Mapping Forest Aboveground Biomass with Phenological Information Extracted from Remote Sensing Images in Subtropical Evergreen Broadleaf Forests
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
2.1. Study Area
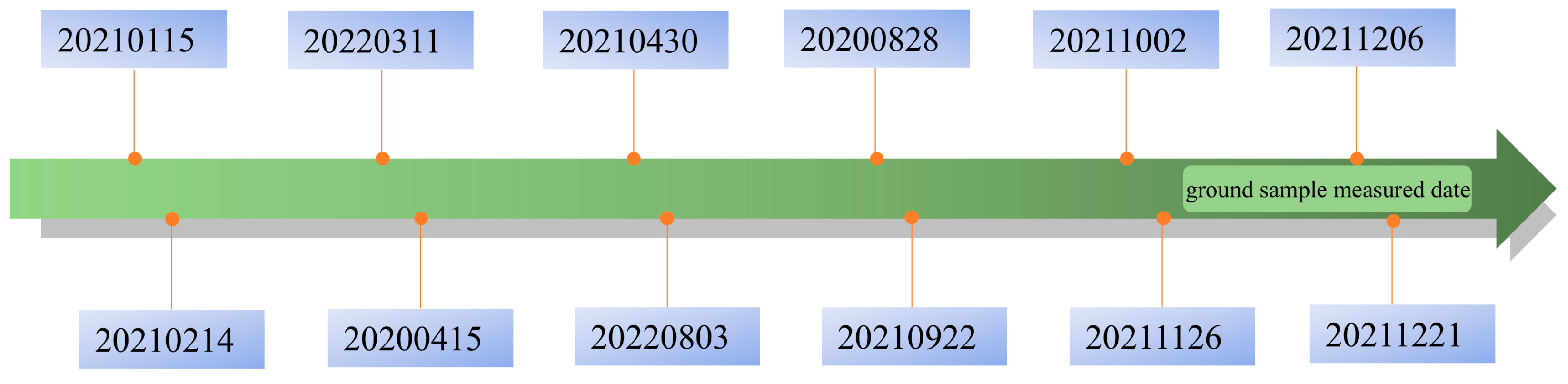
2.2. Ground Measured Data
2.3. Remote Sensing Data and Pre-Processing
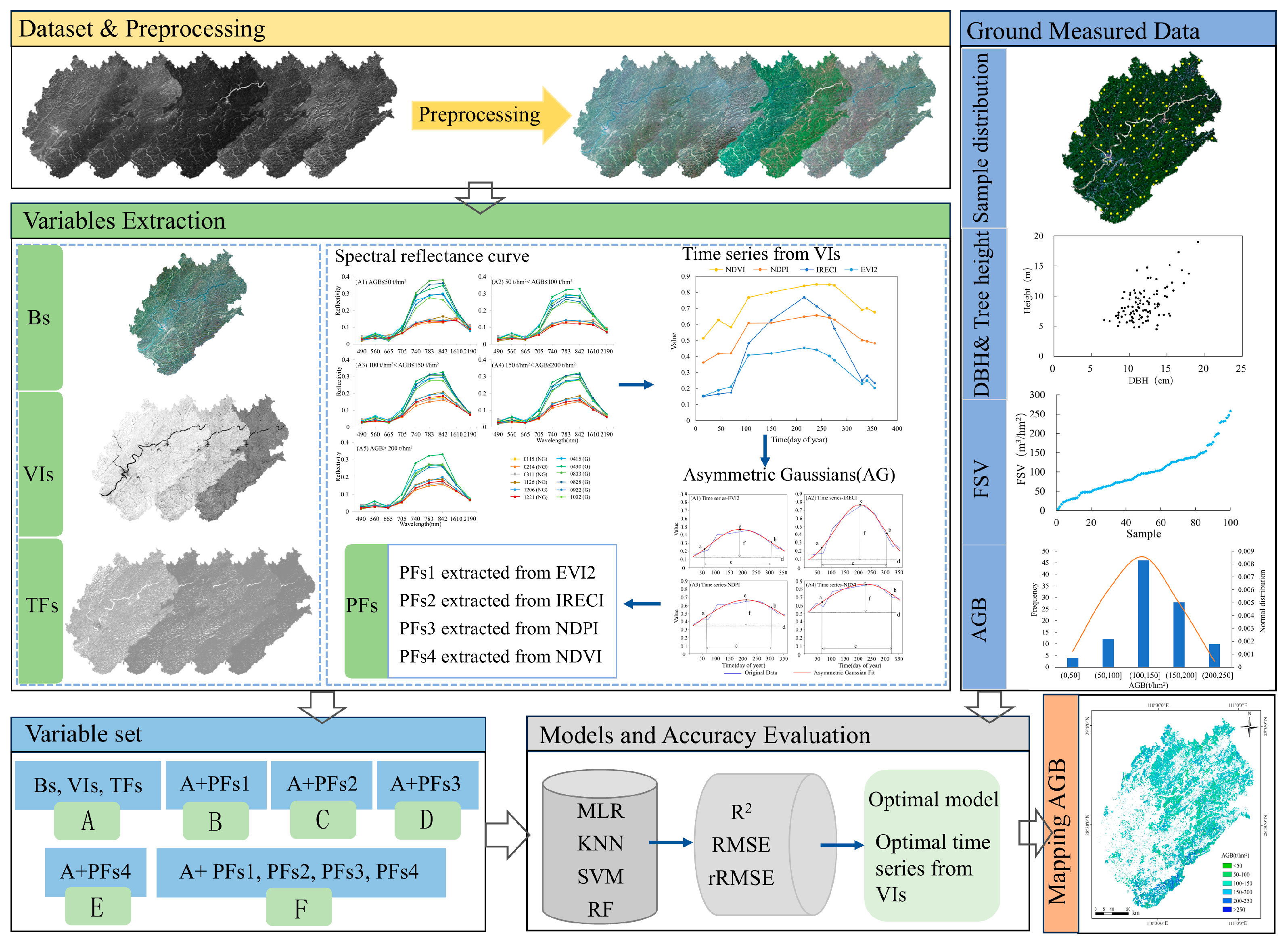
3. Methods
3.1. Spectral and Texture Features
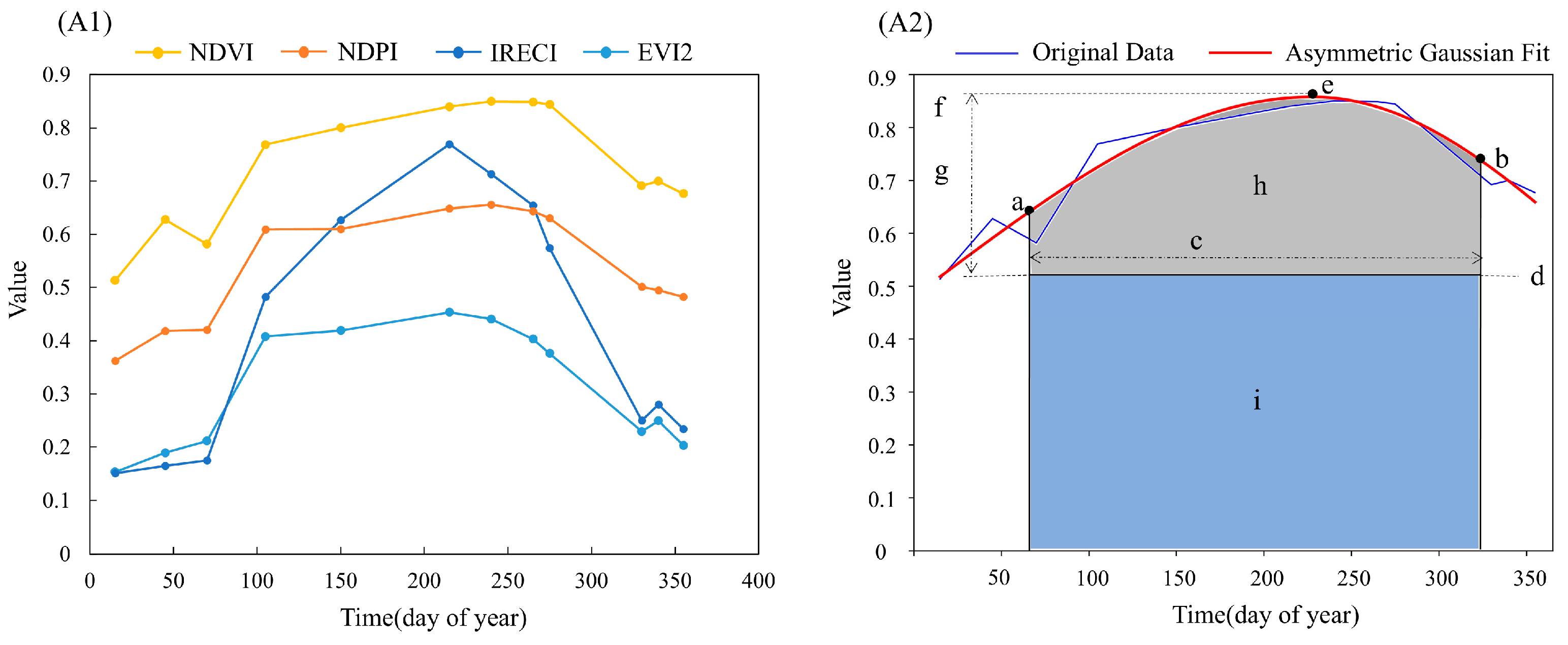
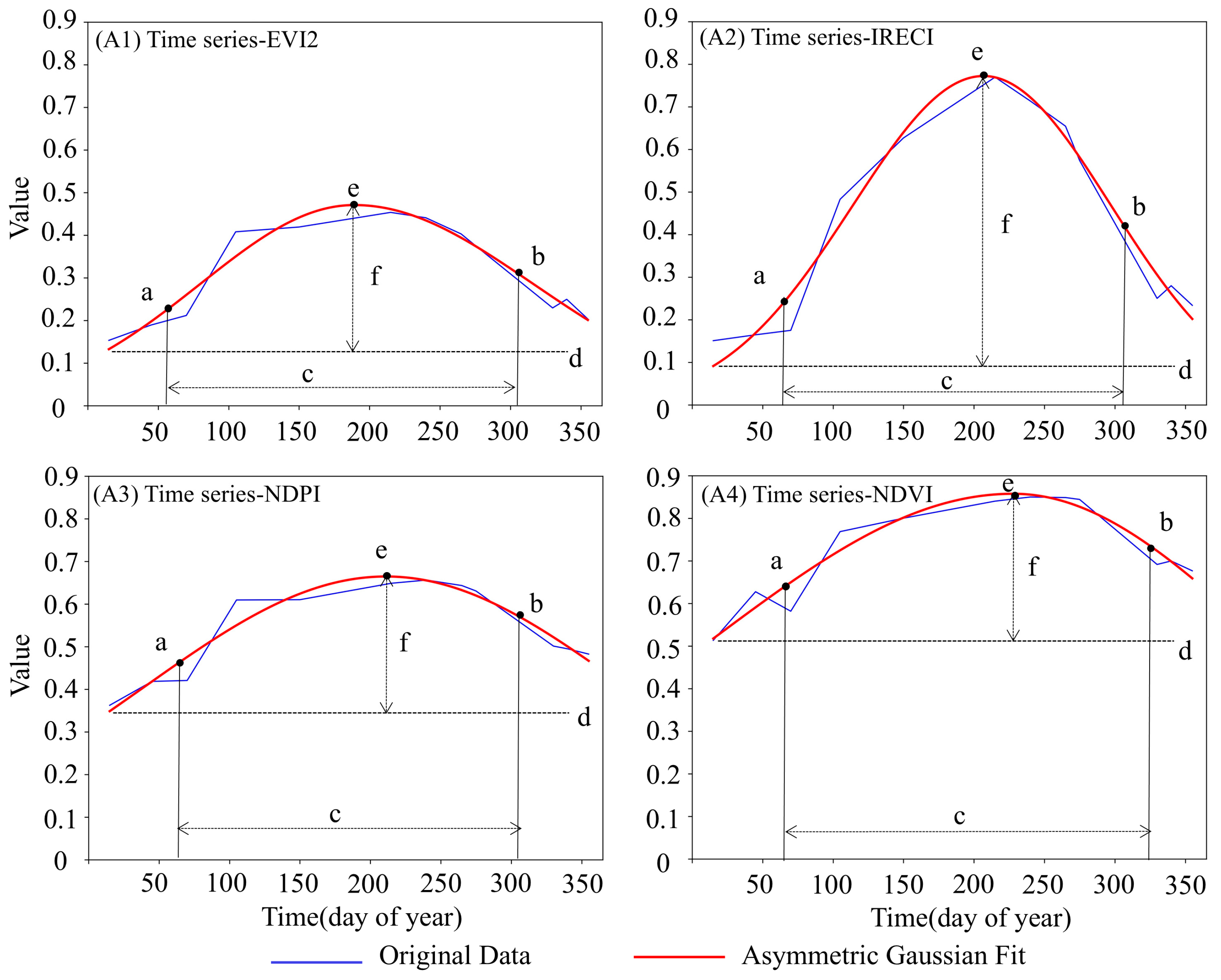
3.2. Phenological Features
3.3. Variables Sets
3.4. Models and Accuracy Evaluation in Mapping Forest AGB
4. Results
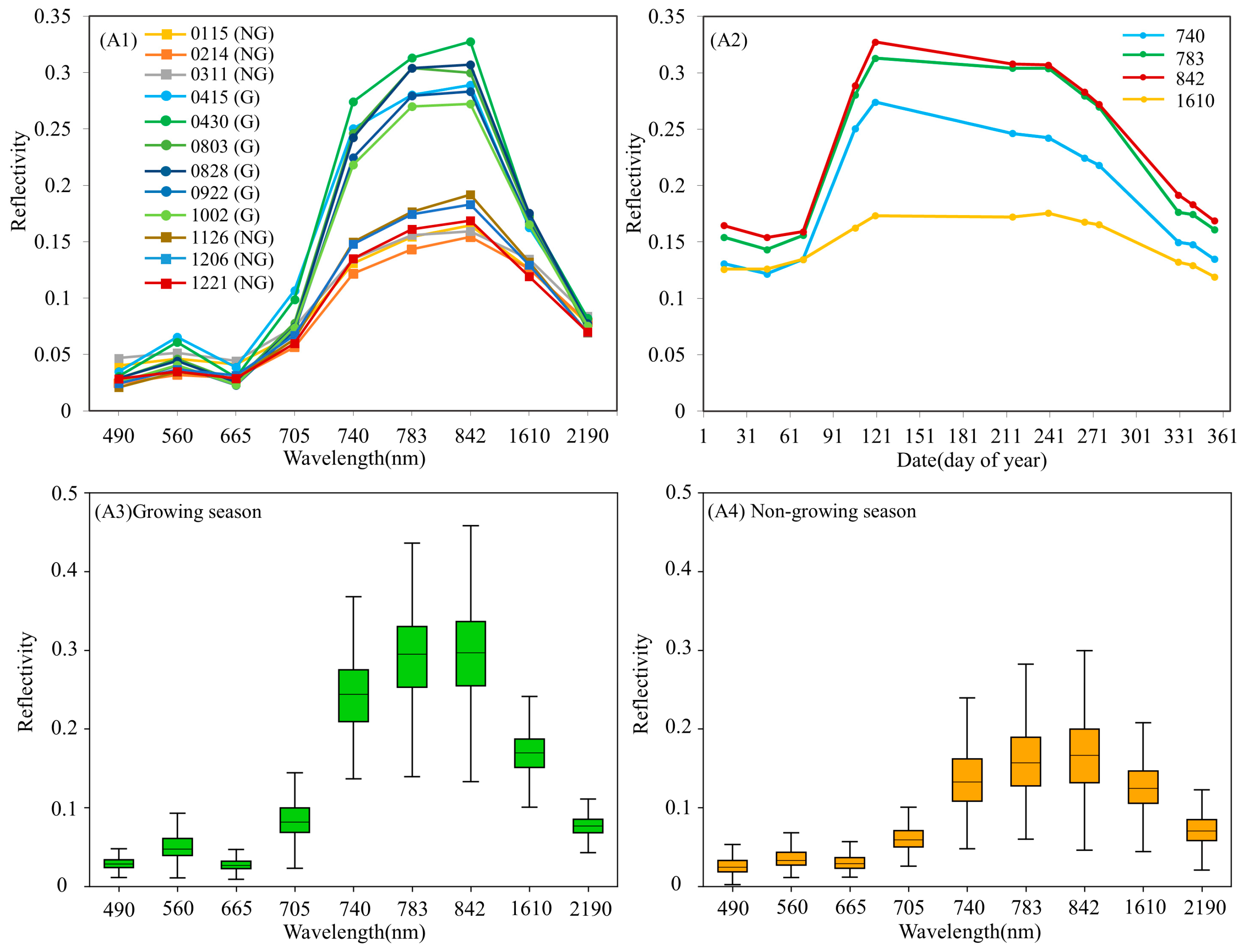
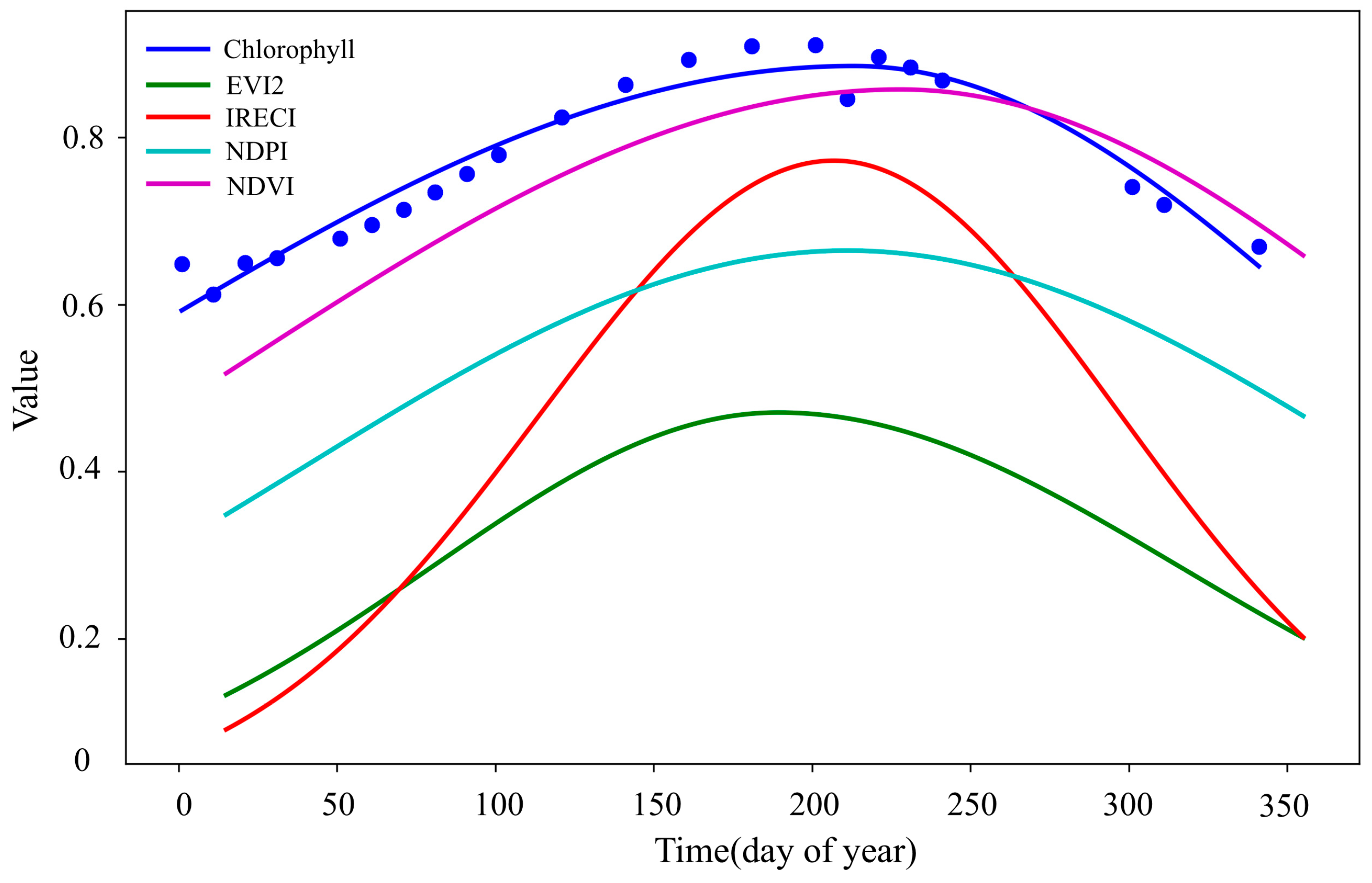
4.1. The Results of Spectral Response in Subtropical Evergreen Broadleaf Forests
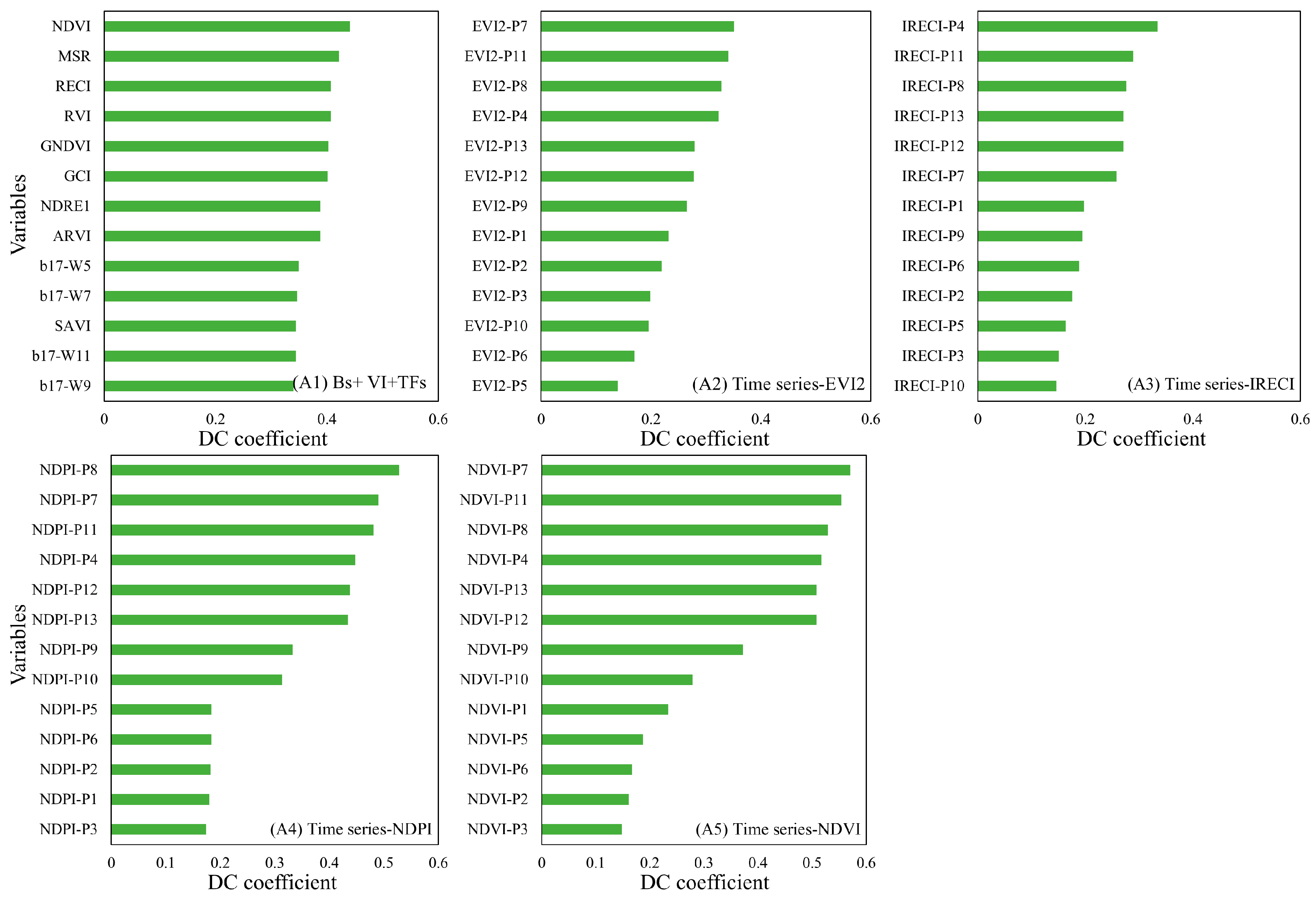
4.2. The Sensitivity Between the Forest AGB and the Extracted Phenological Features
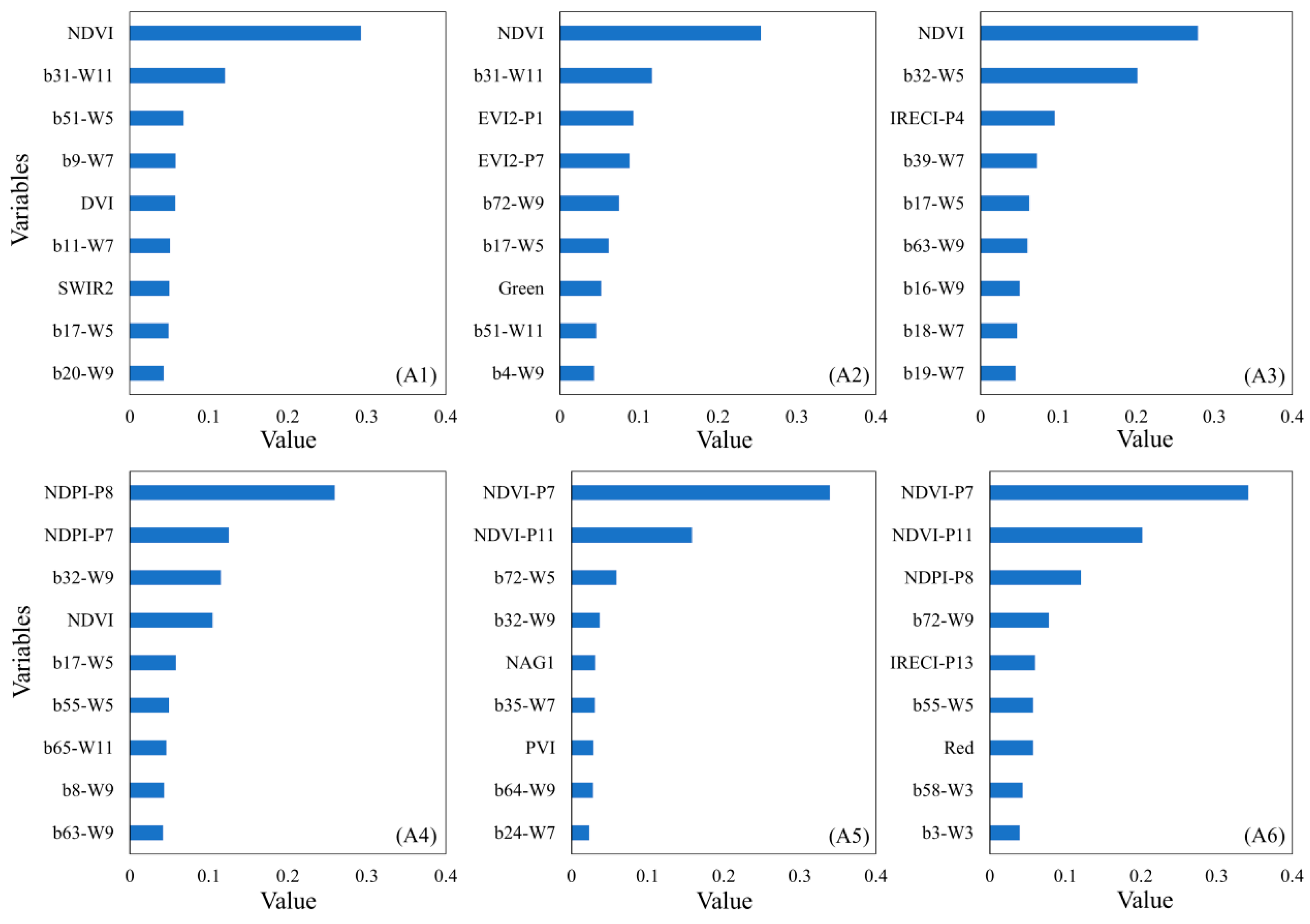
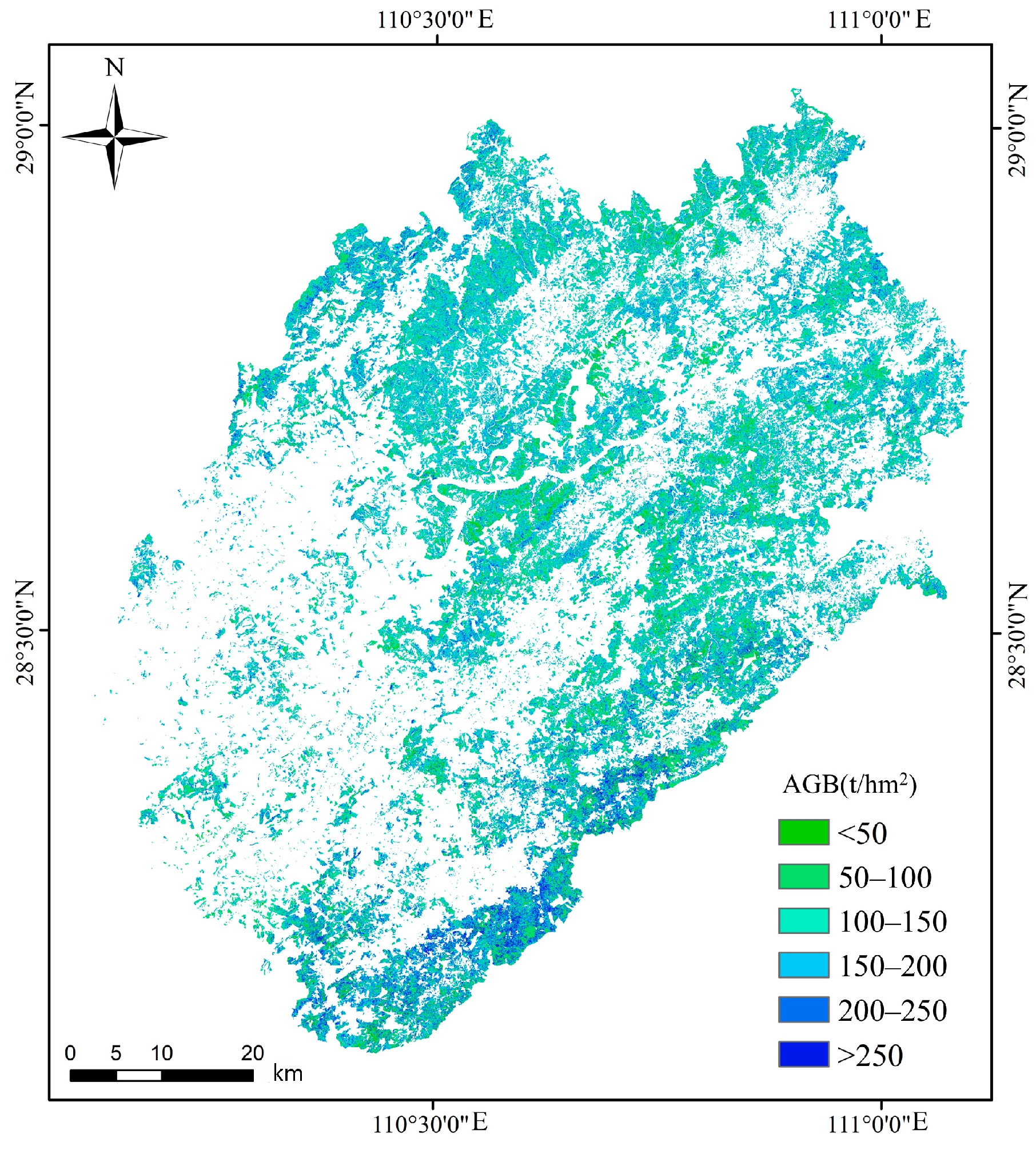
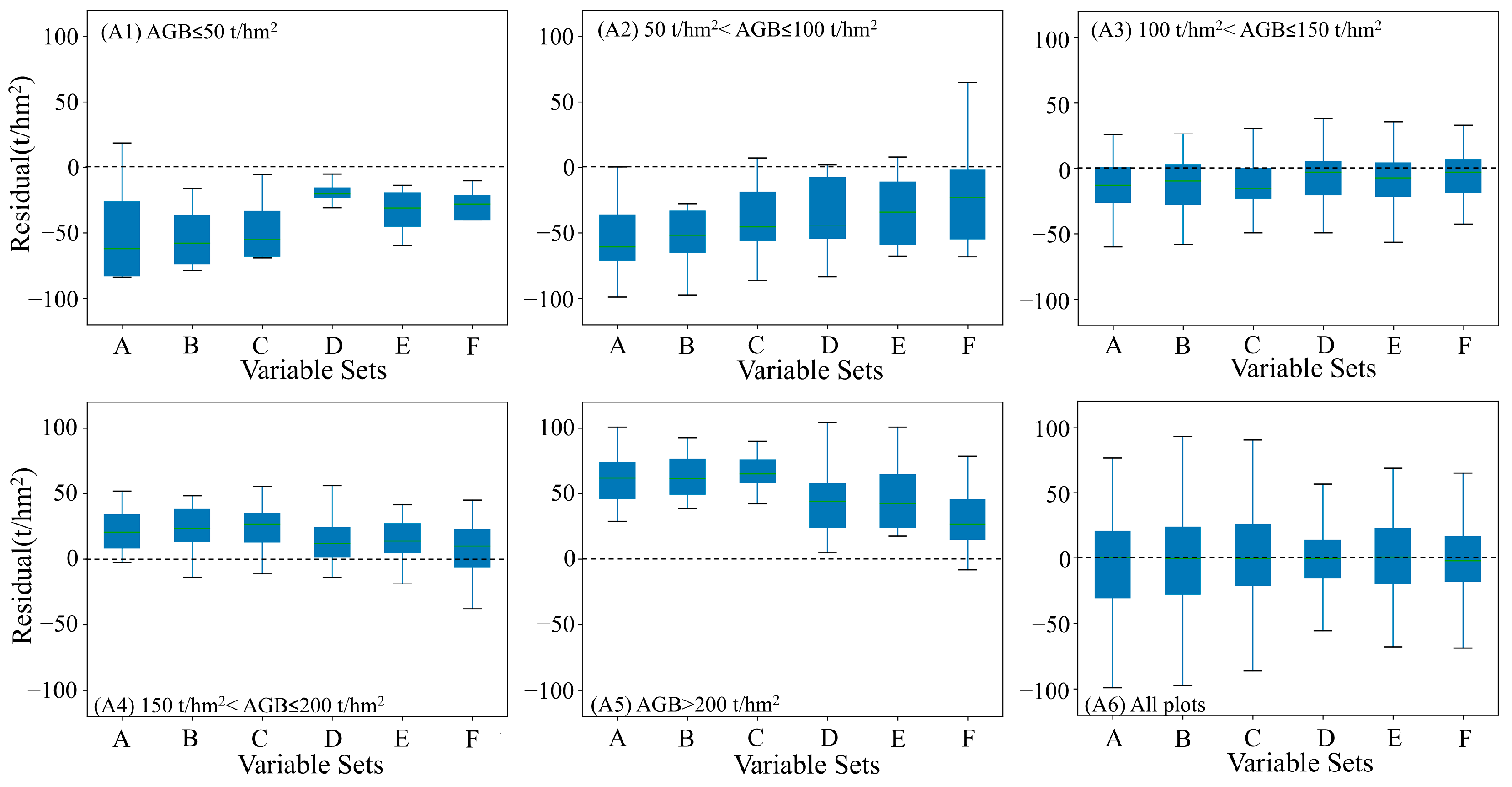
4.3. The Results of Mapping AGB
5. Discussion
5.1. Interpretation the Phenological Features in Broadleaf Evergreen Forests
5.2. Potential of Phenological Features on AGB Mapping
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Araujo, E.C.G.; Sanquetta, C.R.; Dalla Corte, A.P.; Pelissari, A.L.; Orso, G.A.; Silva, T.C. Global review and state-of-the-art of biomass and carbon stock in the Amazon. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 331, 117251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, D.S.; Chen, Q.; Wang, G.X.; Liu, L.J.; Li, G.Y.; Moran, E. A survey of remote sensing-based aboveground biomass estimation methods in forest ecosystems. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2016, 9, 63–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, S.; Wong, M.S.; Wu, J.; Shahzad, N.; Irteza, S.M. Approaches of Satellite Remote Sensing for the Assessment of Above-Ground Biomass across Tropical Forests: Pan-tropical to National Scales. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latifi, H.; Fassnacht, F.E.; Hartig, F.; Berger, C.; Hernandez, J.; Corvalan, P.; Koch, B. Stratified aboveground forest biomass estimation by remote sensing data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2015, 38, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ploton, P.; Barbier, N.; Couteron, P.; Antin, C.M.; Ayyappan, N.; Balachandran, N.; Barathan, N.; Bastin, J.F.; Chuyong, G.; Dauby, G.; et al. Toward a general tropical forest biomass prediction model from very high resolution optical satellite images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 