Significant Improvement in Short-Term Green-Tide Transport Predictions Using the XGBoost Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
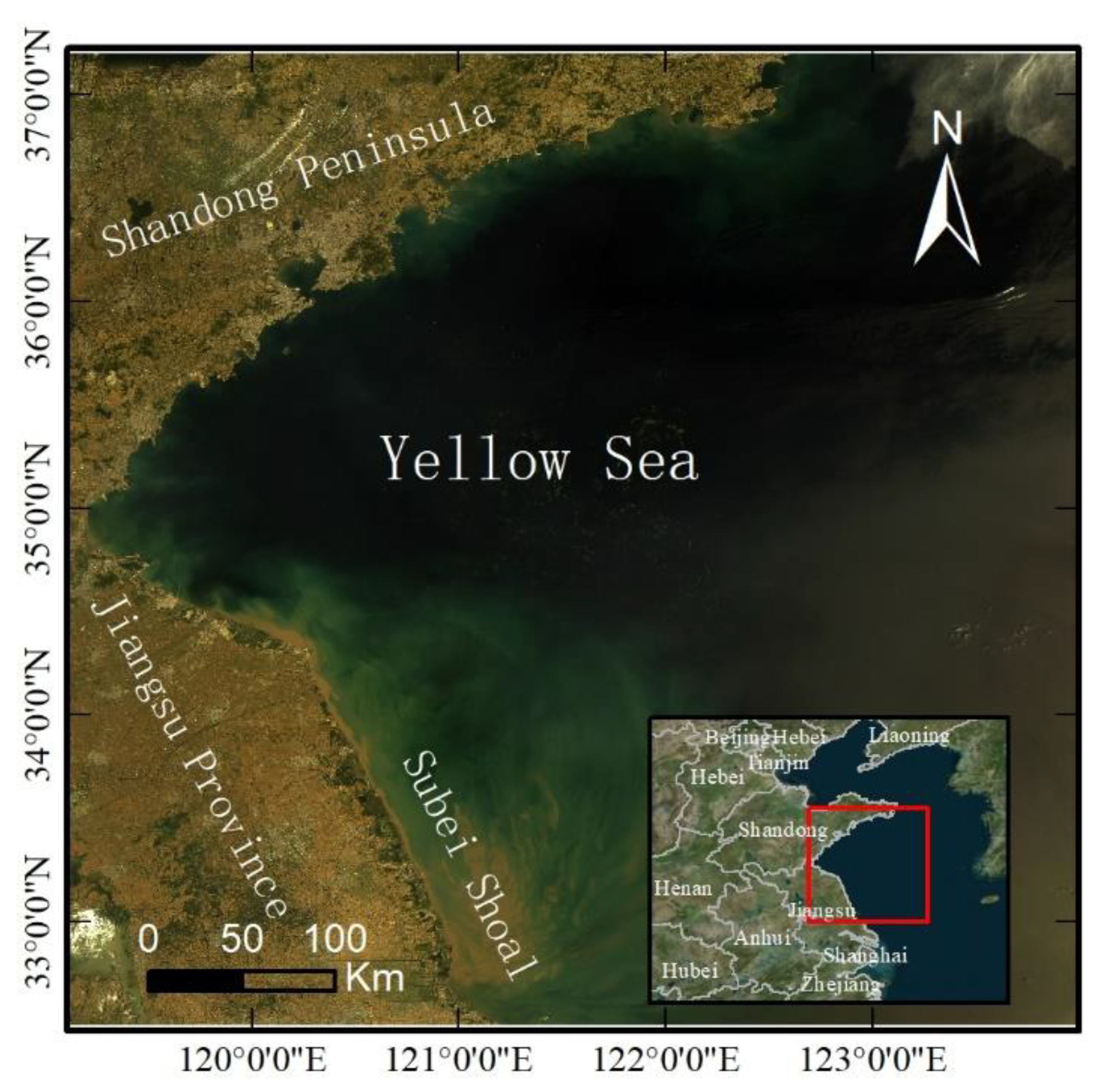
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data and Processing
2.2.1. Satellite Data
2.2.2. Driving-Factor Data
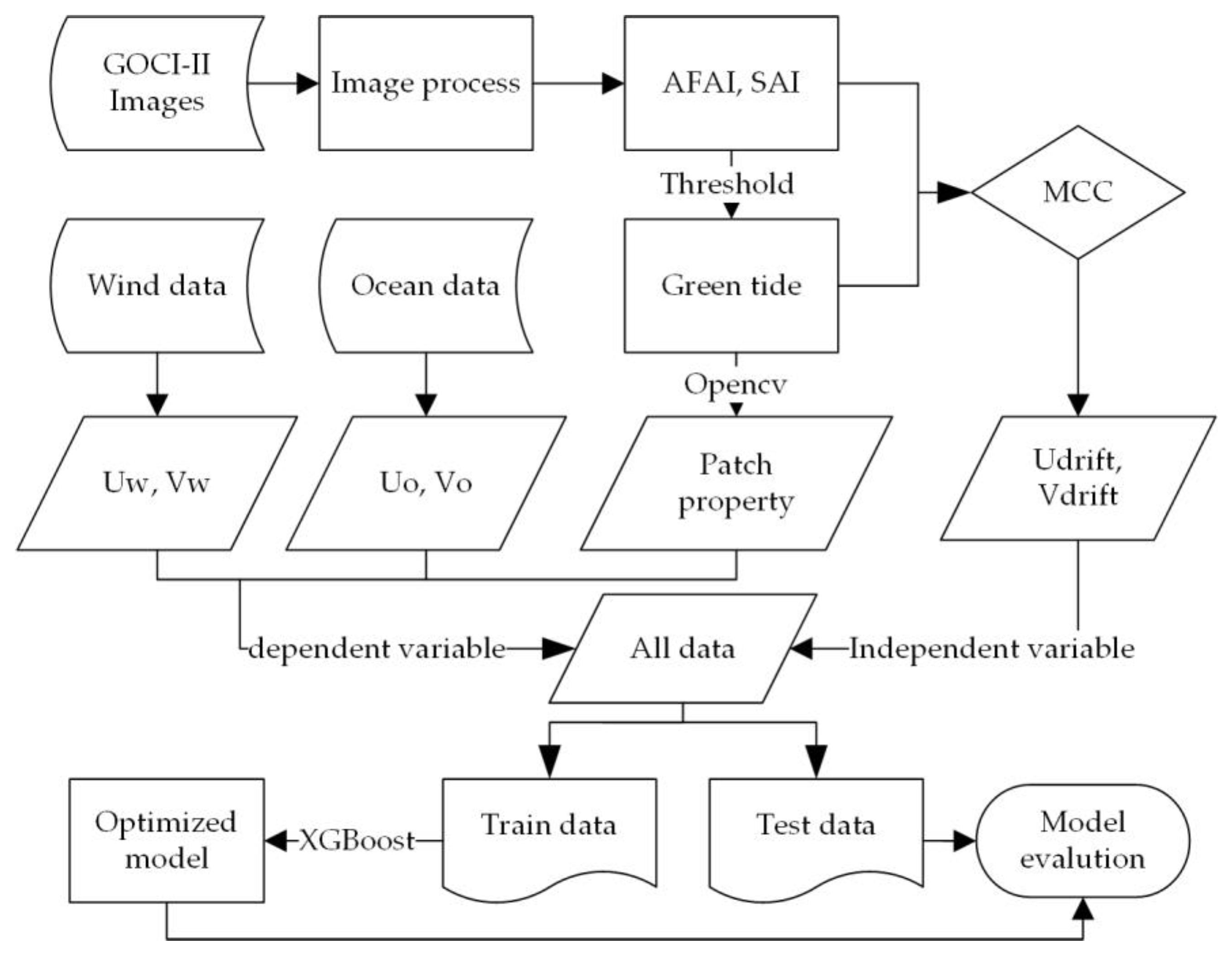
2.3. Method
2.3.1. Numerical Simulation Model
2.3.2. Machine Learning Model
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of the Performance of the OpenDrift Method in Simulating Short-Term Green-Tide Drift
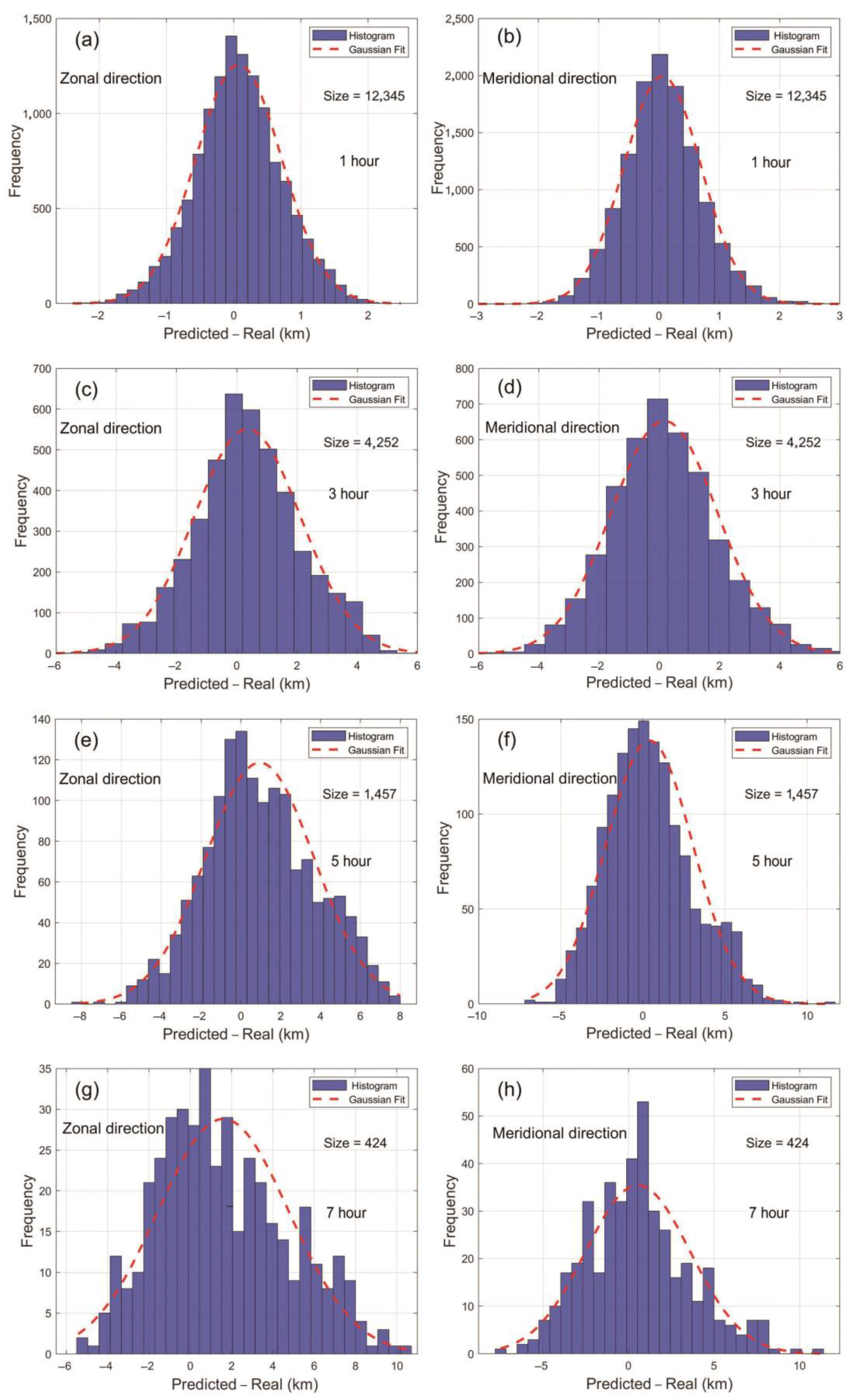
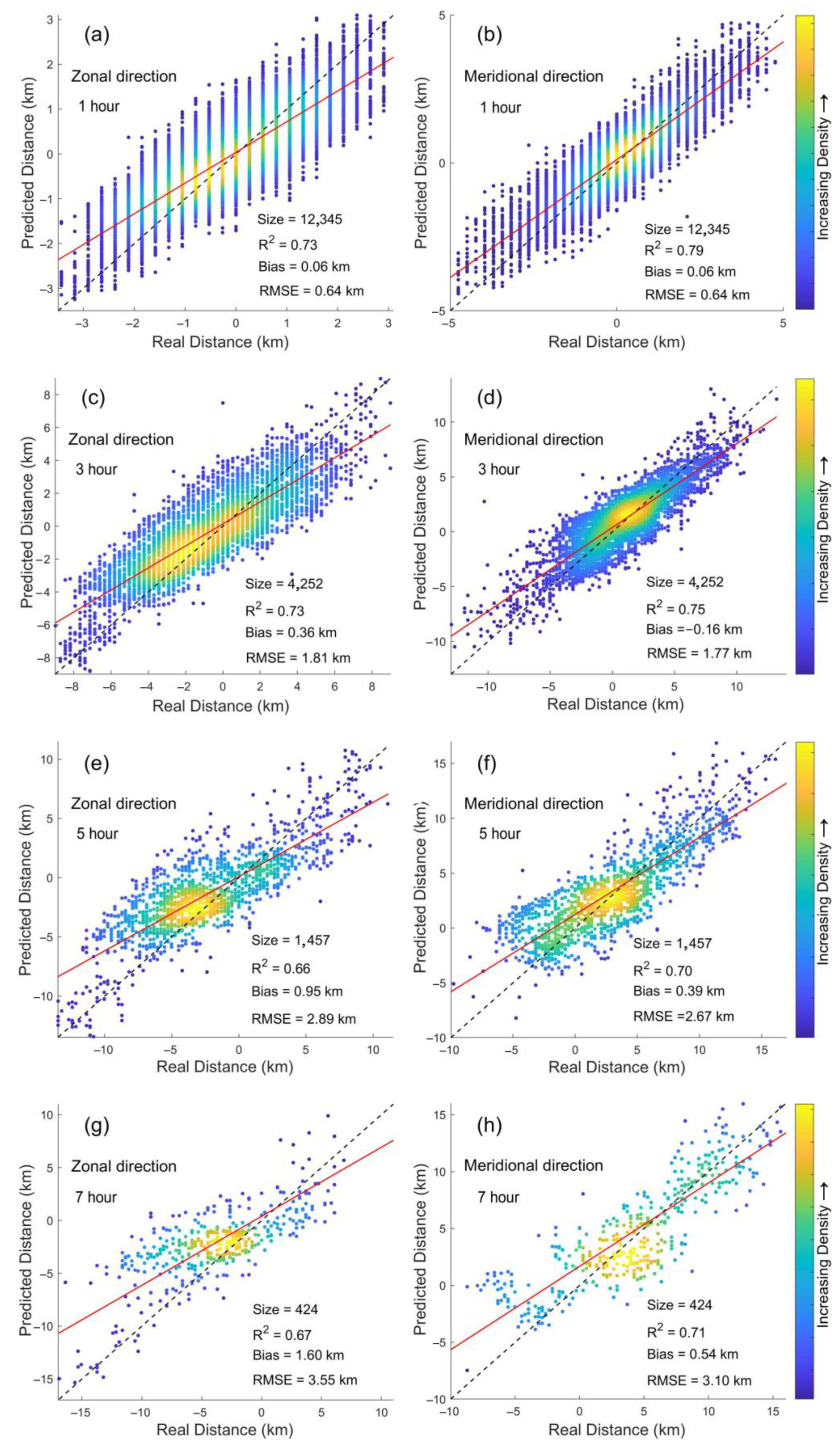
3.2. Analysis of the Performance of the Proposed Method in Simulating Short-Term Green-Tide Drift
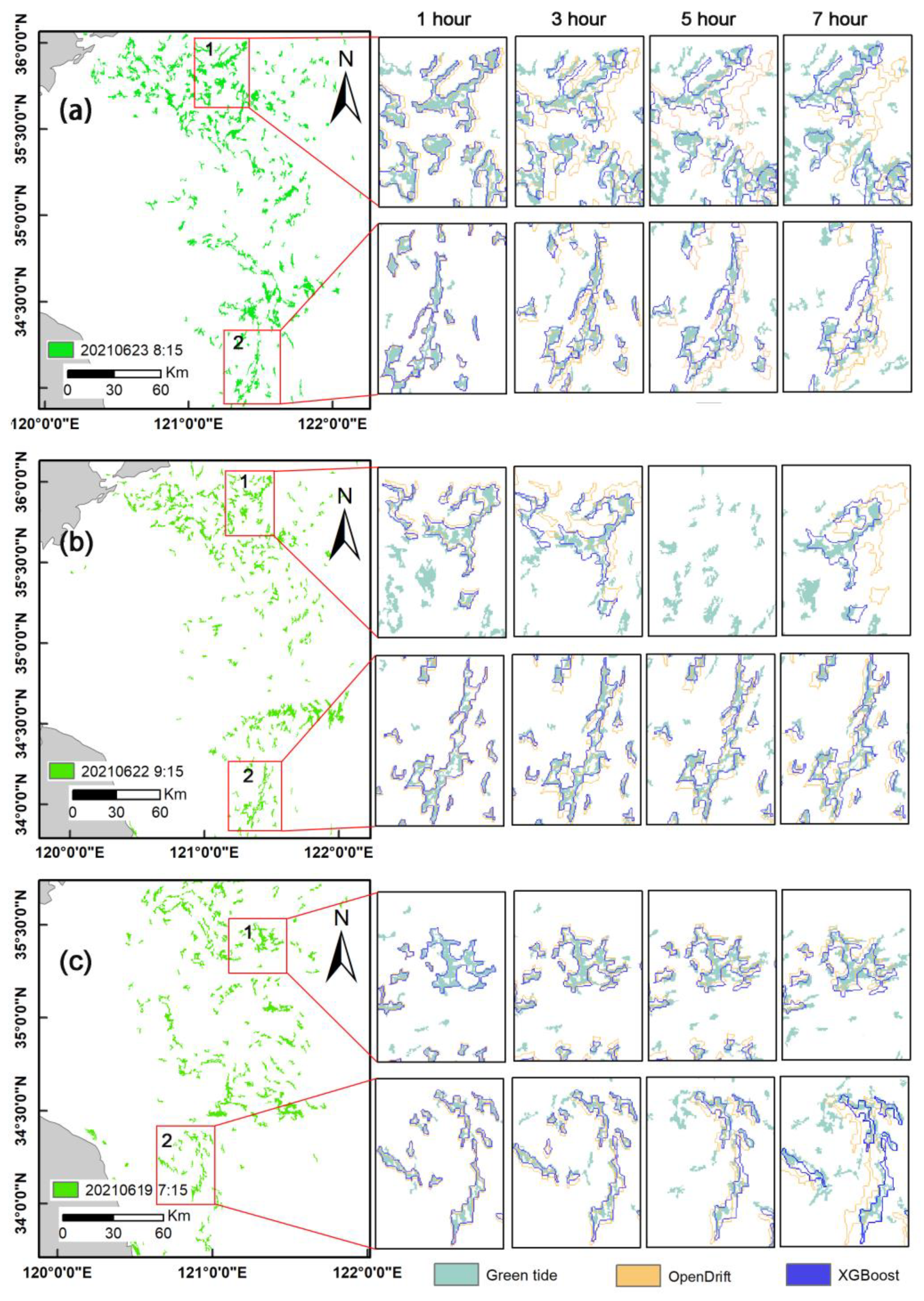
3.3. Visual Comparison of the Performance of the Proposed Method and OpenDrift Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, X.; Yu, Z.; Fu, Y.; Dong, M.; Zhang, J.; Yao, Q. Seasonal and interannual variations of nutrients in the Subei Shoal and their implication for the world’s largest green tide. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 951, 175390–175401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, W.; Chen, J.; He, M.; Ren, S.; Fang, L.; Wang, C.; Jiang, P.; Wang, W. Evolutionary trends and analysis of the driving factors of Ulva prolifera green tides: A study based on the random forest algorithm and multisource remote sensing images. Mar. Environ. Res. 2024, 198, 106495–106509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Gao, Z.; Song, D. Analysis of environmental factors affecting the large-scale long-term sequence of green tide outbreaks in the Yellow Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2021, 260, 