Dietary Diversity and Food Variety in Chinese Children Aged 3–17 Years: Are They Negatively Associated with Dietary Micronutrient Inadequacy?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Dietary Survey and Urbanization Level
2.3. DDS and Food Variety Scores (FVS) Calculation
2.4. Assessment of Nutrients Adequacy and Inadequacy
2.5. Anthropometric Measures
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. General Information
3.2. Association of DDS and FVS with Nutrient Inadequacy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Urban (n = 724) | Rural (n = 1288) | All (n = 2012) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAR ≥ 0.75 | MAR < 0.75 | MAR ≥ 0.75 | MAR < 0.75 | MAR ≥ 0.75 | MAR < 0.75 | |||||||
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |
| DDS | 7.3 | 1.3 | 5.8 | 1.6 | 6.3 | 1.4 | 5.1 | 1.6 | 6.7 | 1.5 | 5.3 | 1.6 |
| OFVS | 21.5 | 5.9 | 16.1 | 5.6 | 17.0 | 5.9 | 13.1 | 4.8 | 18.9 | 6.3 | 14.0 | 5.2 |
| FVS_FV | 8.2 | 3.0 | 5.9 | 2.8 | 7.1 | 3.1 | 5.2 | 2.5 | 7.6 | 3.1 | 5.4 | 2.6 |
| FVS_AF | 6.0 | 2.4 | 3.8 | 2.1 | 3.9 | 2.2 | 2.5 | 1.8 | 4.8 | 2.5 | 2.9 | 2.0 |
References
- Dearth-Wesley, T.; Wang, H.; Popkin, B.M. Under- and overnutrition dynamics in Chinese children and adults (1991–2004). Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 62, 1302–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzioumis, E.; Adair, L.S. Childhood Dual Burden of Under- and Overnutrition in Low- and Middle-inCome Countries: A Critical Review. Food Nutr. Bull. 2014, 35, 230–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.; Wang, Y. Comprehensive Report of 2010–2013 Chinese Nutrition and Health Surveillance; Peking University Medical Press: Beijing, China, 2016; ISBN 978-7-5659-1460-7. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, R.; Li, M.; Yun, C.; Li, W.; Yang, Y.; Piao, J.; Yang, X.; Yang, L. Vitamin D Nutritional Status and its Related Factors for Chinese Children and Adolescents in 2010–2012. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wang, D.; Ouyang, Y.; Huang, F.; Ding, G.; Zhang, B. Do Chinese Children Get Enough Micronutrients? Nutrients 2017, 9, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinese Nutrition Society. Chinese Dietary Guideline; People’s Medical Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2016; ISBN 978-7-117-22214-3/R22215. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.; Yu, K.; Tan, S.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, A.