Prophylactic Neuroprotection of Total Glucosides of Paeoniae Radix Alba against Semen Strychni-Induced Neurotoxicity in Rats: Suppressing Oxidative Stress and Reducing the Absorption of Toxic Components
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
2.2. Herb Preparation
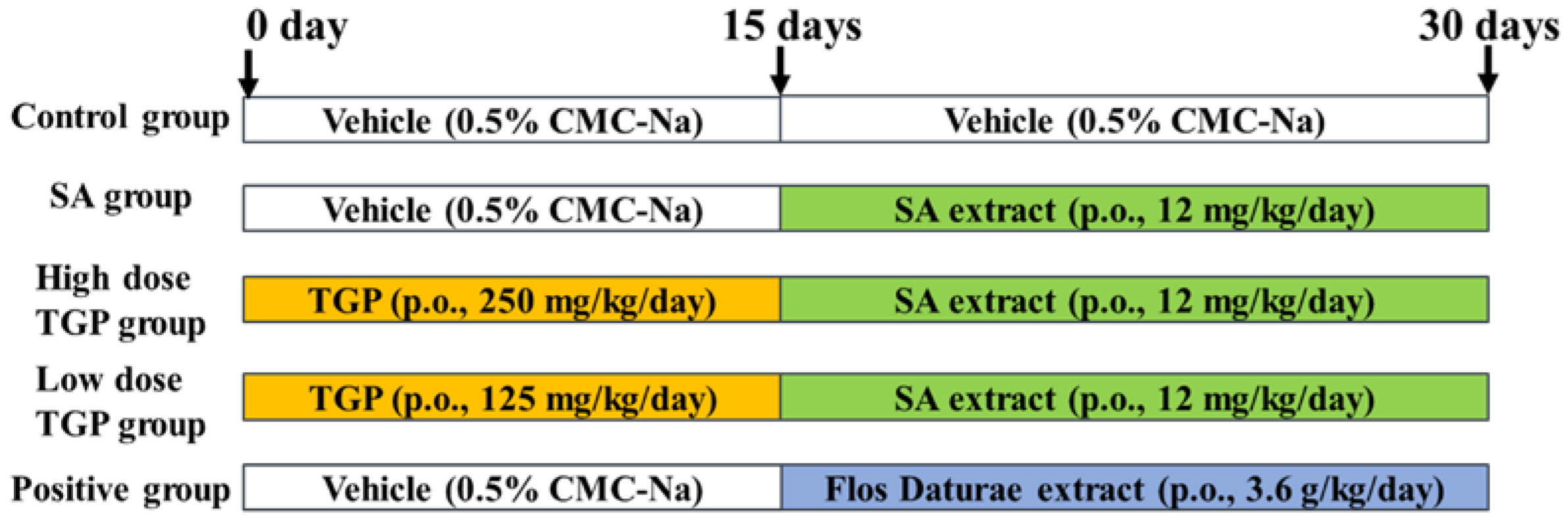
2.3. Animal Treatment
2.4. Physical and Behavioral Testing
2.5. Biochemical Assay and Histopathology
2.5.1. Biochemical Assay
2.5.2. Histological Examination
2.6. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
2.7. HPLC-MS/MS Analysis
2.7.1. Instrumentation and Operation Conditions
2.7.2. Working Solution Preparation
2.7.3. Sample Preparation
2.7.4. Method Validation
2.8. Data Processing
3. Results
3.1. Physical and Behavioral Testing
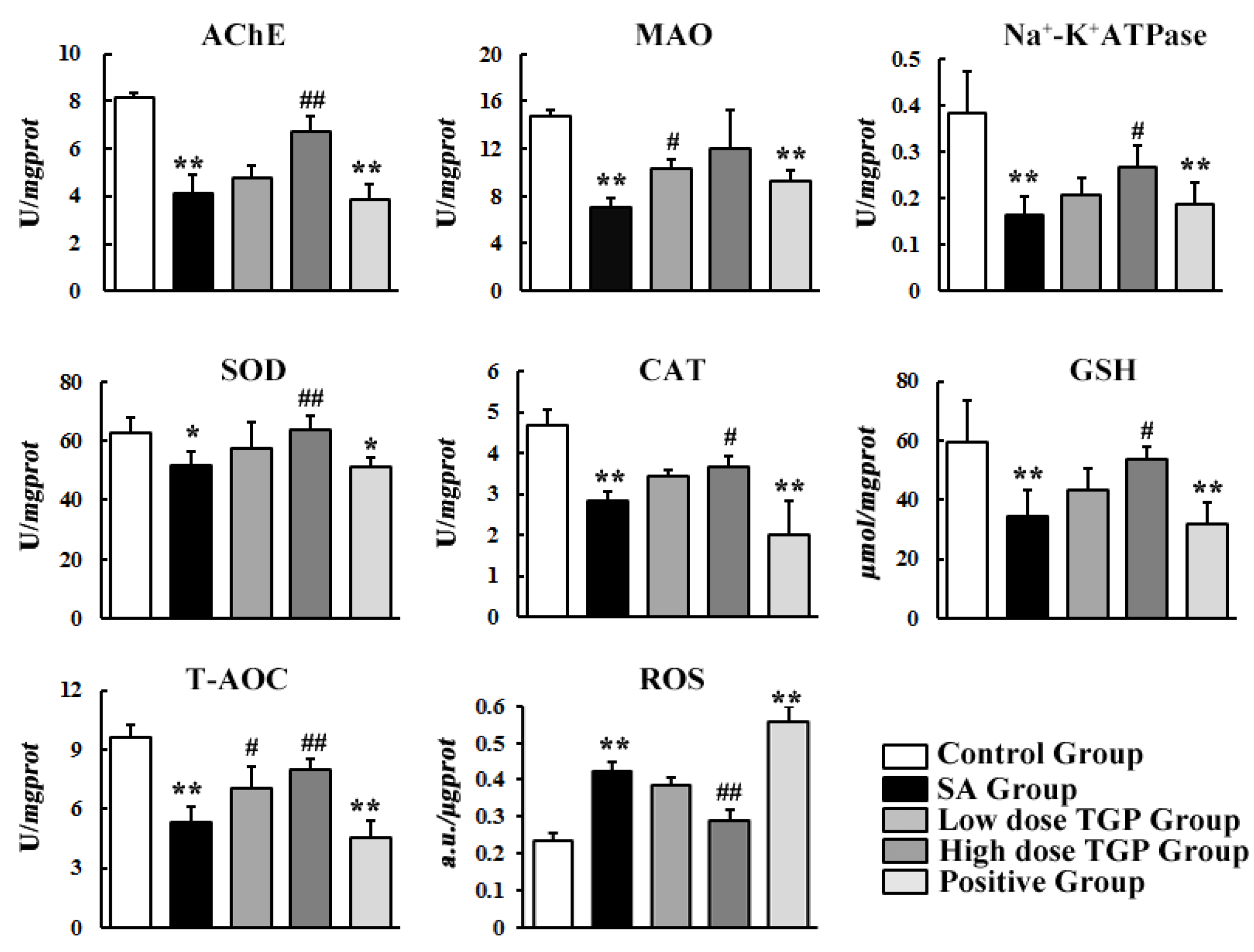
3.2. Biochemical Assay
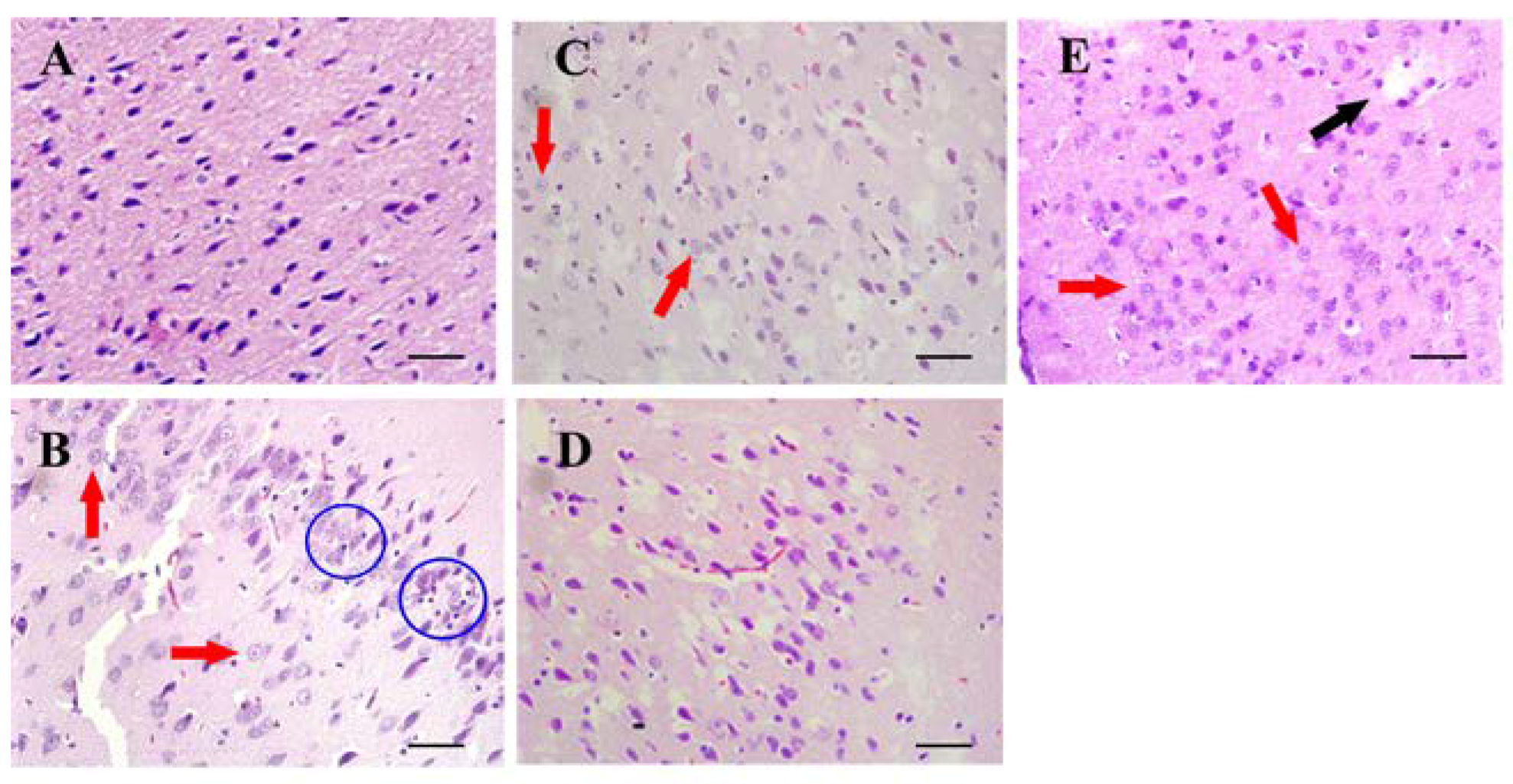
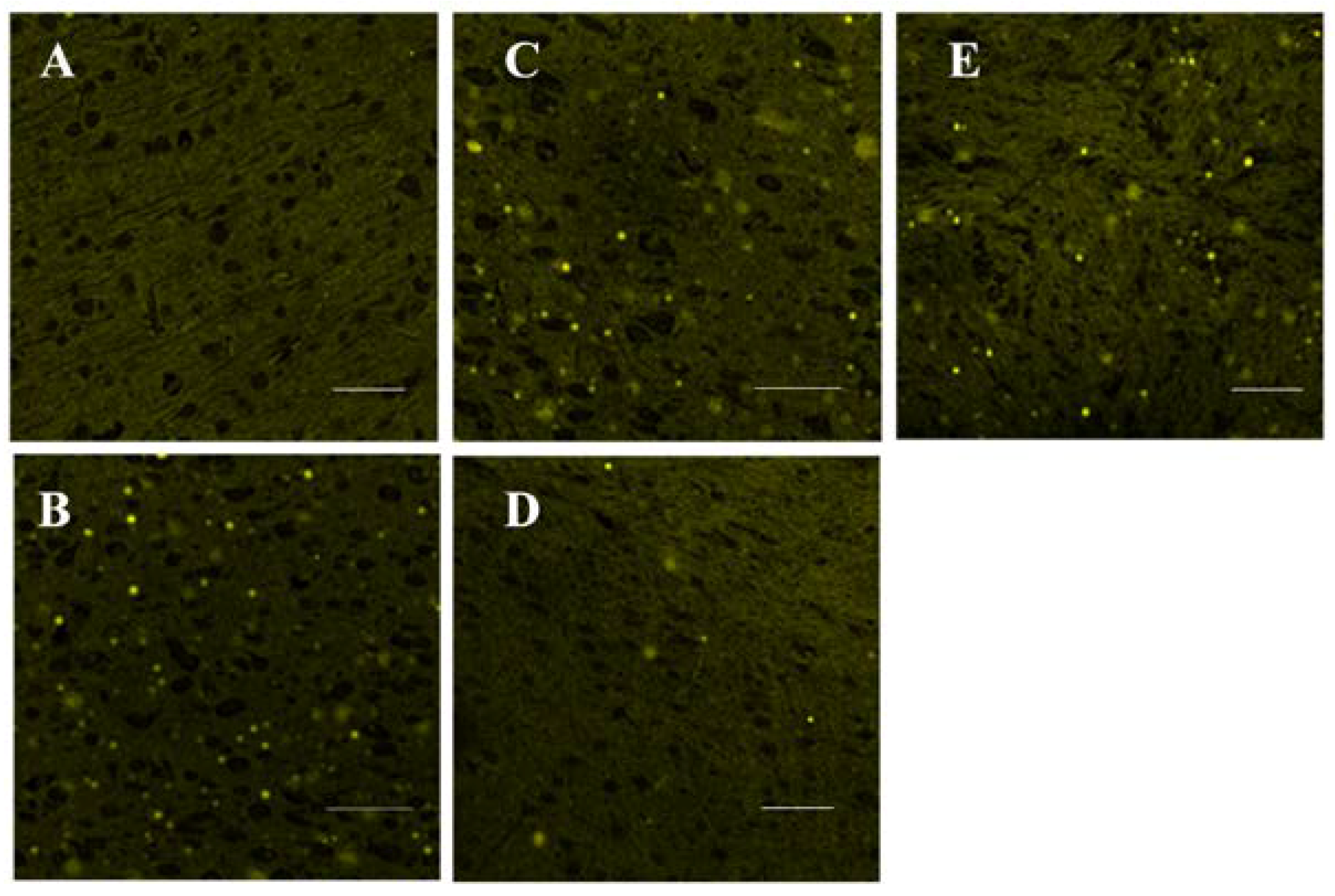
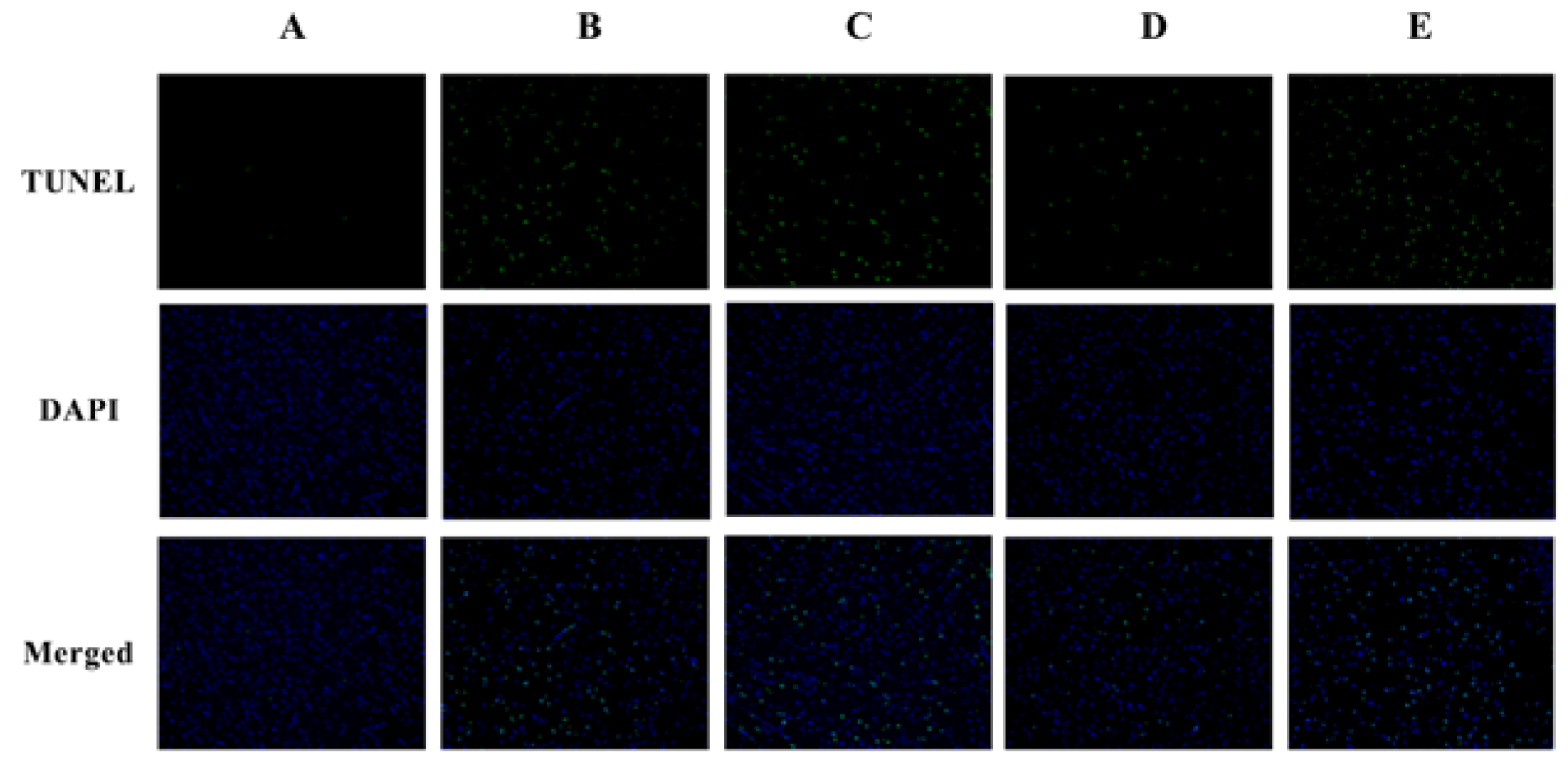
3.3. Histopathological Examination
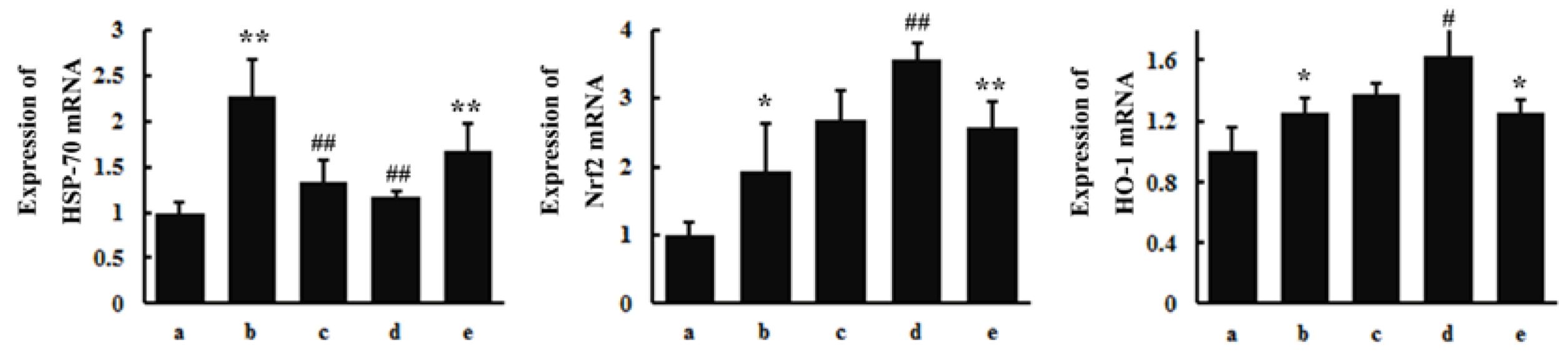
3.4. RT-PCR
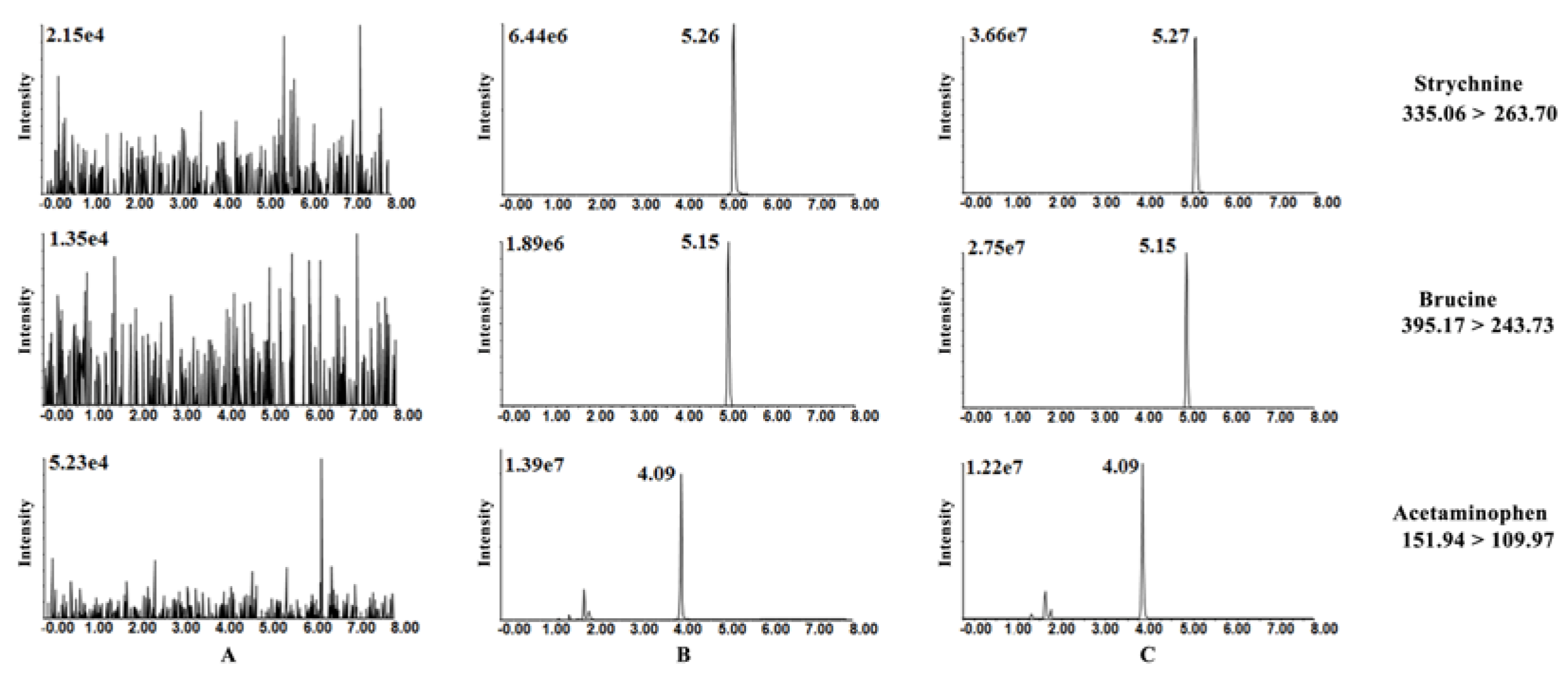
3.5. HPLC-MS/MS Method Validation
3.5.1. Selectivity
3.5.2. Linearity
3.5.3. Precision and Accuracy
3.5.4. Recovery and Matrix Effect
3.5.5. Stability
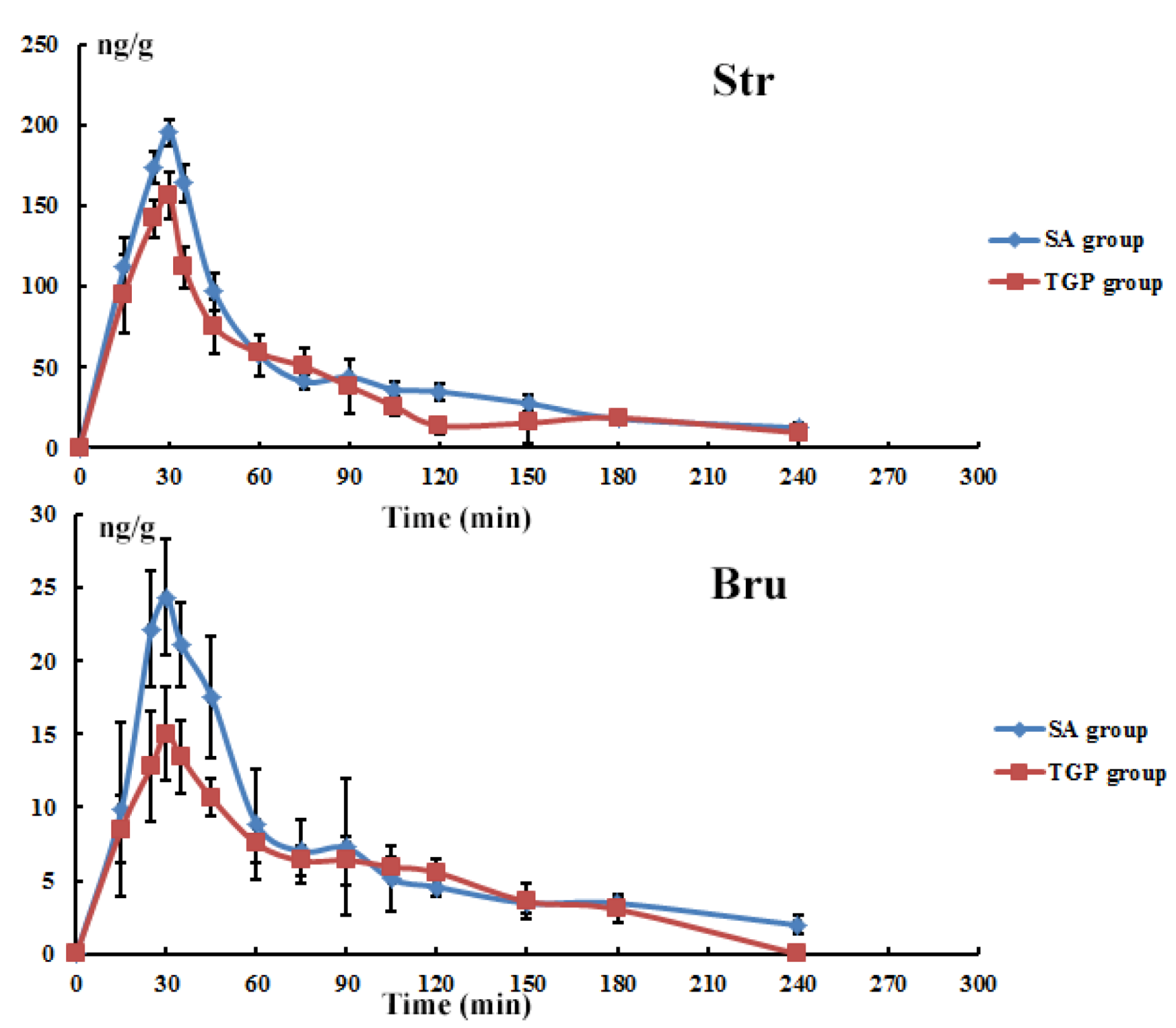
3.6. Tissue Time-Course Following Oral Administration
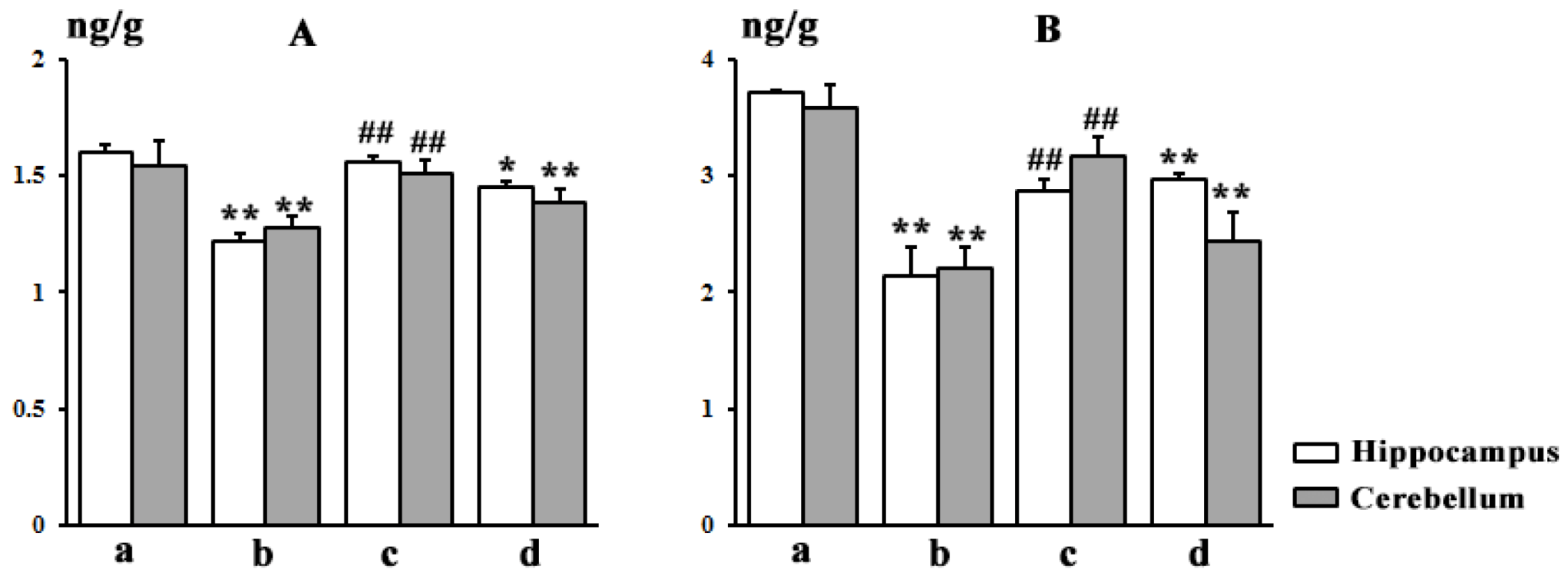
3.7. Brain Distribution
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of TGP on SAs-Induced Neurotoxicity
4.2. Method Development
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Chinese Pharmacopoeia; China Medical Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2015; pp. 50–51. ISBN 978-7-5067-7337-9. [Google Scholar]
- Philippe, G.; Angenot, L.; Tits, M.; Frédérich, M. About the toxicity of some Strychnos species and their alkaloids. Toxicon 2004, 44, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Qu, Y.G.; Wang, D.Y.; Peng, P.; Cai, H.; Gao, Y.; Chen, Z.P.; Cai, B.C. Pharmacological evaluation of total alkaloids from nux vomica: Effect of reducing strychnine contents. Molecules 2014, 19, 4395–4408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Qiao, C.F.; Liang, Z.T.; Xu, H.X.; Zhao, Z.Z.; Cai, Z.W. Alkaloid profiling in crude and