GDP Spatialization and Economic Differences in South China Based on NPP-VIIRS Nighttime Light Imagery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Case Study Area and Data
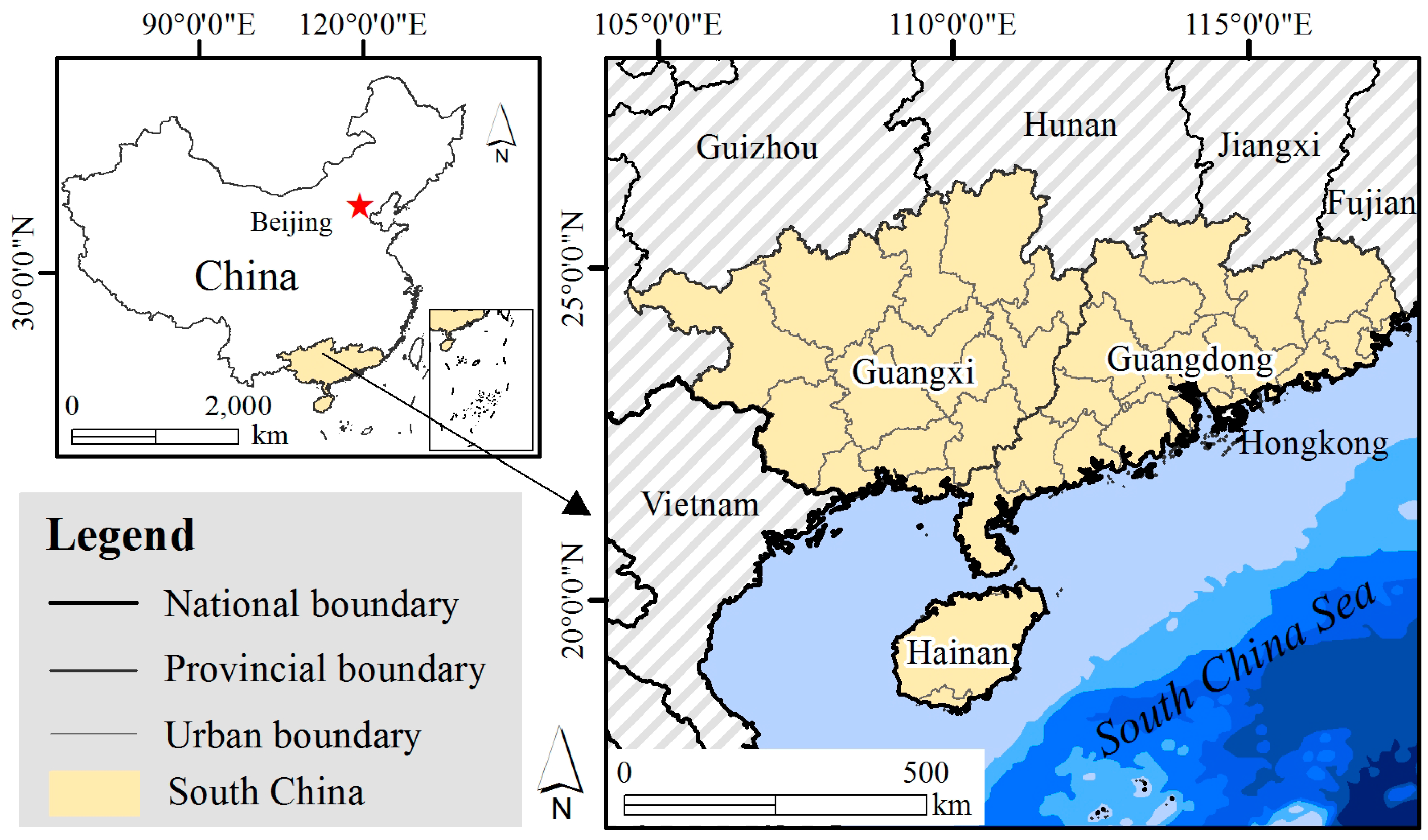
2.1. Case Study Area
2.2. Data Collection
2.2.1. Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) Nighttime Light Data
2.2.2. Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (DMSP) Nighttime Light Data
2.2.3. Statistical Economic Data
2.2.4. Geomorphological Data
3. Methods
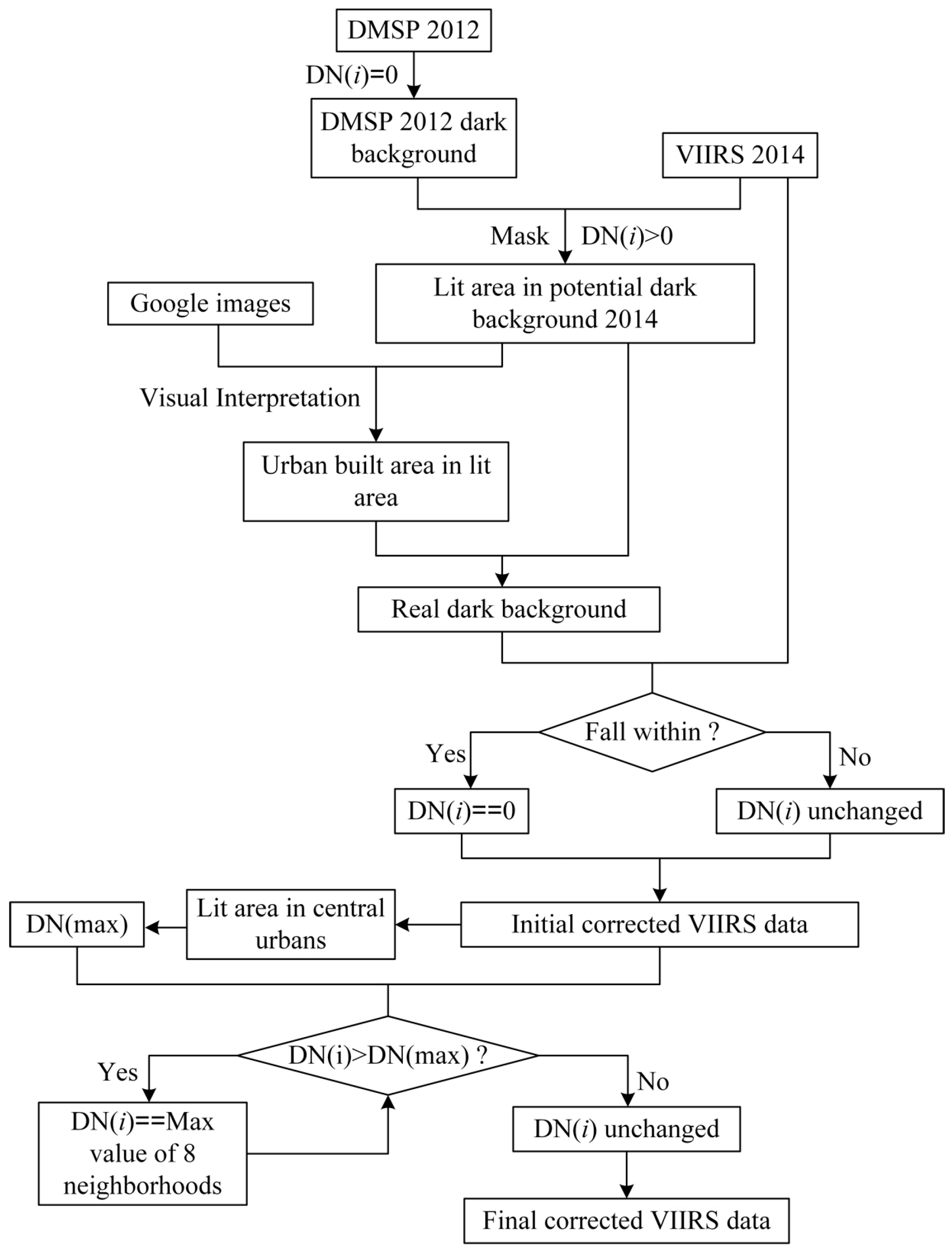
3.1. Correction of the VIIRS Nighttime Light Data
3.2. Calculation of Nighttime Light Indices
3.3. Regression Model and Simulation of GDP
3.4. GDP Spatialization: Correction of Simulated GDP
4. Results
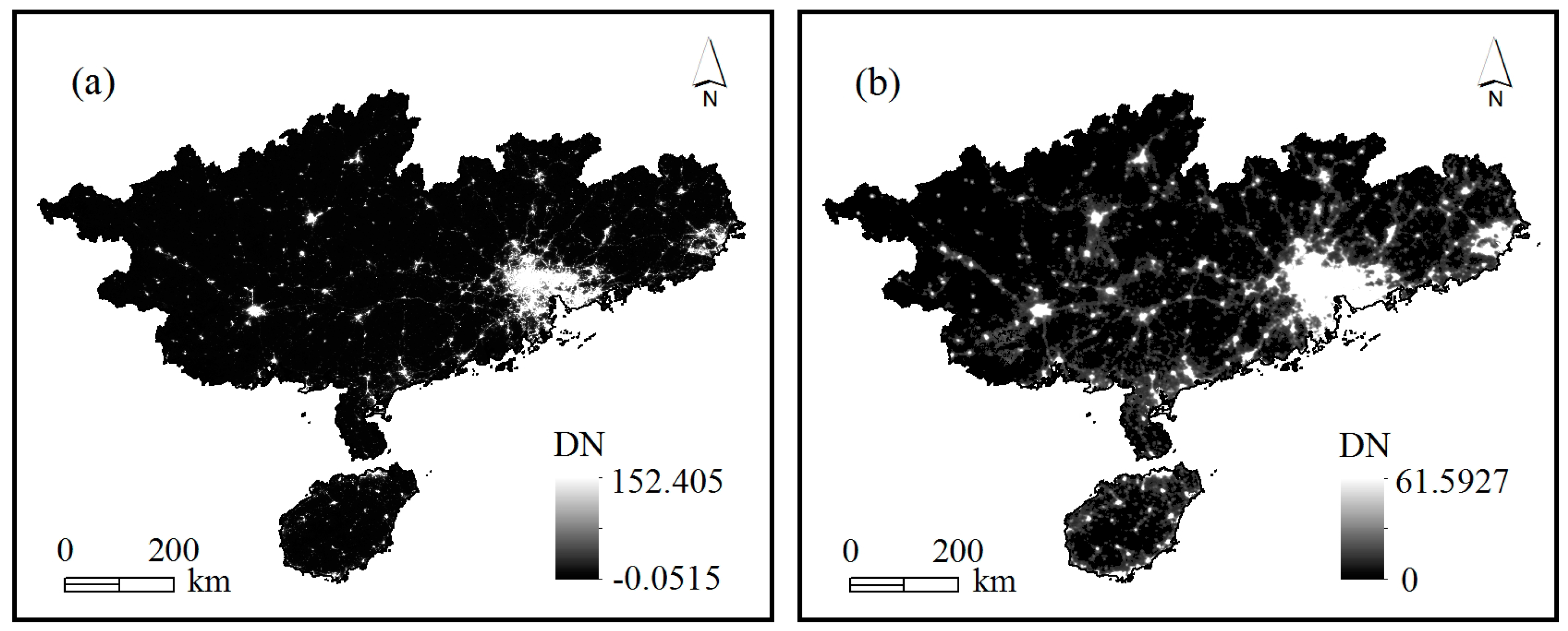
4.1. Correction Results for the VIIRS Nighttime Light Data
4.2. Regression Results
4.3. Spatialization Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix
| Province | Prefecture-Level Unit | Original County-Level Unit | Final County-Level Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guangdong | Guangzhou | Guangzhou Municipality | Guangzhou and Zengcheng and Conghua |
| Guangdong | Guangzhou | Zengcheng Municipality | |
| Guangdong | Guangzhou | Conghua Municipality | |
| Guangdong | Shaoguan | Shaoguan Municipality | Shaoguan and Qujiang |
| Guangdong | Shaoguan | Qujiang County | |
| Guangdong | Shaoguan | Shixing County | Shixing County |
| Guangdong | Shaoguan | Renhua County | Renhua County |
| Guangdong | Shaoguan | Wengyuan County | Wengyuan County |
| Guangdong | Shaoguan | Ruyuan Yao A.C. | Ruyuan Yao A.C. |
| Guangdong | Shaoguan | Xinfeng County | Xinfeng County |
| Guangdong | Shaoguan | Lechang Municipality | Lechang Municipality |
| Guangdong | Shaoguan | Nanxiong Municipality | Nanxiong Municipality |
| Guangdong | Shenzhen | Shenzhen Municipality | Shenzhen Municipality |
| Guangdong | Zhuhai | Zhuhai Municipality | Zhuihai Municipality |
| Guangdong | Shantou | Shantou Municipality | Shantou Municipality |
| Guangdong | Shantou | Nan’ao County | Nan’ao County |
| Guangdong | Foshan | Foshan Municipality | Foshan Municipality |
| Guangdong | Jiangmen | Jiangmen Municipality | Jiangmen Municipality |
| Guangdong | Jiangmen | Taishan Municipality | Taishan Municipality |
| Guangdong | Jiangmen | Kaiping Municipality | Kaiping Municipality |
| Guangdong | Jiangmen | Heshan Municipality | Heshan Municipality |
| Guangdong | Jiangmen | Enping Municipality | Enping Municipality |
| Guangdong | Zhanjiang | Zhanjiang Municipality | Zhanjiang Municipality |
| Guangdong | Zhanjiang | Suixi County | Suixi County |
| Guangdong | Zhanjiang | Xuwen County | Xuwen County |
| Guangdong | Zhanjiang | Lianjiang Municipality | Lianjiang Municipality |
| Guangdong | Zhanjiang | Leizhou Municipality | Leizhou Municipality |
| Guangdong | Zhanjiang | Wuchuan Municipality | Wuchuan Municipality |
| Guangdong | Maoming | Maoming Municipality | Maoming and Dianbai |
| Guangdong | Maoming | Dianbai County | |
