Abstract
With the development of Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) in terms of multi-band, multi-polarization and high-resolution data, space radar remote sensing for archaeology has become a potential field for research. Nevertheless, the archaeological detection capability of this technology has so far not been fully assessed. This paper is a pioneering effort to assess the potential of satellite SAR X-band data in the detection of archaeological marks. We focus on the results obtained from a collaborative contribution jointly carried out by archaeologists and remote sensing experts in order to test the use of COSMO-SkyMed data in different contexts and environmental conditions. The methodological approaches we adopted are based on two different feature-enhancement procedures: (i) multi-temporal analysis performed to reduce noise and highlight archaeological marks; (ii) single-date analysis to assess the ability of the single SAR scene to detect archaeological features like with optical remote sensing. Results from multi-temporal data analysis, conducted using 40 scenes from COSMO-SkyMed X-band Stripmap data (27 February to 17 October 2013), enable us to detect unknown archaeological crop, soil, and shadow marks representing Luoyang city, dating from the Eastern-Han to Northern-Wei Dynasties. Single-date analyses were conducted using COSMO-SkyMed Spotlight scenes acquired for Sabratha (Libya) and Metapontum (southern Italy). These case studies were selected because they are characterized by diverse superficial conditions (desert and Mediterranean area) and archaeological marks (crop, soil and shadow). The results we obtained for both of them show that even a single SAR X-band acquisition is a feasible and effective approach for archaeological prospection. Overall, the methodological approach adopted demonstrated that both multi-temporal and single-date analysis are suitable for the enhancement of archaeological and palaeoenvironmental features.
Keywords:
synthetic aperture radar; archaeological mark; Luoyang; Metapontum; Sabratha; COSMO-SkyMed 1. Introduction
Starting from aerial photos, optical satellite remote sensing has played an important role in the field of archaeological investigations over the last few decades [1,2,3]. Shadow, crop and soil marks [4,5,6,7] are well-known indicators of the presence of ancient buried and surface remains widely used for archaeological photo-interpretation. Their visibility from space is due to the fact that the presence of emerging, shallow and buried remains modifies albedo as well as physical and chemical surface parameters compared to the surrounding areas. Over the years, several papers have analyzed and discussed the use of optical satellite sensors to detect archaeological marks. In particular, before the availability of Very High Resolution (VHR) satellite data (i.e., with a spatial resolution of around 1 m and less), many authors focused on the use of Landsat, SPOT and ASTER or declassified satellite data [8,9,10].
The advent of VHR satellite imagery, such as that provided by Ikonos and QuickBird, has significantly increased interest in space archaeology, as is evident from the greater number of publications in the field spanning from the detection of previously unrecorded sites to greater knowledge and improve management and protection of archaeological areas. Up to now, the use of optical satellite imagery along with aerial photographs in archaeology has been more extensive than radar data. It is nevertheless important to consider that the occurrence of SIR-A/B/C, AIRSAR and SRTM SAR data from the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA)/Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) opened up an era of radar remote sensing in archaeology back in the 1980s at desert sites [11,12] and tropical regions [13,14].
Recently, archaeological investigations conducted by SAR data have moved forward to another stage focusing on archaeological detection and monitoring using backscattering change detection [15,16], polarimetric enhancement [17,18], penetration [19] and deformation anomaly diagnosis [20,21,22] utilizing second-generation spaceborne SAR systems represented by multi-band, polarization and high-resolution systems, e.g., ALOS PALSAR, TerraSAR-X/TanDEM-X, COSMO-SkyMed and Radarsat-2.
All the above-mentioned investigations deal with the penetration or polarimetric capabilities of satellite SAR L and C-band systems, but no one has systematically investigated the potentiality of the SAR X-band to detect archaeological shadow, crop and soil marks, though some experiments have been proposed [23] using simulated data and have correlated shadow/dark marks seen in the SAR images to archaeological features [15,24].
Only in recent years have some investigations been carried out using aerial [25] and space SAR [26] to detect traces of archaeological interest. In particular, the NASA project [25] attempted to devise a systematic method and protocol to survey large areas merging aerial SAR and satellite multispectral data. COSMO-SkyMed data were used to obtain both images and DEMs, but they were considered less useful in detecting archaeological marks or materials associated with archaeological sites. In [26] the use of multitemporal COSMO-SkyMed as a first attempt at identifying known archaeological marks is proposed. In this case, the multi-temporal analysis was adopted to reduce the speckle noise that affects SAR data.
Although several achievements have been made in recent years, the exploitation of SAR remote sensing to detect archaeological marks is still in its infancy, especially for X-band data, such as COSMO-SkyMed (for additional details see [27]). Comparing the currently available satellite SAR systems operating in L and C-bands with those operating in X-band it is expected that the latter will provide information on a larger variety of small archaeological features mainly thanks to its greater geometric resolution.
This paper is a pioneering effort to assess the potential of satellite SAR X-band data in the detection of archaeological marks. We focus on the results obtained from a joint collaborative effort by archaeologists and remote sensing experts to test the use of high-resolution COSMO-SkyMed data in different contexts and environmental conditions. Significant test cases have been selected in Europe, Africa and Asia to extract information about landscape archaeology (e.g., palaeochannels, roads, etc.) as well as smaller features, such as walls and building structures. These research activities have been conducted in the framework of the Chinese-Italian bilateral project “Smart management of cultural heritage sites in Italy and China: Earth Observation and pilot projects” [28].
2. Problem Statement
2.1. Rational Basis for Archaeological Marks
Past human occupation and activities have left traces and marks on the territory including landscape alterations and environmental changes that can be recognized even after centuries and millennia. These are generally subtle traces due, for example, to the presence of scattered remains, such as artifacts, bone, pottery or clusters of building materials, which can still cause alterations that indicate the presence of archaeological sites. Of course, deposit and erosion processes and/or alluvial phenomena tend to mask these marks, which can be more easily detected from a “bird’s eye view” rather than from in situ studies. Aerial or satellite data are able to provide a synoptic view of the area and therefore make the recognition of patterns possible, facilitating the interpretation of single features. Moreover, human presence can also produce more subtle changes, such as those linked to the occurrence of organic material or ash introduced by prehistoric occupants and still visible today in terms of alteration to the soil composition and/or moisture content.
All these marks can be detected from space, since the alteration they produce can be revealed by satellite sensors as they can influence spectral response and radar return. Considering radar microwave systems, responses mainly depend on the superficial roughness, structure (shape and orientation), type and status of material, especially on dielectric properties. In particular, the main variations in dielectric property are principally due to soil moisture and the conductivity of target material.
2.1.1. Shadow Marks
In optical images, shadow marks can be seen in the presence of micro-topographic relief variations that can be made visible by shadowing in low sunlight angle conditions. On the other hand, in radar data, true shadows are very rare at commonly used angles of incidence. Only very steep slopes cause shadows. Therefore, archaeological microrelief (or shadow marks) are usually identifiable from surface roughness. Finally, geometric shapes facilitate the interpretation of the surface roughness as potential archaeological patterns.
2.1.2. Crop Marks
The presence of near surface archaeological deposits influences surface vegetation patterns due to the variation of water or other nutrients. There are two kinds of crop marks, including negative marks above wall foundations and positive marks above the damp or nutritious soil of buried pits and ditches [4]. The crop marks in SAR images are indicated by backscattering anomalies instead of the Near Infrared Red (NIR) spectral separability of optical remote sensing. Multi-temporal analysis is a feasible way of extracting backscattering anomalies linked to buried archaeological remains, particularly when SAR image acquisition covers an entire plant growth cycle. Generally, the crop mark is more evident in the early stage of plant growth, e.g., period from the time the crops revive to the elongation of the wheat.
2.1.3. Soil and Damp Marks
The occurrence of archaeological remains can change soil types and contents (e.g., nutrients, etc.) compared with their surroundings resulting in the well-known phenomenon of soil marks, which appear as a change of color or texture in the absence of vegetation cover. Soil marks could be detected using SAR images by exploiting backscattering anomalies induced by the variations in grain size, soil density and texture.
Damp marks appear on bare ground because buried archaeological remains can alter drainage capability and, in turn, water distribution. The detectability of damp marks is linked to soil type, climate and meteorological conditions, and therefore to acquisition time as well as to the spatial distribution and nature of the remains. Damp marks in SAR images are indicated by backscattering anomalies induced by moisture variation that determines the amplitude of the dielectric constant of soil. Increasing moisture may lead to an increase in radar backscattering due to the increase in the soil’s dielectric constant, while small ponds of water formed by heavy rain can increase specular reflectance locally (i.e., scattering on a nearly smooth surface) on the surface and therefore result in a dark area in the SAR image. Consequently, these marks may be more noticeable after heavy rain because the difference in the soil moisture between the underlying archaeological remains, and surrounding surfaces may be highlighted.
3. Archaeological Feature Extraction from SAR: Methodological Approaches
The extraction of archaeological features from SAR data is a tough challenge. One of the main issues is the low signal/noise ratio, especially considering the complexity of the target and the fact that modern landscapes may mask them. In this study we used X-band (3.1 cm wavelength) COSMO-SkyMed data. It is an Earth observation satellite constellation system run by the Italian Space Agency (ASI), and is intended for both military and civilian use. The constellation includes four identical satellites equipped with SAR sensors with global coverage. The first satellite was launched on 8 June 2007, and the last one on 5 November 2010. There are three basic types of imaging modes, including ScanSAR, Stripmap and Spotlight. In the ScanSAR mode, the sensor acquires large coverage (200 × 200 km) images with a coarse spatial resolution (pixel at 100 m). In the Stripmap mode the acquisition provides medium coverage (40 × 40 km) with fine resolution (pixel ranging from 3 to 5 m) and finally, Spotlight mode provides small coverage (10 × 10 km) with very high resolution (1 m).
Two data processing approaches were adopted (see Figure 1 and Figure 2). The first was based on the multitemporal processing of Stripmap HIMAGE data applied to a case study in China (Luoyang). The spatial resolution has been considered enough for the detection of the features expected in Luoyang (see Section 4.1).
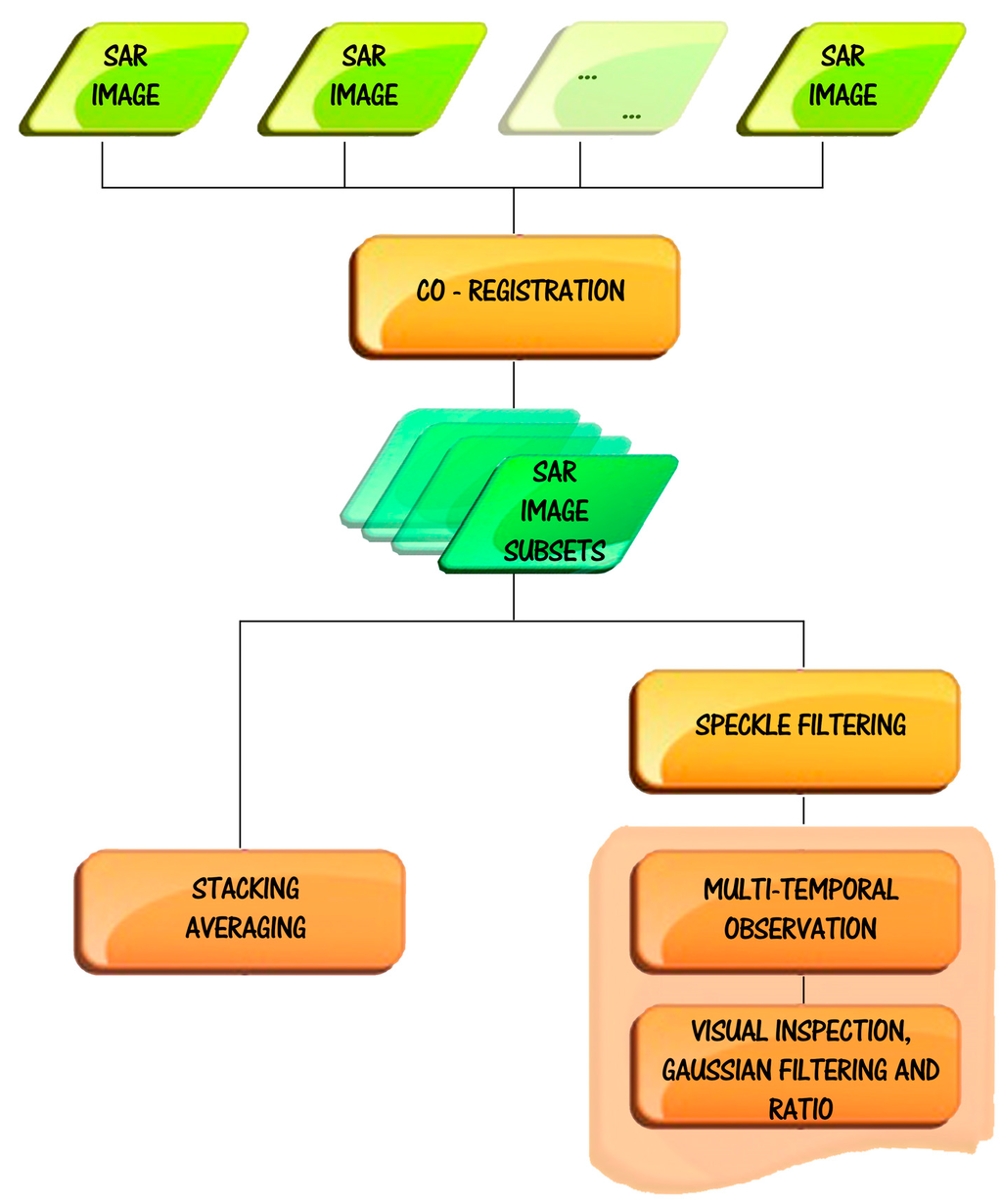
Figure 1.
