Coupling Uncertainties with Accuracy Assessment in Object-Based Slum Detections, Case Study: Jakarta, Indonesia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Case Study
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results
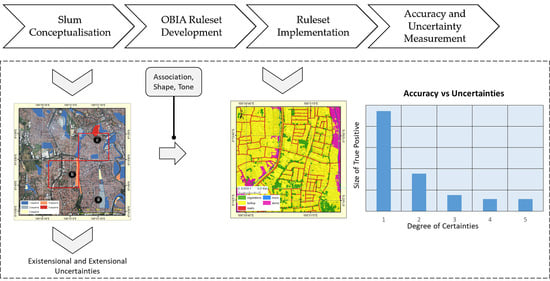
4.1. Slums Conceptualisation
4.2. OBIA Ruleset Development
4.3. Ruleset Implementation
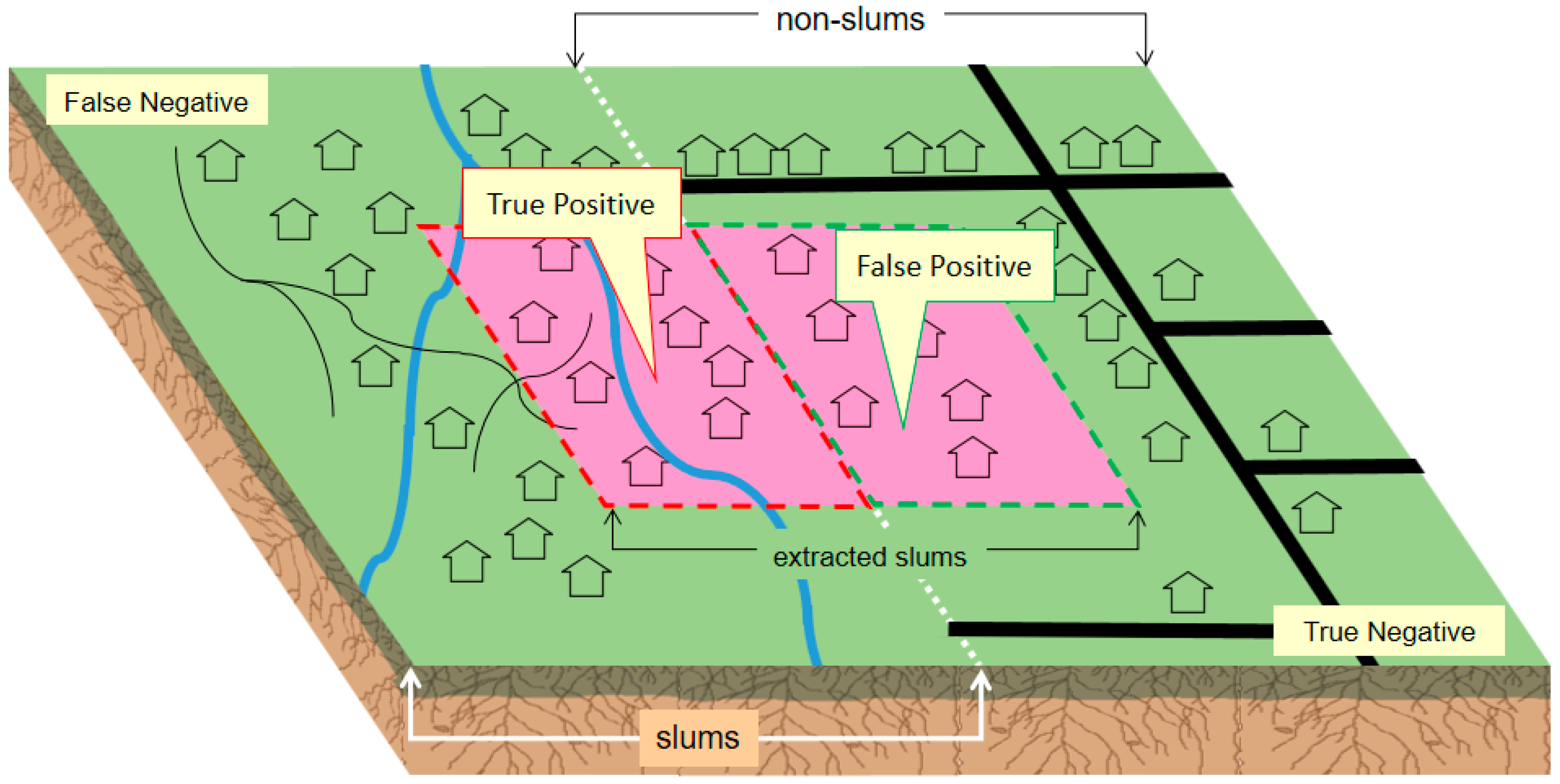
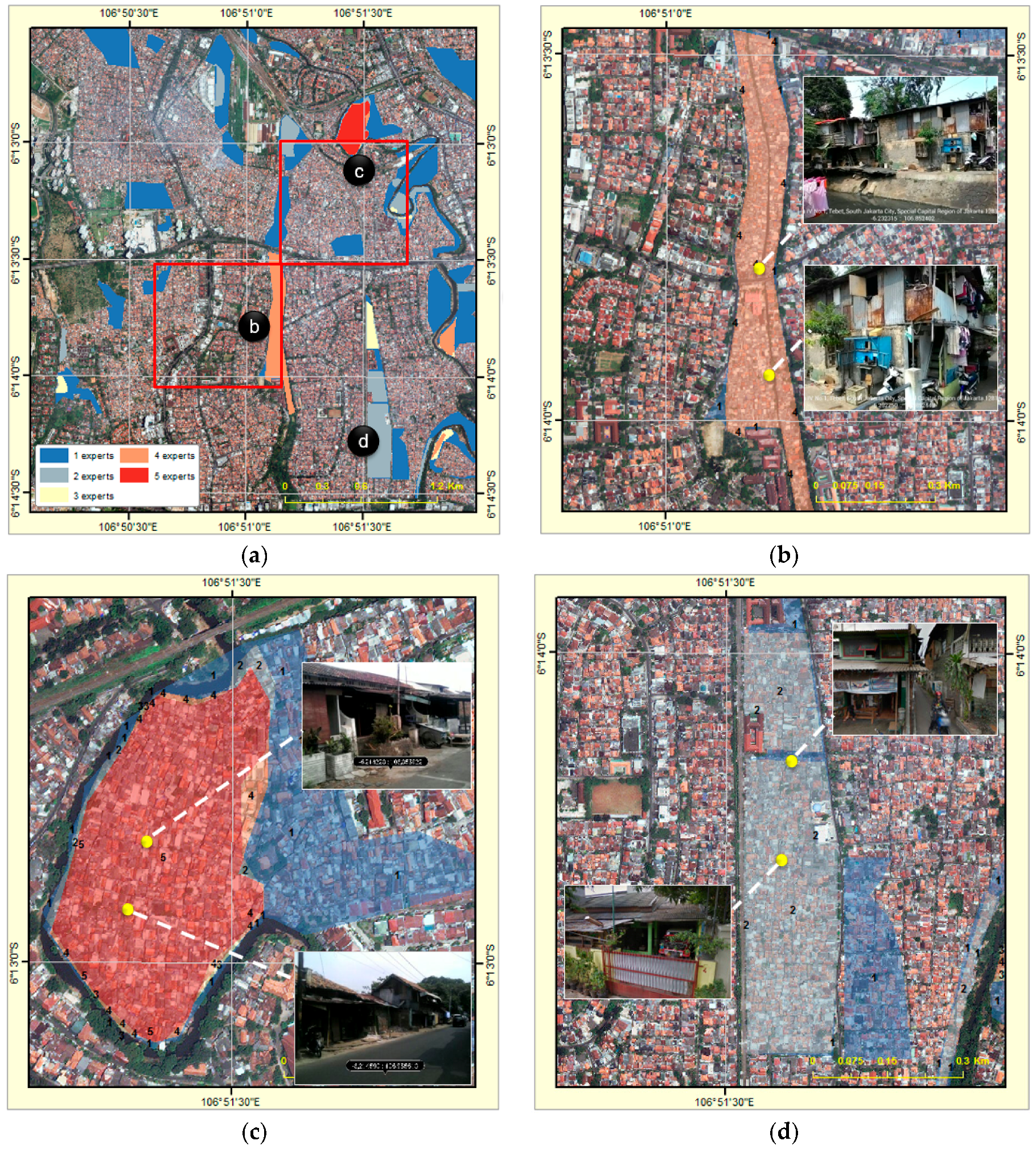
4.4. Accuracy and Uncertainty Measurements
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Open Working Group SDG. Sustainable Development Goals Open Working Group Proposal for Sustainable Development Goals; Division for Sustainable Development, United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations. The Millennium Development Goals Report; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- UN Habitat. Slums Almanac 2015–16. Tracking Improvement in the Lives of Slum Dwellers; UN Habitat: Nairobi, Kenya, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Shoko, M.; Smit, J. Use of Agent Based Modelling in the Dynamics of Slum Growth. S. Afr. J. Geomat. 2013, 2, 54–67. [Google Scholar]
- Kohli, D.; Kerle, N.; Sliuzas, R. Local ontologies for object-based slum identification and classification. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Geographic Object-Based Image Analysis Conference (GEOBIA), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 7–9 May 2012; pp. 201–205. [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann, P.; Strobl, J.; Blaschke, T.; Kux, H. Detecting informal settlements from Quickbird data in Rio de Janeiro using an object based approach. In Object-Based Image Analysis; Lecture Notes in Geoinformation and Cartography; Blaschke, T., Lang, S., Hay, G.J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 531–553. [Google Scholar]
