1. Introduction
The incorporation of Brazil into a long-term remote sensing program has begun with the establishment of the China Brazil Earth Resources Satellite (CBERS) program. The CBERS program has been developed under a cooperation agreement between Brazil and China [
1]. The first satellite (CBERS-1) developed was launched on 14 October 1999 by the Chinese Long March 4B launcher from the Taiyuan Satellite Launch Center in China [
1]. CBERS-1 remained functional until August 2003. The second satellite (CBERS-2) was launched successfully from the same launch center on 21 October 2003 and carried an identical instrument set as CBERS-1.
In 2002, the governments of China and Brazil decided to expand the initial agreement to include the construction of two new additional satellites: CBERS-3 and CBERS-4 as the second generation of the Chinese-Brazilian cooperation effort [
2]. In 2004, a new agreement was signed to build the CBERS-2B, which was launched before CBERS-3, in 2007 and operated until June 2010. The agreement for CBERS-2B was made based on concern of a possible interruption in data acquisition. Unfortunately, despite this agreement and successful operation of CBERS-2B, there was a significant interruption of data acquisition while awaiting the launch of the CBERS-3 and 4 series of sensors.
CBERS-3 was launched in 9 December 2013, also by a Long-March 4B rocket from the Taiyuan base in China; however, the satellite was lost due to a failure on the launcher’s third stage. The launch of CBERS-4 was originally scheduled for December 2015. However, due to the loss of the CBERS-3 satellite, China and Brazil agreed to accelerate the launch schedule. On 7 December 2014, the CBERS-4 was successfully launched from the Taiyuan Satellite Launch Center.
CBERS-4 carries four cameras in the payload module [
3]: (a) Panchromatic and Multispectral Camera (PAN); (b) Multispectral Camera (MUX); (c) Infrared System (IRS); (d) Wide-Field Imager (WFI). Brazil is responsible for both MUX and WFI cameras, while China is responsible for the IRS and PAN. This responsibility division extends to other systems and also the cost of the entire mission, which is 50% for each country [
3].
The success of any remote sensing program depends on the knowledge of the radiometric properties of the sensor from which the data will be available [
4]. A great example of that is the Landsat series of satellites, whose radiometric characteristics have been evaluated and updated continuously [
5,
6,
7,
8]. The radiometric calibration, from pre-launch through end-of-mission, permits users to apply the data as a true quantitative input to Earth study applications.
In conjunction with absolute radiometric calibration, it is essential to have a firm quantitative understanding of the uncertainty of this calibration. This work describes a complete procedure, along with the associated uncertainties, used to calculate the in-flight absolute calibration coefficients for MUX and WFI level 1 images. For this purpose two absolute radiometric calibration techniques were used: (i) reflectance-based approach and (ii) cross-calibration method.
The reflectance-based approach has been widely used with success for orbital sensors [
9,
10,
11]. This method uses the reflectance-based ground truth measurement of a test site (reference surface) along with atmospheric measurement during an overpass of the reference surface by the sensor. The data derived from ground measurement are utilized as input to a radiative transfer code to predict the radiance/reflectance values at sensor (top of atmosphere radiance/reflectance). The predicted at sensor radiance is then compared with the DN count from the sensor to obtain the calibration coefficient for each sensor spectral band. Here, an area at Algodones Dunes region located in the southwestern portion of the United States of America, California, was used as a reference surface.
Whereas for the cross-calibration method the calibration is transferred from a radiometrically well-characterized reference sensor, whose calibration accuracy is known, to a target sensor using near-simultaneous ground observations [
12]. The MUX and WFI on-board CBERS-4 was cross calibrated with the newest Landsat series sensor OLI (Operational Land Imager). This calibrated was performed based on imaging of the Libya-4 Pseudo Invariant Calibration Site (PICS) [
13,
14,
15,
16]. PICS have been used primarily for sensor radiometric stability monitoring, for the purpose of detecting changes in absolute radiometric accuracy [
14].
Additionally, the calibration coefficients have been validated using the cross-calibration technique. Evaluation of the radiometric consistency between both MUX and WFI sensors on-board CBERS-4 and the well calibrated over time Landsat-7 Enhanced Thematic Mapper Plus (ETM+) was performed. The comparison was based on cross-calibration between the three orbital sensors using image pairs from Algodones Dunes.
2. CBERS-4: MUX and WFI
The CBERS-4 satellite has a sun-synchronous orbit with an altitude of 778 km. The local solar time at the equator crossing is always 10:30 a.m. The CBERS-4 incorporates an on-board radiometric calibration system. However, there remains uncertainty in terms of the engineering of the internal calibration system control. Due to this fact, the vicarious calibration performed in this work is even more important.
MUX/CBERS-4 is a multispectral camera with four spectral bands covering the wavelength range from blue to near infrared (450 nm to 890 nm) with a ground resolution of 20 m and a ground swath width of 120 km. The main function of the MUX is to maintain continuity with the previous CBERS sensors [
3]. It is the sensor which ensures global coverage at a standard spatial resolution every 26 days.
WFI/CBERS-4 had a significant improvement in characteristics compared to previous WFI sensor. WFI is also a multispectral camera, featuring four spectral bands covering the range of wavelengths from blue to near infrared. Its ground resolution is 64 m at nadir, without losing the revisit capacity of five days, due to the large Field of View of ±28.63°.
Table 1 shows a summary of the MUX and WFI characteristics.