| Guangdong | Maoming | Gaozhou Municipality | Gaozhou Municipality |
| Guangdong | Maoming | Huazhou Municipality | Huazhou Municipality |
| Guangdong | Maoming | Xinyi Municipality | Xinyi Municipality |
| Guangdong | Zhaoqing | Zhaoqing Municipality | Zhaoqing Municipality |
| Guangdong | Zhaoqing | Guangning County | Guangning County |
| Guangdong | Zhaoqing | Huaiji County | Huaiji County |
| Guangdong | Zhaoqing | Fengkai County | Fengkai County |
| Guangdong | Zhaoqing | Deqing County | Deqing County |
| Guangdong | Zhaoqing | Gaoyao Municipality | Gaoyao Municipality |
| Guangdong | Zhaoqing | Sihui Municipality | Sihui Municipality |
| Guangdong | Huizhou | Huizhou Municipality | Huizhou Municipality |
| Guangdong | Huizhou | Boluo County | Boluo County |
| Guangdong | Huizhou | Huidong County | Huidong County |
| Guangdong | Huizhou | Longmen County | Longmen County |
| Guangdong | Meizhou | Meizhou Municipality | Meizhou and Mei |
| Guangdong | Meizhou | Mei County | |
| Guangdong | Meizhou | Dapu County | Dapu County |
| Guangdong | Meizhou | Fengshun County | Fengshun County |
| Guangdong | Meizhou | Wuhua County | Wuhua County |
| Guangdong | Meizhou | Pingyuan County | Pingyuan County |
| Guangdong | Meizhou | Jiaoling County | Jiaoling County |
| Guangdong | Meizhou | Xingning Municipality | Xingning Municipality |
| Guangdong | Shanwei | Shanwei Municipality | Shanwei Municipality |
| Guangdong | Shanwei | Haifeng County | Haifeng County |
| Guangdong | Shanwei | Luhe County | Luhe County |
| Guangdong | Shanwei | Lufeng Municipality | Lufeng Municipality |
| Guangdong | Heyuan | Heyuan Municipality | Heyuan Municipality |
| Guangdong | Heyuan | Zijin County | Zijin County |
| Guangdong | Heyuan | Longchuan County | Longchuan County |
| Guangdong | Heyuan | Lianping County | Lianping County |
| Guangdong | Heyuan | Heping County | Heping County |
| Guangdong | Heyuan | DongYuan County | DongYuan County |
| Guangdong | Yangjiang | Yangjiang Municipality | Yangjiang and Yangdong |
| Guangdong | Yangjiang | Yangdong County | |
| Guangdong | Yangjiang | Yangxi County | Yangxi County |
| Guangdong | Yangjiang | Yangchun Municipality | Yangchun Municipality |
| Guangdong | Qingyuan | Qingyuan Municipality | Qiangyuan and Qingxin |
| Guangdong | Qingyuan | Qingxin County | |
| Guangdong | Qingyuan | Fogang County | Fogang County |
| Guangdong | Qingyuan | Yangshan County | Yangshan County |
| Guangdong | Qingyuan | Lianshan Zhuang and Yao A.C. | Lianshan Zhuang and Yao A.C. |
| Guangdong | Qingyuan | Liannan Yao A.C. | Liannan Yao A.C. |
| Guangdong | Qingyuan | Yingde Municipality | Yingde Municipality |
| Guangdong | Qingyuan | Lianzhou Municipality | Lianzhou Municipality |
| Guangdong | Dongguan | Dongguan Municipality | Dongguan Municipality |
| Guangdong | Zhongshan | Zhongshan Municipality | Zhongshan Municipality |
| Guangdong | Chaozhou | Chaozhou Municipality | Chaozhou and Chaoan |
| Guangdong | Chaozhou | Chaoan County | |
| Guangdong | Chaozhou | Raoping County | Raoping County |