- Kohli, D.; Warwadekar, P.; Kerle, N.; Sliuzas, R.; Stein, A. Transferability of object-oriented image analysis methods for slum identification. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 4209–4228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuffer, M.; Pfeffer, K.; Sliuzas, R.; Baud, I.; van Maarseveen, M. Capturing the Diversity of Deprived Areas with Image-Based Features: The Case of Mumbai. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, A.; Kerle, N.; Stein, A. Urban social vulnerability assessment with physical proxies and spatial metrics derived from air- and spaceborne imagery and GIS data. Nat. Hazards 2009, 48, 275–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohli, D.; Sliuzas, R.; Kerle, N.; Stein, A. An ontology of slums for image-based classification. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2012, 36, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, P. Defining Robustness Measures for OBIA Framework: A Case Study for Detecting Informal Settlements. In Global Urban Monitoring and Assessment through Earth Observation; Weng, Q., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014; pp. 303–324. [Google Scholar]
- Kuffer, M.; Barros, J.; Sliuzas, R. The development of a morphological unplanned settlement index using very-high-resolution (VHR) imagery. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2014, 48, 138–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, A. The return of the slum: Does language matter? Int. J. Urban Reg. Res. 2007, 31, 697–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forestier, G.; Puissant, A.; Wemmert, C.; Gançarski, P. Knowledge-based region labeling for remote sensing image interpretation. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2012, 36, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrés, S.; Arvor, D.; Mougenot, I.; Libourel, T.; Durieux, L. Ontology-based classification of remote sensing images using spectral rules. Comput. Geosci. 2017, 102, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, N.S.; Seijmonsbergen, A.C.; Bouten, W. Rule Set Transferability for Object-Based Feature Extraction: An Example for Cirque Mapping. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2015, 81, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiede, D.; Lang, S.; Hölbling, D.; Füreder, P. Transferability of OBIA rulesets for IDP camp analysis in darfur. ISPRS 2010, XXXVIII-4/C7, 1682–1777. [Google Scholar]
