The Effect of Place of Residence on Physical Fitness and Adherence to Mediterranean Diet in 3–5-Year-Old Girls and Boys: Urban vs. Rural
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample
2.2. Procedures
2.3. Statistical Analysis
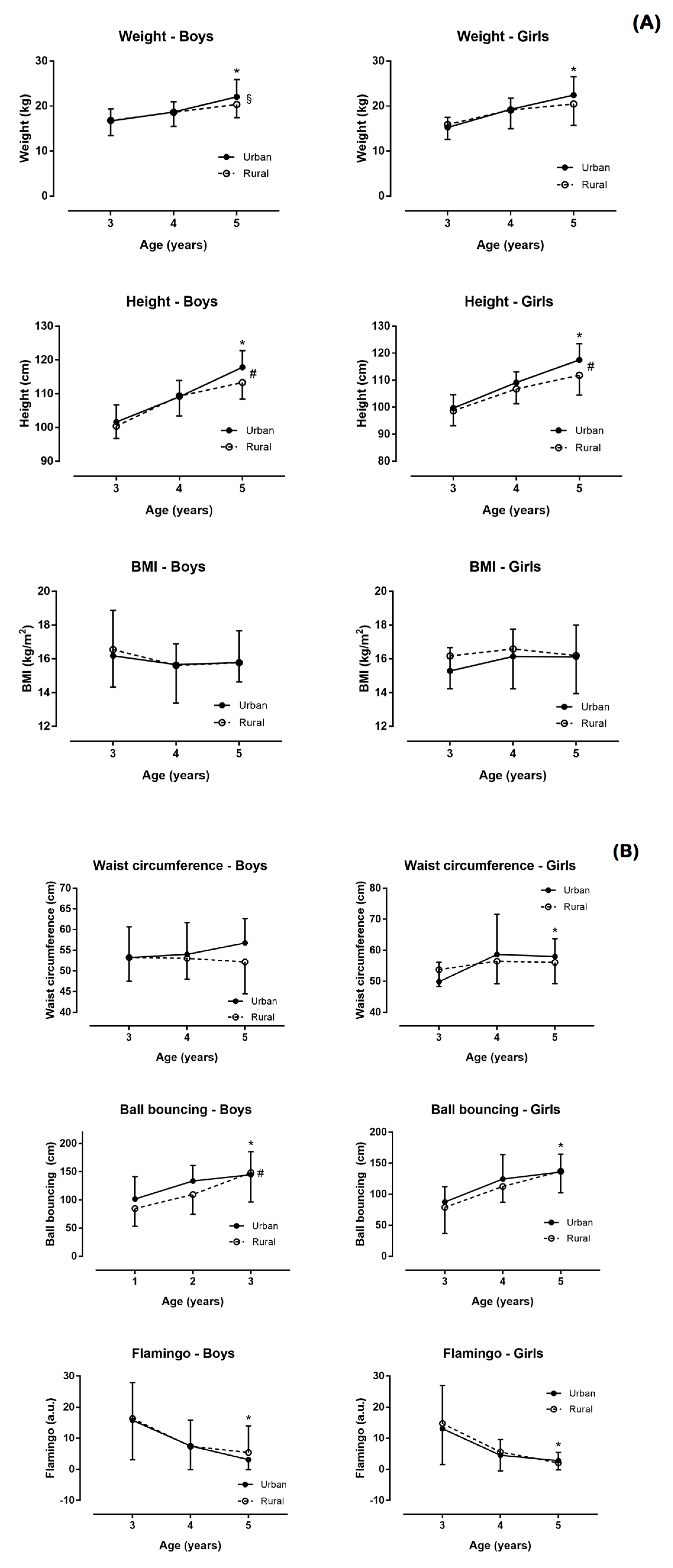
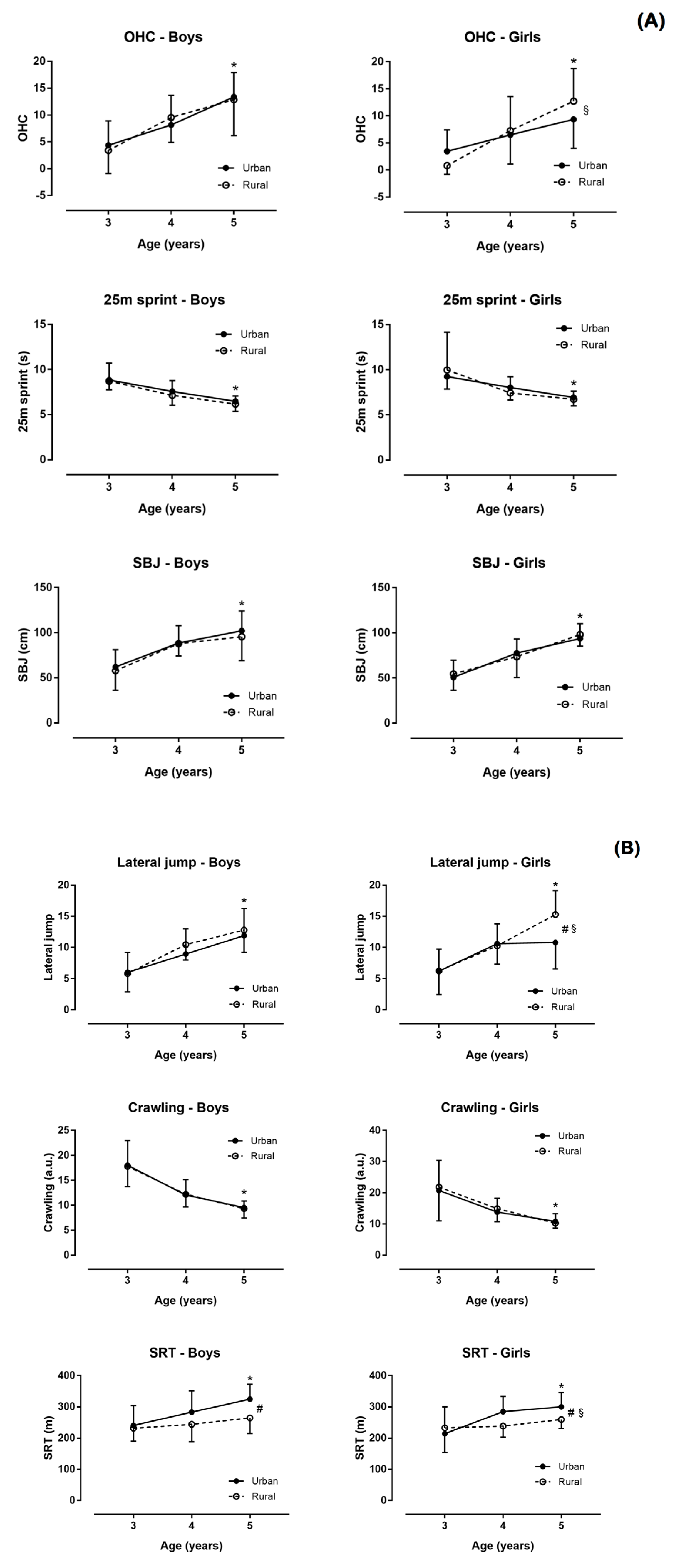
3. Results
3.1. Sex Differences
3.2. Main Effect of Residence
3.3. Main Effect of Age
3.4. Age–Residence Interaction
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ruiz, J.R.; Castro-Pinero, J.; Espana-Romero, V.; Artero, E.G.; Ortega, F.B.; Cuenca, M.M.; Jimenez-Pavón, D.; Chillón, P.; Girela-Rejon, M.J.; Mora, J.; et al. Field-based fitness assessment in young people: The ALPHA health-related fitness test battery for children and adolescents. Br. J. Sports Med. 2011, 45, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayan, C.; Cancela, J.M.; Romero, S.; Alonso, S. Reliability of two field-based tests for measuring cardiorespiratory fitness in preschool children. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2015, 29, 2874–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veldhuizen, S.; Rivard, L.; Cairney, J. Relative age effects in the Movement Assessment Battery for Children-2: Age banding and scoring errors. Child Care Health Dev. 2017, 43, 752–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, M.O.; Kastner, J.; Petermann, F.; Bos, K. Factorial validity of the Movement Assessment Battery for Children-2 (age band 2). Res. Dev. Disabil. 2011, 32, 674–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadenas-Sanchez, C.; Martinez-Tellez, B.; Sanchez-Delgado, G.; Mora-Gonzalez, J.; Castro-Pinero, J.; Lof, M.; Ruiz, J.R.; Ortega, F.B. Assessing physical fitness in preschool children: Feasibility, reliability and practical recommendations for the PREFIT battery. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2016, 19, 910–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega, F.B.; Cadenas-Sanchez, C.; Sanchez-Delgado, G.; Mora-Gonzalez, J.; Martinez-Tellez, B.; Artero, E.G.; Castro-Piñero, J.; Labayen, I.; Chillon, P.; Löf, M.; et al. Systematic Review and Proposal of a Field-Based Physical Fitness-Test Battery in Preschool Children: The PREFIT Battery. Sports Med. 2015, 45, 533–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeng, H.J.; Webster, E.K.; Ulrich, D.A. Reliability for the Test of Gross Motor Development-Third Edition (TGMD-3). Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 2016, 87, A38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latorre-Roman, P.A.; Fernandez-Sanchez, M.; Moriana-Coronas, F.J.; Garcia-Pinillos, F. Design and validation of a cardiorespiratory capacity test for preschool children. S. Afr. J. Res. Sport Phys. Educ. Recreat. 2016, 38, 129–137. [Google Scholar]
