Comparison of Medium Spatial Resolution ENVISAT-MERIS and Terra-MODIS Time Series for Vegetation Decline Analysis: A Case Study in Central Asia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
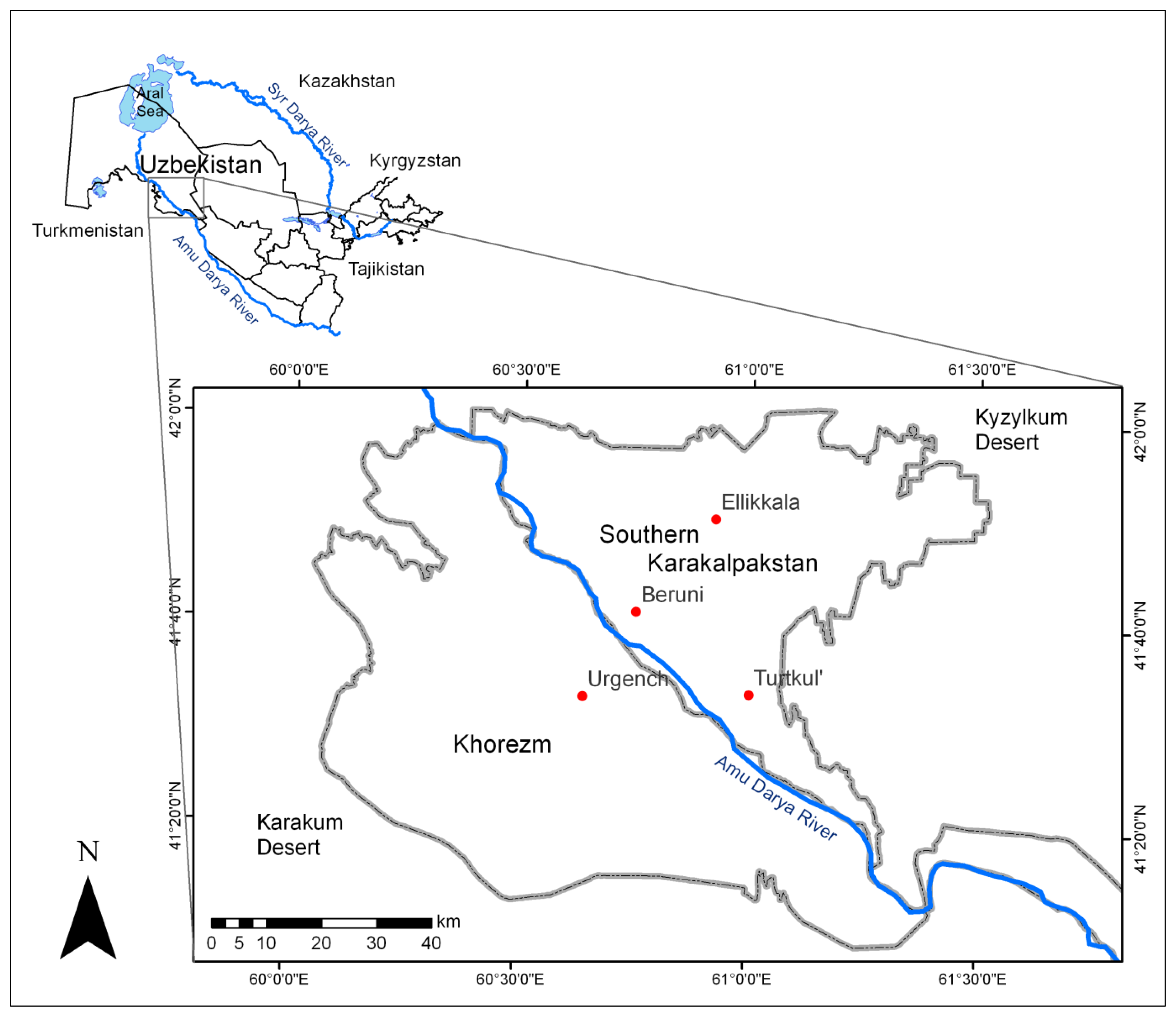
2. Study Area
3. Methods and Material
3.1. Satellite Imagery
3.2. Methods
4. Results and Discussion
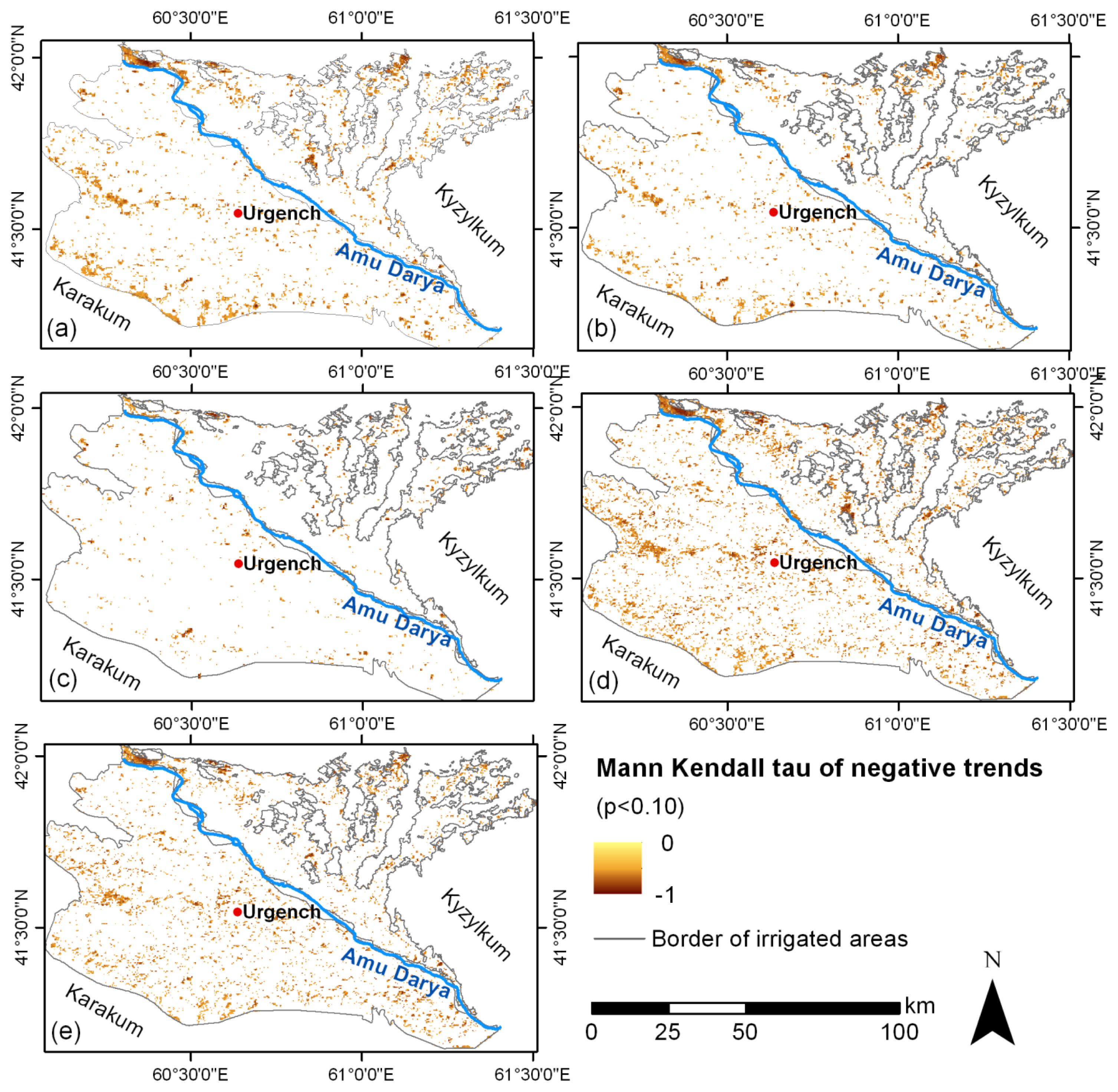
4.1. Vegetation Productivity Decline in the Study Area
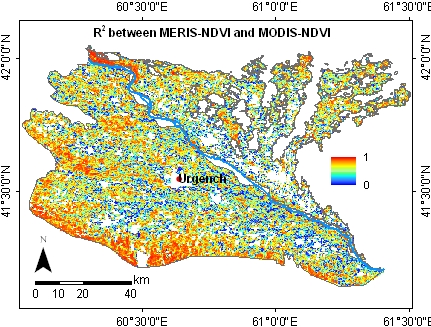
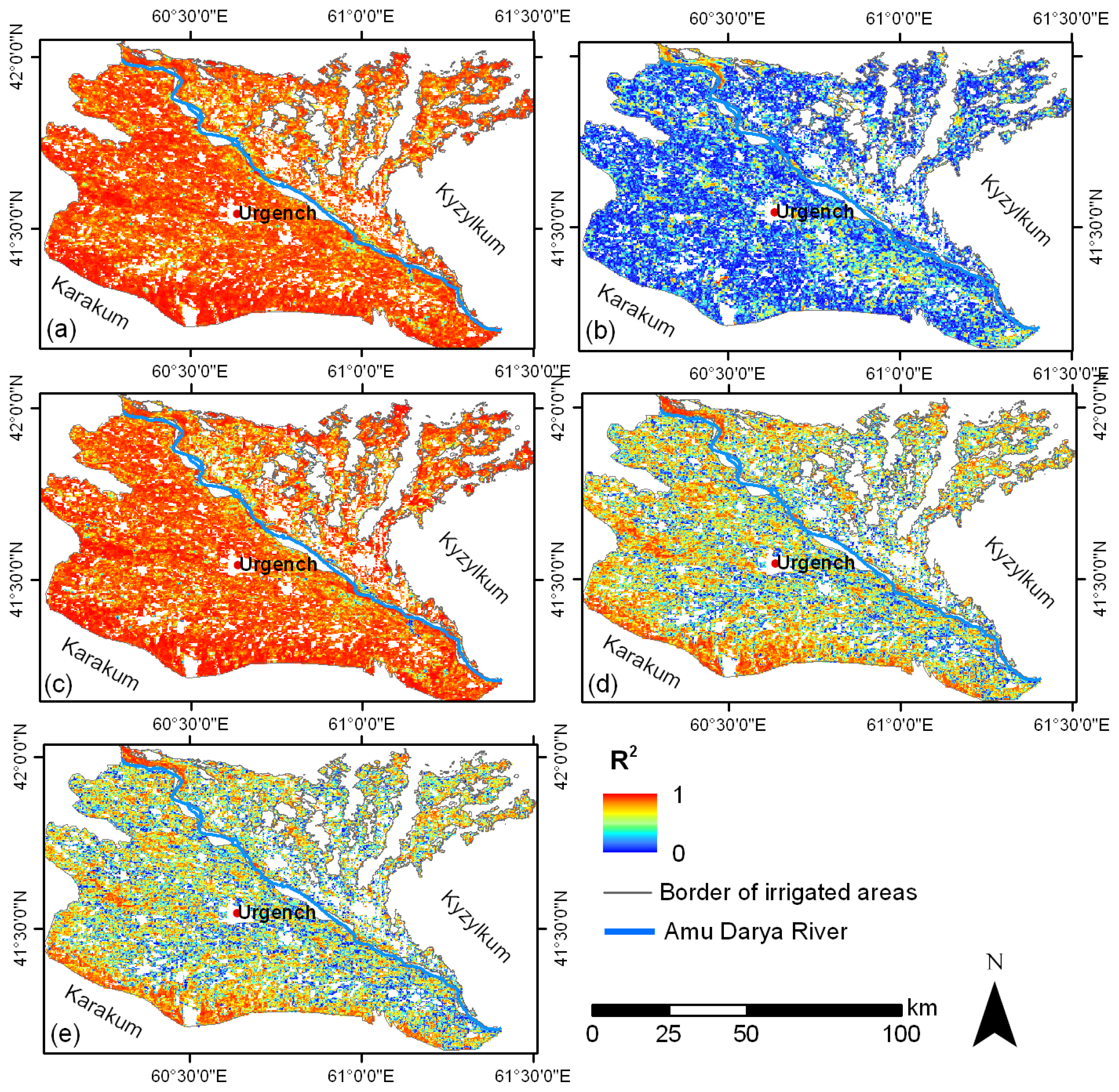
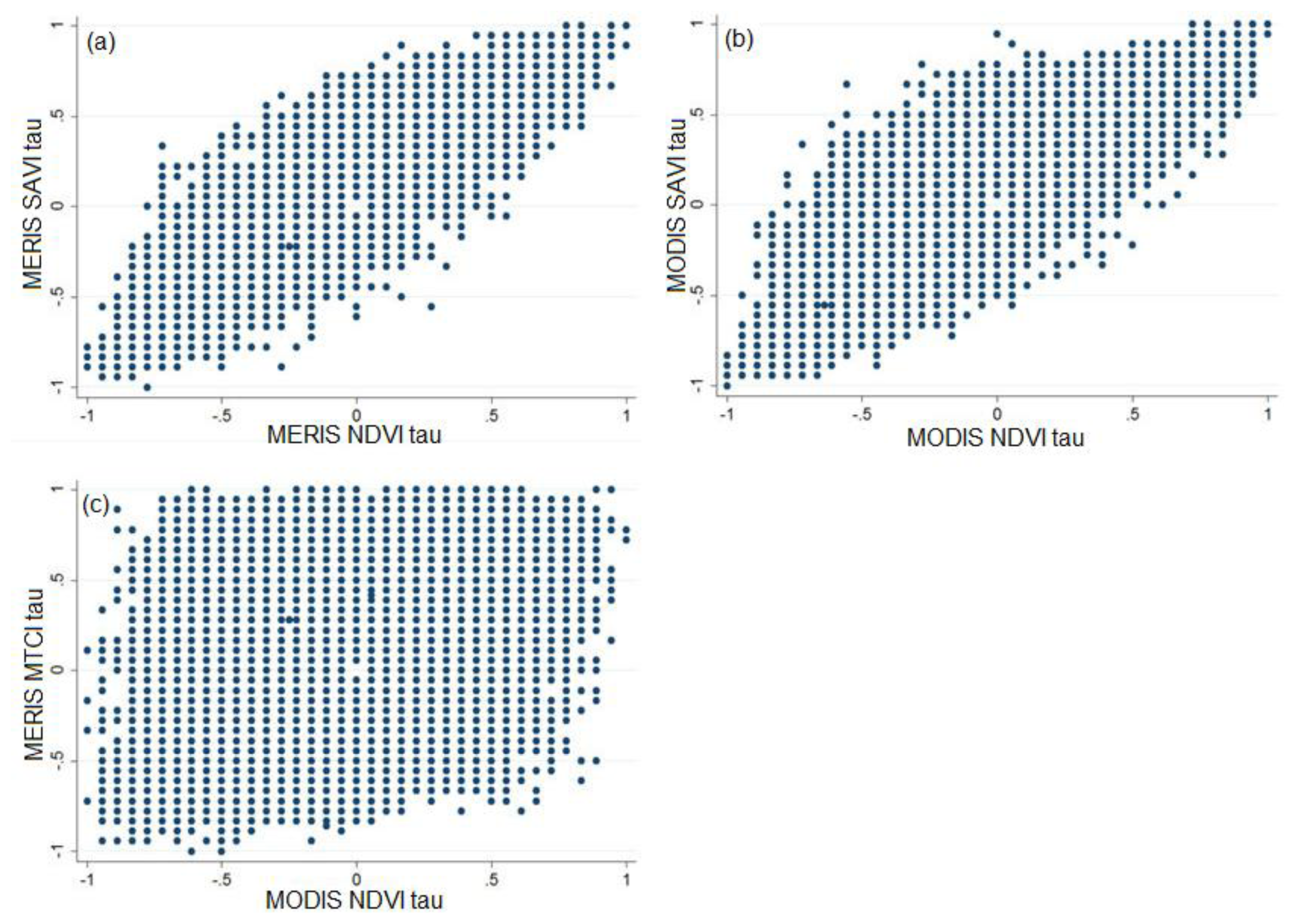
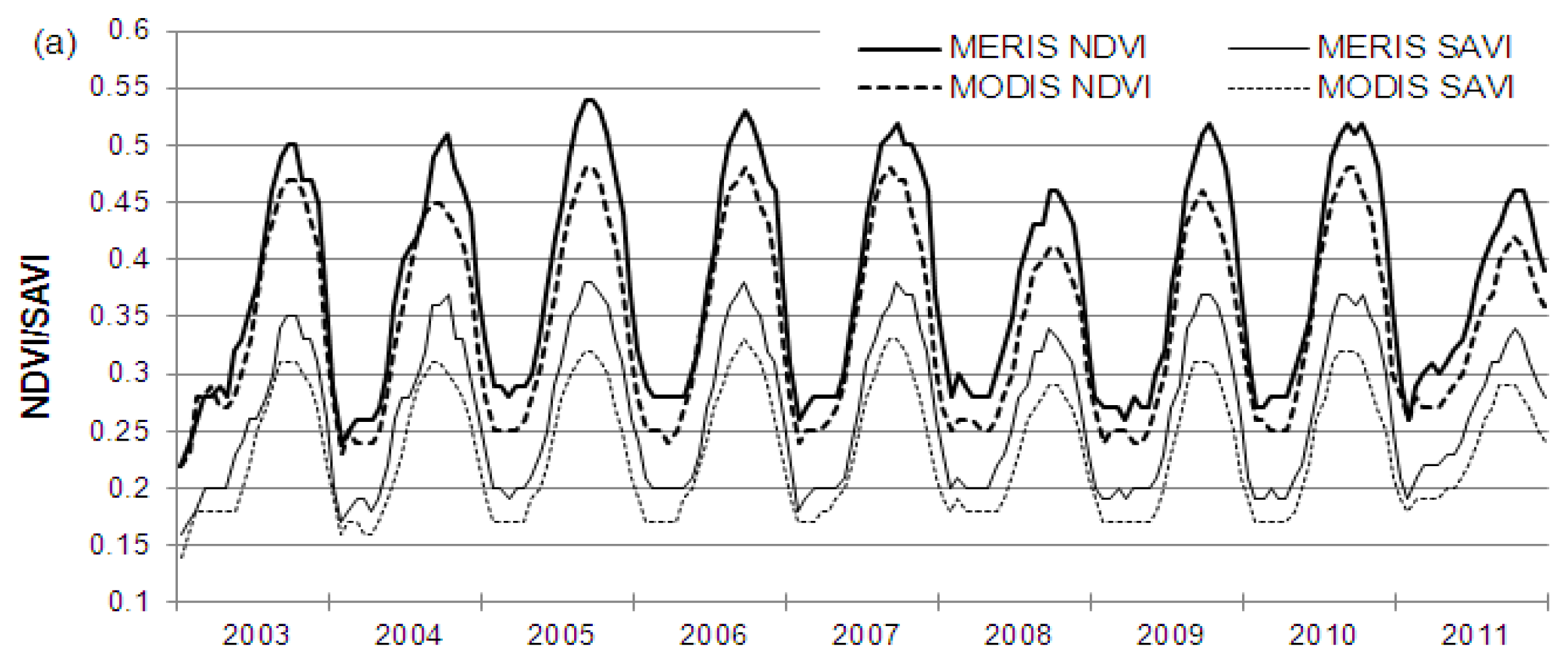
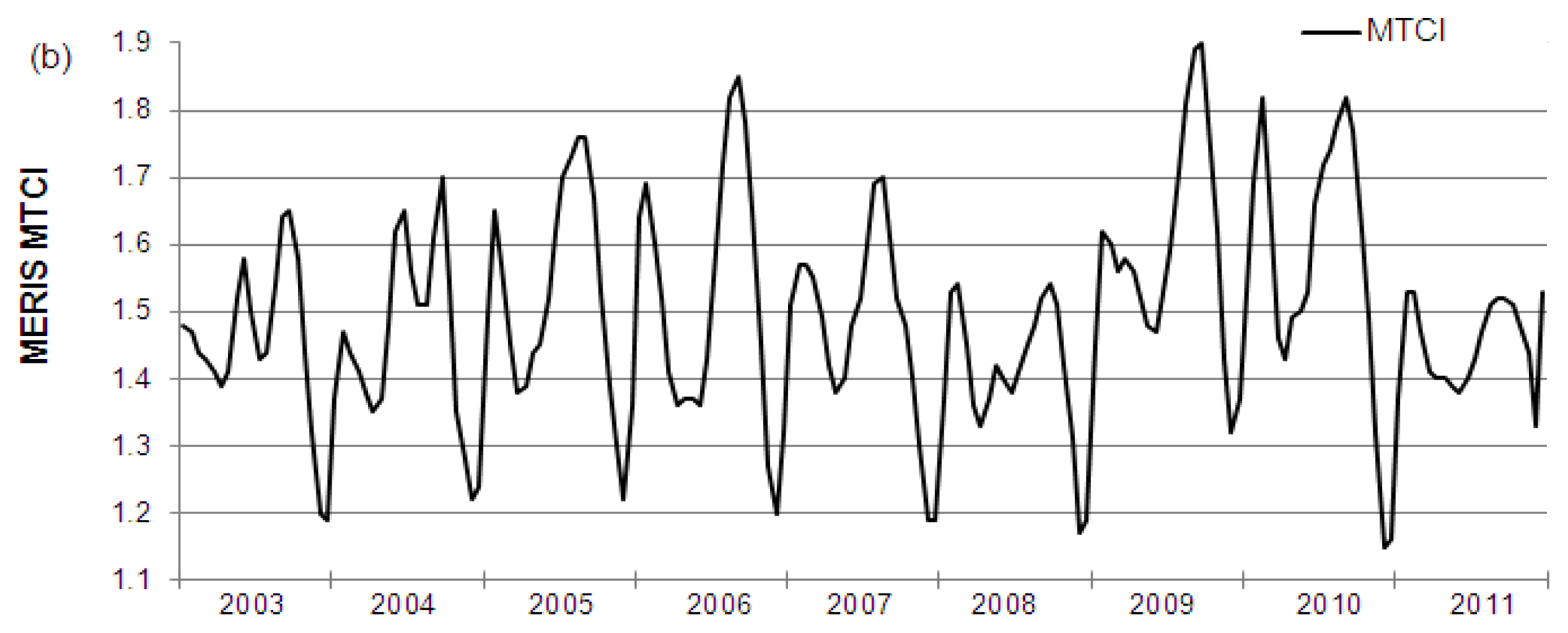
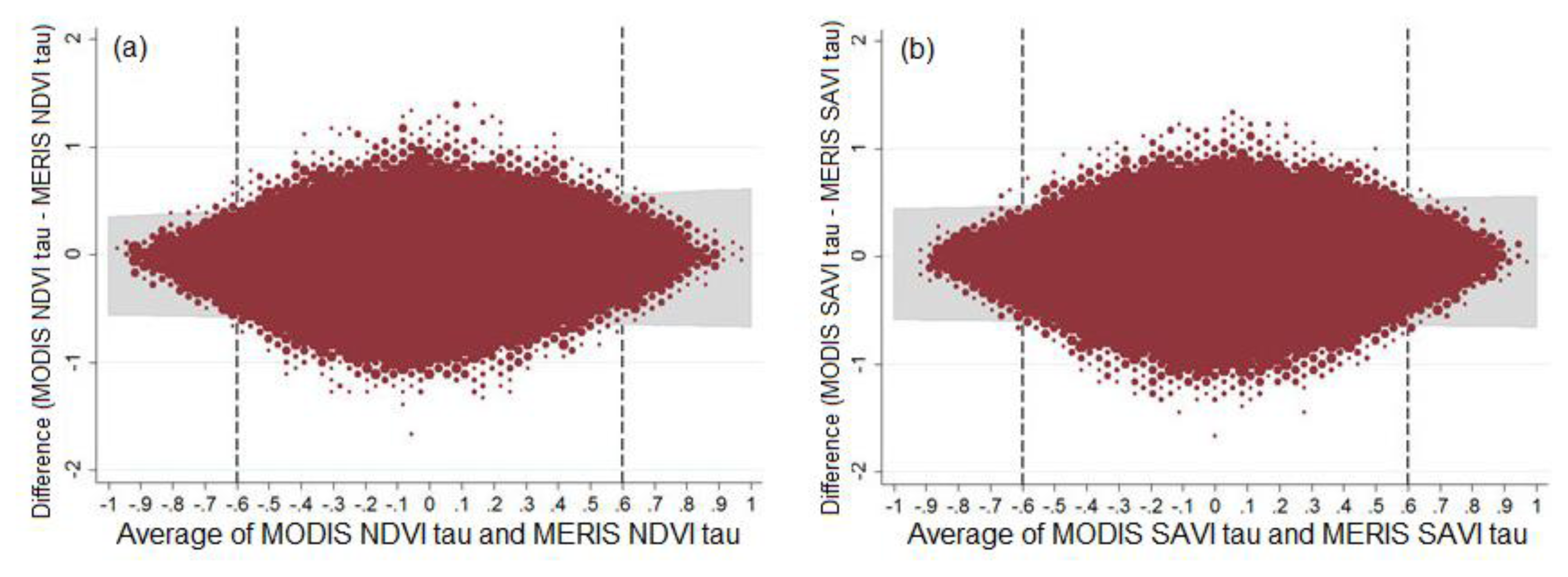
4.2. Comparison of Time Series and Trends
4.2.1. Vegetation Index Time Series