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Y. Dietary diversity scores: An indicator of micronutrient inadequacy instead of obesity for Chinese children. BMC Public Health 2017, 17, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nithya, D.J.; Bhavani, R.V. Dietary diversity and its relationship with nutritional status among adolescents and adults in rural India. J. Biosoc. Sci. 2017, 50, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, G.; Pedro, M.; Seghieri, C.; Nantel, G.; Brouwer, I. Dietary Diversity Score Is a Useful Indicator of Micronutrient Intake in Non-Breast-Feeding Filipino Children. J. Nutr. 2007, 137, 472–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conklin, A.; Monsivais, P.; Khaw, K.-T.; Wareham, N.; Forouhi, N. Dietary Diversity, Diet Cost, and Incidence of Type 2Diabetes in the United Kingdom: A Prospective Cohort Study. PLoS Med. 2016, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danquah, I.A.O.; Galbete, C.; Meeks, K.; Nicolaou, M.; Klipstein-Grobusch, K.; Addo, J.; Aikins, A.D.; Amoah, S.K.; Agyei-Baffour, P.; Boateng, D.; et al. Food variety, dietary diversity, and type 2diabetes in a multi-center cross-sectional study among Ghanaian migrants in Europe and their compatriots in Ghana: The RODAM study. Eur. J. Nutr. 2017, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Fei, Z.; Qiu, C.; Brasher, M.S.; Kraus, V.B.; Zhao, W.; Shi, X.; Zeng, Y. Dietary diversity and cognitive function among elderly people: A population-based study. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2017, 21, 1089–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, G.; Ballard, T.; Dop, M. Guidelines for Measuring Household and Individual Dietary Diversity; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2010; ISBN 978-92-5-106749-9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Zhai, F.; Du, S.; Popkin, B.M. The China Health and Nutrition Survey, 1989–2011. Obes. Rev. 2014, 15, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popkin, B.M.; Du, S.; Zhai, F.; Zhang, B. Cohort profile: The China Health and Nutrition Survey—Monitoring and understanding socio-economic and health change in China, 1989–2011. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2010, 39, 1435–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, C.; Kasper, N.M.; Miller, A.L.; Lumeng, J.C.; Peterson, K.E. Association of Dietary Variety and Diversity with Body Mass Index in US Preschool Children. Pediatrics 2016, 137, e20152307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, G.; Pan, X. China Food Composition Table; Peking University Medical Press: Beijing, China, 2009; ISBN 978-7-81116-727-6. [Google Scholar]
- Chinese Nutrition Society. Chinese Dietary Reference Intakes; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2014; ISBN 978-7-03-041401-4. [Google Scholar]