Multi-temporal Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) data procedures for the enhancement of archaeological marks.
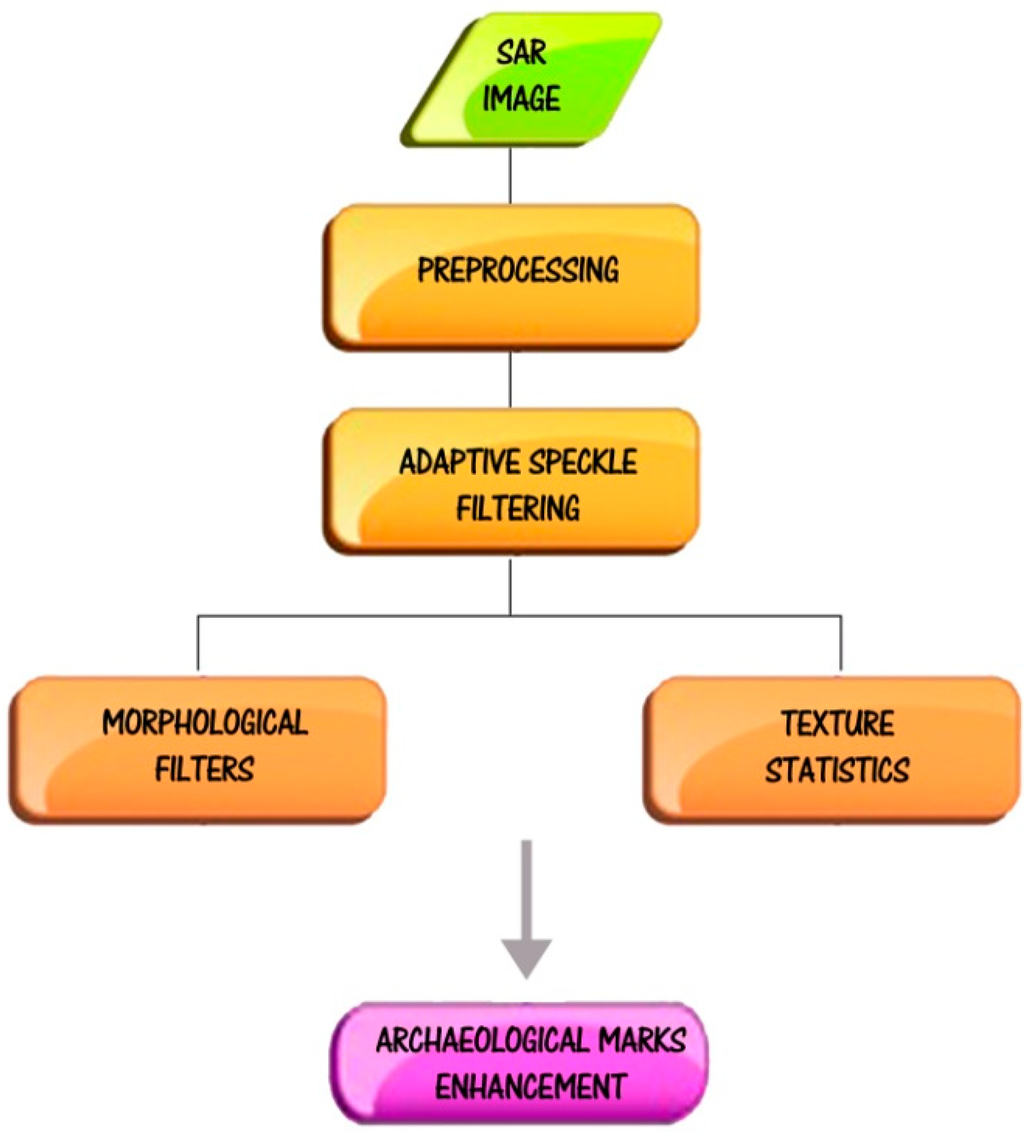
Figure 2.
Single data procedure for the enhancement of archaeological marks. Note that the preprocessing for Spotlight images (for additional details see [29]) upgrades raw data (level 0) to Geocoded Terrain Corrected (GTC) data, namely level 1d product, by means of four steps. The first processing step aims (to obtain Level 1A product) at generating Single-look Complex Slant (SCS) products by means of internal calibration and data focusing. In the second step image detection (amplitude), ellipsoid ground projection and statistics evaluation are performed. The last two steps consists on generating Geocoded Ellipsoid Corrected products (level 1C) and Geocoded Terrain Corrected products (level 1D).
The second approach was based on single date analysis of Enhanced Spotlight data applied to Sabratha in Libya and Metapontum in Italy, where smaller archaeological features compared to Luoyang are expected. In these cases, the multitemporal approach has not been adopted because of the unavailability of a time serie of Spotlight data.
The two approaches we adopted aim to provide two different data processing strategies to cope with the limited availibility of archived data and the size of the expected features.
3.1. Multi-Temporal Analysis
Multi-temporal studies are mainly based on co-registration, speckle filtering, stacking averaging, multi-temporal surveillance consisting of steps of SAR image visual inspection, Gaussian filtering, and ratio change detection (see Figure 1).
In order to cover the growth cycle of plants, multi-temporal SAR data acquired with similar imaging geometries (i.e., repeat cycle) are preferred. In this study (see Table 1), 40 COSMO-SkyMed images, acquired in 2013, were used. For the purpose of multi-temporal analysis, the datasets were co-registered with sub-pixel accuracy in three steps: (1) a first shift is initialized using the satellite orbital parameters; (2) the shift estimation is enhanced (sub-pixel accuracy) by means of a cross-correlation-based function using a grid of image windows; (3) the final shift is further refined by using over-sampled data.

Table 1.
Revisit-cycle acquisition dates for the COSMO-SkyMed data to ensure similar illumination geometry. The data were acquired along the ascending orbit, with Horizontal Transmit-Horizontal Receive (HH) polarization and an angle of incidence of 19.95°.
| No. | Acquisition (Day Month Year) | No. | Acquisition (Day Month Year) | No. | Acquisition (Day Month Year) | No. | Acquisition (Day Month Year) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 27 February 2013 | 11 | 20 April 2013 | 21 | 23 June 2013 | 31 | 26 August 2013 |
| 2 | 3 March 2013 | 12 | 24 April 2013 | 22 | 27 June 2013 | 32 | 30 August 2013 |
| 3 | 7 March 2013 | 13 | 2 May 2013 | 23 | 5 July 2013 | 33 | 7 September 2013 |
| 4 | 15 March 2013 | 14 | 6 May 2013 | 24 | 9 July 2013 | 34 | 11 September 2013 |
| 5 | 19 March 2013 | 15 | 10 May 2013 | 25 | 21 July 2013 | 35 | 15 September 2013 |
| 6 | 23 March 2013 | 16 | 26 May 2013 | 26 | 25 July 2013 | 36 | 23 September 2013 |
| 7 | 31 March 2013 | 17 | 3 June 2013 | 27 | 29 July 2013 | 37 | 27 September 2013 |
| 8 | 4 April 2013 | 18 | 7 June 2013 | 28 | 6 August 2013 | 38 | 9 October 2013 |
| 9 | 8 April 2013 | 19 | 11 June 2013 | 29 | 10 August 2013 | 39 | 13 October 2013 |
| 10 | 16 April 2013 | 20 | 19 June 2013 | 30 | 14 August 2013 | 40 | 17 October 2013 |
Speckle, an unfavorable noise that suppresses feature signals, usually occurs in SAR images due to the coherent nature of the system. Speckle noise reduction is beneficial for archaeological feature extraction. There are several speckle filtering algorithms, including the Lee filter [30], the Lee enhanced filter [31] and the Frost and Kuan filters [32], etc. The performance of an algorithm is evaluated from speckle suppression together with topology preservation, because the presence of geometric features, being quite rare in nature, generally implies signs of archaeological sites and human activity in the distant past. In this study, the enhanced Lee approach [31] was applied as a trade-off between filtering performance and robustness.
For co-registered SAR images, the stacking averaging is helpful in mitigating speckle noise by increasing the Equivalent Number of Looks (ENL). Assuming co-registered images are available, the ENL of the derived stacking-averaged SAR image would be enhanced by a factor of . In such a way, weak archaeological features hidden in a single SAR image could become prominent, particularly for the shadow marks (i.e., microrelief) showing consistent phenomena in all acquisitions. Consequently, the stacking averaging is beneficial for enhancing shadow marks in archaeology using SAR images.
In multi-temporal observation, visual inspection is firstly used to identify regular patterns that generally characterize cultural features. Due to the coherent nature of imaging, archaeological features in a single SAR image may be ambiguous and require feature enhancement techniques. In this study, Gaussian filter and ratio change detection were applied. The Gaussian filter is often used in geometric feature enhancement. Mathematically, it modifies the input signal by convolution with a Gaussian function and uses weighting from the probability density function. This filtering is particularly efficient in reducing speckle noise, preserving radar reflectivity and textural properties.
Experiments in our study proved that this filter is useful to discriminate archaeological signs (crop, soil and damp anomalies) from their surroundings in SAR images. Although multi-temporal SAR images are available, archaeological anomalies are always prominent in one or two acquisitions. The ratio between two data enables us to enhance the difference between the “anomaly” linked to buried-archaeological structures and their surroundings. Moreover, the ratio operator is useful for the further mitigation of multiplicative speckle noises in SAR images.
3.2. Single-Date Analysis
The VHR SAR data proved able to depict urban areas in detail as well as different land use and land cover, providing useful information for investigations for feature extraction and cartographic applications. This capability of VHR SAR images allowed us to consider the use of these data also for archaeological feature extraction and mapping. The topic has already been approached using multi-temporal data analysis based on Stripmap data at a geometric resolution of 3 m (see Section 3.1). SAR remote sensing performance for archaeology would be better if Spotlight mode images were used. Moreover, these may enable us to achieve the performance and quality that is currently available from single-date optical VHR data processing.
One of the main problems for archaeological feature extraction in SAR data is the complexity of the targets under investigation, the subtle return they provide, which means very low signal/noise ratio, and the fact that the visibility of archaeological marks is conditioned, as in the case of optical data, largely by numerous factors, for example (i) vegetation type and phenology for archaeological marks as well as (ii) soil type and superficial conditions in terms of humidity content for soil and damp marks. On the other hand, it is expected that the visibility and extraction of shadow marks should be conditioned less by the above mentioned factors as the SAR signal is sensitive to surface roughness. A compromise is needed to satisfactorily filter out noise, maintaining, at the same time, the subtle signal associated with archaeological features. In fact, speckle noise reduction may be generally beneficial to archaeological feature extraction, but the use of filtering to reduce noise could also filter out the target at the same time.