- Drǎguţ, L.; Blaschke, T. Automated classification of landform elements using object-based image analysis. Geomorphology 2006, 81, 330–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, P.; Blaschke, T.; Strobl, J. Quantifying the robustness of fuzzy rule sets in object-based image analysis. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 7359–7381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, P. Detecting Informal Settlements From Ikonos Image Data Using Methods of Object Oriented Image Analysis—An Example From Cape Town (South Africa). In Proceedings of the Remote Sensing of Urban Areas/Fernerkundung in Urbanen Räumen, Regensburg, Germany, 22–23 June 2001; pp. 107–118. [Google Scholar]
- Albrecht, F. Assessing the spatial accuracy of object-based image classifications. In Proceedings of the Geospatial Crossroad (GI_Forum ’08), Salzburg, Austria, 1–4 July 2008; pp. 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Goodchild, M.F. Uncertainty in Geographical Information; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 2002; p. 266. [Google Scholar]
- Schiewe, J.; Gähler, M. Modelling uncertainty in high resolution remotely sensed scenes using a fuzzy logic approach. In Object-Based Image Analysis; Lecture Notes in Geoinformation and Cartography; Blaschke, T., Lang, S., Hay, G.J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008; pp. 755–768. [Google Scholar]
- Albrecht, F. Uncertainty in Image Interpretation as Reference for Accuracy Assessment in Object-based Image Analysis. In Proceedings of the Accuracy 2010 Symposium, Leicester, UK, 20–23 July 2010; pp. 13–16. [Google Scholar]
- Kohli, D.; Stein, A.; Sliuzas, R. Uncertainty analysis for image interpretations of urban slums. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2016, 60, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demographia World Urban Areas; Belleville. Available online: http://www.demographia.com/db-worldua.pdf (accessed on 13 November 2017).
- Centre on Housing Rights and Evictions. Women, Slums and Urbanization: Examining the Causes and Consequences; Centre on Housing Rights and Evictions (COHRE): Geneva, Switzerland, 2008; pp. 1–134. [Google Scholar]
