Abstract
In the summer of 2010, an Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) hyperspectral calibration and characterization experiment of the Resonon PIKA II imaging spectrometer was conducted at the US Department of Energy’s Idaho National Laboratory (INL) UAV Research Park. The purpose of the experiment was to validate the radiometric calibration of the spectrometer and determine the georegistration accuracy achievable from the on-board global positioning system (GPS) and inertial navigation sensors (INS) under operational conditions. In order for low-cost hyperspectral systems to compete with larger systems flown on manned aircraft, they must be able to collect data suitable for quantitative scientific analysis. The results of the in-flight calibration experiment indicate an absolute average agreement of 96.3%, 93.7% and 85.7% for calibration tarps of 56%, 24%, and 2.5% reflectivity, respectively. The achieved planimetric accuracy was 4.6 m (based on RMSE) with a flying height of 344 m above ground level (AGL).
1. Introduction
AIRBORNE hyperspectral imaging systems are widely used for environment research applications since the development of imaging spectrometers such as AVIRIS (Airborne Visible / Infrared Imaging Spectrometer) and HyMap (Hyperspectral Mapping) [1,2]. Hyperspectral sensing techniques for vegetation applications are widespread and include weed detection [3–5], crop monitoring and yield prediction [6–8], and estimation of biophysical parameters such as water, chlorophyll and nitrogen [9–12]. To date hyperspectral processing techniques for vegetation applications have primarily involved the development and use of narrowband vegetation indices, often times in conjunction with radiative transfer modeling [13,14]. Currently, hyperspectral imaging is generally accomplished by sensors mounted on manned aircraft, and to a limited degree, spaceborne platforms. Manned flights are scheduled months to years in advance for high quality systems such as AVIRIS and HyMap, and have considerable mission costs. In addition, weather conditions can force the cancellation of a mission, as many commercial manned-aircraft systems providers are oversubscribed and cannot accommodate remaining on-station for considerable time periods.
With the recent development of low-cost compact imaging spectrometers and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), a UAV-based hyperspectral imaging system could overcome scheduling and acquisition limitations as well as open new areas of research by providing an on-demand platform that can rapidly collect data and stay on station for hours [15,16]. However, these low-cost hyperspectral systems require radiometric and geometric calibration to allow quantitative scientific analysis [17,18]. To date, several related studies have paired small, lightweight, rotary or fixed-wing UAV platforms with some combination of video, multi-band digital cameras, synthetic aperture radar (SAR), and laser scanning [19–27]. Yet, to our knowledge, few studies have successfully tested pushbroom hyperspectral sensors on small, lightweight, fixed-wing UAVs [28,29].
This paper describes the integration of a sophisticated, light weight commercial off-the-shelf imaging spectrometer with a medium-altitude, long-endurance unmanned aerial vehicle and presents results of a calibration and characterization experiment. The main objectives were to validate laboratory-derived radiometric calibration of the spectrometer and determine obtainable georegistration accuracy from the on-board global positioning system (GPS) and inertial navigation system (INS) for the resulting imagery. Importantly, this study demonstrates several challenges of hyperspectral-UAV systems and provides a means for comparison to future experiments intending to utilize imagery for quantitative scientific analysis in general, and dryland vegetation management applications in particular.
2. System Overview
2.1. Sensor System
The Resonon Airborne Hyperspectral imaging system (Resonon Inc., Bozeman, MT, USA) was chosen for this study due to its UAV-centric design, including its compact size and relatively low cost and weight. The complete system consists of the Resonon PIKA II imaging spectrometer and the P-CAQ airborne data-acquisition unit. The PIKA II is a visible/near-infrared pushbroom system, configurable up to 240 bands in the 400 nm to 900 nm spectral range, with a spectral channel bandwidth of 2.1 nm. The P-CAQ provides the ability to configure the PIKA II, capture and record image data, and synchronize it with the GPS/INS telemetry data provided by the UAV autopilot. Sensor parameters include frame rate, spectral binning, gain and percent shutter (equivalent to integration time over shutter speed). These parameters can be adjusted based on mission requirements in real-time via a ground-based control station. The manufacturer-supplied specifications for the PIKA II and P-CAQ are shown in Table 1. The sensor was calibrated before flight by Resonon in their laboratory using an integrating sphere (Lapsphere, Inc., NH, USA) and the following parameters: 320 cross track pixels, 80 bands (6.2 nm resolution), 3.15 cm ground pixel size, 305 m altitude and 125 frames per second.

Table 1.
Characteristics of the PIKA II and P-CAQ sensor system.
2.2. Platform
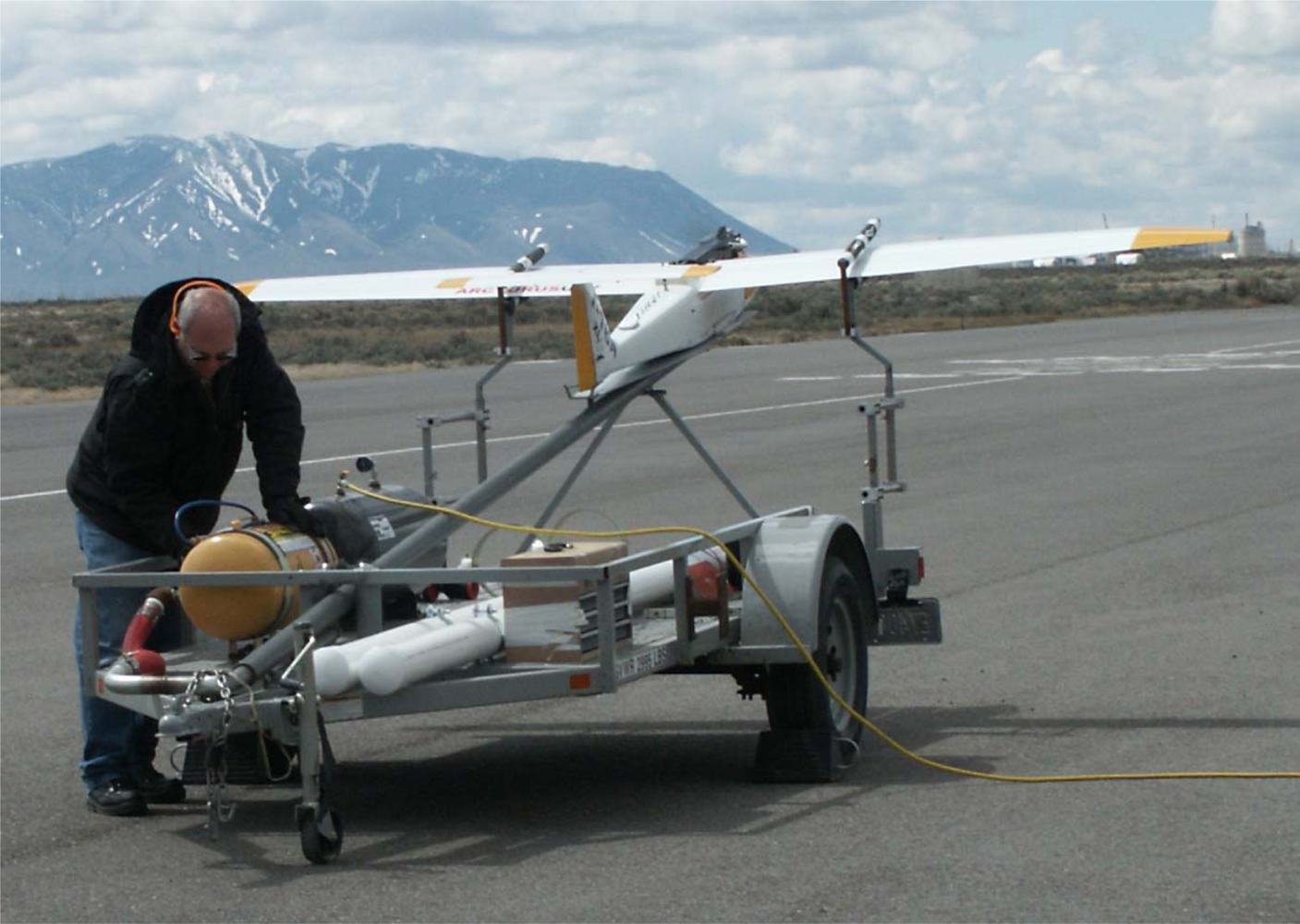
The platform utilized for this experiment is a catapult-launched Arcturus T-16 airframe (Arcturus UAV, Rohnert Park, CA, USA), which is a fixed-wing UAV, shown in Figure 1. It is designed to carry payloads weighing up to 8 kg in a 12,000 cm3 compartment, with an endurance range in excess of 12-h based on flight configuration. The long-endurance is achieved through the wet-wing design and onboard electric generation.

Figure 1.