processed Strychnos nux-vomica seeds by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2007, 45, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Hou, T.; Fang, Y.; Chen, Z.P.; Liu, X.; Cai, H.; Lu, T.L.; Yan, G.J.; Cai, B.C. HPLC determination of strychnine and brucine in rat tissue and the distribution study of processed semen strychni. Yakugaku Zasshi 2011, 131, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breitinger, H.G.; Becker, C.M. The inhibitory glycine receptor-simple views of a complicated channel. Chembiochem 2002, 3, 1042–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.Y.; Hou, C.Z.; Gu, L.Q.; Xing, H.; Zhang, M.Y.; Zhao, L.S.; Bi, K.S.; Chen, X.H. Investigation of the protective effect of Paeonia lactiflora on Semen Strychni-induced neurotoxicity based on monitoring nine potential neurotoxicity biomarkers in rat serum and brain tissue. Metab. Brain Dis. 2017, 32, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, C.Z.; Zhang, R.W.; Zhang, K.X.; Chen, X.H. Total glycosides of Paeony shows Neuroprotective effects against Semen Strychni-induced neurotoxicity by recovering secretion of hormones and improving brain energy metabolism. Metab. Brain Dis. 2017, 32, 2033–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Shen, L.H.; Zhang, J.T. Anti-amnestic and anti-aging effects of ginsenoside Rg1 and Rb1 and its mechanism of action. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2005, 26, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, S.K.; Dhir, A. Berberine: A plant alkaloid with therapeutic potential for central nervous system disorders. Phytother. Res. 2010, 24, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, D.Y.; Dai, S.M. Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects of Paeonia lactiflora Pall., a traditional Chinese herbal medicine. Front. Pharmacol. 2011, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.J.; Qi, X.M.; Wu, Y.G.; Wang, K. Clinical study of total glucosides of paeony for the treatment of diabetic kidney disease in patients with diabetes mellitus. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2016, 48, 1873–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, H.; Yan, C.L.; Xiao, T.; Yuan, D.F.; Xu, J.H. Total glucosides of Paeonia lactiflora Pall inhibit vascular endothelial growth factor-induced angiogenesis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 127, 781–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.L.; Ma, X.M.; Zhu, D.L.; Chen, L.; Jiang, Y.; Zhou, L.L.; Cen, L.; Pi, R.B.; Chen, X.H. Total glucosides of peony attenuates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in C57BL/6 mice. J. Neuroimmunol. 2015, 284, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, K.N.; Yae, C.G.; Hong, J.W.; Cho, D.H.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, E.H. Paeoniflorin, a monoterpene glycoside, attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced neuronal injury and brainmicroglial inflammatory response. Biotechnol. Lett. 2013, 35, 1183–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, S.; May, B.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, A.L.; Lu, C.J.; Xue, C.C. A Pharmacological review of bioactive constituents of Paeonia lactiflora Pallas and Paeonia veitchii Lynch. Phytother. Res. 2016, 30, 1445–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.; Joo, J.C.; Choi, B.Y.; Lindroth, A.M.; Park, S.J.; Park, Y.J. Neuroprotective effects of Paeonia Lactiflora extract against cell death of dopaminergic SH-SY5Y cells is mediated by epigenetic modulation. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Lee, M.K.; Lee, K.Y.; Sung, S.H.; Kim, J.; Kim, Y.C. Chemical constituents isolated from Paeonia lactiflora roots and their neuroprotective activity against oxidative stress in vitro. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2009, 24, 1138–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.Y.; Zheng, S.Q.; Jiang, Z.; Liang, C.; Wang, R.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, Y.R.; Yu, Y.Q. Rapid separation and identification of Strychnos alkaloids metabolites in rats by ultra high performance liquid chromatography with linear ion trap Orbitrap mass spectrometry. J. Sep. Sci. 2014, 37, 764–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.J.; Zhang, M.Y.; Hou, P.H.; Zhang, R.W.; Hou, C.Z.; Bi, K.S.; Chen, X.H. Identification of the toxic components in Semen Strychni and their metabolites in rat serum by high performance liquid chromatography coupled with a Q Exactive high-resolution benchtop quadrupole Orbitrap mass spectrometer. