Monitoring Trends in Light Pollution in China Based on Nighttime Satellite Imagery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
3. Method
3.1. Intercalibration of Nighttime Light Imagery
3.2. Assessment of Observed Direction and Timing of Change
4. Results and Discussions
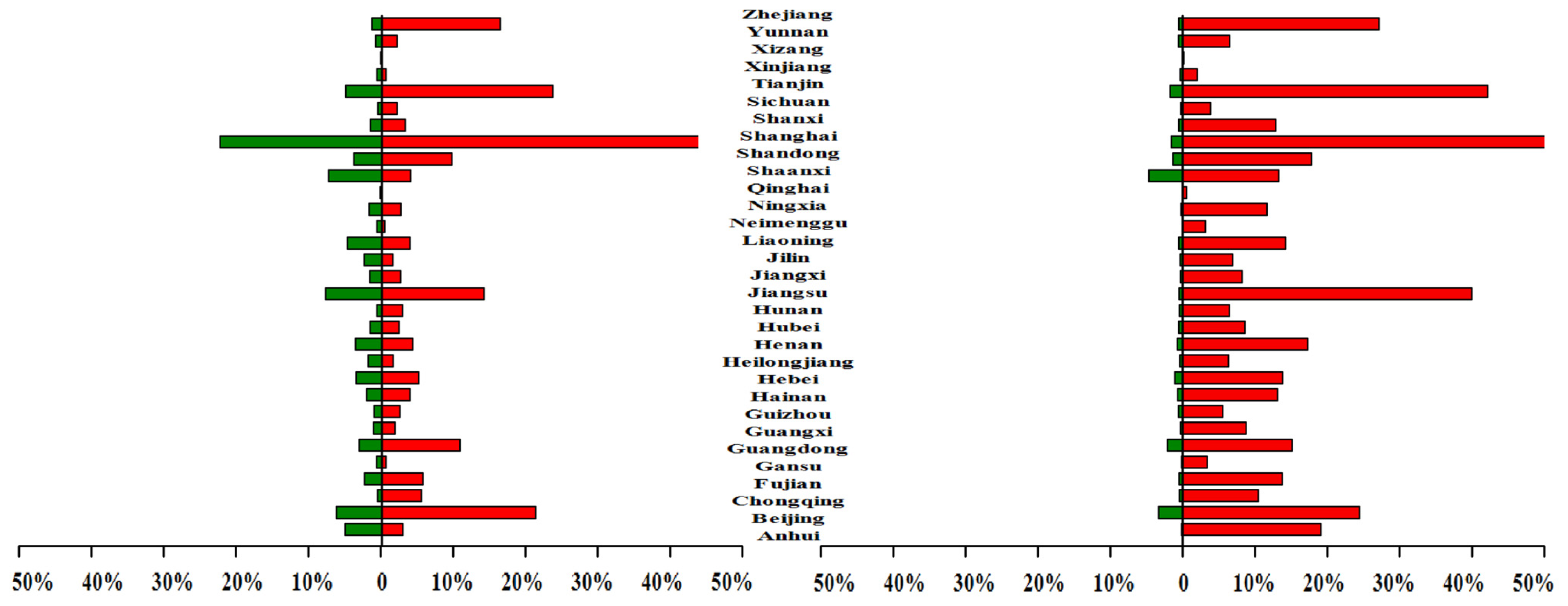
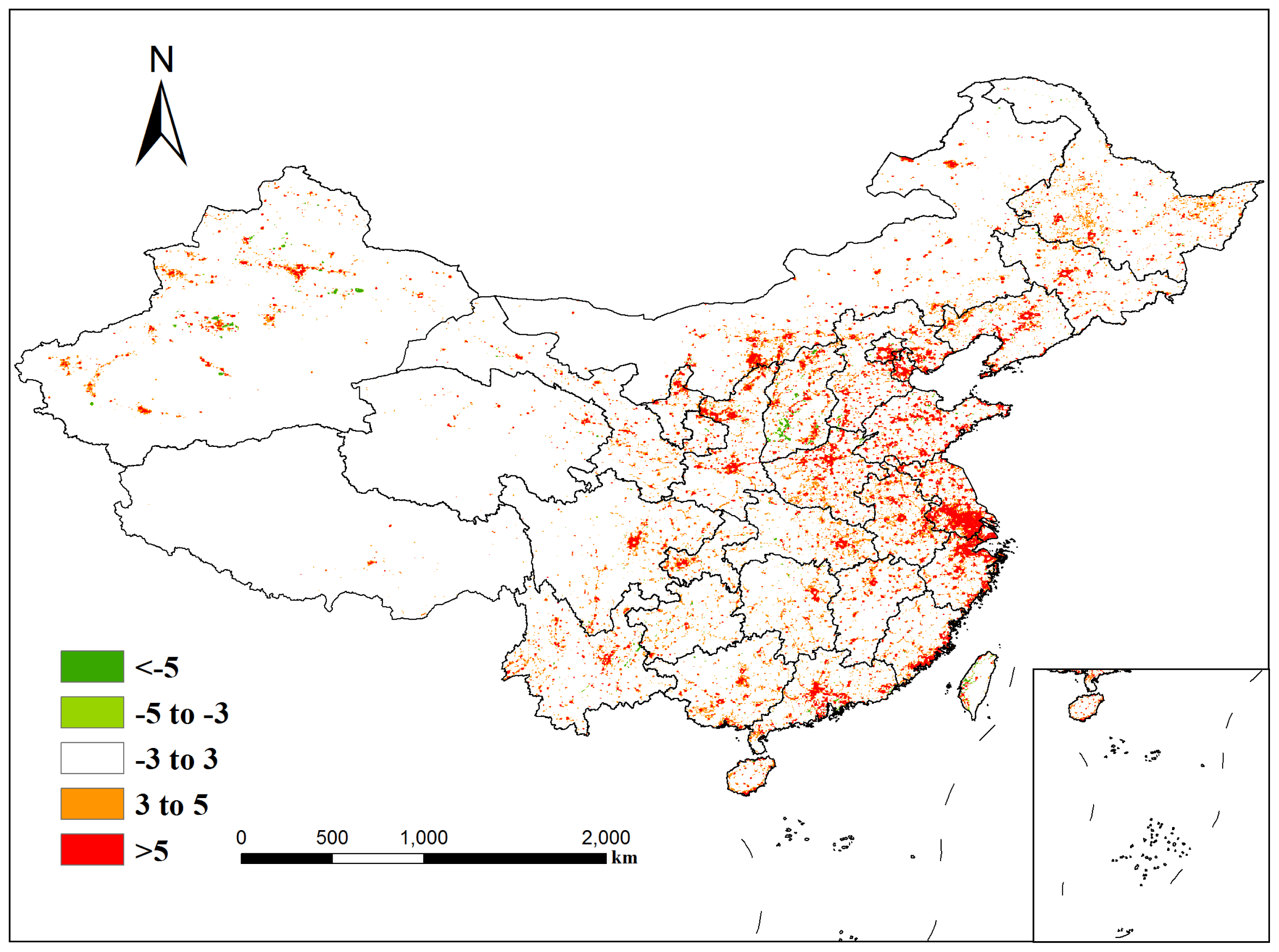
4.1. Temporal Analysis from 1992 to 2012
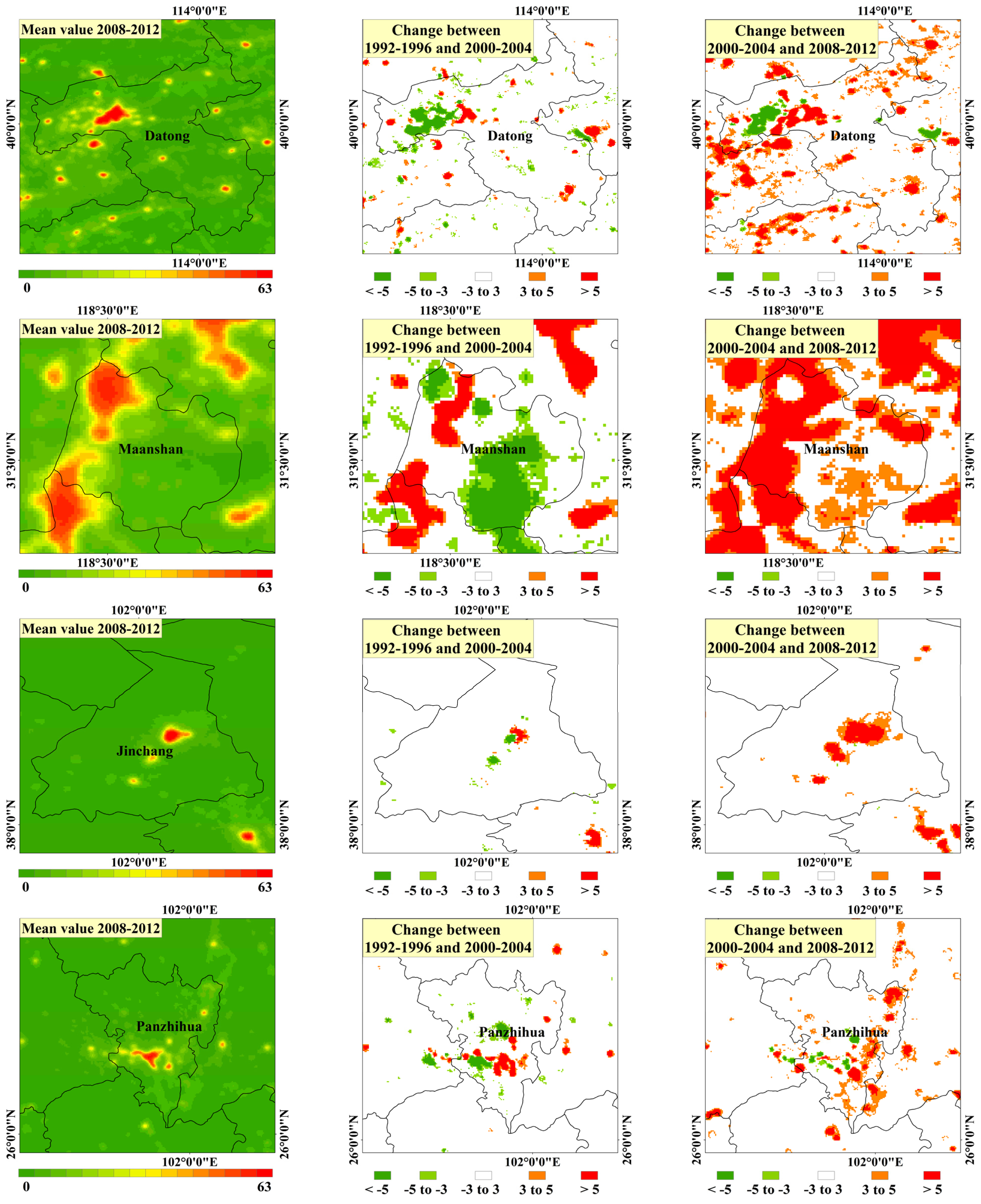
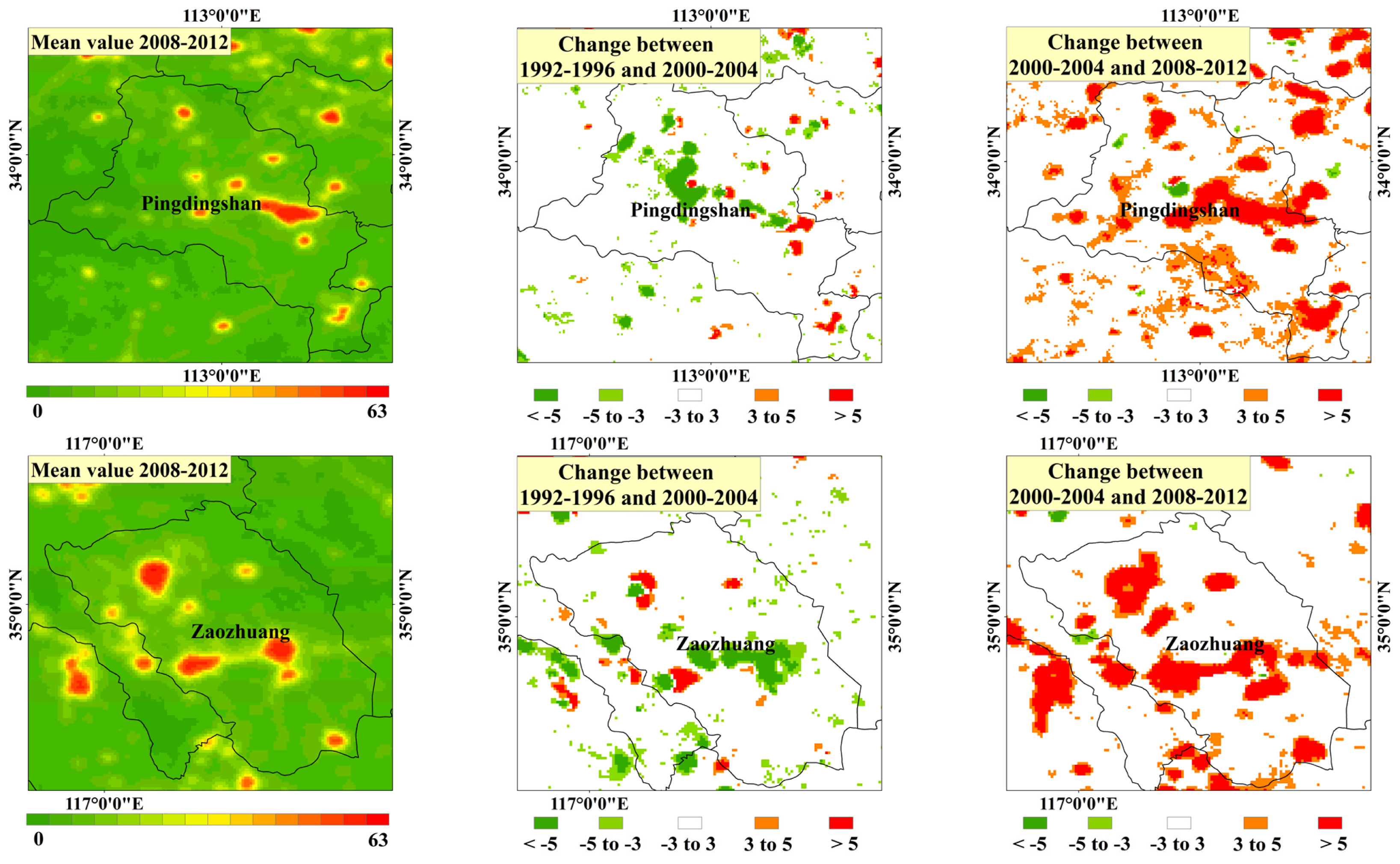
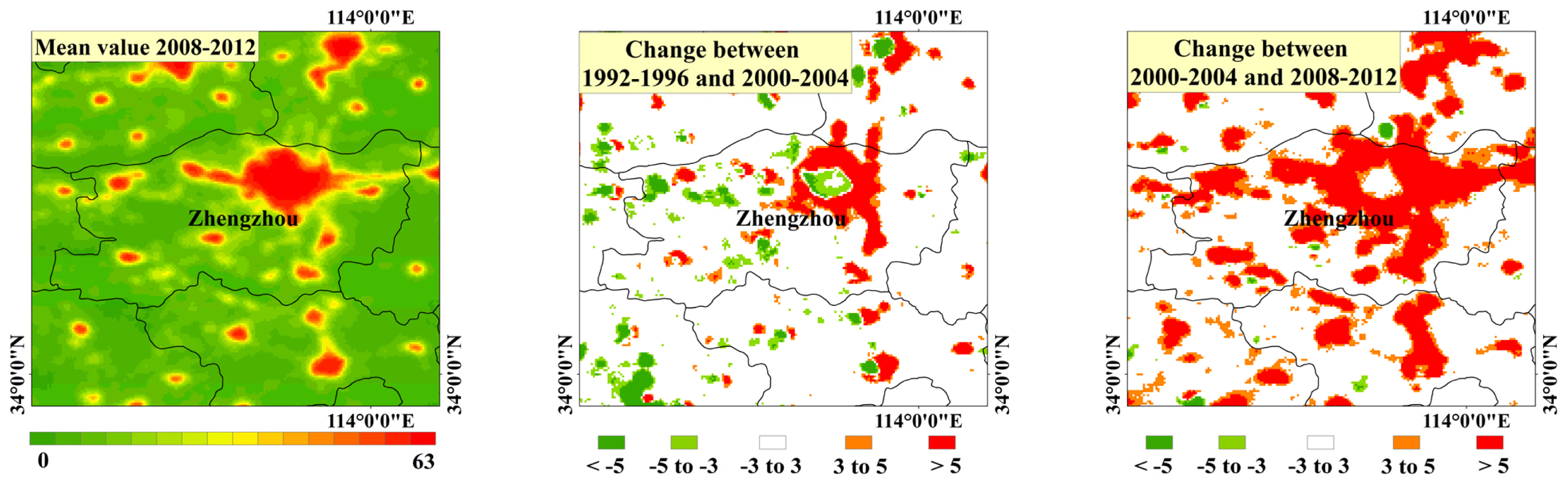
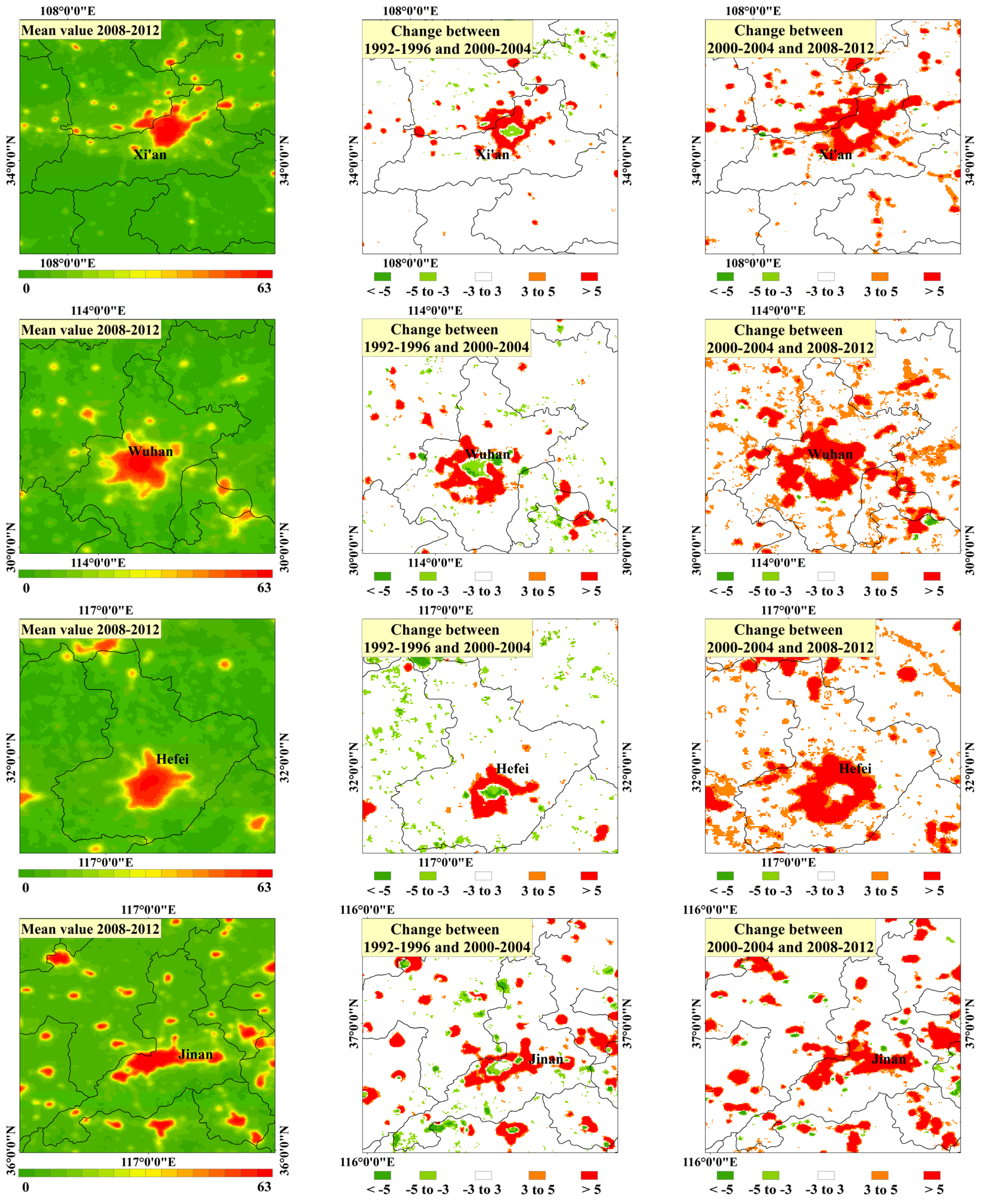
4.2. Special Analysis in Urban Scale
5. Conclusion
Acknowledgment
Conflict of Interest
- Author ContributionsPengpeng Han, Jinliang Huang and Rendong Li conceived and designed the study. Pengpeng Han, Lihui Wang and Yanxia Hu made substantial contributions to acquisition, analysis and interpretation of the data. All authors discussed the basic structure of the manuscript, and Pengpeng Han finished the first draft. Yanxia Hu, Jiuling Wang and Wei Huang reviewed and edited the draft. All authors read and approved the submitted manuscript, agreed to be listed and accepted the version for publication.
References
- Cinzano, P.; Falchi, F.; Elvidge, C.D. The first World Atlas of the artificial sky brightness. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc 2001, 328, 689–707. [Google Scholar]
- Kuechly, H.U.; Kyba, C.C.M.; Ruhtz, T.; Lindemann, C.; Wolter, C.; Fischer, J.; Holker, F. Aerial survey and spatial analysis of sources of light pollution in Berlin, Germany. Remote Sens. Environ 2012, 126, 39–50. [Google Scholar]
- Pun, C.S.J.; So, C.W. Night-sky brightness monitoring in Hong Kong—A city-wide light pollution assessment. Environ. Monit. Assess 2012, 184, 2537–2557. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, P.; Aubrecht, C.; Gil, A.; Longcore, T.; Elvidge, C. Remote sensing to map influence of light pollution on Cory’s shearwater in Sao Miguel Island, Azores Archipelago. European J. Wildl. Res 2012, 58, 147–155. [Google Scholar]