4.2.2. MERIS and MODIS Time Series and Trends
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
- Author ContributionsAll authors contributed to the scientific content and authorship of this manuscript.
References
- Sonnenschein, R.; Kuemmerle, T.; Udelhoven, T.; Stellmes, M.; Hostert, P. Differences in Landsat-based trend analyses in drylands due to the choice of vegetation estimate. Remote Sens. Environ 2011, 115, 1408–1420. [Google Scholar]
- Radke, R.J.; Andra, S.; Al-Kofahi, O.; Roysam, B. Image change detection algorithms: A systematic survey. IEEE Trans. Image Process 2005, 14, 294–307. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Hay, G.J.; Carvalho, L.M.T.; Wulder, M.A. Object-based change detection. Int. J. Remote Sens 2012, 33, 4434–4457. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.-Y.; Ma, Y.-J.; Xu, H.-Y.; Wang, J.-H.; Zhang, D.-S. Impact of land use and land cover change on environmental degradation in lake Qinghai watershed, northeast Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Land Degrad. Dev 2009, 20, 69–83. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Liu, Y. Determination of land degradation causes in Tongyu County, Northeast China via land cover change detection. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf 2010, 12, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Yiran, G.A.B.; Kusimi, J.M.; Kufogbe, S.K. A synthesis of remote sensing and local knowledge approaches in land degradation assessment in the Bawku East District, Ghana. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf 2012, 14, 204–213. [Google Scholar]
- Zanotta, D.C.; Haertel, V. Gradual land cover change detection based on multitemporal fraction images. Pattern Recognit 2012, 45, 2927–2937. [Google Scholar]
- Lambin, E.F.; Strahlers, A.H. Change-vector analysis in multitemporal space: A tool to detect and categorize land-cover change processes using high temporal-resolution satellite data. Remote Sens. Environ 1994, 48, 231–244. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, G.X.; Lin, G.; Warner, T. Using Thematic Mapper data for change detection and sustainable use of cultivated land: A case study in the Yellow River delta, China. Int. J. Remote Sens 2004, 25, 2509–2522. [Google Scholar]
- Stellmes, M.; Udelhoven, T.; Röder, A.; Sonnenschein, R.; Hill, J. Dryland observation at local and regional scale—Comparison of Landsat TM/ETM+ and NOAA AVHRR time series. Remote Sens. Environ 2010, 114, 2111–2125. [Google Scholar]
- Wessels, K.J.; Prince, S.D.; Malherbe, J.; Small, J.; Frost, P.E.; VanZyl, D. Can human-induced land degradation be distinguished from the effects of rainfall variability? A case study in South Africa. J. Arid Environ 2007, 68, 271–297. [Google Scholar]
- Röder, A.; Udelhoven, T.; Hill, J.; del Barrio, G.; Tsiourlis, G. Trend analysis of Landsat-TM and -ETM+ imagery to monitor grazing impact in a rangeland ecosystem in Northern Greece.