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 77689–77698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, A.H.; Su, X.C.; She, D.; Qiu, K.C.; He, Q.M.; Liu, Y.M. LC-MS/MS determination and comparative pharmacokinetics of strychnine, brucine and their metabolites in rat plasma after intragastric administration of each monomer and the total alkaloids from Semen Strychni. J. Chromatogr. B 2016, 1008, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, L.Q.; Wang, X.F.; Liu, Z.Z.; Ju, P.; Zhang, L.H.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Ma, B.J.; Bi, K.S.; Chen, X.H. A study of Semen Strychni-induced renal injury and herb-herb interaction of Radix Glycyrrhizae extract and/or Rhizoma Ligustici extract on the comparative toxicokinetics of strychnine and brucine in rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 68, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.J.; Gu, R.H.; Tang, L.; Chen, Z.E.; Di, R.; Long, C.L. Important poisonous plants in tibetan ethnomedicine. Toxins 2015, 7, 138–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, H.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, R.W.; Shi, H.Y.; Bi, K.S.; Chen, X.H. Antidepressant-like effect of the water extract of the fixed combination of Gardenia jasminoides, Citrus aurantium and Magnolia officinalis in a rat model of chronic unpredictable mild stress. Phytomedicine 2015, 22, 1178–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabassum, S.; Haider, S.; Ahmad, S.; Madiha, S.; Parveen, T. Chronic choline supplementation improves cognitive and motor performance via modulating oxidative and neurochemical status in rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2017, 159, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellman, G.L.; Courtney, K.D.; Anders, V.J.R.; Featherstone, R.M. A new rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1961, 7, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valle, A.M.; Radic, Z.; Rana, B.K.; Mahboubi, V.; Wessel, J.; Shih, P.A.; Rao, F.; O’Connor, D.T.; Taylor, P. Naturally occurring variations in the human cholinesterase genes: Heritability and association with cardiovascular and metabolic traits. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2011, 338, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidel, A.J.; Assmann, K.L.; Werlang, C.C.; Bertoncello, K.T.; Francescon, F.; Rambo, C.L.; Beltrame, G.M.; Calegari, D.; Batista, C.B.; Blaser, R.E.; et al. Subchronic atrazine exposure changes defensive behaviour profile and disrupts brain acetylcholinesterase activity of zebrafish. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2014, 44, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kometiani, Z.; Jariashvili, T. Na/K-ATPase regulation by neurotransmitters in ontogeny. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2000, 108, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sibarov, D.A.; Bolshakov, A.E.; Abushik, P.A.; Krivoi, I.I.; Antonov, S.M. Na+, K+-ATPase functionally interacts with the plasma membrane Na+, Ca2+ exchanger to prevent Ca2+ overload and neuronal apoptosis in excitotoxic stress. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2012, 343, 596–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patlolla, A.K.; Tchounwou, P.B. Serum acetyl cholinesterase as a biomarker of arsenic induced neurotoxicity in sprague-dawley rats. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2005, 3, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmondson, D.E.; Binda, C.; Mattevi, A. Structural insights into the mechanism of amine oxidation by monoamine oxidases A and B. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2007, 464, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huot, P.; Fox, S.H.; Brotchie, J.M. Dopamine reuptake inhibitors in Parkinson’s disease: A review of nonhuman primate studies and clinical trials. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2016, 357, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasr, H.M.; El-Demerdash, F.M.; El-Nagar, W.A. Neuro and renal toxicity induced by chlorpyrifos and abamectin in rats: Toxicity of insecticide mixture. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 1852–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molochkina, E.M.; Zorina, O.M.; Fatkullina, L.D.; Goloschapov, A.N.; Burlakova, E.B. H2O2 modifies membrane structure and activity of acetylcholinesterase. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2005, 157–158, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magistretti, P.J.; Allaman, I. A cellular perspective on brain energy metabolism and functional imaging. Neuron 2015, 86, 883–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, R.; Liu, R.T.; Chen, Y.D. Molecular mechanism on cadmium-induced activity changes of catalase and superoxide dismutase. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 77, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, R.H.; Silva, V.A.; Ahmed, I.; Shreiber, D.I.; Morrison, B. Neuroprotection by genipin against reactive oxygen and reactive nitrogen species-mediated injury in organotypic hippocampal slice cultures. Brain Res. 2014, 1543, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumori, Y.; Northington, F.J.; Hong, S.H.M.; Kayama, T.; Sheldon, R.A.; Vexler, Z.S.; Ferriero, D.M.; Weinstein, P.R.; Liu, J.L. Reduction of caspase-8 and -9 cleavage is associated with increased c-FLIP and increased binding of Apaf-1 and Hsp70 after neonatal hypoxic/ischemic injury in mice overexpressing Hsp70. Stroke 2006, 37, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellezza, I.; Giambanco, I.; Minelli, A.; Donato, R. Nrf2-Keap1 signaling in oxidative and reductive stress. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2018, 1865, 721–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.B.; Cai, H.L.; Li, H.D.; Zhang, L.J.; Li, X.L.; Tang, J.H.; Chen, M.L. HPLC-DAD method for comprehensive quality control of Semen Strychni. Pharm. Biol. 2013, 51, 1378–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Ye, N.S.; Gao, C.; Zhou, T.T.; Ma, J.C. Capillary coated with graphene oxide as stationary phase for the separation of brucine and strychnine by capillary electrophoresis. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2015, 53, 641–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.W.; Zhu, R.H.; Li, H.D.; Yan, M.; Lei, Y.Q. Ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometric method for the determination of strychnine and brucine in mice plasma. J. Chromatogr. B 2011, 879, 2714–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mumin, Y.; Filik, H.; Aydar, S.; Avan, A.A. Electrochemical determination of brucine in urine with a poly (Alizarin Red S)-modified glassy carbon electrode. Anal. Lett. 2016, 49, 2716–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.X.; Tian, Y.; Xu, L.; Zhang, J.; Lu, T.; Zhang, Z.J. Characterisation and identification of dihydroindole-type alkaloids from processed semen strychni by high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with electrospray ionisation ion trap time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Phytochem. Anal. 2014, 25, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.L.; Song, Q.Q.; Li, J.; Zhang, N.; Zhao, Y.F.; Liu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Tu, P.F. An integrated strategy to quantitatively differentiate chemome between Cistanche deserticola and C. tubulosa using high performance liquid chromatography-hybrid triple quadrupole-linear ion trap mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1429, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, P.Y.; Liu, D.; Zheng, Q.; Wu, Q.; Tang, Y.; Yang, M. Elucidation of transport mechanism of Paeoniflorin and the influence of Ligustilide, Senkyunolide I and Senkyunolide A on Paeoniflorin transport through Mdck-Mdr1 cells as Blood-Brain Barrier in vitro model. Molecules 2016, 21, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.; Li, R.; Yu, C.; Xu, T.; Zhang, X.; Dong, M. Paeoniflorin inhibition of 6-hydroxydopamine-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells via suppressing reactive oxygen species-mediated PKCδ/NF-κB pathway. Neuroscience 2015, 285, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Analyte | Collision Energy (eV) | Capillary Voltage (KV) | Cone Voltage (KV) | Structure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Str | 30 | 5 | 20 |  |
| Bru | 34 | 4 | 15 |  |
| IS | 14 | 5 | 39 |  |
| Control Group | SA Group | Low Dose TGP Group | High Dose TGP Group | Positive Group | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body weight | 350.8 ± 10.7 | 279.2 ± 6.1 ** | 292.9 ± 5.4 # | 308.7 ± 11.5 # | 276.8 ± 10.1 ** |
| Coat state | 1.0 ± 0.7 | 2.4 ± 0.5 ** | 2.0 ± 0.7 | 1.4 ± 0.9 # | 2.6 ± 0.5 ** |