- Riegel, K.W. Light pollution. Science 1973, 179, 1285–1291. [Google Scholar]
- Longcore, T.; Rich, C. Ecological light pollution. Front. Ecol. Env 2004, 2, 191–198. [Google Scholar]
- Poulin, C.; Bruyant, F.; Laprise, M.H.; Cockshutt, A.M.; Vandenhecke, J.M.R.; Huot, Y. The impact of light pollution on diel changes in the photophysiology of Microcystis aeruginosa. J. Plan. Res 2014, 36, 286–291. [Google Scholar]
- Dominoni, D.M.; Quetting, M.; Partecke, J. Long-term effect of chronic light pollution on seasonal functions of European blackbirds (Turdus merula). PLOS One 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Tallec, T.; Perret, M.; Thery, M. Light pollution modifies the expression of daily rhythms and behavior patterns in a Nocturnal primate. PLOS One 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaston, K.J.; Bennie, J.; Davies, T.W.; Hopkins, J. The ecological impacts of nighttime light pollution: A mechanistic appraisal. Biol. Rev 2013, 88, 912–927. [Google Scholar]
- Gaston, K.J.; Davies, T.W.; Bennie, J.; Hopkins, J. REVIEW: Reducing the ecological consequences of night-time light pollution: Options and development. J. Appl. Ecol 2012, 49, 1256–1266. [Google Scholar]
- Gallaway, T.; Olsen, R.N.; Mitchell, D.M. The economics of global light pollution. Ecol. Econ 2010, 69, 658–665. [Google Scholar]
- Kyba, C.C.M.; Ruhtz, T.; Fischer, J.; Hölker, F. Cloud coverage acts as an amplifier for ecological light pollution in urban ecosystems. PLOS One 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falchi, F.; Cinzano, P.; Elvidge, C.D.; Keith, D.M.; Haim, A. Limiting the impact of light pollution on human health, environment and stellar visibility. J. Environ. Manag 2011, 92, 2714–2722. [Google Scholar]
