Ambiguity Resolution Strategy for GPS/LEO Integrated Orbit Determination Based on Regional Ground Stations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Mathematical Model
2.2. LEO Satellites and Ground Network
2.3. POD Processing Strategy
2.4. Experimental Schemes
3. Results
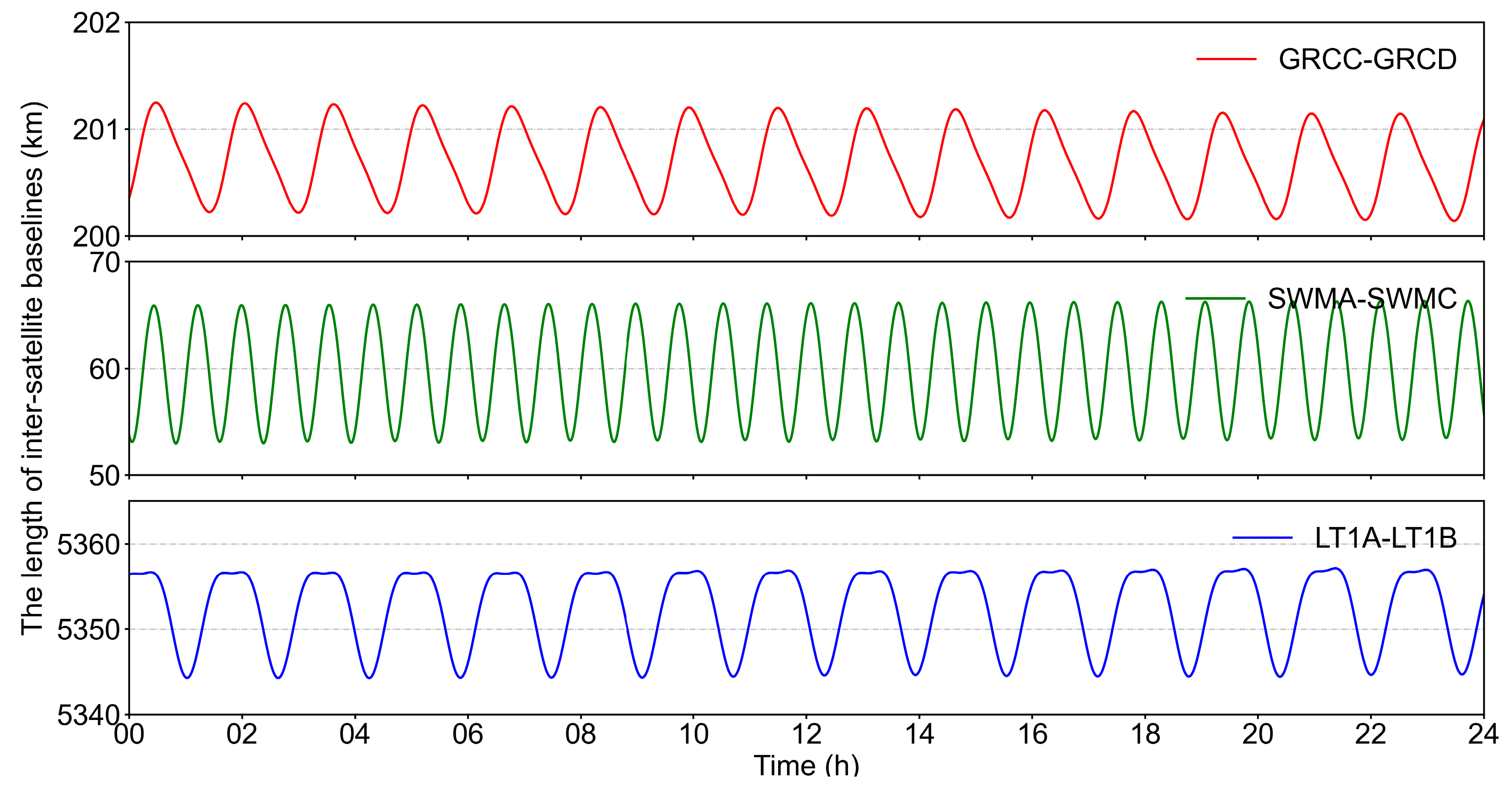
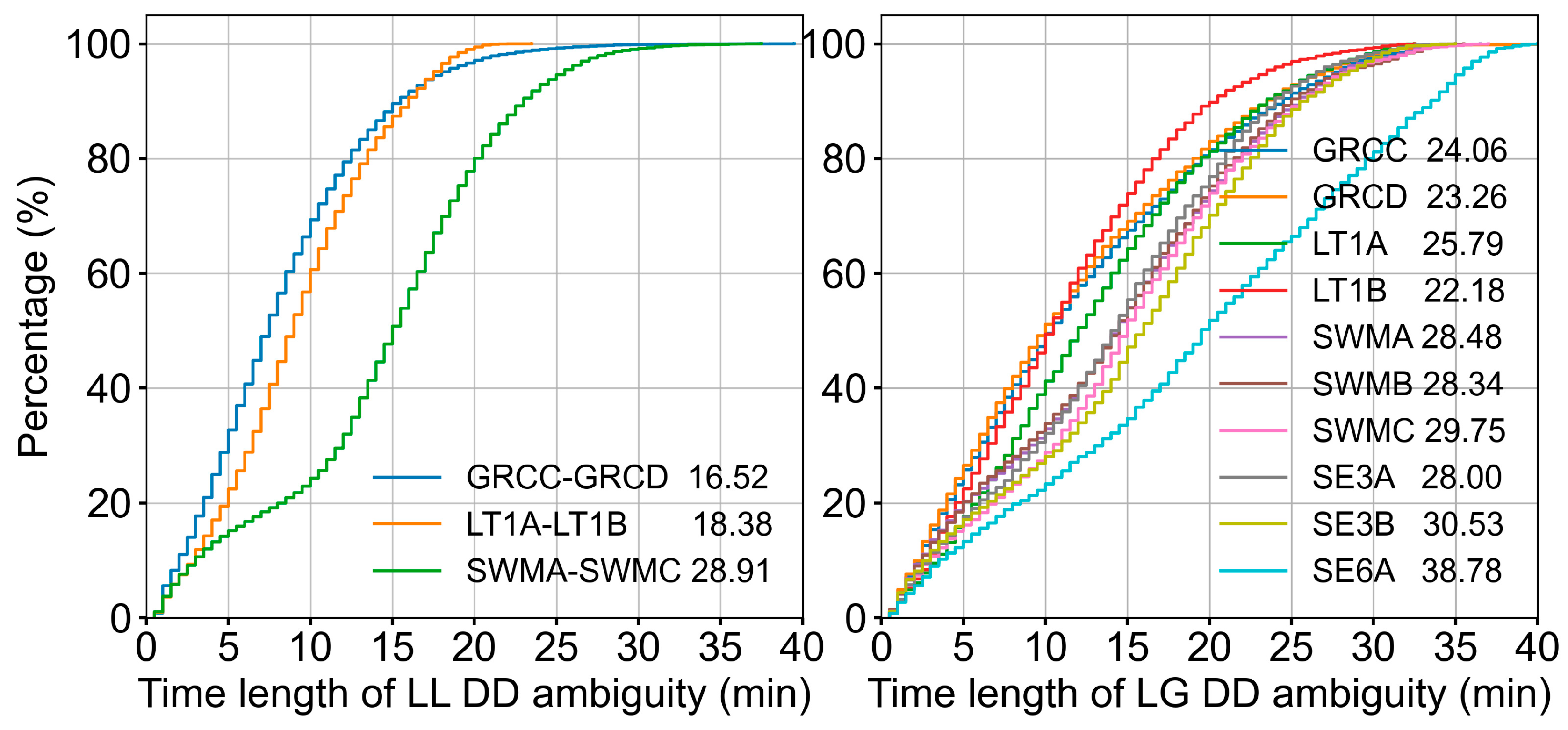
3.1. Independent Baseline Selection
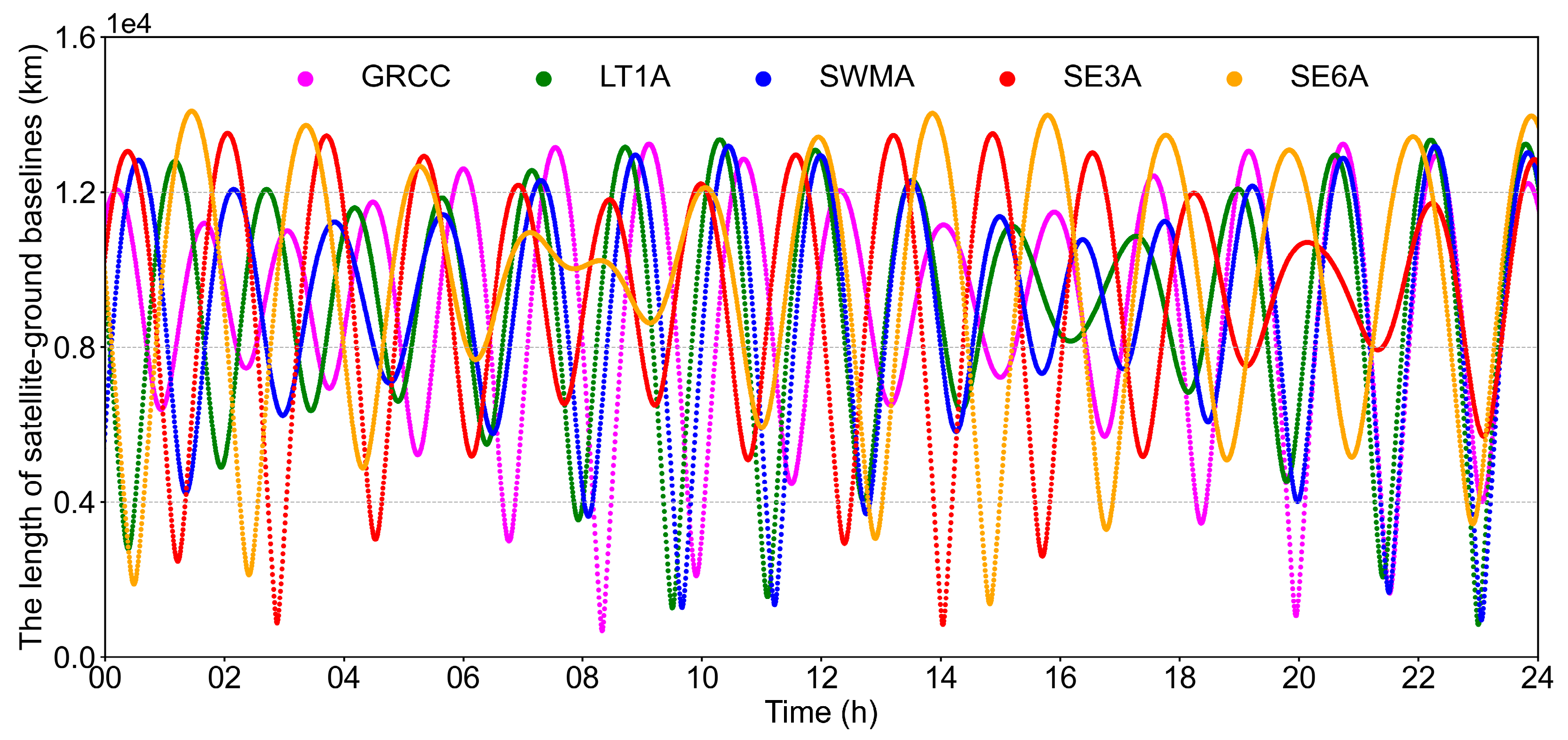
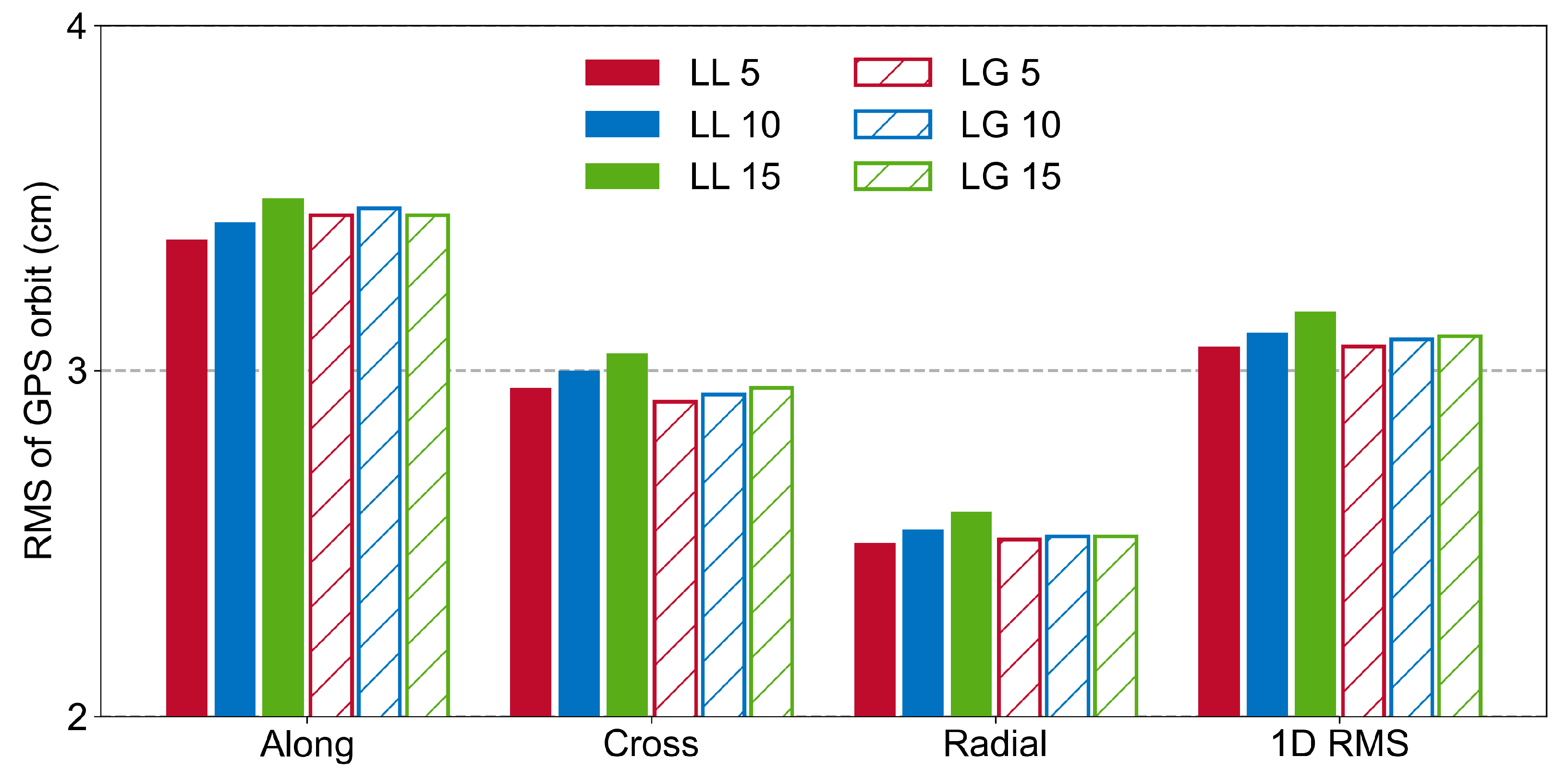
3.2. Common View Time
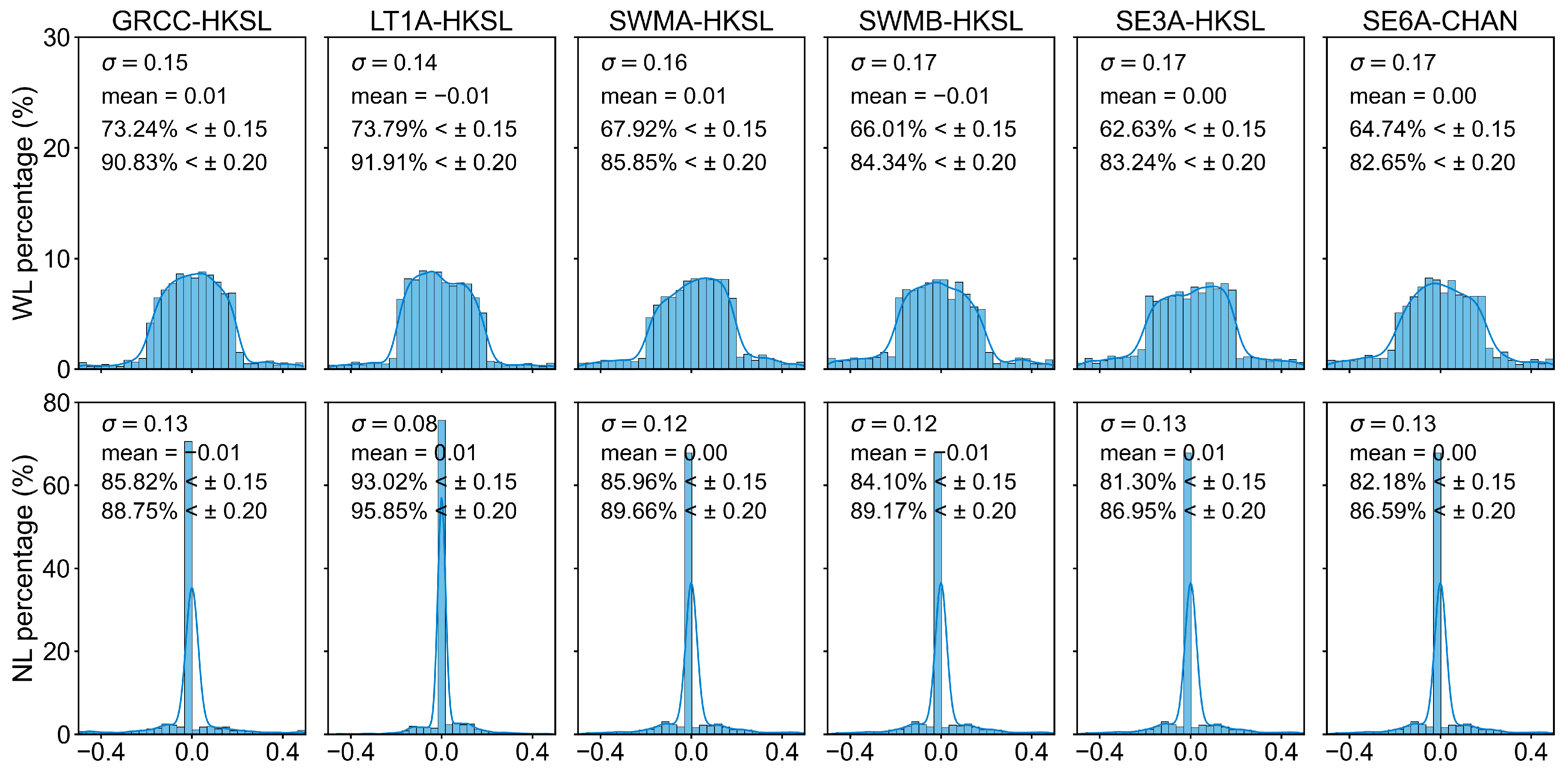
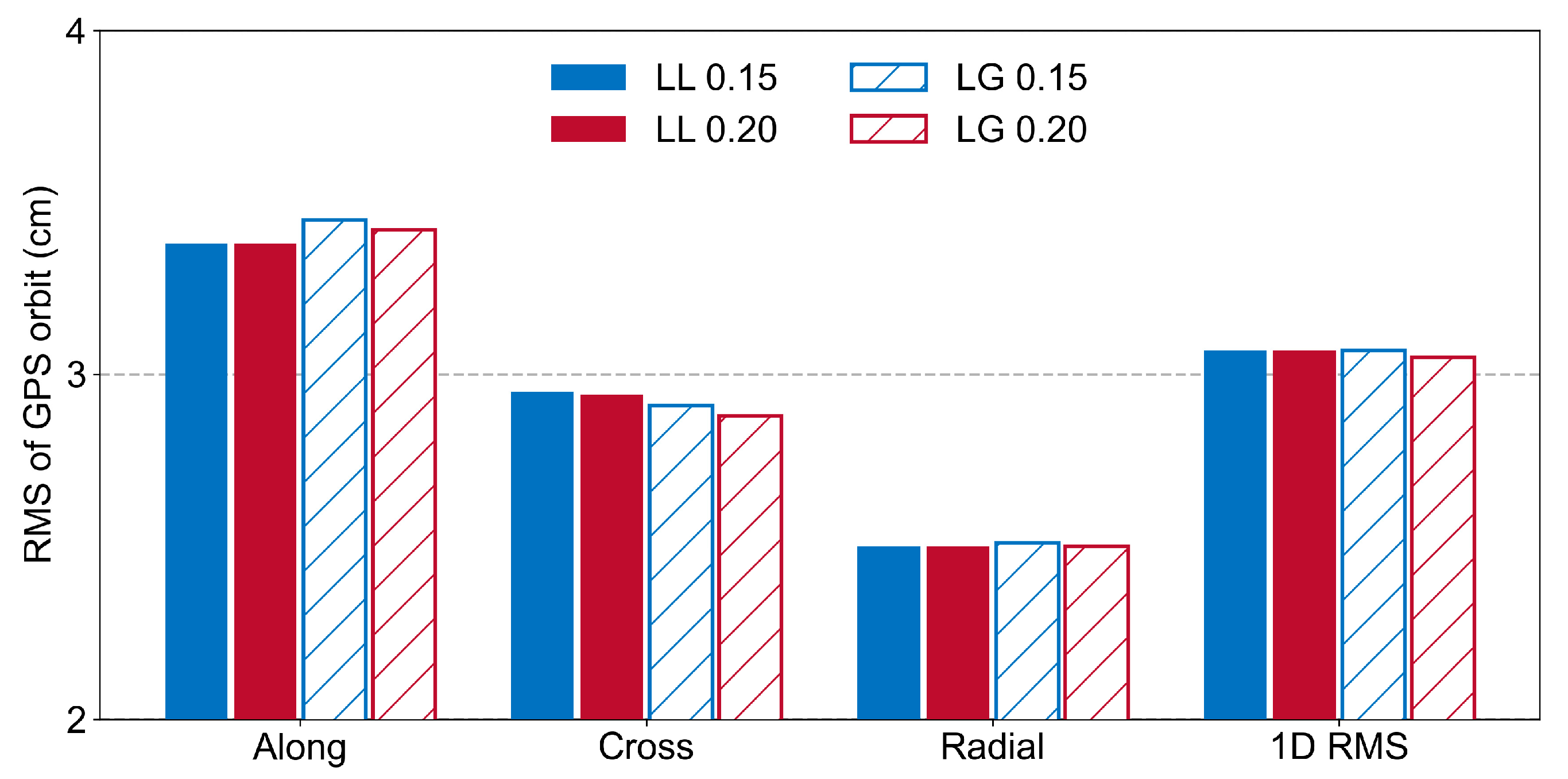
3.3. Ambiguity Resolution Threshold
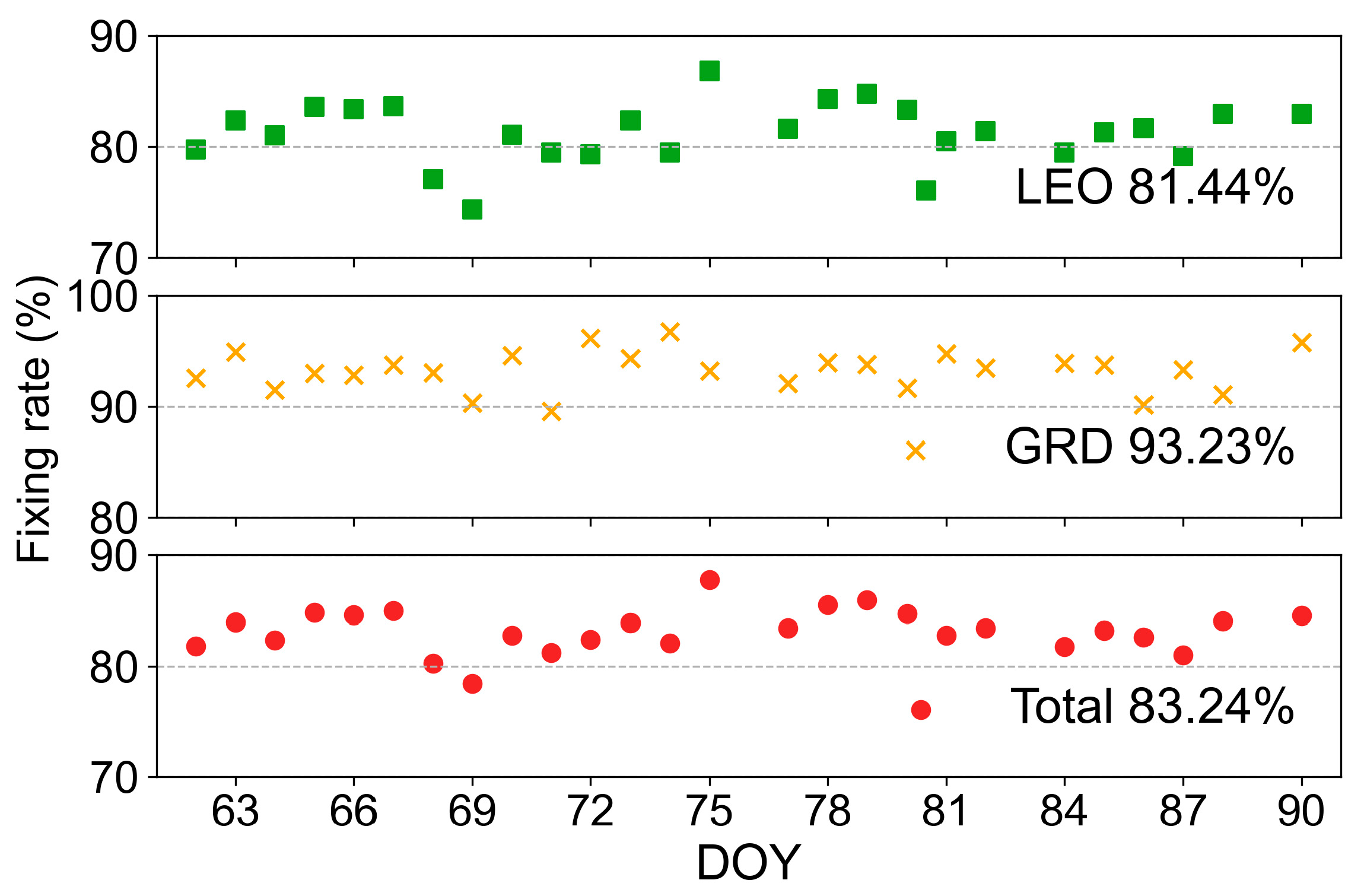
3.4. Comprehensive Experiment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Prol, F.S.; Ferre, R.M.; Saleem, Z.; Valisuo, P.; Pinell, C.; Lohan, E.S.; Elsanhoury, M.; Elmusrati, M.; Islam, S.; Celikbilek, K.; et al. Position, Navigation, and Timing (PNT) Through Low Earth Orbit (LEO) Satellites: A Survey on Current Status, Challenges, and Opportunities. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 83971–84002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Mao, Y.; Ren, X.; Jia, X.; Sun, B. Demand and Key Technology for a LEO Constellation as Augmentation of Satellite Navigation Systems. Satell. Navig. 2024, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackel, S.; Steigenberger, P.; Hugentobler, U.; Uhlemann, M.; Montenbruck, O. Galileo Orbit Determination Using Combined GNSS and SLR Observations. GPS Solut. 