Arcturus T-16 on the catapult launcher at the Idaho National Laboratory (INL) UAV Research Park.
Command and control of the airframe is accomplished by the Cloud Cap Piccolo II Autopilot (Cloud Cap Technology, Hood River, OR, USA) which provides a complete GPS/INS solution needed for autonomous operation of the aircraft. The Piccolo II incorporates three gyroscopes, three 3-axis accelerometers, and a GPS receiver to provide a 50 Hz Total State Extended Kalman Filter navigation solution with an output telemetry stream of 25 Hz.
2.3. System Integration
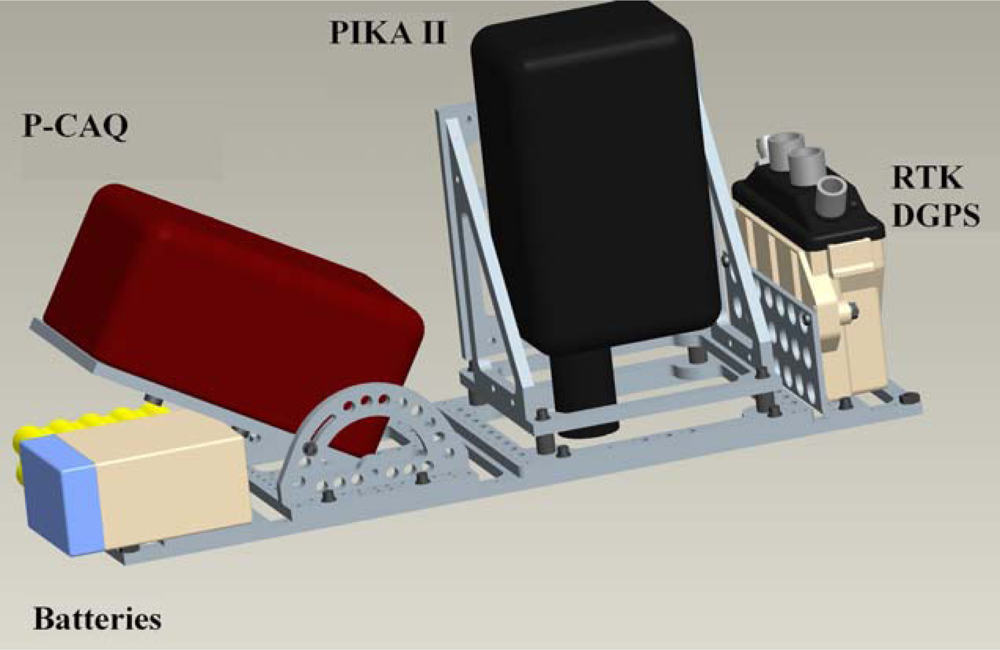
In order to efficiently utilize acquired hyperspectral imagery, automated methods for georeferencing the raw image data are typically implemented; this is referred to as direct georeferencing. To successfully implement direct georeferencing, the following conditions must be met [30]: (1) the position and orientation offset between the GPS, IMU, and sensor must be determined; (2) the offset and orientation must remain constant during each mission; and (3) sensor systems must be clock-synchronized with sufficient accuracy. To achieve this, a mounting and harnessing system was designed to provide vibration isolation, boresight and leveling adjustment, and a fixed offset from the Piccolo II mount (Figure 2). The P-CAQ data acquisition system was interfaced directly to the Piccolo II via an ancillary RS232 serial port for the real-time synchronization of image data with orientation data and in-flight parameter adjustment, such as shutter speed and spectral binning. Furthermore, the Piccolo II was integrated with a NovAtel Differential Global Positioning System (DGPS) receiver in order to provide a full Real-Time Kinematic (RTK) DGPS/INS navigation solution with a reported horizontal and vertical accuracy of up to 2 cm (NovAtel, Inc., Calgary, AB, Canada). The positional precision improves the accuracy of the direct georeferencing workflow, which helps decrease the preprocessing time required to utilize the collected data. Finally, the sensor payload was integrated with the on-board power generation to reduce battery load and extend system endurance.
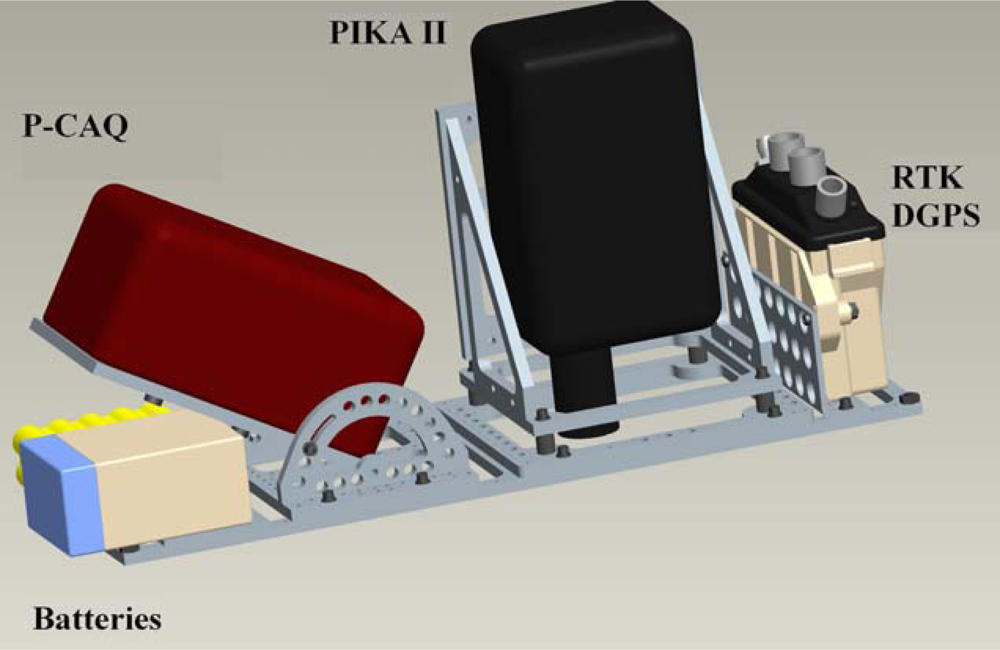
Figure 2.
Modeled design of payload mounting harness.
3. Methods
3.1. Data Collection
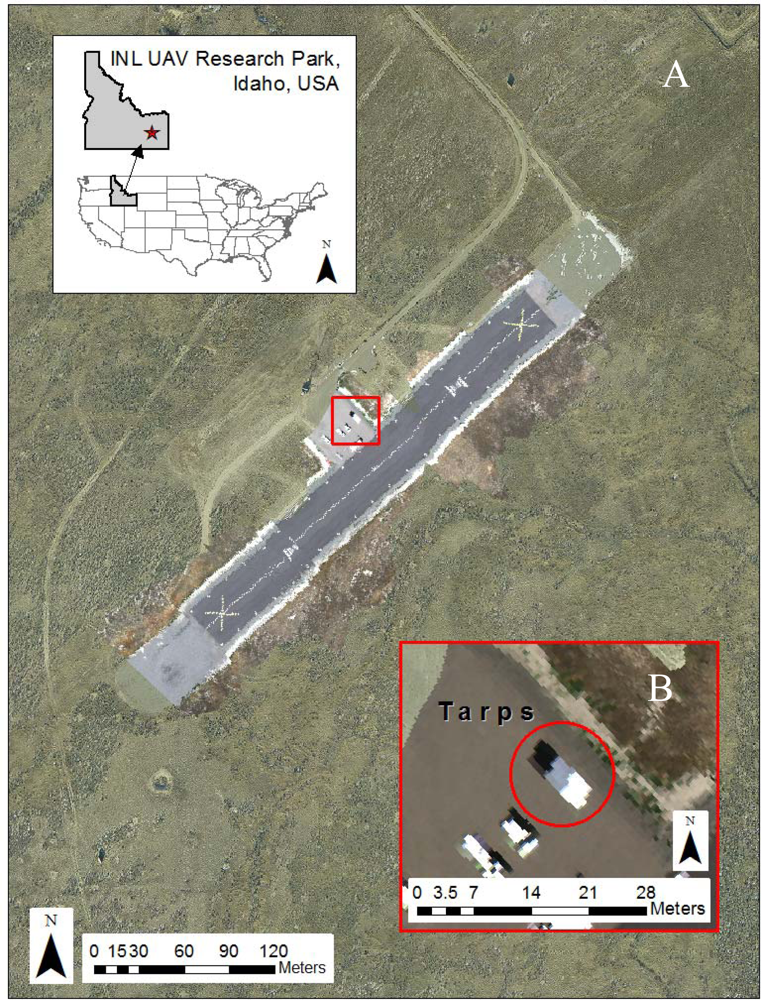
The PIKA II hyperspectral data for this project were collected at Idaho National Laboratory’s (INL’s) UAV Research Park on 27 July 2010, under FAA Certificate of Authorization #2009-WSA-73. The UAV Research Park is located on the 2,046 km2 INL desert site, approximately 60 km west of Idaho Falls, Idaho, USA. Elevations within the UAV Research Park range from 1,480 to 1,490 m. At its center is a 304 m × 30 m black asphalt runway (1,482 m mean sea level (MSL)), which is painted with white fiducial marks ranging from 7.5 cm × 7.5 cm to 1 m × 1 m. PIKA II data were collected on 27 July 2010 from 1:00 to 2:13 pm local time, resulting in 12 overpasses of the runway under predominately clear-sky conditions, however, a few low cumulus clouds were visible well to the north and west of the study area. Table 2 describes the PIKA II flight configuration used in the study. The spectral response was binned to 80 channels resulting in a 6.2 nm spectral channel bandwidth. The binning occurs onboard the aircraft by the P-CAQ, which averages adjacent spectral pixels. An example of a georeferenced 3-band composite of a hyperspectral flight line overlaying an ortho-image base map in shown in Figure 3(A). Figure 3(B) shows a zoomed image of the 3 calibration tarps used for calibration (described below) and visible at the center of the image.