107504–107516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Gao, Z.; Wang, Z. Analysis of the reasons for the outbreak of Yellow Sea green tide in 2021 based on long-term multi-source data. Mar. Environ. Res. 2022, 178, 105649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Q.; Hu, C. Mapping macroalgal blooms in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea using HJ-1 and Landsat data: Application of a virtual baseline reflectance height technique. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 178, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; He, P.; Li, H.; Li, G.; Liu, J.; Jiao, F.; Zhang, J.; Huo, Y.; Shi, X.; Sun, R.; et al. Ulva prolifera green-tide outbreaks and their environmental impact in the Yellow Sea, China. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2019, 6, 825–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Keesing, J.K.; He, P.; Wang, Z.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Y. The world’s largest macroalgal bloom in the Yellow Sea, China: Formation and implications. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2013, 129, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xiao, J.; Fan, S.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, D. Who made the world’s largest green tide in China?—An integrated study on the initiation and early development of the green tide in Yellow Sea. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2015, 60, 1105–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, N.; Wang, X.; Gao, S.; Ai, B.; Li, B.; Shang, H. Collaborative ship scheduling decision model for green tide salvage based on evolutionary population dynamics. Ocean Eng. 2024, 304, 117796–117810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; Yuan, H.; Liu, J.; Sun, Y.; Tong, Y.; Zhao, S.; Xia, J.; Li, S.; Hu, M.; Cao, J.; et