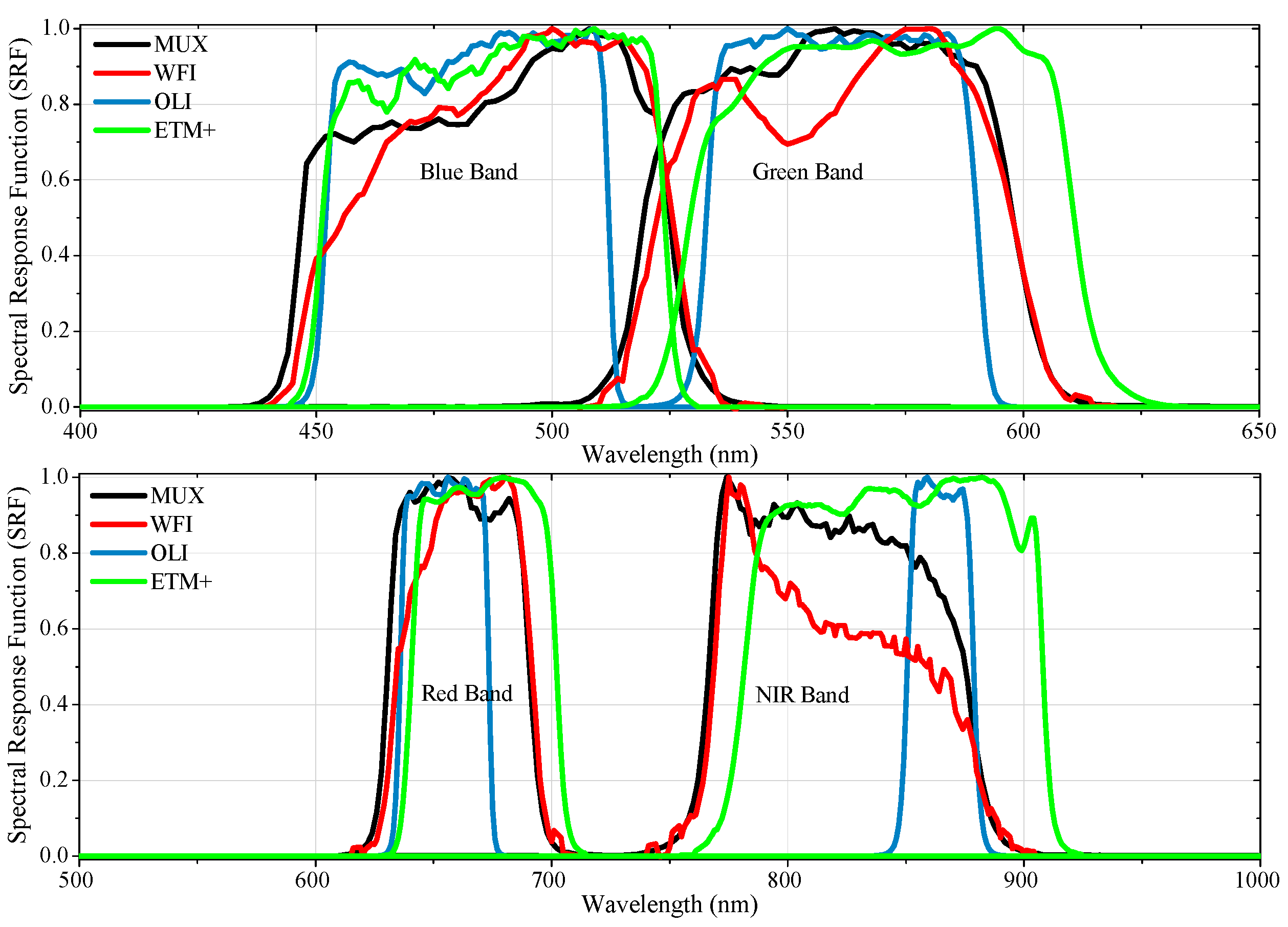
Figure 1 shows the MUX and WFI Spectral Response Function (SRF) profiles. For comparison purposes,
Figure 1 also presents the Landsat-8/OLI and Landsat-7/ETM + SRF.
The relationship between Digital Number (DN) acquired from the sensor and TOA radiance in each spectral band of the MUX and WFI was established by the equation below:
where:
Li is the TOA radiance at band
i in units of (W/(m
2·sr·μm));
DNi is the digital number from the image at band
i;
Gi is the coefficient gain for band
i in units of (W/(m
2·sr·μm))/DN; and
offseti is the coefficient bias for band
i in units of (W/(m
2·sr·μm)). This work will describes the procedure to calculate
Gi and
offseti for both sensors MUX and WFI on-board CBERS-4.
The MUX and WFI image radiance data can then be converted to planetary TOA reflectance data using the conversion equation:
where:
ρλ is the planetary TOA reflectance (unitless);
π is the mathematical constant (unitless);
Lλ is the spectral radiance at the sensor’s aperture (W/(m
2·sr·μm));
d is the Earth-Sun distance (astronomical units);
θz is the solar zenith angle (degrees or radians); and
ESUNλ is mean exoatmospheric solar irradiance (W/(m
2·μm)).
The mean exoatmospheric solar irradiance,
ESUNλ, for MUX and WFI sensors was estimated using the CHKUR Extraterrestrial Solar Spectral Irradiance dataset from MODTRAN 5.2.1 software. It is important to note that an estimate of the
ESUNλ at each spectral band of MUX and WFI is incomplete unless accompanied with uncertainty. The accuracy of the solar spectrum was considered within 1%–2%, then, this uncertainty was propagated (using the Monte Carlo technique described in
Section 6) to the mean solar exoatmospheric irradiance of each sensor spectral band. The
ESUNλ values for MUX and WFI spectral bands are summarized in
Table 2.