Table 2.
PIKA II flight configuration.
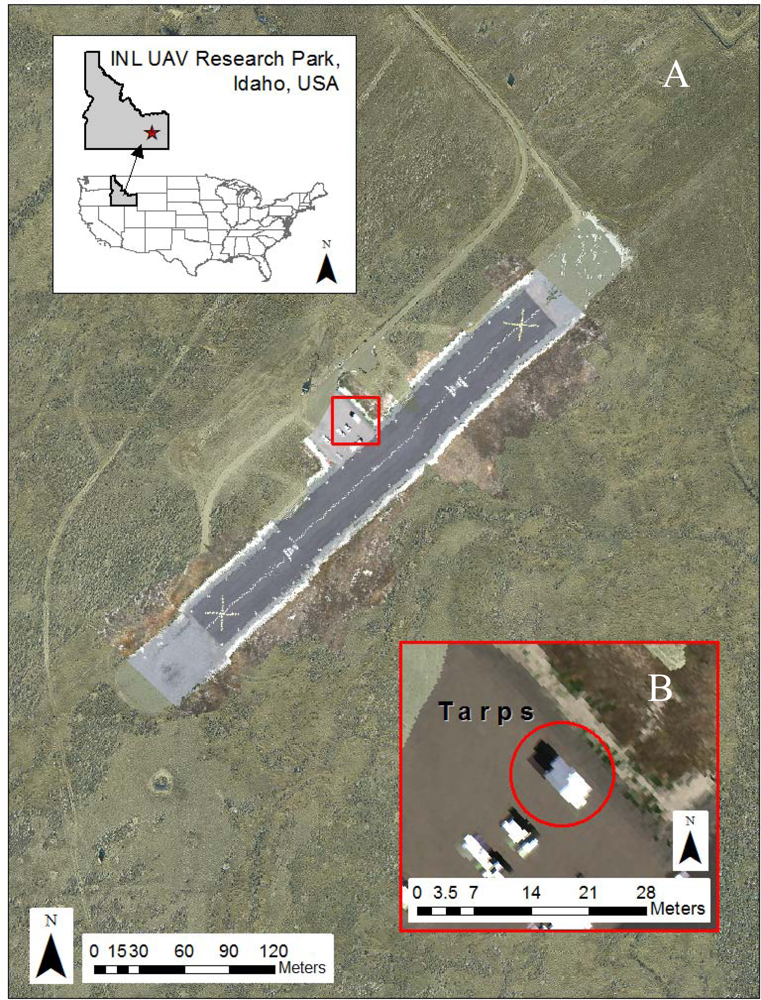
Figure 3.
(A) INL UAV runway with example hyperspectral flightline from 2010. (B) Calibration tarps ranging from 2.5%, 24%, and 56% reflectivity placed north to south, respectively.
During the UAV mission, in situ radiance measurements of a 0.6 × 0.6 m Spectralon white reference panel (Labsphere, North Sutton, NH, USA) were acquired at 30-second intervals using a FieldSpec Pro Spectroradiometer (Analytical Spectral Devices Inc. (ASD), Boulder, CO, USA). The field spectrometer collects spectral data from 350 to 2,500 nm, with a spectral resolution that ranges from 3 to 12 nm. The spectrometer was configured with an 8-degree fore-optic, which provided a ground field of view (FOV) of approximately 8.5 cm when held from approximately 0.6 m above the panel. In addition to the Spectralon panel, three 2.5 × 2.5 m polyester fabric calibration tarps (Group VIII Technologies, Inc., Provo, UT, USA), with reflectivity of 56%, 24%, and 2.5%, were deployed during the over flights. Just after the completion of the over flights, a series of 15 reflectance measurements were acquired for each of the tarps and the Spectralon panel. Conversion to reflectance was accomplished by acquiring a spectral sample of a NIST-traceable Spectralon panel prior to the measurements for each tarp.
3.2. Image Pre-Processing
Pre-processing of the raw PIKA II data was accomplished through the use of Space Computer Corporation’s (Los Angeles, CA, USA) GeoReg software specifically developed to georegister and convert raw digital number data cubes collected by Resonon’s hyperspectral sensors to radiance (μW/steradian/cm2/μm). Conversion to radiance was accomplished by applying vendor-supplied, lab-derived radiometric calibration coefficients The GeoReg software performs georegistration by combining the external orientation data recorded during flight with a camera model (interior orientation) and elevation model. The digital elevation model for this experiment was derived from high-density lidar data collected in 2006 using a Leica Geosystems ALS50-II scanning lidar. The resulting lidar point cloud was processed using the MARS software (Merrick, Boulder, CO, USA) to classify bare-earth returns and then rasterized using Idaho State University’s Boise Center Aerospace Laboratory (BCAL) LiDAR Tools ( http://code.google.com/p/bcal-lidar-tools/) to produce a 1 m bare-earth digital elevation model.
3.3. Geometric Analysis
In order to assess the overall positional accuracy of the direct georeferencing process, a 3-band GeoTIFF true-color composite image was generated for 5 flight lines of the runway. The resulting images were overlaid with the known ground control points (GCPs) with a reported accuracy of ±0.01 m and a high-resolution ortho-rectified aerial image collected in 2006. An initial accuracy assessment was conducted to identify any systematic errors (i.e., roll, pitch, and yaw bias) using 5 control points for each of the images. The ΔX and ΔY for each control point were examined for consistency of magnitude and direction, and then averaged. Due to the inconsistency of measured errors within each flight line, the yaw bias was undeterminable. The resulting averages were further examined for consistency of magnitude and direction, and averaged to obtain an overall adjustment for pitch and roll bias. These biases were used in the GeoReg software, and the data cubes were reprocessed. For each of the reprocessed data cubes, the average RMSEX, RMSEY, overall RMSE and approximate circular standard error were calculated using 20 random check points from each flightline, selected from the reference GCPs (n = 126) according to the method described in the National Spatial Data Infrastructure Geospatial Positioning Accuracy Standards [31].
3.4. Radiometric Analysis
Radiometric calibration is typically conducted in a laboratory environment using an integrating sphere to produce calibration coefficients for each wavelength band recorded by the sensor. These coefficients are then used to convert the digital numbers (DNs) recorded by the sensor into units of radiance. As stated above, vendor-supplied coefficients were applied to each of the data cubes to convert to spectral radiance (μW/steradian/cm2/μm) using the GeoReg Software. No prior geometric corrections were applied to any of the data cubes used for this analysis in order to avoid errors that would be introduced during the resampling process. In-flight calibration experiments similar to those presented by Green and Pavri for AVIRIS [32] were applied to validate the PIKA II’s radiometric calibration under operational conditions. Specifically, our methods include acquiring in situ measurements that describe the atmosphere and surface properties of the Spectralon white reflectance panel at the time of PIKA II overflight. These in situ measurements are used to constrain parameters in the radiative transfer modeling and independently predict at-sensor radiance.