- New Cities Foundation. Jakarta to host 2015 New Cities Summit: “ This is Indonesia’ s Moment”. In New Cities Foundation; New Cities Foundation: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2015; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- UN Habitat. Indonesia Prepares National Report for Habitat III. Available online: http://unhabitat.org/indonesia-prepares-national-report-for-habitat-iii/ (accessed on 24 August 2017).
- Ministry of Public Works and Public Housing. Draft of Technical Documents on Monitoring and Evaluation of Spatial Planning; Ministry of Public Works and Public Housing: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Pratomo, J. Transferability of the Generic and Local Ontology of Slum in Multi-Temporal Imagery, Case Study: Jakarta. Master’s Thesis, University of Twente, Enschede, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Redefining the Spatial Form of Urban Village in Mega Kuningan Jakarta as A New Urban Integrator: A Study of Socio-Economic Aspect in the Forming of Urban Spatial Configuration. Master’s Thesis, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China, 2009.
- Rukmana, D. Planning the Megacity: Jakarta in the Twentieth Century. J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 2008, 74, 263–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sihombing, A. Drawing Kampung through Cognitive Maps Case Study: Jakarta. APCBEE Procedia 2014, 9, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sihombing, A. Living in the Kampungs: A Firsthand Account of Experiences in Jakarta’s Kampungs. Forum J. Postgrad. Stud. Archit. Plan. Landsc. 2007, 7, 15–22. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Bunnell, T.; Yeo, V. Symmetric Development of Informal Settlements and Gated Communities: Capacity of the State—The Case of Jakarta, Indonesia; Asia Research Institute, National University of Singapore: Singapore, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Indonesian Central Board of Statistics. Indikator Rumah Tangga Kumuh [Slum Household Indicator]. Available online: http://sirusa.bps.go.id/index.php?r=indikator/view&id=453 (accessed on 4 October 2016).
