Retrieval of a Temporal High-Resolution Leaf Area Index (LAI) by Combining MODIS LAI and ASTER Reflectance Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
2.1. Ground Experiment
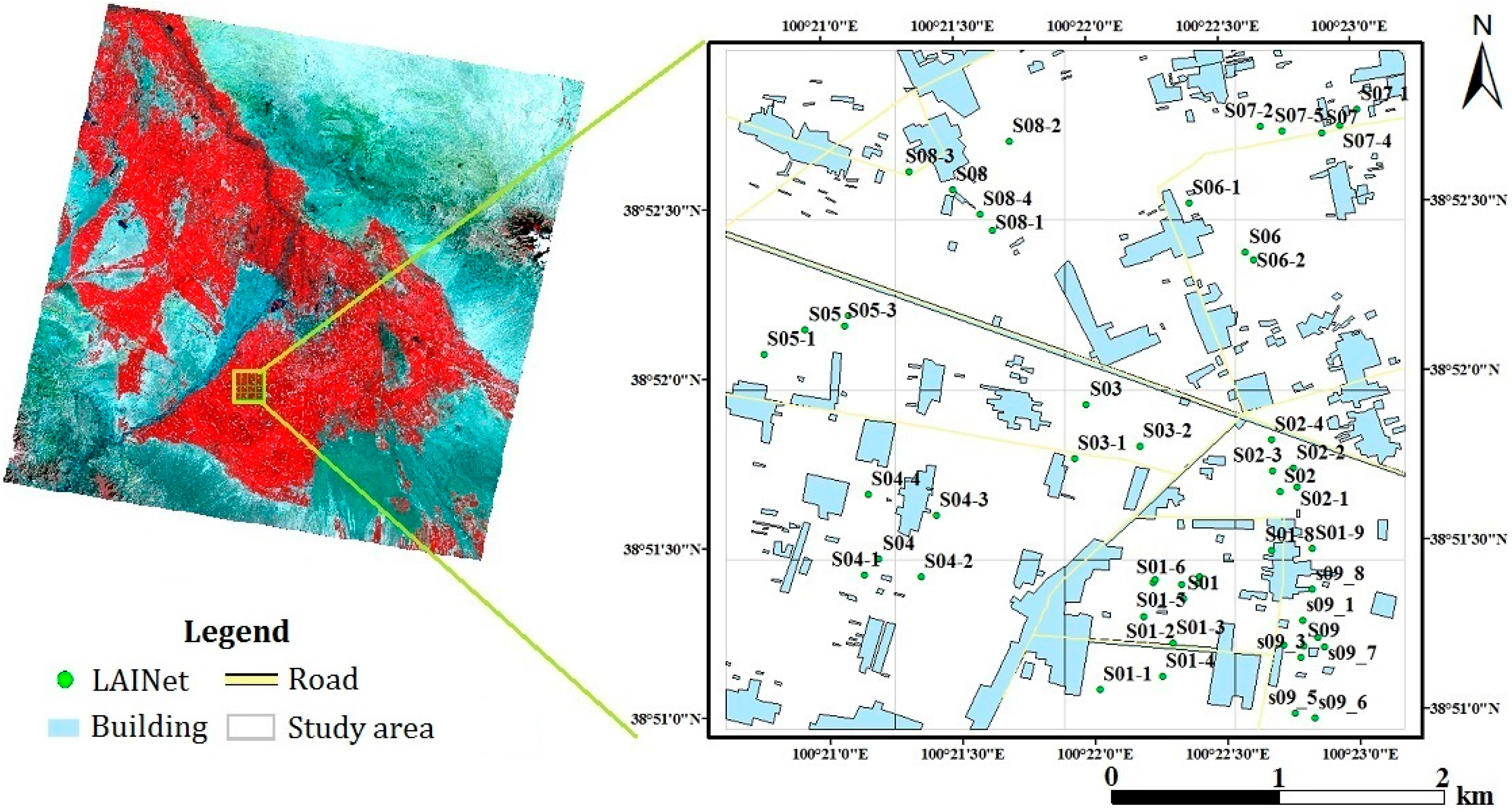
2.2. Data
| Data Source | Spatial Resolution | Temporal Resolution | DOY |
|---|---|---|---|
| MOD15A2 | 1 km | 8 days | 153/161/169/177/185/193/201/209/217/225/233/241/249/257/265 |