- Cadenas-Sanchez, C.; Alcantara-Moral, F.; Sanchez-Delgado, G.; Mora-Gonzalez, J.; Martinez-Tellez, B.; Herrador-Colmenero, M.; Jimenez-Pavón, D.; Femia, P.; Ruiz, J.R.; Ortega, F.B. Assessment of cardiorespiratory fitness in preschool children: Adaptation of the 20 metres shuttle run test. Nutr. Hosp. 2014, 30, 1333–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mora-Gonzalez, J.; Cadenas-Sanchez, C.; Martinez-Tellez, B.; Sanchez-Delgado, G.; Ruiz, J.R.; Leger, L.; Ortega, F.B. Estimating VO(2) max in children aged 5–6 years through the preschool-adapted 20-m shuttle-run test (PREFIT). Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2017, 117, 2295–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estruch, R.; Ros, E.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Covas, M.I.; Corella, D.; Arós, F.; Gómez-Gracia, E.; Ruiz-Gutierrez, V.; Fiol, M.; Lapetra, J.; et al. Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease with a Mediterranean Diet Supplemented with Extra-Virgin Olive Oil or Nuts. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García Cabrera, S.; Herrera Fernández, N.; Rodríguez Hernández, C.; Nissensohn, M.; Román-Vinas, B.; Serra-Majem, L. KIDMED test; prevalence of low adherence to the Mediterranean Diet in children and young; a systematic review. Nutr. Hosp. 2015, 32, 2390–2399. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lahoz, C.; Castillo, E.; Mostaza, J.M.; De Dios, O.; Salinero-Fort, M.A.; Gonzalez-Alegre, T.; García-Iglesias, F.; Estirado, E.; Laguna, F.; Sánchez, V.; et al. Relationship of the Adherence to a Mediterranean Diet and Its Main Components with CRP Levels in the Spanish Population. Nutrients 2018, 10, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosso, G.; Marventano, S.; Buscemi, S.; Scuderi, A.; Matalone, M.; Platania, A.; Giorgianni, G.; Rametta, S.; Nolfo, F.; Galvano, F.; et al. Factors associated with adherence to the Mediterranean diet among adolescents living in Sicily, Southern Italy. Nutrients 2013, 5, 4908–4923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grao-Cruces, A.; Nuviala, A.; Fernandez-Martinez, A.; Porcel-Galvez, A.M.; Moral-Garcia, J.E.; Martínez-Lopez, E.J. Adherence to mediterranean diet in rural urban adolescents of southern spain, life satisfaction, anthropometry, and physical and sedentary activities. Nutr. Hosp. 2013, 28, 1129–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archero, F.; Ricotti, R.; Solito, A.; Carrera, D.; Civello, F.; Di Bella, R.; Bellone, S.; Prodam, F. Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet among School Children and Adolescents Living in Northern Italy and Unhealthy Food Behaviors Associated to Overweight. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandercock, G.R.H.; Ogunleye, A.; Voss, C. Comparison of cardiorespiratory fitness and body mass index between rural and urban youth: Findings from the East of England Healthy Hearts Study. Pediatr. Int. 2011, 53, 718–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.H.; Wu, M.C.; Chang, H.H. Urban-rural disparity in physical fitness of elementary schoolchildren in Taiwan. Pediatr. Int. 2013, 55, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tishukaj, F.; Shalaj, I.; Gjaka, M.; Ademi, B.; Ahmetxhekaj, R.; Bachl, N.; Tschan, H.; Wessner, B. Physical fitness and anthropometric characteristics among adolescents living