Mapping Flooded Rice Paddies Using Time Series of MODIS Imagery in the Krishna River Basin, India
Abstract
:1. Introduction
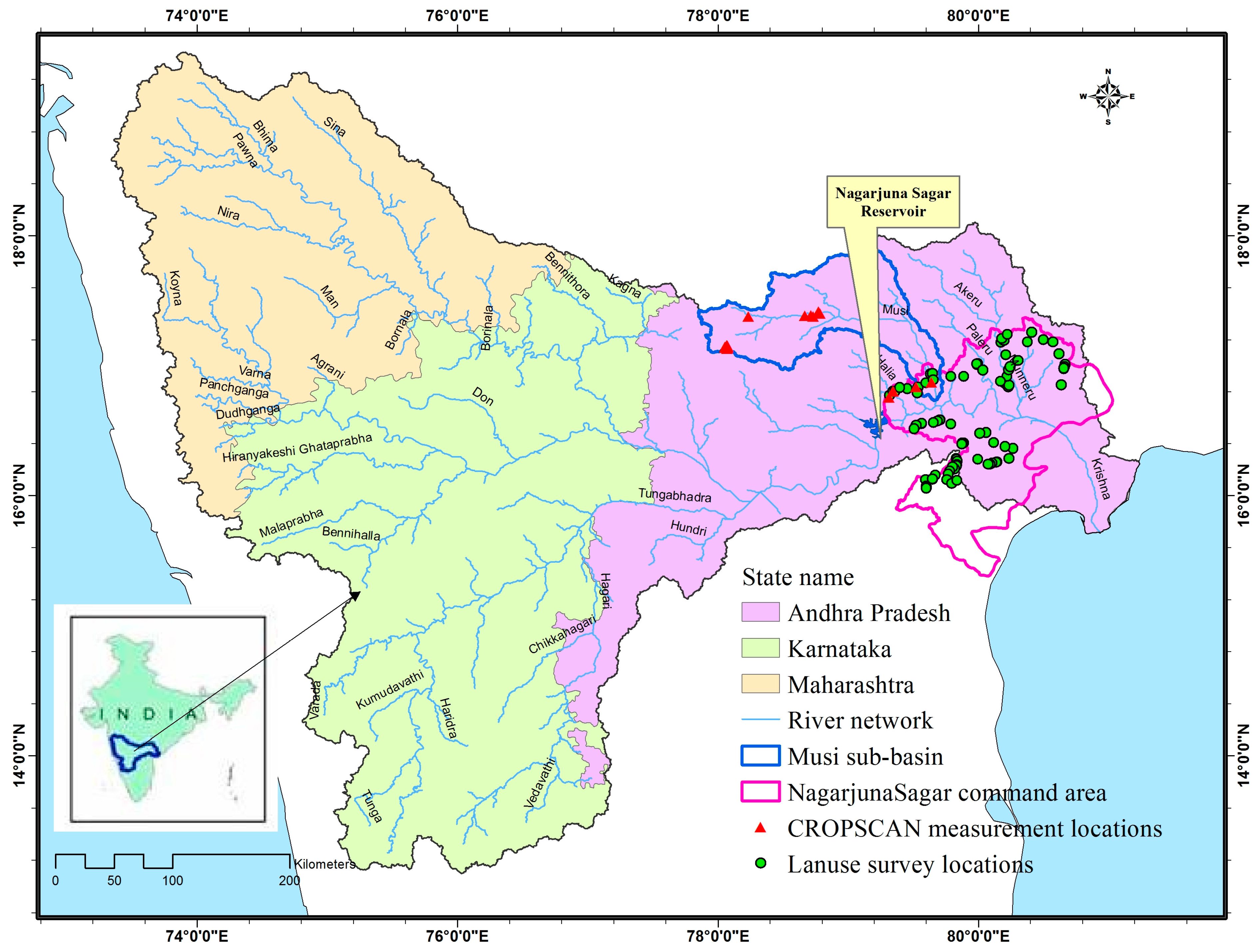
2. Study Area and Dataset
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Datasets and Description
2.2.1. Field Spectral Samples
| MSR16R Bands | Sub-Division | Centre Wavelength (nm) | Band Width (nm) | MODIS Bands |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Band 1 | Visible | 530 | 8.5 | Band 11 |
| Band 2 | Visible | 570 | 9.7 | |
| Band 3 | Visible | 650 | 40.0 | Band 1 |
| Band 4 | NIR | 855 | 40.0 | Band 2 |
| Band 5 | MIR | 1240 | 11.6 | Band 5 |
| Band 6 | SWIR | 1640 | 15.5 | Band 6 |
- Location information (GPS position, location name, date of collection).
- Land use (crop type).
- Vegetation height.
- 12-band reflectance measurements by CROPSCAN.
- Land surface temperature measured by the thermal infrared scanner.
- Soil temperature at the depths of 1 cm, 5 cm and 10 cm.
- Soil moisture content in the top 5 cm by the theta probe soil moisture sensor (model ML2 by Delta-T Devices Ltd.).
- Digital photographs.
2.2.2. MODIS Surface Reflectance Data
| MODIS Bands 2 | Band Width (nm) | Centre Wavelength (nm) | Sub Division | Potential Application 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 459–479 | 470 | Blue | Soil/Vegetation Differences |
| 1 | 620–670 | 648 | Red | Absolute Land Cover Transformation, Vegetation Chlorophyll |
| 2 | 841–876 | 858 | NIR | Cloud Amount, Vegetation Land Cover Transformation |
| 6 | 1628–1652 | 1640 | SWIR | Snow/Cloud Differences |
2.2.3. Field Survey of Land Use
- Location information (GPS position, location name, date of collection).
- Land use/land cover type (class name).
- Fraction of individual land cover types such as cropped canopy and no canopy area (water, fallow lands and weeds) within each crop field.
- Crop types, cropping pattern and cropping calendar (i.e., Kharif, Rabi and summer seasons).
- Agricultural intensification, sources of water and presence of irrigated, rain-fed and supplemental irrigation.
- Characteristics of crops such as plant height, soil texture, and density of plants per square meter;
- Digital photographs.