| Beam walking test | 4.5 ± 0.5 | 2.5 ± 0.6 ** | 2.8 ± 0.4 | 3.6 ± 0.8 ## | 2.8 ± 0.5 ** |
| Analyte | Liner Range (ng/mL) | Regression Equation | r |
|---|---|---|---|
| Str | 0.25–200.0 | y = 6.23 × 10−2x + 8.97 × 10−2 | 0.9910 |
| Bru | 0.05–40.0 | y = 1.09 × 10−1x + 5.62 × 10−2 | 0.9905 |
| Region | SA Group | TGP Group | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Str | Bru | Str | Bru | |
| Cerebral cortex | 42.9 ± 3.0 | 8.4 ± 3.3 | 38.8 ± 3.2 | 7.5 ± 1.3 |
| Hypothalamus | 31.9 ± 9.5 | 9.0 ± 1.3 | 31.2 ± 7.9 | 7.7 ± 1.7 |
| Striatum | 40.9 ± 5.7 | 9.8 ± 3.9 | 35.8 ± 6.1 | 9.5 ± 1.5 |
| Hippocampus | 69.6 ± 4.7 | 28.1 ± 2.7 | 60.1 ± 1.6 * | 19.4 ± 2.3 * |
| Cerebellum | 60.1 ± 2.0 | 14.7 ± 4.3 | 45.5 ± 3.1 * | 11.5 ± 1.6 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Chu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Sun, L.; Chen, X. Prophylactic Neuroprotection of Total Glucosides of Paeoniae Radix Alba against Semen Strychni-Induced Neurotoxicity in Rats: Suppressing Oxidative Stress and Reducing the Absorption of Toxic Components. Nutrients 2018, 10, 514. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10040514
Li S, Chu Y, Zhang R, Sun L, Chen X. Prophylactic Neuroprotection of Total Glucosides of Paeoniae Radix Alba against Semen Strychni-Induced Neurotoxicity in Rats: Suppressing Oxidative Stress and Reducing the Absorption of Toxic Components. Nutrients. 2018; 10(4):514. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10040514
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Shujuan, Yanjie Chu, Ruowen Zhang, Linjia Sun, and Xiaohui Chen. 2018. "Prophylactic Neuroprotection of Total Glucosides of Paeoniae Radix Alba against Semen Strychni-Induced Neurotoxicity in Rats: Suppressing Oxidative Stress and Reducing the Absorption of Toxic Components" Nutrients 10, no. 4: 514. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10040514
APA StyleLi, S., Chu, Y., Zhang, R., Sun, L., & Chen, X. (2018). Prophylactic Neuroprotection of Total Glucosides of Paeoniae Radix Alba against Semen Strychni-Induced Neurotoxicity in Rats: Suppressing Oxidative Stress and Reducing the Absorption of Toxic Components. Nutrients, 10(4), 514. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10040514