| ASTER | 15 m | Varied | 152/167/192/215/224/231/240/247/263 |
| LAINet | ground point | 5 days | 177~232 |
3. Methods
3.1. Methods Overview
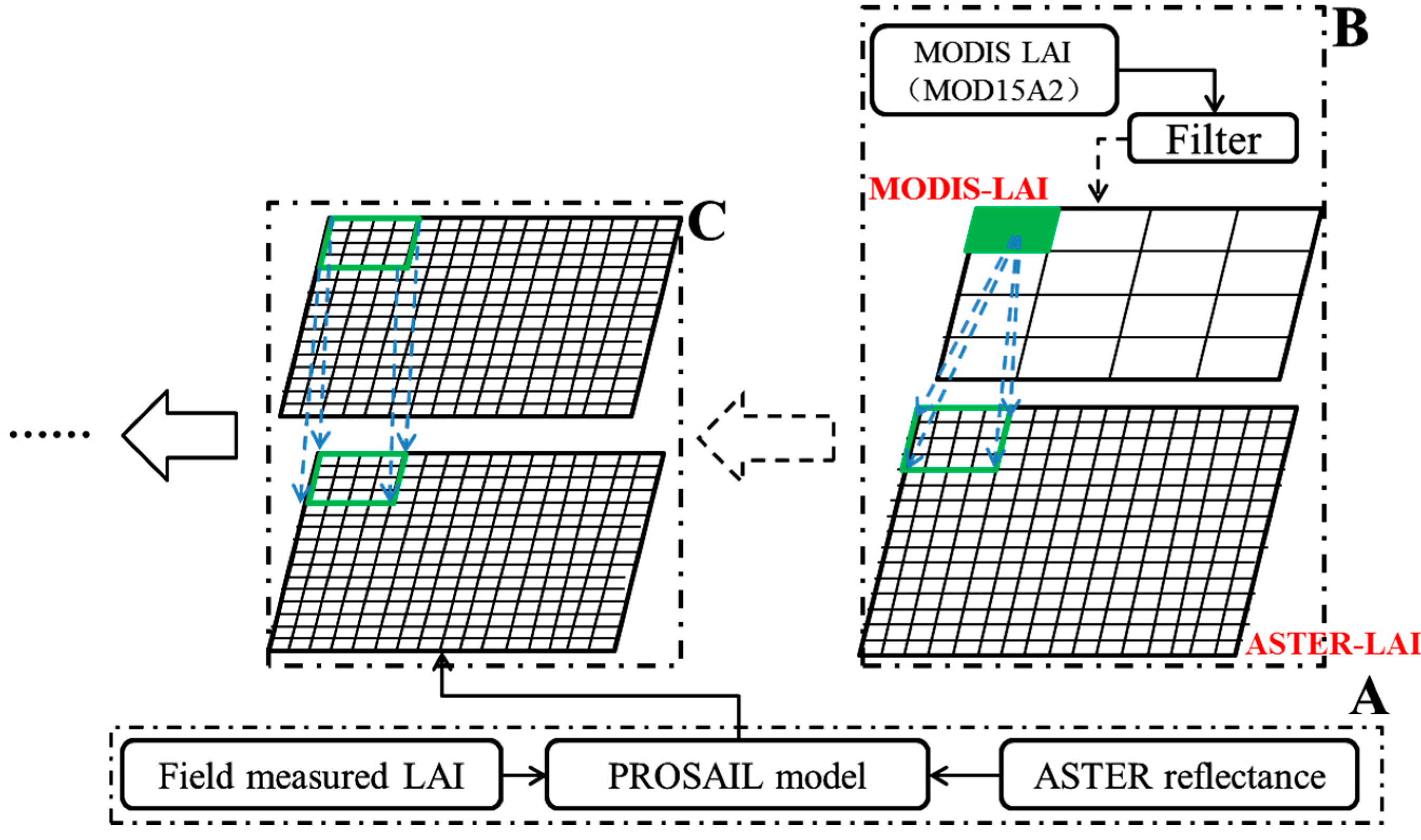
3.2. Step 1: Generating a Look-Up Table Constrained Using Ground Observations
3.3. Step 2: Fitting the LAI Growth Equation
3.4. Step 3: Retrieving the Temporal High-Resolution LAI