6. Uncertainties
Confidence in a measured value requires a quantitative report of its quality, which in turn necessitates the evaluation of the uncertainty associated with the value. So, it is important to emphasize that ground radiometric measurements from the surface, the atmospheric measurements and the determination of calibration coefficients are incomplete unless accompanied by a statement of their uncertainties. The radiometric calibration uncertainty is key in determining the reliability of calibration results.
In this work, two approaches were applied. The first one was the classical method of propagation of uncertainties as described in the Guide to the Expression of Uncertainty in Measurement, known as the GUM [
38]. The GUM provides guidance on how to determine, combine and express uncertainties that are intended to be applicable to a wide range of measurements.
The propagation law of uncertainty was applied when the quantity was calculated indirectly. If
y = f (
x1,
x2, …,
xn) and
x1,
x2,…
xn are quantities with uncertainties σ
x1, σ
x2, …, σ
xn, then, the uncertainty of quantity
f is:
where: ∂
f/∂
xi are the partial derivatives, often referred to as sensitivity coefficients; σ
xi is the standard uncertainty associated with the input estimate
xi ; and σ
xi xj is the estimated covariance associated with
xi and
xj. If the variables
x1,
x2, …,
xn are uncorrelated the covariance is equal to zero.
The second approach was Monte Carlo Simulation [
39]. This method is based on random number generation for each primary quantity, according to their probability distribution function (PDF) and propagated through a mathematical model of measurement. The Monte Carlo simulation uses prior event information, from which subsequent information is obtained. This method uses the concept of probability distribution propagation of input quantities (prior information). This propagation consists of assuming a distribution for each input quantity (uniform distribution, normal or triangular, for example). Then, these distributions are propagated M times (where M is iteration number) by a mathematical model of measurement, and a new distribution is generated as a result. In the end, it is possible to determine the parameters which characterize the output distribution (results). It is a method widely used in metrology, but its application in absolute radiometric calibration work is relatively new [
40,
41].
