MambaMeshSeg-Net: A Large-Scale Urban Mesh Semantic Segmentation Method Using a State Space Model with a Hybrid Scanning Strategy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Inspired by Mamba, we propose MambaMeshSeg-Net, a novel large-scale 3D urban mesh semantic segmentation method based on the SSM, which has linear computational complexity, and is especially suitable for large-scale 3D urban scenes. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work that leverages the SSM for 3D urban mesh semantic segmentation.
- We design an octree-based ordering mechanism with Z-order curves for the 1D serialization of 3D urban meshes and a novel non-continuous scanning approach with a learnable stride size, enabling our SSM-based model to effectively capture 3D urban meshes’ spatial features and their dependencies.
- Our proposed method demonstrates high computational efficiency, outperforming other methods in both data pre-processing and inference time.
- We validate the proposed method through extensive experiments on two real-world datasets. Our model surpasses several state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods in mean F1 score, overall accuracy, and mIoU.
2. Related Work
2.1. Urban Mesh Semantic Segmentation
2.2. Mamba and Its Applications
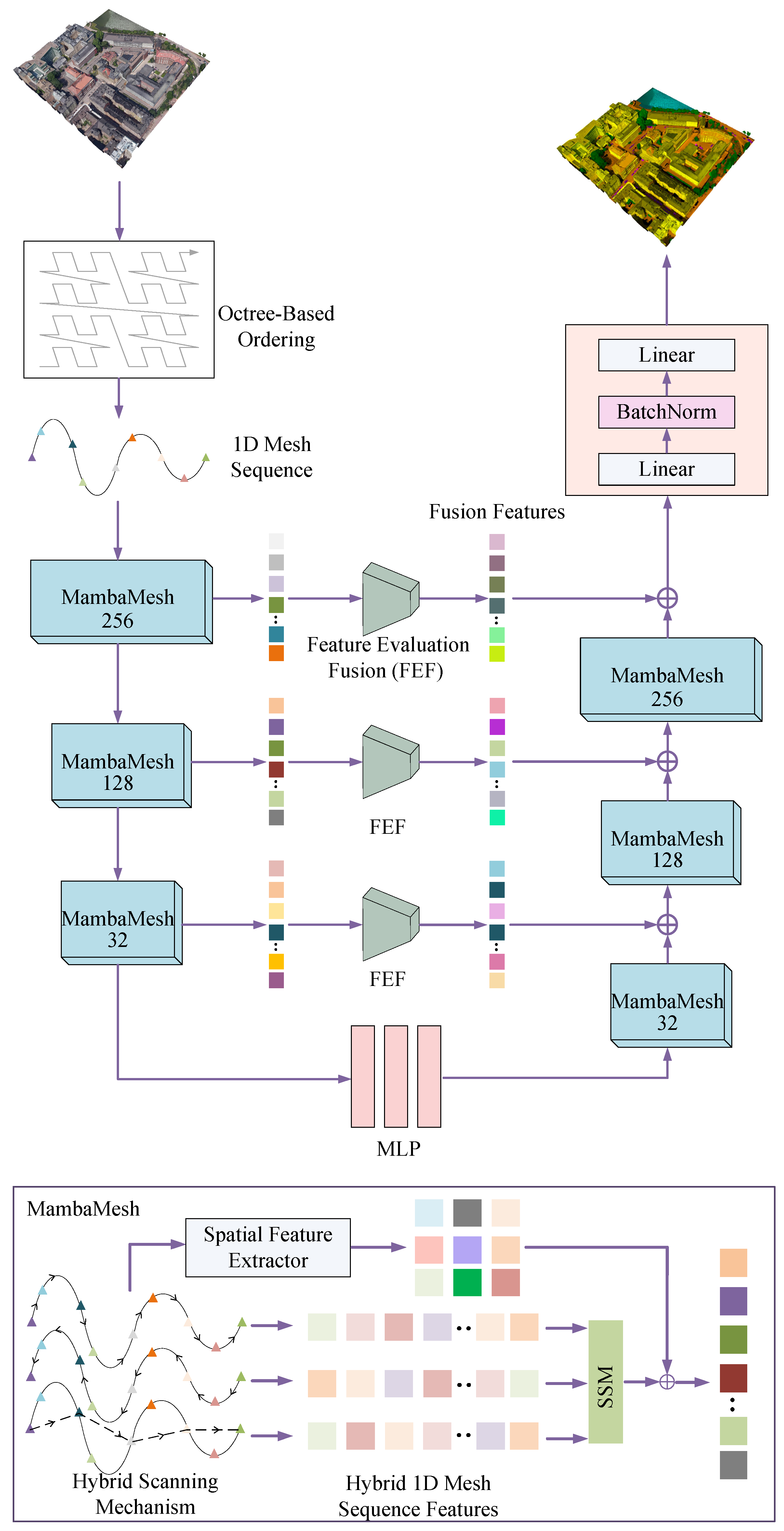
3. Method
3.1. Overview
3.2. Octree-Based Ordering Mechanism
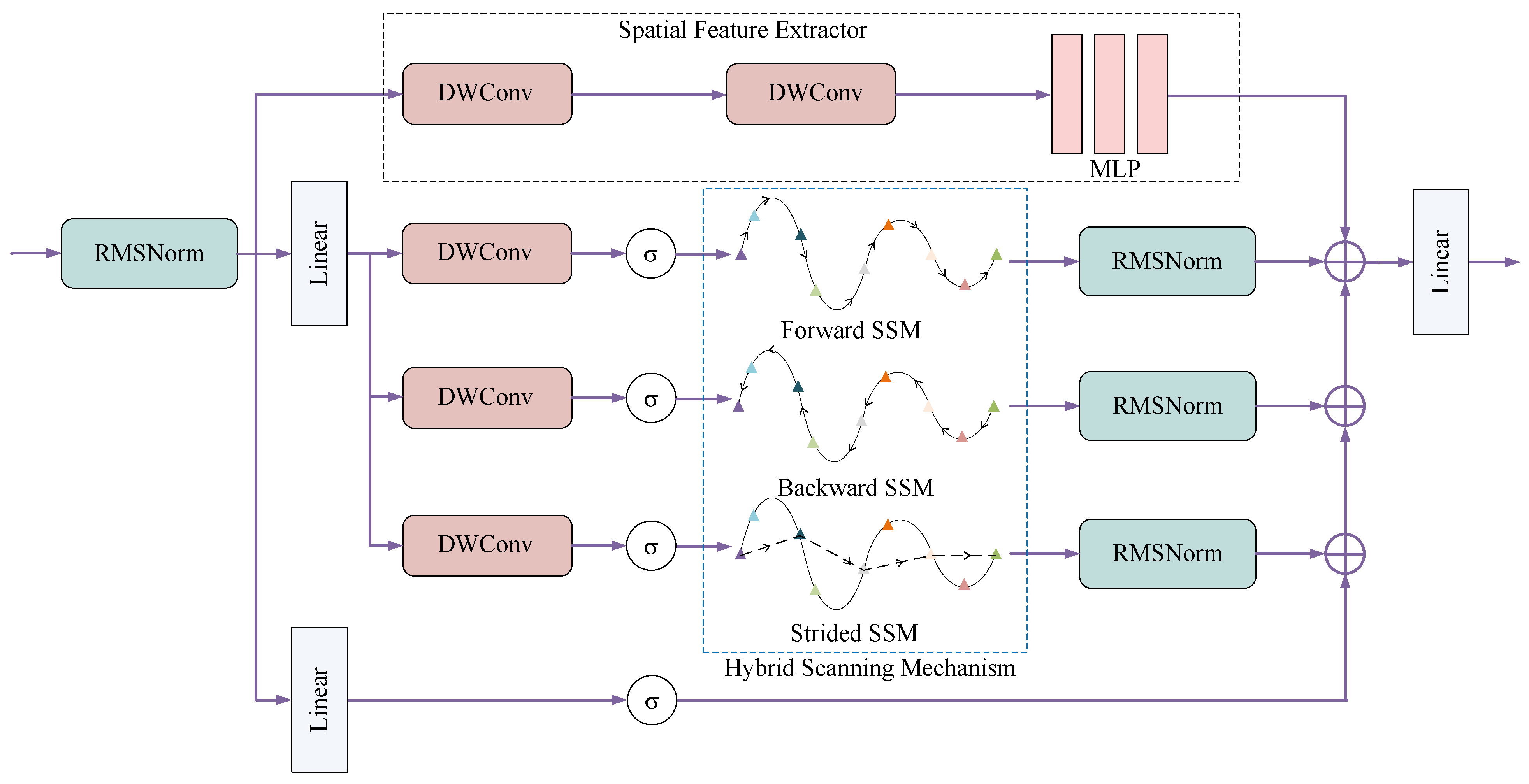
3.3. MambaMesh
3.4. Feature Evaluation Fusion
3.5. Loss Function
4. Experiment
4.1. Dataset
4.2. Implementation Details
4.3. Baselines and Evaluation Metrics
- PointNet++ [49] is the pioneer of point cloud semantic segmentation and the multi-modal method. It learns hierarchical features with increasing scales of contexts and uses PointNet as the local feature learner.
- RF-MRF [18] is a superfacet-based method that includes region growing and MRF-based classification models. RF-MRF leverages both geometric and radiometric features.
- SUM-RF [19] is a superfacet-based model containing region growing and random forest classification models.