2015, 19, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Xu, X.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, J. Precise Orbit Determination for Quad-Constellation Satellites at Wuhan University: Strategy, Result Validation, and Comparison. J. Geod. 2016, 90, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, Q.; Wu, J.; Yuan, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Gong, X.; Wu, Z. Multi-GNSS Products and Services at iGMAS Wuhan Innovation Application Center: Strategy and Evaluation. Satell. Navig. 2022, 3, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Tang, C.; Zhou, S.; Hu, X.; Zhou, X. High-Precision GPS Orbit Determination by Integrating the Measurements from Regional Ground Stations and LEO Onboard Receivers. Satell. Navig. 2024, 5, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Reigber, C.; König, R. Integrated Adjustment of CHAMP, GRACE, and GPS Data. J. Geod. 2004, 78, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Wang, C.; Guo, J.; Yang, G.; Liao, M.; Ma, H.; Liu, J. Enhanced Orbit Determination for BeiDou Satellites with FengYun-3C Onboard GNSS Data. GPS Solut. 2017, 21, 1179–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wei, K.; Xu, T.; Shi, Y.; Wang, D. Enhanced Precise Orbit Determination for GPS and BDS-2/3 with Real LEO Onboard and Ground Observations. Measurement 2024, 224, 113912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, L.; Wang, J.; Tang, L.; Ge, H.; Ge, M.; Schuh, H. Impact of LEO Configuration on GPS Precise Orbit Determination with Un-Differenced Ambiguity Resolution. GPS Solut. 