- Navara, K.J.; Nelson, R.J. The dark side of light at night: physiological, epidemiological, and ecological consequences. J. Pineal Res 2007, 43, 215–224. [Google Scholar]
- Kloog, I.; Haim, A.; Stevens, R.G.; Barchana, M.; Portnov, B.A. Light at night co-distributes with incident breast but not lung cancer in the Female population of Israel. Chronobiol. Int 2008, 25, 65–81. [Google Scholar]
- Kloog, I.; Haim, A.; Stevens, R.G.; Portnov, B.A. Global co-distribution of light at night (LAN) and cancers of prostate, colon, and lung in men. Chronobiol. Int 2009, 26, 108–125. [Google Scholar]
- Lilensten, J.; Moedn, J.; Barthélemy, M.; Thissen, R.; Simon, C.; Lorentzen, D.A.; Dutuit, O.; Amblard, P.O.; Sigernes, F. Polarization in Aurorae: A new dimension for space environments studies. Geophys Res. Lett 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.F.; Yu, B.L.; Huang, Y.X..; Hu, Y.J.; Yin, B.; Chen, Z.Q.; Chen, L.J.; Wu, J.P. Evaluating the ability of NPP-VIIRS nighttime light data to estimate the gross domestic product and the electric power consumption of China at multiple scales: a comparison with DMSP-OLS data. Remote Sens 2014, 6, 1705–1724. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Xu, H.M.; Chen, X.L.; Li, C. Potential of NPP-VIIRS nighttime light imagery for modeling the regional economy of China. Remote Sens 2013, 5, 3057–3081. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, T.; Wu, Y. Hard Light Pollution Complaints. Available online: http://epaper.oeeee.com/H/html/2010-06/30/content_1115916.htm (accessed on 9 April 2014). (In Chinese)
- Ye, P.S. Neon Billboards Too Dizzy To Pay Sewage Charges. Available online: http://gzdaily.dayoo.com/html/2010-04/21/content_937627.htm (accessed on 9 April 2014) . (In Chinese)
