Abstract
Future spaceborne synthetic aperture radar (SAR) missions require complete and frequent coverage of the earth with a high resolution. Terrain Observation by Progressive Scans (TOPS) is a novel wide swath mode but has impaired azimuth resolution. In this paper, an innovative extended TOPS mode named Alamouti Space-time Coding multiple-input multiple-output TOPS (ASTC-MIMO-TOPS) mode combined with digital beam-forming (DBF) in elevation and multi-aperture SAR signal reconstruction in azimuth is proposed. This innovative mode achieves wide-swath coverage with a high geometric resolution and also overcomes major drawbacks in conventional MIMO SAR systems. The data processing scheme of this imaging scheme is presented in detail. The designed system example of the proposed ASTC-MIMO-TOPS mode, which has the imaging capacity of a 400 km wide swath with an azimuth resolution of 3 m, is given. Its system performance analysis results and simulated imaging results on point targets demonstrate the potential of the proposed novel spaceborne SAR mode for high-resolution wide-swath (HRWS) imaging.
1. Introduction
Traditional single channel synthetic aperture radar (SAR) systems suffer from the contradiction between swath width and azimuth resolution: generally no system can have both wide swath coverage and high resolution [1,2]. Wide swath coverage is usually a trade-off for coarse azimuth resolution in systems such as ScanSAR and Terrain Observation by Progressive Scans (TOPS) [3,4,5,6], while the area of high-resolution SAR images are usually very limited and even discontinuous in azimuth in systems such as spotlight mode and sliding spotlight mode [7]. The displaced phase center multiple azimuth beam (DPCMAB) technique [1,8], which employs a small transmit antenna and a large receive antenna splitting into multiple sub-apertures to increase spatial samples in azimuth and reduce the transmit antenna length, can improve the azimuth resolution for a fixed total receive antenna length. Multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) SAR [9,10,11,12,13,14] is the further extension of the DPCMAB technique, in which additional transmitters with different waveform diversities can generate more effective azimuth spatial samples to extend the unambiguous swath width or/and improve the obtained azimuth resolution. However, the cross-correlation noise between the imperfect orthogonal waveforms will impair the image quality of distributed targets, when the mere use of transmitted orthogonal waveforms is adopted.
To implement the high-resolution wide swath (HRWS) mapping capability, a novel Alamouti Space-time Coding multiple-input multiple-output (ASTC-MIMO) TOPS mode combined with digital beam-forming (DBF) in elevation is proposed. In this imaging scheme, the TOPS mode is used to obtain the wide swath coverage, while the ASTC-MIMO technique is used to obtain more gains including array and waveform diversity gains to reduce the desired PRF requirement and the receive antenna length. Furthermore, DBF on receive in elevation is adopted to suppress ambiguous energy and improve the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) for HRWS imaging.
This paper is organized as follows. Section 2 briefly reviews some novel HRWS imaging concepts proposed in recent years, such as TOPS-SAR, MIMO-SAR, and DBF-SAR. The innovative ASTC-MIMO-TOPS mode is presented and its corresponding data processing scheme is given in Section 3. The designed system example is given, while its corresponding performances and imaging results are analyzed to validate the capacity of this innovative imaging mode in Section 4. Some conclusions are reported in Section 5.
2. TOPS Imaging Mode
2.1. Recent Proposed SAR Modes for HRWS Imaging
The TOPS mode requires that the sensor antenna beam can be steered in both elevation and azimuth. In elevation, the antenna beam scans cyclically from sub-swath to sub-swath similar to ScanSAR, while the azimuth beam is swept from aft to fore to shrink the target illumination time, as shown in Figure 1. The azimuth antenna pattern (AAP) could be equivalent to the one of a fixed antenna in stripmap SAR, but shrunk by a factor A [4]:
where r is the slant range, ωr is the azimuth beam steering rate, and vg is the velocity of the footprint. This factor shrinks the target illumination time, and is responsible for its coarser azimuth resolution. However, azimuth beam steering means that echoes of targets with different azimuth locations will be completely weighted by the reduced AAP, and this scheme reduces the scalloping effect in the burst mode, such as azimuth varying azimuth ambiguity to signal ratio (AASR) and noise equivalent sigma zero (NESZ) [4,5].
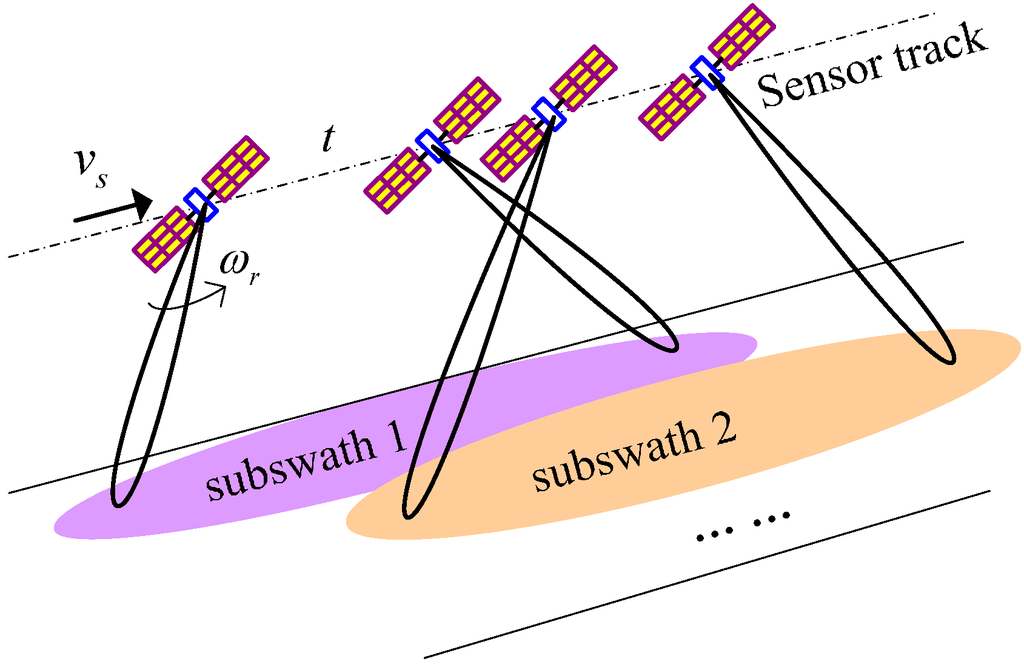
Figure 1.
TOPS mode acquisition geometry.
To improve the azimuth resolution of the TOPS mode, multichannel TOPS with the DPCMAB technique is proposed and its designed system example to obtain 400 km swath width with an azimuth resolution of 5 m is given in [15]. To further improve the HRWS imaging capacity of the multichannel TOPS SAR system, the MIMO technique could be adopted. In the MIMO-SAR configuration, orthogonal waveforms are transmitted simultaneously from different transmit antennas, and both array and diversity gains can be extracted at the receiver to increase information content [10,11,12,13,14]. However, the existing cross-correlation noise between imperfect orthogonal waveforms will seriously impair the quality of the SAR image [10]. The system with two transmitters transmitting Alamouti space-time coding (ASTC) waveforms and N receivers, which is named the ASTC-MIMO-SAR system, can eliminate the cross-correlation noise because of its special code characteristics and pulse compression method [9].
The pair of coding waveforms transmitted simultaneously by Tx1 and Tx2 is shown in Figure 2a, and the time sequence of ASTC-MIMO-SAR is shown in Figure 2b. Echoes can be described in the frequency domain by a vector form R [9]:
where Hi (i = 1, 2) denotes the individual channel response as shown in Figure 2a, Ni (i = 1, 2) is the additive white Gaussian noise, {·}* denotes the matrix transposed operator, and S1 and S2 are different linear frequency modulation (LFM) signals (up-chirp and down-chirp) that are approximatively assumed as a pair of orthogonal signals. The decoder of ASTC is [9]:
After decoding, the receiving signals can be written as:
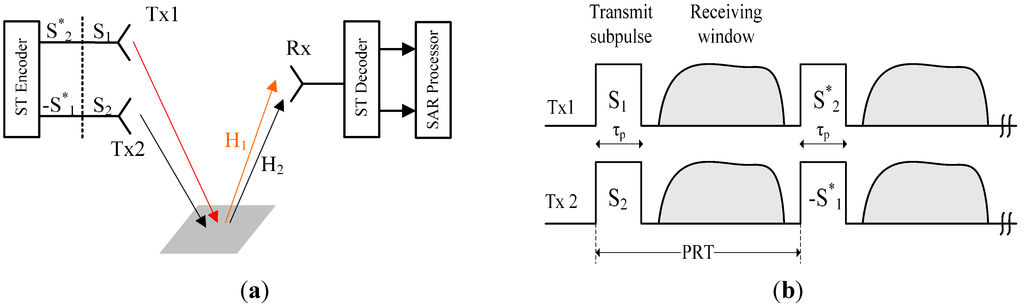
Figure 2.