| Guangdong | Jieyang | Jieyang Municipality | Jieyang and Jiedong |
| Guangdong | Jieyang | Jiedong County | |
| Guangdong | Jieyang | Jiexi County | Jiexi County |
| Guangdong | Jieyang | Huilai County | Huilai County |
| Guangdong | Jieyang | Puning Municipality | Puning Municipality |
| Guangdong | Yunfu | Yunfu Municipality | Yunfu and Yun’an |
| Guangdong | Yunfu | Yun’an County | |
| Guangdong | Yunfu | Xinxing County | Xinxing County |
| Guangdong | Yunfu | Yu’nan County | Yu’nan County |
| Guangdong | Yunfu | Luoding Municipality | Luoding Municipality |
| Guangxi | Nanning | Nanning Municipality | Nanning Municipality |
| Guangxi | Nanning | Yongning County | Yongning County |
| Guangxi | Nanning | Wuming County | Wuming County |
| Guangxi | Nanning | Longan County | Longan County |
| Guangxi | Nanning | Mashan County | Mashan County |
| Guangxi | Nanning | Shanglin County | Shanglin County |
| Guangxi | Nanning | Binyang County | Binyang County |
| Guangxi | Nanning | Heng County | Heng County |
| Guangxi | Liuzhou | Liuzhou Municipality | Liuzhou Municipality |
| Guangxi | Liuzhou | Liujiang County | Liujiang County |
| Guangxi | Liuzhou | Liucheng County | Liucheng County |
| Guangxi | Liuzhou | Luzhai County | Luzai County |
| Guangxi | Liuzhou | Rongan County | Rongan County |
| Guangxi | Liuzhou | Rongshui Miao A.C. | Rongshui Miao A.C. |
| Guangxi | Liuzhou | Sanjiang Dong A.C. | Sanjiang Dong A.C. |
| Guangxi | Guilin | Guilin Municipality | Guilin Municipality |
| Guangxi | Guilin | Yangshuo County | Yangshuo County |
| Guangxi | Guilin | Lingui County | Lingui County |
| Guangxi | Guilin | Lingchuan County | Lingchuan County |
| Guangxi | Guilin | Quanzhou County | Quanzhou County |
| Guangxi | Guilin | Xing’an County | Xing’an County |
| Guangxi | Guilin | Yongfu County | Yongfu County |
| Guangxi | Guilin | Guanyang County | Guanyang County |
| Guangxi | Guilin | Longsheng Ge A.C. | Longsheng Ge A.C. |
| Guangxi | Guilin | Ziyuan County | Ziyuan County |
| Guangxi | Guilin | Pingle County | Pingle County |
| Guangxi | Guilin | Lipu County | Lipu County |
| Guangxi | Guilin | Gongcheng Yao A.C. | Gongcheng Yao A.C. |
| Guangxi | Wuzhou | Wuzhou Municipality | Wuzhou Municipality |
| Guangxi | Wuzhou | Cangwu County | Cangwu County |
| Guangxi | Wuzhou | Teng County | Teng County |
| Guangxi | Wuzhou | Mengshan County | Mengshan County |
| Guangxi | Wuzhou | Cenxi Municipality | Cenxi Municipality |
| Guangxi | Beihai | Beihai Municipality | Beihai Municipality |
| Guangxi | Beihai | Hepu County | Hepu County |
| Guangxi | Fangchenggang | Fangchenggang Municipality | Fangchenggang Municipality |
| Guangxi | Fangchenggang | Fangcheng District | Fangcheng District |
| Guangxi | Fangchenggang | Shangsi County | Shangsi County |
| Guangxi | Fangchenggang | Dongxing Municipality | Dongxing Municipality |
| Guangxi | Qinzhou | Qinzhou Municipality | Qinzhou Municipality |
| Guangxi | Qinzhou | Qinbei District | Qinbei District |