- Yang, X.C.; Yue, W.Z.; Gao, D.W. Spatial improvement of human population distribution based on multi-sensor remote-sensing data: an input for exposure assessment. Int. J. Remote Sens 2013, 34, 5569–5583. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, T.; Zhou, C.H.; Pei, T.; Haynie, S.; Fan, J.F. Quantitative estimation of urbanization dynamics using time series of DMSP/OLS nighttime light data: A comparative case study from China’s cities. Remote Sens. Environ 2012, 124, 99–107. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, N.; Ghosh, T.; Samson, E.L. Mapping spatio-temporal changes of Chinese electric power consumption using night-time imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens 2012, 33, 6304–6320. [Google Scholar]
- Townsend, A.C.; Bruce, D.A. The use of night-time lights satellite imagery as a measure of Australia’s regional electricity consumption and population distribution. Int. J. Remote Sens 2010, 31, 4459–4480. [Google Scholar]
- He, C.Y.; Ma, Q.; Li, T.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Z.F. Spatiotemporal dynamics of electric power consumption in Chinese Mainland from 1995 to 2008 modeled using DMSP/OLS stable nighttime lights data. J. Geogr. Sci 2012, 22, 125–136. [Google Scholar]
- Levin, N.; Duke, Y. High spatial resolution night-time light images for demographic and socio-economic studies. Remote Sens. Environ 2012, 119, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, W.; Peng, J. Exploring factors affecting the relationship between light consumption and GDP based on DMSP/OLS nighttime satellite imagery. Remote Sens. Environ 2013, 134, 111–119. [Google Scholar]
- He, C.; Shi, P.; Li, J.; Chen, J.; Pan, Y.; Li, J.; Zhuo, L.; Ichinose, T. Restoring urbanization process in China in the 1990s by using non-radiance-calibrated DMSP/OLS nighttime light imagery and statistical data. Chin. Sci. Bull 2006, 51, 1614–1620. [Google Scholar]