Up to now, a number of effective speckle filtering algorithms have been developed and currently applied with a high degree of success in diverse fields of application. Nevertheless, it is important to consider that the performance of all the speckle filtering algorithms depends on the processed data set as well as on target characteristics. For the purposes of our analysis, we evaluated the performance obtained from the most popular speckle filtering algorithms. Two main types of SAR speckle filtering algorithms can be identified: (i) multi-look processing and (ii) image domain filtering techniques.
More sophisticated approaches, such as those based on the wavelet filter, are not considered because they require numerous parameters to be set, which means that they cannot be promptly and easily applied to different geographical areas and archaeological features. In order to achieve a satisfactory compromise between the two opposite needs of smoothing noise and protecting detailed information, we adopted an approach based on both speckle reduction applying enhanced Lee, using a small window size (3 × 3 up to 5 × 5 pixels) and feature enhancement filtering (see Figure 2). It is important to note that the presence of speckle in SAR data makes the traditional edge detectors developed for optical images inefficient and feature identification and extraction extremely difficult. To cite an example, the processing of tonal information is not sufficient to reveal all the information stored in the SAR data. Several authors proposed robust detection operators to identify step edges in speckled images, but this methodology may be inadequate for archaeological features with very subtle returns [33,34]. To cope with this issue, after noise removal using enhanced Lee, we also include a textural and morphological filter [35]. The former filter typology is more suited to extracting the complementary information available from the statistical indicators (such as mean, standard deviation coefficient of variation, autocorrelation for lags, etc.). Conversely, the latter filter typology, based on mathematical morphology, is more suited to finding surface discontinuities, changes in material properties and variations in moisture content, etc. Morphological filters [35,36] are nonlinear image transformations based on morphological operations, such as opening, closing or dilation and erosion, which are size and shape sensitive and are found to be effective at making the image sharper.
The capability of the enhancement filters was assessed qualitatively making a trade-off between filtering performance and target preservation. The sum of squares method was found to be one of the most effective at smoothing speckle noise and enhancing details. This is because it provides the quadratic values for each pixel, thus sharpening edges and details. Moreover this filter does not require any parameter and is applied globally, so it is more easily applicable to other geographic areas and archaeological features.
4. Results
4.1. Luoyang Site Case Study
4.1.1. SAR Dataset
In this study, 40 scenes of Stripmap with HIMAGE mode were used. The scenes have been acquired in ascending orbit with HH polarization in the observation period from 27 February to 17 October 2013 (see Table 1) and covered a swath of 40 km over Luoyang city, Henan Province in China (see Figure 3 and Figure 4). The image pixel spacing is 2.264 m and 0.769 m in azimuth and range direction, respectively. Taking into account the 19.95° incidence angle, the calculated ground spatial resolution of SAR images is approximately 3 m.
Figure 3.
Location of Luoyang.
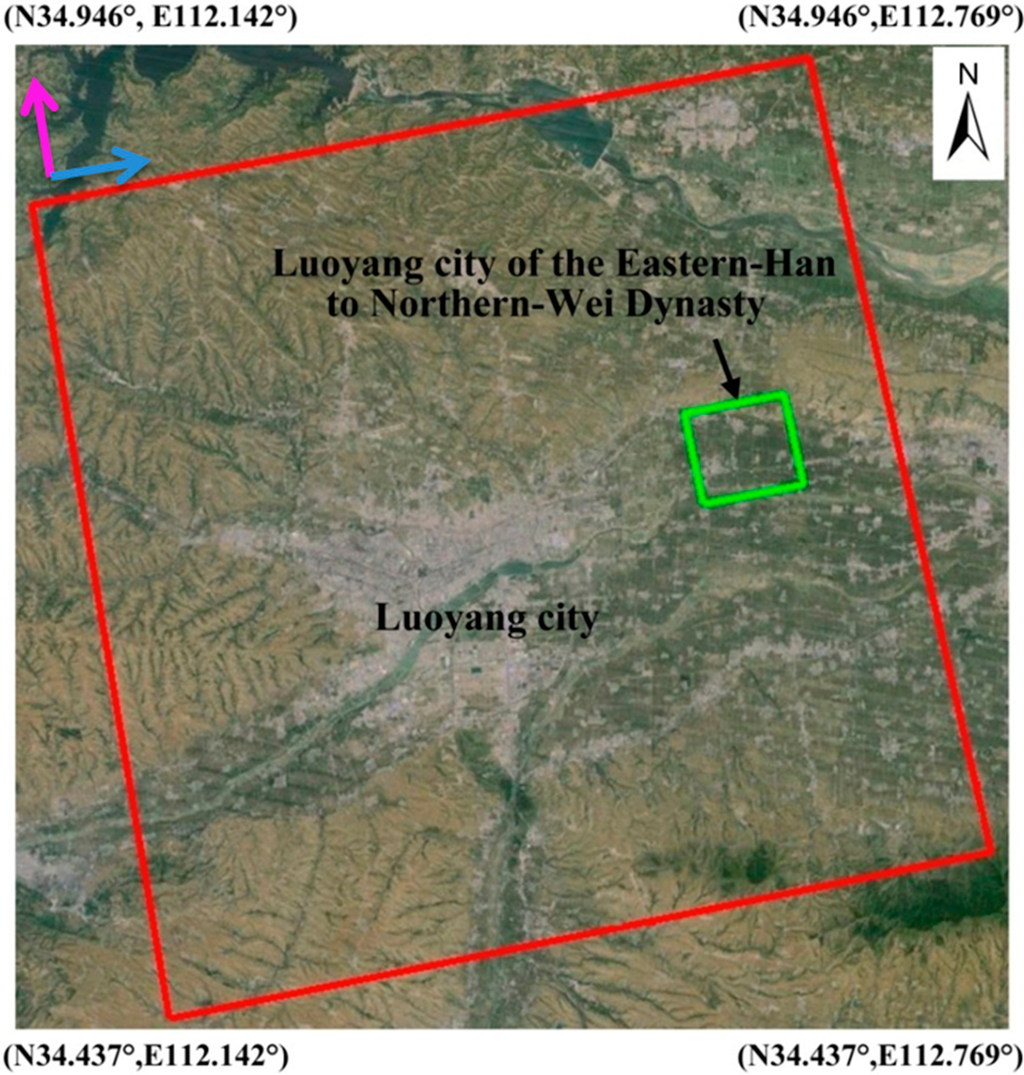
Figure 4.
The swath of Stripmap HIMAGE (highlighted by the red polygon) and the Eastern-Han to Northern-Wei Dynasty city of Luoyang (highlighted by the green polygon) covered by the COSMO-SkyMed in this study (courtesy of Google Earth). The green polygon indicates the Northern-Wei Dynasty Luoyang capital city in Figure 5; purple and blue arrows indicate the flight path and direction of SAR illumination.
4.1.2. Description of Study Site
Luoyang has a temperate climate, characterized by hot, humid summers and cold dry winters. The study site, geologically characterized by silt and clay, is an agricultural area where wheat was cultivated during the period of investigation.
As one of the ancient imperial capitals in Central China, running along the Silk Road’s Chang’an-Tianshan Corridor (nominated a World Heritage site in June 2014), the Eastern-Han to Northern-Wei Dynasty Luoyang city dates back to 100–500 AD and is located to the northeast of the modern Luoyang city in the Henan Province of China (Figure 3 and Figure 4).
In 25 AD, Luoyang was declared the capital of the Eastern-Han Dynasty by Emperor Guangwu of Han and became the focal point of China [37]. In the late 2nd century, China declined into anarchy and the Han capital of Luoyang was finally burned to ashes in 189 AD. In 493 AD, Emperor Xiaowen of the Northern-Wei Dynasty moved the capital from Datong to Luoyang, and brought the ancient Luoyang city into a new period of prosperity reflected by the construction of the famous Longmen Grottoes.
After more than 1500 years have passed, the prosperity of the Eastern-Han to Northern-Wei Dynasty Luoyang city has disappeared, leaving behind chronological documents as well as ancient buried remains including ancient walls, the remains of imperial palaces, and urban settlements [38]. Figure 5 shows the rediscovered Northern-Wei Dynasty Luoyang capital city (whose area is marked by the blue polygon in Figure 4 based on the chronological documents and field archaeological campaigns). It is clear that archaeological details are missing from this map. It should be noted that the imperial palace region (highlighted by the purple rectangle) is fully under field investigation and excavation, including the Taji Hall Remains, Building Remains No. 3 and No. 2, and the Changhe Gate (illustrated by image subsets (a), high resolution optical image and (b), photos from field campaign).
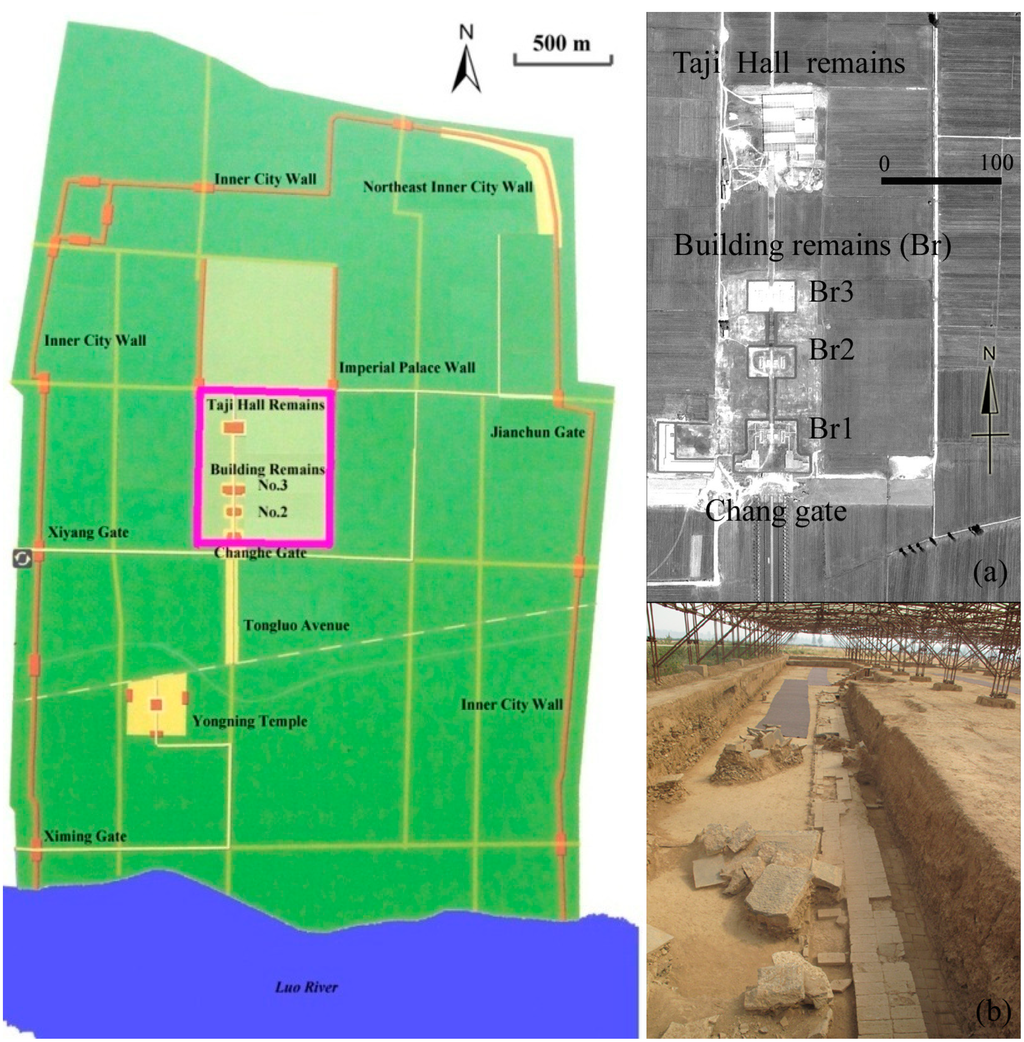
Figure 5.
Layout of Easten Han to Northern-Wei Dynasty Luoyang Capital City located (from [38]). In Figure 4 green box denotes its location. (a) detail of the imperial palace area highlighted by the pink rectangle from panchromatic satellite Pleiades image (b) photo of the excavation in Taiji Hall.