200, 140–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Gilani, H.; Ahmad, S.R. Forest Aboveground Biomass Estimation and Mapping through High-Resolution Optical Satellite Imagery-A Literature Review. Forests 2021, 12, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dube, T.; Mutanga, O. Evaluating the utility of the medium-spatial resolution Landsat 8 multispectral sensor in quantifying aboveground biomass in uMgeni catchment, South Africa. Isprs J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 101, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McRoberts, R.E.; Naesset, E.; Gobakken, T. Optimizing the k-Nearest Neighbors technique for estimating forest aboveground biomass using airborne laser scanning data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 163, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xiao, X.; Bajgain, R.; Starks, P.; Steiner, J.; Doughty, R.B.; Chang, Q. Estimating leaf area index and aboveground biomass of grazing pastures using Sentinel-1, Sentinel-2 and Landsat images. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 154, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, E.M.O.; Silva, S.H.G.; Acerbi-Junior, F.W.; Carvalho, M.C.; Carvalho, L.M.T.; Scolforo, J.R.S.; Wulder, M.A. Object-based random forest modelling of aboveground forest biomass outperforms a pixel-based approach in a heterogeneous and mountain tropical environment. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2019, 78, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, R.M.; Rosser, N.J.; Donoghue, D.N.M. Improving above ground biomass estimates of Southern Africa dryland forests by combining Sentinel-1 SAR and Sentinel-2 multispectral imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 282, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gong, W.; Xing, Y.; Hu, X.; Gong, J. Estimation of the forest stand mean height and aboveground biomass in Northeast China using SAR Sentinel-1B, multispectral Sentinel-2A, and DEM imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 151, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Zhao, W.G.; Long, J.P.; Liu, Z.H.; Yang, P.S.; Zhang, T.C.; Ye, Z.L.; Wang, Q.Y.; Matinfar, H.R. Mapping Forest Growing Stem Volume Using Novel Feature Evaluation Criteria Based on Spectral Saturation in Planted Chinese Fir Forest. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Coops, N.C.; Innes, J.L.; Sheppard, S.R.J.; Fu, L.; Ruan, H.; She, G. Estimation of forest biomass dynamics in subtropical forests using multi-temporal airborne LiDAR data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 178, 158–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; Liu, X.; van Dijk, A.; Yue, C.; He, B. Continuous woody vegetation biomass estimation based on temporal modeling of Landsat data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 110, 102811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.C.; Li, R.H.; Zhu, Z.; Xue, Y.F.; Ding, H.; Wang, X.Y.; Na, J.M.; Xia, W.J. SCARF: A new algorithm for continuous prediction of biomass dynamics using machine learning and Landsat time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2024, 314, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.Y.; Lin, H.; Long, J.P.; Liu, Z.H.; Ye, Z.L.; Zheng, H.N.; Yang, P.S. Mapping Forest Stock Volume Using Phenological Features Derived from Time-Serial Sentinel-2 Imagery in Planted Larch. Forests 2024, 15, 995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arevalo, P.; Baccini, A.; Woodcock, C.E.; Olofsson, P.; Walker, W.S. Continuous mapping of aboveground biomass using Landsat time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 288, 113483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Jones, S.; Soto-Berelov, M.; Haywood, A.; Hislop, S. Landsat Time-Series for Estimating Forest Aboveground Biomass and Its Dynamics across Space and Time: A Review. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caparros-Santiago, J.A.; Rodriguez-Galiano, V.; Dash, J. Land surface phenology as indicator of global terrestrial ecosystem dynamics: A systematic review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2021, 171, 330–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dronova, I.; Taddeo, S. Remote sensing of phenology: Towards the comprehensive indicators of plant community dynamics from species to regional scales. J. Ecol. 2022, 110, 1460–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, S.; Garcia Millan, V.E.; Eklundh, L. Assessing Forest Phenology: A Multi-Scale Comparison of Near-Surface (UAV, Spectral Reflectance Sensor, PhenoCam) and Satellite (MODIS, Sentinel-2) Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decuyper, M.; Chavez, R.O.; Lohbeck, M.; Lastra, J.A.; Tsendbazar, N.; Hacklander, J.; Herold, M.; Vagen, T.-G. Continuous monitoring of forest change dynamics with satellite time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 269, 112829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.W.; Li, N.; Zang, Z.; Lu, D.S.; Wang, G.X.; Wang, N. Examining phenological variation of on-year and off-year bamboo forests based on the vegetation and environment monitoring on a New Micro-Satellite (VENμS) time-series data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 42, 2203–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara, B.; Gandini, M. Assessing the performance of smoothing functions to estimate land surface phenology on temperate grassland. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 37, 1801–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Morisette, J.T.; Wolfe, R.E.; Gao, F.; Ederer, G.A.; Nightingale, J.; Pedelty, J.A. An Enhanced TIMESAT Algorithm for Estimating Vegetation Phenology Metrics From MODIS Data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2011, 4, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.L.; Wardlow, B.D.; Xiang, D.X.; Hu, S.; Li, D.R. A review of vegetation phenological metrics extraction using time-series, multispectral satellite data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 237, 111511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Chen, Y.; Shen, M.; Chen, J.; Zhou, J.; Wang, C.; Yang, W. A simple method to improve the quality of NDVI time-series data by integrating spatiotemporal information with the Savitzky-Golay filter. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 217, 244–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Lunetta, R.S.; Wheeler, B.; Iiames, J.S.; Campbell, J.B. An evaluation of time-series smoothing algorithms for land-cover classifications using MODIS-NDVI multi-temporal data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 174, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kross, A.; Fernandes, R.; Seaquist, J.; Beaubien, E. The effect of the temporal resolution of NDVI data on season onset dates and trends across Canadian broadleaf forests. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1564–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Gao, S.; Zhang, H.K.; Schaaf, C.; Wang, W.; Ye, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tran, K.H. Analyzing GOES-R ABI BRDF-adjusted EVI2 time series by comparing with VIIRS observations over the CONUS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2024, 302, 113972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.X.; Wu, C.Y.; Peng, D.L.; Xu, S.G.; Gonsamo, A.; Jassal, R.S.; Arain, M.A.; Lu, L.L.; Fang, B.; Chen, J.M. Improved modeling of land surface phenology using MODIS land surface reflectance and temperature at evergreen needleleaf forests of central North America. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 176, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, D.; Detto, M.; Nelson, B.W.; Chen, M.; Guan, K.; Wu, S.; Yan, Z.; Wu, J. Multi-scale integration of satellite remote sensing improves characterization of dry-season green-up in an Amazon tropical evergreen forest. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 246, 111865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.M.; Yang, J.L.; Zhao, N.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.F.; Wilson, J.P.; Yue, T.X. Estimation of China’s forest stand biomass carbon sequestration based on the continuous biomass expansion factor model and seven forest inventories from 1977 to 2013. For. Ecol. Manage. 2019, 448, 528–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Chen, A.; Peng, C.; Zhao, S.; Ci, L. Changes in forest biomass carbon storage in China between 1949 and 1998. Science 2001, 292, 2320–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.K.; Lei, Y.C. Assessment of Forest Vegetation Biomass and Carbon Storage in China; China Forestry Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, D.; Wang, C.; Chen, J.; Shen, M.; Shen, B.; Yan, R.; Li, Z.; Karnieli, A.; Chen, J.; Yan, Y.; et al. The superiority of the normalized difference phenology index (NDPI) for estimating grassland aboveground fresh biomass. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 264, 112578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.Q.; Zhu, X.L.; Shen, Z.Y.; Wu, J.; Xu, S.; Liang, Z.C.; Wang, J.T. Investigating the urban-induced microclimate effects on winter wheat spring phenology using Sentinel-2 time series. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2020, 294, 108153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, R.; Liu, R.; Xu, M.; Liu, Y.; Zuo, L.; Ge, Q. The relationship between threshold-based and inflexion-based approaches for extraction of land surface phenology. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 199, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jönsson, P.; Eklundh, L. TIMESAT—A program for analyzing time-series of satellite sensor data. Comput. Geosci. 2004, 30, 833–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Jia, L.; Menenti, M.; Gorte, B. On the performance of remote sensing time series reconstruction methods—A spatial comparison. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 187, 367–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, P.; Pinardi, M.; Bolpagni, R.; Gillier, J.M.; Zinke, P.; Nedelcut, F.; Bresciani, M. Assessing macrophyte seasonal dynamics using dense time series of medium resolution satellite data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 216, 230–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.D.; Lin, H.; Liu, Z.H.; Ye, Z.L.; Li, X.Y.; Long, J.P. A Combined Strategy of Improved Variable Selection and Ensemble Algorithm to Map the Growing Stem Volume of Planted Coniferous Forest. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Lin, H.; Long, J.P.; Xu, X.D. Mapping the Growing Stem Volume of the Coniferous Plantations in North China Using Multispectral Data from Integrated GF-2 and Sentinel-2 Images and an Optimized Feature Variable Selection Method. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melaas, E.K.; Sulla-Menashe, D.; Gray, J.M.; Black, T.A.; Morin, T.H.; Richardson, A.D.; Friedl, M.A. Multisite analysis of land surface phenology in North American temperate and boreal deciduous forests from Landsat. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 186, 452–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Wu, S.; Lee, C.K.F.; Serbin, S.P.; Wolfe, B.T.; Ng, M.K.; Ely, K.S.; Bogonovich, M.; Wang, J.; Lin, Z.; et al. Monitoring leaf phenology in moist tropical forests by applying a superpixel-based deep learning method to time-series images of tree canopies. Isprs J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2022, 183, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brelsford, C.C.; Nybakken, L.; Kotilainen, T.K.; Robson, T.M. The influence of spectral composition on spring and autumn phenology in trees. Tree Physiol. 2019, 39, 925–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klosterman, S.; Richardson, A.D. Observing Spring and Fall Phenology in a Deciduous Forest with Aerial Drone Imagery. Sensors 2017, 17, 2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Moreno-Martínez, Á.; Muñoz-Marí, J.; Campos-Taberner, M.; Camps-Valls, G. Estimation of vegetation traits with kernel NDVI. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2023, 195, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.Y.; Gonsamo, A.; Gough, C.M.; Chen, J.M.; Xu, S.G. Modeling growing season phenology in North American forests using seasonal mean vegetation indices from MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 147, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhao, T.; Luo, Y.; Li, Y.; Yan, K.; Lu, L.; Tran, N.N.; Wu, X.; Ma, X. Evaluating the potential of H8/AHI geostationary observations for monitoring vegetation phenology over different ecosystem types in northern China. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 112, 102933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Liang, L.; Schwartz, M.D.; Donnelly, A.; Wang, Z.; Schaaf, C.B.; Liu, L. Evaluating the potential of MODIS satellite data to track temporal dynamics of autumn phenology in a temperate mixed forest. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 160, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detsch, F.; Otte, I.; Appelhans, T.; Hemp, A.; Nauss, T. Seasonal and long-term vegetation dynamics from 1-km GIMMS-based NDVI time series at Mt. Kilimanjaro, Tanzania. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 178, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Liu, Q.H.; Lin, S.R.; Huete, A.; Liu, L.Y.; Croft, H.; Clevers, J.; Zeng, Y.L.; Wang, X.H.; et al. A novel red-edge spectral index for retrieving the leaf chlorophyll content. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2022, 13, 2771–2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tompalski, P.; Wulder, M.A.; White, J.C.; Hermosilla, T.; Riofrio, J.; Kurz, W.A. Developing aboveground biomass yield curves for dominant boreal tree species from time series remote sensing data. For. Ecol. Manage. 2024, 561, 121894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.L.; Liu, D.S. Improving forest aboveground biomass estimation using seasonal Landsat NDVI time-series. Isprs J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 102, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.N.; Long, J.P.; Zang, Z.; Lin, H.; Liu, Z.H.; Zhang, T.C.; Yang, P.S. Interpreting the Response of Forest Stock Volume with Dual Polarization SAR Images in Boreal Coniferous Planted Forest in the Non-Growing Season. Forests 2023, 14, 1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, S.; Okujeni, A.; Pflugmacher, D.; van der Linden, S.; Hostert, P. Combining simulated hyperspectral EnMAP and Landsat time series for forest aboveground biomass mapping. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 98, 102307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

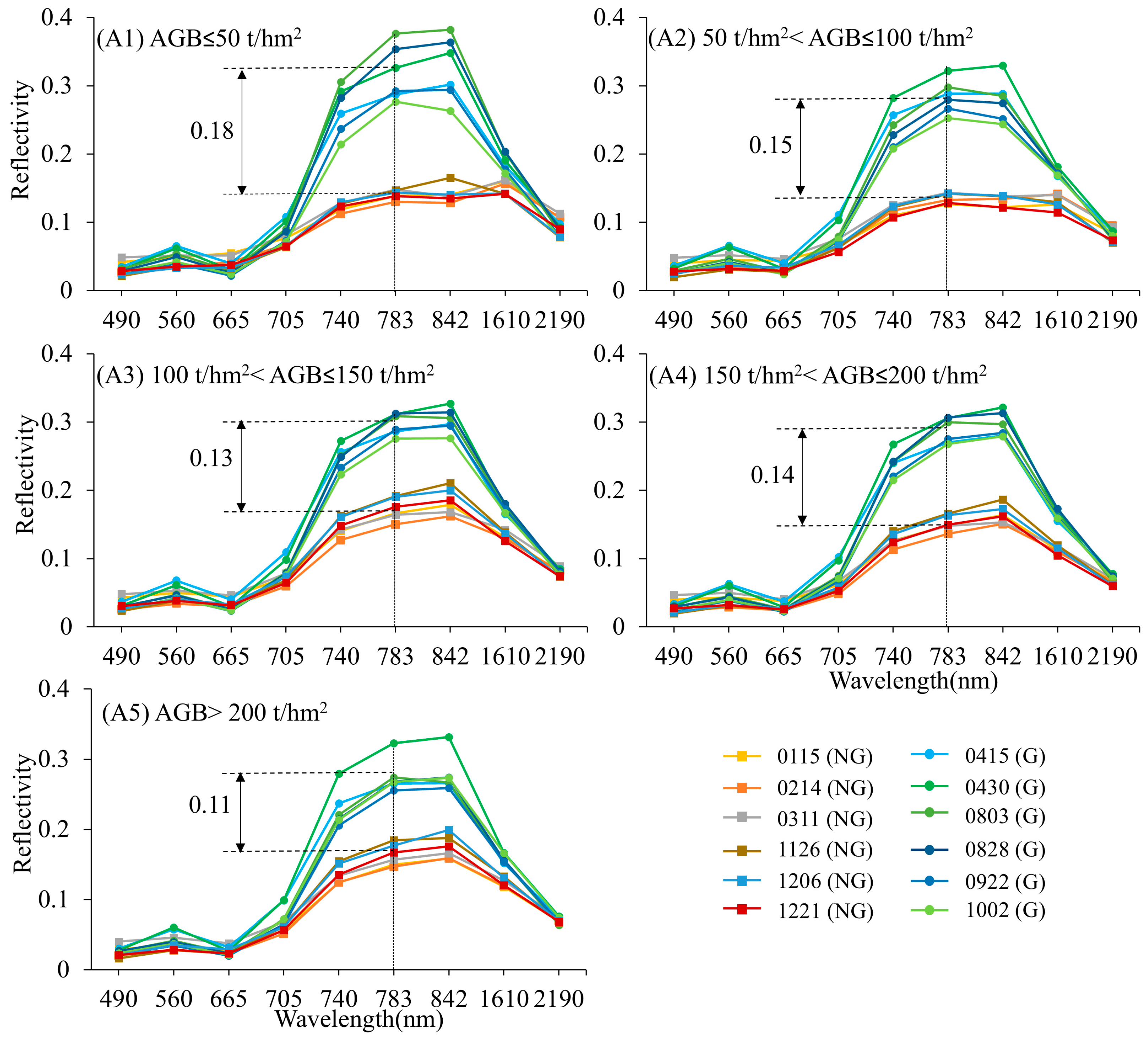
| Sample | Number | Mean (t/hm2) | SD | CV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 t/hm2 < AGB ≤ 50 t/hm2 | 4 | 42.02 | 2.52 | 5.99 |
| 50 t/hm2 < AGB ≤ 100 t/hm2 | 12 | 78.66 | 16.04 | 20.39 |
| 100 t/hm2 < AGB ≤ 150 t/hm2 | 46 | 127.93 | 12.13 | 9.48 |
| 150 t/hm2 < AGB ≤ 200 t/hm2 | 28 | 169.51 | 14.11 | 14.11 |
| AGB > 200 t/hm2 | 10 | 225.47 | 15.29 | 15.29 |
| Total | 100 | 139.97 | 45.46 | 32.48 |
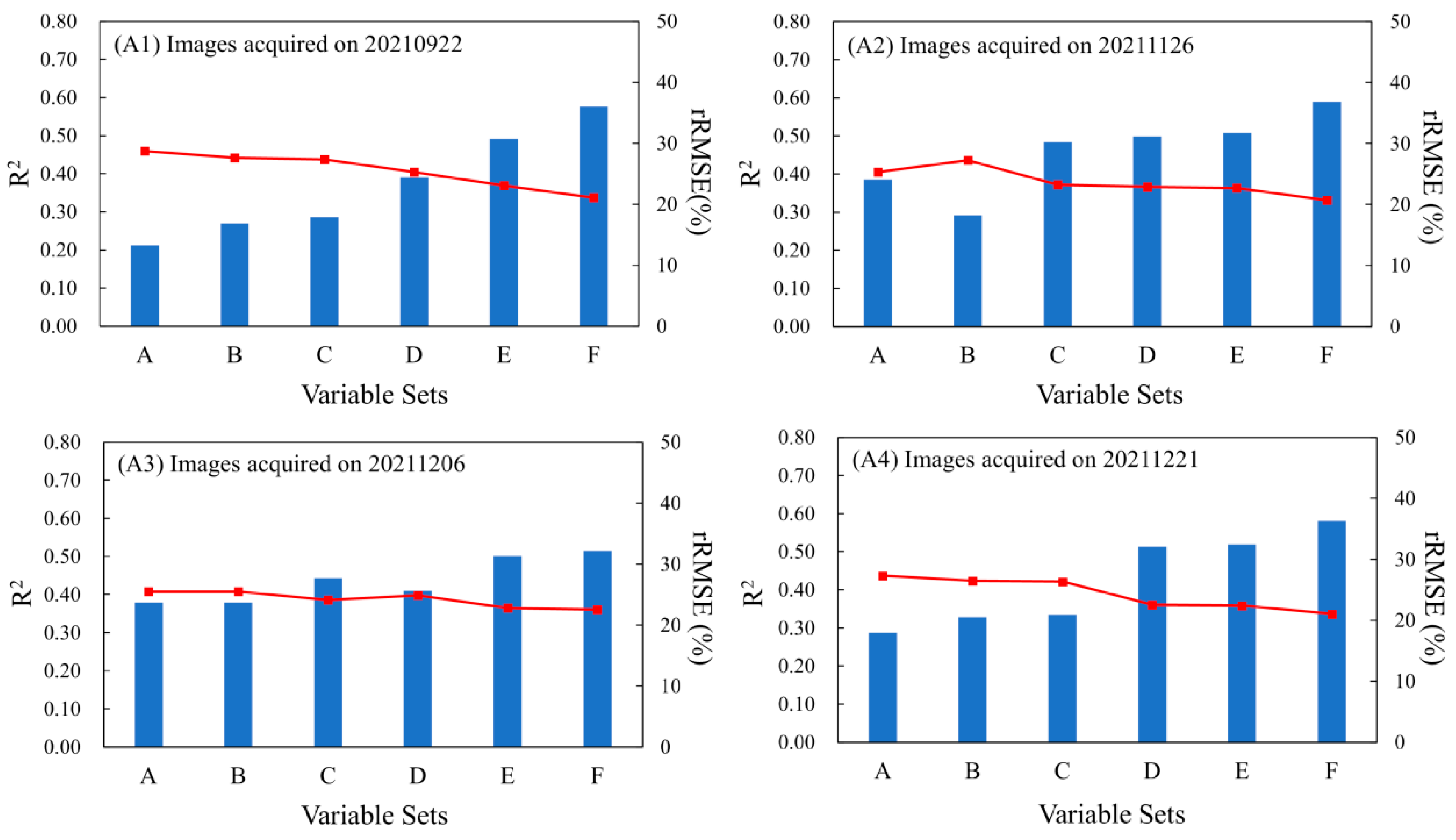
| Number | Variable Set | Description |
|---|---|---|
| A | Bs, VI, TFs | Images acquired on 21 December 2021 |
| B | A + PFs1 | EVI2 time series |
| C | A + PFs2 | IRECI time series |
| D | A + PFs3 | NDPI time series |
| E | A + PFs4 | NDVI time series |
| F | A + All PFs | Composite time series |