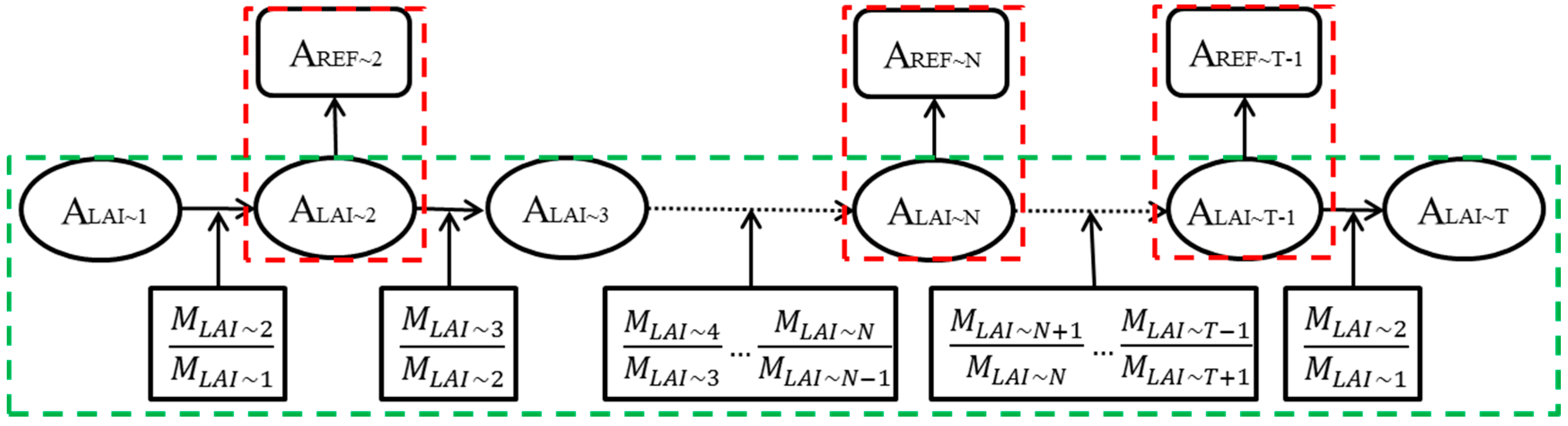
3.5. Step 4: Calculating the Information Entropy and Maximum Probability
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. PROSAIL Model Parameters Determined through Fixed Ground Measurements
| ID | DOY | Lon | Lat |
|---|---|---|---|
| 258 | 192, 207, 222 | 100.36976E | 38.854710N |
| 259 | 192, 207, 222 | 100.35221E | 38.856950N |