4.1.3. Reconnaissance of Archaeological Marks in Luoyang
The reconnaissance of archaeological marks was performed by the inspection of both single date and the stacking-averaged data. This was made up of 40 scenes (see Figure 6). The two approaches provide similar results for the detection of shadow marks. Ground truth clarified that the shadow marks were related to rammed earth structures (to an approximate height from 20 cm to 3 m) belonging to the Northeast Inner City Wall, marked by the red arrows in Figure 6.
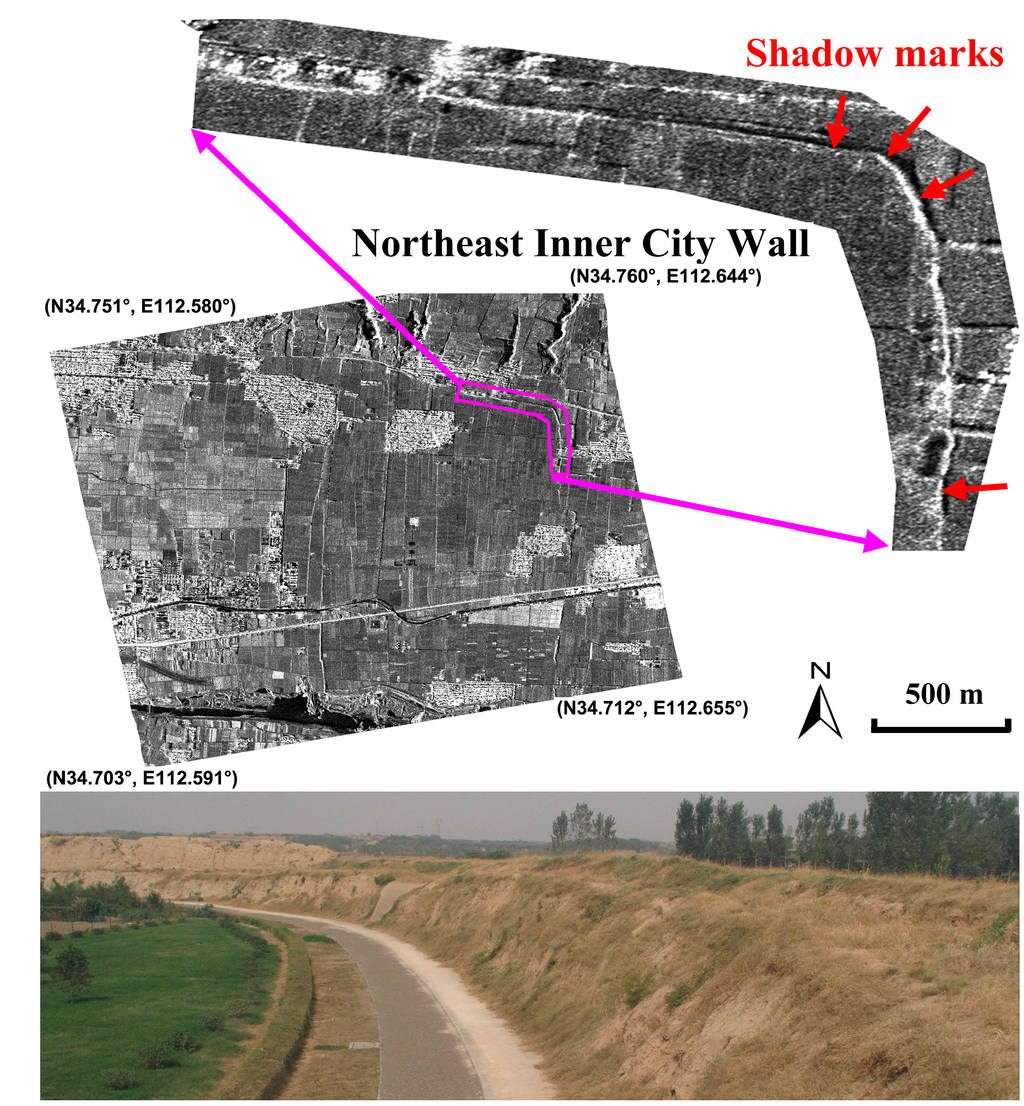
Figure 6.
Shadow marks of the Northeast Inner City Wall on the Eastern-Han to Northern-Wei Dynasty Luoyang city site (highlighted by the green polygon in Figure 4) using a stacking-averaged SAR image. The ancient wall is highlighted by the purple polygon with its details illustrated in the upper subset. Shadow marks are shown by red arrows. Lower image shows a detail of the City wall.
As regards the crop marks multi-temporal analysis did not provide relevant results. The best results have been from the analysis of single date, among which the scene acquired on 19 March 2013, as illustrated in Figure 7. In order to enhance the crop anomalies, the subset image covering the ancient capital city was firstly performed by Gaussian filter, as illustrated in Figure 7. Two regular features linked to subsurface archaeological remains can be clearly identified, marked by “a” and “b”. According to the archaeologists, feature “a” with positive crop marks, probably corresponds to a man-made pit with rich nutrients, and feature “b”, linked to negative crop marks, due to vegetation stress, is interpreted as buried foundations of buildings. Then the ratio change detection method was applied by comparing the SAR amplitude images of 19 March 2013 (the numerator) and 11 June 2013 (the denominator), as illustrated in Figure 8. Previous investigations indicated that the winter wheat on the archaeological site revived and was in the elongation phase on 19 March 2013 and was harvested on 11 June 2013. Consequently, the crop marks of SAR images can be maximized through the ratio between those two acquisitions. However, in this case, the ratio performance is worse than the Gaussian filtering (see Figure 8), possibly due to noise occurrences on the two acquisitions. In short, the preliminary results demonstrated that the optimal selection of one SAR image is effective, as currently used for optical images, for detecting buried archaeological remains.
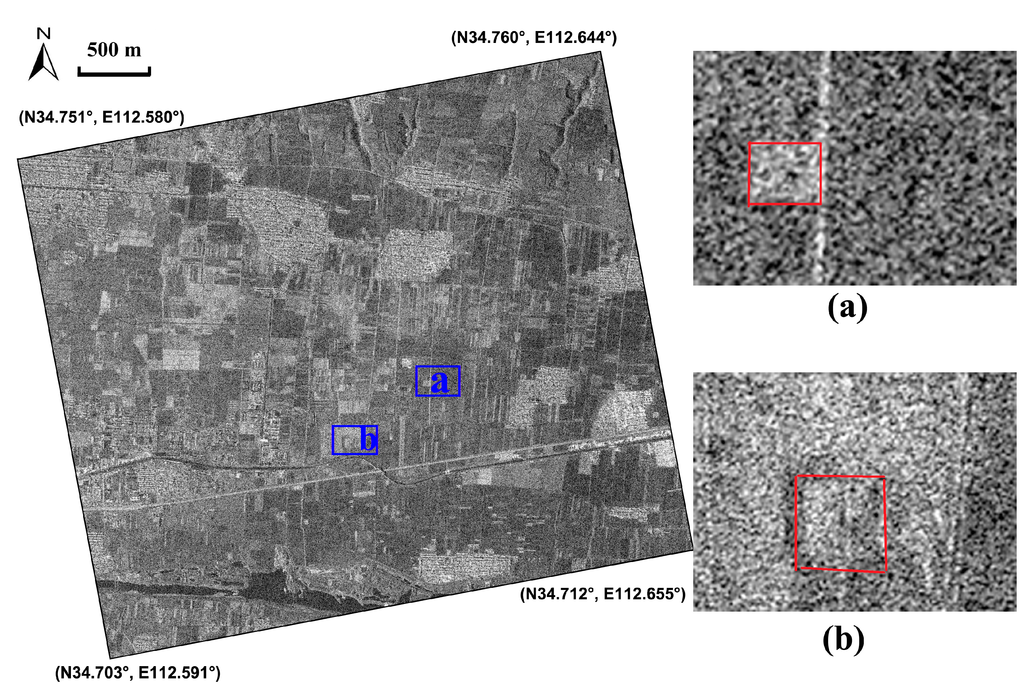

Figure 7.
Crop marks relating to the Eastern-Han to Northern-Wei Dynasty Luoyang city site (highlighted by the green polygon in Figure 4) on the SAR image of 19 March 2013 performed by the Gaussian filter. Positive and negative crop marks have been detected, marked by (a) and (b).
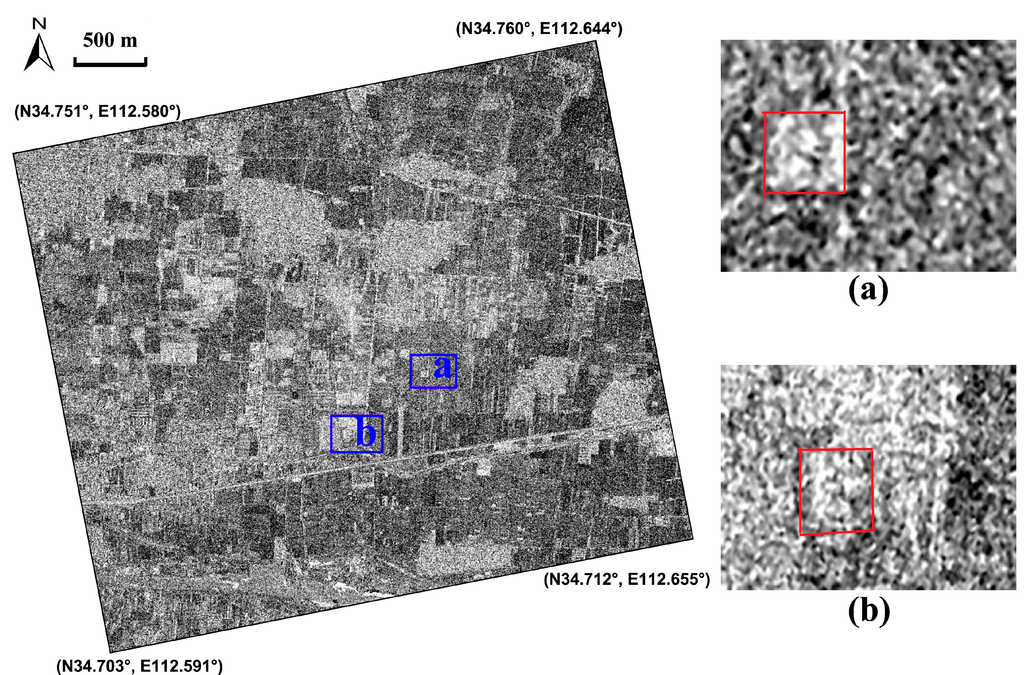

Figure 8.
Crop marks relating to the Eastern-Han to Northern-Wei Dynasty Luoyang city site (highlighted by the green polygon in Figure 4). The scene shows the ratio calculated using the amplitude of SAR images of 19 March 2013 and 11 June 2013. Positive and negative crop marks were detected, marked by (a) and (b).
On 22–24 July 2013, Luoyang was hit by a flood caused by heavy rain, i.e., the accumulated precipitation record in this period was 102 mm in the downtown region. The disaster brought damage and economic loss to the city; at the same time, it provided an opportunity for soil and damp mark enhancement linked to buried-archaeological structures. We applied the multi-temporal SAR images of 25 July and 29 July 2013 for analysis. After visual inspection, we found that the soil marks related to buried structures on the Gaussian filtered image of 25 July 2013 (one day after the heavy rain) were clearly noticeable. The corresponding result is illustrated in Figure 9. Rectangular and linear features highlighted by red arrows correspond to an ancient palatial structure and settlement foundations of walls or buildings, respectively, as interpreted by local archaeologists. A numerical comparison of radar backscattering in sigma-nought between natural dry soil and damp marks (highlighted by green and blue polygons, respectively, in Figure 9) was also conducted using sample-averaged backscattering values, indicating a difference of 3.65 dB vs. 3.28 dB.