2025, 29, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, K.; Ma, F.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Q.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, H.; Meng, Y.; Bian, L. Integrated Precise Orbit Determination of Multi-GNSS and Large LEO Constellations. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Männel, B.; Sakic, P.; Ge, M.; Schuh, H. Integrated Processing of Ground- and Space-Based GPS Observations: Improving GPS Satellite Orbits Observed with Sparse Ground Networks. J. Geod. 2020, 94, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, P.J.G. An Optimality Property of the Integer Least-Squares Estimator. J. Geod. 1999, 73, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, P.J.G. Integer aperture GNSS ambiguity resolution. Artif. Satell. 2003, 38, 79–88. [Google Scholar]
- Teunissen, P.J.G. Theory of Integer Equivariant Estimation with Application to GNSS. J. Geod. 2003, 77, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, P.J.G.; Massarweh, L. Theory for the Ambiguity Function Method: Probability Model and Global Solution. J. Geod. 2025, 99, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, P.J.G. Success Probability of Integer GPS Ambiguity Rounding and Bootstrapping. J. Geod. 1998, 72, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.; Bock, Y. Global Positioning System Network Analysis with Phase Ambiguity Resolution Applied to Crustal Deformation Studies in California. J. Geophys. Res. 1989, 94, 3949–3966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blewitt, G. Carrier Phase Ambiguity Resolution for the Global Positioning System Applied to Geodetic Baselines up to 2000 Km. J. Geophys. Res. 1989, 94, 10187–10203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Li, J.; Guo, J.; Yang, C.; Zhao, Q. Near Real-Time Multi-GNSS Orbits, Clock and Observable-Specific Biases at Wuhan University. GPS Solut. 2024, 28, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Guo, J.; Xu, S.; Zhao, Q. Undifferenced Ambiguity Resolution for Precise Multi-GNSS Products to Support Global PPP-AR. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroes, R.; Montenbruck, O.; Bertiger, W.; Visser, P. Precise GRACE Baseline Determination Using GPS. GPS Solut. 2005, 9, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Geng, J.; Chen, X.; Zhao, Q. Enhanced Orbit Determination for Formation-Flying Satellites Through Integrated Single- and Double-Difference GPS Ambiguity Resolution. GPS Solut. 2020, 24, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Švehla, D.; Rothacher, M. Kinematic Orbit Determination of LEOs Based on Zero or Double-Difference Algorithms Using Simulated and Real SST GPS Data. In Vistas for Geodesy in the New Millennium; Ádám, J., Schwarz, K.P., Eds.; International Association of Geodesy Symposia; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002; Volume 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäggi, A.; Hugentobler, U.; Bock, H.; Beutler, G. Precise Orbit Determination for GRACE Using Undifferenced or Doubly