| 286 | 192, 207, 222 | 100.35146E | 38.869710N |
| 229 | 192, 207, 222 | 100.34615E | 38.867900N |
| Variables | Unit | Range | Variables | Unit | Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cab | µg/cm2 | 30 | - | 0.232 | |
| Cm | g/cm2 | 0.008 | VIS | km | 20 |
| Cw | cm | 0.0191 | degree | 20~30 | |
| N | - | 1.518 | degree | 35~45 | |
| LAI | m2/m2 | 0~6.5 | degree | 125 | |
| ALA | degree | 45 |
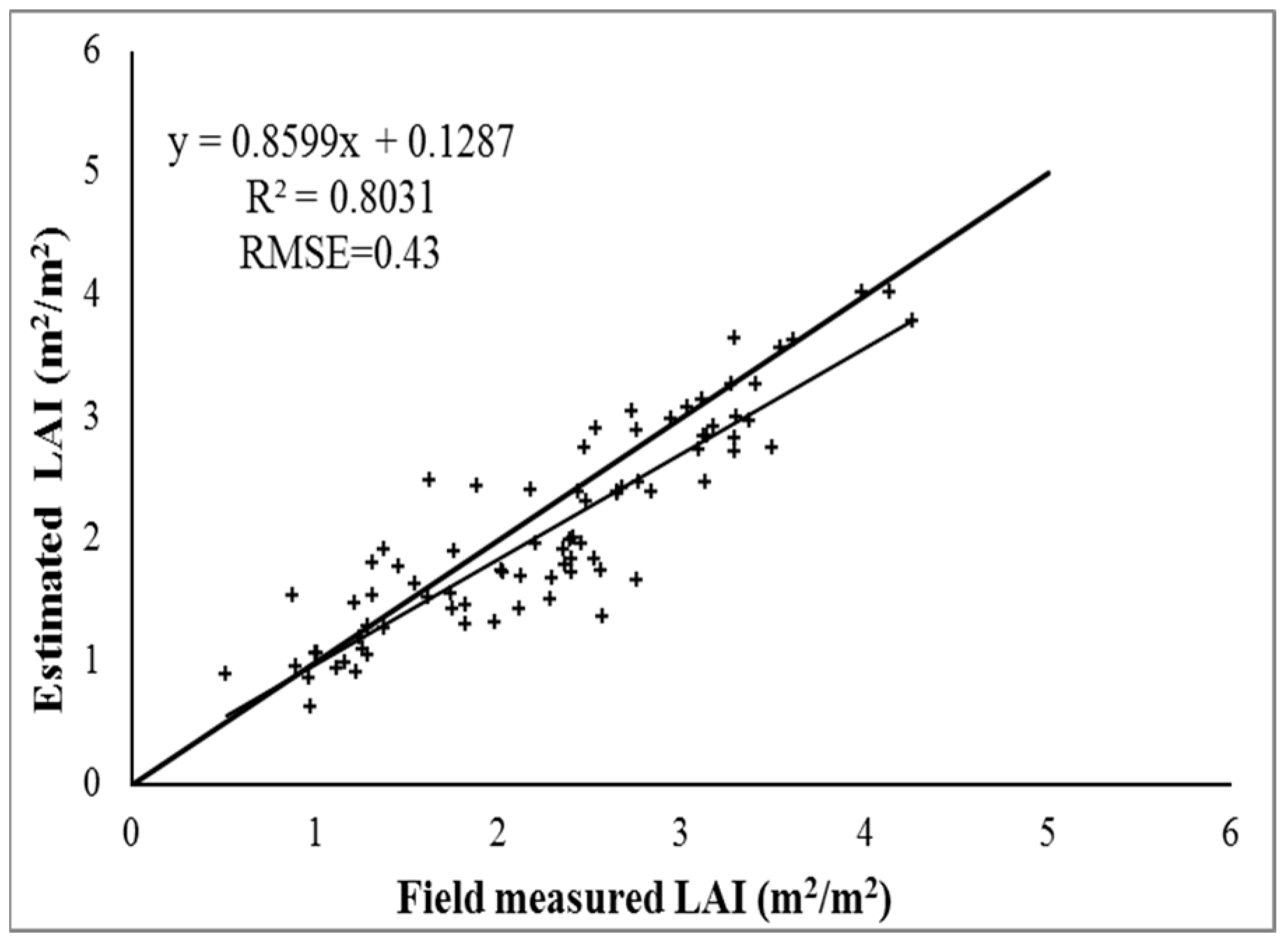
4.2. Evaluation of the Performance of the Estimated LAI
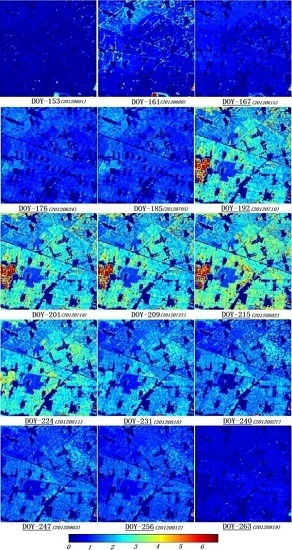
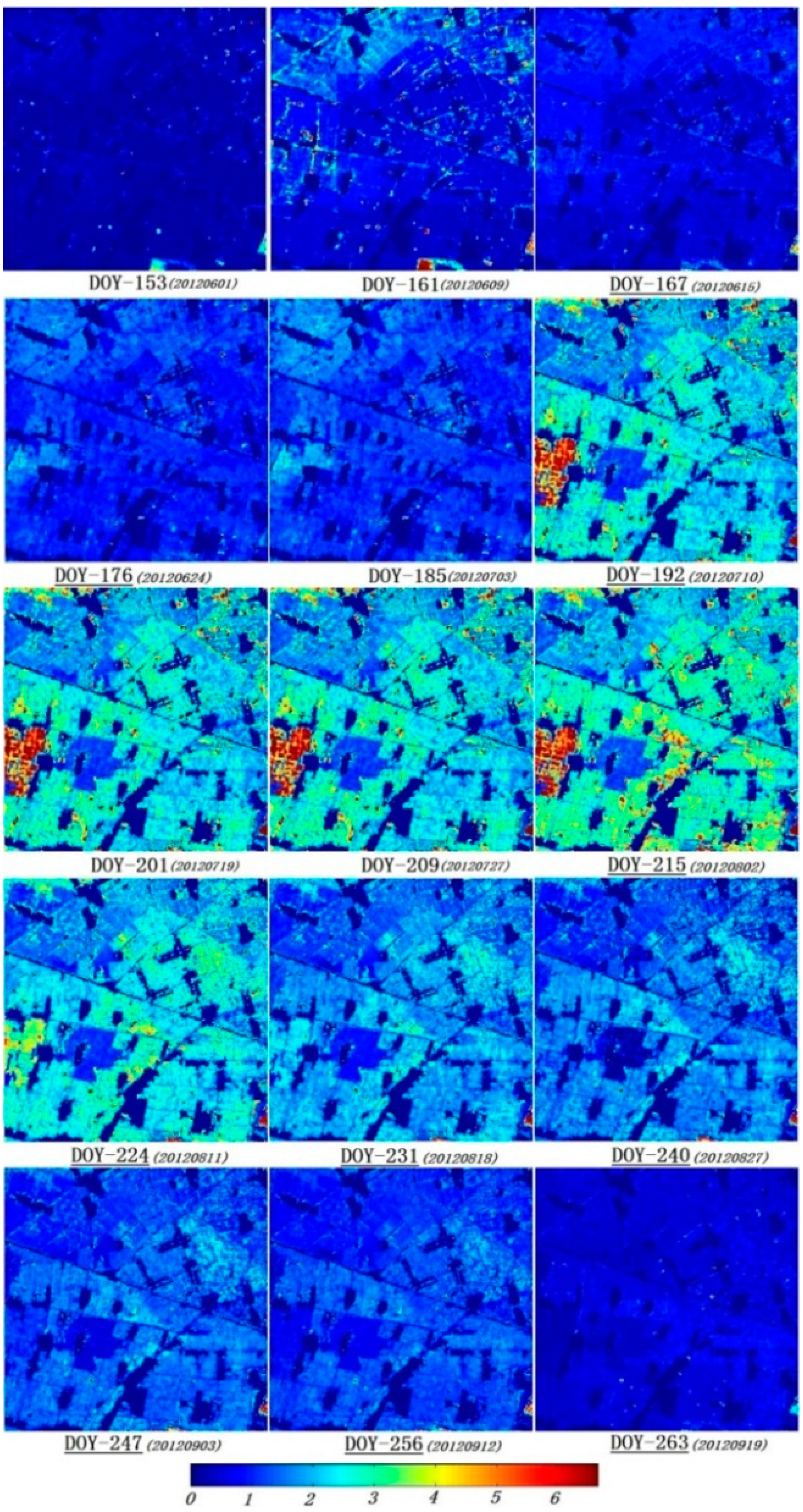
4.3. The Time-Series Analysis of the Estimated LAI
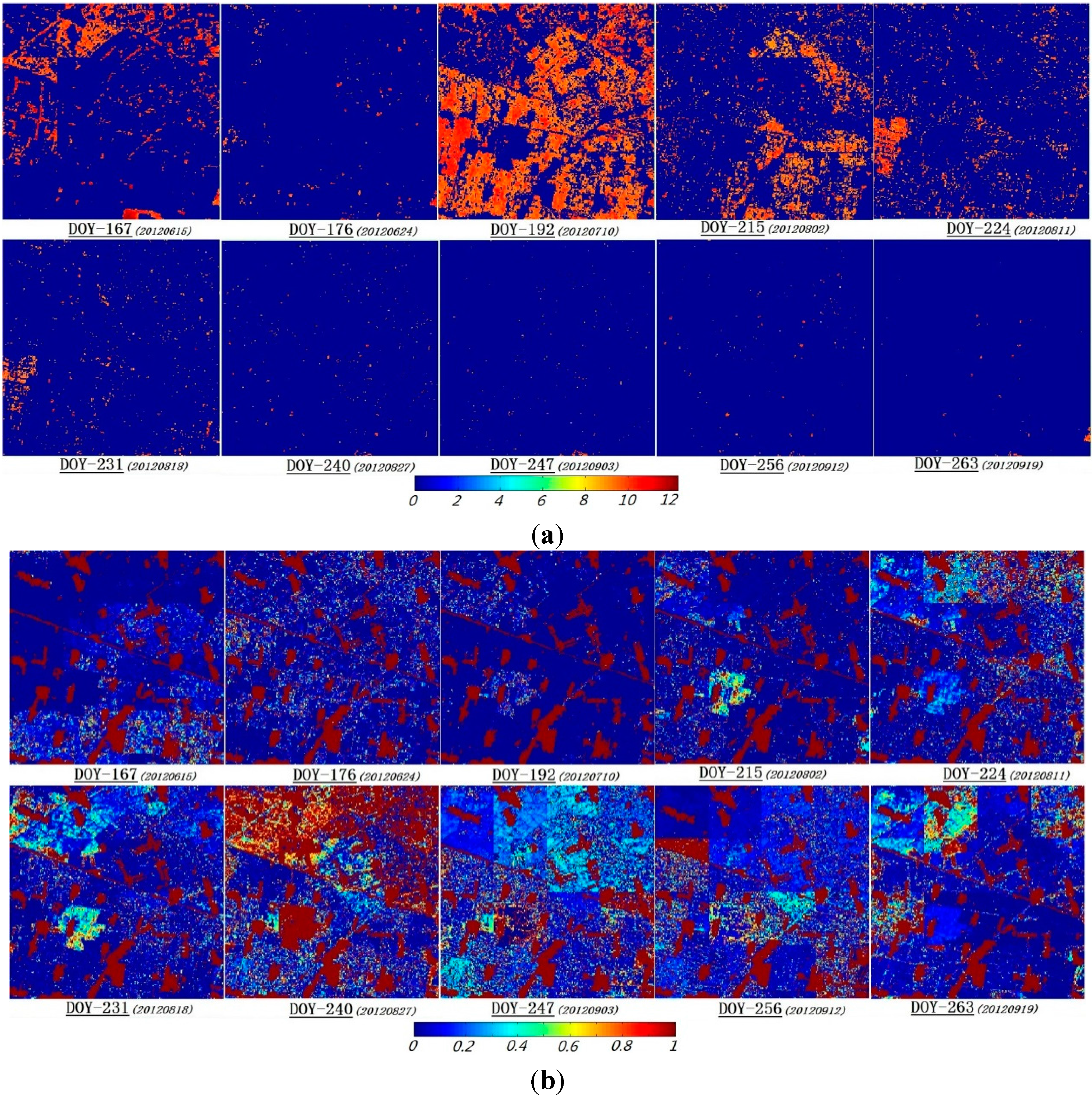
4.4. The Uncertainty Analysis for the LAI Inversion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The determination coefficient R2 and RMSE between the estimated and measured LAIs are 0.80 and 0.43, respectively. Thus, using multisource data to invert time-series and high-resolution LAIs is feasible, and it is an effective method to solve the problems with current remote sensing products, for which the resolution is low and the time is discontinuous.