- He, C.; Ma, Q.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Q. Modeling the spatiotemporal dynamics of electric power consumption in Mainland China using saturation-corrected DMSP/OLS nighttime stable light data. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letu, H.; Hara, M.; Yagi, H.; Naoki, K.; Tana, G.; Nishio, F.; Shuhei, O. Estimating energy consumption from night-time DMPS/OLS imagery after correcting for saturation effects. Int. J. Remote Sens 2010, 31, 4443–4458. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; He, C.; Zhang, Q.; Han, L.; Du, S. Timely and accurate national-scale mapping of urban land in China using Defense Meteorological Satellite Program’s Operational Linescan System nighttime stable light data. J. Appl. Remote Sens 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, M.J. Estimation of light pollution using satellite remote sensing and geographic information system techniques. GISci. Remote Sens 2012, 49, 609–621. [Google Scholar]
- Bennie, J.; Davies, T.W.; Duffy, J.P.; Inger, R.; Gaston, K.J. Contrasting trends in light pollution across Europe based on satellite observed night time lights. Sci. Rep 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, X.; Huang, J.; Rozelle, S.; Uchida, E. Growth population and industrialization and land expansion of China. J. Urban Econ 2008, 63, 96–115. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.H.; Song, S. Rural-urban migration and urbanization in China: Evidence from time-series and cross-section analyses. China Econ. Rev 2003, 14, 386–400. [Google Scholar]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China, China City Statistical Yearbook 2012; China Statistical Press: Beijing, China, 2013. (In Chinese)