Differenced GPS Data. Adv. Space Res. 2007, 39, 1612–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Li, X.; Wu, J.; Yuan, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W. Precise Orbit Determination for LEO Satellites with Ambiguity Resolution: Improvement and Comparison. JGR Solid. Earth 2021, 126, e2021JB022491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenbruck, O.; Gill, E. Satellite Orbits: Models, Methods, and Applications, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, M.; Gendt, G.; Dick, G.; Zhang, F.P. Improving Carrier-Phase Ambiguity Resolution in Global GPS Network Solutions. J. Geod. 2005, 79, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landerer, F.W.; Flechtner, F.M.; Save, H.; Webb, F.H.; Bandikova, T.; Bertiger, W.I.; Bettadpur, S.V.; Byun, S.H.; Dahle, C.; Dobslaw, H.; et al. Extending the Global Mass Change Data Record: GRACE Follow-On Instrument and Science Data Performance. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL088306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Jiang, K.; Guo, X.; Lian, Y.; Li, M. Precise Orbit Determination of the LuTan Satellite Using GPS, BDS-2, and BDS-3 Signals. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2024, 35, 096314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenbruck, O.; Hackel, S.; Jäggi, A. Precise Orbit Determination of the Sentinel-3A Altimetry Satellite Using Ambiguity-Fixed GPS Carrier Phase Observations. J. Geod. 2018, 92, 711–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berzosa-Molina, J.; Peter, H.; Fernández, J.; Féménias, P. Copernicus