- PTV2 [50] is a multi-modal method that integrates Grouped Vector Attention, a Position Encoding Multiplier, and Partition-based Pooling, enabling efficient and comprehensive data understanding.
- PSSNet [20] is the first deep-learning model for urban meshes with a two-step pipeline and is a superfacet-based model. It uses planarity-sensible features to over-segment urban meshes and adopts a GNN-based model to encode local and photometric features.
- UrbanSegNet [44] is an end-to-end multi-modal model that incorporates diffusion perceptron blocks and a vertex spatial attention mechanism.
- PTV3 [51] is a multi-modal model that offers a broader receptive field, improved performance, and a faster processing speed compared to PTV2.
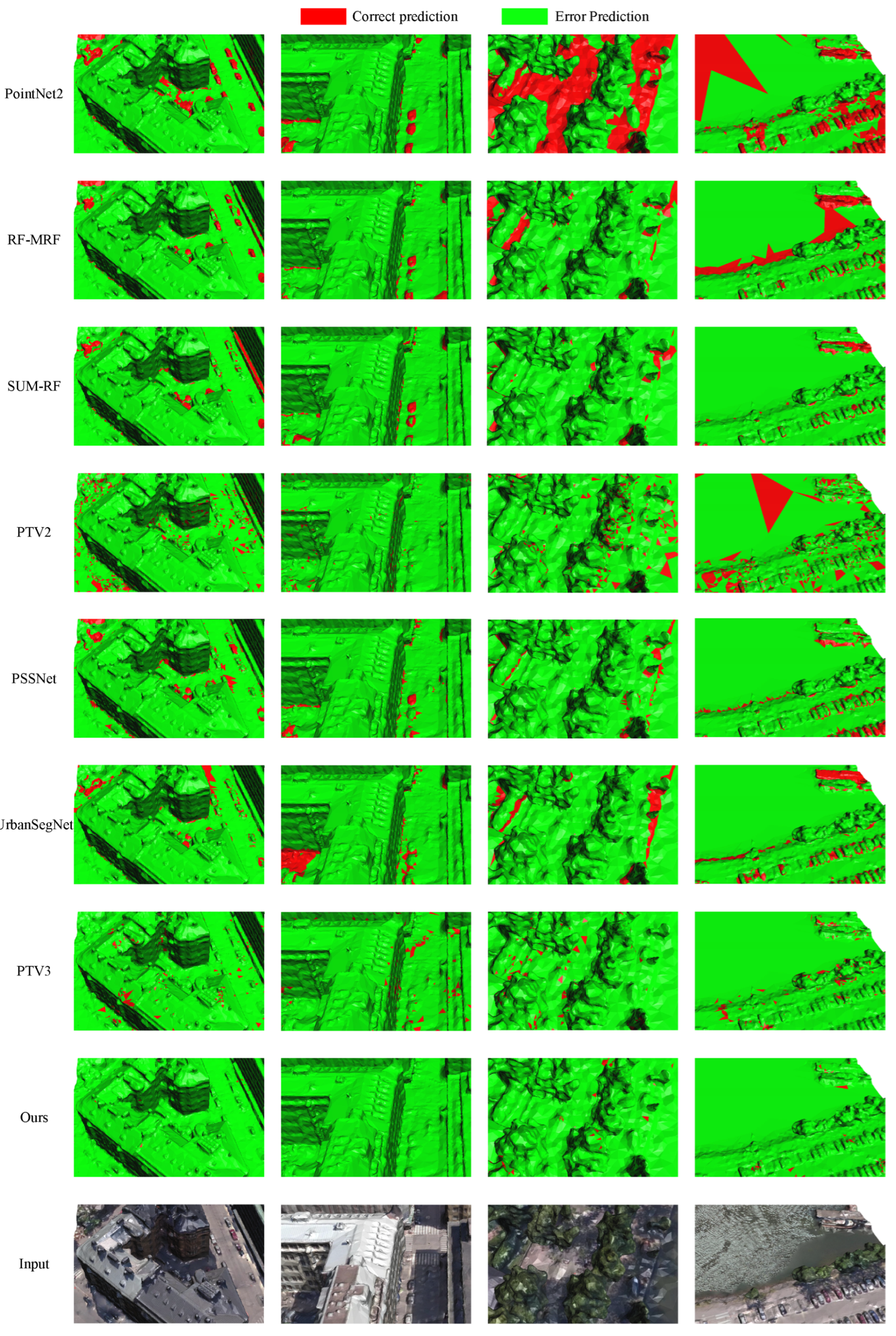
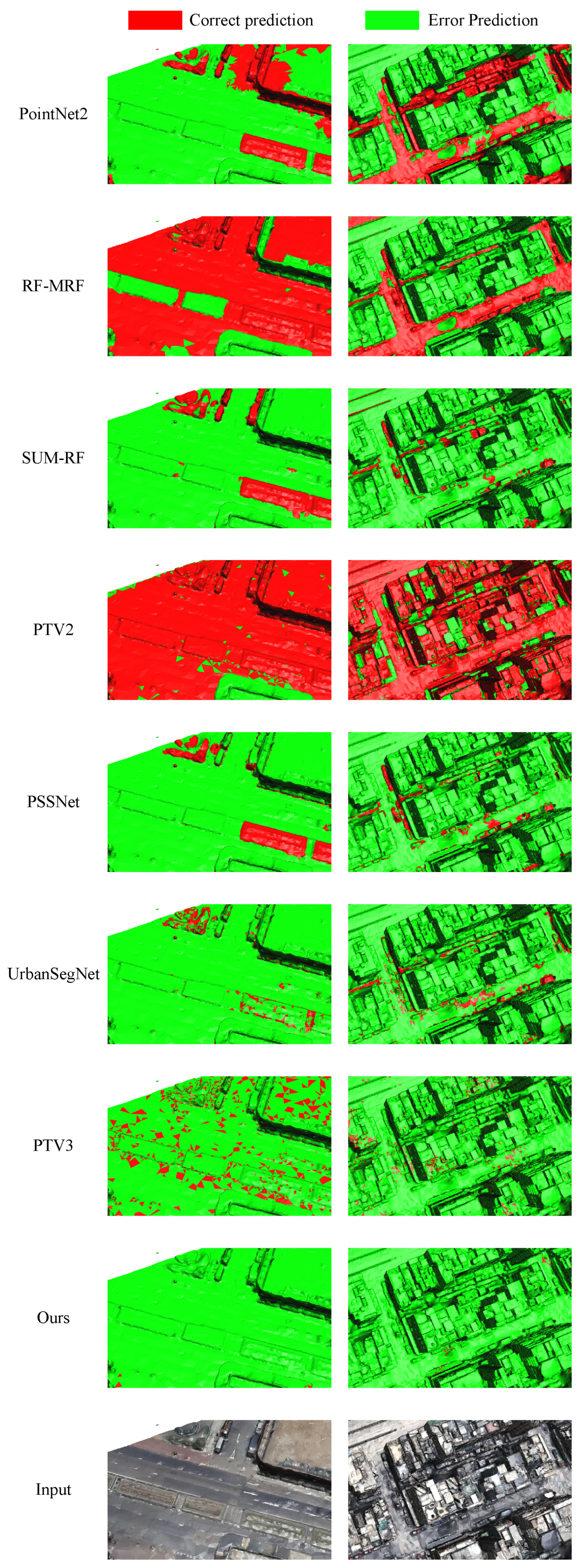
4.4. Experimental Result Analysis
4.4.1. Evaluation and Analysis on SUM
4.4.2. Evaluation and Analysis on seMet Dataset
4.4.3. Efficiency Analysis
4.5. Ablation Study
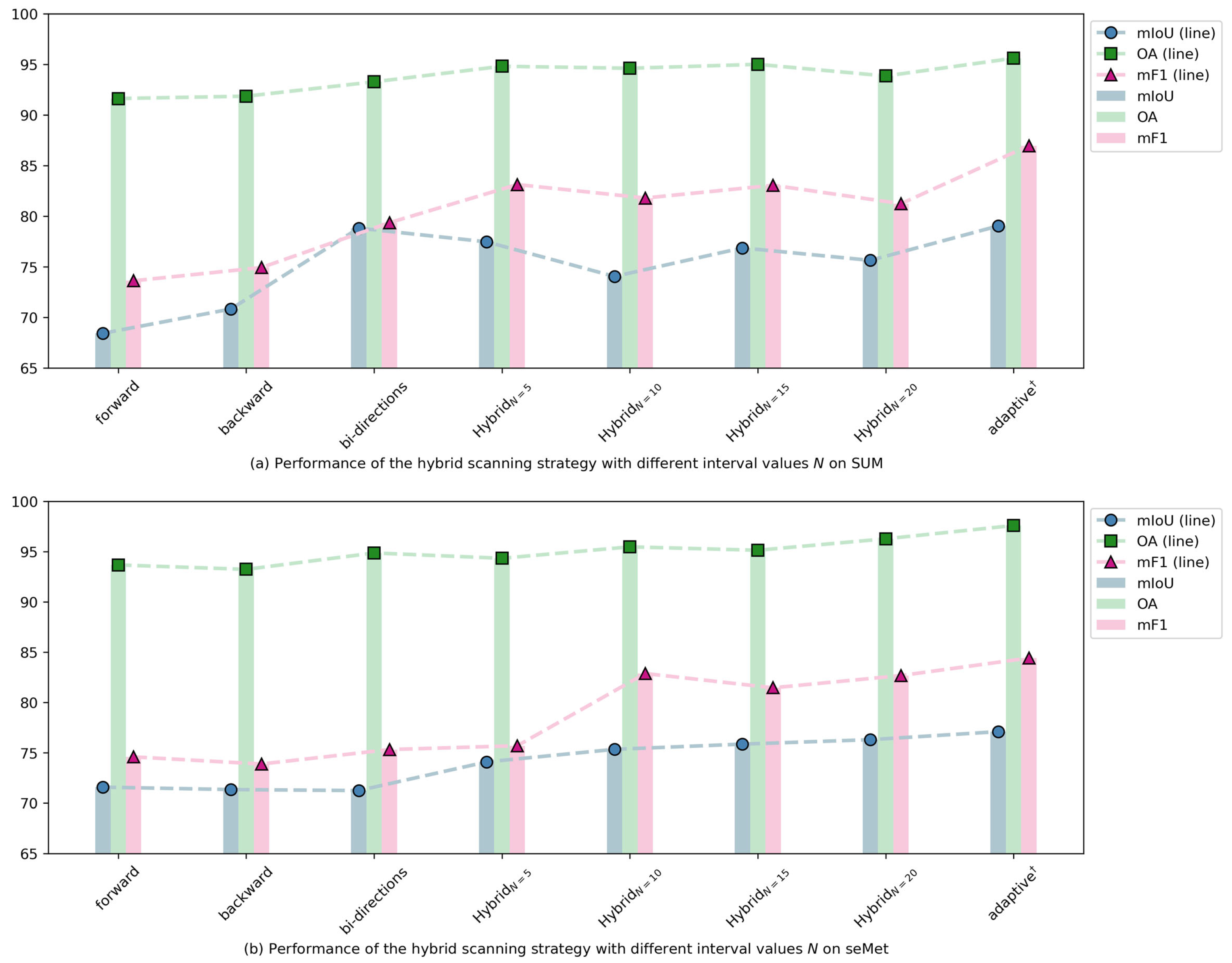
4.5.1. Analysis of Hybrid Scanning Strategy
4.5.2. Octree Depth Analysis
4.5.3. Analysis of Each Component
- In our model, the hybrid scanning strategy is utilized to capture the spatial features of urban meshes. To verify its effectiveness, we removed the hybrid scanning strategy and retained only the dual-scanning mechanism, followed by conducting ablation experiments.
- To validate the effectiveness of the Feature Evaluation Fusion module, we removed this module and performed ablation experiments.
- To demonstrate that the Spatial Feature Extractor can effectively compensate for the limitations of the Mamba model in extracting 3D spatial features, we removed the Mamba model and conducted ablation experiments.
4.6. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shan, P.; Sun, W. Research on 3D urban landscape design and evaluation based on geographic information system. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeing, G. Spatial information and the legibility of urban form: Big data in urban morphology. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2021, 56, 102013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.; Khan, S.; Ehsan, M.; Rehman, F.U.; Al-Shuhail, A. Estimating the total volume of running water bodies using geographic information system (GIS): A case study of Peshawar Basin (Pakistan). Sustainability 2022, 14, 3754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazaheri, H.; Goli, S.; Nourollah, A. A Survey of 3D Space Path-Planning Methods and Algorithms. ACM Comput. Surv. 2024, 57, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Liu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Yan, X.; Xie, K.; Huang, H. Capturing, reconstructing, and simulating: The urbanscene3d dataset. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; pp. 93–109. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Lu, B.; Alipour, M. Optimized structural inspection path planning for automated unmanned aerial systems. Autom. Constr. 2024, 168, 105764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Shen, S.; Hu, L.; Hu, Z. Variational building modeling from urban MVS meshes. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), Qingdao, China, 10–12 October 2017; pp. 318–326. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Nan, L. Feature-preserving 3D mesh simplification for urban buildings. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 173, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Zhou, B.; Wang, H.H. Urban landscape ecological design and stereo vision based on 3D mesh simplification algorithm and artificial intelligence. Neural Process. Lett. 2021, 53, 2421–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Xue, F.; Zhang, Q.; Xie, K.; Fu, C.W.; Huang, H. UrbanBIS: A large-scale benchmark for fine-grained urban building instance segmentation. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH 2023 Conference Proceedings, Los Angeles CA USA, 6–10 August 2023; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.J.; Liu, E.X.; Poh, H.J.; Wang, B.; Gao, S.P.; Png, C.E.; Li, K.W.; Chong, S.H. 3D traffic noise mapping using unstructured surface mesh representation of buildings and roads. Appl. Acoust. 2017, 127, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Cao, J.; Philip, S.Y. Deep learning for spatio-temporal data mining: A survey. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2020, 34, 3681–3700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauwers, D. Functional road categorization: New concepts and challenges related to traffic safety, traffic managment and urban design: Reflections based on practices in Belgium confronted with some Eastern European cases. In Proceedings of the Transportation and Land Use Interaction, Bucharest, Romania, 23–25 October 2008; Politechnica Press: Rome, Italy, 2008; pp. 149–164. [Google Scholar]
- Galvão, G.; Vieira, M.; Louro, P.; Vieira, M.A.; Véstias, M.; Vieira, P. Visible Light Communication at Urban Intersections to Improve Traffic Signaling and Cooperative Trajectories. In Proceedings of the 2023 7th International Young Engineers Forum (YEF-ECE), Lisbon, Portugal, 7 July 2023; pp. 60–65. [Google Scholar]
- Herb, M.; Weiherer, T.; Navab, N.; Tombari, F. Lightweight semantic mesh mapping for autonomous vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Xian, China, 30 May–5 June 2021; pp. 6732–6738. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, S.; Kerofsky, L.; Kumar, V.R.; Yogamani, S. Neural Rendering based Urban Scene Reconstruction for Autonomous Driving. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.06826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Xu, Y.; Chen, G.; Li, H.; Lin, K.Y.; Jiang, C. Urban radiance field representation with deformable neural mesh primitives. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2023; pp. 465–476. [Google Scholar]