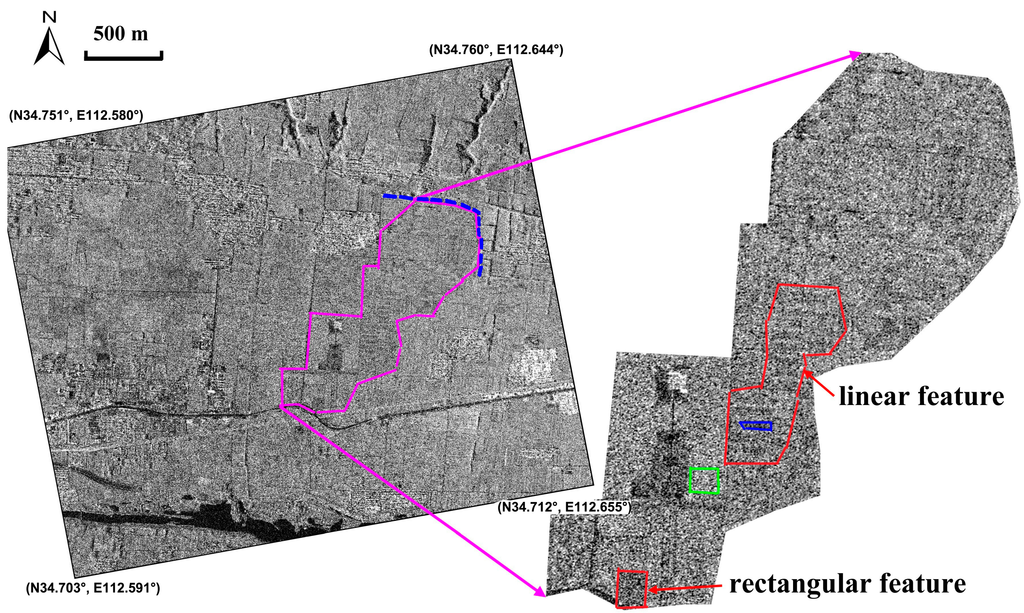
Figure 9.
Soil and damp marks of the Eastern-Han to Northern-Wei Dynasty Luoyang city site (highlighted by the green polygon in Figure 4) on the acquisition image of 25 July 2013 after a flood disaster. Rectangular and linear features highlighted by red arrows correspond to an ancient palatial structure and settlement foundations of walls or buildings, respectively, as interpreted by a local archaeologist. Green and blue polygons highlight the samples of natural dry soil and damp archaeological marks. The Northeast Inner City Wall is marked by a dotted blue line.
4.2. Sabratha and Metaponto Case Studies
In order to assess the capability of single date analysis from COSMO-SkyMed in different contexts and environmental conditions, we selected two significant test cases: one in Sabratha in Libya, and the second in Metapontum (Italy, Europe). The first is mainly characterized by micro-relief, visible thanks to shadow marks; the second shows the presence of soil, damp and crop marks depending on the moisture content and vegetation cover, which change with the seasons. For each test site, one COSMO-SkyMed reading, acquired in Enhanced Spotlight Mode (for additional details see [27]) was used, to detect unrecorded information close to known and unknown archaeological and palaeoenvironmental features. The Spotlight image was first compared with a multi-temporal image set available from Google Earth, then processed in order to enhance the information content, i.e., to maximize the signal/noise ratio. To this aim, noise was reduced using different approaches including one based on adaptive filtering, in particular the Lee enhanced algorithm, and the square of the summation (Sum2).
4.2.1. Description of Study Areas
The first study area is the archaeological site of Sabratha, on the coast of Libya (Figure 10), 64 km west of Tripoli [39], characterized by an arid climate in a desert environment.
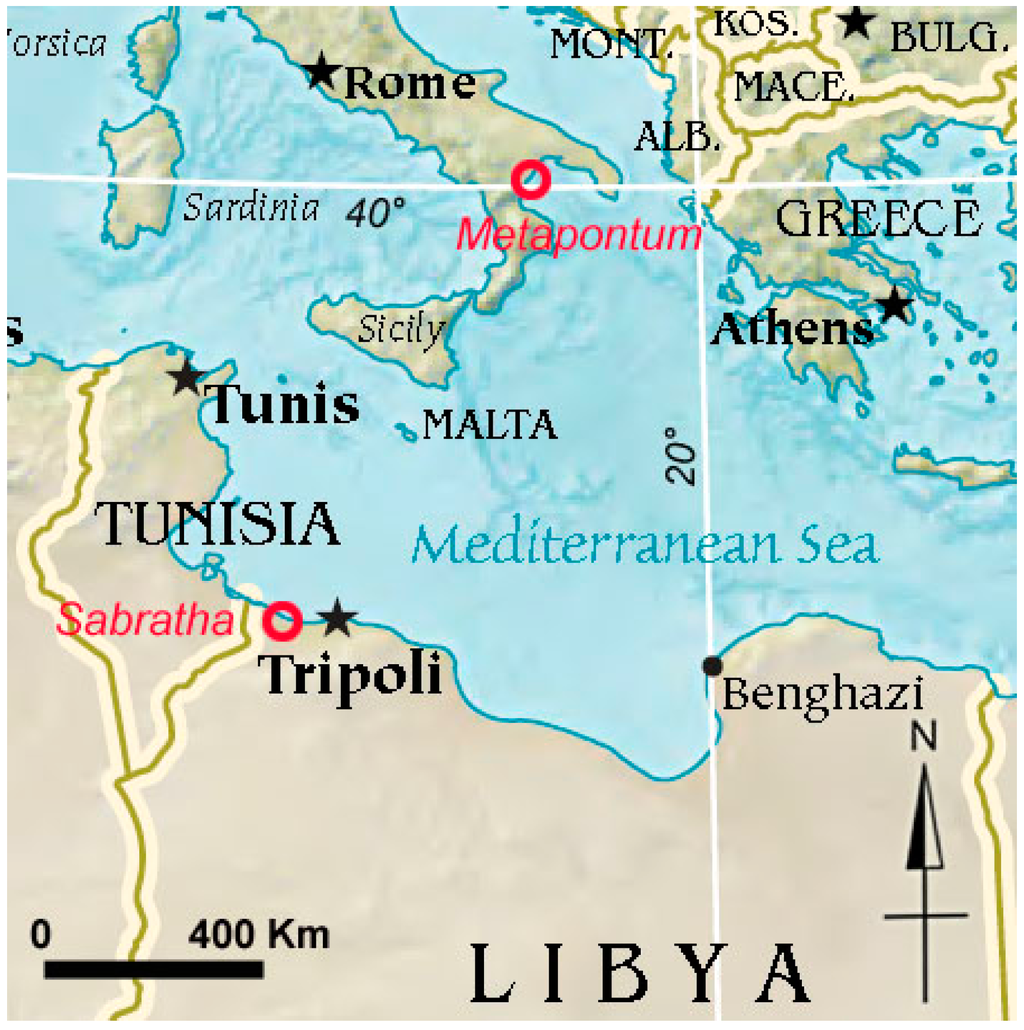
Figure 10.
Location of Sabratha and Metaponto.
It was founded in the seventh century BC by the Phoenicians of Tyre in one of the few natural harbors in Tripolitania and soon became a trading post at the mouth of a major caravan route. Because of its strategic location, Sabratha experienced rapid development and soon fell under the control of Carthage. Passing briefly to the Kingdom of Numidia under Masinissa, Sabratha was later taken by the Romans in 46 BC, and the city enjoyed new prosperity. At the time of the Severi, the city was completely rebuilt and embellished largely because Emperor Septimius Severus was born in nearby Leptis Magna.
At its heyday, Sabratha had about 20,000 inhabitants. Decline loomed from the fourth century, with the gradual fall of the Roman Empire and the first incursions of the Berber people. In 439 the Vandal Genseric captured the city, but was driven out by the Byzantines, who began a partial reconstruction. With the arrival of the Arabs in the seventh century, Sabratha totally lost its importance since the only center in Tripolitania was now the city of Oea (modern-day Tripoli). For the purpose of our investigations, we selected a test site in Sabratha. It is an unexplored area of about 3 ha between the Roman town and the amphitheater. On site it is possible to observe micro-relief, stone materials from collapsed walls, and some traces of walls and foundations, which suggest the presence of buried structures.
The second area of study is the archaeological site of Metapontum, located between the Basento and Bradano rivers, near the Ionian Sea (Figure 10). It has the typical Mediterranean climate. In the Corinne land-cover maps, the investigated area is classified as arable with prevailing wheat cultivations.
It is one of the most important archaeological areas in the south of Italy. Several archaeological campaigns [39,40] have established human presence there since the mid 8th century BC when Metapontum was founded by Greeks coming from the Achaea region. Between Greek colonization (700 BC to 200 BC) and the Roman age (200 BC to 400 AD), the territory was characterized by an intensive use of soil as revealed by the several rural sites that can be observed from surface surveys and excavations, and also the presence of an extensive system of parallel land divisions [40,41]. In particular, these lines are thought to have been a network of country lanes or drainage canals. Another important element in the history of Metapontum is the spatial and temporal relationship between the hydrography and the human settlements. The rivers Bradano and Basento between which Metapontum is located, changed their floodplains several times, influencing the settlement pattern. These spatial features linked to ancient human transformations of the landscape represent one of the most significant traces of ancient human activities, which need to be protected. Unfortunately, due to the destructive effects of mechanized agriculture, these traces of the human and geological past are increasingly difficult to identify using solely optical images. For this reason it has been decided to also use SAR data, such as COSMO-SkyMed acquired in Enhanced Spotlight Mode, in order to assess their ability to detect archaeological and palaeoenvironmental features, in particular roads, palaeoriverbeds and palaeochannels.
4.2.2. Results
At the archaeological site of Sabratha, the processing and interpretation of remote sensing data focused on an area characterized by lesser-known archaeological features. They are composed of linear micro-relief, visible from optical images by means of shadow marks, attributable to shallow remains (walls, foundation) close to the Sabratha amphitheater.
The COSMO-SkyMed Spotlight scene acquired on 12.12.2012 provides a stunningly detailed map of the features (see Figure 11b and Figure 12a–d) thanks to the high resolution of the image and the effect of double bounce in backscattering as shown in Figure 13 (see also [42]). The same micro-relief could be observed from a multi-temporal image set available from Google Earth shown in Figure 11c–f. However, compared with the Spotlight image, the visibility of micro-relief is reduced in three of them (October 2009, 20 August 2011, 26 May 2012 in Figure 11c–e)) and similar in one (16 February 2013, in Figure 11f).
A significant improvement of the Spotlight scene in terms of the visibility of archaeological micro-relief was achieved using adaptive and statistical filtering (Figure 12). In particular, the best results were obtained by calculating the sum of squares of the Lee filtering products (Figure 12d), which reduced the noise in the surroundings of the features, enhancing the micro-reliefs of archaeological interest.