- National Bureau of Statistics of China, China Statistical Yearbook for Regional Economy 2012; China Statistical Press: Beijing, China, 2012. (In Chinese)
- Baugh, K.; Elvidge, C.D.; Ghosh, T.; Ziskin, D. Development of a 2009 stable lights product using DMSP-OLS data. Proc. Asia-Pacific Adv. Net 2010, 30, 114–130. [Google Scholar]
- Small, C.; Elvidge, C.D. Night on Earth: mapping decadal changes of anthropogenic night light in Asia. Int. J. Appl. Earth. Obs 2013, 22, 40–52. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Chen, X.L.; Zhao, Y.S.; Xu, J.; Chen, F.R.; Li, H. Automatic intercalibration of night-time light imagery using robust regress. Remote. Sens. Lett 2012, 4, 46–55. [Google Scholar]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Sutton, P.C.; Ghosh, T. A global poverty map derived from satellite data. Comp. Geosci 2009, 35, 1652–1660. [Google Scholar]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Ziskin, D.; Baugh, K.E.; Tuttle, B.T.; Ghosh, T.; Pack, D.W. A fifteen year record of global natural gas flaring derived from satellite data. Energies 2009, 2, 595–622. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.F.; He, C.Y.; Zhang, Q.F.; Huang, Q.X.; Yang, Y. Extracting the dynamics of urban expansion in China using DMSP-OLS nighttime light data from 1992 to 2008. Landsc. Urban Plan 2012, 106, 62–72. [Google Scholar]
- National Bureau of Statistics in China, China City Statistical Yearbook 2013; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2014. (In Chinese)
- Statistical Information of ShanXi, Shanxi Statistical Yearbook 1999; China Statistical Press: Beijing, China, 1997. (In Chinese)
- Miller, S.D.; Straka, W., III; Mills, S.P.; Elvidge, C.D.; Lee, T.F.; Solbrig, J.; Walther, A.; Heidinger, A.K.; Weiss, S.C. Illuminating the capabilities of the Suomi National Polar-Orbiting Partnership (NPP) Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) day/night band. Remote Sens 2013, 5, 6717–6766. [Google Scholar]