2.2.4. Agricultural Statistical Data

3. Methods
3.1. Growth Stages of Rice
3.2. Identification of Flooded Paddy Rice
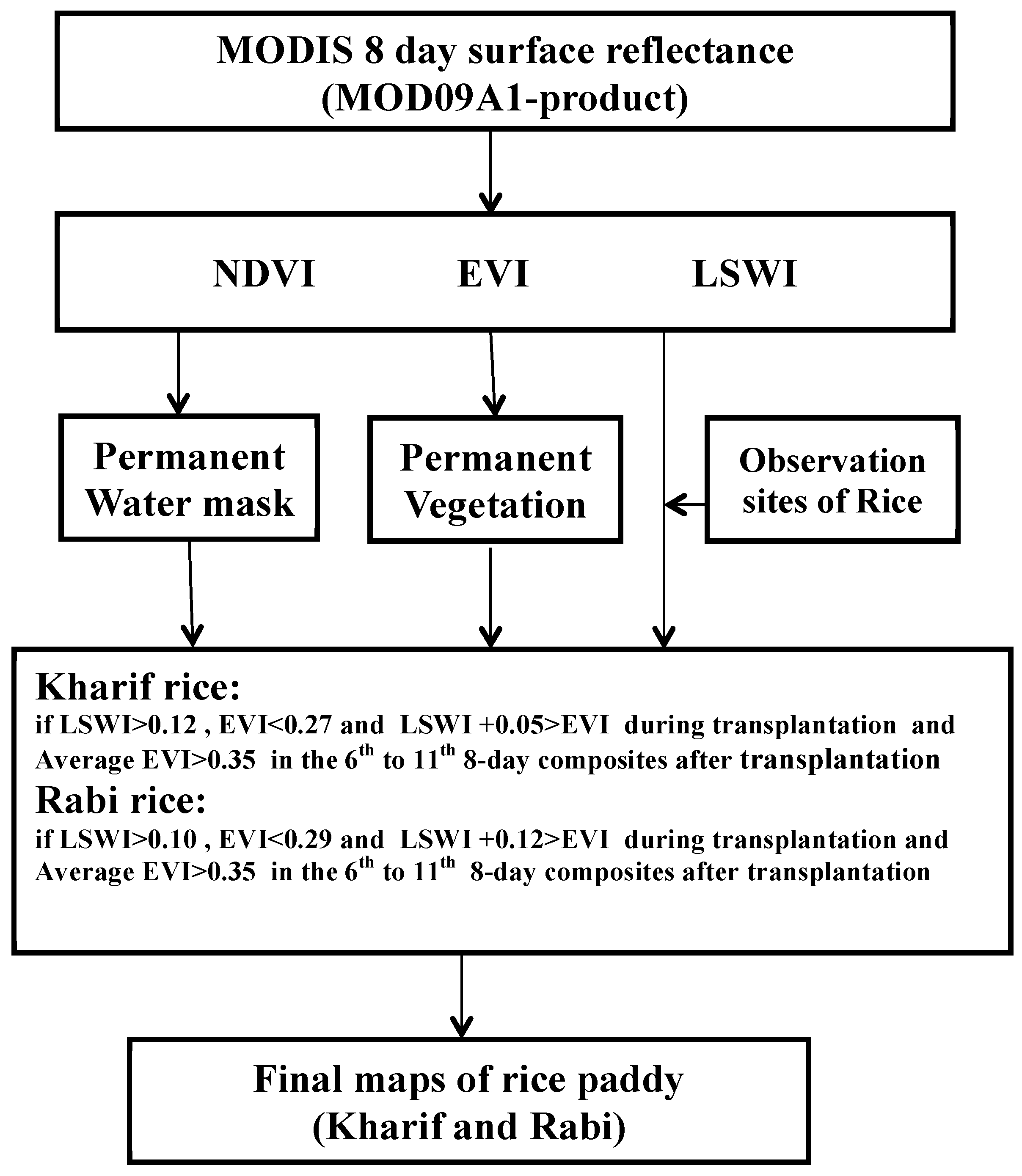
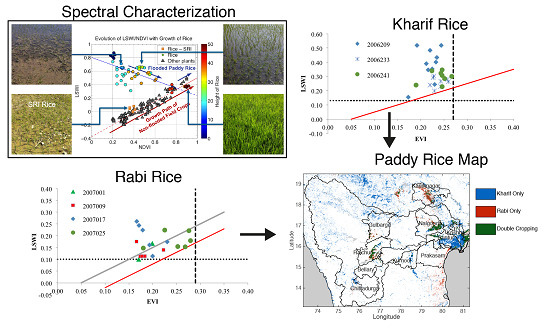
4. Results and Discussion
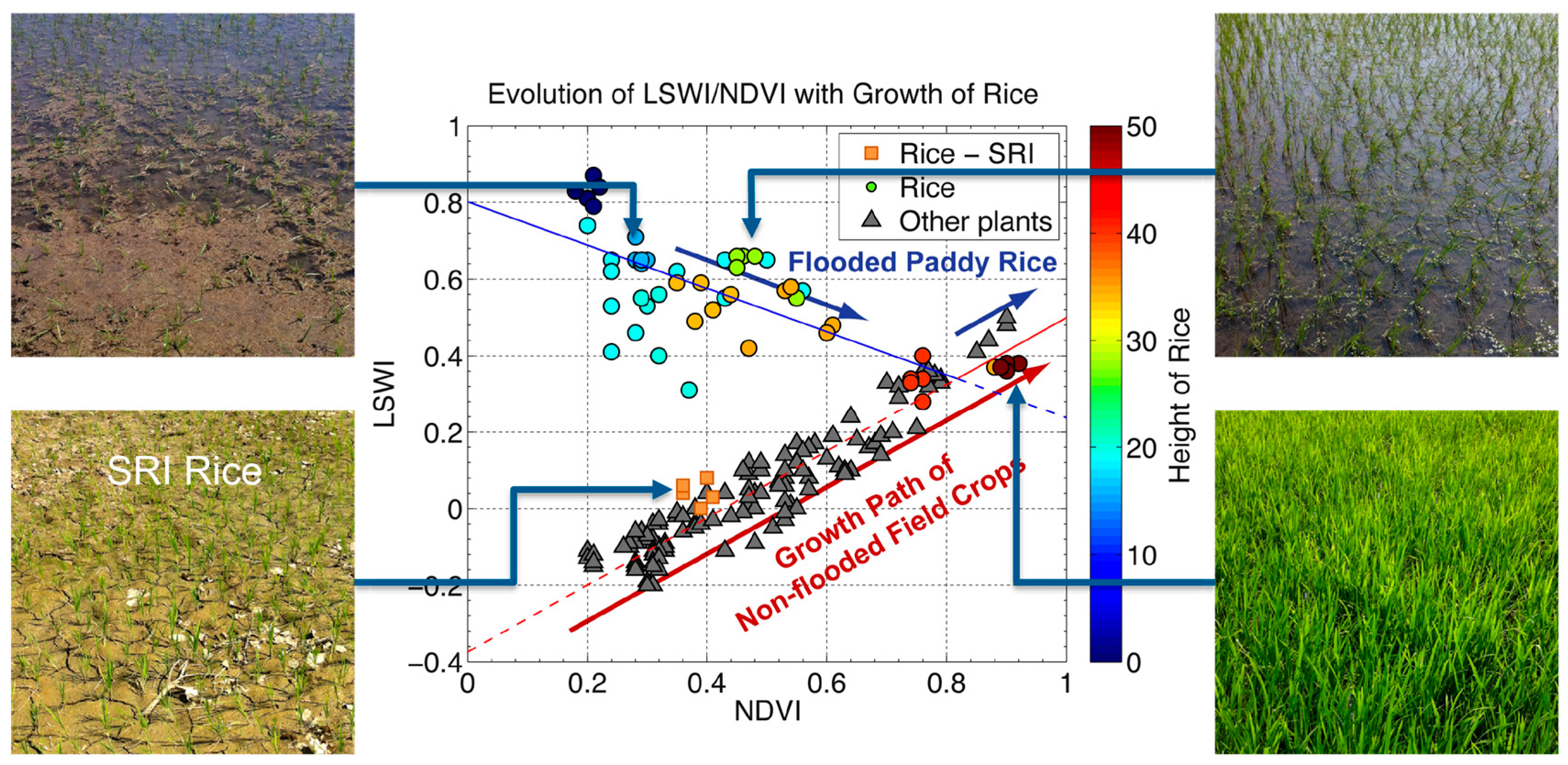
4.1. Spectral Characteristics from Ground Reflectance
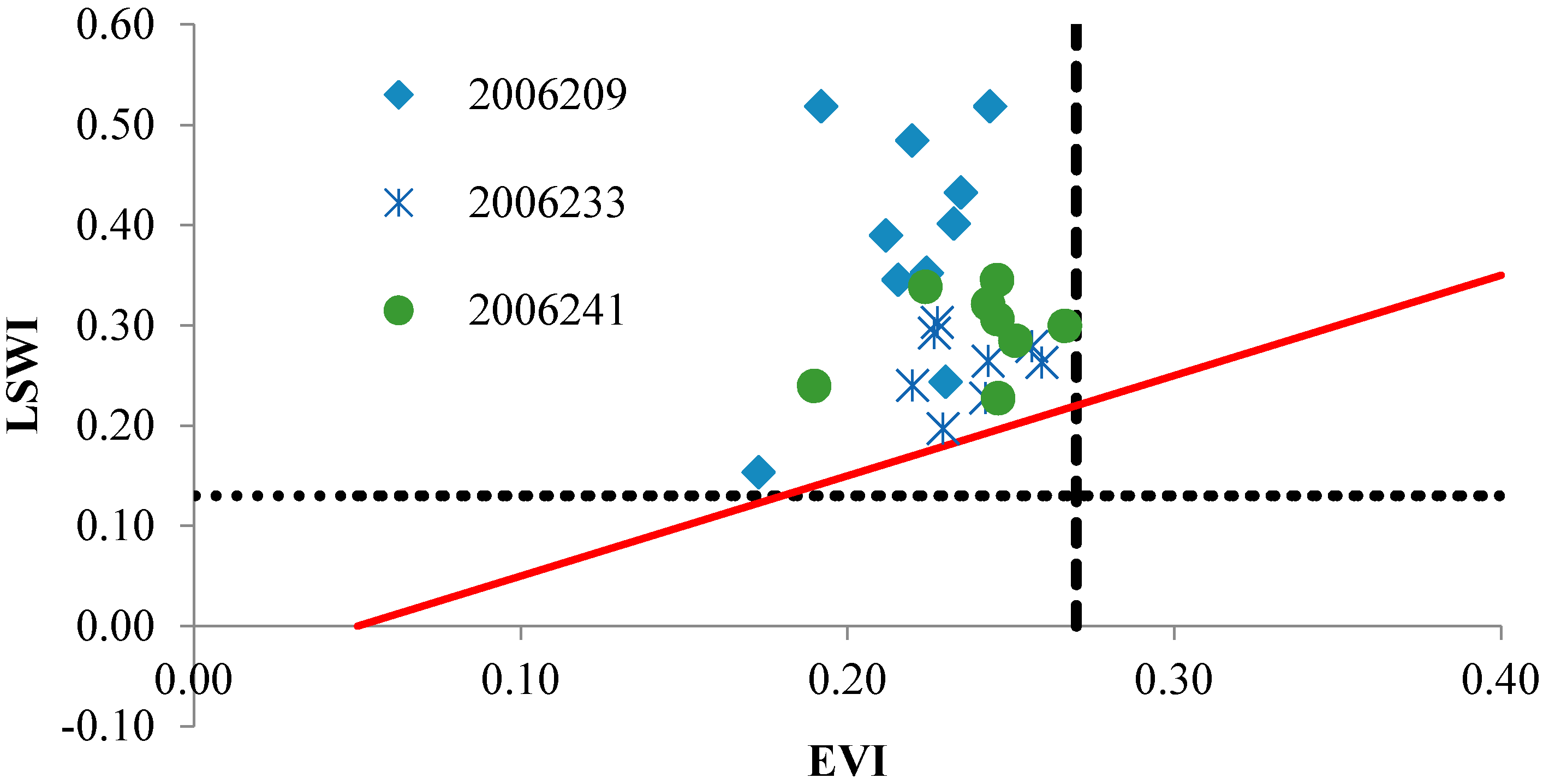
4.2. Decision Rules for Mapping Kharif and Rabi Rice Paddy Using MODIS Indices
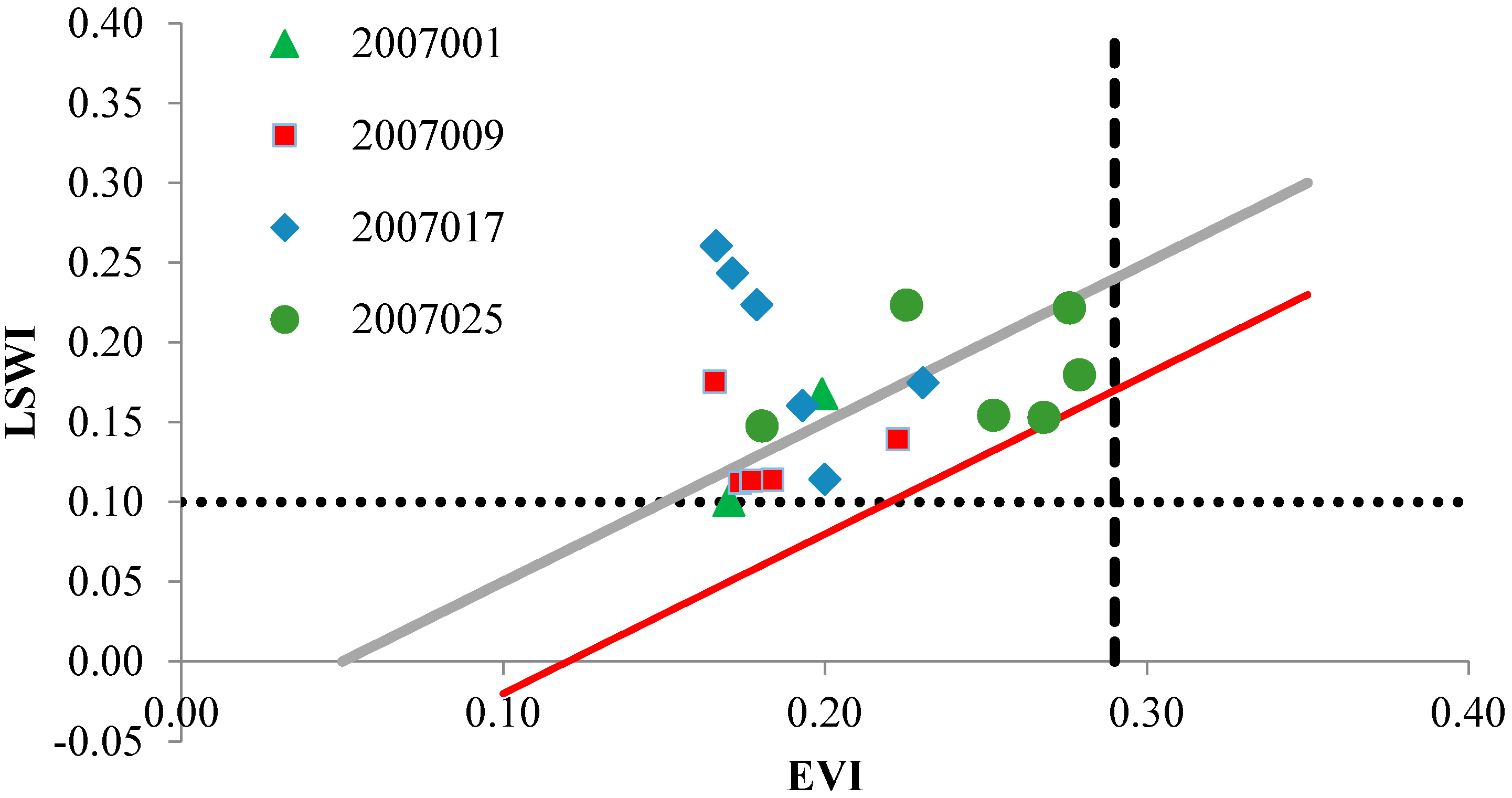