3.4.1. In situ Spectral Measurements
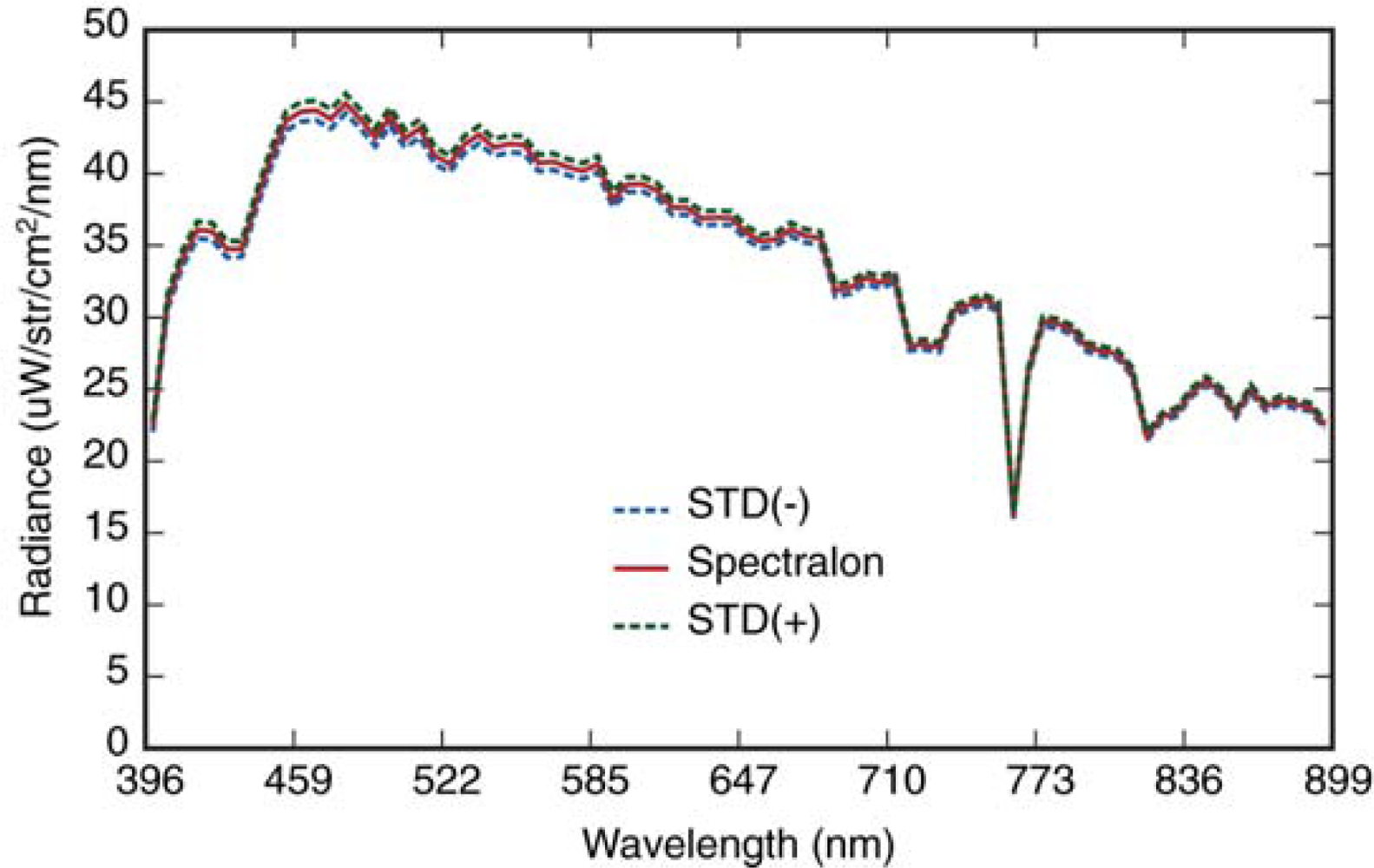
Using the field spectrometer (ASD) discussed above, fifteen spectral reflectance measurements of each calibration tarp were acquired between 11:00 and 11:30 am under clear sky conditions. The 15 spectra were averaged and subsequently used as input for the radiative transfer modeling process (MODTRAN). In addition, radiance measurements (n = 120) were acquired of the Spectralon reference panel [33] at 30 s intervals during the UAV over passes in order to characterize any uncertainty that might have been associated with potential changes in atmospheric conditions. The mean and standard deviation of the resampled Spectralon radiance data are shown in Figure 4. Specific weather conditions (wind speed, temperature, relative humidity, solar radiation and pressure) were also obtained in five minute intervals as recorded by a NOAA weather tower located 2.75 km west of the runway.
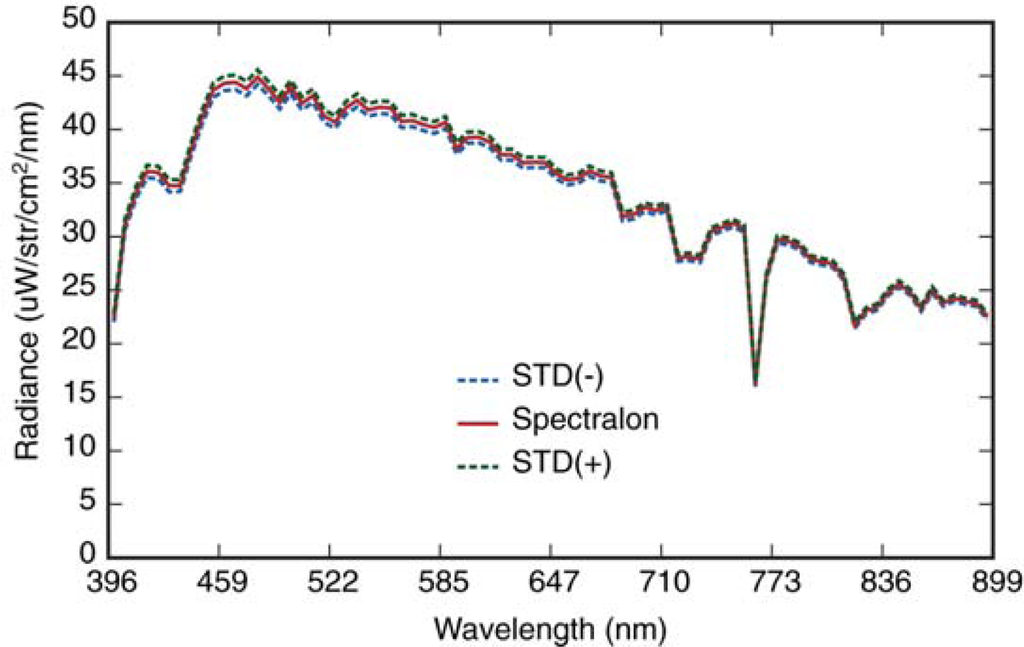
Figure 4.
ASD measured radiance of Spectralon calibration panel. Mean and standard deviation (STD = ±1σ) are shown.
3.4.2. Radiative Transfer Modeling
The derived mean ASD reflectance spectra for each calibration tarp were input into the MODTRAN4 V3.1 radiative transfer code to predict at-sensor radiance for the PIKA II mission [34]. The MODTRAN runs were constrained by the PIKA II sensor characteristics, flight parameters, and atmospheric conditions at the time of acquisition (summarized in Table 3). Reflectance signatures were resampled to the PIKA II spectral calibration parameters.

Table 3.
MODTRAN parameters.
3.4.3. PIKA II Radiometric Evaluation
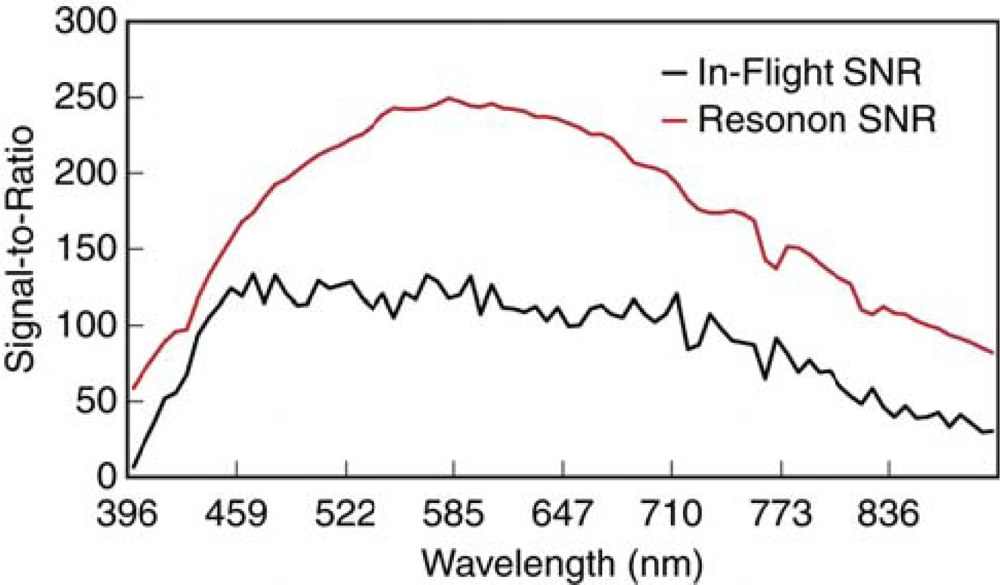
In order to evaluate the radiometric calibration and in-flight stability of the PIKA II sensor, the regions-of-interest (ROIs) associated with the three calibration tarps were manually identified in each of 12 runway overpasses. Nine pixels were selected from the center of each tarp and the spectra were examined for noise and adjacency effects. First, to evaluate the radiometric quality of each of the data cubes the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) was calculated as described by Fujimoto et al. [35]. This method uses the ratio of the mean to the standard deviation of a homogenous area within a scene to obtain an estimation of SNR for each band. For this study, the ROI of the 56% reflectance was used. SNRs of each individual image were averaged to obtain the estimated achievable SNR for the PIKA II.
