20(S)-Ginsenoside Rh2 Induce the Apoptosis and Autophagy in U937 and K562 Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Hoechst 33258 Staining Assay
2.4. Growth Inhibition Assay
2.5. Apoptosis Analysis
2.6. ROS Determination
2.7. Mitochondrial Membrane Potential (MMP) Assessment
2.8. Quantification of Apoptosis and Autophagy Related Gene by qRT-PCR
2.9. Caspase-9, Caspase-3 Activity Assay
2.10. Monodansylcadaverine (MDC) Staining Assay for Autophagy Detection
2.11. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.12. Western Blotting Analysis
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
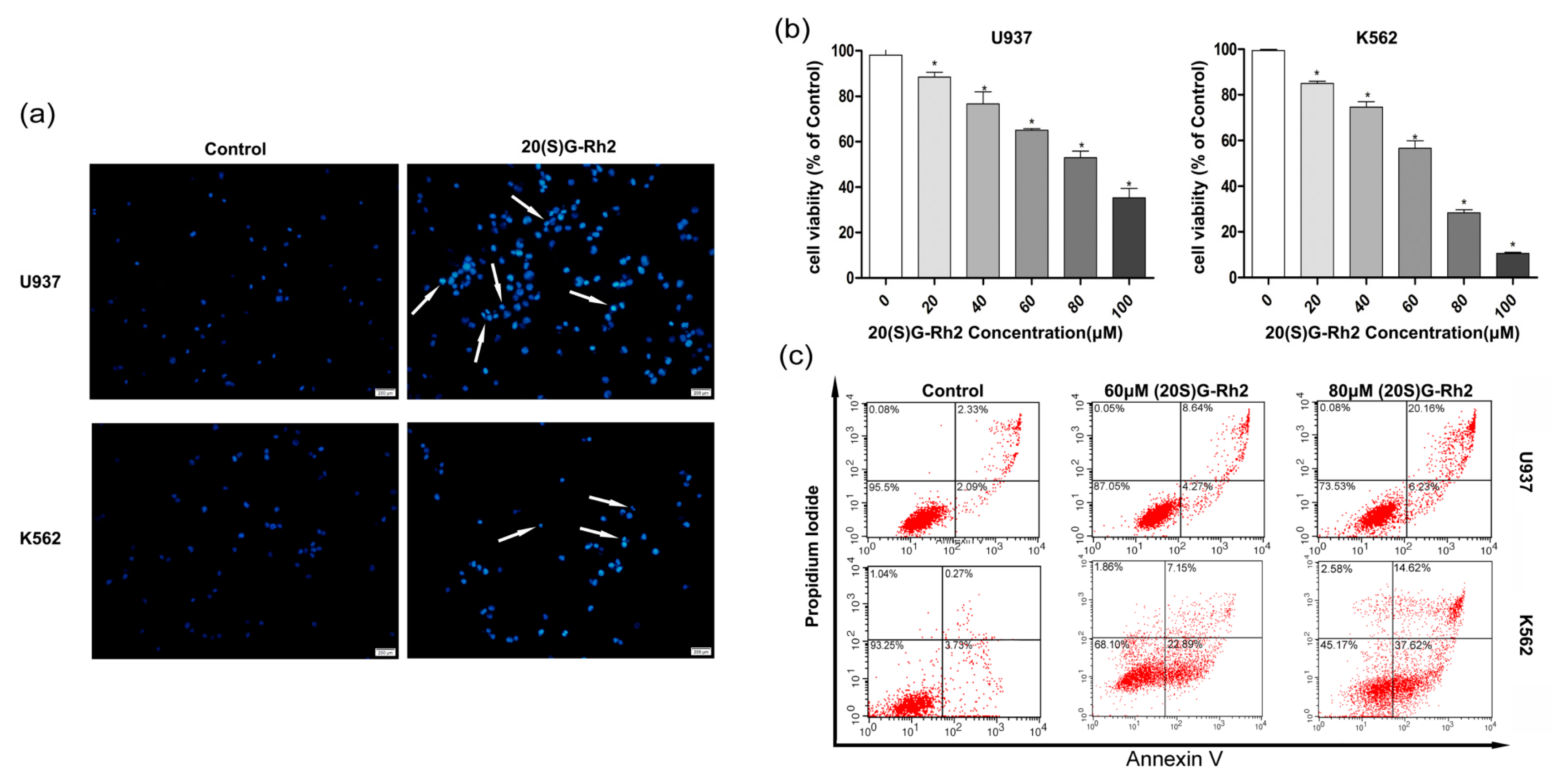
3.1. 20(S)-GRh2 Inhibits Proliferation of Myeloid Leukemia Cell Lines through Apoptotic Cell Death
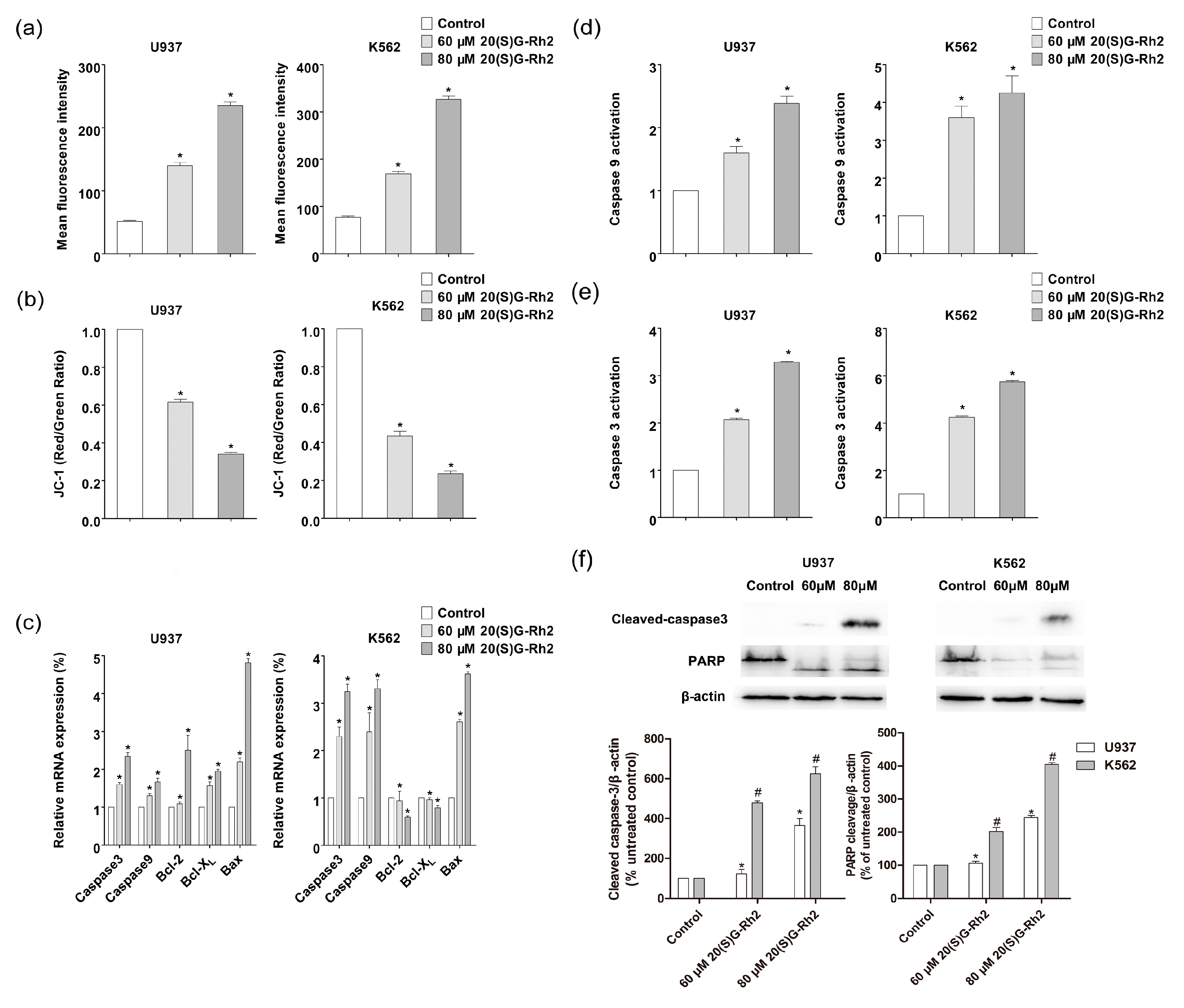
3.2. 20(S)-GRh2 Treatment Induces Cells Apoptosis through Mitochondrial Apoptosis Pathway
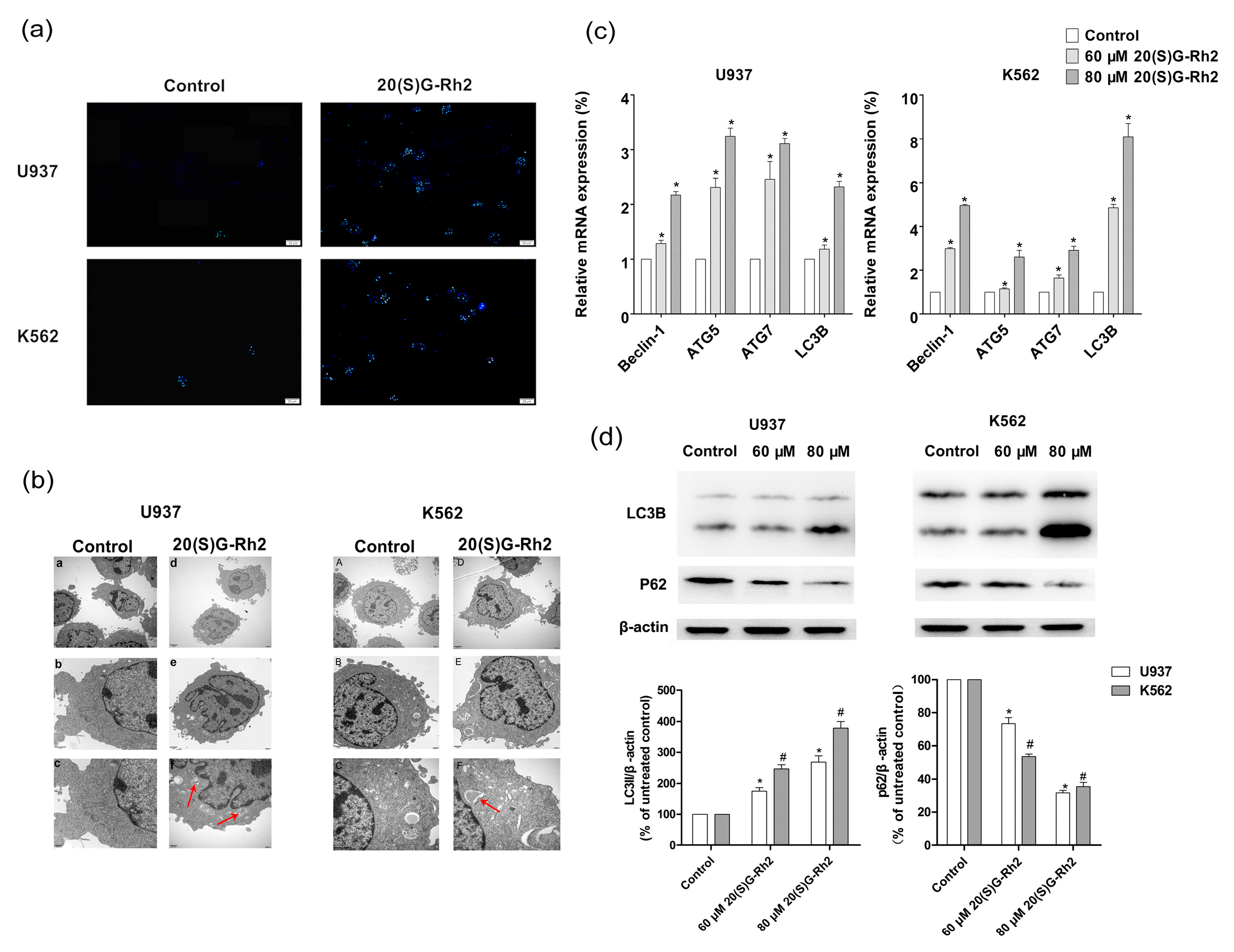
3.3. 20(S)-GRh2 Induces Autophagy in Myeloid Leukemia Cells
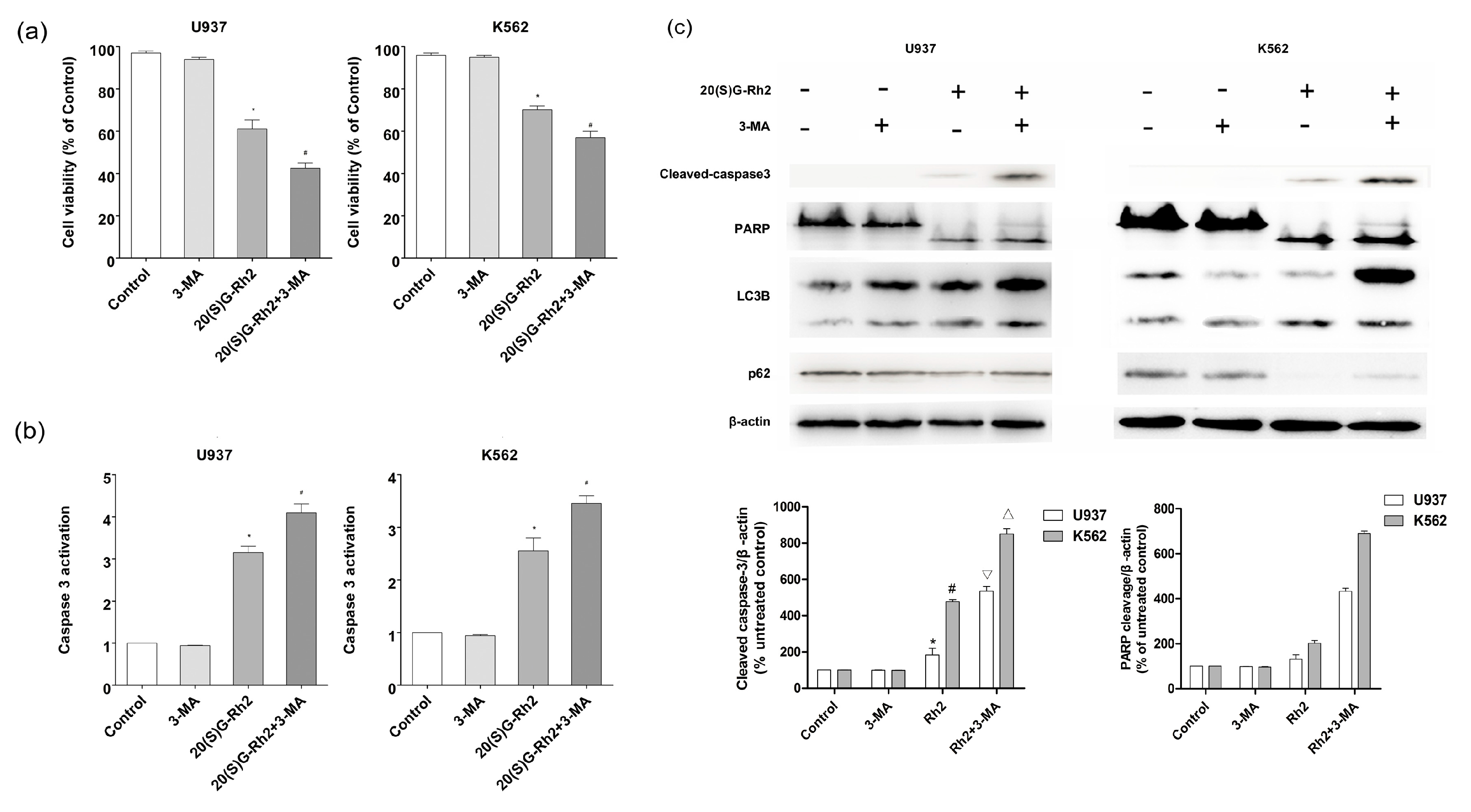
3.4. Effect of Autophagy Inhibitor (3-MA) on 20(S)-GRh2 Induced Apoptosis and Autophagy
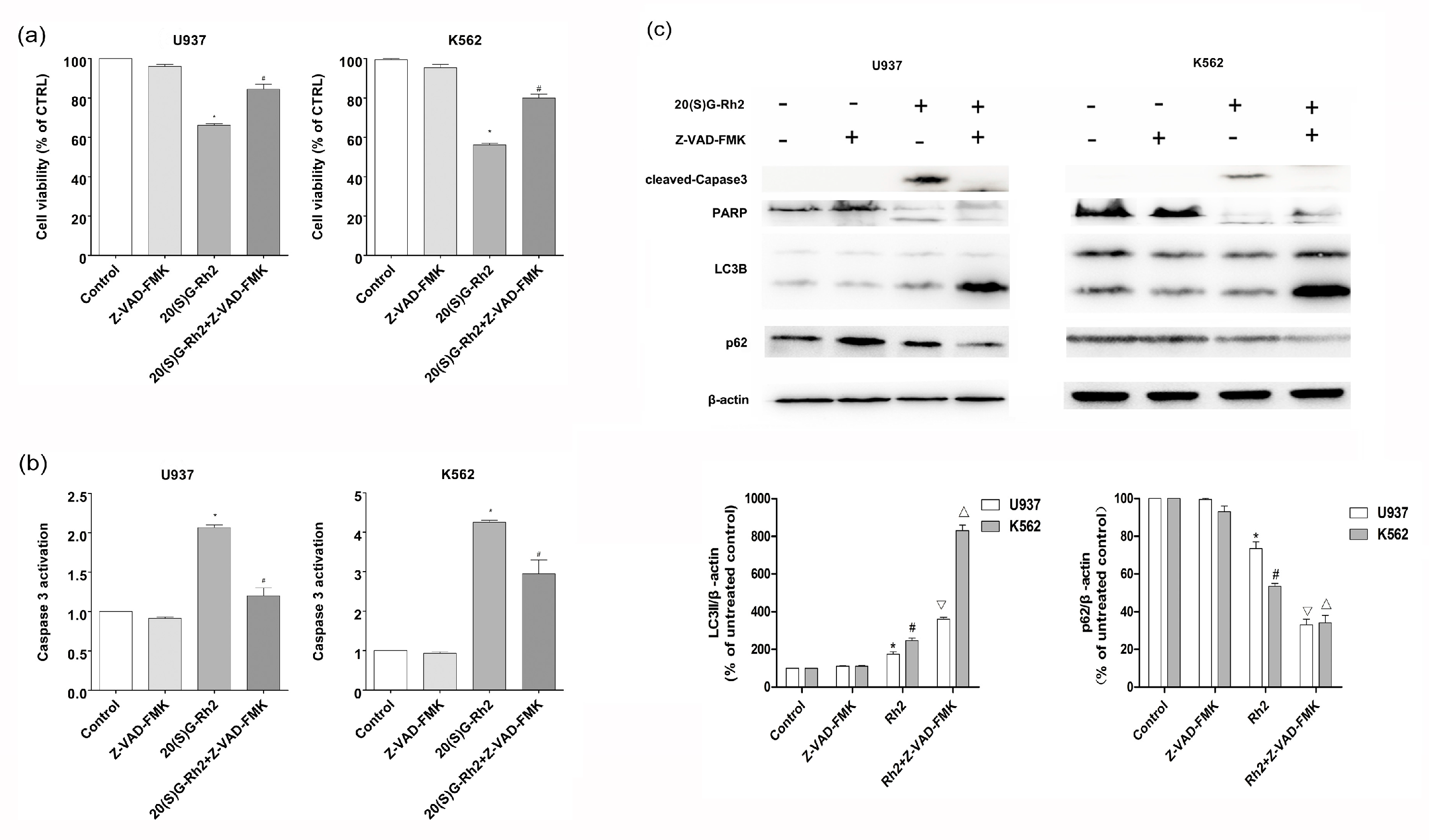
3.5. Effect of Apoptosis Inhibitor (Z-VAD-FMK) on 20(S)-GRh2 Induced Autophagy and Apoptosis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhowmik, T.; Gomes, A. NKCT1 (purified Naja kaouthia protein toxin) conjugated gold nanoparticles induced Akt/mTOR inactivation mediated autophagic and caspase 3 activated apoptotic cell death in leukemic cell. Toxicon 2016, 121, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Ren, W.; Chen, K. MiR-34a promotes apoptosis and inhibits autophagy by targeting HMGB1 in acute myeloid leukemia cells. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 41, 1981–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Döhner, H.; Weisdorf, D.J.; Bloomfield, C.D. Acute myeloid leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1136–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robison, L. Late effects of acute lymphoblastic leukemia therapy in patients diagnosed at 0–20 years of age. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program 2011, 2011, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barisone, G.; Satake, N.; Lewis, C.; Duong, C.; Chen, C.; Lam, K.; Nolta, J.; Dίaz, E. Loss of MCD3 induces apoptosis of Reh human precursor B acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2015, 54, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Büchner, T.; Hiddemann, W.; Wörmann, B.; Löffler, H.; Gassmann, W.; Haferlach, T.; Fonatsch, C.; Haase, D.; Schoch, C.; Hossfeld, D.; et al. Double induction strategy for acute myeloid leukemia: The effect of high-dose cytarabine with mitoxantrone instead of standard-dose cytarabine with daunorubicin and 6-thioguanine: A randomized trial by the German AML cooperative group. Blood 1999, 93, 4116. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tallman, M.S.; Gilliland, D.G.; Rowe, J.M. Drug therapy for acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2005, 106, 1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.-H.; Lo, H.-L.; Tang, W.-C.; Hsiao, H.H.-Y.; Yang, P.-M. A gene expression signature-based approach reveals the mechanisms of action of the Chinese herbal medicine berberine. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, A.S.; Che, C.-M.; Leung, K.-W. Recent advances in ginseng as cancer therapeutics: A functional and mechanistic overview. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2015, 32, 256–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.-Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wan, J.-Y.; Zhang, C.-F.; Anderson, S.; He, X.; Yu, C.; He, T.-C.; Qi, L.-W.; Yuan, C.-S. Protopanaxadiol, an active ginseng metabolite, significantly enhances the effects of fluorouracil on colon cancer. Nutrients 2015, 7, 799–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.-J.; Jeon, J.-N.; Jang, M.-G.; Oh, J.Y.; Kwon, W.-S.; Jung, S.-K.; Yang, D.-C. Ginsenoside profiles and related gene expression during foliation in Panax ginseng meyer. J. Ginseng Res. 2014, 38, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, L.; Johnson, M.; Wells, A.; Dasgupta, A. Effect of the traditional Chinese medicines Chan Su, Lu-Shen-Wan, Dan Shen, and Asian ginseng on serum digoxin measurement by Tina-quant (Roche) and Synchron LX system (Beckman) digoxin immunoassays. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2003, 17, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, T.K.; Choi, S.Y. A case-control study of ginseng intake and cancer. Int. J. Epidemiol. 1990, 19, 871–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Q.Q.; Li, J.; Feng, Z.Q.; Zhao, L.C.; Luo, L.; You, Z.M.; Li, D.Y.; Xia, J.; Zuo, G.W.; Chen, D.L. Effect of ginsenoside Rh2 on the migratory ability of HepG2 liver carcinoma cells: Recruiting histone deacetylase and inhibiting activator protein 1 transcription factors. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 10, 1779–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.T.; Song, G.Y.; Chau, V.M.; Phan, V.K.; Jin, L.G.; Boo, H.J.; Kang, H.K.; Kim, Y.H. Steamed ginseng-leaf components enhance cytotoxic effects on human leukemia HL-60 cells. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 58, 1111–1115. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, T.; Wang, Y.N.; Zhou, C.X.; Wu, L.M.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, Q.H.; Zhang, X.L.; Yao, J.H.; Wang, M.; Fang, J.P. Ginsenoside Rh2 and Rg3 inhibit cell proliferation and induce apoptosis by increasing mitochondrial reactive oxygen species in human leukemia Jurkat cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 15, 3591–3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.J.; Yuan, D.H.; Xing, T.C.; Su, H.L.; Zhang, S.J.; Wen, J.S.; Bai, Q.Q.; Dang, D.M. Ginsenoside Rh2 inhibiting HCT116 colon cancer cell proliferation through blocking Pdz-binding kinase/T-Lak cell-originated protein kinase. J. Ginseng Res. 2016, 40, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, T.; Wang, J.C.; Xu, W.; Xu, L.H.; Lao, C.H.; Ye, Q.X.; Fang, J.P. 20(s)-ginsenoside Rh2 induces apoptosis in human Leukaemia Reh cells through mitochondrial signaling pathways. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2014, 37, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, T.; Wang, J.C.; Wang, Y.N.; Wang, Y.Y.; Cai, J.Y.; Wang, M.; Chen, Q.D.; Song, J.; Yu, Z.Q.; Huang, W.; et al. Inhibition of autophagy potentiates anticancer property of 20(s)-ginsenoside Rh2 by promoting mitochondria-dependent apoptosis in human acute lymphoblastic leukaemia cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 27336–27349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, K.S.; Cho, S.H.; Shin, J.S.; Kim, D.H.; Choi, J.H.; Choi, S.Y.; Rhee, Y.K.; Hong, H.D.; Lee, K.T. Ginsenoside Rh2 induces cell cycle arrest and differentiation in human leukemia cells by upregulating TGF-β expression. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.H.; Li, J.; Xia, J.; Jiang, R.; Zuo, G.W.; Li, X.P.; Chen, Y.; Xiong, W.; Chen, D.L. Ginsenoside 20(s)-Rh2 as potent natural histone deacetylase inhibitors suppressing the growth of human leukemia cells. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2015, 242, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; He, H.; Dou, G.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, M.; Li, P.; Huang, X.; Chen, H.; Li, L. Ginsenoside 20(s)-Rh2 induces apoptosis and differentiation of acute myeloid leukemia cells: Role of orphan nuclear receptor Nur77. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 7687–7697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.-S.; Lin, Y.; Li, H.; Li, Y.; Song, Z.; Jin, Y.-H. The identification of molecular target of (20s) ginsenoside Rh2 for its anti-cancer activity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaminskyy, V.O.; Zhivotovsky, B. Free radicals in cross talk between autophagy and apoptosis. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 21, 86–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhopadhyay, S. Unraveling the Intricate Molecular Mechanism between Apoptosis and Autophagy during Cellular Stress. Ph.D. Thesis, Sambalpur University, Odisha, India, 28 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, D.; Zhu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, L.; Yu, Y.; Ouyang, L. Fluoxetine induces autophagic cell death via eEF2k-AMPK-mTOR-ULK complex axis in triple negative breast cancer. Cell Prolif. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.S.; Chen, Y.H.; Chen, N.; Wang, L.J.; Chen, D.X.; Weng, H.L.; Dooley, S.; Ding, H.G. Hydrogen sulfide promotes autophagy of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shatz, O.; Holland, P.; Elazar, Z.; Simonsen, A. Complex relations between phospholipids, autophagy, and neutral lipids. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2016, 41, 907–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenberg-Lerner, A.; Bialik, S.; Simon, H.U.; Kimchi, A. Life and death partners: Apoptosis, autophagy and the cross-talk between them. Cell Death Differ. 2009, 16, 966–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mai, T.T.; Moon, J.; Song, Y.; Viet, P.Q.; Phuc, P.V.; Lee, J.M.; Yi, T.H.; Cho, M.; Cho, S.K. Ginsenoside F2 induces apoptosis accompanied by protective autophagy in breast cancer stem cells. Cancer Lett. 2012, 321, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colosetti, P.; Puissant, A.; Robert, G.; Luciano, F.; Jacquel, A.; Gounon, P.; Cassuto, J.-P.; Auberger, P. Autophagy is an important event for megakaryocytic differentiation of the chronic myelogenous leukemia K562 cell line. Autophagy 2014, 5, 1092–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, J.V.; Hughes, T.P.; Apperley, J.F. Chronic myeloid leukemia. ASH Educ. Program Book 2003, 2003, 132–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabretta, B.; Perrotti, D. The biology of CML blast crisis. Blood 2004, 103, 4010–4022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Druker, B.J. Translation of the Philadelphia chromosome into therapy for CML. Blood 2008, 112, 4808–4817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundström, C.; Nilsson, K. Establishment and characterization of a human histiocytic lymphoma cell line (U-937). Int. J. Cancer 1976, 17, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, N.; Shinohara, Y. Cytotoxic effect and apoptosis induction by silver nanoparticles in HeLa cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 390, 733–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, Y.S.; Oh, H.; Rhee, S.G.; Do Yoo, Y. Regulation of reactive oxygen species generation in cell signaling. Mol. Cells 2011, 32, 491–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatai, T.; Matsuzawa, A.; Inoshita, S.; Mochida, Y.; Kuroda, T.; Sakamaki, K.; Kuida, K.; Yonehara, S.; Ichijo, H.; Takeda, K. Execution of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1)-induced apoptosis by the mitochondria-dependent caspase activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 26576–26581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birkinshaw, R.W.; Czabotar, P.E. The BCL-2 family of proteins and mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilisation. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 72, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klionsky, D.; Abdelmohsen, K.; Abe, A.; Abedin, M.; Abeliovich, H.; Acevedo Arozena, A.; Adachi, H.; Adams, C.; Adams, P.; Adeli, K.; et al. Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy (3rd edition). Autophagy 2016, 12, 1–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Guo, W.; Gao, Y.; Liu, Y. Ginsenoside Rh2 inhibits growth of glioblastoma multiforme through mTor. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 2607–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, D.R. Apoptotic pathways: Ten minutes to dead. Cell 2005, 121, 671–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, X.M.; Bai, X.; Jiang, H.F.; He, P.; Wang, J.H. 20-(s)-ginsenoside Rg3 induces apoptotic cell death in human leukemic U937 and HL-60 cells through PI3K/Akt pathways. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2014, 25, 1072–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.J.; Peng, K.J.; Wang, L.H.; Wen, B.; Zhou, L.; Luo, T.; Su, M.; Li, J.J.; Luo, Z.Y. Ginsenoside Rh2 inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in human leukemia cells via TNF-α signaling pathway. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2016, 48, 750–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, Z.M.; Zhao, L.; Xia, J.; Wei, Q.; Liu, Y.M.; Liu, X.Y.; Chen, D.L.; Li, J. Down-regulation of phosphoglucose isomerase/autocrine motility factor enhances gensenoside Rh2 pharmacological action on leukemia KG1α cells. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 1099–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wang, X.R.; Wang, Y.L. Ginsenoside Rh2 mitigates pediatric leukemia through suppression of Bcl-2 in Leukemia cells. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 37, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ham, Y.M.; Lim, J.H.; Na, H.K.; Choi, J.S.; Park, B.D.; Yim, H.; Lee, S.K. Ginsenoside-Rh2-induced mitochondrial depolarization and apoptosis are associated with reactive oxygen species-and ca2+-mediated c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase 1 activation in Hela cells. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2006, 319, 1276–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.-M.; Kim, S.-J.; Kim, J.-S.; Kang, H.-S. Reactive oxygen species mediated ginsenoside Rg3-and Rh2-induced apoptosis in hepatoma cells through mitochondrial signaling pathways. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 2736–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zorov, D.B.; Juhaszova, M.; Sollott, S.J. Mitochondrial ROS-induced ROS release: An update and review. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Bioenerg. 2006, 1757, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchetti, P.; Decaudin, D.; Macho, A.; Zamzami, N.; Hirsch, T.; Susin, S.A.; Kroemer, G. Redox regulation of apoptosis: Impact of thiol oxidation status on mitochondrial function. Eur. J. Immunol. 1997, 27, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroemer, G. The proto-oncogene Bcl-2 and its role in regulating apoptosis. Nat. Med. 1997, 3, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safaeian, L.; Abed, A.; Vaseghi, G. The role of Bcl-2 family proteins in pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 741, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, S.; Tortola, L.; Perlot, T.; Wirnsberger, G.; Novatchkova, M.; Nitsch, R.; Sykacek, P.; Frank, L.; Schramek, D.; Komnenovic, V. A dual role for autophagy in a murine model of lung cancer. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.S.; Vats, S.; Chia, A.Y.-Q.; Tan, T.Z.; Deng, S.; Ong, M.S.; Arfuso, F.; Yap, C.T.; Goh, B.C.; Sethi, G. Dual role of autophagy in hallmarks of cancer. Oncogene 2018, 1, 1142–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, H.-U.; Friis, R.; Tait, S.W.; Ryan, K.M. Retrograde signaling from autophagy modulates stress responses. Sci. Signal. 2017, 10, eaag2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.-R.; Lei, H.-Y.; Liu, M.-T.; Wang, J.-R.; Chen, S.-H.; Jiang-Shieh, Y.-F.; Lin, Y.-S.; Yeh, T.-M.; Liu, C.-C.; Liu, H.-S. Autophagic machinery activated by dengue virus enhances virus replication. Virology 2008, 374, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, X.; Wang, P.; Yang, S.; Zhang, K.; Liu, Q.; Wang, X. Sonodynamic therapy induces the interplay between apoptosis and autophagy in K562 cells through ROS. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2015, 60, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhuang, J.; Yin, J.; Xu, C.; Mu, Y.; Lv, S. 20(S)-Ginsenoside Rh2 Induce the Apoptosis and Autophagy in U937 and K562 Cells. Nutrients 2018, 10, 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10030328
Zhuang J, Yin J, Xu C, Mu Y, Lv S. 20(S)-Ginsenoside Rh2 Induce the Apoptosis and Autophagy in U937 and K562 Cells. Nutrients. 2018; 10(3):328. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10030328
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhuang, Jianjian, Juxin Yin, Chaojian Xu, Ying Mu, and Shaowu Lv. 2018. "20(S)-Ginsenoside Rh2 Induce the Apoptosis and Autophagy in U937 and K562 Cells" Nutrients 10, no. 3: 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10030328
APA StyleZhuang, J., Yin, J., Xu, C., Mu, Y., & Lv, S. (2018). 20(S)-Ginsenoside Rh2 Induce the Apoptosis and Autophagy in U937 and K562 Cells. Nutrients, 10(3), 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10030328





