, 735–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancuso, C.; Bates, T.E.; Butterfield, D.A.; Calafato, S.; Cornelius, C.; De Lorenzo, A.; Dinkova Kostova, A.T.; Calabrese, V. Natural antioxidants in Alzheimer’s disease. Expert. Opin. Investig. Drugs 2007, 16, 1921–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picone, P.; Bondì, M.L.; Montana, G.; Bruno, A.; Pitarresi, G.; Giammona, G.; Di Carlo, M. Ferulic acid inhibits oxidative stress and cell death induced by Ab oligomers: Improved delivery by solid lipid nanoparticles. Free Radic. Res. 2009, 43, 1133–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picone, P.; Nuzzo, D.; Di Carlo, M. Ferulic acid: A natural antioxdant against oxidative stress induced by oligomeric Abeta on sea urchin embryo. Biol. Bull. 2013, 224, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sgarbossa, A.; Giacomazza, D.; Di Carlo, M. Ferulic Acid: A hope for Alzheimer’s disease therapy for plants. Nutrients 2015, 15, 5764–5782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patti, A.M.; Al-Rasad, K.; Katsiki, N.; Banerjee, Y.; Nikolic, D.; Vanella, L.; Giglio, R.V.; Giannone, V.A.; Montalto, G.; Rizzo, M. Effect of a Natural Supplement Containing Curcuma longa, Guggul, and Chlorogenic Acid in Patients With Metabolic Syndrome. Angiology 2015, 66, 856–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amato, A.; Caldara, G.F.; Nuzzo, D.; Baldassano, S.; Picone, P.; Rizzo, M.; Mulè, F.; Di Carlo, M. NAFLD and Atherosclerosis are Prevented by a Natural Dietary Supplement Containing Curcumin, Silymarin, Guggul, Chlorogenic Acid and Inulin in Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet. Nutrients 2017, 9, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuzzo, D.; Picone, P.; Caruana, L.; Vasto, S.; Barera, A.; Caruso, C.; Di Carlo, M. Inflammatory mediators as biomarkers in brain disorders. Inflammation 2014, 37, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitmer, R.A. Type 2 diabetes and risk of cognitive impairment and dementia. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2007, 7, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.G.; Krenz, A.; Toussaint, L.E.; Maurer, K.J.; Robinson, S.; Yan, A.; Torres, L.; Bynoe, M.S. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease induces signs of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) in wild-type mice and accelerates pathological signs of AD in an AD model. J. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 13, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldassano, S.; Rappa, F.; Amato, A.; Cappello, F.; Mulè, F. GLP-2 as beneficial factor in the glucose homeostasis in mice fed a high fat diet. J. Cell. Physiol. 2015, 230, 3029–3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldassano, S.; Amato, A.; Rappa, F.; Cappello, F.; Mulè, F. Influence of endogenous glucagon like peptide-2on lipid disorders in mice fed a high fat diet. Endocr. Res. 2016, 41, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Liu, Q.; Kalavagunta, P.K.; Huang, Q.; Lv, W.; An, X.; Chen, H.; Wang, T.; Heriniaina, R.M.; Qiao, T.; et al. Normal diet Vs High fat diet—A comparative study: Behavioral and neuroimmunological changes in adolescent male mice. Metab. Brain Dis. 2018, 33, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, K.; Hughes, C.F.; Ward, M.; Hoey, L.; McNulty, H. Diet, nutrition and the ageing brain: Current evidence and new directions. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2018, 77, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirmi, S.; Ferlazzo, N.; Lombardo, G.E.; Ventura-Spagnolo, E.; Gangemi, S.; Calapai, G.; Navarra, M. Neurodegenerative Diseases: Might Citrus Flavonoids Play a Protective Role? Molecules 2016, 21, 1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farías, G.A.; Guzmán-Martínez, L.; Delgado, C.; Maccioni, R.B. Nutraceuticals: A novel concept in prevention and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease and related disorders. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2014, 42, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, F.; Riezzo, G.; Chiloiro, M.; De Michele, G.; Chimienti, G.; Marconi, E.; D’Attoma, B.; Linsalata, M.; Clemente, C. Metabolic effects of a diet with inulin-enriched pasta in healthy young volunteers. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2010, 16, 825–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nohr, L.A.; Rasmussen, L.B.; Straand, J. Resin from the mukul myrrh tree, guggul, can it be used for treating hypercholesterolemia? A randomized, controlled study. Complement. Ther. Med. 2009, 17, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.J.; Li, Z.H.; Liu, L.; Tang, W.X.; Wang, Y.; Dong, M.R.; Xiao, C. Curcumin Attenuates Beta-Amyloid-Induced Neuroinflammation via Activation of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor-Gamma Function in a Rat Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 19, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciacca, M.F.M.; Romanucci, V.; Zarrelli, A.; Monaco, I.; Lolicato, F.; Spinella, N.; Galati, C.; Grasso, G.; D’Urso, L.; Romeo, M.; et al. Inhibition of Aβ Amyloid Growth and Toxicity by Silybins: The Crucial Role of Stereochemistry. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2017, 8, 1767–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebai, O.; Belkhir, M.; Sanchez-Gomez, M.V.; Matute, C.; Fattouch, S.; Amri, M. Differential Molecular Targets for Neuroprotective Effect of Chlorogenic Acid and its Related Compounds Against Glutamate Induced Excitotoxicity and Oxidative Stress in Rat Cortical Neurons. Neurochem. Res. 2017, 42, 3559–3572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, C.; Sepulveda, M.F.; Elliott, J.; Harris, P.A.; Bailey, S.R. Dietary fructan carbohydrate increases amine production in the equine large intestine: Implications for pasture-associated laminitis. J. Anim. Sci. 2007, 11, 2949–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruciani-Guglielmacci, C.; López, M.; Campana, M.; le Stunff, H. Brain Ceramide Metabolism in the Control of Energy Balance. Front. Physiol. 2017, 12, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jana, A.; Hogan, E.L.; Pahan, K. Ceramide and neurodegeneration: Susceptibility of neurons and oligodendrocytes to cell damage and death. J. Neurol. Sci. 2009, 15, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaurasia, B.; Summers, S.A. Ceramides—Lipotoxic Inducers of Metabolic Disorders. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 26, 538–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavez, J.A.; Holland, W.L.; Bar, J.; Sandhoff, K.; Summers, S.A. Acid ceramidase overexpression prevents the inhibitory effects of saturated fatty acids on insulin signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 20, 20148–20153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, T.; Paris, D.; Town, T.; Rojiani, A.M.; Sparks, D.L.; Delledonne, A.; Crawford, F.; Abdullah, L.I.; Humphrey, J.A.; Dickson, D.W.; et al. Cholesterol accumulates in senile plaques of Alzheimer disease patients and in transgenic APP(sw) mice. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2001, 60, 778–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.P.; Tang, Y.; Zhou, S.; Toh, B.H.; McLean, C.; Li, H. Cholesterol involvement in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2010, 43, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urizar, N.L.; Liverman, A.B.; Dodds, D.T.; Silva, F.V.; Ordentlich, P.; Yan, Y.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Heyman, R.A.; Mangelsdorf, D.J.; Moore, D.D. A natural product that lowers cholesterol as an antagonist ligand for FXR. Science 2002, 296, 1703–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huseini, H.F.; Larijani, B.; Heshmat, R.; Fakhrzadeh, H.; Radjabipour, B.; Toliat, T.; Raza, M. The efficacy of Silybum marianum (L.) Gaertn. (silymarin) in the treatment of type II diabetes: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, clinical trial. Phytother. Res. 2006, 20, 1036–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, G.C.M. Amelioration of obesity, glucose intolerance, and oxidative stress in high-fat diet and low-dose streptozotocininduced diabetic rats by combination consisting of “curcumin with piperine and quercetin”. ISRN Pharmacol. 