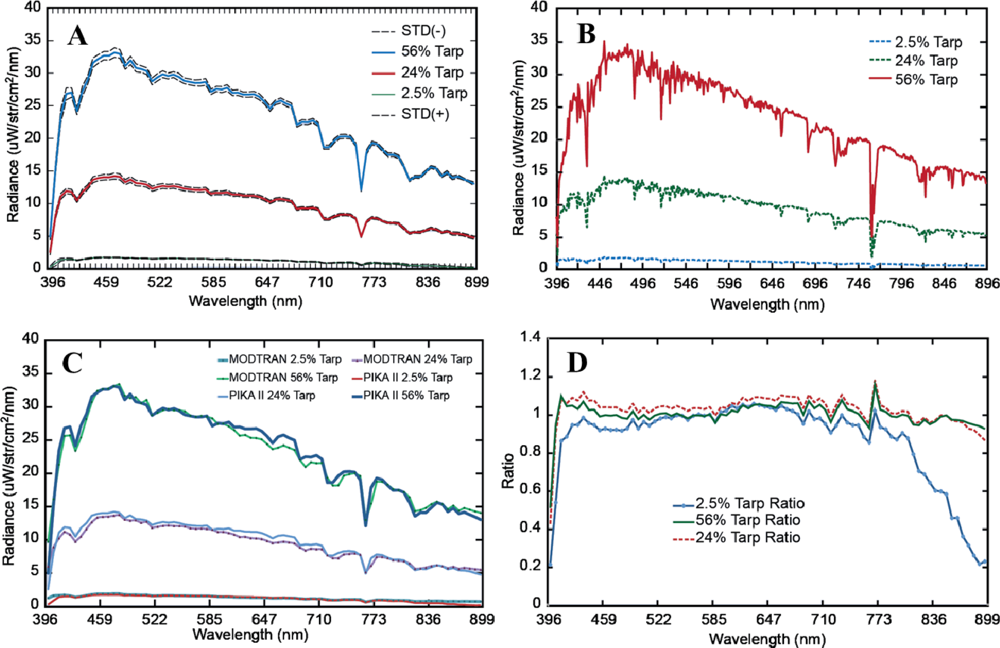
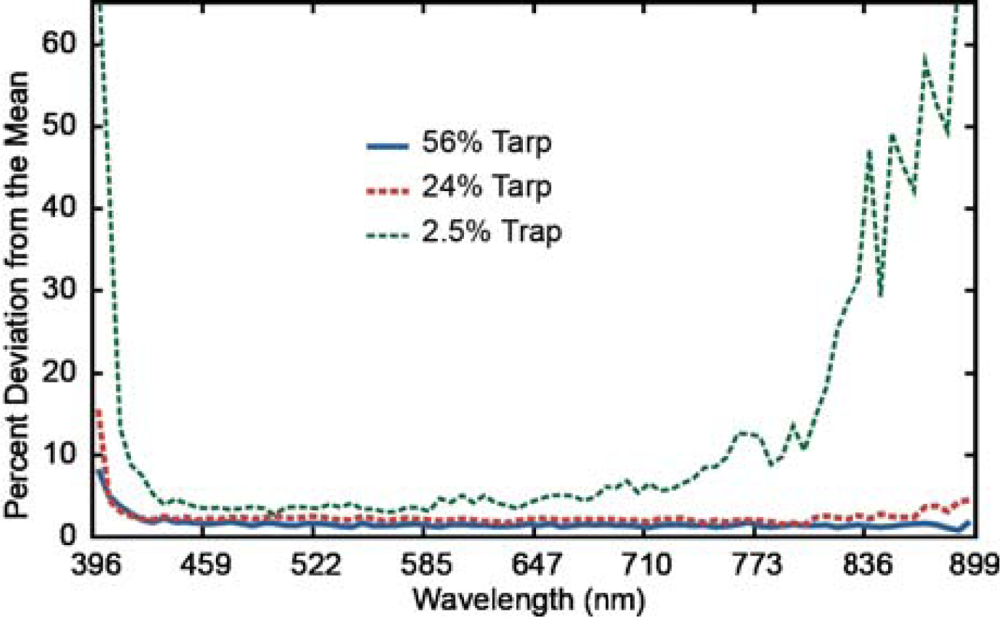
Second, the average PIKA II measured radiance spectra of the 12 overpasses was compared with the MODTRAN predicted radiance for each of the three calibration tarps. It is important to note that during the initial analysis of the data, the PIKA II radiance values were observed to be approximately twice the predicted value. It was discovered that a difference in internal hardware between the airborne P-CAQ and the P-CAQ used in the laboratory for calibration resulted in a bit shift and caused the resulting factor of 2 increase in the derived radiance. As a result, all of the PIKA II data was divided by 2 before comparison. For further comparison, the ratio of PIKA II measured radiance over the MODTRAN predicted radiance was calculated for each of the tarps in order to determine where residual errors occurred. Finally, the intraflight stability of the PIKA II was evaluated by comparing the mean spectrum for each of the calibration tarps for all 12 overpasses and calculating the deviation from the mean.
4. Results and Discussions
4.1. Geometric Correction
The initial georegistration accuracy assessment, presented in Table 4, indicates an approximate 4.3 degrees of positive pitch bias and 2.8 degrees of positive roll bias. These biases were most likely introduced while mounting the sensor payload and the Piccolo II autopilot into the UAV airframe.
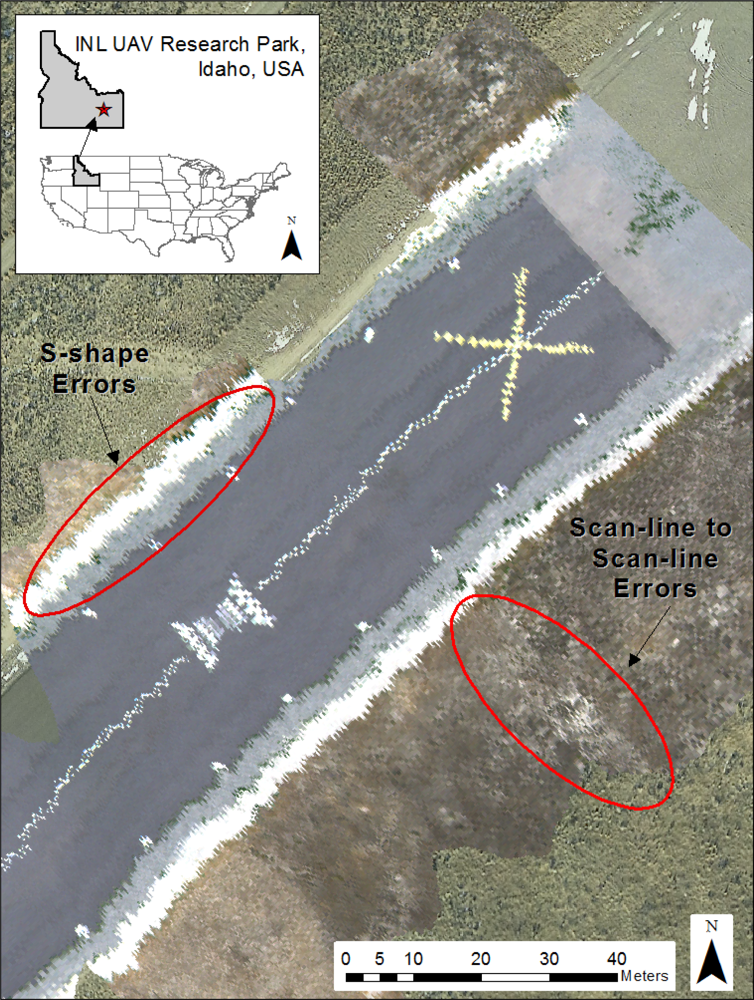
Subsequent georegistration accuracy assessment of the 20 check points resulted in an average overall RMSER of 4.6326 m and an approximated circular standard error of 7.8497 m. Results for all 5 images are summarized in Table 5. The largest source of error appears to be related to poor estimations of yaw angle. This is most apparent just after rapid changes in aircraft attitude during periods of level flight. These turbulent events result in new heading estimations and an apparent pivot in the resulting image. Also, runway image observations indicate the presence of two additional, relatively higher-frequency error patterns (Figure 5). The first is a scan-line to scan-line error, which is the highest frequency error. It most likely results from differential movement or vibration of the airframe [36]. The second, lower-frequency error, which is S-shaped, is likely to be a result of the Kalman filters used to predict aircraft position and orientation from the 25 Hz telemetry stream acquired from the Piccolo II autopilot.