- Dubovyk, O.; Menz, G.; Conrad, C.; Kan, E.; Machwitz, M.; Khamzina, A. Spatio-temporal analyses of cropland degradation in the irrigated lowlands of Uzbekistan using remote-sensing and logistic regression modeling. Environ. Monit. Assess 2013, 185, 4775–4790. [Google Scholar]
- Dubovyk, O.; Menz, G.; Khamzina, A. Trend Analysis of MODIS Time-Series Using Different Vegetation Indices for Monitoring of Cropland Degradation and Abandonment in Central Asia. Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Munich, Germany, 22–27 July 2012; pp. 6589–6592.
- Li, L.; Ustin, S.; Palacios-Orueta, A.; Jacquemoud, S.; Whiting, M. Remote Sensing Based Assessment of Biophysical Indicators for Land Degradation and Desertification. In Recent Advances in Remote Sensing and Geoinformation Processing for Land Degradation Assessment; Röder, A., Hill, J., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009; pp. 15–44. [Google Scholar]
- Tottrup, C.; Rasmussen, M.S. Mapping long-term changes in savannah crop productivity in Senegal through trend analysis of time series of remote sensing data. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ 2004, 103, 545–560. [Google Scholar]
- Huete, A.; Didan, K.; Miura, T.; Rodriguez, E.; Gao, X.; Ferreira, L. Overview of the radiometric and biophysical performance of the MODIS vegetation indices. Remote Sens. Environ 2002, 83, 195–213. [Google Scholar]
- Jeganathan, C.; Dash, J.; Atkinson, P.M. Mapping the phenology of natural vegetation in India using a remote sensing-derived chlorophyll index. Int. J. Remote Sens 2010, 31, 5777–5796. [Google Scholar]
- Diouf, A.; Lambin, E.F. Monitoring land-cover changes in semi-arid regions: Remote sensing data and field observations in the Ferlo, Senegal. J. Arid Environ 2001, 48, 129–148. [Google Scholar]
- Dash, J.; Curran, P.J. The MERIS terrestrial chlorophyll index. Int. J. Remote Sens 2004, 25, 5403–5413. [Google Scholar]
- Huete, A. A soil-adjusted vegetation index (SAVI). Remote Sens. Environ 1988, 25, 295–309. [Google Scholar]
- Fensholt, R.; Rasmussen, K.; Nielsen, T.T.; Mbow, C. Evaluation of earth observation based long term vegetation trends—Intercomparing NDVI time series trend analysis consistency of Sahel from AVHRR GIMMS, Terra MODIS and SPOT VGT data. Remote Sens. Environ 2009, 113, 1886–1898. [Google Scholar]
- Fensholt, R.; Proud, S.R. Evaluation of Earth Observation based global long term vegetation trends—Comparing GIMMS and MODIS global NDVI time series. Remote Sens. Environ 2012, 119, 131–147. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, H.; Udelhoven, T.; Fensholt, R.; Pflugmacher, D.; Hostert, P. How Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) trendsfrom Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer (AVHRR) and Système Probatoire d’Observation de la Terre VEGETATION (SPOT VGT) time series differ in agricultural areas: An Inner Mongolian case study. Remote Sens 2012, 4, 3364–3389. [Google Scholar]
- Si, Y.; Schlerf, M.; Zurita-Milla, R.; Skidmore, A.; Wang, T. Mapping spatio-temporal variation of grassland quantity and quality using MERIS data and the PROSAIL model. Remote Sens. Environ 2012, 121, 415–425. [Google Scholar]
- Zurita-Milla, R.; Clevers, J.G.P.W.; van Gijsel, J.A.E.; Schaepman, M.E. Using MERIS fused images for land-cover mapping and vegetation status assessment in heterogeneous landscapes. Int. J. Remote Sens 2011, 32, 973–991. [Google Scholar]
- Almond, S.; Boyd, D.S.; Dash, J.; Curran, P.J.; Hill, R.A.; Foody, G.M. Estimating Terrestrial Gross Primary Productivity with the Envisat Medium Resolution Imaging Spectrometer (MERIS) Terrestrial Chlorophyll Index (MTCI). Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Honolulu, HI, USA, 25–30 July 2010; pp. 4792–4795.