The uncertainty of the reflectance-based method has traditionally been estimated using the classical method (ISO-GUM [
10,
42]; therefore, this work utilized this approach in almost all the stages of the measurement performed. However, there are some limitations related to the ISO-GUM uncertainty framework [
39]: (i) linearization of the model provides an inadequate representation; (ii) assumption of Gaussian distribution of the measurand; (ii) calculation of the effective degrees of freedom. Therefore, in some situations where the model is nonlinear or complex or the model does not allow an analytical solution and/or the probability distribution of the measurand is not Gaussian, it is necessary to use alternative methods.
As previously mentioned, the output from MODTRAN is the propagated hyperspectral TOA radiance at each nanometer. Therefore, before performing the comparison between the predicted at-sensor radiance and DN from the sensor, it is necessary to average the output data of MODTRAN with respect to the Spectral Response Function (SRF) of the sensor to find the band averaged at-sensor radiance values for each spectral band. Although the equation used to make this weighting is not complicated (see Equation (4)), the uncertainties calculation by the classical method of uncertainty propagation is complex because it is difficult to determine the complete set of partial derivatives required by this method and estimate the existing covariances. This was a step where a Monte Carlo Simulation approach was used. The Monte Carlo approach was also applied to evaluate the Spectral Band Adjustment Factor (SBAF) and its associated uncertainty.
As typically done in sensor calibration works, the uncertainties values were quoted as one-sigma (1σ) percentages (confidence level of 68.3%) [
42].
7. Results and Discussion
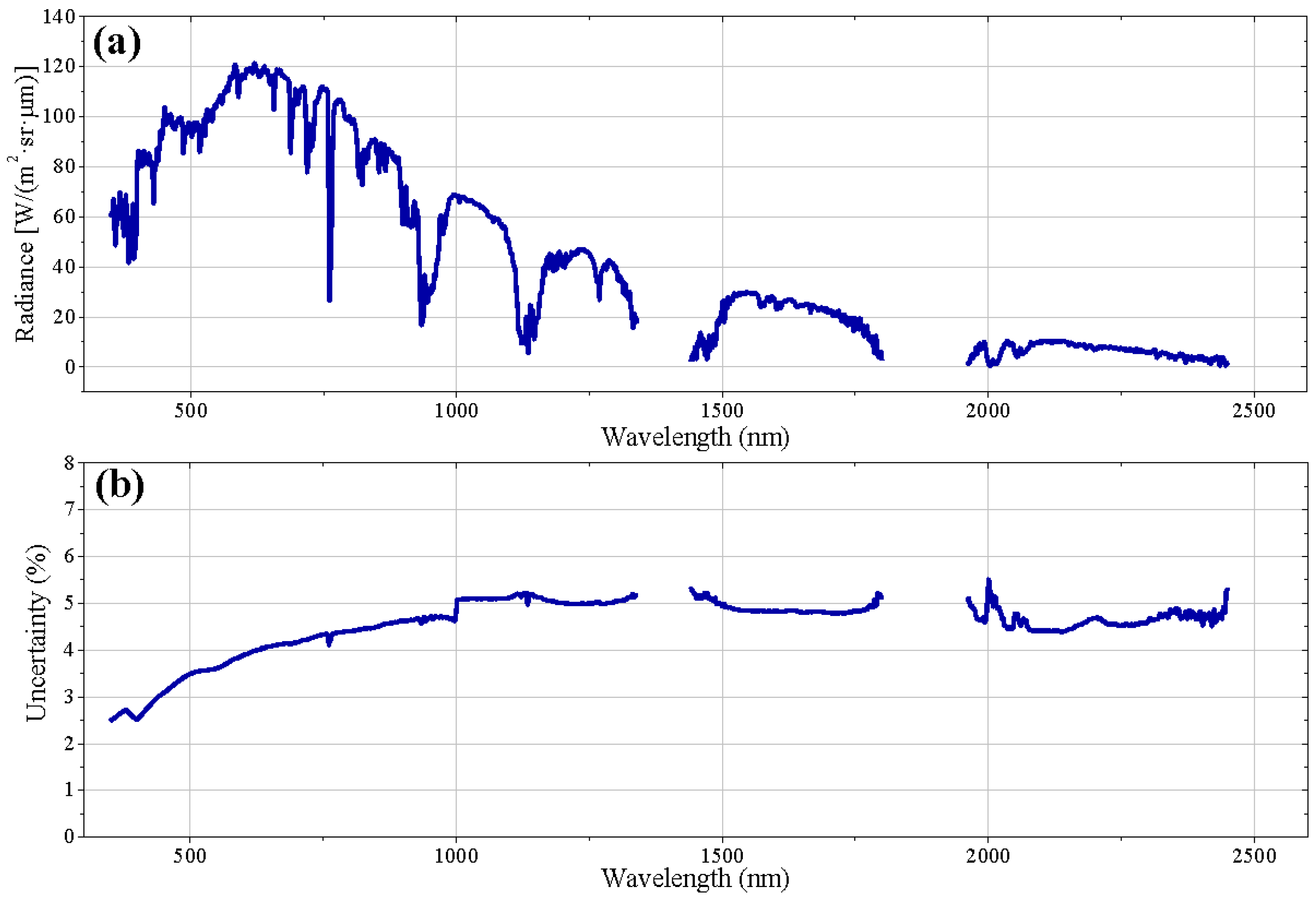
The first component to the reflectance-based approach is the surface reflectance at the time of sensor overpass, in this case of the CBERS-4 satellite.
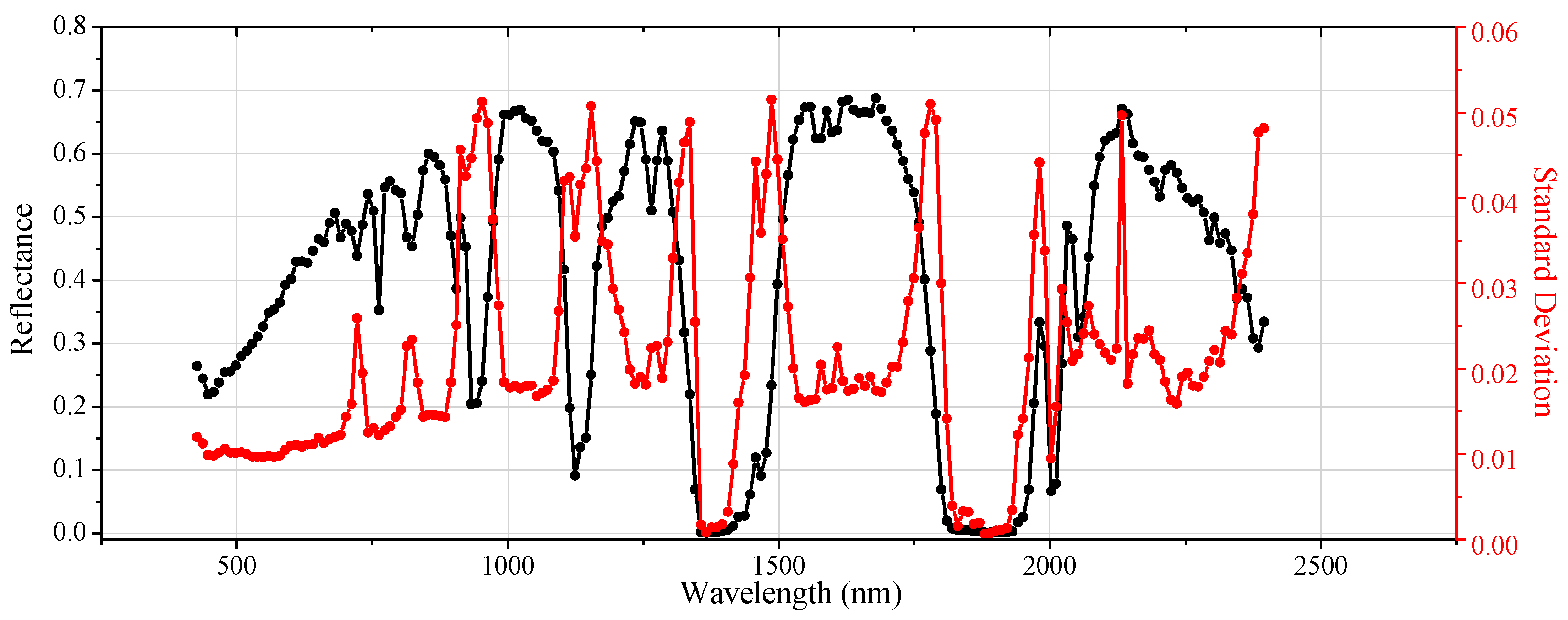
Figure 7a shows the spectral reflectance derived for the Algodones Dunes sand surface on 9 March 2015. In addition, the coefficient of variation (CV) defined as the ratio between the standard deviation and the average is shown as a percentage in
Figure 7b. The gaps around 1400 and 1800 nm are due to strong water vapor absorption near those wavelengths and the 2400–2500 nm spectral region shows larger variability primarily due to decreasing signal level.