al. A review of physical, chemical, and biological green tide prevention methods in the Southern Yellow Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 180, 113772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Guo, Y.; Li, X. Weekly green tide mapping in the Yellow Sea with deep learning: Integrating optical and synthetic aperture radar ocean imagery. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2024, 16, 4189–4207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Yu, T.; Xu, J.; Pan, X.; Shao, W.; Zuo, J.; Yu, Y. Monitoring and Forecasting Green Tide in the Yellow Sea Using Satellite Imagery. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Wu, M.; Wei, J.; He, Y.; Niu, L.; Li, H.; Xu, G. Adaptive Threshold Model in Google Earth Engine: A Case Study of Ulva prolifera Extraction in the South Yellow Sea, China. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3240–3264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, X.; Li, H.; Wang, L.; Sun, W.; Li, Y. A comprehensive review of remote sensing techniques for monitoring Ulva prolifera green tides. Front. Mar. Sci. 2025, 12, 1546289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Qi, L.; Hu, L.; Cui, T.; Xing, Q.; He, M.; Wang, N.; Xiao, Y.; Sun, D.; Lu, Y.; et al. Mapping Ulva prolifera green tides from space: A revisit on algorithm design and data products. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2023, 116, 103173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Cao, M.; Zheng, L.; Xiao, Y.; Qi, L.; Xing, Q.; Kim, K.; Sun, D.; Wang, N.; Guo, M.; et al. Remote Sensing of Ulva Prolifera Green Tide in the Yellow Sea Using Multisource Satellite Data: Progress and prospects. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2024, 12, 110–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Hu, C.; HE, M. Remote estimation of biomass of Ulva prolifera macroalgae in the Yellow Sea. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 192, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Fan, D.; Ji, Q.; Obodoefuna, D.C. Dynamic Diurnal Changes in Green Algae Biomass in the Southern Yellow Sea Based on GOCI Images. J. Ocean Univ. China 2020, 19, 811–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Cui, T.; Gong, J.; Liu, R.; Chen, X.; Liang, X. Remote sensing estimation of the biomass of floating Ulva prolifera and analysis of the main factors driving the interannual variability of the biomass in the Yellow Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 140, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podlejski, W.; Berline, L.; Nerini, D.; Doglioli, A.; Lett, C. A new Sargassum drift model derived from features tracking in MODIS images. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 188, 114629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, H.; Li, J.; Wang, Q.; Zou, B.; Shi, L.; Xu, M.; Liu, S.; Wan, J.; Zeng, Z.; Chen, Y. A multi-module with a two-way feedback method for Ulva drift-diffusion. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2023, 42, 118–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, Y.B.; Choi, B.J.; Kim, Y.H.; Park, Y.G. Tracing floating green algae blooms in the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea using GOCI satellite data and Lagrangian transport simulations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 156, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Ge, J.; Liu, D.; Ding, P.; Chen, C.; Wei, X. The