Implementation of ASTC-MIMO-SAR TOPS mode. (a) Waveforms transmitted in ASTC-MIMO-SAR. (b) The time sequence of ASTC-MIMO-SAR.
Due to ||S1||2 = ||S2||2, it is noticed that two diversity gains are extracted and the cross-correlation noise between different waveforms does not exist. However, a doubled PRF is required as a pair of waveforms consists of four sub-pulses to be transmitted. Moreover, in the MIMO-SAR geometry, a simple assumption that the individual channel response is unchanged in the delay time between two transmit sub-pulses is assumed. However, the SAR platform moving continuously and two different coded sub-pulses transmitting in different pulse repetition intervals (PRIs) induces the time variant channel. Therefore, the lower PRF is designed and the channel variance becomes more significant in such a system.
DBF use in the SAR system has been hotly discussed in recent years due to quick and expedient beam direction changing and null steering operation by an active phased array antenna, which can be used in different SAR imaging modes. Furthermore, this technique can be used in both azimuth and elevation.
The novel Scan-On-REceive (SCORE) technique [16,17,18] requires a small antenna with a wide beam to illuminate a wide swath on the ground and a large receive antenna with a sharp high gain beam to scan on receive echoes as shown in Figure 3. The narrow scanning beam can compensate for the loss of the wide illuminating beam. Moreover, the null steering technique can be used to suppress range ambiguities. In DBF-SAR with the SCORE capacity, not only are ambiguities suppressed but also SNR will be seriously increased, especially at swath edges. Compared with conventional multiple sub-antennas in elevation, the SCORE technique seriously reduces the amount of data and the data rate in the spaceborne SAR system. The major drawbacks of this technique are the receive gain loss during pulse chasing and the useful information loss of multiple channels in elevation. It should be noticed that the receive gain loss caused by the mountain effect could not be neglected when the receive antenna exceeds 1 m [10].
The other example of beamforming in elevation for high-resolution wide swath imaging is intrapulse beamsteering, as shown in Figure 4. It enables illumination of a wide imaged swath with a sequence of narrow and high gain transmit antenna beams. Different from ScanSAR, multiple sub-pulses in a single PRI are transmitted to different sub-swaths in sequence, and echoes from different sub-swaths corresponding to different sub-pulses are received by all sub-apertures in elevation simultaneously. As a result, echoes corresponding to different sub-pulses will temporary overlap in the receiving window. As sub-pulses are transmitted by different elevation antenna beams, as shown in Figure 4, echoes could be separated by adjusting the receive beam pointing direction. Furthermore, null steering can also be adopted to suppress ambiguities caused by different sub-pulses.
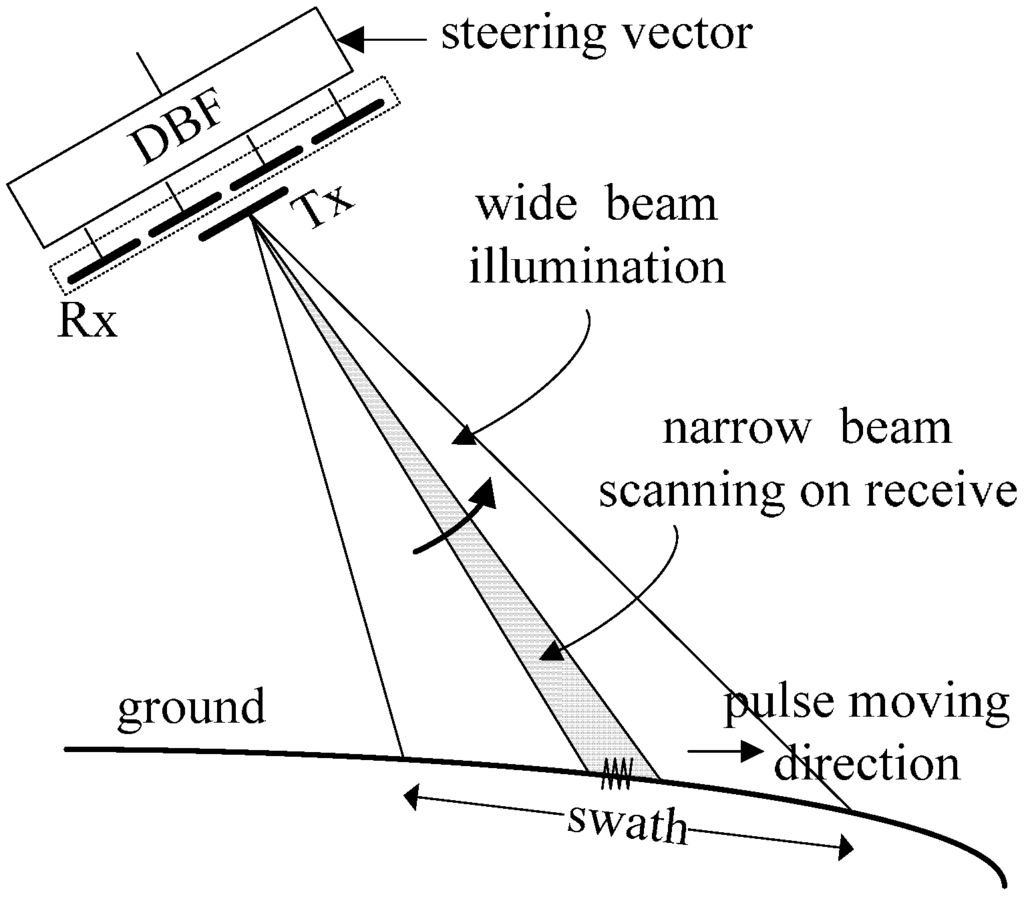
Figure 3.
SCan-On-REceive (SCORE) in elevation.
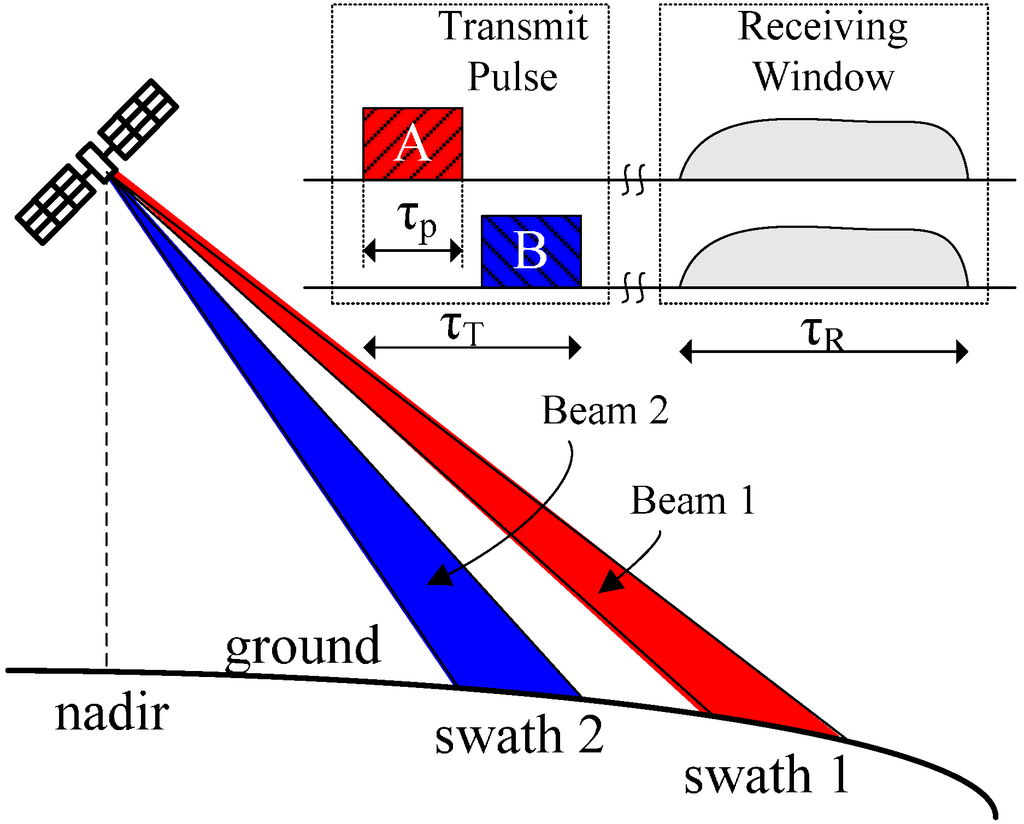
Figure 4.
Intrapulse beamsteering in elevation acquisition geometry.