4.3. Spatial Distribution of MODIS-Derived Rice Paddies
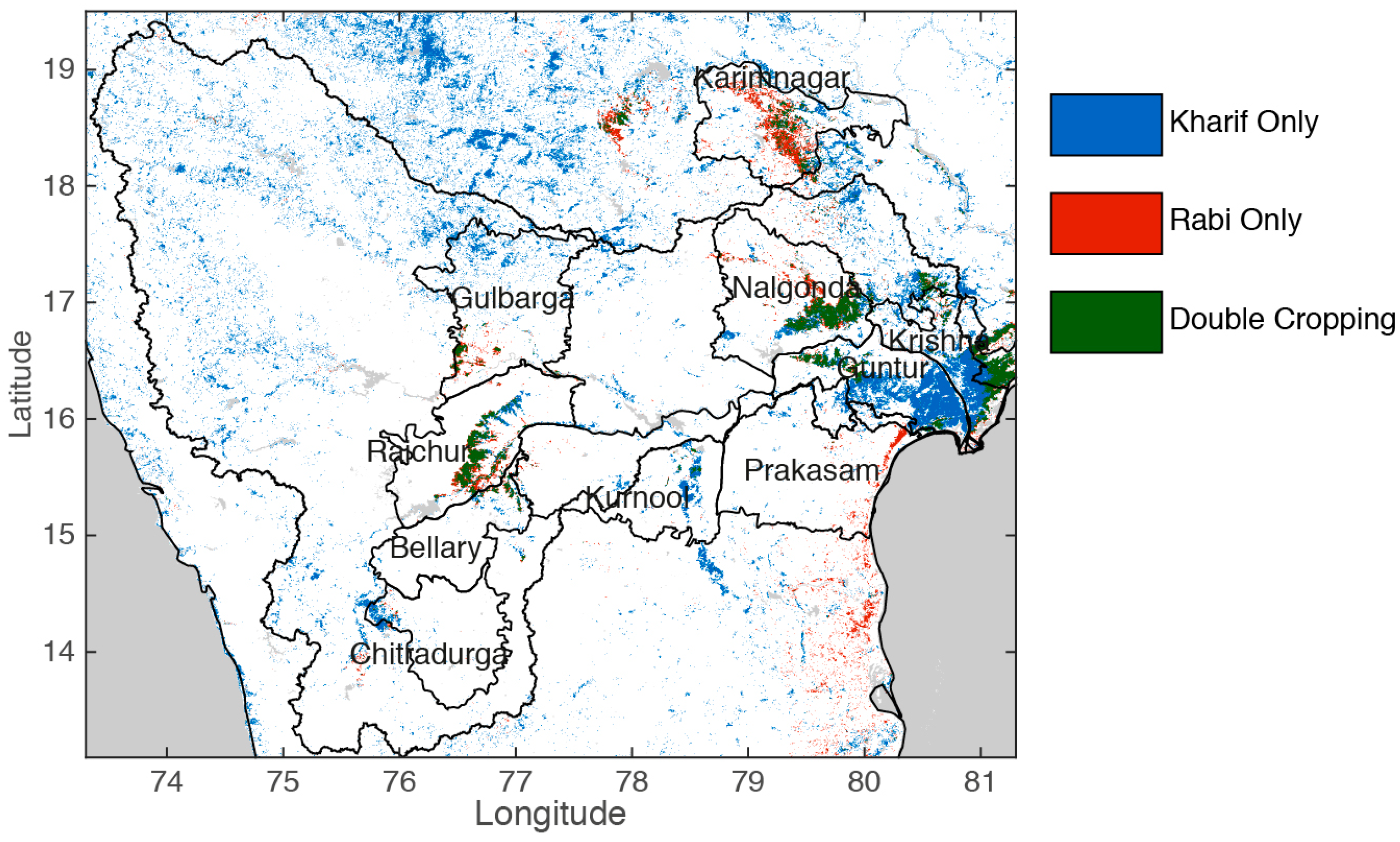
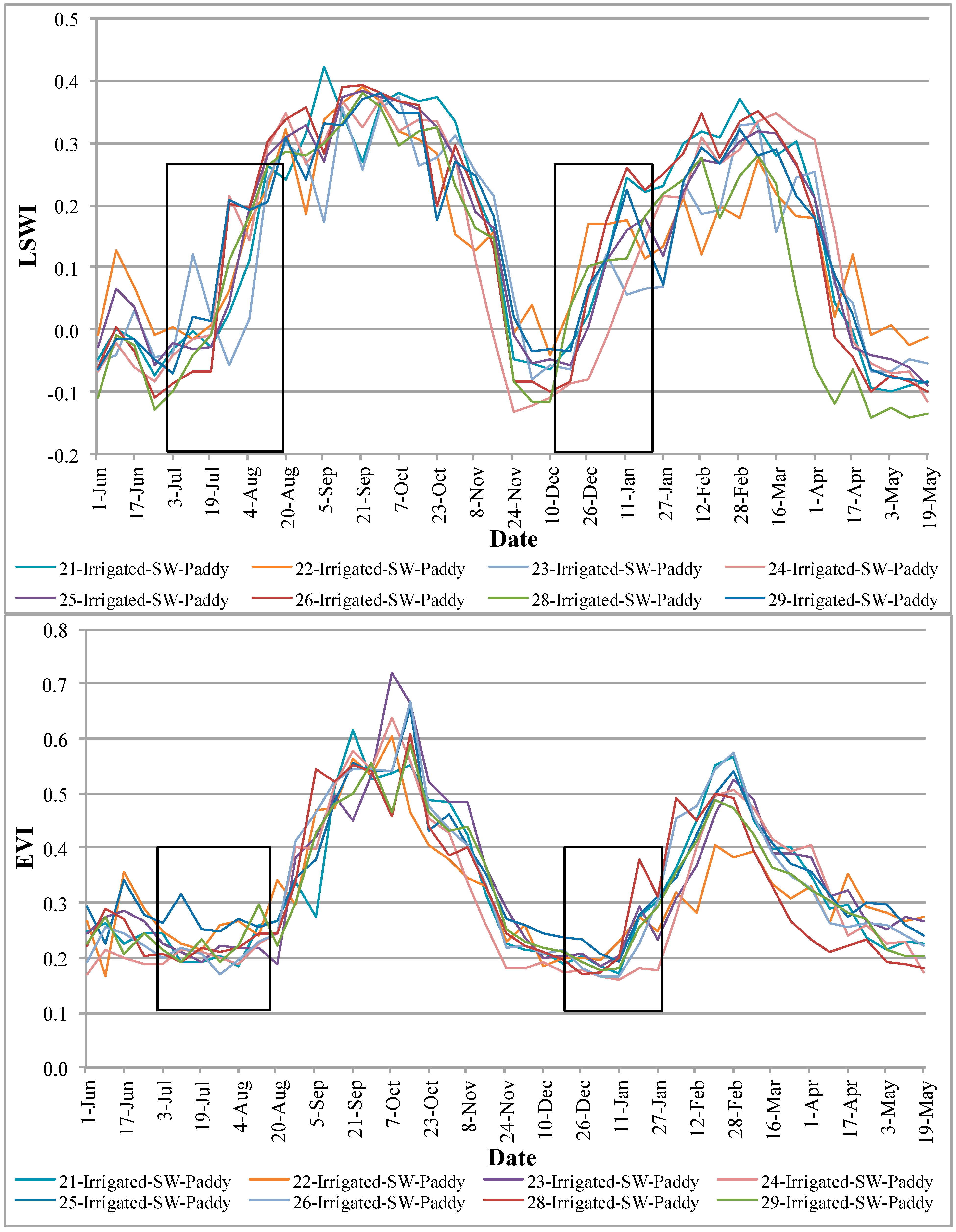
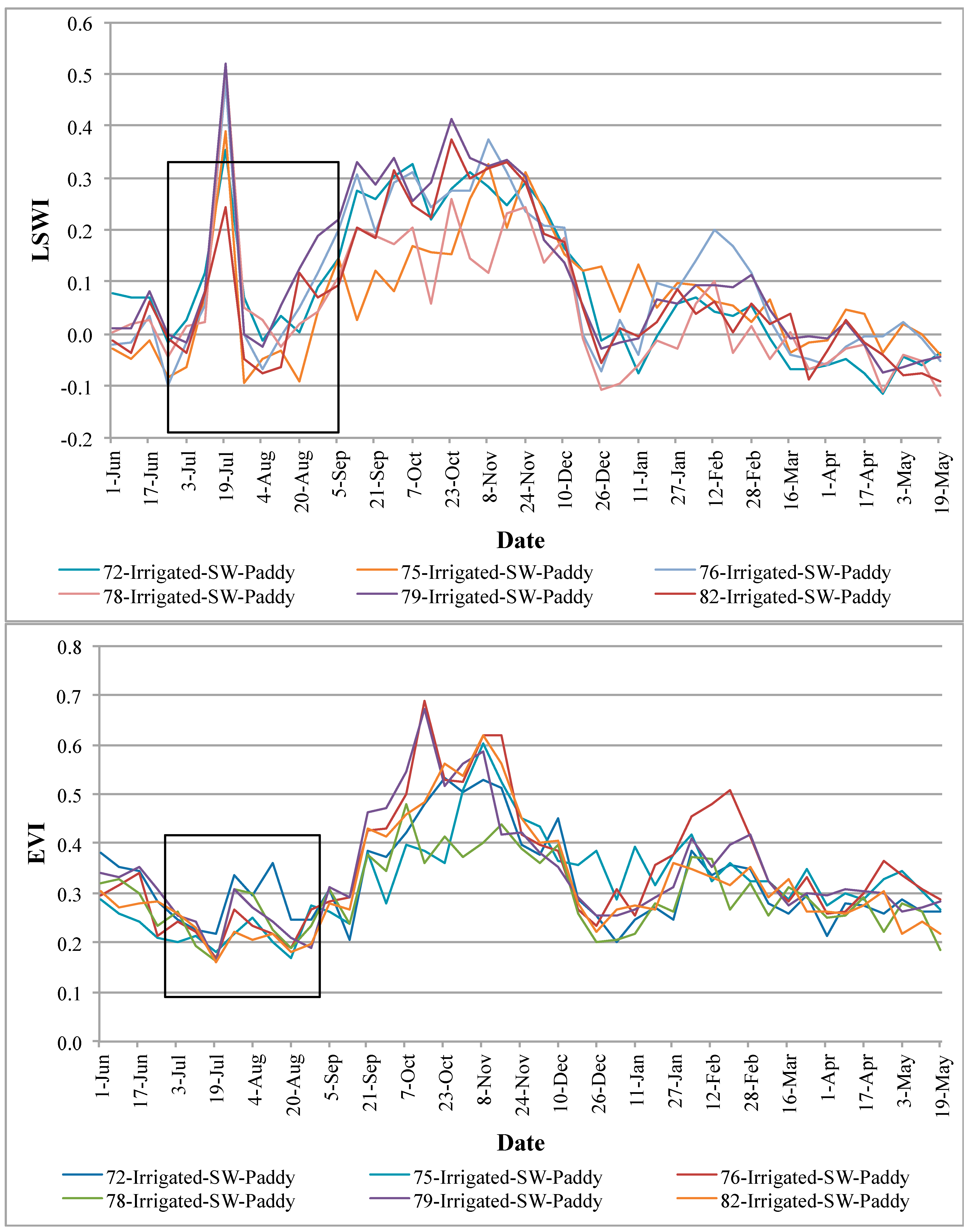
4.4. Vegetation Phenology of Various Rice Pixels from Different Zones/Regions in the Basin
- (a)
- Cropping intensities (e.g., double or single crop);
- (b)
- Crop calendar (i.e., when a crop begins and when it is harvested); and
- (c)
- Crop health and vigor (indicated by magnitude of NDVI).