- Harris, A.; Dash, J. The potential of the MERIS Terrestrial Chlorophyll Index for carbon flux estimation. Remote Sens. Environ 2010, 114, 1856–1862. [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, D.S.; Almond, S.; Dash, J.; Curran, P.J.; Hill, R.A. Phenology of vegetation in Southern England from Envisat MERIS terrestrial chlorophyll index (MTCI) data. Int. J. Remote Sens 2011, 32, 8421–8447. [Google Scholar]
- Fensholt, R.; Sandholt, I.; Stisen, S. Evaluating MODIS, MERIS, and VEGETATION vegetation indices using in situ measurements in a semiarid environment. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens 2006, 44, 1774–1786. [Google Scholar]
- Dash, J.; Jeganathan, C.; Atkinson, P.M. The use of MERIS Terrestrial Chlorophyll Index to study spatio-temporal variation in vegetation phenology over India. Remote Sens. Environ 2010, 114, 1388–1402. [Google Scholar]
- Dubovyk, O.; Menz, G.; Conrad, C.; Thonfeld, F.; Khamzina, A. Object-based identification of vegetation cover decline in irrigated agro-ecosystems in Uzbekistan. Quat. Int 2013, 311, 163–174. [Google Scholar]
- Dubovyk, O.; Menz, G.; Conrad, C.; Lamers, J.P. A.; Lee, A.; Khamzina, A. Spatial targeting of land rehabilitation: A relational analysis of cropland productivity decline in arid Uzbekistan. Erdkunde 2013, 67, 167–181. [Google Scholar]
- Chub, E.V. Climate Change and Its Impact on Natural Resources Potential of the Republic of Uzbekistan; Central Asian Hydrometeorological Research Institute named after V.A. Bugayev: Tashkent, Uzbekistan, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- UZSTAT, Crop Statistics for Khorezm Province 1998–2009; Unpublished work; 2010.
- Djanibekov, N.; Rudenko, I.; Lamers, J.; Bobojonov, I. Pros and Cons of Cotton Production in Uzbekistan. In Food Policy for Developing Countries: Food Production and Supply Policies; Pinstrup-Andersen, P., Cheng, F., Eds.; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 13–27. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrakhimov, M.; Khamzina, A.; Forkutsa, I.; Paluasheva, G.; Lamers, J.P.A.; Tischbein, B.; Vlek, P.L.G.; Martius, C. Groundwater table and salinity: Spatial and temporal distribution and influence on soil salinization in Khorezm region (Uzbekistan, Aral Sea Basin). Irrig. Drain. Syst 2007, 21, 219–236. [Google Scholar]
- Akramkhanov, A.; Martius, C.; Park, S.J.; Hendrickx, J.M.H. Environmental factors of spatial distribution of soil salinity on flat irrigated terrain. Geoderma 2011, 163, 55–62. [Google Scholar]
- ESA, MERIS Product Handbook. Issue 2.1; European Space Agency: Frascati, Italy, 2006.
- Vermote, E.F.; Kotchenova, S.Y.; Ray, J.P. MODIS Surface Reflectance User’s Guide; MODIS Land Surface Reflectance Science Computing Facility: College Park, MD, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, J.F.; Smith, D.M.S.; Lambin, E.F.; Turner, B.L.; Mortimore, M.; Batterbury, S.P.J.; Downing, T.E.; Dowlatabadi, H.; Fernández, R.J.; Herrick, J.E.; et al. Global desertification: Building a science for dryland development. Science 2007, 316, 847–851. [Google Scholar]
- Prince, S.D.; Becker-Reshef, I.; Rishmawi, K. Detection and mapping of long-term land degradation using local net production scaling: Application to Zimbabwe. Remote Sens. Environ 2009, 113, 1046–1057. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson, S.E.; Tucker, C.J.; Ba, M.B. Desertification, drought, and surface vegetation: An example from the West African Sahel. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc 1998, 79, 815–829. [Google Scholar]
- Wessels, K.J.; Prince, S.D.; Frost, P.E.; van Zyl, D. Assessing the effects of human-induced land degradation in the former homelands of northern South Africa with a 1 km AVHRR NDVI time-series. Remote Sens. Environ 2004, 91, 47–67. [Google Scholar]
- Akramkhanov, A.; Kuziev, R.; Sommer, R.; Martius, C.; Forkutsa, O.; Massucati, L. Soils and Soil Ecology in Khorezm. In Cotton, Water, Salts and Soums; Martius, C., Rudenko, I., Lamers, J.P.A., Vlek, P.L.G., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 37–58. [Google Scholar]
- Clevers, J.G.P.W.; Schaepman, M.E.; Mücher, C.A.; de Wit, A.J.W.; Zurita-Milla, R.; Bartholomeus, H.M. Using MERIS on Envisat for land cover mapping in the Netherlands. Int. J. Remote Sens 2007, 28, 637–652. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Gitelson, A.A.; Viña, A.; Verma, S.B.; Rundquist, D.C.; Arkebauer, T.J.; Keydan, G.; Leavitt, B.; Ciganda, V.; Burba, G.G.; Suyker, A.E. Relationship between gross primary production and chlorophyll content in crops: Implications for the synoptic monitoring of vegetation productivity. J. Geophys. Res 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouse, J.; Haas, R.; Schell, J. Monitoring the Vernal Advancement and Retrogradation (Greenwave Effect) of Natural Vegetation; Texas A and M University: College Station, TX, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Le, Q.B.; Tamene, L.; Vlek, P.L.G. Multi-pronged assessment of land degradation in West Africa to assess the importance of atmospheric fertilization in masking the processes involved. Glob. Planet. Chang 2012, 92–93, 71–81. [Google Scholar]
- Huete, A.R.; Jackson, R.D.; Post, D.F. Spectral response of a plant canopy with different soil backgrounds. Remote Sens. Environ 1985, 17, 37–53. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Chova, L.; Zurita-Milla, R.; Alonso, L.; Amoros-Lopez, J.; Guanter, L.; Camps-Valls, G. Gridding artifacts on medium-resolution satellite image time series: MERIS case study. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens 2011, 49, 2601–2611. [Google Scholar]
- Holben, B.N. Characteristics of maximum-value composite images from temporal AVHRR data. Int. J. Remote Sens 1986, 7, 1417–1434. [Google Scholar]
- Dash, J.; Lankester, T.; Hubbard, S.; Curran, P.J. Signal-to-Noise Ratio for MTCI and NDVI Time Series Data. Proceedings of the 2nd MERIS/(A)ATSR User Workshop, Rome, Italy, 22–26 September 2008.