2.2. ASTC-MIMO-TOPS
This innovative spaceborne ASTC-MIMO-TOPS SAR system is mainly based on the TOPS mode, which has wide swath imaging capability but a coarse azimuth resolution. The modified ASTC-MIMO technique is used to improve the obtained azimuth resolution of the TOPS mode, and DBF on receive in elevation is adopted to suppress ambiguity energy and improve the system SNR. Compared with other MIMO-SAR systems with phase coded orthogonal waveforms, the cross-correlation noise between imperfect orthogonal waveforms could be eliminated in ASTC-MIMO-SAR due to its special code characteristics and pulse compression method of ASTC waveforms. However, in conventional ASTC-MIMO-SAR systems, four sub-pulses are transmitted by two separated sub-apertures during two pulse repetition intervals (PRIs), as shown in Figure 2b, and it requires a doubled PRF than the nominal MIMO-SAR system. Moreover, the long delay between different sub-pulses due to the low PRF in HRWS SAR systems makes the time varying channel variance become more significant, which will degrade the diversity and SNR performance. To overcome two main drawbacks in the conventional ASTC-MIMO-SAR system, a pair of sub-pulses will be transmitted in a single PRI. Echoes corresponding to sub-pulses with different waveforms can be extracted through the steering sharp receive beam based on the relation between the time delay and the looking angle in the SAR imaging geometry. The steering sharp beam is generated by combining all signals received by different sub-apertures in elevation. It should be noted that just two transmitters could be adopted in ASTC-MIMO-SAR systems due to their special method of coding ASTC waveforms.
Furthermore, multiple transmitting beams to illuminate different sub-swaths could be adopted to improve the azimuth resolution of the burst mode. As a result, more sub-pulses should be transmitted by different transmitting beams with different time delays in the proposed ASTC-MIMO-TOPS mode. Figure 5 shows the imaging scheme of the proposed mode in both azimuth and elevation. As shown in Figure 5, two sub-antennas named T1 and T2 transmit orthogonal ASTC waveforms, and the larger receive antenna divided into M sub-apertures in azimuth is used to receive echoes. This scheme could obtain effective phase centers in a single PRI, which is more than the number of effective phase centers in the single-input multiple-output (SIMO) SAR system with the same antenna. In elevation, two sub-swaths (for example, sub-swath 1 and sub-swath 3, as shown in Figure 5b) are illuminated in sequence by transmitting different sub-pulses via different elevation beams. This means that the TOPS mode with four sub-swaths only requires a two-burst imaging scheme for such wide swath coverage, as shown in Figure 5b, and the obtained azimuth resolution of the TOPS mode would be only about twice rather than four times coarser than the stripmap mode with the same case. To separate echoes corresponding to different sub-pulses, the high gain sharp receive beams generated by a large elevation antenna are scanned to receive desired echoes, while unwanted echoes of other sub-pulses are received with a very low antenna gain and could even be neglected. Echoes of different sub-swaths seem to be more easily separated via DBF in elevation than echoes corresponding to different sub-pulses for the same sub-swath based on the side-looking SAR imaging geometry.
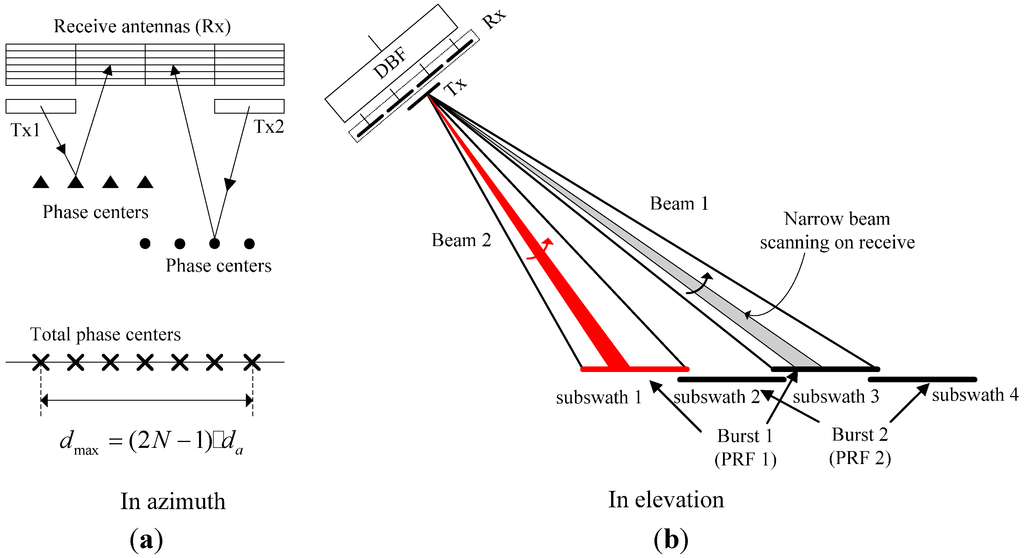
Figure 5.
ASTC-MIMO-TOPS imaging scheme in both azimuth and elevation.
Both sub-pulses being transmitted into different sub-swaths and a pair of phase coded sub-pulses of ASTC waveforms should be transmitted in a single PRI. Therefore, two different transmitting time sequences can be adopted in the proposed ASTC-MIMO-TOPS mode, as shown in Figure 6. With the transmitting time sequence shown in Figure 6a, the beam pointing direction in elevation only needs to be adjusted twice while transmitting different sub-pulses in a single PRI. However, this method leads to a shorter time delay between two adjoining sub-pulses for the same sub-swath, which requires a larger antenna in elevation to generate a narrower receive beam to distinguish echoes corresponding to different sub-pulses for the same swath. The other transmitting time sequence shown in Figure 6b, which changes the order of the transmitted small duration sub-pulses, requires four adjustments to the elevation beam transmit direction in a single PRI. Although the number of adjustments to the beam direction increased, it brings a desirable result in the form of the longer time delay τd between two sub-pulses illuminating the same sub-swath, which can reduce the size of the whole receive antenna in elevation. In this paper, the second transmitting time sequence will be adopted, since it can reduce the complexity of the SAR system. Furthermore, the elevation beam steering can be expediently and quickly implemented via an active phased array antenna.
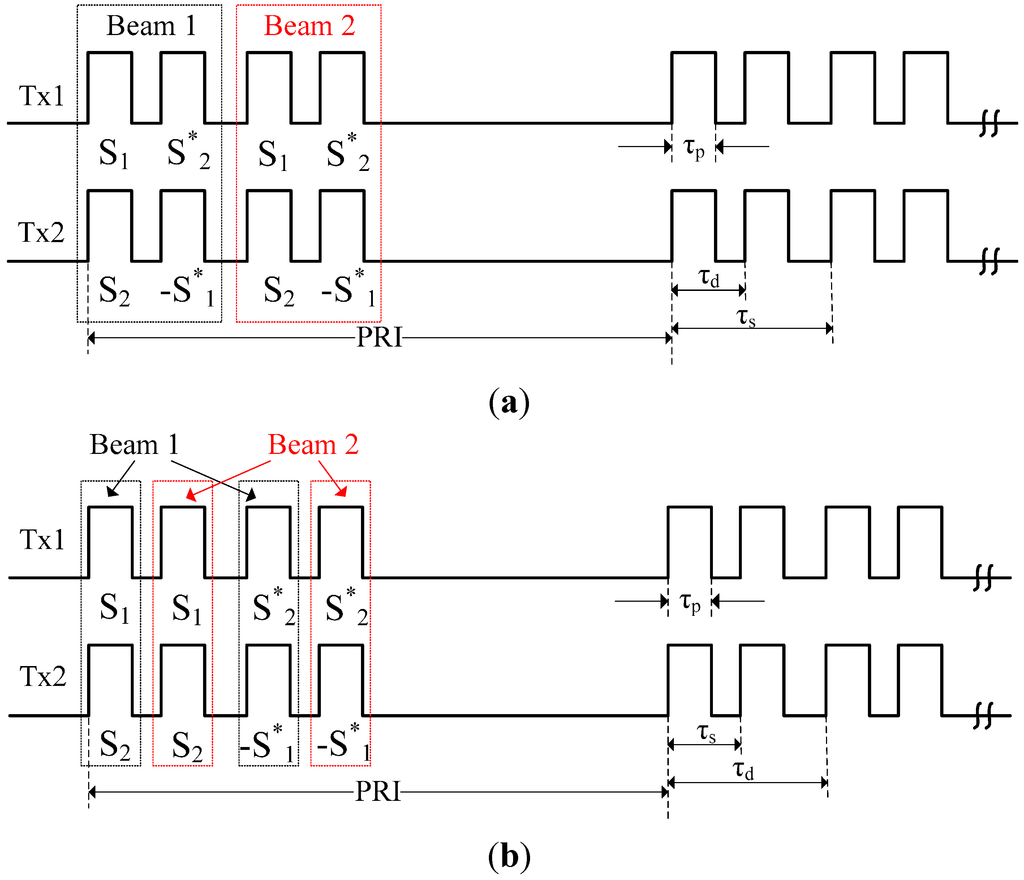
Figure 6.
The transmitting time sequence of ASTC-MIMO-TOPS mode. (a) The first transmitting time sequence. (b) The second transmitting time sequence.