| Guangxi | Qinzhou | Lingshan County | Lingshan County |
| Guangxi | Qinzhou | Pubei County | Pubei County |
| Guangxi | Guigang | Guigang Municipality | Guigang Municipality |
| Guangxi | Guigang | Gangbei District | Gangbei and Qintang |
| Guangxi | Guigang | Qintang District | |
| Guangxi | Guigang | Pingnan County | Pingnan County |
| Guangxi | Guigang | Guiping Municipality | Guiping Municipality |
| Guangxi | Yulin | Yulin Municipality | Yulin Municipality |
| Guangxi | Yulin | Rong County | Rong County |
| Guangxi | Yulin | Luchuan County | Luchuan County |
| Guangxi | Yulin | Bobai County | Bobai County |
| Guangxi | Yulin | Xingye County | Xingye County |
| Guangxi | Yulin | Beiliu Municipality | Beiliu Municipality |
| Guangxi | Baise | Baise Municipality | Baise Municipality |
| Guangxi | Baise | Tianyang County | Tianyang County |
| Guangxi | Baise | Tiandong County | Tiandong County |
| Guangxi | Baise | Pingguo County | Pingguo County |
| Guangxi | Baise | Debao County | Debao County |
| Guangxi | Baise | Jingxi County | Jingxi County |
| Guangxi | Baise | Napo County | Napo County |
| Guangxi | Baise | Lingyun County | Lingyun County |
| Guangxi | Baise | Leye County | Leye County |
| Guangxi | Baise | Tianlin County | Tianlin County |
| Guangxi | Baise | Xilin County | Xilin County |
| Guangxi | Baise | Longlin Ge A.C. | Longlin Ge A.C. |
| Guangxi | Hezhou | Hezhou Municipality | Hezhou Municipality |
| Guangxi | Hezhou | Zhaoping County | Zhaoping County |
| Guangxi | Hezhou | Zhongshan County | Zhongshan County |
| Guangxi | Hezhou | Fuchuan Yao A.C. | Fuchuan Yao A.C. |
| Guangxi | Hechi | Hechi Municipality | Hechi Municipality |
| Guangxi | Hechi | Nandan County | Nandan County |
| Guangxi | Hechi | Tiane County | Tiane County |
| Guangxi | Hechi | Fengshan County | Fengshan County |
| Guangxi | Hechi | Donglan County | Donglan County |
| Guangxi | Hechi | Luocheng Mulao A.C. | Luocheng Mulao A.C. |
| Guangxi | Hechi | Huanjiang Maonan A.C. | Huangjiang Maonan A.C. |
| Guangxi | Hechi | Bama Yao A.C. | Bama Yao A.C. |
| Guangxi | Hechi | Du’an Yao A.C. | Du’an Yao A.C. |
| Guangxi | Hechi | Dahua Yao A.C. | Dahua Yao A.C. |
| Guangxi | Hechi | Yizhou Municipality | Yizhou Municipality |
| Guangxi | Laibin | Laibin Municipality | Laibin Municipality |
| Guangxi | Laibin | Xincheng County | Xincheng County |
| Guangxi | Laibin | Xiangzhou County | Xiangzhou County |
| Guangxi | Laibin | Wuxuan County | Wuxuan County |
| Guangxi | Laibin | Jinxiu Yao A.C. | Jinxiu Yao A.C. |
| Guangxi | Laibin | Heshan Municipality | Heshan Municipality |
| Guangxi | Chongzuo | Chongzuo Municipality | Chongzuo Municipality |
| Guangxi | Chongzuo | Fusui County | Fusui County |
| Guangxi | Chongzuo | Ningming County | Ningming County |
| Guangxi | Chongzuo | Longzhou County | Longzhou County |
| Guangxi | Chongzuo | Daxin County | Daxin County |
| Guangxi | Chongzuo | Tiandeng County | Tiandeng County |
| Guangxi | Chongzuo | Pingxiang Municipality | Pingxiang Municipality |