- Rouhani, M.; Lafarge, F.; Alliez, P. Semantic segmentation of 3D textured meshes for urban scene analysis. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 123, 124–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Nan, L.; Boom, B.; Ledoux, H. SUM: A benchmark dataset of semantic urban meshes. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 179, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weixiao, G.; Nan, L.; Boom, B.; Ledoux, H. PSSNet: Planarity-sensible semantic segmentation of large-scale urban meshes. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2023, 196, 32–44. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, H.; Yi, L.; Funkhouser, T.; Niessner, M.; Guibas, L.J. TextureNet: Consistent Local Parametrizations for Learning From High-Resolution Signals on Meshes. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, S.; Pan, H.; Liu, Y.; Tong, X. PFCNN: Convolutional neural networks on 3D surfaces using parallel frames. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 13578–13587. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, H.; Akhtar, N.; Shah, M.; Mian, A. Geometric feature learning for 3D meshes. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.01801. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, R.; Xia, M.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, C. A deep-learning model for semantic segmentation of meshes from UAV oblique images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2022, 43, 4774–4792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, H.; Qi, C.R.; Deschaud, J.E.; Marcotegui, B.; Goulette, F.; Guibas, L.J. Kpconv: Flexible and deformable convolution for point clouds. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 6411–6420. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, E.; Kwon, Y.; Kim, C.; Choi, W.; Sohn, H.G. Multi-source point cloud registration for urban areas using a coarse-to-fine approach. GIScience Remote Sens. 2024, 61, 2341557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y.; Haffner, P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE 1998, 86, 2278–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, A.; Dao, T. Mamba: Linear-time sequence modeling with selective state spaces. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2312.00752. [Google Scholar]
- Witharana, C.; Ouimet, W.B.; Johnson, K.M. Using LiDAR and GEOBIA for automated extraction of eighteenth–late nineteenth century relict charcoal hearths in southern New England. GIScience Remote Sens. 2018, 55, 183–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landrieu, L.; Simonovsky, M. Large-scale point cloud semantic segmentation with superpoint graphs. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 4558–4567. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Niessner, M.; Shewchuk, J.R.; Guibas, L.J. Quadriflow: A scalable and robust method for quadrangulation. In Proceedings of the Computer Graphics Forum, Delft, Netherlands, 16–20 April 2018; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; Volume 37, pp. 147–160. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, L.; Xing, S.; Lu, Y.; Fu, T. Biomamba: A pre-trained biomedical language representation model leveraging mamba. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2408.02600. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Huang, Y.; Xu, J.; Pei, B.; Chen, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, K.; Lu, T.; Wang, L. Video mamba suite: State space model as a versatile alternative for video understanding. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.09626. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, L. Vision mamba: A comprehensive survey and taxonomy. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.04404. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Yang, H.; Zhou, H.Y.; Yu, L.; Liang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zheng, H.; Wang, S. Swin-UMamba†: Adapting Mamba-based vision foundation models for medical image segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2024. early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatamizadeh, A.; Kautz, J. Mambavision: A hybrid mamba-transformer vision backbone. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.08083. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Kissling, W.D. Performance, effectiveness and computational efficiency of powerline extraction methods for quantifying ecosystem structure from light detection and ranging. GIScience Remote Sens. 2023, 60, 2260637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhang, X.; Pun, M.O. Rs 3 mamba: Visual state space model for remote sensing image semantic segmentation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2024, 21, 6011405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Xia, B.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Xu, S. A novel mamba architecture with a semantic transformer for efficient real-time remote sensing semantic segmentation. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, R.; Liu, F.; Liu, H.; Zheng, B.; Hu, C. DC-Mamba: A Novel Network for Enhanced Remote Sensing Change Detection in Difficult Cases. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Li, G.; Song, R.; Gao, W.; Liu, S. Octattention: Octree-based large-scale contexts model for point cloud compression. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–27 February 2022; Volume 36, pp. 625–633. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, M.; Long, J.; Feng, M.; Li, B.; Kai, H. OctFormer: Efficient octree-based transformer for point cloud compression with local enhancement. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Washington, DC, USA, 7–14 February 2023; Volume 37, pp. 470–478. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Goyal, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Dollár, P. Focal loss for dense object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2980–2988. [Google Scholar]
- Zi, W.; Li, J.; Chen, H.; Chen, L.; Du, C. UrbanSegNet: An urban meshes semantic segmentation network using diffusion perceptron and vertex spatial attention. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2024, 129, 103841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingma, D.P. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhuo, Z.; Ji, Z.; Wei, Z.; Li, J.; Li, Q. Leader population learning rate schedule. Inf. Sci. 2023, 623, 455–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebeida, M.S.; Davidson, A.A.; Patney, A.; Knupp, P.M.; Mitchell, S.A.; Owens, J.D. Efficient maximal Poisson-disk sampling. ACM Trans. Graph. (TOG) 2011, 30, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, J.M.; Liu, W.; Zang, Y.; Afzal, M.K.; Bello, S.A.; Muhammad, A.U.; Wang, C.; Li, J. Deep learning-based semantic segmentation of urban-scale 3D meshes in remote sensing: A survey. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2023, 121, 103365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.R.; Yi, L.; Su, H.; Guibas, L.J. Pointnet++: Deep hierarchical feature learning on point sets in a metric space. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Lao, Y.; Jiang, L.; Liu, X.; Zhao, H. Point transformer v2: Grouped vector attention and partition-based pooling. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 33330–33342. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Jiang, L.; Wang, P.S.; Liu, Z.; Liu, X.; Qiao, Y.; Ouyang, W.; He, T.; Zhao, H. Point Transformer V3: Simpler Faster Stronger. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 4840–4851. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, A.; Johnson, I.; Timalsina, A.; Rudra, A.; Ré, C. How to train your hippo: State space models with generalized orthogonal basis projections. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2206.12037. [Google Scholar]
| Method | Terra. | H-veg. | Build. | Water | Vehi. | Boat | mIoU | OA | mF1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PointNet++ [49] | 52.15 | 55.63 | 75.45 | 67.40 | 0 | 1.04 | 41.90 | 78.41 | 53.62 |
| RF-MRF [18] | 26.25 | 72.13 | 68.93 | 6.29 | 10.72 | 0 | 30.71 | 72.19 | 23.10 |
| SUM-RF [19] | 76.68 | 90.31 | 92.22 | 35.69 | 43.69 | 0.91 | 57.95 | 90.35 | 67.96 |
| PTV2 [50] | 82.84 | 89.62 | 93.59 | 87.42 | 19.86 | 18.75 | 65.35 | 93.10 | 70.80 |
| PSSNet [20] | 86.54 | 95.37 | 93.53 | 82.23 | 59.63 | 28.02 | 74.22 | 94.69 | 82.30 |
| UrbanSegNet [44] | 75.72 | 90.65 | 94.78 | 86.20 | 62.03 | 78.75 | 93.86 | 86.89 | |
| PTV3 [51] | 87.32 | 92.25 | 94.21 | 88.48 | 49.38 | 32.42 | 74.01 | 94.69 | 79.36 |
| MambaMeshSeg-Net | 41.54 |
| Method | Terra. | H-veg. | Build. | Vehi. | mIoU | OA | mF1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PointNet++ [49] | 59.97 | 0 | 91.80 | 0 | 37.94 | 91.12 | 44.22 |
| RF-MRF [18] | 23.02 | 51.08 | 85.92 | 4.86 | 41.21 | 85.82 | 51.68 |
| SUM-RF [19] | 85.99 | 65.06 | 95.86 | 47.44 | 73.59 | 95.85 | 83.38 |
| PTV2 [50] | 53.88 | 34.94 | 84.71 | 14.44 | 46.99 | 85.15 | 63.77 |
| PSSNet [20] | 79.13 | 71.81 | 95.53 | 25.06 | 67.88 | 95.78 | 82.30 |
| UrbanSegNet [44] | 73.48 | 81.82 | 96.89 | 74.93 | 95.86 | 84.37 | |
| PTV3 [51] | 84.20 | 45.25 | 95.46 | 41.46 | 66.59 | 95.38 | 70.51 |
| MambaMeshSeg-Net | 46.9 |
| Dataset | Model | Pre-Process Time (s) | Inference Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SUM | PointNet++ [49] | 81.17 | 4.58 |
| RF-MRF [18] | 44.83 | 6.17 | |
| SUM-RF [19] | 30.91 | 3.42 | |
| PTV2 [50] | 0.77 | 83.75 | |
| PSSNet [20] | 520.21 | 102.96 | |