According to [
43], reflectance values higher than 0.3 over the entire spectral range are preferred. The selected reference surface at Algodones Dunes presents reflectance higher than 0.3 in almost the entire spectral range. As seen in
Figure 7a, the average reference surface reflectance factor was between 0.08 and 0.30 from 350–600 nm and between 0.30 and 0.49 from 600–2500 nm. Scott
et al. (1996) [
43] suggest that a certain surface is sufficiently spatially uniform if the Coefficient of Variation (CV) is lower than 5%. The average relative CV of the spectral measurements ranged from 2.5% to 5.0%, indicating that the reference surface at Algodones Dunes presents a spatial uniformity better than 5%.
The weather on 9 and 10 March 2015 was clear with no clouds. The atmosphere was stable during the entire period of measurement, from 9 a.m. to 12:30 p.m. (local time), as well as the time around CBERS-4 overpass. The atmospheric conditions for both dates are summarized in
Table 5.
Aerosol optical depth (AOD) is a measure of radiation extinction due to the interaction of radiation with aerosol particles in the atmosphere. According to [
27], the variation in AOD with wavelength defines the attenuation of solar irradiance as a function of wavelength and provides the basis for retrieving the columnar size distribution of the atmospheric aerosol. An AOD lower than 0.1 indicates clear sky, whereas value of 1 corresponds to very hazy conditions [
44]. Here, the mean AOD at 550 nm was 0.066 ± 0.017 and 0.046 ± 0.014 during the measurements on 9 and 10 March 2015, respectively, indicating that the Algodones Dunes region presents low aerosol loading.
Columnar water vapor was derived from the solar extinction data using a modified Langley approach. The water content was (1.055 ± 0.014) g/cm2 on 9 March 2015 and (0.476 ± 0.005) g/cm2 on 10 March 2015.
The surface reflectance, geometric and atmospheric conditions were used as inputs to MODTRAN.
Figure 8 gives the at-sensor radiance (TOA radiance) predicted by MODTRAN.
Table 6 presents the band-averaged TOA radiance (using Equation (4)) for each of the four multispectral bands of MUX and WFI derived from the spectral curve in
Figure 1.
Table 6 also presents the average DN from the image for each band based on the 8 × 15 grid (120 pixels) for MUX and based on the 2 × 5 grid (10 pixels) for WFI.
Past work with the reflectance-based method as used here indicated that the method presented absolute uncertainties of ±5%, and estimated that improvements should result in an uncertainty of ±3% in the middle of the visible portion of the spectrum [
21]. In this work, as can been seen in
Table 6, the uncertainty in the TOA Radiance predicted by MODTRAN ranged from 3.1% to 4.4% in the four MUX and WFI spectral bands. There are several sources of uncertainty in this method: (i) surface characterization; (ii) atmospheric characterization; (iii) radiative transfer code; (iv) determination of the site-average DNs. Here, the main source of uncertainty was the reflectance surface (about 2.5%–5.0%), which supports the importance of properly choosing a reference surface for calibration.
To determine the two radiometric calibration coefficients,
Gi and
offseti, for MUX and WFI, two points were considered. With the reflectance-based method it was possible to obtain one point (see
Table 6) and through cross-calibration another point was generated. The cross-calibration results between CBERS-4 and Landsat-8 using images acquired from Libya-4 can be seen in
Table 7. In order to convert the values in Landsat-8/OLI image to TOA reflectance the methodology presented in [
45] was used. The radiance values of the MUX and WFI sensors,
Lλ,MUX and
Lλ,WFI, were estimated using Equation (8),
i.e., the radiance values were obtained from the OLI sensor radiance,
Lλ,OLI.