| Hainan | Haikou | Haikou Municipality | Haikou Municipality |
| Hainan | Sanya | Sanya Municipality | Sanya Municipality |
| Hainan | Provincial county | Wuzhishan Municipality | Wuzhishan Municipality |
| Hainan | Provincial county | Qionghai Municipality | Qionghai Municipality |
| Hainan | Provincial county | Danzhou Municipality | Danzhou Municipality |
| Hainan | Provincial county | Wenchang Municipality | Wenchang Municipality |
| Hainan | Provincial county | Wanning Municipality | Wanning Municipality |
| Hainan | Provincial county | Dongfang Municipality | Dongfang Municipality |
| Hainan | Provincial county | Ding’an County | Ding’an County |
| Hainan | Provincial county | Tunchang County | Tunchang County |
| Hainan | Provincial county | Chengmai County | Chengmai County |
| Hainan | Provincial county | Lingao County | Lingao County |
| Hainan | Provincial county | Baisha Li A.C. | Baisha Li A.C. |
| Hainan | Provincial county | Changjiang Li A.C. | Changjiang Li A.C. |
| Hainan | Provincial county | Ledong Li A.C. | Ledong Li A.C. |
| Hainan | Provincial county | Lingshui Li A.C. | Lingshui Li A.C. |
| Hainan | Provincial county | Baoting Li and Miao A.C. | Baoting Li and Miao A.C. |
| Hainan | Provincial county | Qiongzhong Li and Miao A.C. | Qiongzhong Li and Miao A.C. |
References
- Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.E.; Kihn, E.A.; Kroehl, H.W.; Davis, E.R.; Davis, C.W. Relation between satellite observed visible-near infrared emissions, population, economic activity and electric power consumption. Int. J. Remote. Sens. 1997, 18, 1373–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doll, C.N.H.; Muller, J.P.; Morley, J.G. Mapping regional economic activity from night-time light satellite imagery. Ecol. Econ. 2006, 57, 75–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.Z.; Currit, N.; Samson, E. Net primary production and gross domestic product in China derived from satellite imagery. Ecol. Econ. 2011, 70, 921–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, D.J. Multi-scale analysis of the relationship between economic statistics and DMSP-OLS night light images. GISci. Remote. Sens. 2013, 50, 483–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doll, C.N.H.; Muller, J.P.; Elvidge, C.D. Night-time imagery as a tool for global mapping of socioeconomic parameters and greenhouse gas emissions. Ambio 2000, 29, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, T.; Powell, R.L.; Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.E.; Sutton, P.C.; Anderson, S. Shedding light on the global distribution of economic activity. Open Geogr. J. 2010, 3, 148–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letu, H.; Hara, M.; Yagi, H.; Naoki, K.; Tana, G.; Nishio, F.; Shuhei, O. Estimating energy consumption from night-time DMPS/OLS imagery after correcting for saturation effects. Int. J. Remote. Sens. 2010, 31, 4443–4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.Z.; Ghosh, T.; Samson, E. Mapping spatio-temporal changes of Chinese electric power