As the TOPS mode requires antenna beam steering in both azimuth and elevation, all transmit and receive sub-antennas should have the beam steering capability in both azimuth and elevation. The configuration of the whole receive antenna is shown in Figure 7; it consists of multiple phased array sub-antennas whose azimuth beam steering and elevation beam scanning on receive are controlled by the steering raw and the elevation scanning vector, respectively. The steering raw in azimuth and the scanning vector in elevation can be preloaded onboard with the system requirement according to the designed SAR imaging geometry. Echoes from multiple along-track (in azimuth) spatial channels can be combined coherently via azimuth signal reconstruction algorithms in [19,20,21,22] to suppress azimuth ambiguity energy, while signals received by all sub-apertures in elevation are combined to form a sharp and high gain steering beam to extract spatial diversity and suppress range ambiguous energy. Azimuth beam steering is implemented by an analog beam-forming (ABF), and elevation beam scanning is achieved by a DBF net for each sub-antenna as shown in Figure 5. Azimuth beam steering is operated in the slow time domain, while the scanning on receive in elevation is taken in the fast time domain. Although the DBF net can also be adopted to control the azimuth beam steering law, it requires more analogue-to-digital (A/D) converters, which leads to a seriously increased system load, cost, and complexity.
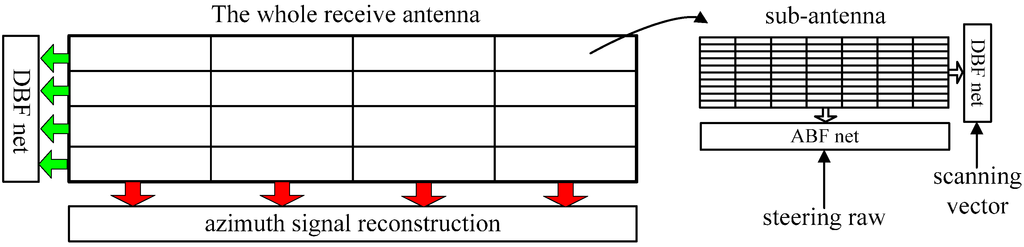
Figure 7.
The structure of the whole receive antenna.
3. Signal Processing
As the ASTC-MIMO-TOPS mode is combined with digital beam-forming (DBF) in elevation and multi-aperture SAR signals reconstruction in azimuth, there are five major processing steps to handle the raw data of this mode: DBF on receive for each sub-array antenna in elevation; spatial processing in elevation to implement echoes separation corresponding to different sub-pulses transmitted by the same sub-antenna in azimuth to illuminate the same sub-swath; ASTC decoding; azimuth signal reconstruction; and monostatic TOPS SAR imaging. The block diagram of raw data processing of the proposed mode is shown in Figure 8.
3.1. DBF on Receive for Each Sub-Array in Elevation
Although different sub-pulses used to illuminate different sub-swaths are transmitted through different elevation beams, their corresponding echoes are still received by the whole antenna and recorded in the receiving window, similar to range ambiguities obtained through sidelobes of the receive antenna pattern in elevation. However, echoes from different sub-swaths could be separated by the steering receive beam, which is controlled by the receive array weighting vector and generated by each sub-antenna in elevation. Furthermore, to suppress range ambiguities and interference between echoes from different sub-swaths, the null steering method can be used to receive echoes and transmit sub-pulses, which makes ambiguity and interference energy arrive at the receive antenna with a very low antenna gain, as shown in Figure 9. In this simulation, the designed system parameters are listed in Table 1.
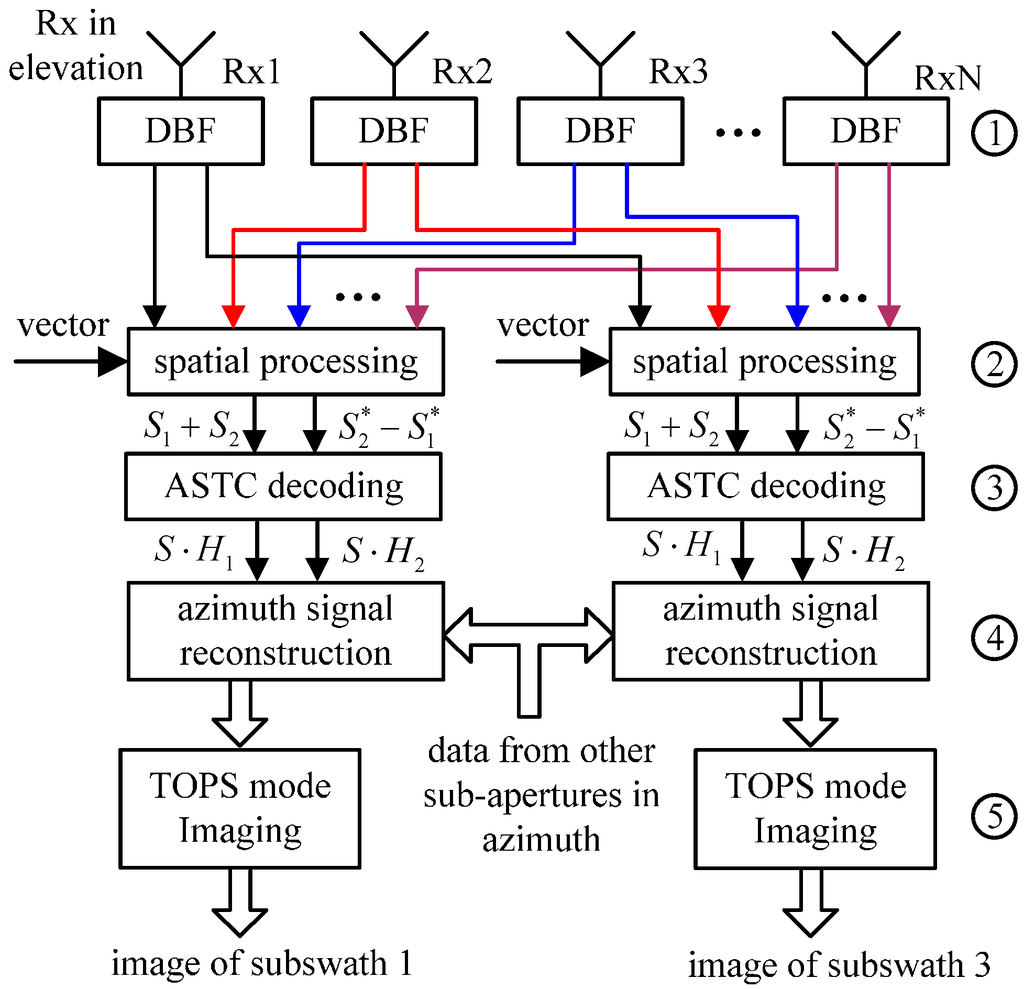
Figure 8.
The block diagram of raw data processing of the proposed mode.
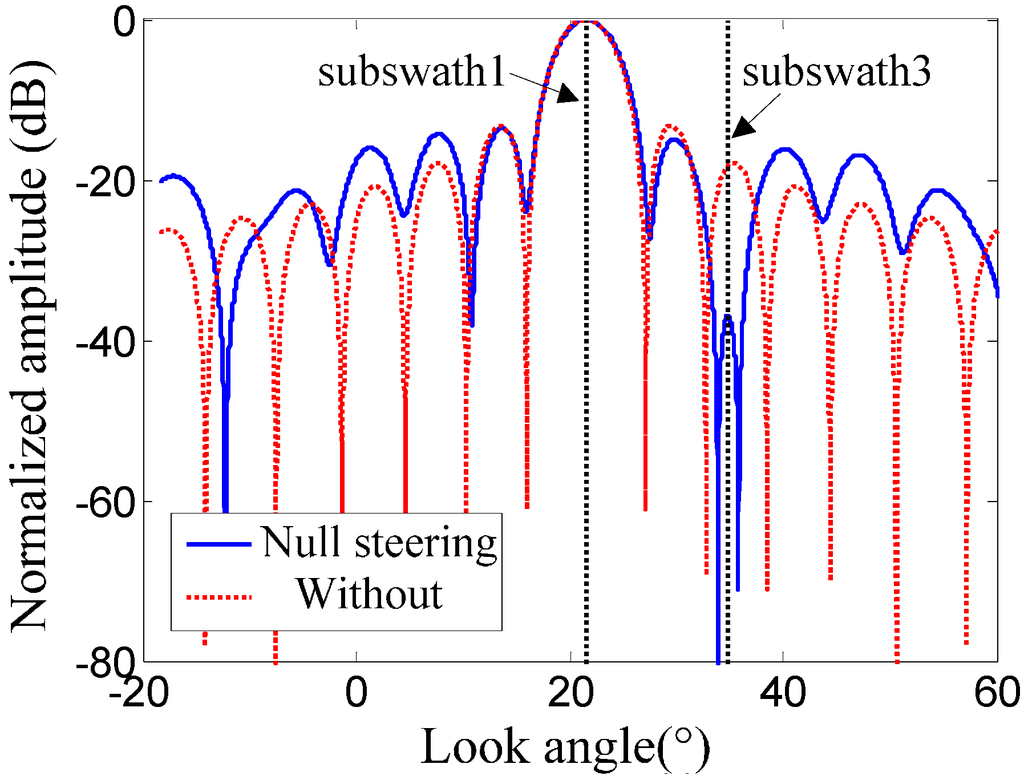
Figure 9.