- Ministry of Public Works and Public Housing. Panduan Penyusunan SPPIP dan RPKPP [Guideline for Urban Settlement and Infrastructure Development]; Ministry of Public Works and Public Housing: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- UN Habitat. The Challange of Slum, Global Report on Human Settlements 2003; Earthscan Publication Ltd.: Nairobi, Kenya, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Arvor, D.; Durieux, L.; Andrés, S.; Laporte, M.A. Advances in Geographic Object-Based Image Analysis with ontologies: A review of main contributions and limitations from a remote sensing perspective. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2013, 82, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Guo, Q.; Kelly, M. A framework of region-based spatial relations for non-overlapping features and its application in object based image analysis. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2008, 63, 461–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaschke, T. Object based image analysis for remote sensing. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2010, 65, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drǎguţ, L.; Tiede, D.; Levick, S.R. ESP: A tool to estimate scale parameter for multiresolution image segmentation of remotely sensed data. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 859–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baatz, M.; Schäpe, A. Multiresolution Segmentation: An optimization approach for high quality multi-scale image segmentation. In Angewandte Geographische Informationsverarbeitung XII; Strobl, J., Blaschke, T., Griesebner, G., Eds.; Wichmann: Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; pp. 12–23. [Google Scholar]
- Whiteside, T.G.; Boggs, G.S.; Maier, S.W. Comparing object-based and pixel-based classifications for mapping savannas. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2011, 13, 884–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, D.M.W. Evaluation: From Precision, Recall and F-Factor to ROC, Informedness, Markedness & Correlation. J. Mach. Learn. Technol. 2011, 2, 37–63. [Google Scholar]
- Molenaar, M. Three Conceptual Uncertainty Levels for Spatial Objects. In Proceedings of the International Archieves of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 16–22 July 2000; ISPRS: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000; pp. 670–677. [Google Scholar]
- Trimble Germany GmbH. User Guide—eCognition® Developer, 9.1.1 ed.; Trimble: Munich, Germany, 2015; p. 256. [Google Scholar]
- Van Coillie, F.; Gardin, S.; Anseel, F.; Ducyk, W.; Verbeke, L.P.C.; de Wulf, R.R. Variability of Operator Performance in Remote-sensing Image Interpretation: The Importance of Human and External Factors. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 754–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.; Bertolini, L.; te Brömmelstroet, M.; Milakis, D.; Papa, E. Accessibility instruments in planning practice: Bridging the implementation gap. Transp. Policy 2017, 53, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Characteristics | Local Expert | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | ||
| 1 | Located on/close the river bank/railroad | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| 2 | Small building size | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| 3 | Irregular building orientation | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| 4 | Poor roof material | √ | √ | √ | ||
| 5 | Built on illegal land | √ | ||||
| Real World Domain | Image Domain | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Located on the riverbank/near railroad | Association: Distance to River/Railroad |
| 2 | Small building size | Size: Small |
| 3 | Irregular building orientation | Shape: compactness |
| 4 | Poor Roof material | Tone: Asbestos, corrugated iron |