2012, 2012, 957283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajik, N.; Tajik, M.; Mack, I.; Enck, P. The potential effects of chlorogenic acid, the main phenolic components in coffee, on health: A comprehensive review of the literature. Eur. J. Nutr. 2017, 56, 2215–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, B. Oxidative stress and the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2013, 2013, 316523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Morúa, A.; Soto-Urquieta, M.G.; Franco-Robles, E.; Zúñiga-Trujillo, I.; Campos-Cervantes, A.; Pérez-Vázquez, V.; Ramírez-Emiliano, J. Curcumin decreases oxidative stress in mitochondria isolated from liver and kidneys of high-fat diet-induced obese mice. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2013, 15, 905–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, N.; Rashid, S.; Nafees, S.; Hasan, S.K.; Shahid, A.; Majed, F.; Sultana, S. Protective effect of Chlorogenic acid against methotrexate induced oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis in rat liver: An experimental approach. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2017, 25, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Souza, C.T.; Araujo, E.P.; Bordin, S.; Ashimine, R.; Zollner, R.L.; Boschero, A.C.; Saad, M.J.; Velloso, L. Consumption of a fat-rich diet activates a proinflammatory response and induces insulin resistance in the hypothalamus. Endocrinology 2015, 146, 4192–4199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Dong, Y.; Duan, S.; Zhu, D.; Deng, L. Corrigendum to “Metabolic Syndrome, Inflammation, and Cancer”. Mediat. Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 1. Available online: https://scholar.google.com.hk/scholar?hl=zh-CN&as_sdt=0%2C5&q=Corrigendum+to+%22Metabolic+Syndrome%2C+Inflammation%2C+and+Cancer%22.&btnG= (accessed on 21 December 2017). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, J.N.; Zong, Y.; Zhong, L.M.; Li, Y.M.; Zhang, W.; Bian, L.G.; Ai, Q.L.; Liu, Y.D.; Sun, J.; Lu, D. Gastrodin inhibits expression of inducible NO synthase, cyclooxygenase-2 and proinflammatory cytokines in cultured LPS-stimulated microglia via MAPK pathways. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Ingredient (g/kg) | STD | HFD |
|---|---|---|
| Acid Casein 741 | 200 | 265.00 |
| l-Cystine | 2.8 | 4 |
| Maltodextrine—0032 | 33.2 | 160 |
| Sucrose | 300 | 90 |
| Cellulose (Arbocel) | 50 | 65.5 |
| Soybean oil | 25 | 30 |
| Lard | 19 | 220 |
| Vitamin mix AIN-93-VX-PF2439 | 10 | 13 |
| Mineral mix AIN-93G-MX-PF2348 | 45 | 48 |
| Choline bitartrate | 1.9 | 3 |
| Calcium Phosphate dibasic | 13 | 3.4 |
| Total Energy | ||
| Kcal/g | 3.5 | 6 |
| Protein, % | 18.5 | 23 |
| Carbohydrate, % | 60 | 38 |
| Fat, % | 3 | 34 |
| STD | Untreated-HFD | NDS Treated-HFD | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body Weight (g) | 25.1 ± 1.1 | 33.1 ± 0.66 * | 27.1 ± 0.7 # | * p < 0.05; # p < 0.05 |
| TG (mg/dL) | 49 ± 4.2 | 68.7 ± 3.2 * | 55 ± 2.9 # | * p < 0.05; # p < 0.05 |
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 85.8 ± 4.8 | 112.6 ± 5.2 * | 90 ± 7.1 # | * p < 0.05; # p < 0.05 |
| LDL | 37 ± 5.2 | 62.6 ± 5.5 * | 43 ± 4.3 # | * p < 0.05; # p < 0.05 |
| HDL | 52.8 ± 4.2 | 36 ± 3.8 * | 49.5 ± 2.9 # | * p < 0.05; # p < 0.05 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nuzzo, D.; Amato, A.; Picone, P.; Terzo, S.; Galizzi, G.; Bonina, F.P.; Mulè, F.; Di Carlo, M. A Natural Dietary Supplement with a Combination of Nutrients Prevents Neurodegeneration Induced by a High Fat Diet in Mice. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10091130
Nuzzo D, Amato A, Picone P, Terzo S, Galizzi G, Bonina FP, Mulè F, Di Carlo M. A Natural Dietary Supplement with a Combination of Nutrients Prevents Neurodegeneration Induced by a High Fat Diet in Mice. Nutrients. 2018; 10(9):1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10091130
Chicago/Turabian StyleNuzzo, Domenico, Antonella Amato, Pasquale Picone, Simona Terzo, Giacoma Galizzi, Francesco Paolo Bonina, Flavia Mulè, and Marta Di Carlo. 2018. "A Natural Dietary Supplement with a Combination of Nutrients Prevents Neurodegeneration Induced by a High Fat Diet in Mice" Nutrients 10, no. 9: 1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10091130
APA StyleNuzzo, D., Amato, A., Picone, P., Terzo, S., Galizzi, G., Bonina, F. P., Mulè, F., & Di Carlo, M. (2018). A Natural Dietary Supplement with a Combination of Nutrients Prevents Neurodegeneration Induced by a High Fat Diet in Mice. Nutrients, 10(9), 1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10091130