Table 5.
Accuracy computations in meters (NSSDA 1998) [31]. For all images RMSEMIN/RMSEMAX were between 0.6 m and 1.0 m and thus the following equation was used to approximate circular standard error (Accuracyr): 2.4477 × 0.5 × (RMSEX + RMSEY). RMSER = sqrt[∑((x data, i − x check, i)2 + (y data, i − y check, i)2)/n], where i represents coordinates of the ith check point and n represents the number of check points.
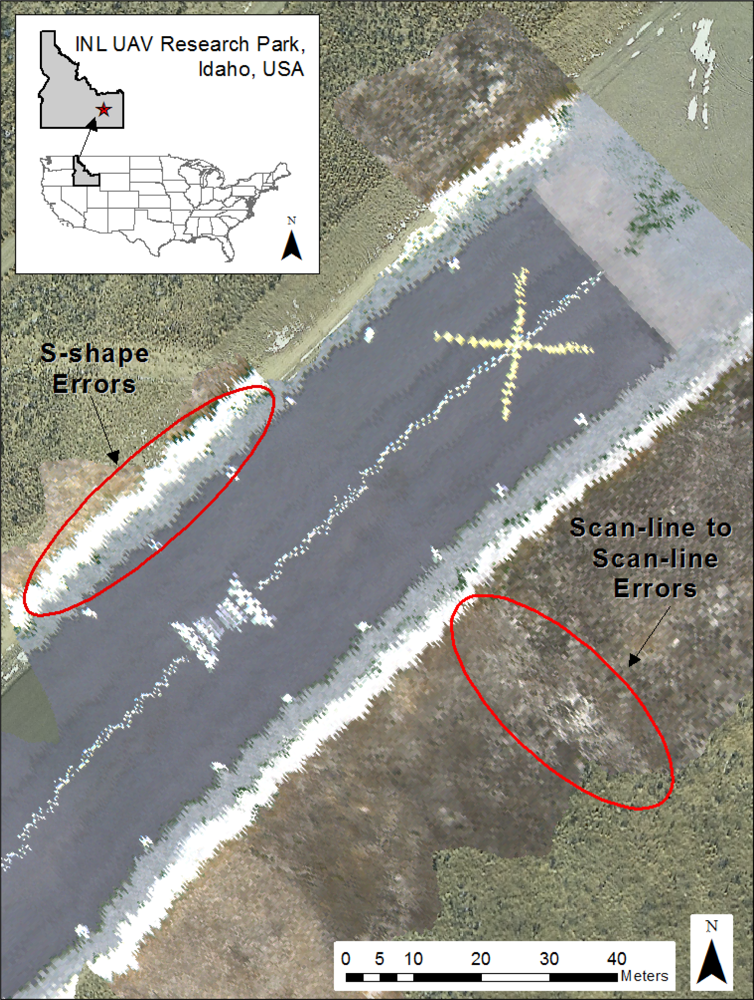
Figure 5.
Examples of geometric errors (scan-line to scan-line and S-shape) apparent in the flightline imagery analyzed in this study. Note the scan-line to scan-line errors indicated by the linear runway markers.
These results are consistent with other findings, in that the application of autopilots designed for small UAVs are limited when used for directly georeferencing remotely sensed image data [23]. This is primarily due to the accuracy of the microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) inertial sensors and the time synchronization between image acquisition and the telemetry data. Because the PIKA II records at a higher rate than the GPS/INS, an interpolation method is used in GeoReg to link the GPS and image data, resulting in georegistration errors. Incorporation of a fiber-optic gyroscope could improve results; however, as Gurtner et al. [37] state, this would be counter to the low-cost nature of the intended approach.
4.2. Radiometric Analysis
The in-flight calibration results show a high degree of congruency between the PIKA II measured radiance and the MODTRAN predicted radiance. Figure 6(A) shows the average PIKA II spectra, and Figure 6(B) shows the high-resolution MODTRAN modeled signatures. The average PIKA II measured and resampled MODTRAN predicted at-sensor radiance for each tarp is shown in Figure 6(C). The MODTRAN spectral radiance values were resampled in ENVI to the PIKA II response using a Gaussian model with FWHM equal to the band spacing of the PIKA II. For the 56% and 24% calibration tarps, there was an absolute average agreement of 96.3% (∼2% with 1 standard deviation) and 93.7% (∼3% with 1 standard deviation) respectively. This is comparable to Green and Pavri’s reported results for AVIRIS [32]; however, results should only be used as a general comparison since AVIRIS collects spectral information from 400 to 2,500 nm, and the PIKA II collects data from 400 to 900 nm. In addition, we used an averaged spectrum of all 12 overpasses where Green and Pavri present results from a single overpass. For the 2.5% tarp, the absolute average agreement drops to 85.7%, with increasing residuals after the 798 nm channel (Figure 6(D)).
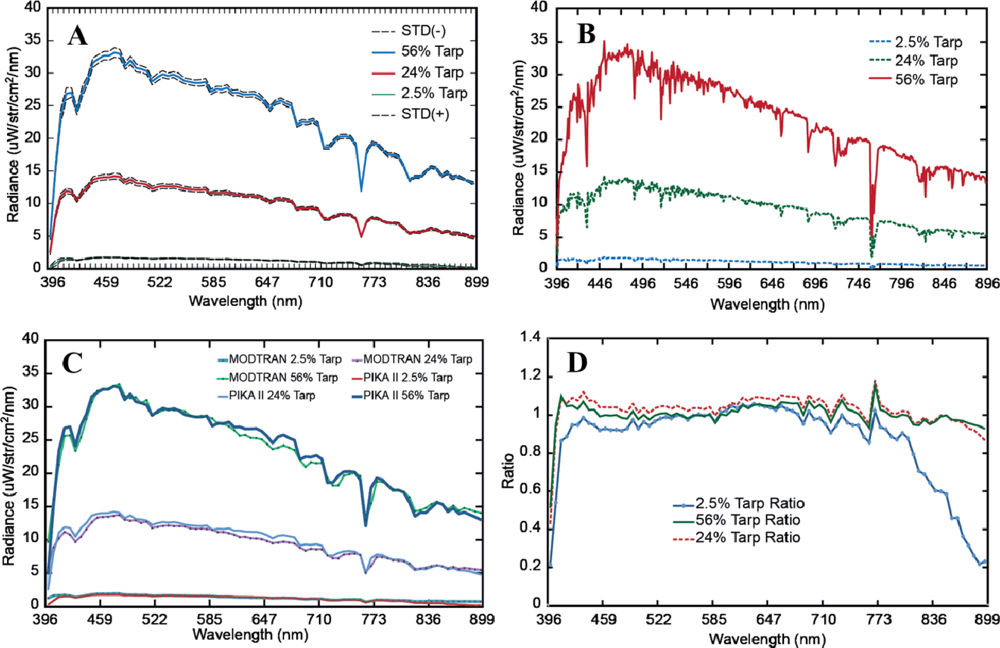
Figure 6.
(A) Pika II measured radiance of calibration tarps. Standard deviation (STD = ±1σ). (B) MODTRAN predicted radiance of calibration tarps. (C) Comparison of MODTRAN predicated and PIKA II measured radiance of calibration tarps. (D) The ratio of the PIKA II measured radiance over the MODTRAN predicted radiance of calibration tarps.
In order to further evaluate the quality of the acquired image data, the SNR was estimated from the 56% tarp ROI which resulted in an average maximum value of 133, with peaks at 465, 478, 566, and 591 nm, as shown in Figure 7. While this is much lower than reported AVIRIS and HyMap SNRs, any direct comparisons cannot be made because of the differences in spectral and spatial resolution. However, the SNR is sufficient for many mapping applications and follows a similar response as Resonon’s reported SNR for the PIKA II (Figure 7 and under conditions stated in Section 2.1). Differences between the data reported in Figure 7 are expected because Resonon’s SNR was recorded under 100% saturation conditions (i.e., integrating sphere) whereas our data results are from a tarp with 56% reflectance. Improvements to the SNR of our system could be made with slower flying speeds, allowing lower integration times, and an increase in flight altitude. In addition, the PIKA II provides the ability to adjust sensor configuration, and special consideration should be taken when evaluating the trade-offs between spectral resolution, spatial resolution, and achievable signal-to-noise ratio with respect to the intended application.