| Phenological Features | EVI2 Time Series | IRECI Time Series | NDPI Time Series | NDVI Time Series |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SOS (day of year) | 56 | 62 | 63 | 68 |
| EOS (day of year) | 312 | 317 | 318 | 323 |
| LOS (day) | 256 | 255 | 255 | 255 |
| BV | 0.18 | 0.17 | 0.40 | 0.58 |
| MAXMUN | 0.47 | 0.77 | 0.66 | 0.86 |
| AP | 0.26 | 0.55 | 0.25 | 0.28 |
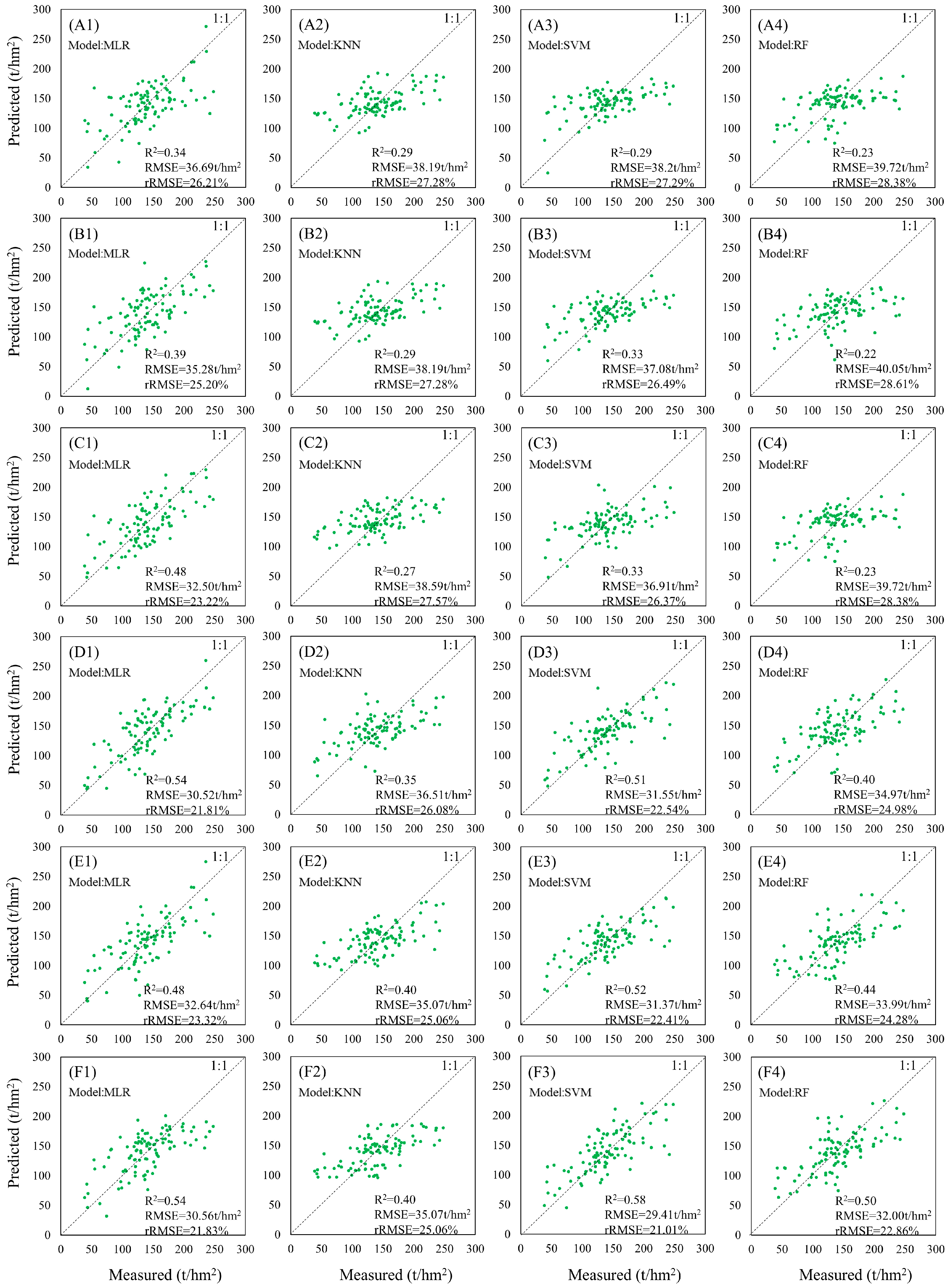
| A | B | C | D | E | F | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MLR | R2 | 0.34 | 0.39 | 0.48 | 0.54 | 0.48 | 0.54 |
| RMSE (t/hm2) | 36.69 | 35.28 | 32.5 | 30.52 | 32.64 | 30.56 | |
| rRMSE (%) | 26.21 | 25.20 | 23.22 | 21.81 | 23.32 | 21.83 | |
| SVM | R2 | 0.29 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.51 | 0.52 | 0.58 |
| RMSE (t/hm2) | 38.20 | 37.08 | 36.91 | 31.55 | 31.37 | 29.41 | |
| rRMSE(%) | 27.29 | 26.49 | 26.37 | 22.54 | 22.41 | 21.01 | |
| KNN | R2 | 0.29 | 0.29 | 0.27 | 0.35 | 0.40 | 0.40 |
| RMSE (t/hm2) | 38.19 | 38.19 | 38.59 | 36.51 | 35.07 | 35.07 | |
| rRMSE (%) | 27.28 | 27.28 | 27.57 | 26.08 | 25.06 | 25.06 | |
| RF | R2 | 0.23 | 0.22 | 0.23 | 0.40 | 0.44 | 0.50 |
| RMSE (t/hm2) | 39.72 | 40.05 | 39.72 | 34.97 | 33.99 | 32.00 | |
| rRMSE (%) | 28.38 | 28.61 | 28.38 | 24.98 | 24.28 | 22.86 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, P.; Long, J.; Lin, H.; Zhang, T.; Ye, Z.; Liu, Z. Mapping Forest Aboveground Biomass with Phenological Information Extracted from Remote Sensing Images in Subtropical Evergreen Broadleaf Forests. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1599. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091599
Yang P, Long J, Lin H, Zhang T, Ye Z, Liu Z. Mapping Forest Aboveground Biomass with Phenological Information Extracted from Remote Sensing Images in Subtropical Evergreen Broadleaf Forests. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(9):1599. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091599
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Peisong, Jiangping Long, Hui Lin, Tingchen Zhang, Zilin Ye, and Zhaohua Liu. 2025. "Mapping Forest Aboveground Biomass with Phenological Information Extracted from Remote Sensing Images in Subtropical Evergreen Broadleaf Forests" Remote Sensing 17, no. 9: 1599. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091599
APA StyleYang, P., Long, J., Lin, H., Zhang, T., Ye, Z., & Liu, Z. (2025). Mapping Forest Aboveground Biomass with Phenological Information Extracted from Remote Sensing Images in Subtropical Evergreen Broadleaf Forests. Remote Sensing, 17(9), 1599. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091599