- Elvidge, C.D.; Zhizhin, M.; Hsu, F.C.; Baugh, K.E. VIIRS nightfire: satellite pyrometry at night. Remote Sens 2013, 5, 4423–4449. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, C.; Xiong, J.; Blonski, S.; Liu, Q.; Uprety, S.; Shao, X.; Bai, Y.; Weng, F. Suomi NPP VIIRS sensor data record verification, validation, and long-term performance monitoring. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos 2013, 118, 664–678. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, C.Y.; Shao, X.; Uprety, S. Detecting light outages after severe storms using the S-NPP/VIIRS day/night band radiances. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett 2013, 10, 1582–1586. [Google Scholar]
- Le Borgne, P.; Pere, S.; Roquet, H. Night time detection of Saharan dust using infrared window channels: Application to NPP/VIIRS. Remote Sens. Environ 2013, 137, 264–273. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, K.F.; Huang, C.; Yu, B.L.; Yin, B.; Huang, Y.X.; Wu, J.P. Evaluation of NPP-VIIRS nighttime light composite data for extracting built-up urban areas. Remote Sens. Lett 2014, 5, 358–366. [Google Scholar]


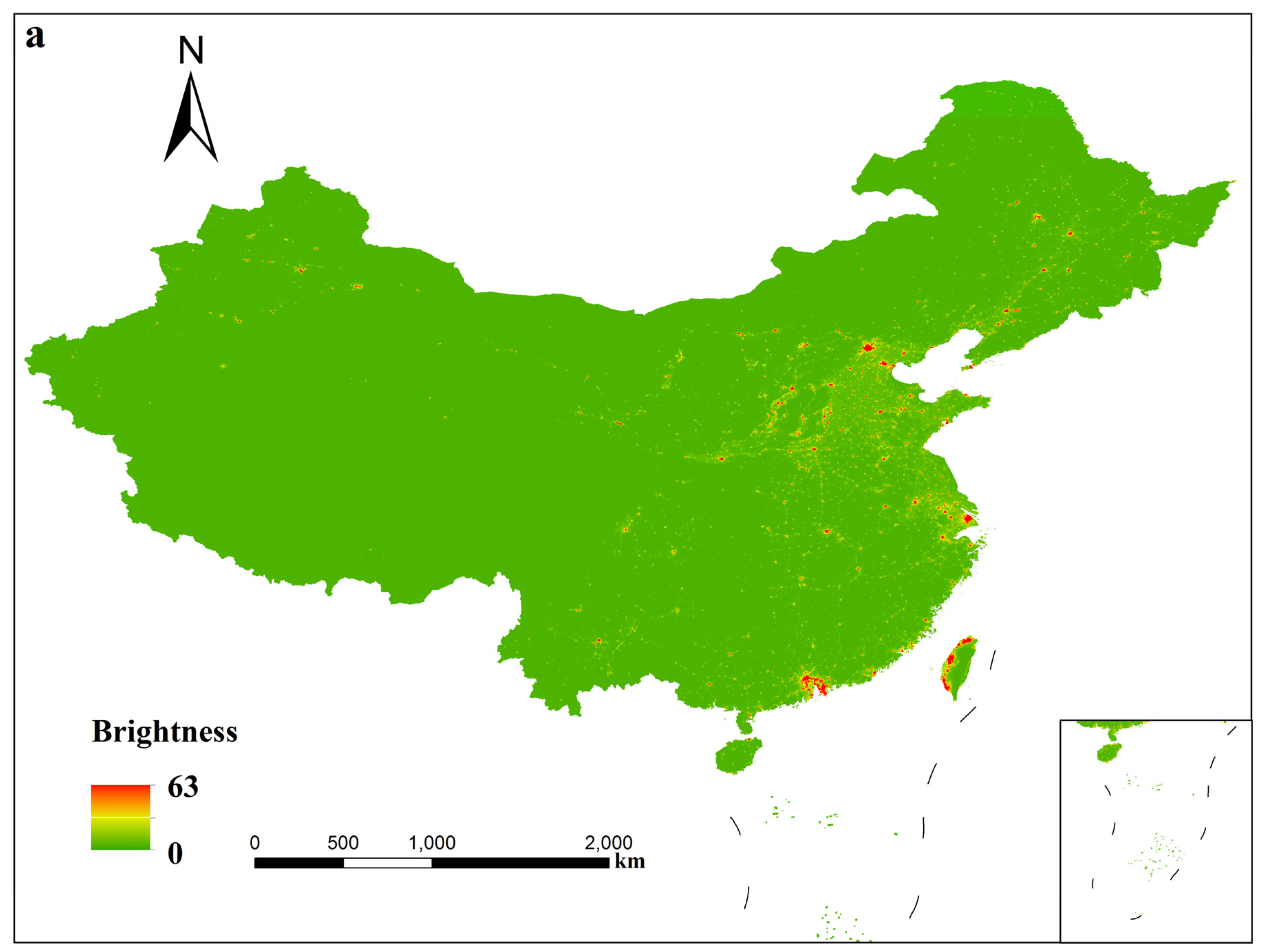
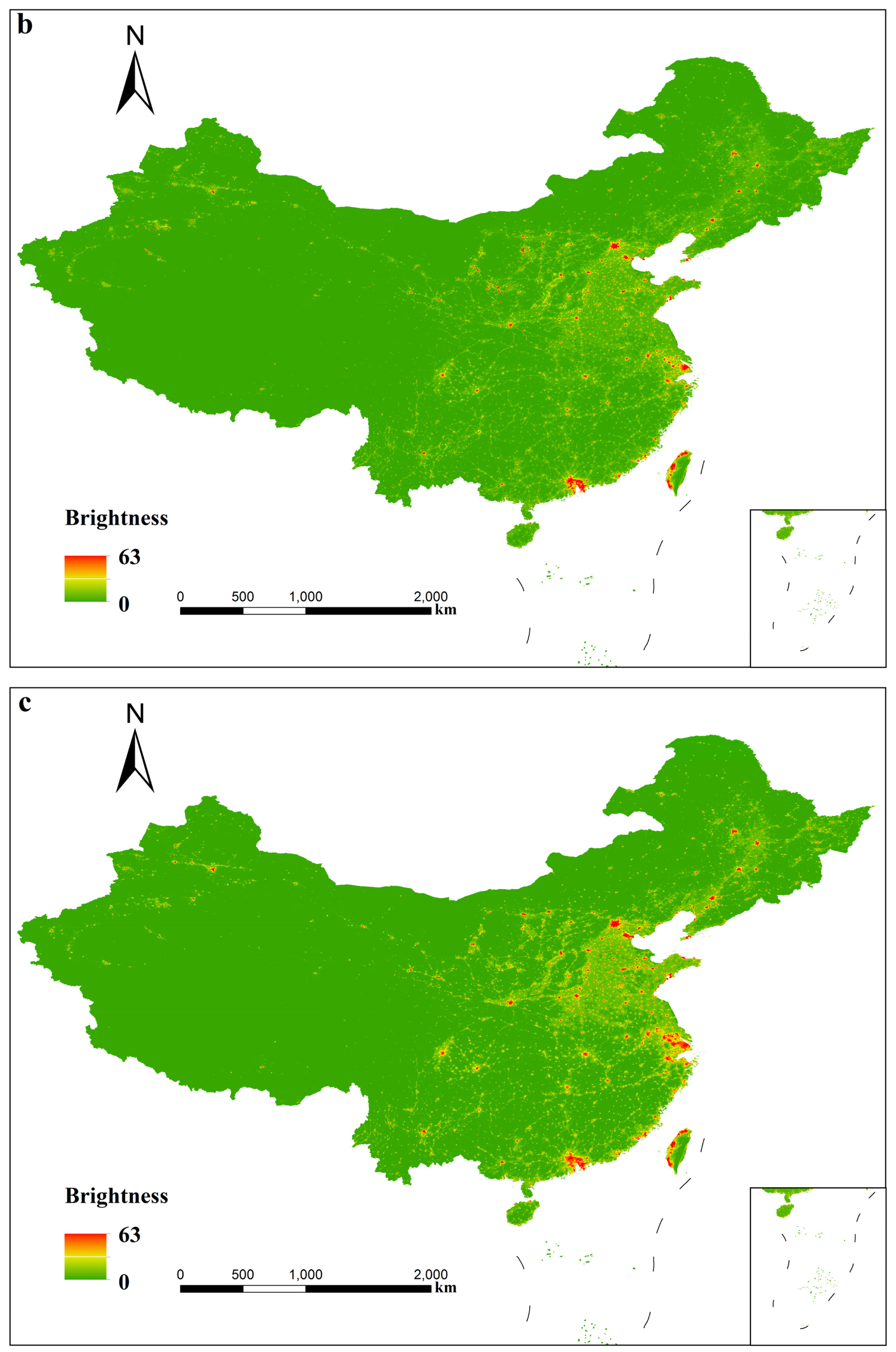
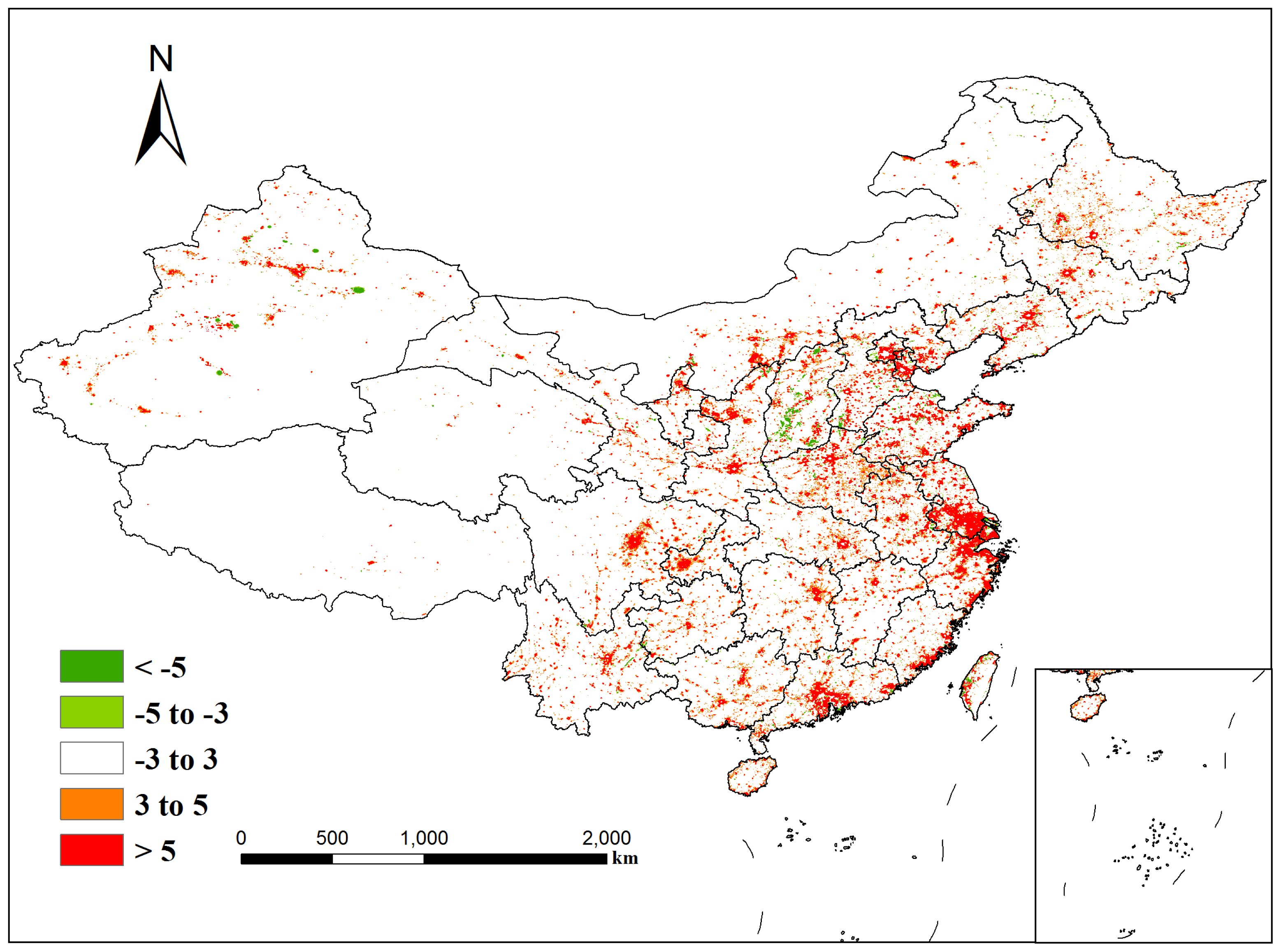
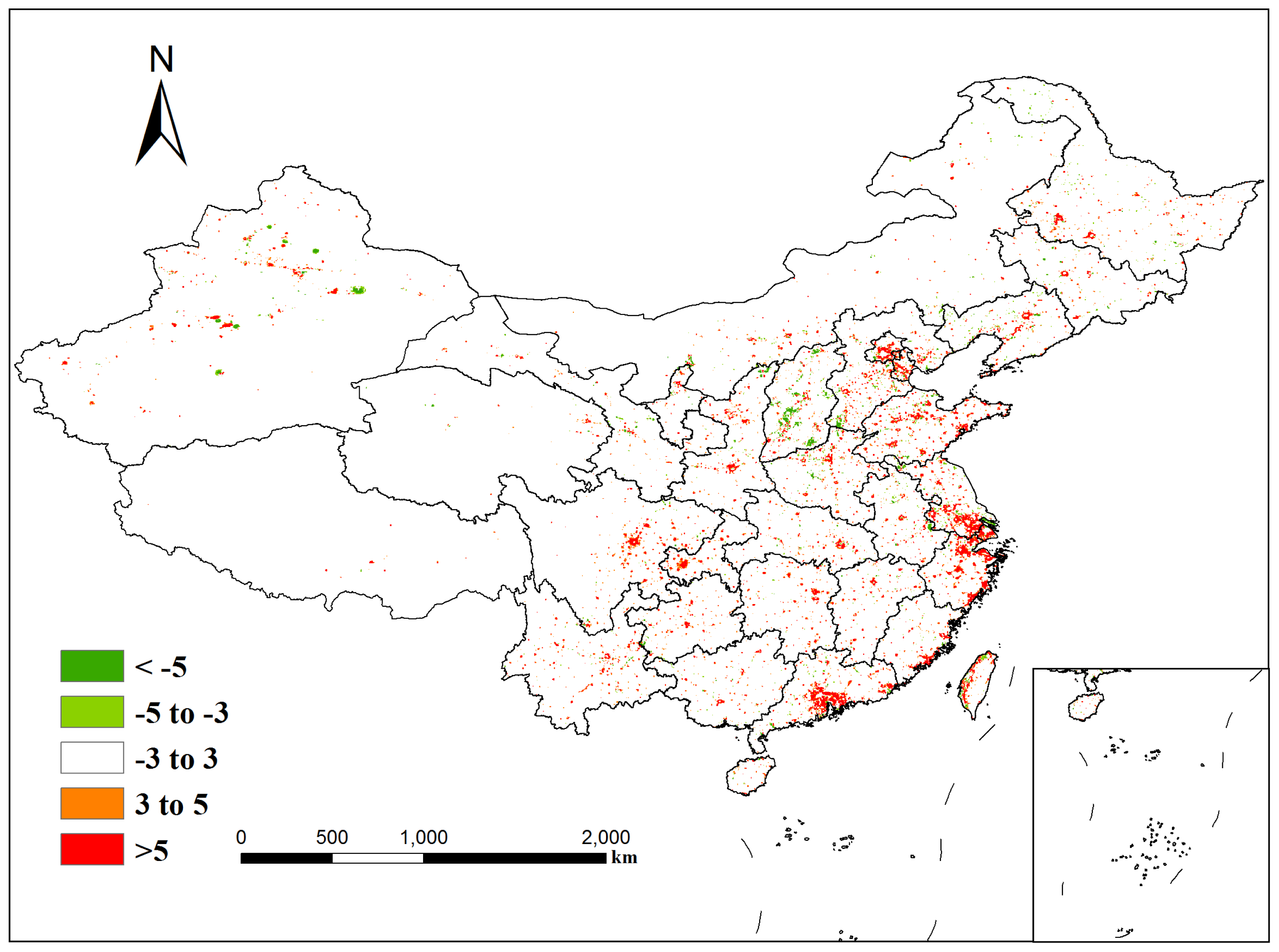
| Satellite | Year | a | b | c | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F10 | 1992 | 0.0021 | 1.0297 | −1.1242 | 0.8977 |
| 1993 | 0.0025 | 1.1260 | −0.9544 | 0.9022 | |
| F12 | 1994 | 0.0016 | 1.1312 | −1.1391 | 0.8902 |
| 1995 | 0.0082 | 0.6370 | 1.2033 | 0.8592 | |
| 1996 | 0.0097 | 0.5778 | 1.4918 | 0.8272 | |
| F14 | 1997 | 0.0009 | 1.0722 | 0.4025 | 0.8233 |
| 1998 | 0.0050 | 0.8729 | 0.5210 | 0.8538 | |