Lagrangian-based Floating Macroalgal Growth and Drift Model (FMGDM v1.0): Application to the Yellow Sea green tide. Geosci. Model Dev. 2021, 14, 6049–6070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Q.; An, D.; Zheng, X.; Wei, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, L.; Tian, L.; Chen, J. Monitoring seaweed aquaculture in the Yellow Sea with multiple sensors for managing the disaster of macroalgal blooms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 231, 111279–111290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara-Hernández, J.A.; Enriquez, C.; Zavala-Hidalgo, J.; Cuevas, E.; van Tussenbroek, B.; Uribe-Martínez, A. Sargassum transport towards Mexican Caribbean shores: Numerical modeling for research and forecasting. J. Mar. Syst. 2024, 241, 103923–103939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Cheng, P.; Wang, M.; Hu, C.; Xie, Y.; Mao, K. Where does floating Sargassum in the East China Sea come from? Harmful Algae 2023, 129, 102523–102533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, H.; Li, F. Green tide in the yellow sea from generation to extinction and the controlling factor. Oceanol. Limn. Sin. 2022, 53, 1338–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putman, N.F.; Lumpkin, R.; Olascoaga, M.J.; Trinanes, J.; Goni, G.J. Improving transport predictions of pelagic Sargassum. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2020, 529, 151398–151405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Fang, Z.; Liang, J.; Song, X. Estimating Ulva prolifera green tides of the Yellow Sea through ConvLSTM data fusion. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 324, 121350–121363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Gu, F.