- Hatloy, A.; Torheim, L.; Oshaug, A. Food variety—A good indicator of nutritional adequacy of the diet? A case study from an urban area in Mali, West Africa. Eur. J. Nutr. 1998, 52, 891–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, S.P.; Poos, M.I. Dietary reference intakes: Summary of applications in dietary assessment. Public Health Nutr. 2002, 5, 843–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, S.P. Using DRIs for dietary assessment. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 17 (Suppl. 1), 299S–301S. [Google Scholar]
- Schuette, L.K.; Song Wo Fau-Hoerr, S.L.; Hoerr, S.L. Quantitative use of the Food Guide Pyramid to evaluate dietary intake of college students. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 1996, 96, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onis, M. WHO Child Growth Standards based on length/height, weight and age. Acta Pædiatr. 2006, 95, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO Multicentre Growth Reference Study Group. WHO Child Growth Standards: Length/Height-for-Age, Weight-for-Age, Weight-for-Length, Weight-for-Height and Body Mass Index-for-Age: Methods and Development; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006; 312p. [Google Scholar]
- National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. Screening for Overweight and Obesity among School-Age Children and Adolescents; Industrial Standards of Hygiene WS/T 586-2018; National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2018.
- National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. Screening Standard for Malnutrition of School-Age Children and Adolescents; Industrial Standards of Hygiene WS/T 456-2014; National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Li, Y.; Wedick, N.; Lai, J.; He, Y.; Hu, X.; Liu, A.; Du, S.; Zhang, J.; Yang, X.; Chen, C.; et al. Lack of dietary diversity and dyslipidaemia among stunted overweight children: The 2002 China National Nutrition and Health Survey. Public Health Nutr. 2010, 14, 896–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steyn, N.P.; Nel, J.H.; Nantel, G.; Kennedy, G.; Labadarios, D. Food variety and dietary diversity scores in children: Are they good indicators of dietary adequacy? Public Health Nutr. 2006, 9, 644–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moursi, M.; Arimond, M.; Dewey, K.; Trèche, S.; Ruel, M.; Delpeuch, F. Dietary Diversity Is a Good Predictor of the Micronutrient Density of the Diet of 6- to 23-Month-Old Children in Madagascar 1–3. J. Nutr. 2008, 138, 2448–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirmiran, P.; Azadbakht, L.; Esmaillzadeh, A.; Azizi, F. Dietary diversity score in adolescents—A good indicator of the nutritional adequacy of diets: Tehran lipid and glucose study. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 13, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azadbakht, L.; Esmaillzadeh, A. Dietary diversity score is related to obesity and abdominal adiposity among Iranian female youth. Public Health Nutr. 2011, 14, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Assessing and Managing Children at Primary Health-Care Facilities to Prevent Overweight and Obesity in the Context of the Double Burden of Malnutrition; Updates for the Integrated Management of Childhood Illness (IMCI); World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; ISBN 9789241550123. [Google Scholar]
- Ruel, M.T. Is Dietary Diversity an Indicator of Food Security or Dietary Quality? A Review of Measurement Issues and Research Needs. Food Nutr. Bull. 2003, 24, 231–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
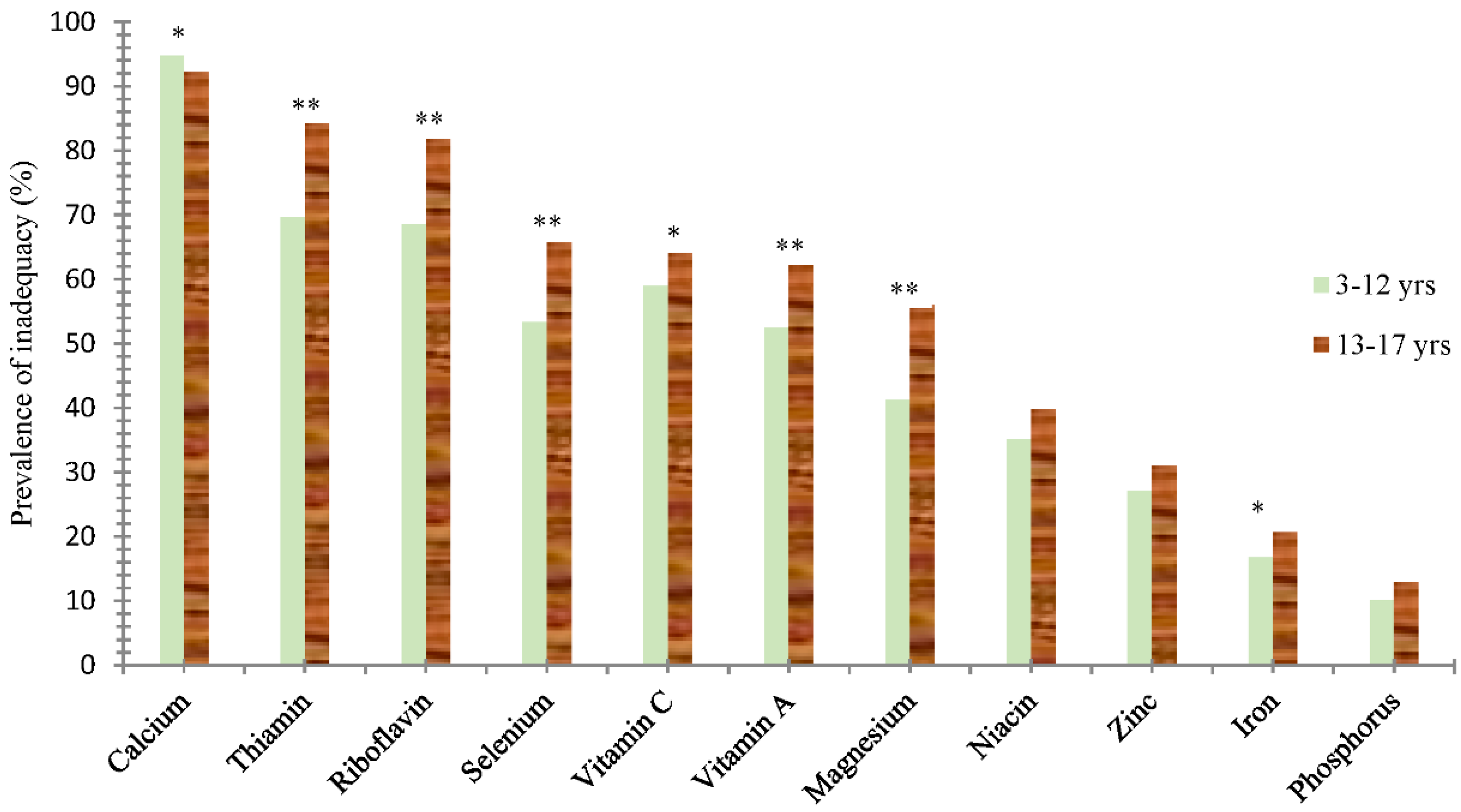
| Children (3–12 years, n = 1485) | Adolescents (13–17 years, n = 527) | Total (n = 2012) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Region | ||||||
| Urban (n, %) | 499, 33.60 | 225, 42.69 | 724, 35.98 | |||
| Rural (n, %) | 986, 66.40 | 302, 57.31 | 1288, 64.02 | |||
| p for Chi-square | 0.0002 | |||||
| Gender | ||||||
| Boys (n, %) | 775, 52.19 | 269, 51.04 | 1044, 51.89 | |||
| Girls (n, %) | 710, 47.81 | 258, 48.96 | 968, 48.11 | |||
| p for Chi-square | 0.65 | |||||
| Anthropometric measures | ||||||
| HAZ (mean, SD) | 0.37, 1.40 | −0.11 **, 1.09 | 0.25, 1.35 | |||
| BAZ (mean, SD) | 0.13, 1.45 | −0.06 **, 1.13 | 0.08, 1.37 | |||
| Wasting (n, %) | 147, 9.90 | 49, 9.30 | 196, 9.74 | |||
| Overweight and Obesity (n, %) | 323, 21.75 | 80, 15.18 ** | 403, 20.03 | |||
| Dietary diversity and food variety | ||||||
| DDS below recommendation (n, %) | 1151, 77.51 | 406. 77.04 | 1557, 77.39 | |||
| FVS below recommendation (n, %) | 353, 23.77 | 105, 19.92 | 458, 22.76 | |||
| FVS_FV below recommendation (n, %) | 223, 15.02 | 71, 13.47 | 294, 14.61 | |||
| DDS (mean, SD) | 6.10, 1.67 | 6.14, 1.67 | 6.11, 1.67 | |||
| OFVS (mean, SD) | 16.53, 6.35 | 17.28 *, 6.32 | 16.73, 6.35 | |||
| FVS_FV (mean, SD) | 6.51, 3.12 | 6.84 *, 3.07 | 6.60, 3.11 | |||
| FVS_AF (mean, SD) | 3.85, 2.41 | 4.21 **, 2.65 | 3.95, 2.48 | |||
| NAR | Intake | NAR | Intake | NAR | Intake | |
| NAR of nutrient and nutrient intake † | ||||||
| Energy | 0.83, 0.18 | 1533.21, 558.42 | 0.77 **, 0.20 | 2049.58 **, 755.70 | 0.81, 0.19 | 1668.50, 656.54 |
| Vitamin A | 0.66, 0.32 | 434.36, 495.44 | 0.59 **, 0.31 | 600.71 **, 1365.02 | 0.64, 0.32 | 477.93, 820.87 |
| Thiamine | 0.65, 0.24 | 0.64, 0.34 | 0.60 **, 0.22 | 0.85 **, 0.37 | 0.64, 0.23 | 0.70, 0.36 |
| Riboflavin | 0.66, 0.26 | 0.65, 0.38 | 0.59 **, 0.23 | 0.82 **, 0.45 | 0.64, 0.25 | 0.69, 0.40 |