consumption using night-time imagery. Int. J. Remote. Sens. 2012, 33, 6304–6320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baugh, K.; Hsu, F.C.; Elvidge, C.; Zhizhin, M. Nighttime lights compositing using the VIIRS day-night band: Preliminary results. Proc. Asia Pac. Adv. Netw. 2013, 35, 70–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Baugh, K.; Zhizhin, M.; Hsu, F.C. Why VIIRS data are superior to DMSP for mapping nighttime lights. Proc. Asia Pac. Adv. Netw. 2013, 35, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, H.M.; Chen, X.L.; Li, C. Potential of NPP-VIIRS nighttime light imagery for modeling the regional economy of China. Remote. Sens. 2013, 5, 3057–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Zhou, C.H.; Pei, T.; Haynie, S.; Fan, J.F. Responses of Suomi-NPP VIIRS-derived nighttime lights to socioeconomic activity in China’s cities. Remote. Sens. Lett. 2014, 5, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.F.; Yu, B.L.; Huang, Y.X.; Hu, Y.J.; Yin, B.; Chen, Z.Q.; Chen, L.J.; Wu, J.P. Evaluating the ability of NPP-VIIRS nighttime light data to estimate the gross domestic product and the electric power consumption of China at multiple scales: A comparison with DMSP-OLS data. Remote. Sens. 2014, 6, 1705–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Ziskin, D.; Baugh, K.E.; Tuttle, B.T.; Ghosh, T.; Pack, D.W.; Erwin, E.H.; Zhizhin, M. A fifteen year record of global natural gas flaring derived from satellite data. Energies 2009, 2, 595–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Zhou, Y.K.; Zhou, C.H.; Haynie, S.; Pei, T.; Xu, T. Night-time light derived estimation of spatio-temporal characteristics of urbanization dynamics using DMSP/OLS satellite data. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2015, 158, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Propastin, P.; Kappas, M. Assessing satellite-observed nighttime lights for monitoring socioeconomic parameters in the Republic of Kazakhstan. GISci. Remote. Sens. 2012, 49, 538–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.M.; Zhou, C.H.; Chai, H.X.; Zhao, S.M.; Liu, H.J.; Zhou, Z.P. Research and compilation of the Geomorphologic Atlas of the People’s Republic of China (1:1,000,000). J. Geogr. Sci. 2011, 21, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.M.; Zhou, C.H.; Li, B.Y.; Shen, Y.C.; Zhang, B.P. Structure and contents of layered classification system of digital geomorphology for China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2011, 21, 771–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.C.; Zhao, S.M.; Cheng, W.M. Analysis of land cover change on basic geomorphic types in Shanxi Province. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2016, 18, 210–219. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Cheng, W.M.; Huang, K.; Wang, N.; Liu, Q.Y. Research on land cover change in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region during the last 10 years based on different geomorphic units. J. Nat. Res. 2016, 31, 252–264. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Cheng, W.M.; Huang, K. Spatial characteristics of urban development and its correlation with macro geomorphology in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region for recent 21 years. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2015, 17, 917–926. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Cheng, W.M.; Liu, Q.Y.; Wang, N. Spatiotemporal measurement of urbanization levels based on multiscale units: A case study of the Bohai Rim Region in China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 531–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Cheng, W.M.; Zhou, C.H.; Li, M.C.; Wang, N.; Liu, Q.Y. Spatial differentiation and morphologic characteristics of China’s urban core zones based on geomorphologic partition. J. Appl. Remote. Sens. 2017, 11, 016041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.M.; Chai, H.X.; Fang, Y.; Zhou, C.H.; Tian, C.Y. Analysis of cultivated land based on water resources regionalization and geomorphologic characteristics in Xinjiang, China. J. Nat. Res. 2012, 27, 1809–1822. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Cheng, W.M.; Zhou, C.H.; Chen, X.; Tian, C.Y. Suitability evaluation of land cultivation in Xinjiang based on multiple natural geographical factors. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2015, 17, 846–854. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, W.; Oliva, P.; Giglio, L.; Csiszar, I.A. The new VIIRS 375 m active fire detection data product: Algorithm description and initial assessment. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2014, 143, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.F.; Yu, B.L.; Hu, Y.J.; Huang, C.; Chen, Y.; Huang, Y.X.; Chen, Z.Q.; Wu, J.P. Modeling and mapping total freight traffic in China using NPP-VIIRS nighttime light composite data. GISci. Remote. Sens. 2015, 52, 274–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Zhou, Y.K.; Wang, Y.J.; Zhou, C.H.; Haynie, S.; Xu, T. Diverse relationships between Suomi-NPP VIIRS night-time light and multi-scale socioeconomic activity. Remote. Sens. Lett. 2014, 5, 652–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhuo, L.; Shi, P.J.; Ichinose, T. The study on urbanization process in China based on DMSP/OLS data: Development of a light index for urbanization level estimation. J. Remote. Sens. 2003, 7, 168–175. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, L.; Shi, P.J.; Chen, J.; Ichinose, T. Application of compound night light index derived from DMSP/OLS data to urbanization analysis in China in the 1990s. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2003, 58, 893–902. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Nordhaus, W. A test of the new VIIRS lights data set: Population and economic output in Africa. Remote. Sens. 2015, 7, 4937–4947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.L.; Shi, K.F.; Hu, Y.J.; Huang, C.; Chen, Z.Q.; Wu, J.P. Poverty Evaluation Using NPP-VIIRS Nighttime Light Composite Data at the County Level in China. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote. Sens. 2015, 8, 1217–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Wei, A.X.; Mi, X.N.; Sun, G.T. An approach of GDP spatialization in Hebei province using NPP-VIIRS nighttime light data. J. Xinyang Norm. Univ.: Nat. Sci. Ed. 2016, 29, 152–156. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