- Wessels, K.J.; Prince, S.D.; Reshef, I. Mapping land degradation by comparison of vegetation production to spatially derived estimates of potential production. J. Arid Environ 2008, 72, 1940–1949. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric tests against trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar]
- Kendall, M.G. A new measure of rank correlation. Biometrika 1938, 30, 81–93. [Google Scholar]
- De Jong, R.; de Bruin, S.; de Wit, A.; Schaepman, M.E.; Dent, D.L. Analysis of monotonic greening and browning trends from global NDVI time-series. Remote Sens. Environ 2011, 115, 692–702. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Wessels, K.J.; van den Bergh, F.; Scholes, R.J. Limits to detectability of land degradation by trend analysis of vegetation index data. Remote Sens. Environ 2012, 125, 10–22. [Google Scholar]
- Shoji, T.; Kitaura, H. Statistical and geostatistical analysis of rainfall in central Japan. Comput. Geosci 2006, 32, 1007–1024. [Google Scholar]
- Bland, J.M.; Altman, D.G. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 1986, 327, 307–310. [Google Scholar]
- Bréon, F.-M.; Vermote, E. Correction of MODIS surface reflectance time series for BRDF effects. Remote Sens. Environ 2012, 125, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Curran, P.J.; Dash, J. [Report on] Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document: Chlorophyll Index. Available online: http://www.esa.int (accessed on 4 Auguest 2013).
- Slay, B.; Juraev, A. The Return of Drought Conditions to Central Asia: Update and Possible Impact on Food Security (“Fast Facts” from Central Asia’s Reservoirs, and Official Socio-Economic Data); UNDP Regional Bureau for Europe and CIS: Bratislava, Slovakia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Thenkabail, P.S.; Smith, R.B.; de Pauw, E. Hyperspectral vegetation indices and their relationships with agricultural crop characteristics. Remote Sens. Environ 2000, 71, 158–182. [Google Scholar]
- Curran, P.J.; Steele, C.M. MERIS: The re-branding of an ocean sensor. Int. J. Remote Sens 2005, 26, 1781–1798. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, R.D.; Huete, A.R. Interpreting vegetation indices. Prev. Vet. Med 1991, 11, 185–200. [Google Scholar]
- Fensholt, R.; Langanke, T.; Rasmussen, K.; Reenberg, A.; Prince, S.D.; Tucker, C.; Scholes, R.J.; Le, Q.B.; Bondeau, A.; Eastman, R.; et al. Greenness in semi-arid areas across the globe 1981–2007—An Earth Observing Satellite based analysis of trends and drivers. Remote Sens. Environ 2012, 121, 144–158. [Google Scholar]
| Spectrum | MERIS-MTCI | MERIS-NDVI/SAVI | MODIS-NDVI/SAVI |
|---|---|---|---|
| red band | 8 (677.5–685 nm) | band 7 (660–670 nm) | band 1 (620–670 nm) |
| nir band | 10 (750–757.5 nm) | band 13 (855–875 nm) | band 2 (841–876 nm) |
| red edge | band 9 (703.75–713.75 nm) | - | - |
| Vegetation Index | MERIS | MODIS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ha | % of Study Area | % of Irrigated Land | ha | % of Study Area | % of Irrigated Land | |
| NDVI | 57,724.02 (66,774.50) | 6.8 (7.8) | 14.1 (16.3) | 85,509.82 (126,079.78) | 10.0 (14.8) | 20.1 (30.8) |
| SAVI | 43,826.66 (43,836.65) | 5.1 (5.1) | 10.7 (10.7) | 60,537.16 (72,469.40) | 7.1 (8.5) | 14.8 (17.7) |
| MTCI | 22,472.32 (20,352.45) | 2.6 (2.4) | 5.5 (5.0) | - | - | - |
| Linear Regression | R2 of Time Series | R2 of Trends | |
|---|---|---|---|
| MERIS | NDVI vs. SAVI | 0.90 (0.92) | 0.84 (0.84) |
| MERIS | MTCI vs. NDVI | 0.22 (0.18) | 0.11 (0.07) |
| MERIS | MTCI vs. SAVI | 0.25 (0.21) | 0.17 (0.12) |
| MODIS | NDVI vs. SAVI | 0.88 (0.86) | 0.83 (0.76) |
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Tüshaus, J.; Dubovyk, O.; Khamzina, A.; Menz, G. Comparison of Medium Spatial Resolution ENVISAT-MERIS and Terra-MODIS Time Series for Vegetation Decline Analysis: A Case Study in Central Asia. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 5238-5256. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs6065238
Tüshaus J, Dubovyk O, Khamzina A, Menz G. Comparison of Medium Spatial Resolution ENVISAT-MERIS and Terra-MODIS Time Series for Vegetation Decline Analysis: A Case Study in Central Asia. Remote Sensing. 2014; 6(6):5238-5256. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs6065238
Chicago/Turabian StyleTüshaus, Julia, Olena Dubovyk, Asia Khamzina, and Gunter Menz. 2014. "Comparison of Medium Spatial Resolution ENVISAT-MERIS and Terra-MODIS Time Series for Vegetation Decline Analysis: A Case Study in Central Asia" Remote Sensing 6, no. 6: 5238-5256. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs6065238
APA StyleTüshaus, J., Dubovyk, O., Khamzina, A., & Menz, G. (2014). Comparison of Medium Spatial Resolution ENVISAT-MERIS and Terra-MODIS Time Series for Vegetation Decline Analysis: A Case Study in Central Asia. Remote Sensing, 6(6), 5238-5256. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs6065238