Antenna beam pattern with null steering for range ambiguous suppression.

Table 1.
System parameters and requirements.
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Carrier frequency | 9.65 GHz |
| Sensor height (over earth) | 630 km |
| Sensor velocity | 7545 m/s |
| Incident angle range | 18°~50° |
| Transmit sub-antenna size | 2.4 m × 0.3 m |
| Transmit sub-antenna T/R elements | 24 × 15 |
| Azimuth receive antenna length | 9.6 m |
| Azimuth receive sub-antennas | 4 |
| Peak Tx Power | 2880 W |
| System temperature | 300 K |
| Pulse duration | 40 μs |
| Pulse bandwidth | 100 MHz |
| Sampling frequency | 120 MHz |
| Noise figure and system losses | 5.7 dB |
| Boltzmann constant | 1.38 × 10−23 J/K |
| RASR, AASR | <−24 dB |
| NEσ° | <−20 dB |
| BAQ | 8:3 |
| Operation time in a single orbit | 200 s |
As the side-looking angle of each sub-swath is considered after the system design, the receive array vector can be preloaded on the satellite to reduce the system complexity. In this paper, we use multiple sub-array antennas in elevation to receive echoes to overcome the major drawbacks of the novel SCORE technique onboard (receive gain loss from topography and elevation information loss). Furthermore, the block diagram of implementation of the SCORE technique for each sub-array antenna is shown in Figure 10. It is assumed that K digital channels, each of which consists of P element antennas, are adopted in each sub-array antenna. To form a sharp and high gain receive beam, the data stream of the sub-aperture k is multiplied by a time varying complex coefficient wn,k(τ) and shifted by a time delay Dn,k. The complex coefficient and the time delay can be expressed as follows [23]:
where d is the distance between the phase centers of two adjacent sub-apertures in elevation, θ(τ) is the steering angle as a function of the fast time τ, Kr is the linear frequency modulation rate, and τc indicates the fast time of the swath center. Afterwards, the data streams from different sub-apertures are summed up to result the output signal, which is provisionally saved onboard in an individual channel and would be later downloaded to the ground. The complex multiplication, time shifting, and signal summation are adopted to form a narrow and high gain receive beam, which follows the radar pulse as it travels on the ground, as shown in Figure 10.
3.2. Spatial Processing in Elevation
For example, sub-pulses with different waveforms S1 and S2* are transmitted in sequence by T1 with a short time delay through the same elevation transmit beam. Afterwards, the time delay between the two sub-pulses means that echoes of targets with different slant ranges corresponding to different sub-pulses are received and recorded in the same position of the receiving window. However, according to the side-looking SAR imaging geometry, they arrive at the receive antenna with different angles, and different angular diversities can be extracted by DBF in elevation. To distinguish between different looking angles, the total size of the receive antenna in elevation should be:
where Rfar and θinc,max are the farthest slant range and the maximum incident angle, respectively. Afterwards, the signals received by different elevation sub-array antennas should be combined to form a sharper receive beam and achieve null steering operation to separated temporal mixed echoes.
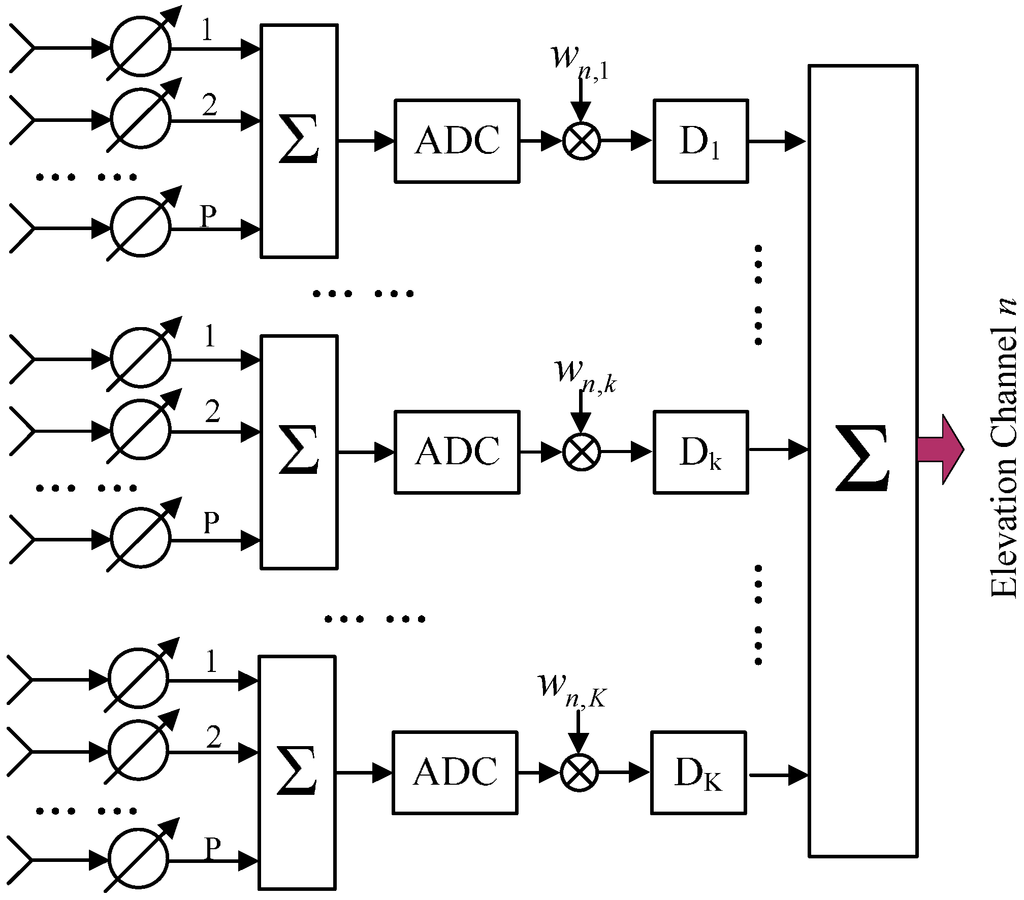
Figure 10.
The block diagram of implementation of SCORE.
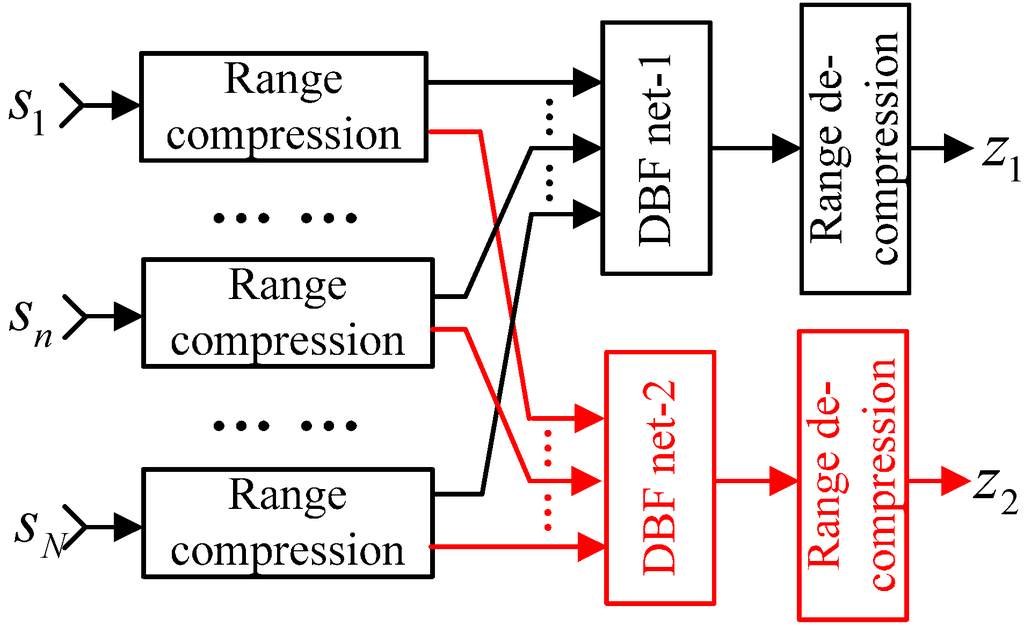
Figure 11.
The block diagram of spatial processing in elevation.