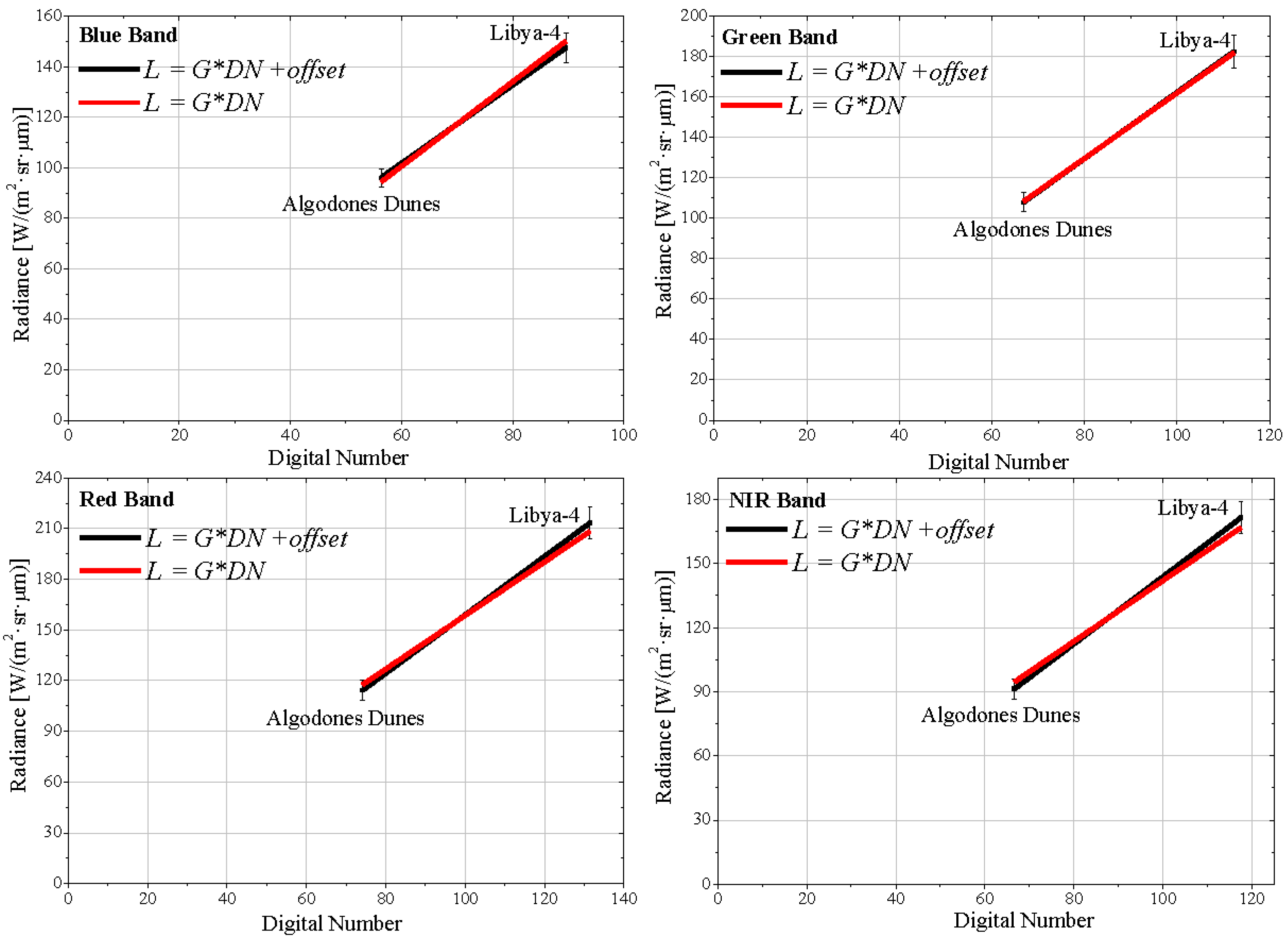
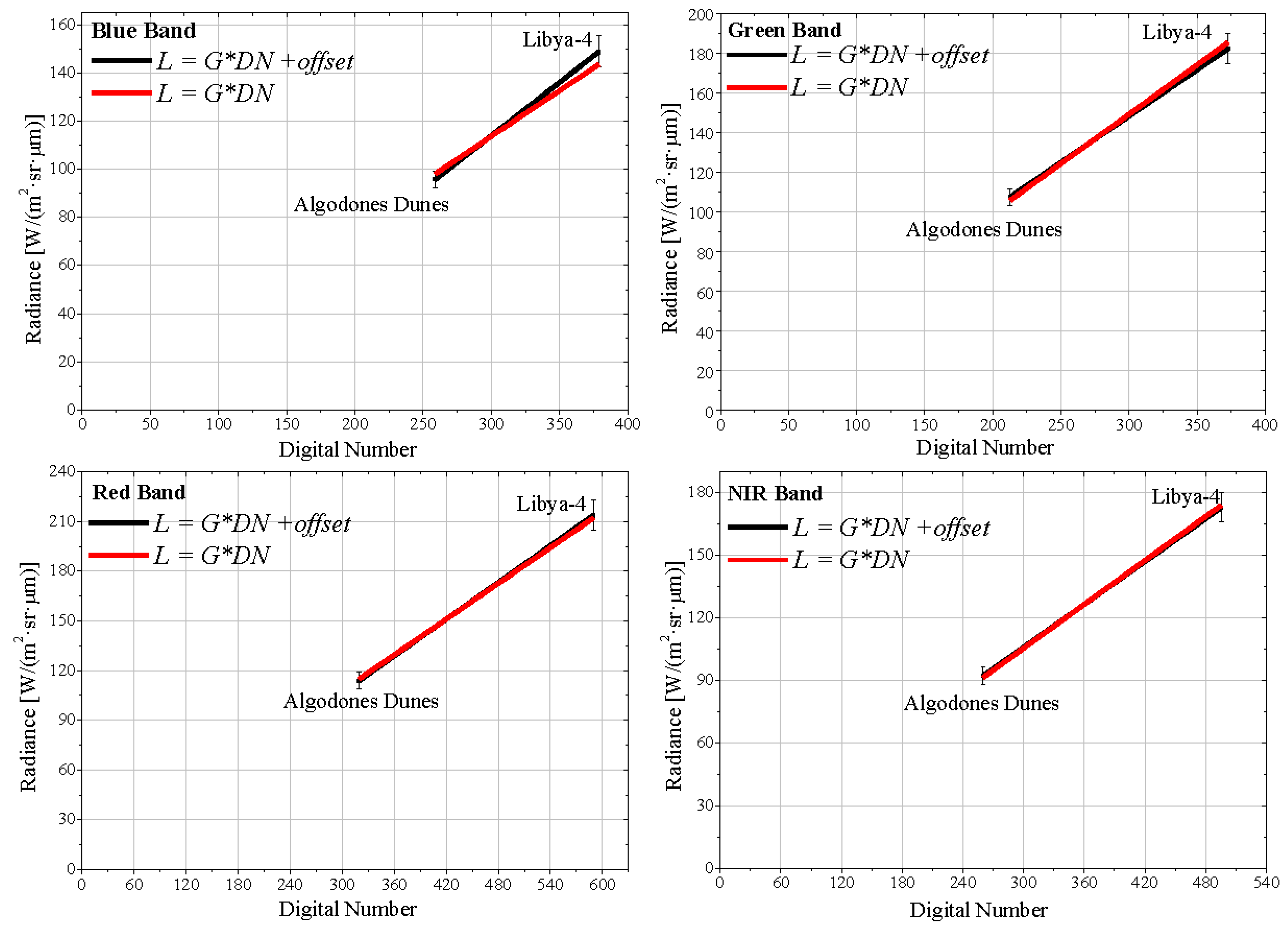
The calibration gains for the MUX and WFI sensors are computed by linearly regressing their predicted at-sensor radiances against the measured raw counts. The measurements over Algodones Dunes and from the Libya-4 PICS are used together during regression to achieve a greater dynamic range. The regression slope provides the radiometric gain of the sensor. The linear fits were implemented using the Method of Least Squares [
46]. Using the ISO-GUM method (called also “Law of propagation of uncertainty”, see
Section 6) was possible to estimate the uncertainties of the coefficients slope or intercept [
46]. Two sets of calibration slopes are computed: one using the standard linear fit with an offset term, and second without an offset term, where the linear regression is forced through origin. The two sets of regression plots for the CBERS-4 MUX and WFI bands are shown in
Figure 9 and
Figure 10, respectively. The calibration coefficients derived from these linear regressions are listed in
Table 8.
Taking into account the uncertainties, all the intercept coefficients (with free intercept) are consistent with zero, indicating that the offseti from Equation (1) is zero, i.e., there was no statistical evidence for using offsets other than zero for all spectral bands on both sensors. This result was expected, since when there is no incident energy on the sensor aperture the expected response is zero. Regarding the gain coefficients, the uncertainties ranged from 8.8%–13.6%. It is important to note that in this fit, with free intercepts, the degree of freedom is zero.
The zero-intercept linear fits yield very good coefficients of determination, ranging from 0.98 to 1.00, in all four spectral bands of MUX and WFI. The slopes (gain coefficient) were determined with uncertainties within 2.8%–3.5% for both MUX and WFI sensors.
As mentioned earlier, a calibration coefficient validation was performed using cross-calibration techniques. A comparison was done between Landsat-7 ETM+ and at-sensor reflectance derived from MUX and WFI measurements. To convert the values in the Landsat-7 image to TOA reflectance the methodology presented in [