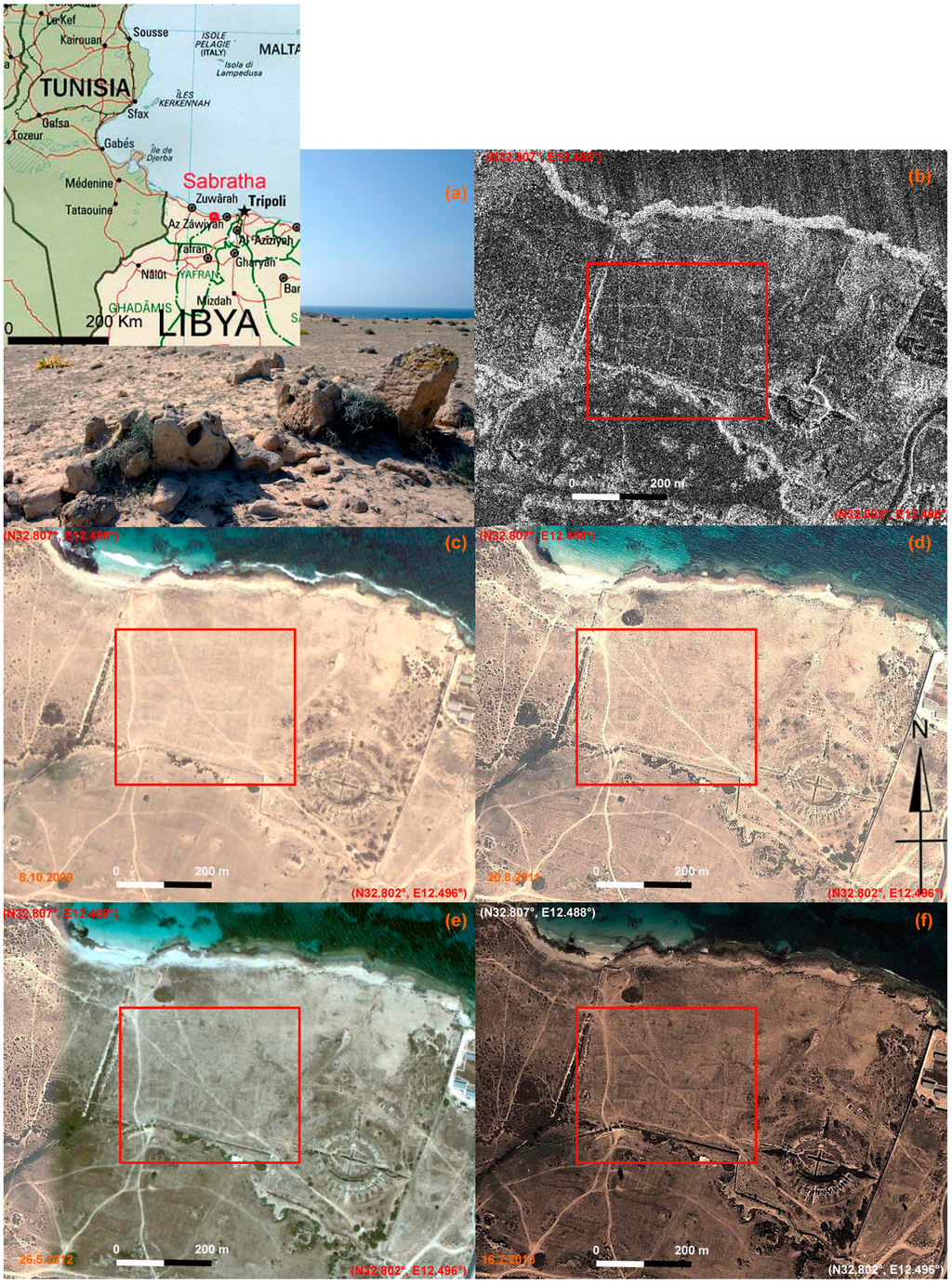
Figure 11.
Detecting unknown archaeological features in Sabratha (Libya). (a) detail of an area characterized by the presence of micro-relief and traces of archaeological interest; (b) The archaeological features are clearly visible from the COSMO-SkyMed Spotlight image acquired on 12 December 2012, at 1m geometric resolution, in ascending orbit, with an angle of incidence of 27.320° and HH polarization; (c–f) Google Earth scenes on 8 October 2009, 20 August 2011, 26 May 2012 and 16 February 2013. The red boxes indicate the area with micro-relief (or shadow marks) whose visibility is less than in the Spotlight image in three of them (October 2009, 20 August 2011, 26 May 2012) and similar in one of them (16 February 2013).
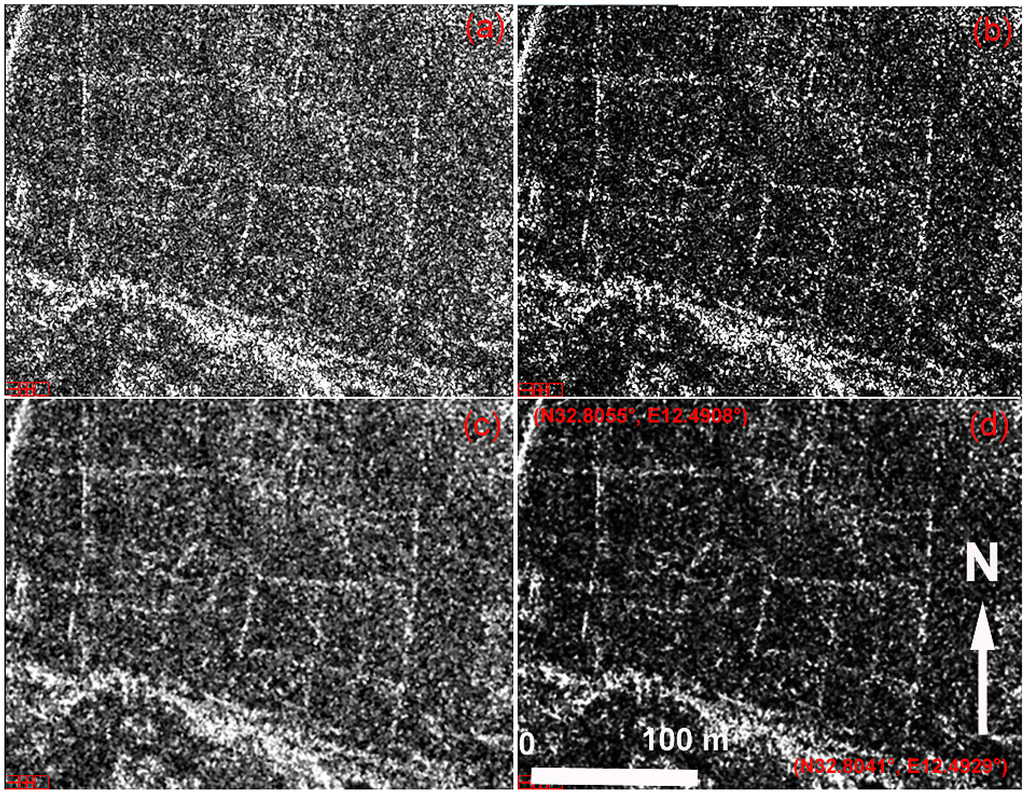
Figure 12.
Sabratha (Libya): Enhancement of the COSMO-SkyMed Spotlight scene in the red box in Figure 12. In detail: (a) raw data; (b) Sum^2; (c) enhanced Lee filter; (d) SUM^2 of the enhanced Lee filter result.
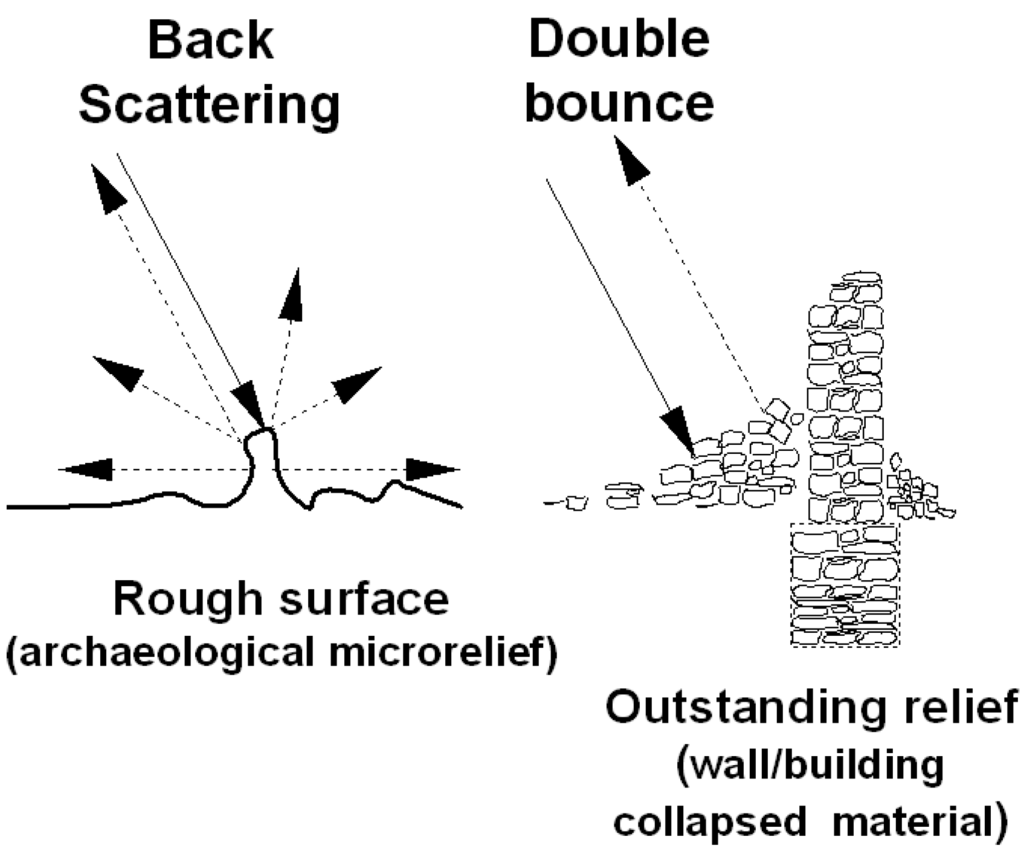
Figure 13.
Model of the response of elementary scattering mechanisms to the presence of archaeological microrelief and traces.
In Metapontum, a number of features related to palaeochannels, palaeoriverbeds, ancient roads and land divisions were investigated. They are very clearly visible from the available COSMO-SkyMed Spotlight image shown in Figure 14. For the sake of brevity, we shall discuss only the results obtained for two palaeochannels (A and B) and a road in the ancient urban fabric dating back to Greek colonization.
In Figure 15, a multi-temporal image set available from Google Earth centers on a palaeochannel named A. The four scenes cover a temporal interval from May to September in different years (2004, 2006, 2013). In all four scenes, the palaeochannel feature, linked to variations in moisture content and vegetation cover lacks the typical curvilinear shape thus making it difficult to identify and map. Conversely, the axis is clearer from the Spotlight scene in Figure 16a and its enhanced version in Figure 16b.
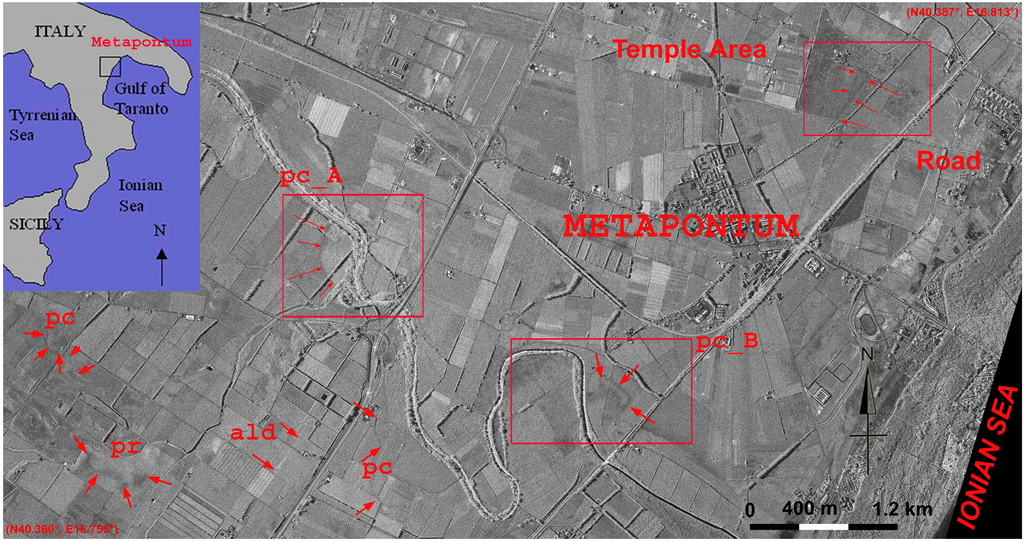
Figure 14.
Metapontum (Southern Italy): a number of archaeological and palaeoenvironmental features are visible from the COSMO-SkyMed Spotlight image acquired on 14 November 2011 at 1 m geometric resolution, in a descending orbit, with an angle of incidence of 41.5° and HH polarization. The image shows palaeoriverbeds (pr), palaeochannels (pc), ancient land divisions (ald) and ancient roads. Red boxes denote the three investigated areas in relation to an ancient road and the palaeochannels A and B (indicated as pc_A and pc_B, respectively; see Figure 15, Figure 17 and Figure 19). Upper left : location of Metapontum in Southern Italy.