In conventional spaceborne SAR systems, the large pulse duration is usually adopted to achieve the desired SNR, and the signal energy of the scattered targets will span the whole pulse duration before range compression. Moreover, the narrow receive beams of sub-array antennas are continuously steered during the whole receive time, and echo of each point target will be received with a time variant antenna gain. It is hard to extract different angular diversities from the mixed signals. Therefore, range compression should be taken in each receive channel before combining all signals in elevation into one. After taking range compression, received signals by multiple elevation channels can be expressed as matrix form by:
with
where S(τ) represents the echoes received by multiple elevation sub-array antennas in elevation, Z(τ) indicates the echoes corresponding to sub-pulses with different polarizations, []T is the matrix transposed operator, dr is the height of the sub-array antenna in elevation, and θi(τ) is the looking angle corresponding to the i-th sub-pulse. Since θ1 ≠ θ2 for each range sample time, A(τ) is the matrix with column full rank, and its pseudo-inverse matrix A+(τ) can be calculated. Afterwards, by multiplying, the complex coefficient matrix S(τ) can be obtained as follows:
Compared with the real-time DBF operation onboard, namely SCORE, it can be seen that spatial processing is with the same principle and therefore named as the second DBF step on the ground. As the ASTC waveforms are compressed via the decoding matrix instead of the matched filter, the compressed signals should be de-compressed as shown in Figure 11.
3.3. ASTC Decoding
After spatial processing in elevation to separate echoes which are recorded in the same position of the receiving window, ASTC waveforms are decoded with the decoding matrix defined as follows:
with
where Rref1 and Rref2 are the reference range in channel 1 and 2, respectively. The decoding processing is the same as in Equation (3). Figure 12 shows the compression results handled by the ASTC decoder, the matched filter of s1, and the matched filter of s2. To distinguish echoes corresponding to different transmitters, |H1|:|H2| = 4:1 is assumed in this simulation. From Figure 12, it can be seen that the ASTC waveforms consisting of chirp signals are well compressed via the ASTC decoder, while the cross-correlation noise between the up and down chirp signals is very high, handled by the traditional matched filter of the chirp signal.
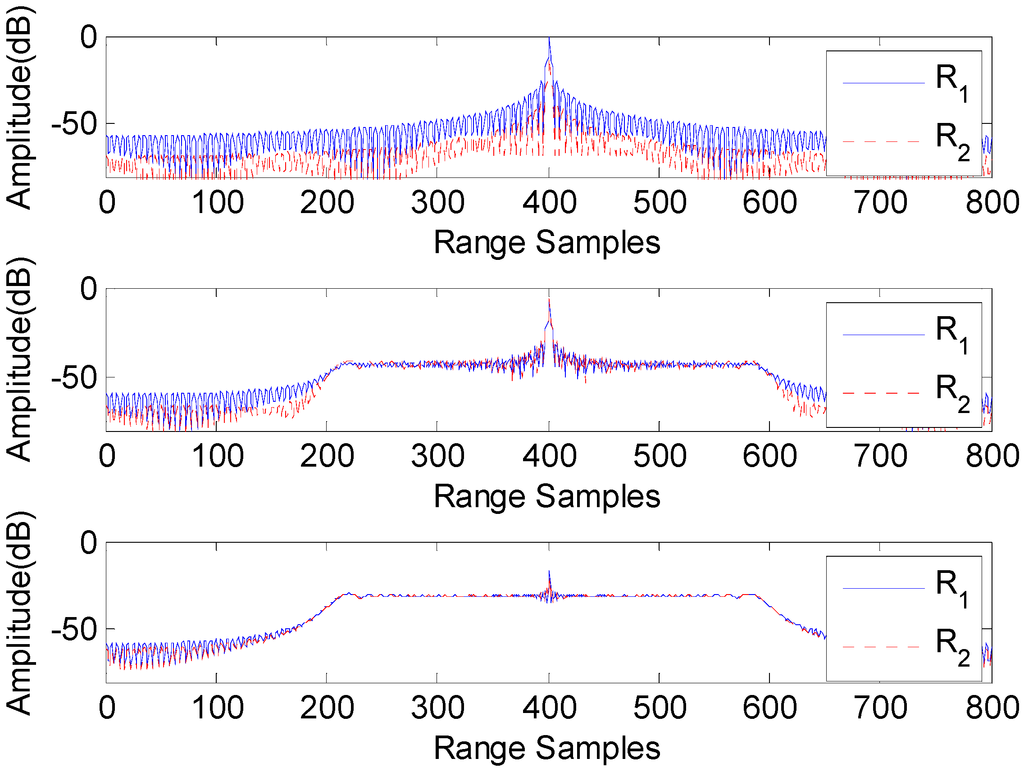
Figure 12.
Range compressions by ASTC decoding (top), the first matched filter (middle), and the second matched filter (bottom).
3.4. Azimuth Signal Reconstruction
Leading to uniform spatial and time sampling of the received signal in azimuth in such system, the operated system PRF should be satisfied with the following relation:
where da is the distance between two adjacent sub-apertures in azimuth. However, such a rigid selection of the selected PRF may be in conflict with the timing diagram selection and may exclude the opportunity to use an increased PRF for the improved azimuth ambiguity suppression.
There are two major methods to resolve the problem of nonuniform sampling of multichannel SAR signal. One is reconstruction algorithms, which is based on resolving a system of linear equations to unambiguously recover the aliased azimuth spectrum; the other is space-time approach null steering, which is based on adjusting weighting coefficients of azimuth channels to steer nulls to angles of the ambiguous Doppler frequencies.
To avoid the Doppler spectrum aliasing, the TOPS raw data of a single burst in each azimuth channel could be divided into several data blocks before the FFT operation in azimuth. Afterwards, each block is with its individual Doppler centroid, which should be carefully maintained during the azimuth multichannel data reconstruction. An efficient full-aperture multichannel TOPS raw data preprocessor is proposed in [23], which avoids any data block divisions.
3.5. Monostatic TOPS SAR Imaging
Several imaging algorithms for the TOPS mode have been proposed in recent years [4,6,24,25,26]. After the abovementioned processing steps, the resulting raw data can be processed as the monostatic TOPS raw data.
4. System Example
To demonstrate the innovative proposed multichannel TOPS mode SAR system, the designed system example is given with the system parameters listed in Table 1. The selection of some important system parameters will be presented in detail in this section. Moreover, its system performances are analyzed and an imaging experiment on simulated point targets is carried out to validate the proposed system for its spaceborne HRWS imaging capacity.
4.1. System Example
As nadir echoes can be reduced by a careful design of transmit antenna pattern and DBF on receive in elevation with null steering via a large receive antenna, the dark gray strips shown in Figure 13 only indicate the direction signal reception. The incident angle varies from 19.3° to 47.7° to obtain about 400 km swath coverage; PRF of 1240 Hz and 1140 Hz, respectively, are chosen for the two bursts.
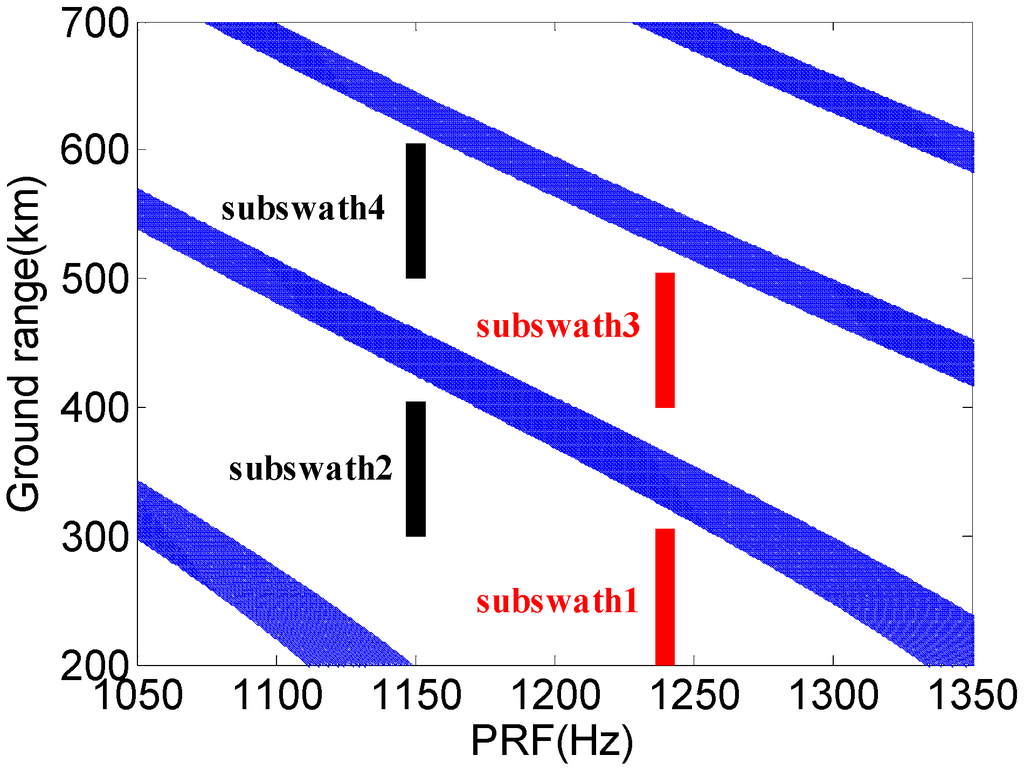
Figure 13.
The selected timing diagram.