- (2)
- The quantity of high-resolution remote-sensing observation data is an important factor for the inversion accuracy throughout the time series. In this paper, nine images of high-resolution remote-sensing observation data were used to update the background information, which constitutes nearly two-thirds of the inversion results. However, when the data are rarely updated, depending solely on the model’s prediction may lead to predicted values that gradually deviate from the real values; this deviation cannot be corrected until the observation data are provided.
- (3)
- Calculating the information entropy and maximum probability of the probability distribution not only quantitatively expresses the uncertainties of various states in the inversion process but also provides the change in the uncertainty during the information interaction process. The results demonstrate that in most cases, high-resolution observation data can provide effective information to update the background information. Thus, this method is feasible for inverting temporal high-resolution LAIs by incorporating the coarse-resolution LAI products and high-resolution remote-sensing observation data.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, J.M.; Black, T.A. Defining leaf area index for non-flat leaves. Plant Cell Environ. 1992, 15, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, R.; Miller, J.R.; Hu, B.; Rubinstein, I.G. A multi-scale approach to mapping effective leaf area index in boreal picea mariana stands using high spatial resolution CASI imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 3547–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myneni, R.; Hoffman, S.; Knyazikhin, Y.; Privette, J.; Glassy, J.; Tian, Y.; Wang, Y.; Song, X.; Zhang, Y.; Smith, G. Global products of vegetation leaf area and fraction absorbed PAR from year one of MODIS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 214–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, F.; Cernicharo, J.; Lacaze, R.; Baret, F.; Weiss, M. Geov1: LAI, FAPAR essential climate variables and fcover global time series capitalizing over existing products. Part 2: Validation and intercomparison with reference products. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 137, 310–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Liang, S.; Wang, J.; Chen, P.; Yin, X.; Zhang, L.; Song, J. Use of general regression neural networks for generating the glass leaf area index product from time-series MODIS surface reflectance. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, R.; Chen, J.M. Retrospective retrieval of long-term consistent global leaf area index (1981–2011) from combined AVHRR and MODIS data. J. Geophys. Res.: Biogeosci. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinty, B.; Andredakis, I.; Clerici, M.; Kaminski, T.; Taberner, M.; Verstraete, M.; Gobron, N.; Plummer, S.; Widlowski, J.L. Exploiting the MODIS albedos with the two-stream inversion package (JRC-TIP): 1. Effective leaf area index, vegetation, and soil properties. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Sanpedro, M.C.; Le Toan, T.; Moreno, J.; Kergoat, L.; Rubio, E. Seasonal variations of leaf area index of agricultural fields retrieved from landsat data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 810–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colomboa, R.; Bellingerib, D.; Fasolinic, D.; Marinob, C.M. Retrieval of leaf area index in different vegetation types using high resolution satellite data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 86, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Muñoz, J.C.; Sobrino, J.A.; Gillespie, A.; Sabol, D.; Gustafson, W.T. Improved land surface emissivities over agricultural areas using ASTER NDVI. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 103, 474–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Manso, O.; Fernández-Manso, A.; Quintano, C. Estimation of aboveground biomass in mediterranean forests by statistical modelling of ASTER fraction images. Int. J. Appl. Earth Observ. Geoinf. 2014, 31, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, J.; Song, C. Mapping leaf area index using spatial, spectral, and temporal information from multiple sensors. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 119, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Anderson, M.C.; Kustas, W.P.; Wang, Y. Simple method for retrieving leaf area index from landsat using MODIS leaf area index products as reference. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2012, 6, 063554–063551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Jiang, C.; Li, W.; Wei, S.; Baret, F.; Chen, J.M.; Garcia-Haro, J.; Liang, S.; Liu, R.; Myneni, R.B. Characterization and intercomparison of global moderate resolution leaf area index (LAI) products: Analysis of climatologies and theoretical uncertainties. J. Geophys. Res.: Biogeosci. 2013, 118, 529–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, P. Uncertainties in crop, soil and weather inputs used in growth models: Implications for simulated outputs and their applications. Agric. Syst. 1995, 48, 361–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulder, M.A.; White, J.C.; Nelson, R.F.; Næsset, E.; Ørka, H.O.; Coops, N.C.; Hilker, T.; Bater, C.W.; Gobakken, T. Lidar sampling for large-area forest characterization: A review. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 121, 196–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cheng, G.; Liu, S.; Xiao, Q.; Ma, M.; Jin, R.; Che, T.; Liu, Q.; Wang, W.; Qi, Y. Heihe watershed allied telemetry experimental research (HiWATER): Scientific objectives and experimental design. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 94, 1145–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Han, W.; Wang, J.; Ma, M. Crop leaf area index observations with a wireless sensor network and its potential for validating remote sensing products. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Han, W.; Fu, L.; Li, C.; Song, J.; Zhou, H.; Bo, Y.; Wang, J. LAINET—A wireless sensor network for coniferous forest leaf area index measurement: Design, algorithm and validation. Comput. Electron. Agr. 2014, 108, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Press, W.H.; Teukolsky, S.A. Savitzky-golay smoothing filters. Comput. Phys. 1990, 4, 669–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Liang, S.; Kuusk, A. Retrieving leaf area index using a genetic algorithm with a canopy radiative transfer model. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 85, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Woodcock, C.E.; Wang, Y.; Privette, J.L.; Shabanov, N.V.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, Y.; Buermann, W.; Dong, J.; Veikkanen, B. Multiscale analysis and validation of the MODIS LAI product: I. Uncertainty assessment. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 414–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Lü, C.; Yu, B. Assessing the potential productivity of winter wheat using wofost in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. J. Nat. Resour. 2010, 25, 475–487. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, X. A methodology for estimating leaf area index by assimilating remote sensing data into crop model based on temporal and spatial knowledge. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2013, 23, 550–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquemoud, S.; Baret, F. Prospect: A model of leaf optical properties spectra. Remote Sens. Environ. 1990, 34, 75–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoef, W. Light scattering by leaf layers with application to canopy reflectance modeling: The sail model. Remote Sens. Environ. 1984, 16, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosgood, B.; Jacquemoud, S.; Andreoli, G.; Verdebout, J.; Pedrini, G.; Schmuck, G. Leaf Optical Properties EXperiment 93 (LOPEX93); Report EUR-16095-EN; European Commission, Joint Research Centre, Institute for Remote Sensing Applications: Ispra, Italy, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Jacquemoud, S.; Baret, F.; Hanocq, J.F. Modeling spectral and bidirectional soil reflectance. Remote Sens. Environ. 1992, 41, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J. A dynamic bayesian network data fusion algorithm for estimating leaf area index using time-series data from in situ measurement to remote sensing observations. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 1106–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Qu, Y.; Wang, J.; Liang, S.; Liu, Y. Estimating leaf area index from MODIS and surface meteorological data using a dynamic bayesian network. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 127, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E. A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst. Techn. J. 1948, 27, 379–423, 623–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Strahler, A.H. Geometric-optical modeling of a conifer forest canopy. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1985, GE-23, 705–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanner, W.; Li, X.; Strahler, A. On the derivation of kernels for kernel-driven models of bidirectional reflectance. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos. 1995, 100, 21077–21089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qu, Y.; Han, W.; Ma, M. Retrieval of a Temporal High-Resolution Leaf Area Index (LAI) by Combining MODIS LAI and ASTER Reflectance Data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 195-210. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70100195
Qu Y, Han W, Ma M. Retrieval of a Temporal High-Resolution Leaf Area Index (LAI) by Combining MODIS LAI and ASTER Reflectance Data. Remote Sensing. 2015; 7(1):195-210. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70100195
Chicago/Turabian StyleQu, Yonghua, Wenchao Han, and Mingguo Ma. 2015. "Retrieval of a Temporal High-Resolution Leaf Area Index (LAI) by Combining MODIS LAI and ASTER Reflectance Data" Remote Sensing 7, no. 1: 195-210. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70100195
APA StyleQu, Y., Han, W., & Ma, M. (2015). Retrieval of a Temporal High-Resolution Leaf Area Index (LAI) by Combining MODIS LAI and ASTER Reflectance Data. Remote Sensing, 7(1), 195-210. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70100195