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhuang, Z.; Chen, G. Parameterization Method of Wind Drift Factor Based on Deep Learning in the Oil Spill Model. J. Ocean. Univ. China 2023, 22, 1505–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. XGBoost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System, A Scalable Tree Boosting System. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, S.; Shi, X.; Wang, G.; Zhou, L.; Hu, B.; Hu, L.; Yang, G.; Liu, Y.; Yao, Z.; Liu, S. Sediment accumulation and budget in the Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea and East China Sea. Mar. Geol. 2017, 390, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Dong, P.; Li, G. Hydrodynamic processes and their impacts on the mud deposit in the Southern Yellow Sea. Mar. Geol. 2015, 360, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Xu, T. An evolving marine environment and its driving forces of algal blooms in the Southern Yellow Sea of China. Mar. Environ. Res. 2022, 178, 105635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Shen, F.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, S. Identifying algal bloom types and analyzing their diurnal variations using GOCI-II data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2025, 136, 104377–104389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhao, S.; Sun, Y.; Cui, Q.; Wu, L.; Gao, S.; Zhang, J.; He, P. Review of the development of the green tide and the process of control in the southern Yellow Sea in 2022. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2024, 302, 108772–108781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.G.; Li, Y.M.; Wang, Q.; Liu, G.; Zheng, Z.B.; Mu, M.; Li, Y. Tempo-spatial dynamics of water quality and its response to river flow in estuary of taihu lake based on GOCI imagery. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 28079–28101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Liu, Y.; Sun, C.; Wei, X.; Li, H.; Han, Z. A study of the environmental factors influencing the growth phases of Ulva prolifera in the southern Yellow Sea, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 135, 1016–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, M.; Dou, X.; Zhao, C.; Zhu, J. Exploring the Green Tide Transport Mechanisms and Evaluating Leeway Coefficient Estimation via Moderate-Resolution Geostationary Images. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagestad, K.F.; Röhrs, J.; Breivik, Ø.; Ådlandsvik, B. OpenDrift v1.0: A generic framework for trajectory modelling. Geosci. Model. Dev. 2018, 11, 1405–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röhrs, J.; Sutherland, G.; Jeans, G.; Bedington, M.; Sperrevik, A.K.; Dagestad, K.-F.; Gusdal, Y.; Mauritzen, C.; Dale, A.; LaCasce, J.H. Surface currents in operational oceanography: Key applications, mechanisms, and methods. J. Oper. Oceanogr. 2023, 16, 60–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
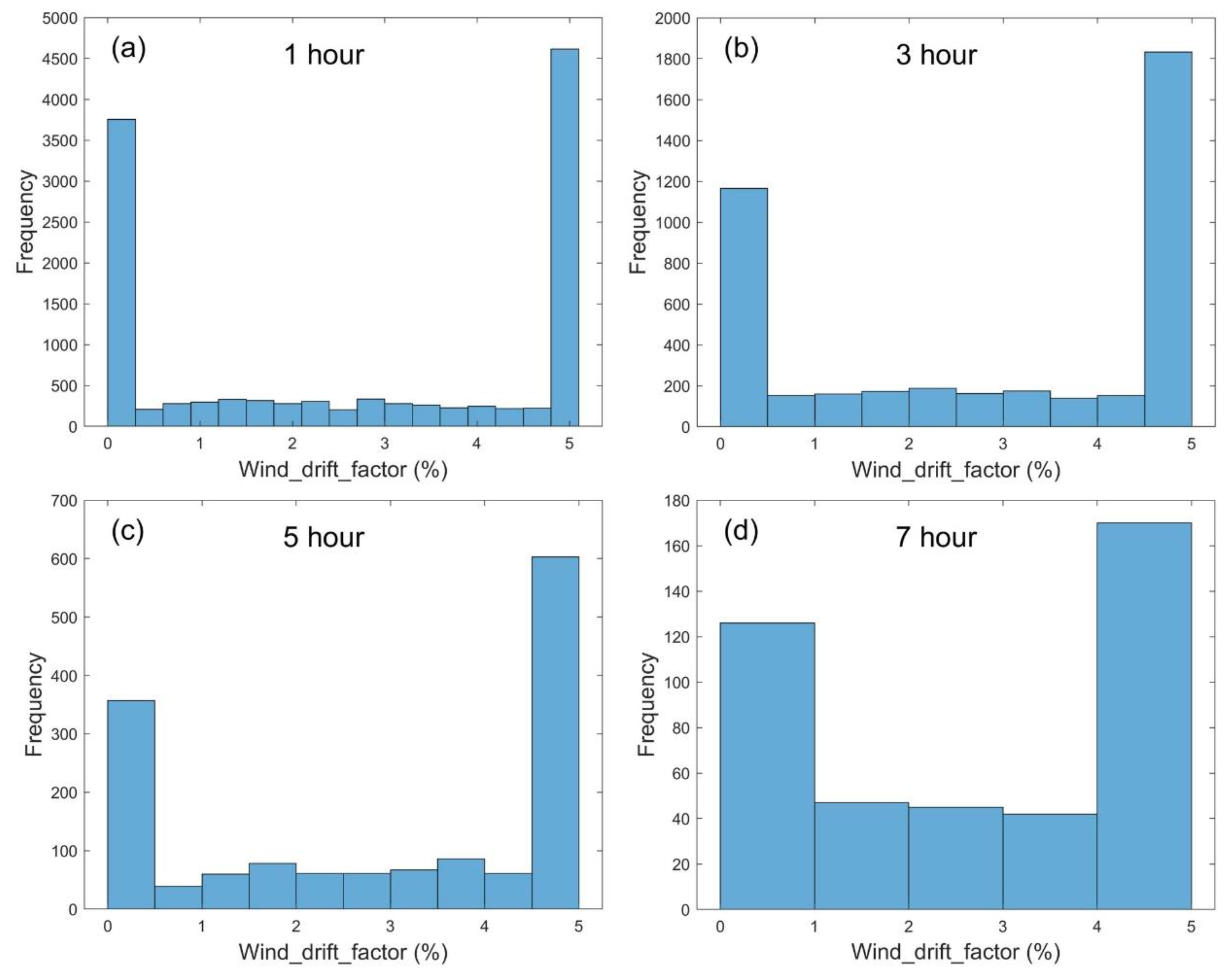
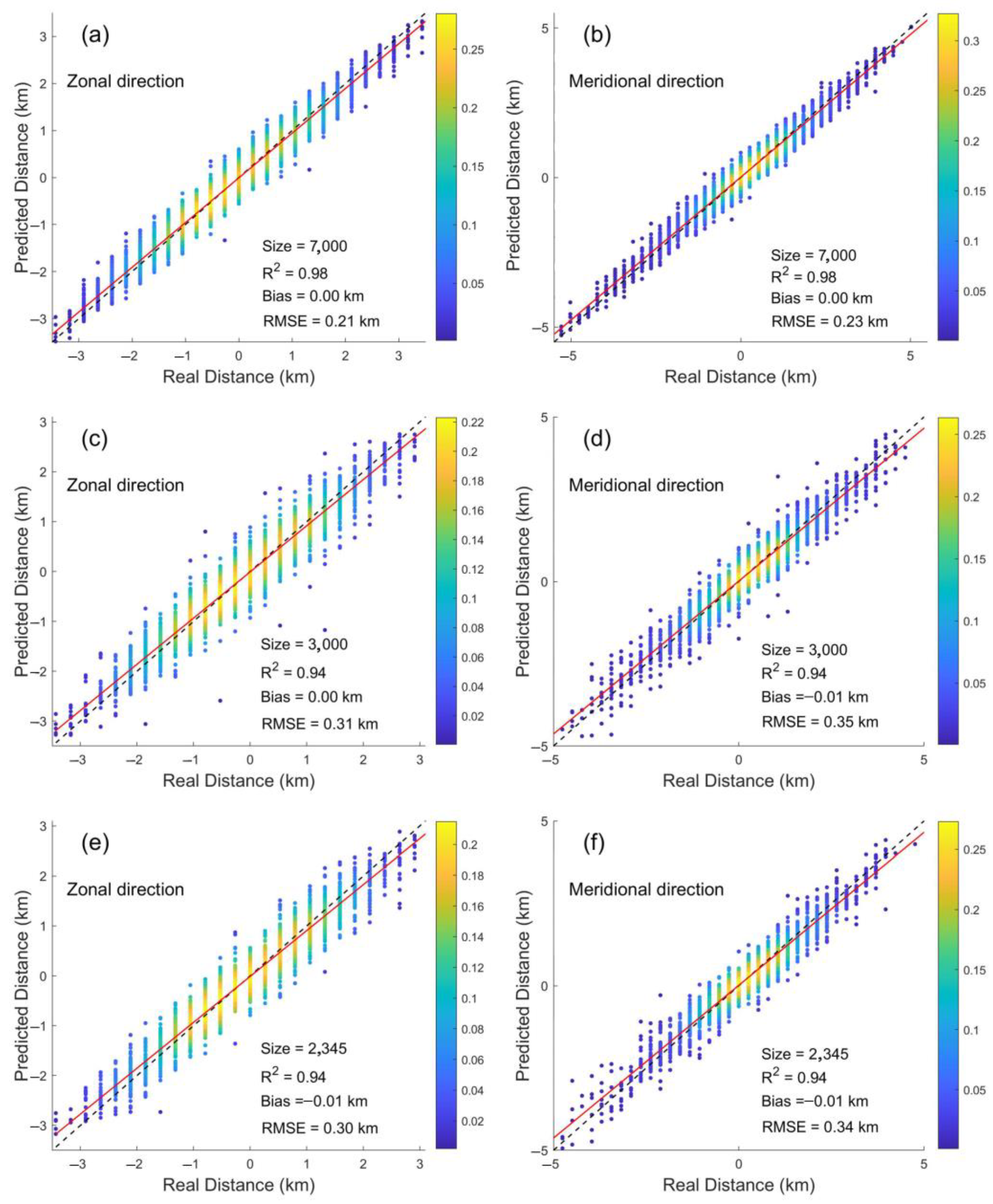
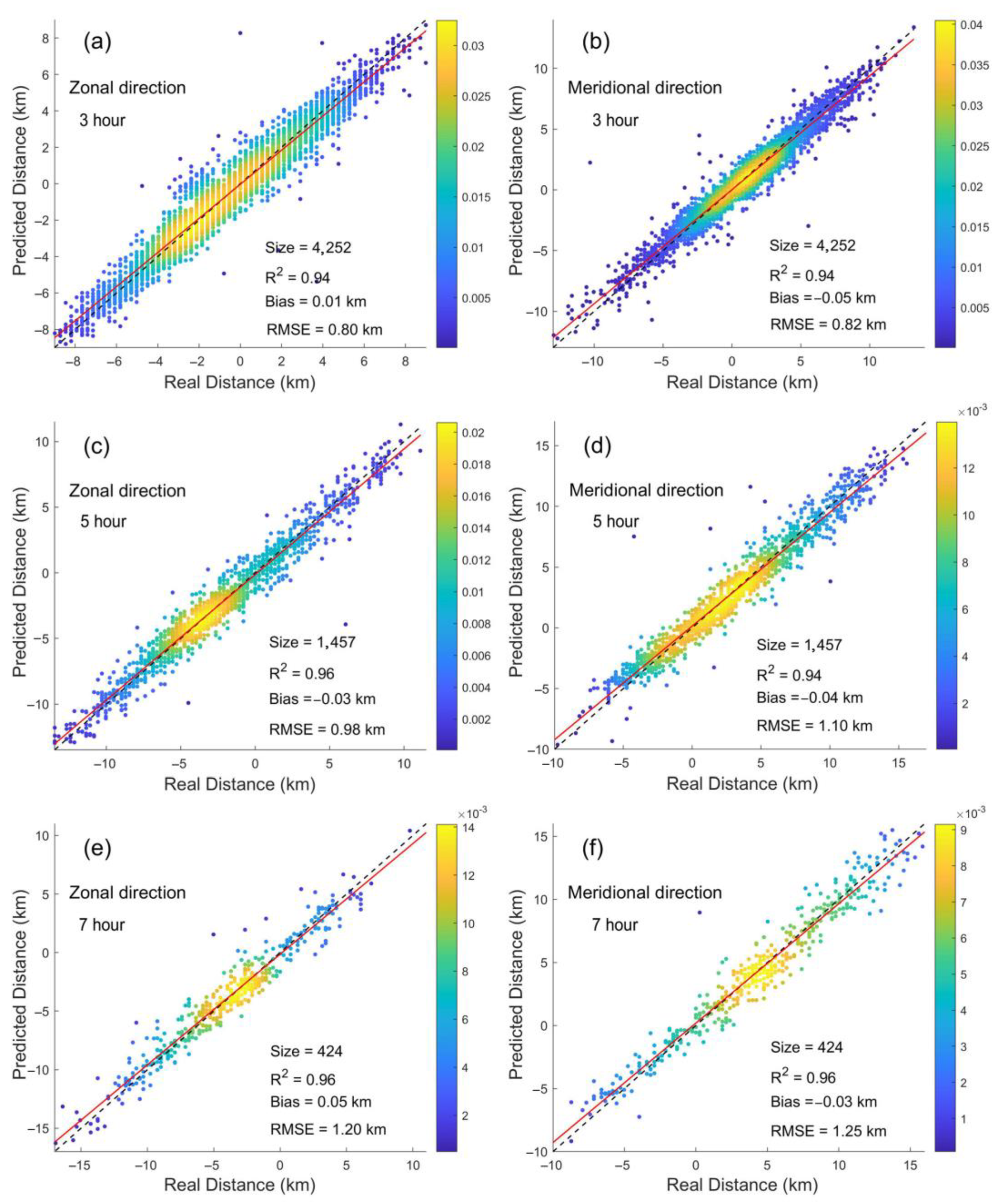



| Year | Date |
|---|---|
| 2021 | 4 June, 5 June, 6 June, 7 June, 19 June, 20 June, 22 June, 23 June, 1 July, 9 July, 10 July |
| 2023 | 3 June, 6 June, 8 June, 9 June, 11 June, 12 June, 13 June, 14 June, 15 June, 22 June, 24 June, 27 June, 5 July, 9 July, 10 July |
| 2024 | 3 June, 6 June, 7 June, 8 June, 9 June, 10 June, 13 June, 15 June, 18 June, 23 June, 25 June, 26 June, 27 June, 30 June, 3 July |