| Vitamin C | 0.67, 0.30 | 54.69, 45.58 | 0.65, 0.29 | 79.23 **, 94.82 | 0.67, 0.30 | 61.11, 63.25 |
| Calcium | 0.36, 0.22 | 333.06, 231.11 | 0.40 **, 0.22 | 430.06 **, 258.23 | 0.37, 0.22 | 358.47, 242.23 |
| Iron | 0.90, 0.16 | 14.81, 8.89 | 0.89, 0.16 | 20.05 **, 11.18 | 0.90, 0.16 | 16.18, 9.82 |
| Zinc | 0.89, 0.17 | 7.55, 3.42 | 0.87, 0.18 | 10.19 **, 4.22 | 0.89, 0.17 | 8.24, 3.83 |
| Selenium | 0.75, 0.25 | 33.76, 20.68 | 0.69 **, 0.25 | 45.85 **, 25.60 | 0.74, 0.25 | 36.92, 22.70 |
| α-vitamin E | 0.73, 0.29 | 8.26, 6.58 | 0.64 **, 0.31 | 11.13 **, 9.87 | 0.71, 0.30 | 9.01, 7.68 |
| Niacin | 0.84, 0.21 | 10.33, 5.43 | 0.84, 0.21 | 14.68 **, 8.03 | 0.84, 0.21 | 11.47, 6.50 |
| Phosphorus | 0.97, 0.10 | 697.98, 312.14 | 0.95 *, 0.12 | 935.39 **, 367.00 | 0.96, 0.11 | 760.17, 343.56 |
| Sodium | 0.97, 0.14 | 4.37, 3.36 | 0.97, 0.15 | 6.10 **,8.02 | 0.97, 0.14 | 4.82, 5.07 |
| Magnesium | 0.84, 0.19 | 203.20, 91.22 | 0.78 **, 0.20 | 278.78 **, 127.80 | 0.83, 0.19 | 223.00, 107.32 |
| Potassium | 0.80, 0.21 | 1.35, 0.70 | 0.75 **, 0.21 | 1.82 **, 1.01 | 0.79, 0.21 | 1.47, 0.82 |
| MAR (mean, SD) | 0.76, 0.15 | 0.73 *, 0.15 | 0.75, 0.15 | |||
| DDS | OFVS | FVS_FV | FVS_AF | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low (<5) | Medium (5–6) | High (≥7) | Low (<13) | Medium (13–19) | High (≥19) | Low (<5) | Medium (5–7) | High (≥8) | Low (<3) | Medium (3–4) | High (≥5) | |||||||||||||
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |
| NAR | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Energy | 0.7 a | 0.2 | 0.8 b | 0.2 | 0.9 c | 0.2 | 0.7 a | 0.2 | 0.8 b | 0.2 | 0.9 c | 0.2 | 0.8 a | 0.2 | 0.8 b | 0.2 | 0.9 c | 0.2 | 0.7 a | 0.2 | 0.7 b | 0.2 | 0.8 c | 0.2 |
| Vitamin A | 0.4 a | 0.3 | 0.6 b | 0.3 | 0.7 c | 0.3 | 0.5 a | 0.4 | 0.6 b | 0.3 | 0.8 c | 0.3 | 0.5 a | 0.3 | 0.6 b | 0.3 | 0.8 c | 0.3 | 0.3 a | 0.3 | 0.5 b | 0.3 | 0.7 c | 0.3 |
| Thiamine | 0.5 a | 0.2 | 0.6 b | 0.2 | 0.7 c | 0.2 | 0.6 a | 0.2 | 0.6 b | 0.2 | 0.7 c | 0.2 | 0.6 a | 0.2 | 0.6 b | 0.2 | 0.7 c | 0.2 | 0.5 a | 0.2 | 0.5 b | 0.2 | 0.7 c | 0.2 |
| Riboflavin | 0.4 a | 0.2 | 0.6 b | 0.2 | 0.8 c | 0.2 | 0.5 a | 0.2 | 0.6 b | 0.2 | 0.8 c | 0.2 | 0.5 a | 0.2 | 0.6 b | 0.2 | 0.8 c | 0.2 | 0.3 a | 0.2 | 0.4 b | 0.2 | 0.7 c | 0.2 |
| Vitamin C | 0.5 a | 0.3 | 0.7 b | 0.3 | 0.8 c | 0.3 | 0.6 a | 0.3 | 0.7 b | 0.3 | 0.8 c | 0.3 | 0.5 a | 0.3 | 0.7 b | 0.3 | 0.8 c | 0.2 | 0.5 a | 0.3 | 0.6 b | 0.3 | 0.7 c | 0.3 |
| Calcium | 0.2 a | 0.2 | 0.3 b | 0.2 | 0.5 c | 0.2 | 0.3 a | 0.2 | 0.3 b | 0.2 | 0.5 c | 0.2 | 0.3 a | 0.2 | 0.3 b | 0.2 | 0.5 c | 0.2 | 0.2 a | 0.2 | 0.3 b | 0.2 | 0.4 c | 0.2 |