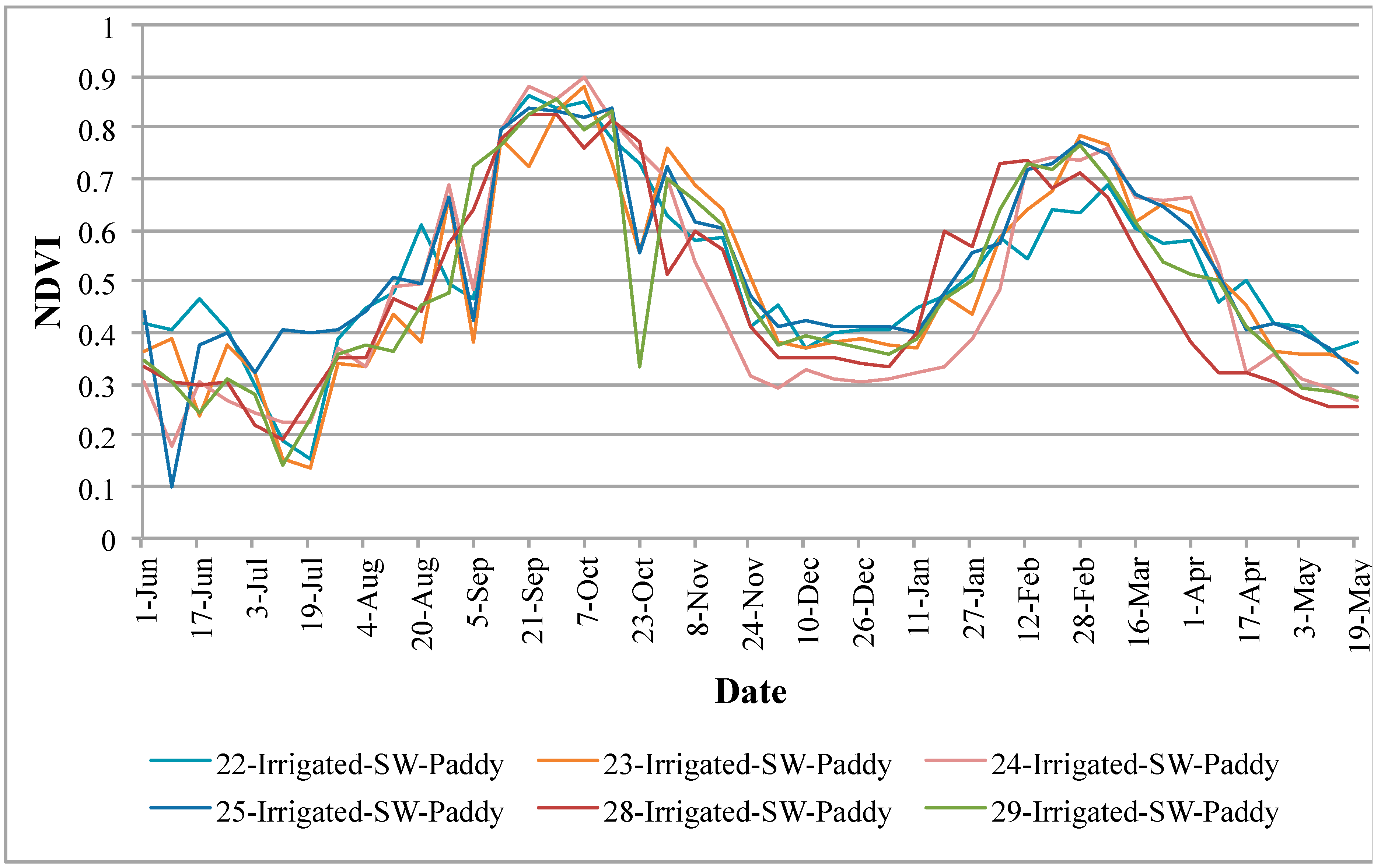
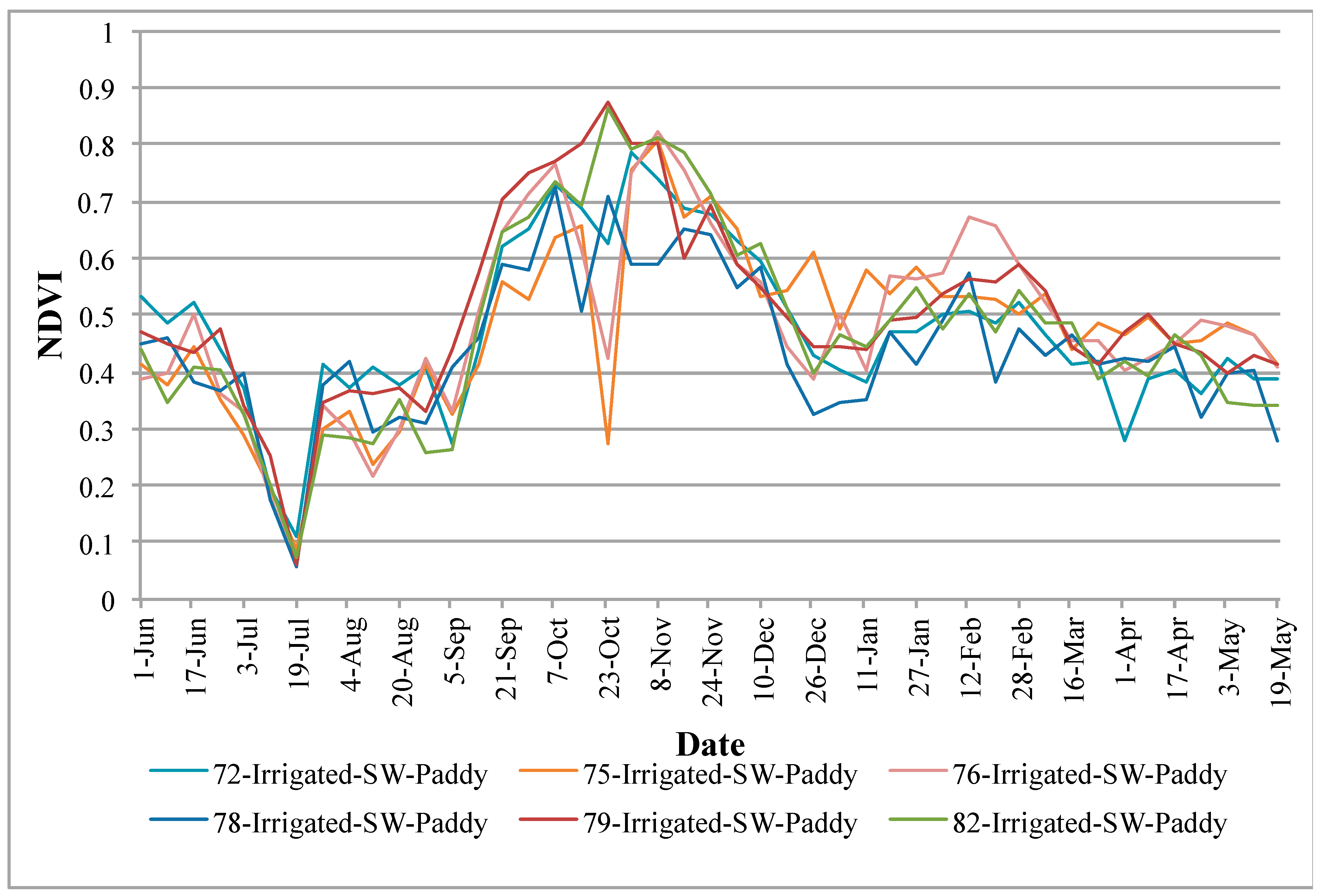
4.5. Accuracy Assessment from Field Observations
| MODIS Classification | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ground Reference | Category | Rice | Non Rice | Total | Producer Accuracy |
| Rice | 29 | 15 | 44 | 66% | |
| Non rice | 5 | 42 | 47 | 89% | |
| Total | 34 | 57 | 91 | ||
| User Accuracy | 85% | 74% | |||
| Overall Accuracy 78% | |||||
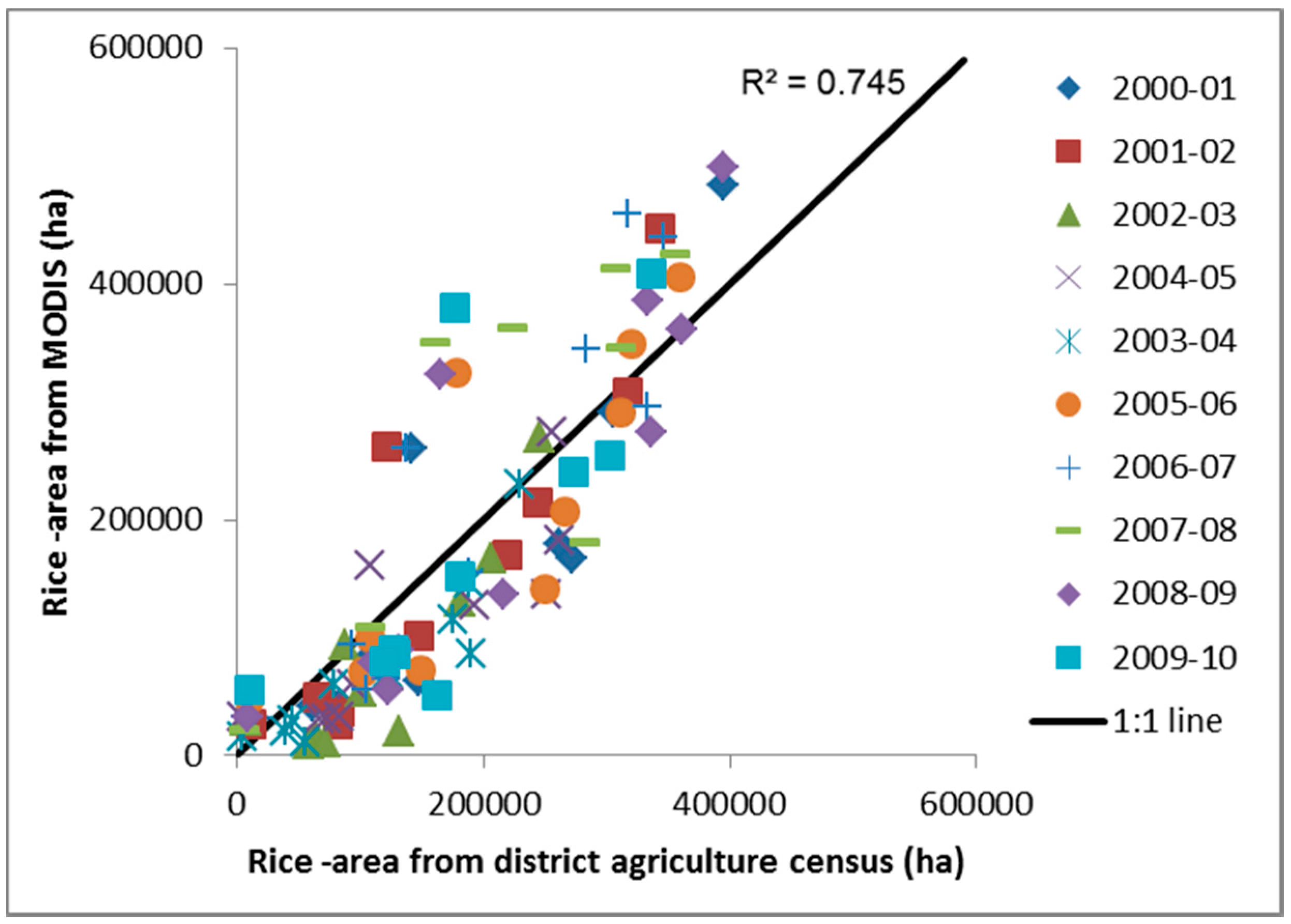