| Time Interval (h) | Model | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | + 0.07 + 0.12 + 0.14 | 0.62 0.50 0.59 |
| 3 | + 0.32 + 0.12 + 0.27 | 0.57 0.72 0.68 |
| 5 | + 0.40 + 0.21 + 0.26 | 0.54 0.60 0.60 |
| 7 | + 0.43 + 1.52 + 0.40 | 0.64 0.11 0.43 |
| Time Interval (h) | Sample Size (N) | N (k > 0.50) | N (S > 10 km2) | Savg (S > 10 km2) | Smax (km2) | k (Smax) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 152 | 152 | 55 | 48.88 | 352.31 | 0.53 |
| 2 | 134 | 133 | 53 | 43.99 | 189.48 | 0.57 |
| 3 | 133 | 129 | 54 | 41.24 | 157.98 | 0.62 |
| 4 | 116 | 109 | 50 | 41.18 | 157.98 | 0.57 |
| 5 | 98 | 90 | 39 | 39.16 | 142.43 | 0.47 |
| 6 | 60 | 50 | 32 | 38.15 | 142.43 | 0.43 |
| 7 | 57 | 52 | 27 | 37.28 | 136.08 | 0.55 |
| 8 | 57 | 52 | 28 | 36.71 | 136.08 | 0.54 |
| 9 | 52 | 51 | 23 | 32.45 | 136.08 | 0.51 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ji, M.; Zhao, C. Significant Improvement in Short-Term Green-Tide Transport Predictions Using the XGBoost Model. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1636. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091636
Ji M, Zhao C. Significant Improvement in Short-Term Green-Tide Transport Predictions Using the XGBoost Model. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(9):1636. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091636
Chicago/Turabian StyleJi, Menghao, and Chengyi Zhao. 2025. "Significant Improvement in Short-Term Green-Tide Transport Predictions Using the XGBoost Model" Remote Sensing 17, no. 9: 1636. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091636
APA StyleJi, M., & Zhao, C. (2025). Significant Improvement in Short-Term Green-Tide Transport Predictions Using the XGBoost Model. Remote Sensing, 17(9), 1636. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091636