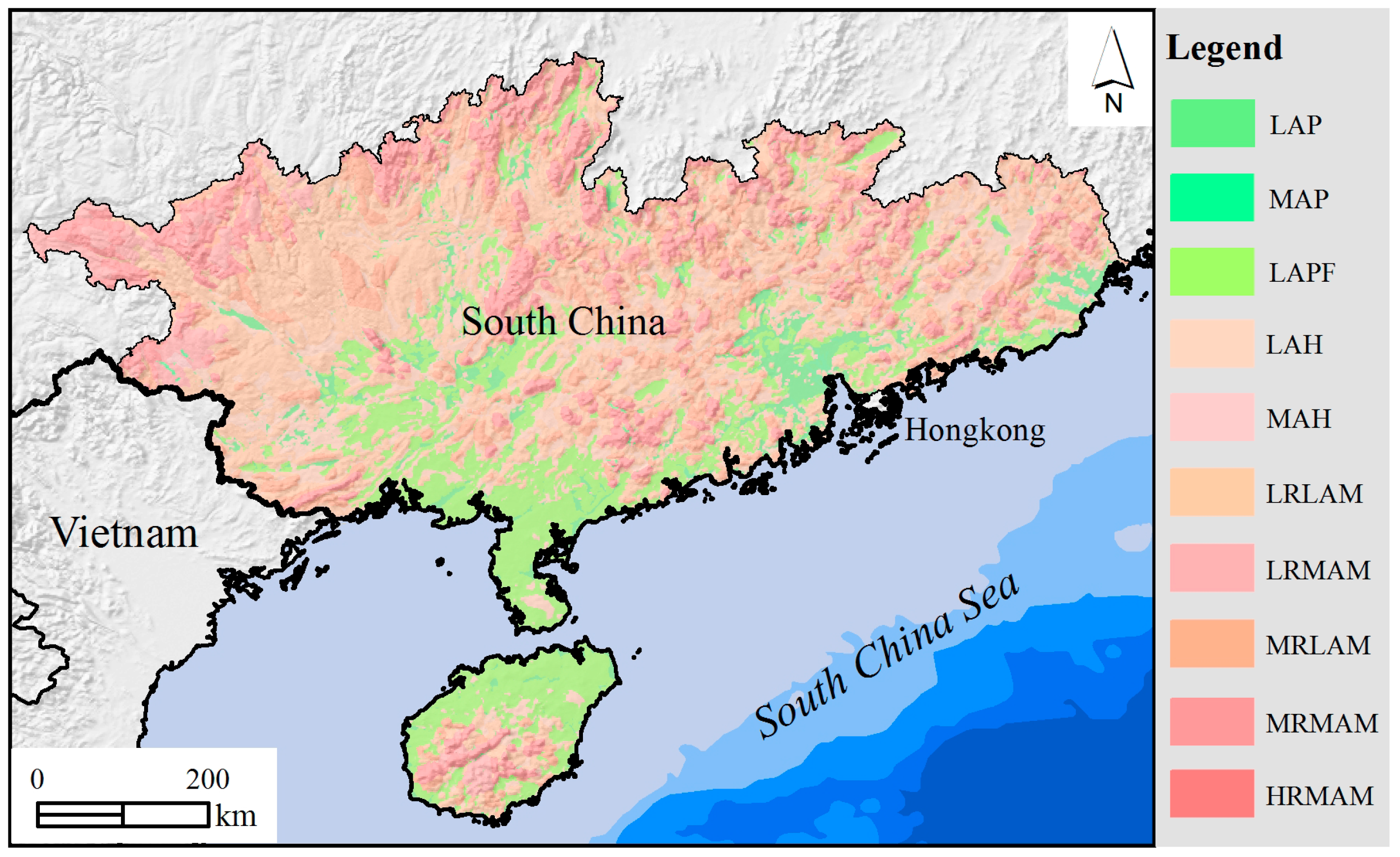
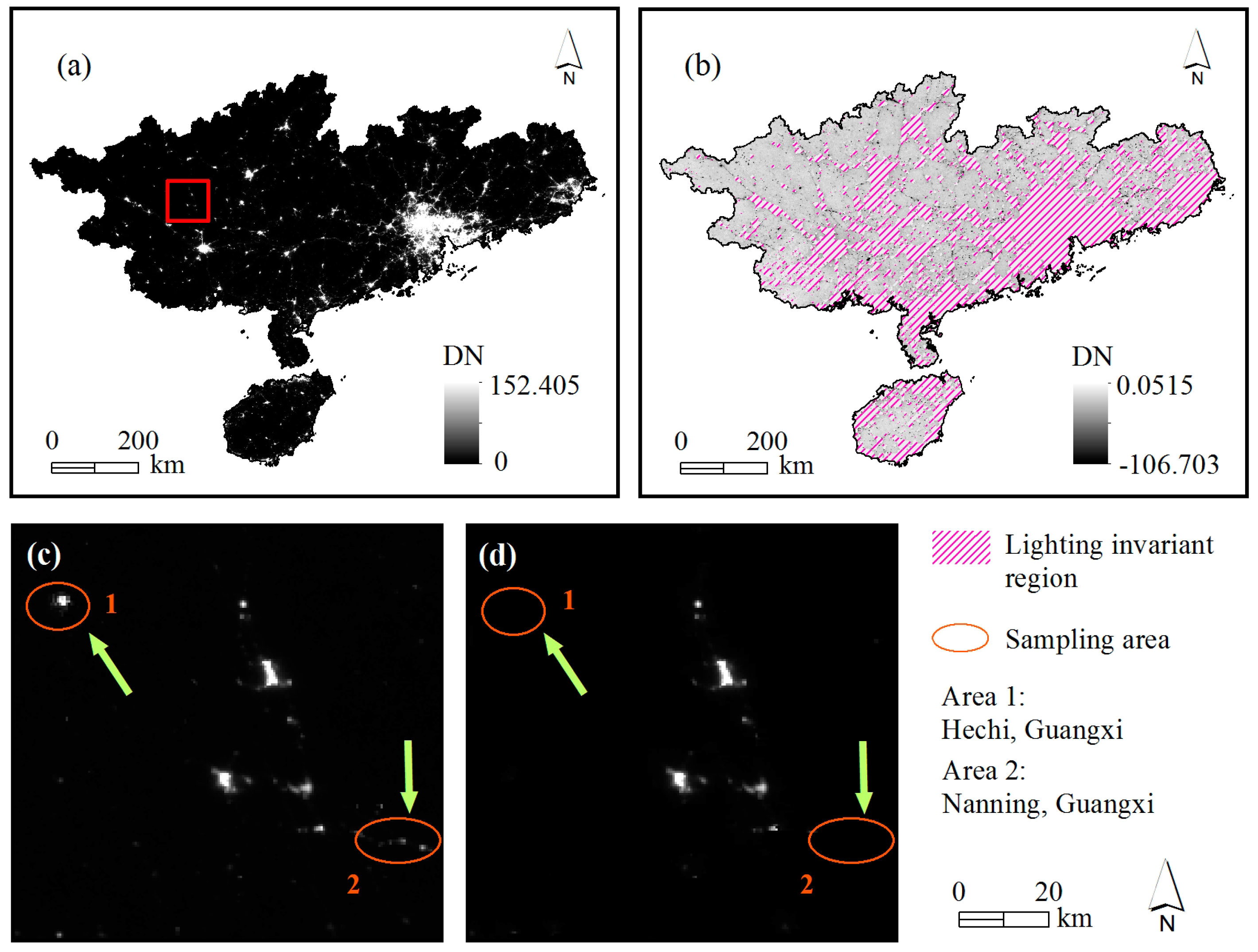

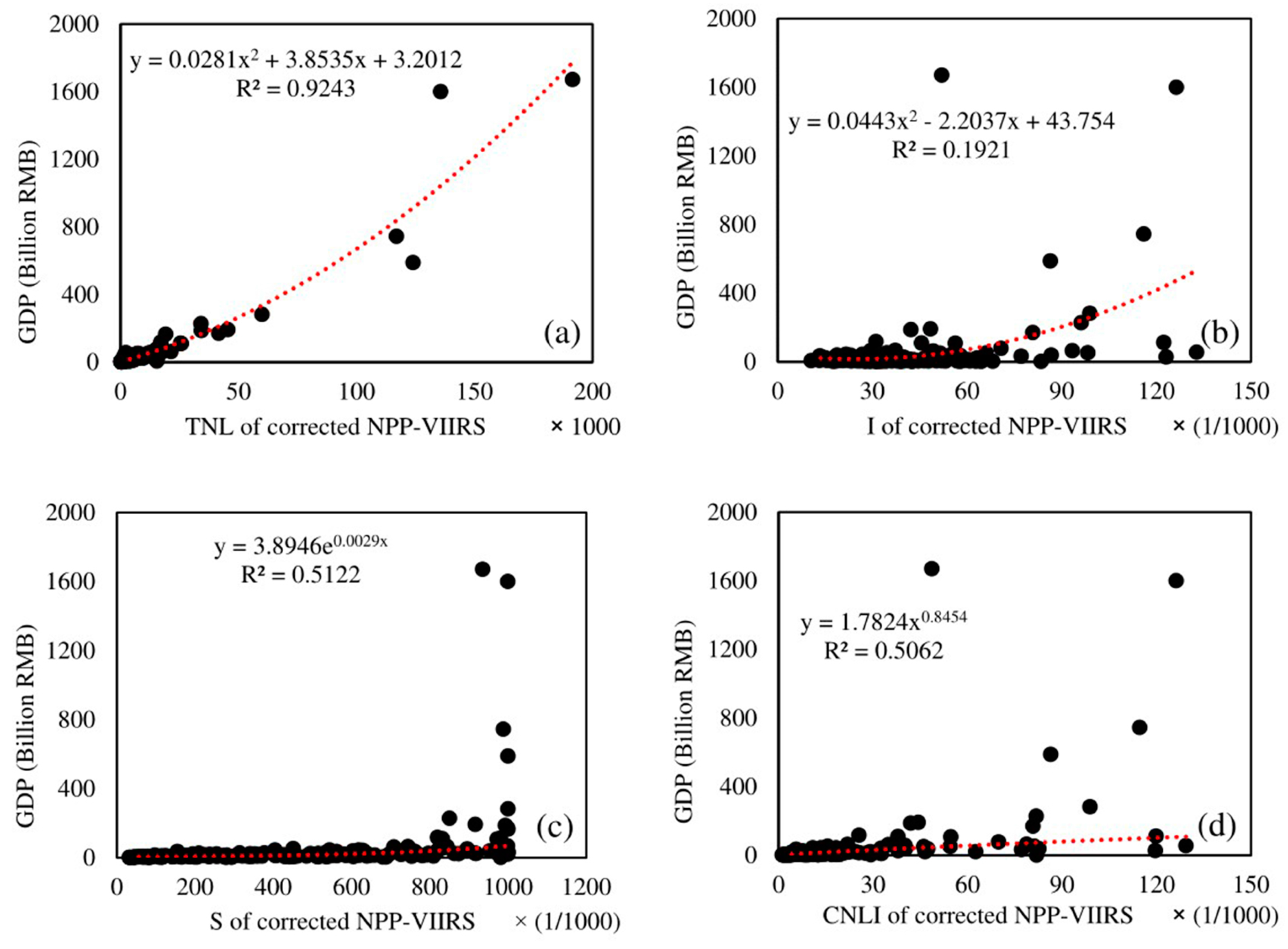
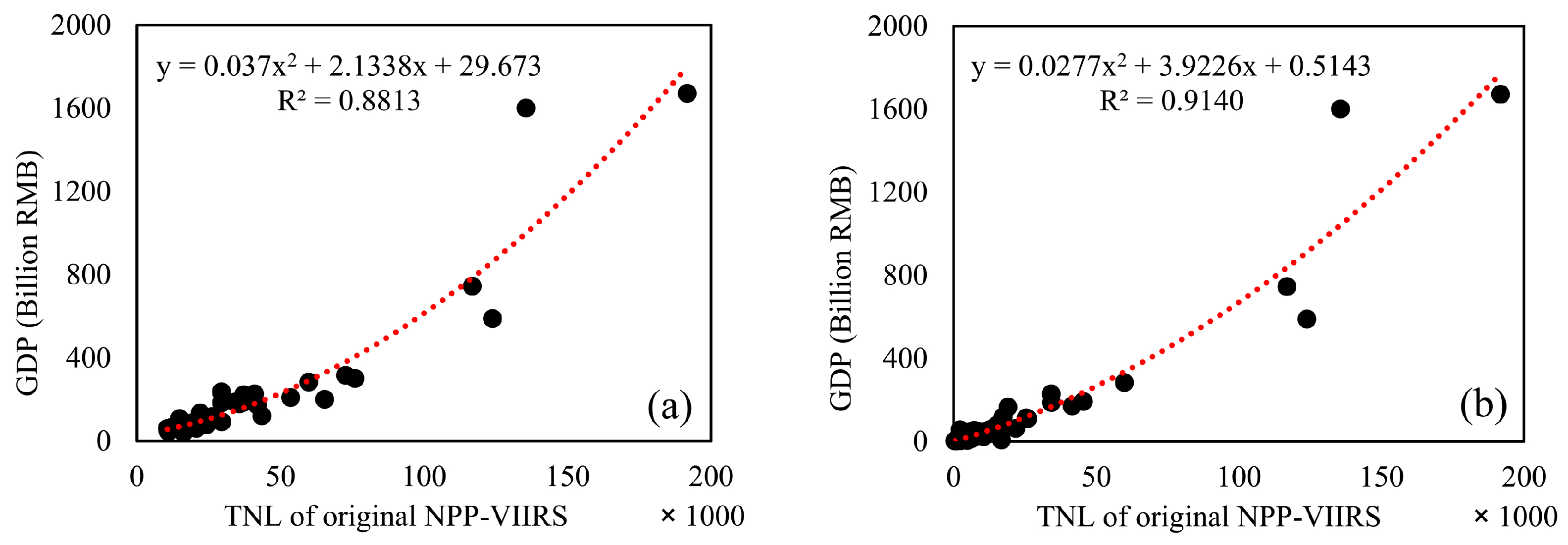
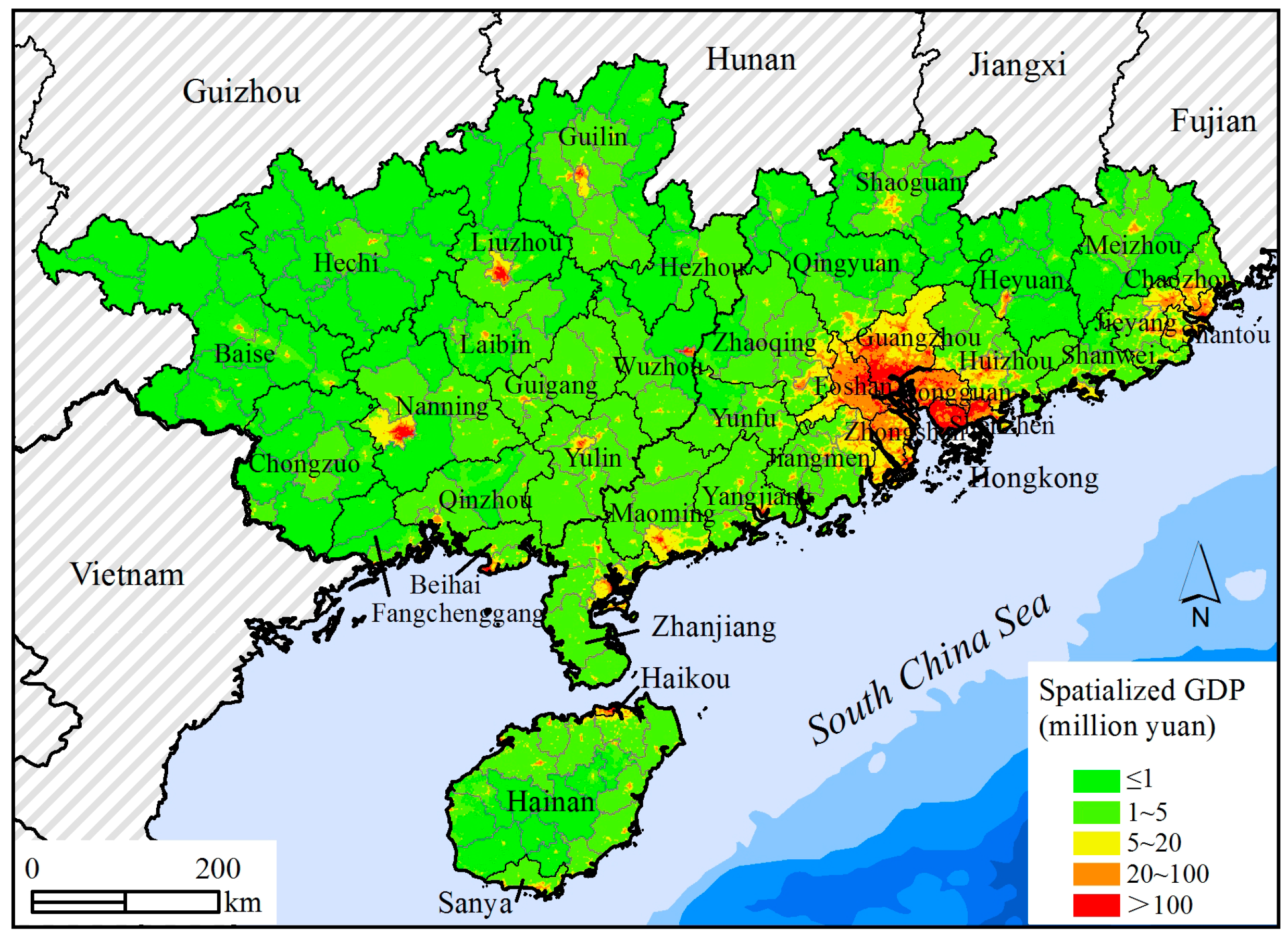
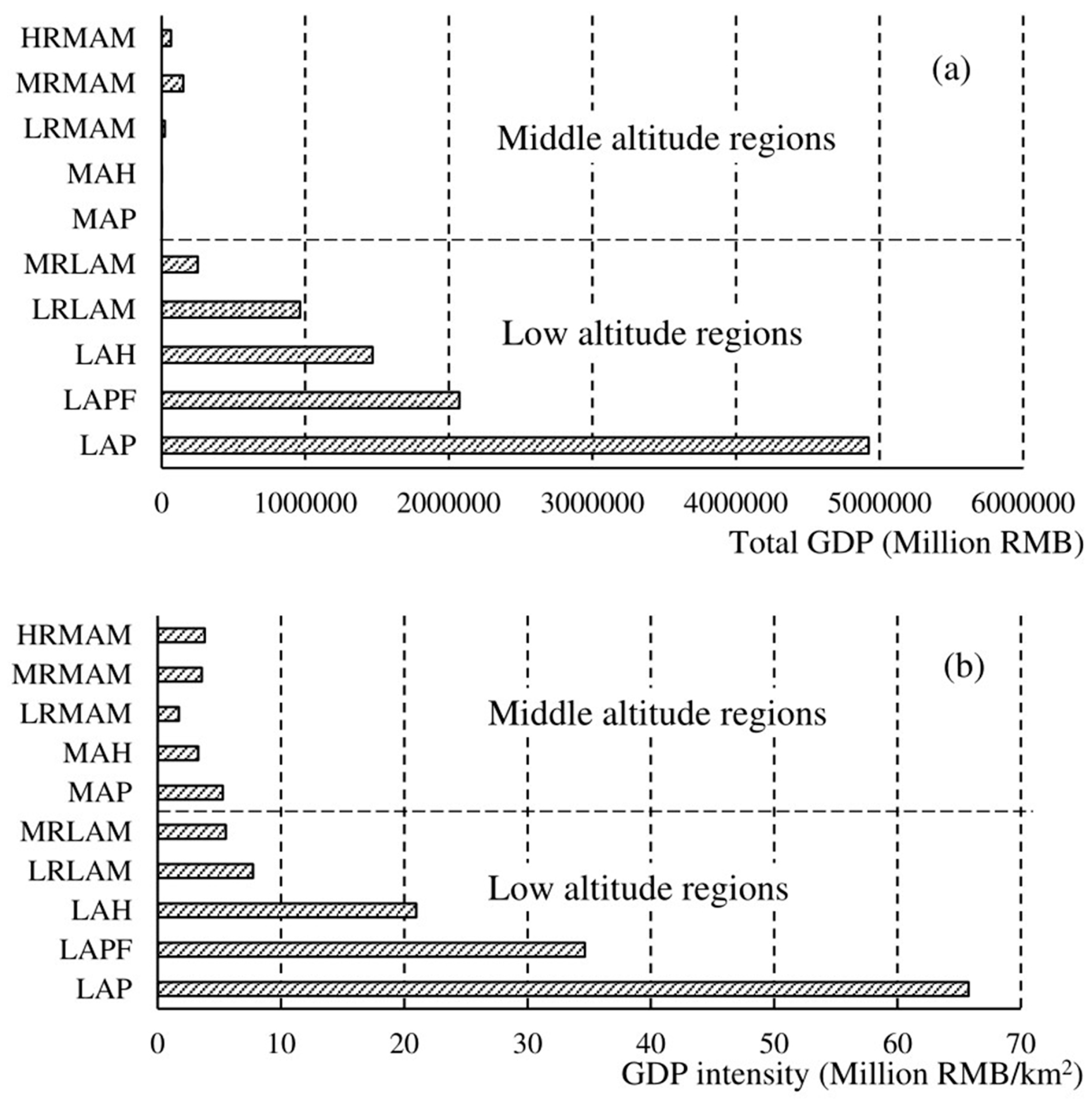
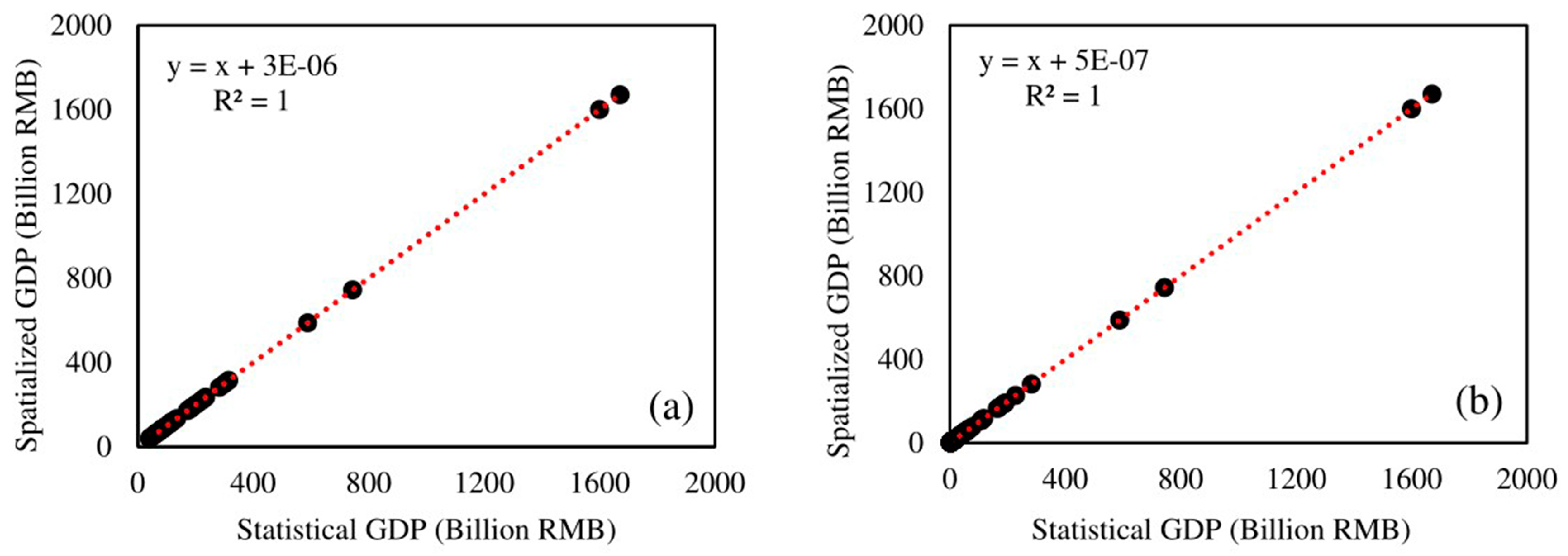
| Basic Geomorphological Types | Type Abbreviation | Altitude | Relief |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low altitude plain | LAP | <1000 m | <30 m |
| Middle altitude plain | MAP | 1000 m–3500 m | <30 m |
| Low altitude platform | LAPF | <1000 m | >30 m |
| Low altitude hill | LAH | <1000 m | <200 m |
| Middle altitude hill | MAH | 1000 m–3500 m | <200 m |
| Low-relief low altitude mountain | LRLAM | <1000 m | 200 m–500 m |
| Low-relief middle altitude mountain | LRMAM | <1000 m | 200 m–500 m |
| Middle-relief low altitude mountain | MRLAM | 1000 m–3500 m | 500 m–1000 m |
| Middle-relief middle altitude mountain | MRMAM | 1000 m–3500 m | 500 m–1000 m |
| High-relief middle altitude mountain | HRMAM | 1000 m–3500 m | 1000 m–2500 m |
| Region and Data | Percent of Relative Error of the Simulated GDP (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High Accuracy | Moderate Accuracy | Inaccuracy | ||
| Prefectural level | Corrected NPP-VIIRS data | 63.16 | 28.95 | 7.89 |
| Original NPP-VIIRS data | 57.89 | 34.22 | 7.89 | |
| County level | Corrected NPP-VIIRS data | 49.47 | 25.79 | 24.74 |
| Original NPP-VIIRS data | 46.31 | 28.95 | 24.74 | |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, M.; Cheng, W.; Zhou, C.; Li, M.; Wang, N.; Liu, Q. GDP Spatialization and Economic Differences in South China Based on NPP-VIIRS Nighttime Light Imagery. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 673. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9070673
Zhao M, Cheng W, Zhou C, Li M, Wang N, Liu Q. GDP Spatialization and Economic Differences in South China Based on NPP-VIIRS Nighttime Light Imagery. Remote Sensing. 2017; 9(7):673. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9070673
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Min, Weiming Cheng, Chenghu Zhou, Manchun Li, Nan Wang, and Qiangyi Liu. 2017. "GDP Spatialization and Economic Differences in South China Based on NPP-VIIRS Nighttime Light Imagery" Remote Sensing 9, no. 7: 673. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9070673
APA StyleZhao, M., Cheng, W., Zhou, C., Li, M., Wang, N., & Liu, Q. (2017). GDP Spatialization and Economic Differences in South China Based on NPP-VIIRS Nighttime Light Imagery. Remote Sensing, 9(7), 673. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9070673