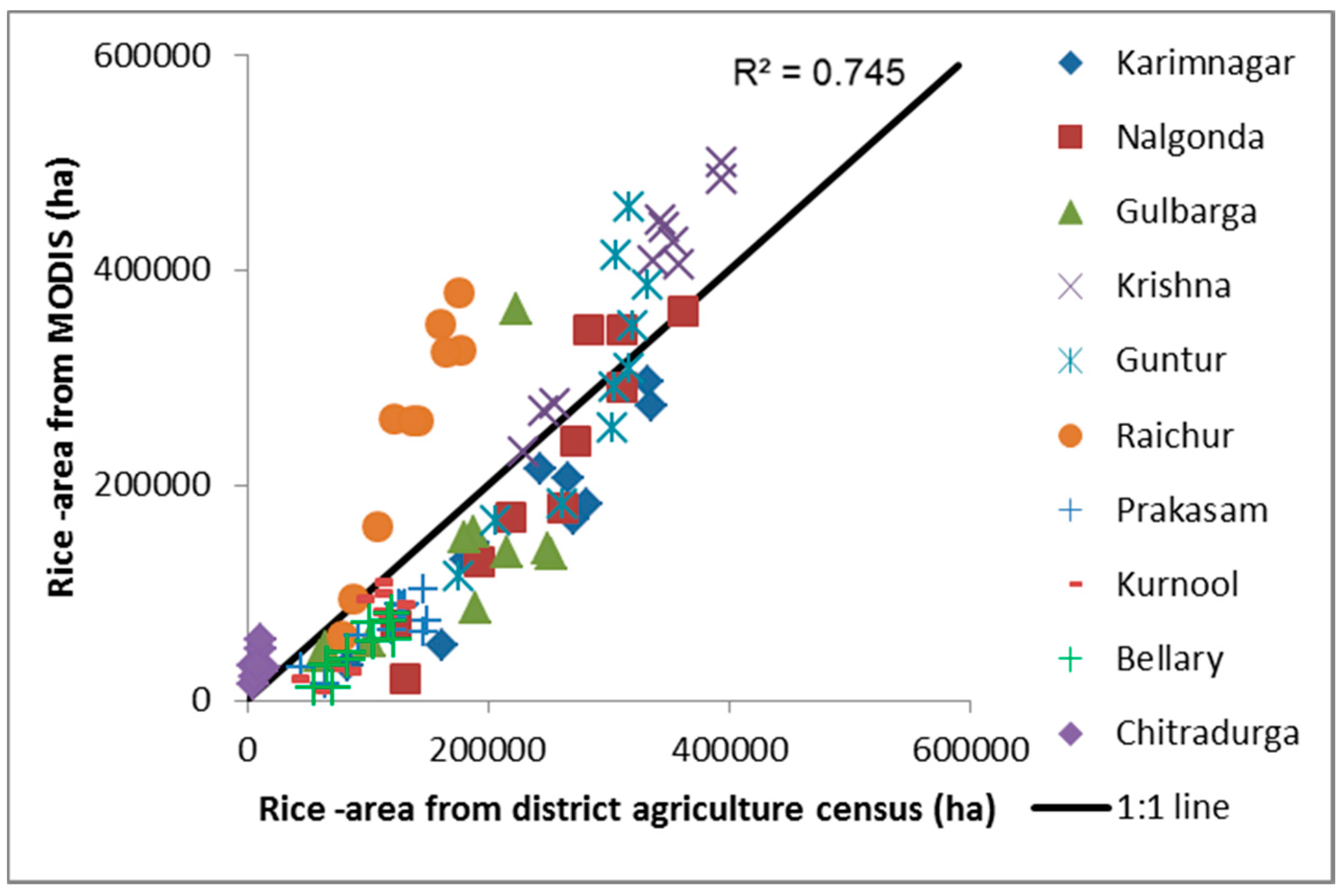
4.6. Rice Area Fractions (RAFs)
4.7. Accuracy Assessment from Agriculture Statistics
| Year | t | Threshold | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2000–2001 | 0.641374 | 2.262 | Yes |
| 2001–2002 | 0.019064 | 2.262 | Yes |
| 2002–2003 | 2.709525 | 2.262 | No |
| 2003–2004 | 3.295548 | 2.262 | No |
| 2004–2005 | 1.968029 | 2.262 | Yes |
| 2005–2006 | 0.208269 | 2.262 | Yes |
| 2006–2007 | 1.133377 | 2.262 | Yes |