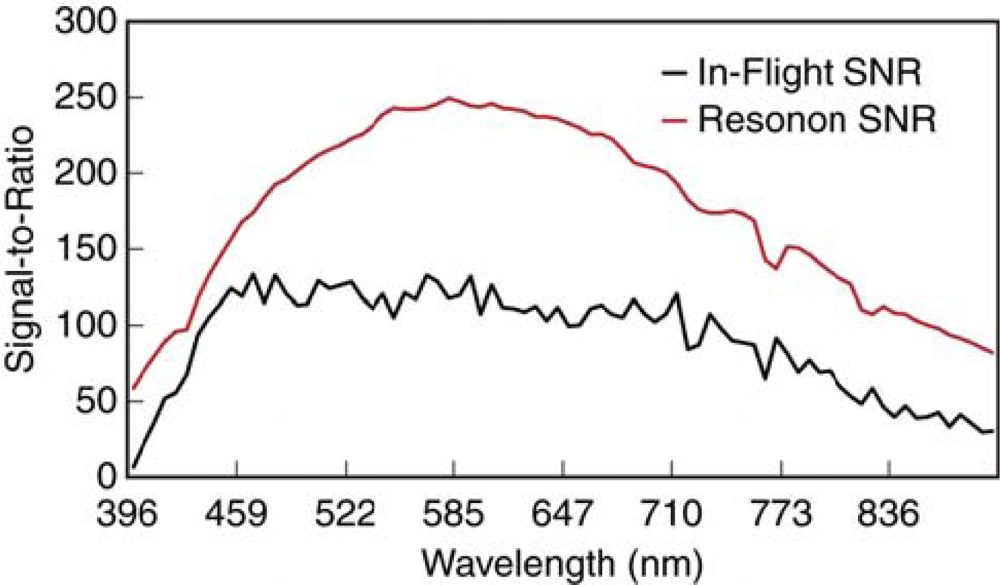
Figure 7.
Average signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) estimated in-flight from the 56% tarp and as provided by Resonon for the PIKA II.
Finally, the intraflight stability of the PIKA II was evaluated for all three tarps. Overall, the variation between the 12 overpasses was fairly consistent between the 427 and 729 nm channels, with a baseline variation of 1.51%, 2.19%, and 4.32% for the 56%, 24%, and 2.5% tarps, respectively. When the entire spectral range is evaluated, minimal increases in the percent mean deviation were observed for the 56% tarp (+0.15%) and the 24% (+0.30%); however, the 2.5% tarp increased from 9.36% to 13.68% (Figure 8). These results demonstrate that the PIKA II’s radiometric calibration and intraflight stability perform well under operational conditions for the spectral range between 409 and 804 nm. However, the stability for darker targets is degraded below 427 and above 804 nm due to the lower SNR. This is likely due to the decreased SNR on each end of the spectral response of the PIKA and the low reflectivity of the tarp (2.5%). Small changes in path radiance and systems noise could easily account for this error and is highlighted with the absolute average agreement calculations.
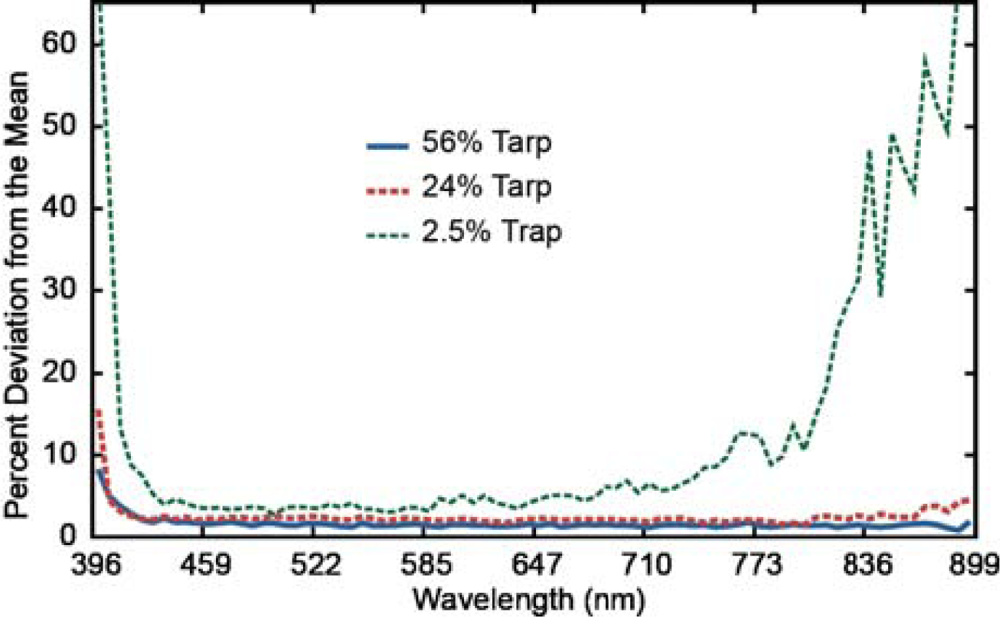
Figure 8.
The percent deviation from the mean for the 12 overpasses of the 3 calibration tarps.
5. Conclusions
While this research experiment demonstrated the ability to collect and directly georeference hyperspectral data acquired from a UAV platform through the autopilot navigation data, the utility of the data is limited by the achieved accuracy. The georeferencing was found to have an average RMSER of 4.63 m and an approximated circular standard error of 7.85 m. The limited accuracy resulted from sensor accuracies of the INS and the state-estimation process implemented by the autopilot, which was designed for autonomous navigation and not for remote sensing applications. Utilization of these data was further complicated by the dynamic image formation process of pushbroom sensors, the PIKA II narrow field of view, and the vibration from the aircraft, which together results in weak internal image geometry [38]. One path to improve the results is to incorporate more accurate inertial measurement devices, but this would increase the cost and complexity of the overall system. The second path is to develop better post-processing methodologies, such as the utilization of point correspondence and mutual information workflows [39].
The PIKA II in-flight radiometric calibration experiment and associated SNR estimates suggested that the system, under operating conditions described herein, may be of limited use for quantitative remote sensing of vegetation applications, such as vegetation stress studies requiring the red edge or specific bands such as 530 and 570 nm for Photochemical Reflectance Indices (PRI) [40,41]. The average agreement of the modeled radiance between the PIKA II and reflective tarps was 85.7%–96.3%. The estimated SNR using the 56% reflective tarp had an average maximum value of 133. Improved radiometric performance of the PIKA II could be achieved through applying a specific airborne configuration, such as a reduction in band numbers or an increase in flight altitude. Ultimately, a UAV-mounted PIKA II system could overcome scheduling and acquisition limitations for some applications as well as open new areas of research by providing an on-demand platform that can rapidly collect data and stay on station for hours.
Future work will focus on improving the post-processing georeferencing workflow to increase positional accuracy. In addition, the incorporation of a low-cost magnetometer will be investigated to improve yaw measurements and reduce geometric error. Finally, radiometric calibration will continue to be evaluated during future flight campaigns in order to optimize sensor performance.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Jodie Boyce and Mark McKay for their support and dedication in developing a safe and reliable UAV platform; without their help we would never have made it off the ground. The authors also thank Casey Smith and Rand Swanson of Resonon, Inc. for coming to Idaho and taking the time to help ensure a successful data collection, and Carol Moore for her editorial assistance.
References
- Vane, G.; Green, R.O.; Chrien, T.G.; Enmark, H.T.; Hansen, E.G.; Porter, W.M. The airborne visible/infrared imaging spectrometer (AVIRIS). Remote Sens. Environ 1993, 44, 27–143. [Google Scholar]
- Cocks, T.; Jenssen, R.; Stewart, A.; Wilson, I.; Shields, T. The HYMAP Airborne Hyperspectral Sensor: The System, Calibration, and Performance. Proceedings of the 1st EARSEL Workshop on Imaging Spectroscopy, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–8 October 1998; pp. 37–42.
