Serum Antioxidant Associations with Metabolic Characteristics in Metabolically Healthy and Unhealthy Adolescents with Severe Obesity: An Observational Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Measurements
2.4. Statistical Analyses
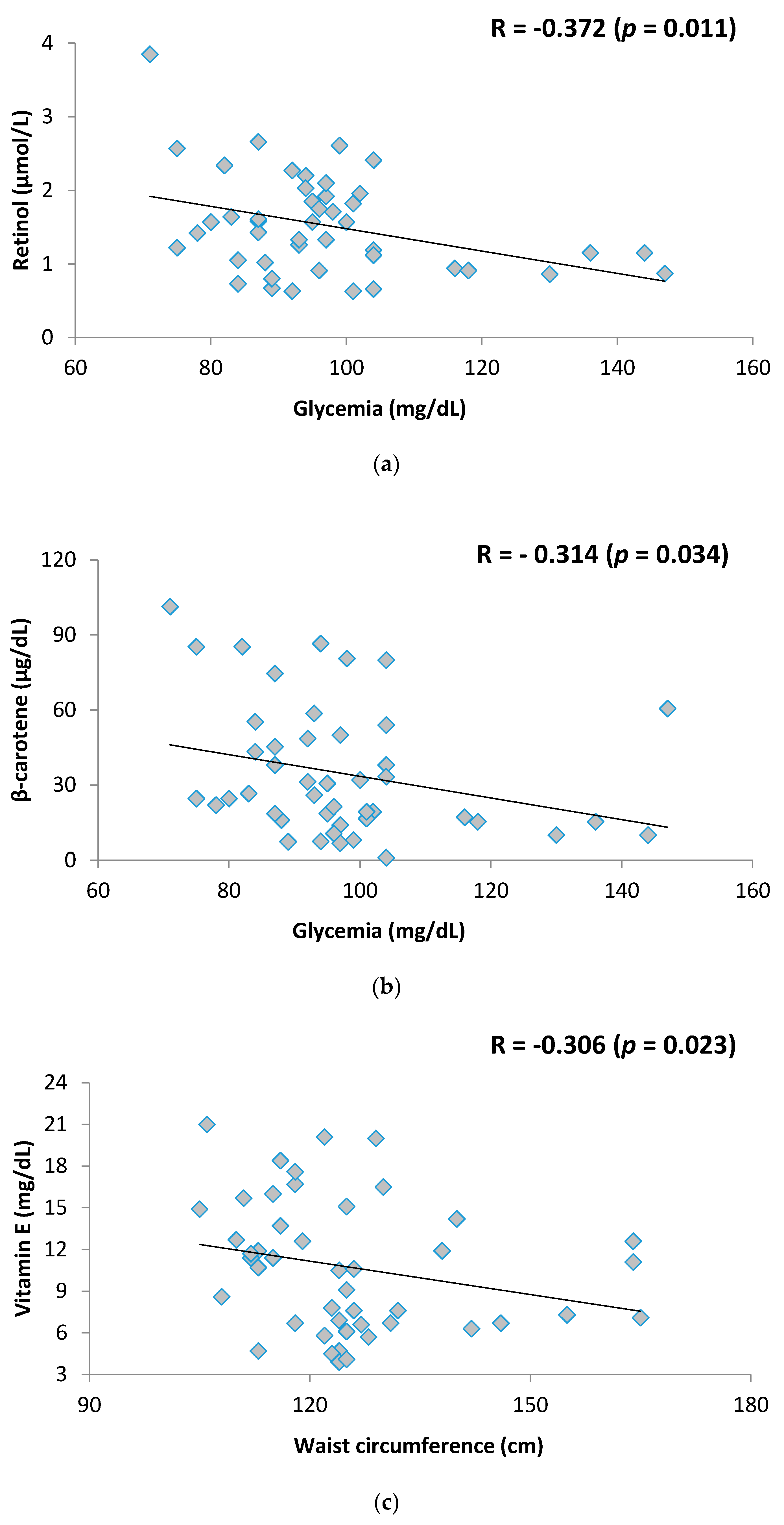
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cali, A.M.; Caprio, S. Obesity in children and adolescents. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, S31–S36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.C.; Gortmaker, S.L.; Taveras, E.M. Trends and racial/ethnic disparities in severe obesity among US children and adolescents, 1976–2006. Int. J. Pediatr. Obes. 2011, 6, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prince, R.L.; Kuk, J.L.; Ambler, K.A.; Dhaliwal, J.; Ball, G.D. Predictors of metabolically healthy obesity in children. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 1462–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blüher, S.; Schwarz, P. Metabolically healthy obesity from childhood to adulthood—Does weight status alone matter? Metabolism 2014, 63, 1084–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, K.C.; Cha, S.C.; Sung, J.W.; So, M.S.; Byrne, C.D. Metabolically healthy obese subjects are at risk of fatty liver but not of pre-clinical atherosclerosis. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2014, 24, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weib, J.; Rau, M.; Geier, A. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2014, 111, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, O.P.; Ronquillo, D.; Caamaño, M.D.; Martínez, G.; Camacho, M.; López, V.; Rosado, J.L. Zinc, Iron and Vitamins A, C and E Are Associated with Obesity, Inflammation, Lipid Profile and Insulin Resistance in Mexican School-Aged Children. Nutrients 2013, 5, 5012–5030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO (World Health Organization). Growth Reference Data for 5–19 Years. BMI-for-Age (5–19 Years). Percentiles 2007. Available online: http://www.who.int/growthref/en/ (accessed on 20 January 2016).
- Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults. Executive summary of the third report of The National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). JAMA 2001, 285, 2486–2497. [Google Scholar]
- De Ferranti, S.D.; Gauvreau, K.; Ludwig, D.S.; Neufeld, E.J.; Newburger, J.W.; Rifai, N. Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome in American adolescents: Findings from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Circulation 2004, 110, 2494–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brazilian Society of Cardiology; Brazilian Society of Hypertension; Brazilian Society of Nephrology. VI Brazilian Guideline on Hypertension. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2010, 95, 1S–51S. [Google Scholar]
- International Vitamin A Consultative Group. IVACG Statement—Maternal Night Blindness: A new indicator of vitamin A deficiency. In Proceedings of the International Vitamin A Consultative Group, Washington, DC, USA, 12–15 February 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Sauberlich, H.E.; Dowdy, R.P.; Skala, J.H. Laboratory Tests for the Assessment of Nutritional Status; CRC Press: Cleveland, OH, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Viulleumier, J.P.; Keller, H.E.; Gysel, D.; Hunziker, F. Clinical chemical methods for the routine assesment of the vitmin status in human populations. Part I. The fat soluble vitamins A and E, and beta-carotene. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 1983, 53, 265–272. [Google Scholar]
- Koletzko, B. Pediatric Nutrition in Practice; Karger: Basel, Switzerland, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, C.M.; Perry, I.J. Does inflammation determine metabolic health status in obese and non obese adults? J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, E1610–E1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Y. Tracking of blood pressure from childhood to adulthood: A systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Circulation 2008, 117, 3171–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.; Cui, M.; You, X.; Chen, M.; Piao, X.; Jin, G. A role of 1,25(OH)2D3 supplementation in rats with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis induced by choline-deficient diet. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2015, 25, 556–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, T.; Cheng, Y.F.; Lai, C.Y.; Hsu, L.W.; Chang, Y.C.; Deng, J.Y.; Huang, Y.Z.; Honda, H.; Chen, K.D.; Wang, C.C.; et al. Impact of artificial sunlight therapy on the progress of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in rats. J. Hepatol. 2011, 55, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raj, M. Obesity and cardiovascular risk in children and adolescents. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 16, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, M.G.; Pegoraro, M.; Sandrini, F.; Macuco, E.C. Risk factors for the development of atherosclerosis in childhood and adolescence. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2008, 90, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roberson, L.L.; Aneni, E.C.; Maziak, W.; Agatston, A.; Feldman, T.; Rouseff, M.; Tran, T.; Blaha, M.J.; Santos, R.D.; Sposito, A.; et al. Beyond BMI: The “Metabolically healthy obese” phenotype & its association with clinical/subclinical cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality—A systematic review. BMC Public Health 2014, 14, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Garcia, E.; Guallar-Castillon, L.; Leon-Muñoz, F.; Rodriguez-Artalejo, F. Prevalence and determinants of metabolically healthy obesity in Spain. Atherosclerosis 2013, 231, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carcamo, J.M.; Pedraza, A.; Borquez-Ojeda, O.; Golde, D.W. Vitamin C suppresses TNF alpha-induced NF kappa B activation by inhibiting I kappa B alpha phosphorylation. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 12995–13002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villaça Chaves, G.; Pereira, S.E.; Saboya, C.J.; Ramalho, A. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and its relationship with the nutritional status of vitamin A in individuals with class III obesity. Obes. Surg. 2008, 18, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teske, M.; Melges, A.P.; de Souza, F.I.S.; Fonseca, F.L.; Sarni, R.O. Plasma concentrations of retinol in obese children and adolescents: Relationship to metabolic syndrome components. Rev. Paul. Pediatr. 2014, 32, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasmeen, R.; Jeyakumar, S.M.; Reichert, B.; Yang, F.; Ziouzenkova, O. The contribution of vitamin A to autocrine regulation of fat depots. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1821, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansego, M.L.; De Marco, G.; Ivorra, C.; Lopez-Izquierdo, R.; Morcillo, S.; Rojo-Martínez, G.; González-Albert, V.; Martinez, F.; Soriguer, F.; Martín-Escudero, J.C.; et al. The nutrigenetic influence of the interaction between dietary vitamin E and TXN and COMT gene polymorphisms on waist circumference: A case control study. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, S.; Naseem, I. Role of vitamin A in type 2 diabetes mellitus biology: Effects of intervention therapy in a deficient state. Nutrition 2015, 31, 901–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| General Characteristics | MHO (n = 14) | MUO (n = 46) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anthropometric Variables | |||
| BMI-kg/m2 | 45.4 ± 4.4 | 46.5 ± 8.0 | 0.740 |
| WC-cm | 120.4 ± 12.0 | 125.4 ± 14.6 | 0.217 |
| Clinical Variables | |||
| SAH-% | 28.6 | 76.1 | 0.001 * |
| NAFLD-% | 14.3 | 78.3 | <0.001 * |
| Biochemical Variables | |||
| Glycemia-mg/dL | 96.8 ± 9.6 | 97.1 ± 16.5 | 0.605 |
| HOMA-IR | 3.7 ± 1.7 | 3.6 ± 1.6 | 0.979 |
| Total cholesterol-mg/dL | 203.1 ± 46.7 | 198.0 ± 33.8 | 0.773 |
| HDL-c-mg/dL | 51.9 ± 7.7 | 45.1 ± 10.0 | 0.022 * |
| LDL-c-mg/dL | 114.1 ± 38.3 | 125.0 ± 33.0 | 0.315 |
| Triglycerides-mg/dL | 104.2 ± 37.3 | 135.3 ± 50.4 | 0.028 * |
| CRP-mg/dL | 2.4 ± 1.1 | 3.4 ± 3.4 | 0.986 |
| Antioxidant Micronutrient | Mean ± SD | Cut-Off Points for Inadequacy | Inadequacy-% (n) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin C-mg/L | 1.5 ± 0.6 | <4.6 | 91.7 (55) |
| β-carotene-µg/dL | 35.0 ± 25.7 | ≤40 | 66.7 (40) |
| Selenium-µg/dL | 79.8 ± 23.4 | <70 | 36.7 (22) |
| Retinol-µmol/L | 1.5 ± 0.6 | <1.05 | 26.7 (16) |
| Zinc-µg/L | 87.7 ± 24.5 | <75 | 18.3 (11) |
| Vitamin E-mg/dL | 10.6 ± 4.4 | <0.5 | 10.0 (6) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stenzel, A.P.; Carvalho, R.; Jesus, P.; Bull, A.; Pereira, S.; Saboya, C.; Ramalho, A. Serum Antioxidant Associations with Metabolic Characteristics in Metabolically Healthy and Unhealthy Adolescents with Severe Obesity: An Observational Study. Nutrients 2018, 10, 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10020150
Stenzel AP, Carvalho R, Jesus P, Bull A, Pereira S, Saboya C, Ramalho A. Serum Antioxidant Associations with Metabolic Characteristics in Metabolically Healthy and Unhealthy Adolescents with Severe Obesity: An Observational Study. Nutrients. 2018; 10(2):150. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10020150
Chicago/Turabian StyleStenzel, Ana Paula, Roberta Carvalho, Patricia Jesus, Aline Bull, Silvia Pereira, Carlos Saboya, and Andrea Ramalho. 2018. "Serum Antioxidant Associations with Metabolic Characteristics in Metabolically Healthy and Unhealthy Adolescents with Severe Obesity: An Observational Study" Nutrients 10, no. 2: 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10020150
APA StyleStenzel, A. P., Carvalho, R., Jesus, P., Bull, A., Pereira, S., Saboya, C., & Ramalho, A. (2018). Serum Antioxidant Associations with Metabolic Characteristics in Metabolically Healthy and Unhealthy Adolescents with Severe Obesity: An Observational Study. Nutrients, 10(2), 150. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10020150