| Iron | 0.8 a | 0.2 | 0.9 b | 0.2 | 1.0 c | 0.1 | 0.8 a | 0.2 | 0.9 b | 0.2 | 1.0 c | 0.1 | 0.8 a | 0.2 | 0.9 b | 0.2 | 1.0 c | 0.1 | 0.7 a | 0.2 | 0.8 b | 0.2 | 0.9 c | 0.1 |
| Zinc | 0.8 a | 0.2 | 0.9 b | 0.2 | 0.9 c | 0.1 | 0.8 a | 0.2 | 0.9 b | 0.2 | 1.0 c | 0.1 | 0.8 a | 0.2 | 0.9 b | 0.2 | 0.9 c | 0.1 | 0.7 a | 0.2 | 0.8 b | 0.2 | 0.9 c | 0.1 |
| Selenium | 0.5 a | 0.3 | 0.7 b | 0.2 | 0.9 c | 0.2 | 0.6 a | 0.3 | 0.8 b | 0.2 | 0.9 c | 0.2 | 0.6 a | 0.3 | 0.7 b | 0.3 | 0.8 c | 0.2 | 0.5 a | 0.3 | 0.6 b | 0.3 | 0.8 c | 0.2 |
| α-vitamin E | 0.6 a | 0.3 | 0.7 b | 0.3 | 0.8 c | 0.3 | 0.6 a | 0.3 | 0.7 b | 0.3 | 0.8 c | 0.3 | 0.6 a | 0.3 | 0.7 b | 0.3 | 0.8 c | 0.3 | 0.5 a | 0.4 | 0.5 b | 0.3 | 0.7 c | 0.3 |
| Niacin | 0.7 a | 0.3 | 0.8 b | 0.2 | 0.9 c | 0.2 | 0.8 a | 0.2 | 0.8 b | 0.2 | 0.9 c | 0.2 | 0.8 | 0.2 a | 0.8 b | 0.2 | 0.9 c | 0.2 | 0.6 a | 0.2 | 0.7 b | 0.3 | 0.9 c | 0.2 |
| Phosphorus | 0.9 a | 0.2 | 1.0 b | 0.1 | 1.0 c | 0.0 | 0.9 a | 0.2 | 1.0 b | 0.1 | 1.0 c | 0.0 | 0.9 a | 0.2 | 1.0 b | 0.1 | 1.0 c | 0.1 | 0.8 a | 0.2 | 0.9 b | 0.2 | 1.0 c | 0.1 |
| Sodium | 0.9 a | 0.2 | 1.0 a | 0.1 | 1.0 b | 0.1 | 1.0 a | 0.2 | 1.0 a | 0.1 | 1.0 b | 0.1 | 1.0 a | 0.2 | 1.0 a | 0.1 | 1.0 b | 0.1 | 0.9 a | 0.3 | 1.0 a | 0.2 | 1.0 b | 0.1 |
| Magnesium | 0.7 a | 0.2 | 0.8 b | 0.2 | 0.9 c | 0.2 | 0.8 a | 0.2 | 0.8 b | 0.2 | 0.9 c | 0.2 | 0.8 a | 0.2 | 0.8 b | 0.2 | 0.9 c | 0.2 | 0.7 a | 0.2 | 0.8 b | 0.2 | 0.8 c | 0.2 |
| Potassium | 0.6 a | 0.2 | 0.8 b | 0.2 | 0.9 c | 0.2 | 0.7 a | 0.2 | 0.8 b | 0.2 | 0.9 c | 0.2 | 0.7 a | 0.2 | 0.8 b | 0.2 | 0.9 c | 0.2 | 0.6 a | 0.2 | 0.7 b | 0.2 | 0.8 c | 0.2 |
| MAR ‖ | 0.6 a | 0.2 | 0.7 b | 0.2 | 0.8 c | 0.1 | 0.6 a | 0.2 | 0.7 b | 0.2 | 0.8 c | 0.1 | 0.6 a | 0.2 | 0.7 b | 0.2 | 0.8 c | 0.1 | 0.6 a | 0.2 | 0.6 b | 0.2 | 0.8 c | 0.1 |
| DDS | OFVS | FVS_FV | FVS_AF | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Β | SE | p | Β | SE | p | Β | SE | p | Β | SE | p | |
| NAR | ||||||||||||
| Vitamin A | 0.054 | 0.005 | <0.0001 | 0.013 | 0.001 | <0.0001 | 0.032 | 0.002 | <0.0001 | 0.040 | 0.003 | <0.0001 |
| Thiamine | 0.011 | 0.003 | 0.000 | 0.003 | 0.001 | <0.0001 | 0.010 | 0.002 | <0.0001 | 0.010 | 0.002 | <0.0001 |
| Riboflavin | 0.062 | 0.003 | <0.0001 | 0.014 | 0.001 | <0.0001 | 0.022 | 0.001 | <0.0001 | 0.043 | 0.002 | <0.0001 |
| Vitamin C | 0.040 | 0.004 | <0.0001 | 0.014 | 0.001 | <0.0001 | 0.040 | 0.002 | <0.0001 | 0.017 | 0.003 | <0.0001 |
| Niacin | 0.031 | 0.003 | <0.0001 | 0.006 | 0.000 | <0.0001 | 0.011 | 0.001 | <0.0001 | 0.030 | 0.002 | <0.0001 |
| α-vitamin E | 0.013 | 0.004 | 0.001 | 0.003 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.007 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.009 | 0.003 | 0.002 |
| Calcium | 0.043 | 0.003 | <0.0001 | 0.009 | 0.001 | <0.0001 | 0.010 | 0.001 | <0.0001 | 0.026 | 0.002 | <0.0001 |