With the maximum incident angle of 47.7° and the farthest slant range 890 km, Figure 14 shows the relation between the short time delay and the minimum antenna height. A total receive antenna with a height of 4.4 m, which consists of four sub-array apertures, is chosen, while two sub-pulses are transmitted in sequence with a time delay of 50 μs.
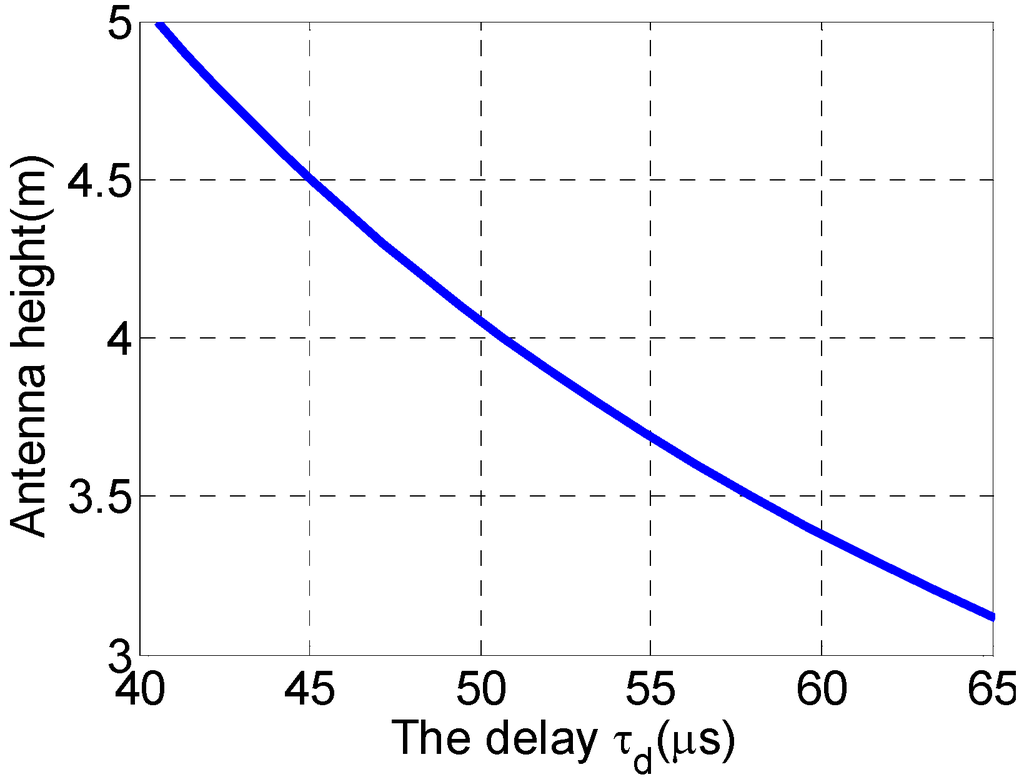
Figure 14.
The receive antenna height selection.
To obtain the desired azimuth resolution ρaz, the azimuth beam rotation rate can be approximately described as follows:
where La is the transmit antenna length and Rc is the slant range of imaging center in the sub-swath. To obtain continuous TOPS-SAR image in each sub-swath, the timeline should be
where TB_i is the burst duration for the burst i; ϑ0 is the angular interval to be exploited for azimuth data focusing; and ε is the ratio between the overlap coverage and the single burst effective imaging scene. This leads to a linear system of two equations in the unknown TB_i in the two-burst mode MIMO-TOPS SAR system. It should be noted that two sub-swaths are simultaneously illuminated during each burst and Rc_i is the slant range in the farther sub-swath for the burst i. Different sub-swaths with the same burst require different azimuth beam steering laws for the same azimuth resolution, but we chose the same azimuth beam steering law to reduce the system complexity. The detailed designed results of the presented ASTC-MIMO-TOPS imaging mode are listed in Table 2.

Table 2.
The designed system example results of the proposed mode.
| Swath 1 | Swath 2 | Swath 3 | Swath 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Incident angle (°) | 19.3–28.3 | 27.5–35.5 | 35.1–42.1 | 41.7–47.7 |
| PRF(Hz) | 1240 | 1150 | 1240 | 1150 |
| Slant range (km) | 681.8 | 726.6 | 783.9 | 850.2 |
| Swath depth (km) | 105 | 105 | 105 | 100 |
| Burst duration (s) | 2.09 | 2.13 | 2.09 | 2.13 |
| Rotation rate (°/s) | 0.88 | 0.81 | 0.88 | 0.81 |
| Date rate (Gbps) | 6.90 | 7.12 | 6.90 | 7.12 |
| AASR(dB) | −24.32 dB | −23.18 dB | −24.32 dB | −23.18 dB |
4.2. Performance Analysis
Different from the ScanSAR mode, the azimuth ambiguity to signal ratio (AASR) in the TOPS mode will almost be invariable in each sub-swath and the small decline caused by the limited squinted angle may even be neglected. The range ambiguity to signal ratio (RASR) in each sub-swath varies from near to far range and is less than −30 dB, as shown in Figure 15a, which takes account of the two DBF operation steps (real time SCORE onboard and spatial processing on the ground) in elevation.
In the SAR system, Noise Equivalent Sigma Zero (NEσ°) is a very important performance parameter that is a measure of the sensitivity of the system to areas of low radar backscatter. It represents the value of the backscatter coefficient corresponding to a signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), where SNR = 1. The NEσ° is a function of antenna gain, which can be given as follows:
where R is the average transmit and receive slant range, θi is the incident angle, γ is the local slope angle, K is the Boltzmann constant, T is the radar receiver temperature, Br is the bandwidth of the radar pulse, F is the noise figure, and Latm and Lsys represent the system losses and the atmospheric losses, respectively. The NEσ° values shown in Figure 15b in all sub-swaths are below −22 dB and satisfy the system requirements listed in Table 2.
Since two sub-swaths such as sub-swath 1 and sub-swath 3 are simultaneously illuminated and imaged, their date rates are the same as shown in Table 2. As a result, the down link speed requirement is 7.12 Gbps. Furthermore, the operation time is a single orbit of 200 s, which requires an on-board data-storage requirement of about 180 GB.
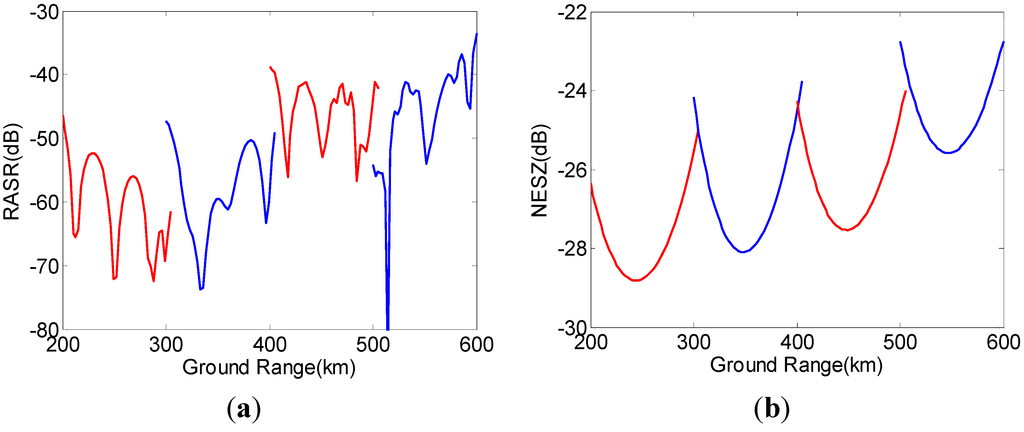
Figure 15.
The selected timing diagram. (a) RASR. (b) NESZ.
4.3. Imaging Simulation
To further validate the proposed high-resolution wide swath imaging mode, an experiment on simulated point targets is carried out. The designed scene consisting of nine point targets is shown in Figure 16a, and its imaging result is shown in Figure 16b. Contour plots of three point targets (P1, P2, and P3) are shown in Figure 16c–e, all of which show well-focused behavior and validate the proposed imaging mode. Imaging parameters of point targets P1, P2, and P3 including resolution, peak side lobe ratio (PSLR), and integrated side lobe ratio (ISLR) are evaluated and listed in Table 3.

Table 3.