- Mitchell, J.; Glenn, N. Leafy spurge (Euphorbia esula L.) classification performance using hyperspectral and multispectral sensors. Rangeland Ecol. Manag 2009, 62, 16–27. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Slaughter, D.C.; Staab, E.S. Robust hyperspectral vision-based classification for multi-season weed mapping. ISPRS J. Photogramm 2012, 69, 65–73. [Google Scholar]
- Hestir, E.L.; Khanna, S.; Andrew, M.E.; Santos, M.J.; Viers, J.H.; Greenberg, J.A.; Rajapakse, S.S.; Ustin, S.L. Identification of invasive vegetation using hyperspectral remote sensing in the California Delta ecosystem. Remote Sens. Environ 2008, 112, 4034–4047. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Everitt, J. Using spectral distance, spectral angle and plant abundance derived from hyperspectral imagery to characterize crop yield variation. Precis. Agric 2012, 13, 62–75. [Google Scholar]
- Corp, L.A.; Middleton, E.M.; Campbell, P.E.; Huemmrich, K.F.; Daughtry, C.S.T.; Russ, A.; Cheng, Y.B. Spectral indices to monitor nitrogen-driven carbon uptake in field corn. J. Appl. Remote Sens 2010, 4, 043555–043555. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, X.; Sakai, K.; Sasao, A; Shin-Ichi, A. Estimation of citrus yield from canopy spectral features determined by airborne hyperspectral imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens 2009, 30, 4621–4642. [Google Scholar]
- Haboudane, D.; Tremblay, N; Miller, J.R.; Vigneault, P. Remote estimation of crop chlorophyll content using spectral indices derived from hyperspectral data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens 2008, 46, 423–437. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Middleton, E.M.; Gao, B.; Cheng, Y. Using E0-1 hyperion to simulate products for a coniferous forest: The fraction of PAR absorbed by chlorophyll (fAPARchl) and Leaf Water Content (LWC). IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens 2012, 50, 1844–1852. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, J.; Glenn, N.; Sankey, T.; Derryberry, D.; Germino, M. Hyperspectral remote sensing of sagebrush canopy nitrogen. Remote Sens. Environ 2012, 124, 217–223. [Google Scholar]
- Kokaly, R.F.; Asner, G.P.; Ollinger, S.V.; Martin, M.E.; Wessman, C.A. Characterizing canopy biochemistry from imaging spectroscopy and its application to ecosystem studies. Remote Sens. Environ 2009, 113, S78–S91. [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman, H.; Segl, K.; Itzerott, H.; Bach, A.; Wagner, J.; Hill, B.; Heim, K.; Oppermann, K.; Heldens, W.; Stein, E.; et al. Hyperspectral Algorithms: Report in the Frame of EnMAP Preparation Activities; Scientific Technical Report STR 10/08. Deutsches GeoForschungsZentrum GFZ: Potsdam, Germany, 2010.
- Jacquemond, S.; Verhouf, W.; Baret, F.; Bacour, C.; Zarco-Tejada, P.J.; Asner, G.P.; François, C.; Ustin, S. PROSPECT + SAIL models: A review of use for vegetation characterization. Remote Sens. Environ 2009, 113, S56–S66. [Google Scholar]
- Acevo-Herrera, R.; Aguasca, A.; Bosch-Lluis, X.; Camps, A.; Martínez-Fernández, J.; Sánchez-Martín, N.; Pérez-Gutiérrez, C. Design and first results of an UAV-borne L-band radiometer for multiple monitoring purposes. Remote Sens 2010, 2, 1662–1679. [Google Scholar]
- Rango, A.; Havstad, K.; Estell, R. The utilization of historical data and geospatial technology advances at the jornada experimental range to support western America ranching culture. Remote Sens 2011, 3, 2089–2109. [Google Scholar]
- Green, R.O. Spectral calibration requirement for earth-looking imaging spectrometers in the solar-reflected spectrum. Appl. Opt 1998, 37, 683–690. [Google Scholar]
- Schaepman-Strub, G.; Schaepman, M.E.; Painter, T.H.; Dangel, S.; Martonchik, J.V. Reflectance quantities in optical remote sensing—Definitions and case studies. Remote Sens. Environ 2006, 103, 27–42. [Google Scholar]
- Hunt, E.R.; Everitt, J.H.; Ritchie, J.C.; Moran, M.S.; Booth, D.T.; Anderson, G.L. Applications and research using remote sensing for rangeland management. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sensing 2003, 69, 675–693. [Google Scholar]
- Hardin, P.J.; Jackson, M.W. An unmanned aerial vehicle for rangeland photography. Rangeland Ecol. Manag 2005, 58, 439–442. [Google Scholar]
- Laliberte, A.S.; Rango, A. Texture and scale in object-based analysis of subdecimeter resolution unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens 2009, 47, 761–770. [Google Scholar]
- Berni, J.A.J.; Zarco-Tejada, P.J.; Suarez, L.; Fereres, E. Thermal and narrowband multispectral remote sensing for vegetation monitoring from an unmanned aerial vehicle. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens 2009, 47, 722–738. [Google Scholar]
- Nagai, M.; Chen, T.; Shibasaki, R.; Kumagai, H.; Ahmed, A. UAV-Borne 3-D mapping system by multisensor integration. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens 2009, 47, 701–708. [Google Scholar]
- Laliberte, S.A.; Goforth, M.A.; Steele, C.M.; Rango, A. Multispectral remote sensing from unmanned aircraft: Image processing workflow and application for rangeland environments. Remote Sens 2011, 3, 2529–2551. [Google Scholar]
- Kelcey, J.; Lucieer, A. Sensor correction of a 6-band multispectral imaging sensor for UAV remote sensing. Remote Sens 2012, 4, 1462–1493. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.; Hyyppä, A. Mini-UAV-borne LIDAR for fine-scale mapping. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett 2011, 8, 426–430. [Google Scholar]
- Koo, V.C.; Chan, Y.K.; Gobi, V.; Chua, M.Y.; Lim, C.H.; Lim, C.-S.; Thum, C.C.; Lim, T.S.; Ahmad, Z.; Mahmood, K.A.; et al. A new unmanned aerial vehicle synthetic aperture radar for environmental monitoring. Prog. Electromagn. Res 2012, 122, 245–268. [Google Scholar]
- Watts, A.C.; Ambrosia, V.G.; Hinkley, E.A. Unmanned aircraft systems in remote sensing and scientific research: Classification and considerations of use. Remote Sens 2012, 4, 1671–1692. [Google Scholar]
- Zarco-Tejada, P.J.; Gonzalez-Dugo, V.; Berni, J.A.J. Fluorescence, temperature and narrow-band indices acquired from a UAV platform for water stress using a micro-hyperspectral images and a thermal camera. Remote Sens. Environ 2012, 117, 322–337. [Google Scholar]
- Skaloud, J. Problems in Direct-Georeferencing by INS/DGPS in the Airborne Environment. Proceedings of the ISPRS Workshop WG III/1, Barcelona, Spain, 25–26 November 1999; pp. 25–26.
- Federal Geographic Data Committee, Geospatial Positioning Accuracy Standards, Part 3: National Standards for Spatial Data Accuracy. Subcommittee for Base Cartographic Data; Standard FGDC-STD-007.3-1998; Federal Geographic Data Committee: Reston, WV, USA, 1998.
- Green, R.; Pavri, B.; AVIRIS in-flight Calibration Experiment, Sensitivity Analysis, and Intraflight Stability. Proceedings of the 9th JPL Airborne Earth Science Workshop, Pasadena, CA, USA, 23–25 February 2000; pp. 207–221.
- Anderson, K.; Milton, E.J.; Rollin, E.M. Sources of Uncertainty in Vicarious Calibration: Understanding Calibration Target Reflectance. Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Toulouse, France, 21–25 July 2003; pp. 2072–2074.
- Berk, A.; Bernstein, L.S.; Anderson, G.P.; Acharya, P.K.; Robertson, D.C.; Chetwynd, J.H.; Adler-Golden, S.M. MODTRAN cloud and multiple scattering upgrades with application to AVIRIS. Remote Sens. Environ 1998, 65, 367–375. [Google Scholar]
- Fujimoto, N.; Takahashi, Y.; Moriyama, T.; Shimada, M.; Wakabayashi, H.; Nakatani, Y.; Obayani, S. Evaluation of SPOT HRV Image Data Received in Japan. Proceedings of the International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 10–14 July 1989; pp. 463–466.
- Lee, C.; Bethel, J. Georegistration of airborne hyperspectral image data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens 2001, 39, 1347–1351. [Google Scholar]
- Gurtner, A.; Greer, D.G.; Glassock, R.; Mejias, L.; Walker, R.A.; Boles, W.W. Investigation of fish-eye lenses for small-UAV aerial photography. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens 2009, 47, 709–721. [Google Scholar]
- McKeown, D.M., Jr.; Cochran, S.D.; Ford, S.J.; McClone, J.C.; Shufelt, J.A.; Yocum, D.A. Fusion of HYDICE hyperspectral data with panchromatic imagery for cartographic feature extraction. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens 1999, 37, 1261–1277. [Google Scholar]
- Cariou, C.; Chehdi, K. Automatic Georeferencing of airborne pushbroom scanner images with missing ancillary data using mutual information. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens 2008, 46, 1290–1306. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, B. An operational method for estimating signal to noise ratios from data acquired with imaging spectrometers. Remote Sens. Environ 1993, 43, 23–33. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, G.M.; Curran, P.J. The Effects of Signal Noise on the Remote Sensing of Foliar Biochemical Concentration. Proceedings of the JPL AVIRIS Airborne Geoscience Workshop, Pasadena, CA, USA, 25–29 October 1993; pp. 161–164.