7] was used. To determine TOA reflectance from MUX and WFI images, Equation (2) was used. The spectral radiance at the sensor’s aperture was estimated by applying Equation (1), where the calibration coefficients,
Gi and
offseti, are shown in
Table 8. The solar exoatmospheric spectral irradiances for MUX and WFI bands are summarized in
Table 2.
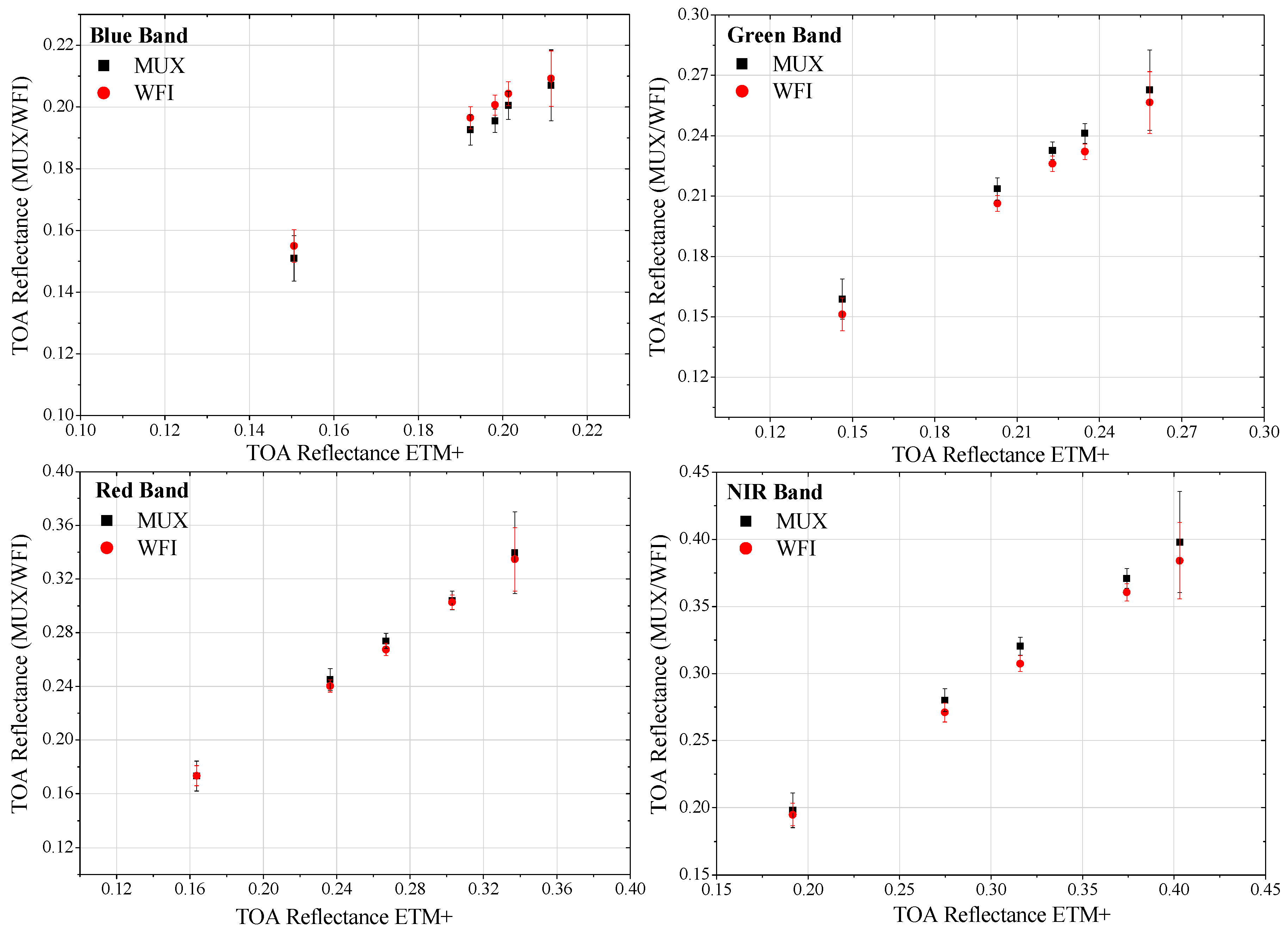
Figure 11 shows a graphic of ETM+ TOA reflectance as a function of MUX and WFI TOA reflectance values for the five ROIs using the
Gi with zero-intercept linear fits.
It is clearly possible to verify in
Figure 11 that the relationship between Landsat-7 (ETM+) TOA reflectance and CBERS-4 (MUX and WFI) TOA reflectance is linear, supporting the idea that the detector response is linear. Furthermore, the reflectance values of the three sensors (ETM+, MUX and WFI) are compatible within the associated uncertainty with each of them.
Table 9 provides the percentage differences in TOA reflectance of the five ROIs between MUX/WFI and ETM+ similar bands after applied the spectral band adjustment. A negative sign in the difference indicates that the value measured by the ETM+ sensor band is higher than the corresponding CBERS-4 sensors bands. On average the absolute difference between CBERS-4 (MUX and WFI) and Landsat-7/EMT+ in the analogous bands was 3.3% and 2.2% when it was used the calibration coefficients determined with free intercept and when forced zero intercept, respectively. This result reinforces the idea that the coefficient
offseti from Equation (1) is zero (as mentioned earlier), since the difference between CBERS-4 and Landsat-7 is lower when it uses only the gain coefficient (forced zero intercept).
A convenient way to assess the consistency of these results is to compare them with the calibration uncertainties estimated. The uncertainties in the gain coefficients for zero-intercept linear fits ranged from 2.8% to 3.4%; therefore, the associated uncertainties cover the differences. Thus, in all of the four MUX and WFI spectral bands, these results are well within the specified calibration uncertainties. Remembering that the uncertainties values were quoted with a confidence level of 68.3% (as one-sigma percentages).
8. Conclusions