| UrbanSegNet [44] | 231.63 | 36.57 | |
| PTV3 [51] | 0.77 | 23.17 | |
| MambaMeshSeg-Net | |||
| seMet | PointNet++ [49] | 44.25 | 5.75 |
| RF-MRF [18] | 184.25 | 20.25 | |
| SUM-RF [19] | 78.25 | 9.00 | |
| PTV2 [50] | 1.59 | 138.25 | |
| PSSNet [20] | 1083.25 | 234.03 | |
| UrbanSegNet [44] | 326.40 | 53.72 | |
| PTV3 [51] | 1.59 | 33.00 | |
| MambaMeshSeg-Net |
| Dataset | Scanning Mode | mIoU | OA | mF1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SUM | forward | 68.43 | 91.63 | 73.62 |
| backward | 70.83 | 91.86 | 74.93 | |
| bi-directions | 78.82 | 93.28 | 79.36 | |
| 77.47 | 94.82 | 83.13 | ||
| 74.05 | 94.62 | 81.80 | ||
| 76.87 | 95.01 | 83.06 | ||
| 75.64 | 93.86 | 81.24 | ||
| adaptive † | 79.04 | 95.61 | 86.97 | |
| seMet | forward | 71.58 | 93.68 | 74.59 |
| backward | 71.34 | 93.24 | 73.88 | |
| bi-directional | 71.24 | 94.87 | 75.32 | |
| 74.09 | 94.34 | 75.70 | ||
| 75.34 | 95.48 | 82.88 | ||
| 75.86 | 95.14 | 81.46 | ||
| 76.30 | 96.28 | 82.68 | ||
| adaptive † | 77.10 | 97.60 | 84.42 |
| Dataset | Octree Depth | mIoU | OA | mF1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SUM | 8 | 73.42 | 94.38 | 81.28 |
| 7 | 75.73 | 95.14 | 83.29 | |
| 6 | 79.04 | 95.61 | 86.97 | |
| 5 | 56.41 | 89.73 | 66.50 | |
| 4 | 58.94 | 91.23 | 67.78 | |
| seMet | 8 | 64.43 | 93.33 | 76.30 |
| 7 | 79.93 | 97.10 | 87.71 | |
| 6 | 77.10 | 97.60 | 84.42 | |
| 5 | 75.14 | 96.23 | 83.76 | |
| 4 | 68.53 | 96.02 | 76.14 |
| Dataset | HSS | SFE | FEF | mIoU | OA | mF1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SUM | ✓ | ✓ | 74.83 | 92.37 | 77.82 | |
| ✓ | ✓ | 78.80 | 94.42 | 80.61 | ||
| ✓ | ✓ | 78.82 | 93.28 | 79.36 | ||
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 79.01 | 95.61 | 86.97 | |
| seMet | ✓ | ✓ | 70.04 | 94.83 | 75.19 | |
| ✓ | ✓ | 68.17 | 94.46 | 73.24 | ||
| ✓ | ✓ | 71.24 | 94.87 | 75.32 | ||
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 77.10 | 97.60 | 84.42 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zi, W.; Chen, H.; Li, J.; Wu, J. MambaMeshSeg-Net: A Large-Scale Urban Mesh Semantic Segmentation Method Using a State Space Model with a Hybrid Scanning Strategy. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1653. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091653
Zi W, Chen H, Li J, Wu J. MambaMeshSeg-Net: A Large-Scale Urban Mesh Semantic Segmentation Method Using a State Space Model with a Hybrid Scanning Strategy. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(9):1653. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091653
Chicago/Turabian StyleZi, Wenjie, Hao Chen, Jun Li, and Jiangjiang Wu. 2025. "MambaMeshSeg-Net: A Large-Scale Urban Mesh Semantic Segmentation Method Using a State Space Model with a Hybrid Scanning Strategy" Remote Sensing 17, no. 9: 1653. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091653
APA StyleZi, W., Chen, H., Li, J., & Wu, J. (2025). MambaMeshSeg-Net: A Large-Scale Urban Mesh Semantic Segmentation Method Using a State Space Model with a Hybrid Scanning Strategy. Remote Sensing, 17(9), 1653. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091653