| Iron | 0.017 | 0.002 | <0.0001 | 0.004 | 0.000 | <0.0001 | 0.008 | 0.000 | <0.0001 | 0.009 | 0.001 | <0.0001 |
| Zinc | 0.023 | 0.002 | <0.0001 | 0.004 | 0.001 | <0.0001 | 0.008 | 0.001 | <0.0001 | 0.018 | 0.001 | <0.0001 |
| Selenium | 0.048 | 0.001 | <0.0001 | 0.011 | 0.001 | <0.0001 | 0.009 | 0.002 | <0.0001 | 0.032 | 0.002 | <0.0001 |
| Phosphorus | 0.016 | 0.001 | <0.0001 | 0.003 | 0.000 | <0.0001 | 0.004 | 0.000 | <0.0001 | 0.007 | 0.001 | <0.0001 |
| Sodium | 0.000 | 0.002 | 0.754 | −0.001 | 0.001 | 0.061 | −0.003 | 0.001 | 0.018 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.375 |
| Magnesium | 0.015 | 0.002 | <0.0001 | 0.004 | 0.000 | <0.0001 | 0.009 | 0.001 | <0.0001 | 0.004 | 0.002 | 0.024 |
| Potassium | 0.036 | 0.003 | <0.0001 | 0.009 | 0.001 | <0.0001 | 0.017 | 0.001 | <0.0001 | 0.018 | 0.002 | <0.0001 |
| MAR | 0.029 | 0.002 | <0.0001 | 0.007 | 0.000 | <0.0001 | 0.013 | 0.001 | <0.0001 | 0.019 | 0.001 | <0.0001 |
| DDS (Ref.: low, <5) | OFVS (Ref.: low, <13) | FVS_FV (Ref.: low, <5) | FVS_AF (Ref.: low, <3) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Medium (5–6) | High (≥7) | Medium (13–19) | High (≥19) | Medium (5–7) | High (≥8) | Medium (3–4) | High (≥5) | |||||||||
| OR | 95% CI | OR | 95% CI | OR | 95% CI | OR | 95% CI | OR | 95% CI | OR | 95% CI | OR | 95% CI | OR | 95% CI | |
| Inadequacy of micronutrient | ||||||||||||||||
| Vitamin A | 0.7 | 0.5, 0.9 | 0.4 | 0.3, 0.6 | 0.9 | 0.7, 1.1 | 0.5 | 0.4, 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.5, 0.7 | 0.3 | 0.2, 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.4, 0.7 | 0.3 | 0.2, 0.4 |
| Thiamine | 0.7 | 0.5, 1.1 | 0.7 | 0.5, 1.1 | 0.8 | 0.6, 1.1 | 0.7 | 0.5, 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.6, 1.1 | 0.5 | 0.3, 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.5, 1.1 | 0.4 | 0.4, 0.7 |
| Riboflavin | 0.3 | 0.2, 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.07, 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.3, 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.1, 0.2 | 0.6 | 0.4, 0.8 | 0.2 | 0.18, 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.1, 0.4 | 0.1 | 0.1, 0.2 |
| Vitamin C | 0.7 | 0.5, 0.9 | 0.5 | 0.3, 0.6 | 0.8 | 0.6, 1.0 | 0.5 | 0.4, 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.4, 0.7 | 0.3 | 0.2, 0.3 | 0.8 | 0.6, 1.0 | 0.7 | 0.5, 0.9 |
| Calcium | 1.5 | 0.6, 3.8 | 0.6 | 0.2, 1.4 | 0.9 | 0.4, 2.0 | 0.5 | 0.2, 1.0 | 1.1 | 0.5, 2.5 | 0.7 | 0.4, 1.2 | 1.1 | 0.5, 2.4 | 0.3 | 0.2, 0.7 |
| Iron | 0.6 | 0.5, 0.9 | 0.3 | 0.2, 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.5, 0.9 | 0.4 | 0.3, 0.5 | 0.9 | 0.7, 1.3 | 0.4 | 0.3, 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.6, 1.2 | 0.5 | 0.3, 0.7 |