Brazil and China have a long-term joint space program: the China-Brazil Earth Resources Satellite (CBERS). The last satellite of this program (CBERS-4) was launched on 7 December 2014. The extraction of quantitative information from data collected by sensors on-board CBERS-4 is only possible through a well-performed absolute calibration. This work describes the complete procedure to calculate the in-flight absolute calibration coefficients for sensor MUX and WFI (CBERS-4) images.
The reflectance-based approach and cross-calibration method were applied. An area at the Algodones Dunes region located in southwestern USA was used as a reference surface for the reflectance-based approach. The cross-calibration between both MUX and WFI on-board CBERS-4 and the Operational Land Imager (OLI) on-board Landsat-8 was performed using Libya-4 Pseudo Invariant Calibration Site.
There was no statistical evidence for using offsets other than zero for all bands on both sensors. The gain coefficients are now available for data users: 1.68, 1.62, 1.59 and 1.42 for MUX sensor and 0.379, 0.498, 0.360 and 0.351 for WFI spectral bands blue, green, red and NIR, respectively, in units of (W/(m2·sr·μm))/DN. These coefficients were determined with uncertainties within 2.8%–3.5%. It is noteworthy that this current work is the first one to present the uncertainty in the CBERS series calibration. Thus, the results achieved here are considered as important progress in the calibration of the Brazilian and Chinese satellite.
A procedure to validate the estimated coefficients was performed using cross-calibration techniques. The results were presented as percentage of disagreement between the Landsat-7 EMT+ and at-sensor reflectance reported using the above mentioned coefficients calibration of MUX and WFI. On average, the difference was 2.2% (after application of the spectral band adjustment), indicating good agreement with the well accepted Landsat 7 ETM+ results.
It is important to emphasize the need to preserve the accuracy of the MUX and WFI absolute radiometric calibration by recalibration on-orbit regularly. It is necessary to perform evaluations of the sensor radiometric once on-orbit, as well as during its operational life, to ensure the on-orbit radiometric stability of the instruments.