| 1999 | 0.0007 | 1.0910 | 0.5410 | 0.9143 | |
| F15 | 2000 | 0.0086 | 0.4986 | 2.1741 | 0.8809 |
| 2001 | 0.0012 | 1.0292 | −0.8652 | 0.9126 | |
| 2002 | 0.0008 | 0.9713 | −0.6740 | 0.9629 | |
| 2003 | −0.0126 | 1.7774 | −0.9333 | 0.9166 | |
| F16 | 2004 | −0.0010 | 1.1041 | −0.0450 | 0.9266 |
| 2005 | −0.0036 | 1.3178 | −0.7441 | 0.9646 | |
| 2006 | −0.0056 | 1.3436 | −0.3514 | 0.9707 | |
| 2007 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | |
| 2008 | 0.0012 | 0.9258 | 0.6122 | 0.9855 | |
| 2009 | 0.0070 | 0.4360 | 2.3540 | 0.9030 | |
| F18 | 2010 | 0.0035 | 0.7403 | 0.1945 | 0.9511 |
| 2011 | −0.0025 | 1.1073 | 0.1052 | 0.9584 | |
| 2012 | 0.0085 | 0.2291 | 3.8971 | 0.9252 |
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, P.; Huang, J.; Li, R.; Wang, L.; Hu, Y.; Wang, J.; Huang, W. Monitoring Trends in Light Pollution in China Based on Nighttime Satellite Imagery. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 5541-5558. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs6065541
Han P, Huang J, Li R, Wang L, Hu Y, Wang J, Huang W. Monitoring Trends in Light Pollution in China Based on Nighttime Satellite Imagery. Remote Sensing. 2014; 6(6):5541-5558. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs6065541
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Pengpeng, Jinliang Huang, Rendong Li, Lihui Wang, Yanxia Hu, Jiuling Wang, and Wei Huang. 2014. "Monitoring Trends in Light Pollution in China Based on Nighttime Satellite Imagery" Remote Sensing 6, no. 6: 5541-5558. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs6065541
APA StyleHan, P., Huang, J., Li, R., Wang, L., Hu, Y., Wang, J., & Huang, W. (2014). Monitoring Trends in Light Pollution in China Based on Nighttime Satellite Imagery. Remote Sensing, 6(6), 5541-5558. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs6065541