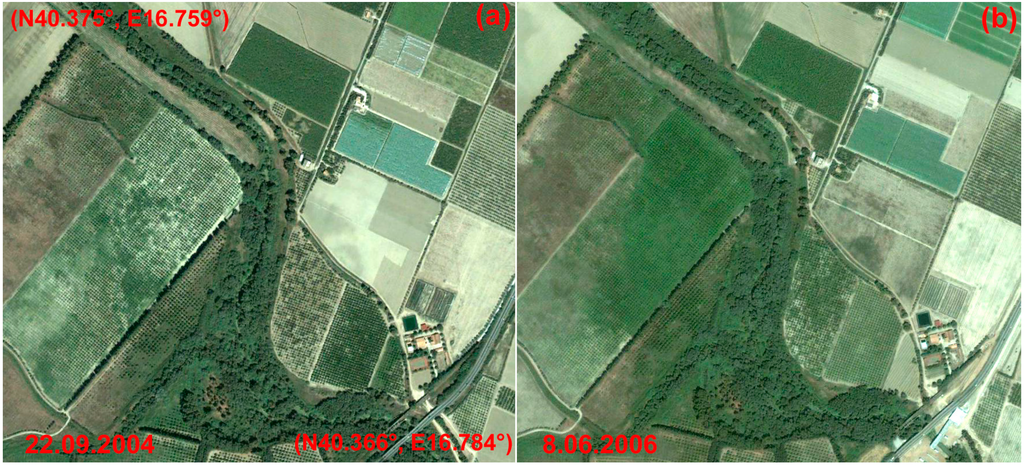
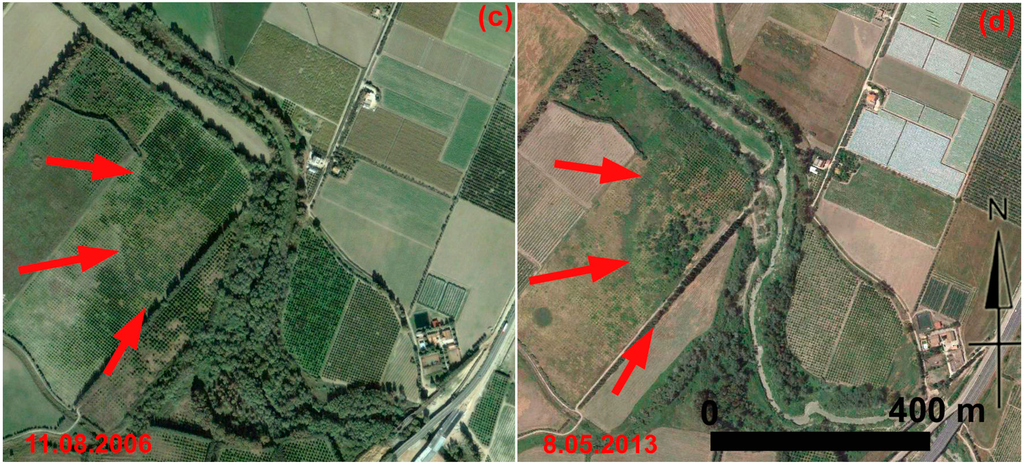


Figure 15.
Metapontum, palaeochannel A (see red box with label pc_A in Figure 14): multi-temporal image set available from Google Earth. In this case, the palaeochannel feature is not curvilinear thus making morphological identification difficult. In detail, Google Earth scenes were acquired on: (a) 22 September 2004; (b) 8 June 2006; (c) 11 August 2006; (d) 8 May 2013.
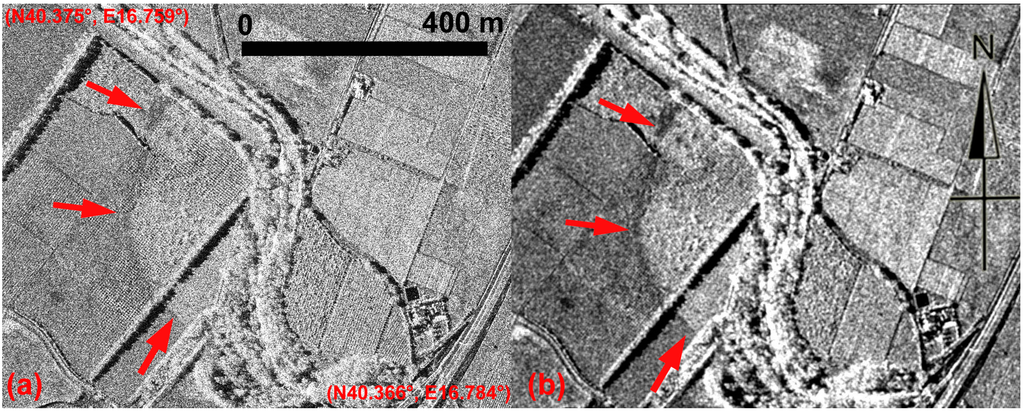

Figure 16.
Metapontum, palaeochannel A. (a) COSMO-SkyMed Spotlight image; (b) SUM^2 of enhanced Lee filter result.
The multi-temporal data set of Figure 17 centers on palaeochannel B, whose visibility changes seasonally depending on the moisture content and vegetation cover. The palaeochannel could be observed thanks to damp marks in the summer scenes shown in Figure 17a–c. On the other hand, crop marks are visible in the spring picture acquired in 2013 (Figure 17d).
Also in this case, the palaeochannel feature is clearly visible in the COSMO-SkyMed Spotlight image (Figure 18). Moreover, a significant improvement was obtained by using the same enhancement approach applied to palaeochannel A.
Lastly, the multi-temporal image set of Figure 19 centers on an ancient road in the urban fabric of Metapontum. In this case, the soil marks of this feature are more visible from the Google Earth scenes than from the unprocessed and processed COSMO-SkyMed Spotlight images (Figure 20).
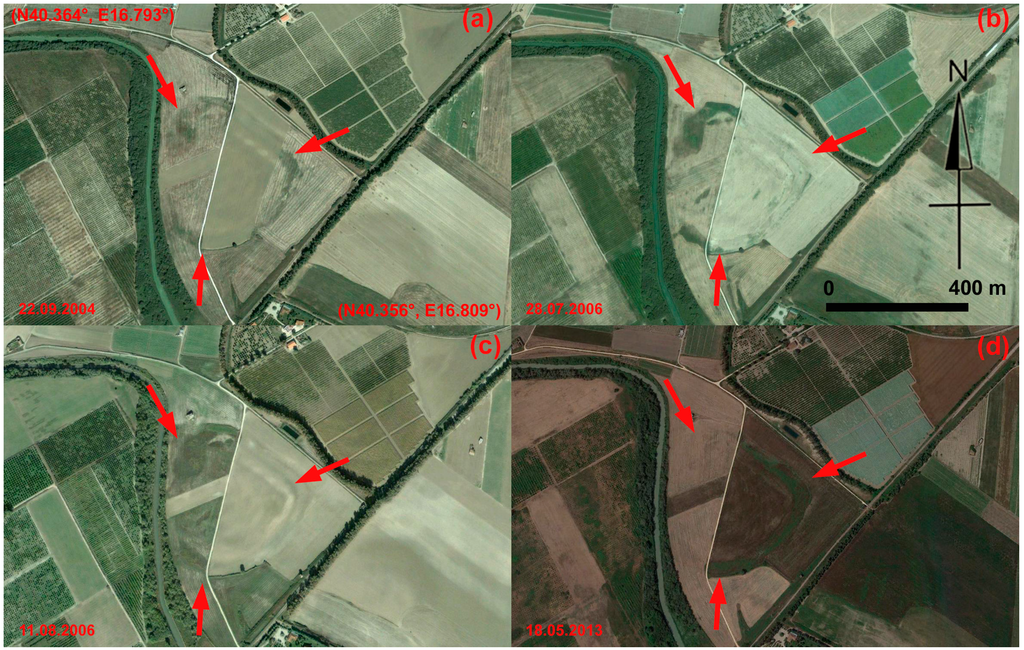

Figure 17.
Metapontum (Southern Italy): multi-temporal data set available from Google Earth of palaeochannel B (see pc_B in Figure 14). The visibility of the palaeochannel B changes seasonally depending on moisture content and vegetation cover. It could be observed thanks to damp marks in the summer scenes shown in Figure 17a–c. Crop marks are visible in the spring picture acquired in 2013 (Figure 17d).

Figure 18.
Metapontum, palaeochannel B. In the COSMO-SkyMed Spotlight image the palaeochannel feature is clearly visible. A significant improvement was achieved by using the enhancement approach described in Section 4.2.
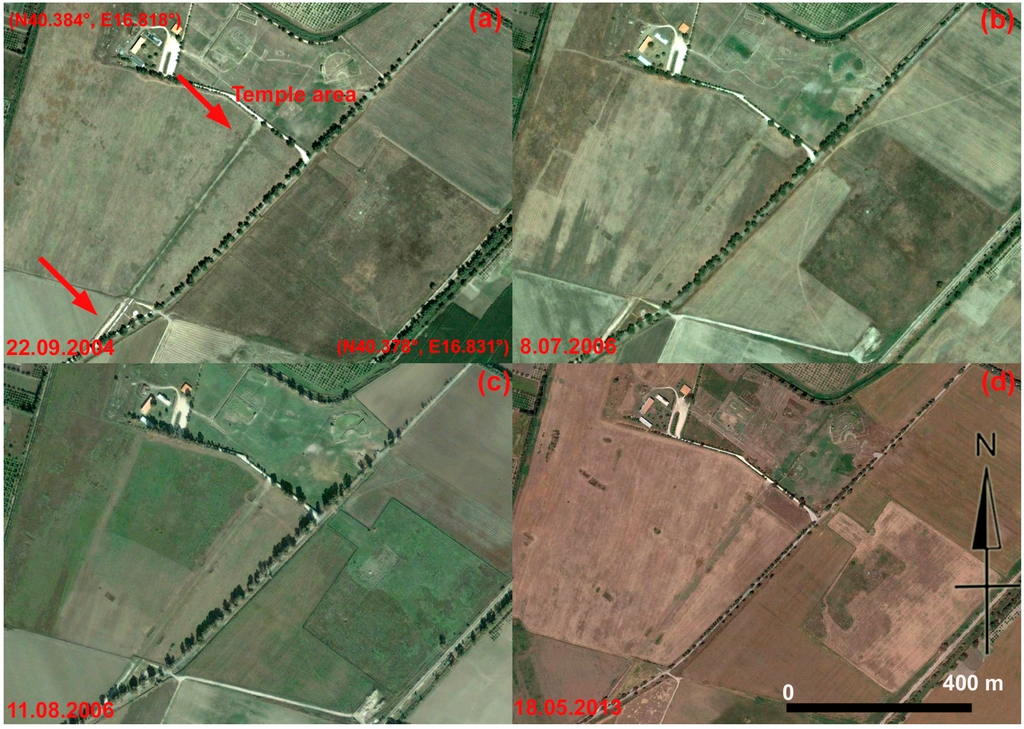

Figure 19.
Metapontum: the temple area and a road (indicated by red arrows) in the ancient Greek town. Google Earth scenes were acquired on: (a) 22 September 2004; (b) 8 June 2006; (c) 11 August 2006; (d) 8 May 2013.
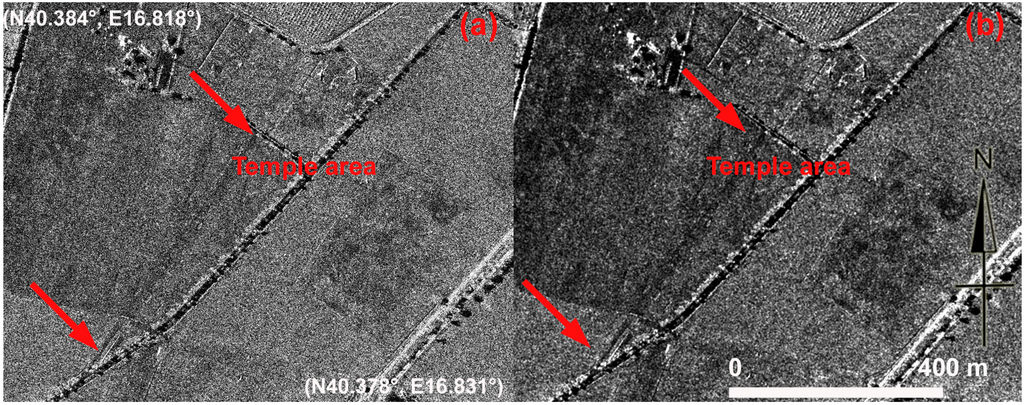

Figure 20.