| 5 | Built in the illegal land | Ancillary data: Land Use Plan |
| Rule | Threshold Value |
|---|---|
| Association: Distance to River/Railroad | 1. Border to river > 0 pixels 2. Border to railroad 0 > pixels |
| Shape: compactness | 1. Compactness ≤ 5 2. Grey-Level Co-occurrence Matrix (GLCM) Dissimilarity ≥ 0.0005 |
| Tone: tile—corrugated iron, asbestos | Mean red/green 1 ≤ tone ≤ 1.075 |
| Ancillary data: Land Use Plan (second scenario) | Mean Layer Tenure > 0.25 |
| Dataset | True Positive | |||||
| 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | ||
| 2015_TA1_EXP | - | 41,321 | - | - | 41,802 |  |
| 2015_TA1_ANC | - | 36,209 | - | - | 36,690 |  |
| 2015_TA2_EXP | 11,397 | 11,938 | 15,155 | 35,486 | 94,480 |  |
| 2015_TA2_ANC | 3905 | 4445 | 7662 | 19,328 | 57,517 |  |
| Dataset | False Positive | |||||
| 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | ||
| 2015_TA1_EXP | - | 31,763 | - | - | 31,281 |  |
| 2015_TA1_ANC | - | 2502 | - | - | 2021 |  |
| 2015_TA2_EXP | 228,686 | 228,146 | 224,929 | 204,598 | 145,604 |  |
| 2015_TA2_ANC | 156,702 | 156,162 | 152,945 | 141,279 | 103,090 |  |
| Dataset | False Negative | |||||
| 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | ||
| 2015_TA1_EXP | - | 56,656 | - | - | 73,609 |  |
| 2015_TA1_ANC | - | 61,768 | - | - | 78,721 |  |
| 2015_TA2_EXP | 7217 | 9701 | 10,280 | 28,408 | 96,939 |  |
| 2015_TA2_ANC | 14,710 | 14,156 | 14,727 | 42,044 | 133,902 |  |
 Highest Value Highest Value  Other Values Other Values | ||||||
| Dataset | Precision | |||||
| 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | ||
| 2015_TA1_EXP | - | 56.54% | - | - | 57.20% |  |
| 2015_TA1_ANC | - | 93.54% | - | - | 94.78% |  |
| 2015_TA2_EXP | 4.75% | 4.97% | 6.31% | 14.78% | 39.35% |  |
| 2015_TA2_ANC | 2.43% | 2.77% | 4.77% | 12.03% | 35.81% |  |
| Dataset | Recall | |||||
| 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | ||
| 2015_TA1_EXP | - | 42.17% | - | - | 36.22% |  |
| 2015_TA1_ANC | - | 36.96% | - | - | 31.79% |  |
| 2015_TA2_EXP | 61.23% | 55.17% | 59.58% | 55.54% | 49.36% |  |
| 2015_TA2_ANC | 20.98% | 23.90% | 34.22% | 31.49% | 30.05% |  |
| Dataset | Accuracy | |||||
| 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | ||
| 2015_TA1_EXP | - | 91.16% | - | - | 89.51% |  |
| 2015_TA1_ANC | - | 93.57% | - | - | 91.93% |  |
| 2015_TA2_EXP | 76.41% | 76.22% | 76.48% | 76.70% | 75.75% |  |
| 2015_TA2_ANC | 82.86% | 82.97% | 83.23% | 81.67% | 76.30% |  |
 Highest Value Highest Value  Other Values Other Values | ||||||
| Dataset | Precision Gain | Recall Gain | Accuracy Gain |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2015_TA1_EXP | 0.66% | −5.95% | −1.65% |
| 2015_TA1_ANC | 1.24% | −5.17% | −1.65% |
| 2015_TA2_EXP | 34.61% | −11.87% | −0.66% |
| 2015_TA2_ANC | 33.38% | 9.07% | −6.56% |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pratomo, J.; Kuffer, M.; Martinez, J.; Kohli, D. Coupling Uncertainties with Accuracy Assessment in Object-Based Slum Detections, Case Study: Jakarta, Indonesia. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9111164
Pratomo J, Kuffer M, Martinez J, Kohli D. Coupling Uncertainties with Accuracy Assessment in Object-Based Slum Detections, Case Study: Jakarta, Indonesia. Remote Sensing. 2017; 9(11):1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9111164
Chicago/Turabian StylePratomo, Jati, Monika Kuffer, Javier Martinez, and Divyani Kohli. 2017. "Coupling Uncertainties with Accuracy Assessment in Object-Based Slum Detections, Case Study: Jakarta, Indonesia" Remote Sensing 9, no. 11: 1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9111164
APA StylePratomo, J., Kuffer, M., Martinez, J., & Kohli, D. (2017). Coupling Uncertainties with Accuracy Assessment in Object-Based Slum Detections, Case Study: Jakarta, Indonesia. Remote Sensing, 9(11), 1164. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9111164