| 2007–2008 | 1.311817 | 2.262 | Yes |
| 2008–2009 | 0.220833 | 2.262 | Yes |
| 2009–2010 | 0.083892 | 2.262 | Yes |
| Year | Rice-Area MODIS (in ha) | Rice-Area Ag. Statistics (in ha) | RMSD (%) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000–2001 | 1,642,652 | 1,790,158 | 4.30% | 0.752 |
| 2001–2002 | 1,641,750 | 1,637,656 | 3.92% | 0.784 |
| 2002–2003 | 802,626 | 1,158,496 | 6.62% | 0.767 |
| 2003–2004 | 783,904 | 1,131,583 | 6.00% | 0.693 |
| 2004–2005 | 1,069,266 | 1,392,069 | 5.50% | 0.819 |
| 2005–2006 | 2,007,764 | 2,055,987 | 3.47% | 0.695 |
| 2006–2007 | 2,200,946 | 1,936,217 | 3.40% | 0.818 |
| 2007–2008 | 1,999,000 | 2,372,458 | 3.93% | 0.681 |
| 2008–2009 | 2,180,915 | 2,236,344 | 3.38% | 0.777 |
| 2009–2010 | 1,819,761 | 1,796,366 | 4.66% | 0.565 |
5. Summary and Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAOSTAT. FAOSTAT 2008. Available online: http://faostat.fao.org/ (accessed on 11 July 2011).