Metapontum. (a) The temple area and road in the ancient Greek town observed from COSMO-SkyMed Spotlight image; (b) enhancement of (a) result of the sum of squares of the Lee algorithm product.
5. Conclusions
This paper for the first time assesses the potential of satellite SAR X-band COSMO-SkyMed data in the detection of archaeological marks (crop, soil and shadow) in different environmental conditions. To this aim, significant case studies were selected in desert (Sabratha, Libya) and vegetated areas (Metapontum, Italy and Luoyang, China).
Moreover, it assesses for the first time the potential of SAR X-band data using two different feature-enhancement procedures: (i) multi-temporal analysis and; (ii) single-date analysis.
A multi-temporal data set, based on 40 scenes of Stripmap HIMAGE data, was used to investigate the Eastern-Han to Northern-Wei Dynasty Luoyang city site (China). The archaeological site, dating back to 100–500 AD, is located in the east-original section of the Silk Road, in the Henan Province (China). Crop, soil and damp marks are only visible from optimal-selected single date due to seasonal nature of these archaeological features. Whereas shadow marks are visible from both single and multitemporal data analysis.
Single data analyses were applied to Sabratha (Libya) and Metapontum (Italy). These case studies were selected because they have diverse superficial conditions (desert and Mediterranean area) and archaeological marks (crop, soil and shadow). In particular, Sabratha is characterized by shadow marks linked to the presence of microrelief and shallow walls; in Metaponto most of the archaeological features is given by vegetation and moisture changes.
Among the key outcomes, our analysis highlights that the methodological approach adopted demonstrated that both multi-temporal and single-date analysis are suitable for the enhancement of archaeological and palaeoenvironmental features.
The main findings of the archaeological investigation performed can be summarized as follows:
- The use of multi-temporal COSMO-SkyMed Stripmap, by stacking-averaging has been beneficial for shadow mark enhancement. On the other hand, visual inspection enabled us to identify the best scenes for the reconnaissance of the “seasonal” archaeological feature (crop, soil, and damp marks). This was probably due to a good match between soil properties and the acquisition parameters of the image itself.
- Single-date analysis was a feasible way to provide an effective and cost-sustainable use of satellite SAR X-band data to detect archaeological features, from the shadow marks (Sabratha) to marks sensitive to vegetation (Luoyang and Metaponto) and moisture variations (Metaponto).
One of the strengths of this research is the demonstration, that even a single COSMO-SkyMed Spotlight acquisition is a feasible and effective approach for archaeological prospection. The reduction of data processing complexity as well as the cost for data will contribute to increasing the use of satellite SAR X-band in archaeological investigations.
The way forward of such type of research is to continue investigations in order to study how the image acquisition parameters (frequency, polarization and angles of incidence) affect and/or enhance the visibility of the diverse archaeological mark typologies (shadow/crop/soil/damp marks).
Acknowledgments
This research was performed within the framework of the project “Smart management of cultural heritage sites in Italy and China: Earth Observation and pilot projects”, funded by the Italian Ministry of Foreign Affairs and the Hundred Talents Program of the Institute of Remote Sensing and Digital Earth, Chinese Academy of Sciences (Y2ZZ27101B). The COSMO-SkyMed data were provided by the Italian Space Agency, under license agreement from Archeocosmo.
Author Contributions
Fulong Chen carried out the multitemporal data processing and wrote Section 2, Section 3.1 and Section 4.1. Ruixia Yang and Dexian Feng carried out radar interpretation of results from the Chinese case study. Pietro Milillo processed COSMO-SkyMed data for Sabratha case study. Nicola Masini and Rosa Lasaponara processed COSMO-SkyMed data for Metaponto case study, devised the single date methodological approach and carried out radar interpretation of results; wrote Section 1, and Section 3.2, Section 4.2 and contribute to Section 2. All the authors contributed to Section 5
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Parcak, S. Satellite Remote Sensing for Archaeology; Routledge Press: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Lasaponara, R.; Masini, N. Satellite Remote Sensing: A New Tool for Archaeology; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Comer, D.; Harrower, M. Mapping Archaeological Landscapes from Space; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; p. 276. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, D.R. Air Photo Interpretation for Archaeologists; St. Martin’s Press: London, UK, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, A.R. Archaeological site detection: The importance of contrast. In Proceedings of the 2007 Annual Conference of the Remote Sensing and Photogrammetry Society, Newcastle, UK, 11–14 September 2007.
- Lasaponara, R.; Masini, N. Detection of archaeological crop marks by using satellite QuickBird. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2007, 34, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalli, R.M.; Pascucci, S.; Pignatti, S. Optimal spectral domain selection for maximizing archaeological signatures: Italy case studies. Sensors 2009, 9, 1754–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, C.D.; Garrod, S.M.; Parker Pearson, M. Landscape archaeology and remote sensing in southern Madagascar. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1998, 19, 1461–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agapiou, A.; Alexakis, D.D.; Hadjimitsis, D.G. Spectral sensitivity of ALOS, ASTER, IKONOS, LANDSAT and SPOT satellite imagery intended for the detection of archaeological crop marks. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altaweel, M. The use of ASTER satellite imagery in archaeological contexts. Archaeol. Prospect. 2005, 12, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCauley, J.F.; Schaber, G.G.; Breed, C.S.; Grolier, M.J.; Haynes, C.V.; Issawi, B.; Elachi, C.; Blom, R. Subsurface valleys and geoarchaeology of the eastern Sahara revealed by shuttle radar. Science 1982, 218, 1004–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Baz, F. Prehistoric artifacts near paleo-channels revealed by radar images in the western desert of Egyp. In Remote Sensing in Archaeology from Spacecraft, Aircraft, on Land, and in the Deep Sea; Boston University: Boston, MA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, D.; Pottier, C.; Fletcher, R.; Hensley, S.; Tapley, I.; Milne, A.; Barbetti, M. A comprehensive archaeological map of the world’s largest preindustrial settlement complex at Angkor, Cambodia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 14277–14282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrison, T.G.; Chapman, B.; Houston, S.; Roman, E.G.; Lopez, J.L. Discovering ancient Maya settlements using airborne radar elevation data. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2011, 38, 1655–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linck, R.; Busche, T.; Buckreuss, S.; Fassbinder, J.W.E.; Seren, S. Possibilities of archaeological prospection by high-resolution X-band satellite radar-a case study from Syria. Archaeol. Prospect. 2013, 20, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cigna, F.; Tapete, D.; Lasaponara, R.; Masini, N. Amplitude change detection with Envisat ASAR to image the cultural landscape of the Nasca region, Peru. Archaeol. Prospect. 2013, 20, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patruno, J.; Dore, R.; Crespi, M.; Pottier, E. Polarimetric multifrequency and multi-incidence SAR sensors analysis for archaeological purposes. Archaeol. Prospect. 2013, 20, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dore, N.; Patruno, J.; Pottier, E.; Crespi, M. New research in polarimetric SAR technique for archaeological purposes using ALOS PALSAR data. Archaeol. Prospect. 2013, 20, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, K. Mapping subsurface archaeology with SAR. Archaeol. Prospect. 2013, 20, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapete, D.; Casagli, N.; Luzi, G.; Fanti, R.; Gigli, G.; Leva, D. Integrating radar and laser-based remote sensing techniques for monitoring structural deformation of archaeological monuments. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2013, 40, 176–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapete, D.; Cigna, F. Rapid mapping and deformation analysis over cultural heritage and rural sites based on persistent scatterer interferometry. Int. J. Geophys. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapete, D.; Fanti, R.; Cecchi, R.; Petrangeli, P.; Casagli, N. Satellite radar interferometry for monitoring and early-stage warning of structural instability in archaeological sites. J. Geophys. Eng. 2012, 9, S10–S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Iorio, A.; Straccia, N.; Carlucci, R. Advancement in automatic monitoring and detection of archaeological sites using a hybrid process of remote sensing, GIS techniques and a shape detection algorithm. In Proceedings of the 30th EARSeL Symposium, Paris, France, 31 May–3 June 2010; pp. 53–63.
- Collins, A. Radar satellite image reveals the full geological extent of Giza’s cave underworld. In Beneath the Pyramids: Egypt’s Greatest Secret Uncovered; Collins, A., Ed.; A.R.E. Press: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Blom, R.G.; Comer, D.C. Detection and Identification of Archaeological Sites Using Radar Data; Final Report: SERDP SI-1260; Strategic Environmental Research and Development Program (SERDP), Environmental Security Technology Certification Program (ESTCP): Alexandria, VA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, C.; di Iorio, A.; Schiavon, G. Analysis of the utility of Cosmo Skymed stripmap to detect buried archaeological features in the region of Rome. Experimental component of WHERE project. In Towards Horizon 2020: Earth Observation and Social Perspectives, Proceedings of the 33rd EARSeL Symposium, Matera, Italy, 3–6 June 2013; Lasaponara, R., Masini, N., Biscione, M., Eds.; European Association of Remote Sensing Laboratories (EARSeL): Münster German; National Research Council (CNR): Roma, Italy, 2013; pp. 203–212. [Google Scholar]
- COSMO-SkyMed System Description & User Guide. COSMO-SkyMed SAR Products Handbook. Available online: http://www.e-geos.it/products/pdf/csk-user_guide.pdf (accessed on 20 December 2014).
- Chen, F.; Gabellone, F.; Lasaponara, R.; Leucci, G.; Masini, N.; Yang, R. Remote Sensing and ICT for Cultural Heritage from European and Chinese Perspectives; Series “Along Silk Road” 1; Institute for Archaeological and Architectural Heritage and Architectural Heritage, National Research Council (CNR-IBAM): Roma, Italy; Institute of Methodologies for Environmental Analysis, National Research Council (CNR-IMAA): Roma, Italy; Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS): Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- COSMO-SkyMed SAR Products Handbook. Available online: http://www.e-geos.it/products/pdf/csk-product%20handbook.pdf (accessed on 20 December 2014).
- Lee, J.-S. Digital image enhancement and noise filtering by use of local statistics. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1980, 2, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, A.; Touzi, R.; Nezry, E. Adaptive speckle filters and scene heterogeneity. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1990, 28, 992–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Fung, K.B. A comparison of digital speckle filters. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 94, Pasadena, CA, USA, 8–12 August 1994; pp. 2129–2133.
- Ganugapati, S.S.; Moloney, C.R. A ratio edge detector for speckled images based on maximum strength edge pruning. In Proceedings of the 1995 International Conference on Image Processing, Washington, DC, USA, 23–26 October 1995; Volume 2.
- Fu, X.; You, H.; Fu, K. A statistical approach to detect edges in SAR images based on square successive difference of averages. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2012, 9, 1094–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, R.A. A new algorithm for image noise reduction using mathematical morphology. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 1995, 4, 554–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rama Bai, M. A new approach for border extraction using morphological methods. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2010, 2, 3832–3837. [Google Scholar]
- Cotterell, A. The Imperial Capitals of China: An Inside View of the Celestial Empire; Pimlico: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, G. On the layout of the Palace-city of the Han-Wei Luoyang city in the light of the Changhemen gate. Chin. Archaeol. 2003, 4, 165–169. [Google Scholar]
- Matthews, K.D., Jr.; Cook, A.W. Cities in the Sand: Leptis Magna and Sabratha in Roman Africa; University of Pennsylvania Press: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1957. [Google Scholar]
- Adamesteanu, D. Le suddivisioni di terra nel Metapontino. In Problèmes de la Terre en Grèce Ancienne; Finley, M.I., Ed.; Mouton: Paris, France, 1973; pp. 49–61. [Google Scholar]
- Carter, J.C. Between the Bradano and Basento: Archaeology of an ancient landscape. In Earth Patterns: Essays in Landscape Archaeology; Kelso, W., Most, R., Eds.; University of Virginia Press: Charlottesville, VA, USA, 1990; pp. 227–243. [Google Scholar]
- Lasaponara, R.; Masini, N. Satellite synthetic aperture radar in archaeology and cultural landscape: An overview. Archaeol. Prospect. 2013, 20, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).