Imaging parameters of simulated point targets.
| Azimuth | Range | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resolution (m) | PSLR (dB) | ISLR (dB) | Resolution (m) | PSLR (dB) | ISLR (dB) | |
| Theoretical | 1.20 | 13.26 | 9.80 | 1.33 | 13.26 | 9.80 |
| P1 | 1.21 | 13.24 | 9.94 | 1.33 | 13.26 | 9.83 |
| P2 | 1.21 | 13.24 | 9.91 | 1.33 | 13.26 | 9.87 |
| P3 | 1.21 | 13.24 | 9.97 | 1.33 | 13.26 | 9.78 |
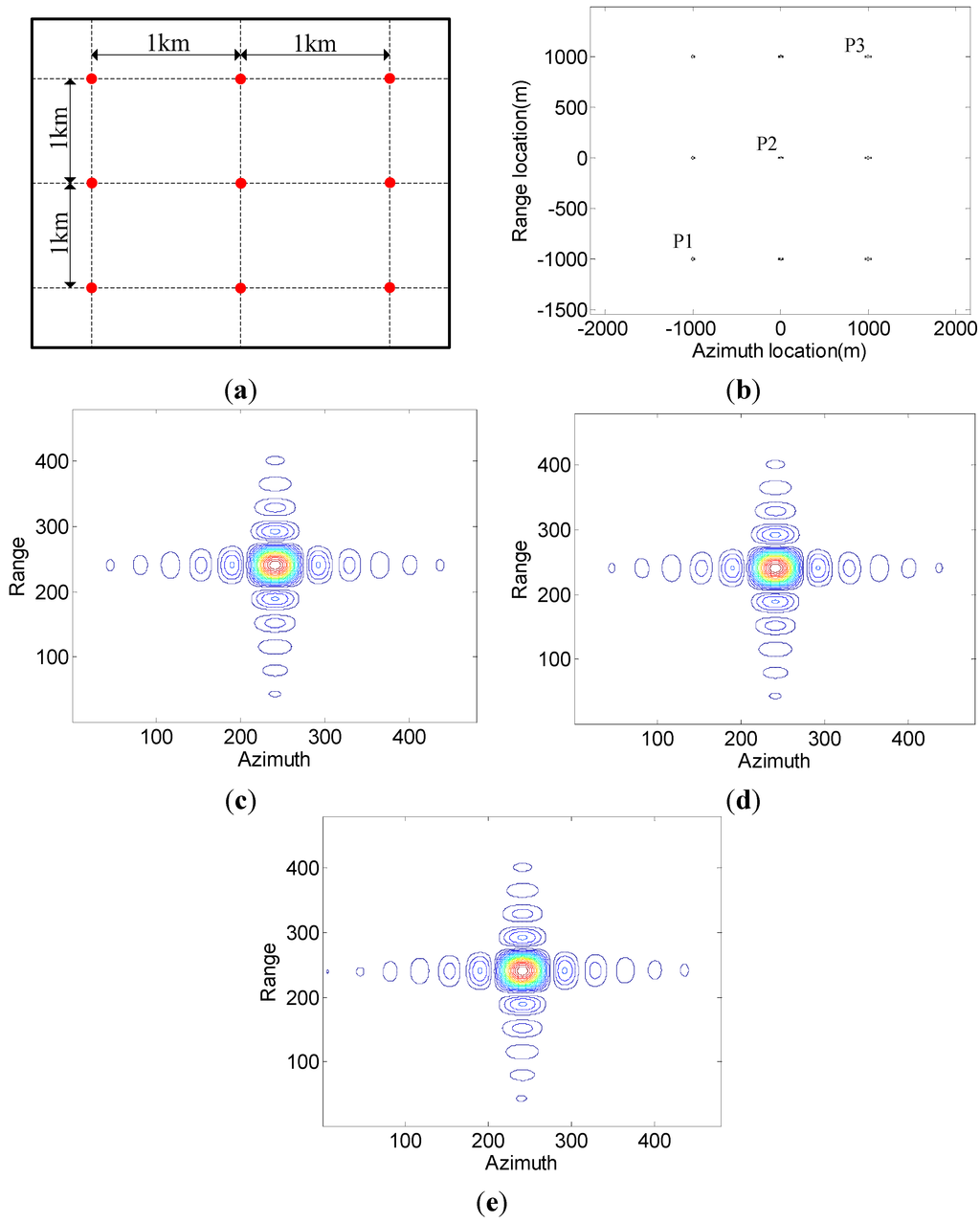
Figure 16.
Imaging experiment on simulated point targets. (a) The designed scene. (b) Imaging result of the designed scene. (c) Contour plots of P1. (d) Contour plots of P2. (e) Contour plots of P3.
5. Conclusions
In this paper, the novel ASTC-MIMO-TOPS mode combined with DBF in elevation is proposed for HRWS imaging. Different from conventional spaceborne SAR systems, four sub-pulses are transmitted in a single PRI by each transmitter to improve the impaired azimuth resolution in TOPS. Echoes corresponding to different sub-pulses are separated by the proposed two-step DBF technique in elevation, which takes advantage of the SCORE technique via the sub-array antenna onboard and the posterior spatial processing step on the ground. This approach reduces the high data rate and the obvious effect of varying mountain height during pulse chasing. The designed example with 400 km swath width and 3 m azimuth resolution and its corresponding performance analysis results are presented to validate the proposed imaging scheme. However, the major disadvantage of such a mode is the high complexity of system and data processing. The antenna with 9.6 m length and 4.4 m height including lots of transmit/receive (T/R) modules will increase the load and the cost of the spaceborne SAR system. However, with the fast development of the electronic technique, this problem will be resolved in future.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 61201433.
Author Contributions
This paper was organized and written by Pingping Huang, and the presented imaging mode was proposed by Wei Xu.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Currie, A.; Brown, M.A. Wide-swath SAR. IEEE Proc. F Radar Signal Process. 1992, 139, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, A.; Johnson, W.T.K.; Huneycutt, B.; Jordan, R.; Hensley, S.; Siqueira, P.; Curlander, J.C. The “myth” of the minimum SAR antenna area constraint. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzner, J.; Bamler, R. Burst-mode and ScanSAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 1917–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Zan, F.; Monti Guarnieri, A. TOPSAR: Terrain observation by progressive scans. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 2352–2360. [Google Scholar]
- Prats, P.; Scheiber, R.; Mittermayer, J.; Meta, A.; Moreira, A. Processing of sliding spotlight and TOPS SAR data using baseband azimuth scaling. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 770–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meta, A.; Mittermayer, J.; Prats, P.; Scheiber, R.; Steinbrecher, U. TOPS imaging with TerraSAR-X: Mode design and perfomance analysis. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2010, 48, 759–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belcher, D.P.; Baker, C.J. High resolution processing of hybrid stripmap/spotlight mode SAR. IEE Proc. Radar Sonar Navig. 1996, 143, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Deng, Y.; Wang, R. Multichannel synthetic aperture radar systems with a planar antenna for future spaceborne microwave remote sensing. IEEE Aerosp. Electron. Syst. Mag. 2012, 46, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junghyo, K.; Alicja, O.; Werner, W. Investigation of MIMO SAR for interferometry. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar (EUSAR), Munich, Germany, 10–12 October 2007.
- Krieger, G.; Gebert, N.; Moreira, A. Multidimensional waveform encoding: A new digital beamforming technique for synthetic aperture radar remote sensing. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 46, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-Q. Space-time coding MIMO-OFDM SAR for high-resolution imaging. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 3094–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-Q. Virtual antenna array analysis for MIMO synthetic aperture radars. Int. J. Antennas Propag. 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-Q. Mitigating range ambiguities in high-PRF SAR with OFDM waveform diversity. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 10, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christallini, D.; Pastina, D.; Lombardo, P. Exploiting MIMO SAR potentialities with efficient cross-track constellation configurations for improved range resolution. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebert, N.; Krieger, G.; Younis, M.; Bordoni, F.; Moreira, A. Ultra wide swath imaging with multi-channel ScanSAR. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Booston, MA, USA, 7–11 July 2008.
- Suess, M.; Grafmueller, B.; Zahn, R. A novel high resolution, wide swath SAR system. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Sydney, NSW, Australia, 9–13 July 2001; pp. 1013–1015.
- Suess, M.; Wiesbeck, W. Side-Looking Synthetic Aperture Radar System. EP 1 241 487, 18 September 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Krieger, G.; Gebert, N.; Moreira, A. Digital beamforming techniques for spaceborne radar remote sensing. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar (EUSAR), Dresden, Germany, 16–18 May 2006.
- Krieger, G.; Gebert, N.; Moreira, A. Unambiguous SAR signal reconstruction from nonuniform displaced phase center sampling. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 1, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Su, T.; Bao, Z. Generation of wide-swath and high-resolution SAR images from multichannel small spaceborne SAR systems. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2005, 2, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, M.; Fischer, C.; Wiesbeck, W. Digital beamforming in SAR systems. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 1735–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebert, N.; Krieger, G.; Moreira, A. Digital beamforming on receive: Techniques and optimization strategies for high-resolution wide-swath SAR imaging. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2009, 45, 564–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Huang, P.; Wang, R.; Deng, Y. Processing of multichannel sliding spotlight and TOPS synthetic aperture radar data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 4417–4429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Huang, P.; Deng, Y. MIMO-TOPS mode for high-resolution ultra-wide-swath full polarimetric imaging. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2011, 121, 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Huang, P.; Deng, Y.; Sun, J.; Shang, X. An efficient approach with scaling factors for TOPS-mode SAR data focusing. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2011, 8, 929–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Huang, P.; Deng, Y. TOPSAR data focusing based on azimuth scaling preprocessing. Adv. Space Res. 2011, 48, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).