| Zinc | 0.6 | 0.5, 0.9 | 0.3 | 0.2, 0.5 | 1.0 | 0.7, 1.3 | 0.5 | 0.3, 0.7 | 0.9 | 0.7, 1.2 | 0.4 | 0.3, 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.4, 0.6 | 0.1 | 0.1, 0.2 |
| Selenium | 0.7 | 0.5, 0.9 | 0.2 | 0.1, 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.3, 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.2, 0.4 | 0.7 | 0.5, 0.9 | 0.5 | 0.4, 0.7 | 0.4 | 0.3, 0.6 | 0.2 | 0.1, 0.2 |
| Niacin | 0.6 | 0.4, 0.8 | 0.3 | 0.3, 0.5 | 0.8 | 0.6, 1.1 | 0.4 | 0.3, 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.6, 1.0 | 0.5 | 0.4, 0.7 | 0.4 | 0.3, 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.1, 0.2 |
| Phosphorus | 0.4 | 0.3, 0.6 | 0.1 | 0.1, 0.3 | 0.8 | 0.5, 1.1 | 0.2 | 0.1, 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.4, 0.9 | 0.2 | 0.1, 0.3 | 0.7 | 0.5, 1.1 | 0.2 | 0.1,0.3 |
| Magnesium | 0.9 | 0.7, 1.3 | 0.6 | 0.4, 0.8 | 1.1 | 0.8, 1.5 | 0.6 | 0.5, 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.6, 1.0 | 0.5 | 0.4, 0.7 | 1.0 | 0.8,1.4 | 0.8 | 0.6, 1.2 |
| OMI | 0.4 | 0.3, 0.6 | 0.2 | 0.1, 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.4, 0.7 | 0.2 | 0.1, 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.4, 0.7 | 0.2 | 0.1, 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.3, 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.1, 0.2 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, T.; Loo-Bouwman, C.A.v.; Zhang, Y.; Man-Yau Szeto, I. Dietary Diversity and Food Variety in Chinese Children Aged 3–17 Years: Are They Negatively Associated with Dietary Micronutrient Inadequacy? Nutrients 2018, 10, 1674. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10111674
Meng L, Wang Y, Li T, Loo-Bouwman CAv, Zhang Y, Man-Yau Szeto I. Dietary Diversity and Food Variety in Chinese Children Aged 3–17 Years: Are They Negatively Associated with Dietary Micronutrient Inadequacy? Nutrients. 2018; 10(11):1674. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10111674
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Liping, Yan Wang, Ting Li, Carolien Annika van Loo-Bouwman, Yumei Zhang, and Ignatius Man-Yau Szeto. 2018. "Dietary Diversity and Food Variety in Chinese Children Aged 3–17 Years: Are They Negatively Associated with Dietary Micronutrient Inadequacy?" Nutrients 10, no. 11: 1674. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10111674
APA StyleMeng, L., Wang, Y., Li, T., Loo-Bouwman, C. A. v., Zhang, Y., & Man-Yau Szeto, I. (2018). Dietary Diversity and Food Variety in Chinese Children Aged 3–17 Years: Are They Negatively Associated with Dietary Micronutrient Inadequacy? Nutrients, 10(11), 1674. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10111674