in urban or rural areas of Kosovo. BMC Public Health 2017, 17, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zongo, P.; Frayon, S.; Antoine-Jonville, S.; Wattelez, G.; Le Roux, P.Y.; Hue, O.; Galy, O. Anthropometric Characteristics and Physical Fitness in Rural and Urban 11-to 16-Year-Old Melanesian Adolescents: A Cross-sectional Study in New Caledonian Schools. Asia Pac. J. Public Health 2017, 29, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ujevic, T.; Sporis, G.; Milanovic, Z.; Pantelic, S.; Neljak, B. Differences between Health-Related Physical Fitness Profiles of Croatian Children in Urban and Rural Areas. Coll. Antropol. 2013, 37, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chillon, P.; Ortega, F.B.; Ferrando, J.A.; Casajus, J.A. Physical fitness in rural and urban children and adolescents from Spain. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2011, 14, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres-Luque, G.; Molero, D.; Lara-Sánchez, A.; Latorre-Ramón, P.; Cachón, J.; Zagalaz, M.L. Influencia del entorno donde se habita (rural vs urbano) sobre la condición física de estudiantes de educación primaria. Apunts Med. del Sport 2014, 49, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, K.L.; Kang, M.; Boswell, B.B.; DuBose, K.D.; Altman, S.R.; Binkley, H.M. Validity and reliability of the medicine ball throw for kindergarten children. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2008, 22, 1958–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hands, B. Changes in motor skill and fitness measures among children with high and low motor competence: A five-year longitudinal study. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2008, 11, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayer, O.; Von Kries, R.; Strauss, A.; Mitschek, C.; Toschke, A.M.; Hose, A.; Koletzko, B.V. Short- and mid-term effects of a setting-based prevention program to reduce obesity risk factors in children: A cluster-randomized trial. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 28, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macau Sport Development Board of Macau SAR Government. Analysis on Physical Fitness of Macao Young Children in 2002. 2003. Available online: www.sport.gov.mo/pt/macaosport/type/show/id/581 (accessed on 10 September 2018).
- Ikeda, T.; Osamu, A. Relationships between test characteristics and movement patterns, physical fitness, and measurement characteristics: Suggestions for developing new test items for 2-to 6-year-old children. Hum. Perform. Meas. 2008, 5, 9–22. [Google Scholar]
- Serra-Majem, L.; Ribas, L.; Ngo, J.; Ortega, R.M.; Garcia, A.; Perez-Rodrigo, C.; Aranceta, J. Food, youth and the Mediterranean diet in Spain. Development of KIDMED, Mediterranean Diet Quality Index in children and adolescents. Public Health Nutr. 2004, 7, 931–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd, R.S.; Cronin, J.B.; Faigenbaum, A.D.; Haff, G.G.; Howard, R.; Kraemer, W.J.; Micheli, L.J.; Myer, G.D.; Oliver, J.L. National strength and conditioning association position statement on long-term athletic development. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2016, 30, 1491–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latorre-Roman, P.A.; Lopez, D.M.; Aguayo, B.B.; Fuentes, A.R.; Garcia-Pinillos, F.; Redondo, M.M. Handgrip strength is associated with anthropometrics variables and sex in preschool children: A cross sectional study providing reference values. Phys. Ther. Sport. 2017, 26, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King-Dowling, S.; Proudfoot, N.A.; Cairney, J.; Timmons, B.W. Validity of field assessments to predict peak muscle power in preschoolers. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 42, 850–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beunen, G.; Thomis, M. Muscular strength development in children and adolescents. Pediatr. Exerc. Sci. 2000, 12, 174–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKay, M.J.; Baldwin, J.N.; Ferreira, P.; Simic, M.; Vanicek, N.; Burns, J.; Norms Project, C. Normative reference values for strength and flexibility of 1,000 children and adults. Neurology 2017, 88, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Tellez, B.; Sanchez-Delgado, G.; Cadenas-Sanchez, C.; Mora-Gonzalez, J.; Martin-Matillas, M.; Lof, M.; Ortega, F.B.; Ruiz, J.R. Health-related physical fitness is associated with total and central body fat in preschool children aged 3 to 5 years. Pediatr. Obes. 2016, 11, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, S.; Ochoa-Aviles, A.; Lachat, C.; Escobar, P.; Verstraeten, R.; Van Camp, J.; Donoso, S.; Rojas, R.; Gardon, G.; Kolsteren, P. Physical fitness among urban and rural Ecuadorian adolescents and its association with blood lipids: A cross sectional study. BMC Pediatr. 2014, 14, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niederer, I.; Kriemler, S.; Zahner, L.; Burgi, F.; Ebenegger, V.; Marques-Vidal, P.; Puder, J.J. BMI Group-Related Differences in Physical Fitness and Physical Activity in Preschool-Age Children: A Cross-Sectional Analysis. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 2012, 83, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otero, J.; Cohen, D.D.; Herrera, V.M.; Camacho, P.A.; Bernal, O.; Lopez-Jaramillo, P. Sociodemographic factors related to handgrip strength in children and adolescents in a middle-income country: The SALUS study. Am. J. Hum. Biol. 2017, 29, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro-Pinero, J.; Perez-Bey, A.; Segura-Jimenez, V.; Aparicio, V.A.; Gomez-Martinez, S.; Izquierdo-Gomez, R.; Marcos, A.; Ruiz, J.R.; Grp, D.S. Cardiorespiratory Fitness Cutoff Points for Early Detection of Present and Future Cardiovascular Risk in Children: A 2-Year Follow-up Study. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2017, 92, 1753–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo, E.R.; Sang, M.K.; Sigei, T.K.; Dingwall, H.L.; Okutoyi, P.; Ojiambo, R.; Otárola-Castillo, E.R.; Pitsiladis, T.; Lieberman, D.E. Physical Fitness Differences Between Rural and Urban Children from Western Kenya. Am. J. Hum. Biol. 2016, 28, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utesch, T.; Dreiskamper, D.; Strauss, B.; Naul, R. The development of the physical fitness construct across childhood. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2018, 28, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolaidis, P.T. Familial aggregation and maximal heritability of exercise participation: A cross-sectional study in schoolchildren and their nuclear families. Sci. Sports 2011, 26, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Girls (n = 167) | Boys (n = 196) | |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 4.0 ± 0.8 | 4.1 ± 0.8 |
| Weight (kg) | 19.0 ± 4.3 | 19.2 ± 3.7 |
| Height (cm) | 108.1 ± 8.6 | 109.8 ± 8.1 |
| BMI (kg·m−2) | 16.0 ± 1.9 | 15.9 ± 2.0 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 55.7 ± 8.9 | 54.3 ± 6.8 |
| MBTT (cm) | 115 ± 39 | 125 ± 44 |
| Flamingo (n) | 6.7 ± 8.6 | 8.5 ± 10.0 |
| Ball bouncing (cm) | 6.9 ± 6.1 | 9.2 ± 6.2 |
| 25 m sprint (s) | 8.0 ± 1.9 | 7.4 ± 1.5 |
| Lateral jump (n) | 9.9 ± 4.6 | 9.5 ± 4.5 |
| SBJ (cm) | 75.6 ± 24.4 | 85.1 ± 26.1 |
| Crawling (s) | 15.0 ± 6.9 | 12.7 ± 4.7 |
| SRT (m) | 260 ± 58 | 275 ± 66 |
| Adherence to Mediterranean Diet | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Good (n) | Good (%) | Average (n) | Average (%) | Poor (n) | Poor (%) | |
| Sex | ||||||
| Girls (n = 134) | 60 | 44.8 | 67 | 50.0 | 7 | 5.2 |
| Boys (n = 158) | 81 | 51.3 | 77 | 48.7 | 0 | 0.0 |
| Age (years) | ||||||
| 3 (n = 74) | 47 | 63.5 | 27 | 36.5 | 0 | 0.0 |
| 4 (n = 119) | 54 | 45.4 | 60 | 50.4 | 5 | 4.2 |
| 5 (n = 98) | 40 | 40.8 | 56 | 57.1 | 2 | 2.0 |
| Residence | ||||||
| Urban (n = 203) | 97 | 47.8 | 103 | 50.7 | 3 | 1.5 |
| Rural (n = 89) | 44 | 49.4 | 41 | 46.1 | 4 | 4.5 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Torres-Luque, G.; Hernández-García, R.; Ortega-Toro, E.; Nikolaidis, P.T. The Effect of Place of Residence on Physical Fitness and Adherence to Mediterranean Diet in 3–5-Year-Old Girls and Boys: Urban vs. Rural. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1855. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10121855
Torres-Luque G, Hernández-García R, Ortega-Toro E, Nikolaidis PT. The Effect of Place of Residence on Physical Fitness and Adherence to Mediterranean Diet in 3–5-Year-Old Girls and Boys: Urban vs. Rural. Nutrients. 2018; 10(12):1855. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10121855
Chicago/Turabian StyleTorres-Luque, Gema, Raquel Hernández-García, Enrique Ortega-Toro, and Pantelis T. Nikolaidis. 2018. "The Effect of Place of Residence on Physical Fitness and Adherence to Mediterranean Diet in 3–5-Year-Old Girls and Boys: Urban vs. Rural" Nutrients 10, no. 12: 1855. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10121855
APA StyleTorres-Luque, G., Hernández-García, R., Ortega-Toro, E., & Nikolaidis, P. T. (2018). The Effect of Place of Residence on Physical Fitness and Adherence to Mediterranean Diet in 3–5-Year-Old Girls and Boys: Urban vs. Rural. Nutrients, 10(12), 1855. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10121855