- Khush, G.S. What it will take to feed 5.0 billion rice consumers in 2030. Plant Mol. Biol. 2005, 59, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neue, H.U. Methane emission from rice fields. Bioscience 1993, 43, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denier Van Der Gon, H. Changes in CH4 emission from rice fields from 1960s to 1990s: 1. Impacts of modern rice technology. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2000, 1, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassmann, R.; Lantin, R.S.; Neue, H.U.; Buendia, L.V.; Corton, T.M.; Lu, Y. Characterization of methane emissions from rice fields in Asia. III. Mitigation options and future research needs. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosystems 2000, 58, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belder, P.; Bouman, B.A.M.; Cabangon, R.; Guoan, L.; Quilang, E.J.P.; Yuanhua, L.; Spiertz, J.H.J.; Tuong, T.P. Effect of water-saving irrigation on rice yield and water use in typical lowland conditions in Asia. Agric. Water Manag. 2004, 65, 193–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisser, D.; Frolking, S.; Douglas, E.M.; Fekete, B.M.; Vörösmarty, C.J.; Schumann, A.H. Global irrigation water demand: Variability and uncertainties arising from agricultural climate data sets. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Boles, S.; Frolking, S.; Salas, W.; Moore, B., III; Li, C.; He, L.; Zhao, R. Observation of flooding and rice transplanting of paddy rice fields at the site to landscape scales in China using VEGETATION sensor data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 3009–3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekar, K.; Sesha Sai, M.V.R.; Roy, P.S.; Dwevedi, R.S. Land Surface Water Index (LSWI) response to rainfall and NDVI using the MODSI Vegetation Index product. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 3987–4005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.Y.; Huang, J.F.; Jackson, T.J. Vegetation water content estimation for corn and soybeans using spectral indices derived from MODIS near- and short-wave infrared bands. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 98, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, T.J.; Chen, D.; Cosh, M.; Li, F.; Anderson, M.; Walthall, C.; Doraiswamy, P.; Hunt, R. Vegetation water content mapping using Landsat data derived normalized difference water index for corn and soybeans. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 92, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Boles, S.; Liu, J.; Zhuang, D.; Frolking, S.; Li, C.; Salas, W.; Moore, B., III. Mapping paddy rice agriculture in southern China using multi-temporal MODIS images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 95, 480–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Boles, S.; Frolking, S.; Li, C.; Babu, J.Y.; Salas, W.; Moore, B., III. Mapping paddy rice agriculture in South and Southeast Asia using multi-temporal MODIS images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 100, 95–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Huang, J.; Huete, A.R.; Peng, D.; Zhang, F. Mapping paddy rice with multi-date moderate-resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS) data in China. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. 2009, 10, 1509–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumma, M.K.; Nelson, A.; Thenkabail, P.S.; Singh, A.N. Mapping rice areas of South Asia using MODIS multi temporal data. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2011, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaesen, K.; Gilliams, S.; Nackaerts, K.; Coppin, P. Ground-measured spectral signatures as indicators of ground cover and leaf area index: The case of paddy rice. Field Crops Res. 2001, 69, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, D.; Teluguntla, P.; Malano, H.M.; George, B.A.; Nawarathna, B.; Radha, A. Analysis of Spectral Measurements in Paddy Rice Field: Implications for Land Use Classification. In Proceedings of the 19th International Congress on Modelling and Simulation (MODSIM), Perth, Australia, 12–16 December 2011; pp. 2009–2015.
- Motohka, T.; Nasahara, K.N.; Miyata, A.; Mano, M.; Tsuchida, S. Evaluation of optical satellite remote sensing for rice paddy phenology in monsoon Asia using a continuous in situ dataset. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 4343–4357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggs, T.W.; Thenkabail, P.S.; Gumma, M.K.; GangadharaRao, T.P.; Turral, H. Irrigated area mapping in heterogeneous landscapes with MODIS time series, ground truth and census data, Krishna Basin, India. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 4245–4266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggs, T.W.; Gaur, A.; Scott, C.A.; Thenkabail, P.S.; GangadharaRao, T.P.; Gumma, M.K.; Acharya, S.; Turral, H. Closing of the Krishna basin: Summary of research, Hydronomic zones and water accounting. In IWMI Research Report 111; International Water Management Institute: Colombo, Srilanka, 2007; p. 44. [Google Scholar]
- Huete, A.R.; Didan, K.; Miura, T.; Rodriguez, E.; Gao, X.; Ferreira, L. Overview of the radiometric and biophysical performance of the MODIS vegetation indices. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibayama, M.; Akiyama, T. Seasonal visible, near-infrared and mid-infrared spectra of rice canopies in relation to LAI and above-ground dry phytomass. Remote Sens. Environ. 1989, 27, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceccato, P.; Gobron, N.; Flasse, S.; Pinty, B.; Tarantola, S. Designing a spectral index to estimate vegetation water content from remote sensing data: Part 1. Theoretical approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 82, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceccato, P.; Flasse, S.; Grégoire, J.M. Designing a spectral index to estimate vegetation water content from remote sensing data: Part 2. Validation and applications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 82, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cihlar, J. Identification of contaminated pixels in AVHRR composite images for studies of land biosphere. Remote Sens. Environ. 1996, 56, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellers, P.J.; Tucker, C.J.; Collatz, G.J.; Los, S.O.; Justice, C.O.; Dazlich, D.A.; Randall, D.A. A global 1° by 1° NDVI data set for climate studies: Part II. The generation of global fields of terrestrial biophysical parameters from the NDVI. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1994, 15, 3519–3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, J.R. Introductory Digital Image Processing: A Remote Sensing Perspective, 3rd ed.; Prentice Hall: Up-per Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2004; p. 544. [Google Scholar]
- Congalton, R.G. A review of assessing the accuracy of classifications of remotely sensed data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1991, 37, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congalton, R.G.; Green, K. Assessing the Accuracy of Remotely Sensed Data: Principles and Practices; CRC: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Thenkabail, P.S.; GangadharaRao, P.; Biggs, T.; Krishna, M.; Turral, H. Spectral matching techniques to determine historical land use/land cover (LULC) and irrigated areas using time-series AVHRR pathfinder datasets in the Krishna River Basin, India. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2007, 73, 1029–1040. [Google Scholar]
- Thenkabail, P.S.; Biradar, C.M.; Noojipady, P.; Dheeravath, V.; Li, Y.J.; Velpuri, M.; Gumma, M.; Reddy, G.P.O.; Turral, H.; Cai, X.L.; et al. Global irrigated area map (GIAM), derived from remote sensing, for the end of the last millennium. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 3679–3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumma, M.K.; Thenkabail, P.S.; Iyyanki, M.V.; Velpuri, N.M.; GangadharaRao, T.P.; Dheeravath, V.; Biradar, C.M.; Nalan, A.S.; Gaur, A. Changes in agricultural cropland areas between a water-surplus year and water-deficit year impacting food security determined using MODIS 250 m time-series data and spectral matching techniques in the Krishna River Basin (India). Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 3495–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, A.; Biggs, T.W.; Gumma, M.K.; Parthasaradhi, G.; Turral, H. Water scarcity effects on equitable water distribution and land use in major irrigation projects a case study in India. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2008, 134, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggs, T.W.; Gangadhara Rao, P.; Bharati, L. Mapping agricultural responses to water supply shocks in large irrigation systems, southern India. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 924–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Teluguntla, P.; Ryu, D.; George, B.; Walker, J.P.; Malano, H.M. Mapping Flooded Rice Paddies Using Time Series of MODIS Imagery in the Krishna River Basin, India. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 8858-8882. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70708858
Teluguntla P, Ryu D, George B, Walker JP, Malano HM. Mapping Flooded Rice Paddies Using Time Series of MODIS Imagery in the Krishna River Basin, India. Remote Sensing. 2015; 7(7):8858-8882. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70708858
Chicago/Turabian StyleTeluguntla, Pardhasaradhi, Dongryeol Ryu, Biju George, Jeffrey P. Walker, and Hector M. Malano. 2015. "Mapping Flooded Rice Paddies Using Time Series of MODIS Imagery in the Krishna River Basin, India" Remote Sensing 7, no. 7: 8858-8882. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70708858
APA StyleTeluguntla, P., Ryu, D., George, B., Walker, J. P., & Malano, H. M. (2015). Mapping Flooded Rice Paddies Using Time Series of MODIS Imagery in the Krishna River Basin, India. Remote Sensing, 7(7), 8858-8882. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70708858