Sentinel–3B—GPS L2C Tracking Tests During Commissioning Phase. Adv. Space Res. 2021, 68, 1023–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Ijssel, J.; Encarnação, J.; Doornbos, E.; Visser, P. Precise Science Orbits for the Swarm Satellite Constellation. Adv. Space Res. 2015, 56, 1042–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenbruck, O.; Hackel, S.; Van den Ijssel, J.; Arnold, D. Reduced Dynamic and Kinematic Precise Orbit Determination for the Swarm Mission from 4 Years of GPS Tracking. GPS Solut. 2018, 22, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ge, M. PANDA software and its preliminary result of positioning and orbit determination. Wuhan Univ. J. Nat. Sci. 2003, 8, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shako, R.; Förste, C.; Abrikosov, O.; Bruinsma, S.; Marty, J.-C.; Lemoine, J.M.; Flechtner, F.; Neumayer, H.; Dahle, C. EIGEN-6C: A High-Resolution Global Gravity Combination Model Including GOCE Data. In Observation of the System Earth from Space—CHAMP, GRACE, GOCE and Future Missions; Flechtner, F., Sneeuw, N., Schuh, W.D., Eds.; Advanced Technologies in Earth Sciences; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, G.; Luzum, B. IERS Conventions 2010; No.36 in IERS Technical Note; Verlag des Bundesamtes für Kartographie und Geodäsie: Frankfurt am Main, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Lyard, F.H.; Allain, D.J.; Cancet, M.; Carrère, L.; Picot, N. FES2014 Global Ocean Tide Atlas: Design and Performance. Ocean. Sci. 2021, 17, 615–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, D.; Meindl, M.; Beutler, G.; Dach, R.; Schaer, S.; Lutz, S.; Prange, L.; Sośnica, K.; Mervart, L.; Jäggi, A. CODE’s New Solar Radiation Pressure Model for GNSS Orbit Determination. J. Geod. 2015, 89, 775–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vielberg, K.; Kusche, J. Extended Forward and Inverse Modeling of Radiation Pressure Accelerations for LEO Satellites. J. Geod. 2020, 94, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruinsma, S. The DTM-2013 Thermosphere Model. J. Space Weather. Space Clim. 2015, 5, A1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäggi, A.; Dach, R.; Montenbruck, O.; Hugentobler, U.; Bock, H.; Beutler, G. Phase Center Modeling for LEO GPS Receiver Antennas and Its Impact on Precise Orbit Determination. J. Geod. 2009, 83, 1145–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouba, J. A Simplified Yaw-Attitude Model for Eclipsing GPS Satellites. GPS Solut. 2009, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.T.; Wu, S.C.; Hajj, G.A.; Bertiger, W.I.; Lichten, S.M. Effects of antenna orientation on GPS carrier phase. Manuscr. Geod. 1993, 18, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mervart, L. Ambiguity Resolution Techniques in Geodetic and Geodynamic Applications of the Global Positioning System. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Berne, Bern, Switzerland, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Teunissen, P.J.G. The Parameter Distributions of the Integer GPS Model. J. Geod. 2002, 76, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Wang, C.; Chen, G.; Xu, X.; Zhao, Q. BDS-3 Precise Orbit and Clock Solution at Wuhan University: Status and Improvement. J. Geod. 2023, 97, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Tian, Y.; Zheng, F.; Hu, Y. Accounting for Signal Distortion Biases for Wide-Lane and Narrow-Lane Phase Bias Estimation with Inhomogeneous Networks. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, B.; Lei, T.; Li, P.; Wang, L.; Huang, G.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Q. Calibration of Inconsistent Receiver-Dependent Pseudorange Bias and Its Impact on Wide-Lane Ambiguity Fixing. GPS Solut. 2025, 29, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massarweh, L.; Verhagen, S.; Teunissen, P.J.G. New LAMBDA Toolbox for Mixed-Integer Models: Estimation and Evaluation. GPS Solut. 2025, 29, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, P.J.G.; Massarweh, L.; Verhagen, S. Vectorial Integer Bootstrapping: Flexible Integer Estimation with Application to GNSS. J. Geod. 2021, 95, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, P.J.G. Best Integer Equivariant Estimation for Elliptically Contoured Distributions. J. Geod. 2020, 94, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, H.; Huang, G.; Wang, L.; Qin, Z.; Xie, S.; Lai, W.; Tian, J. A Simplified GNSS/LEO Joint Orbit Determination Method. Measurement 2024, 236, 115029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
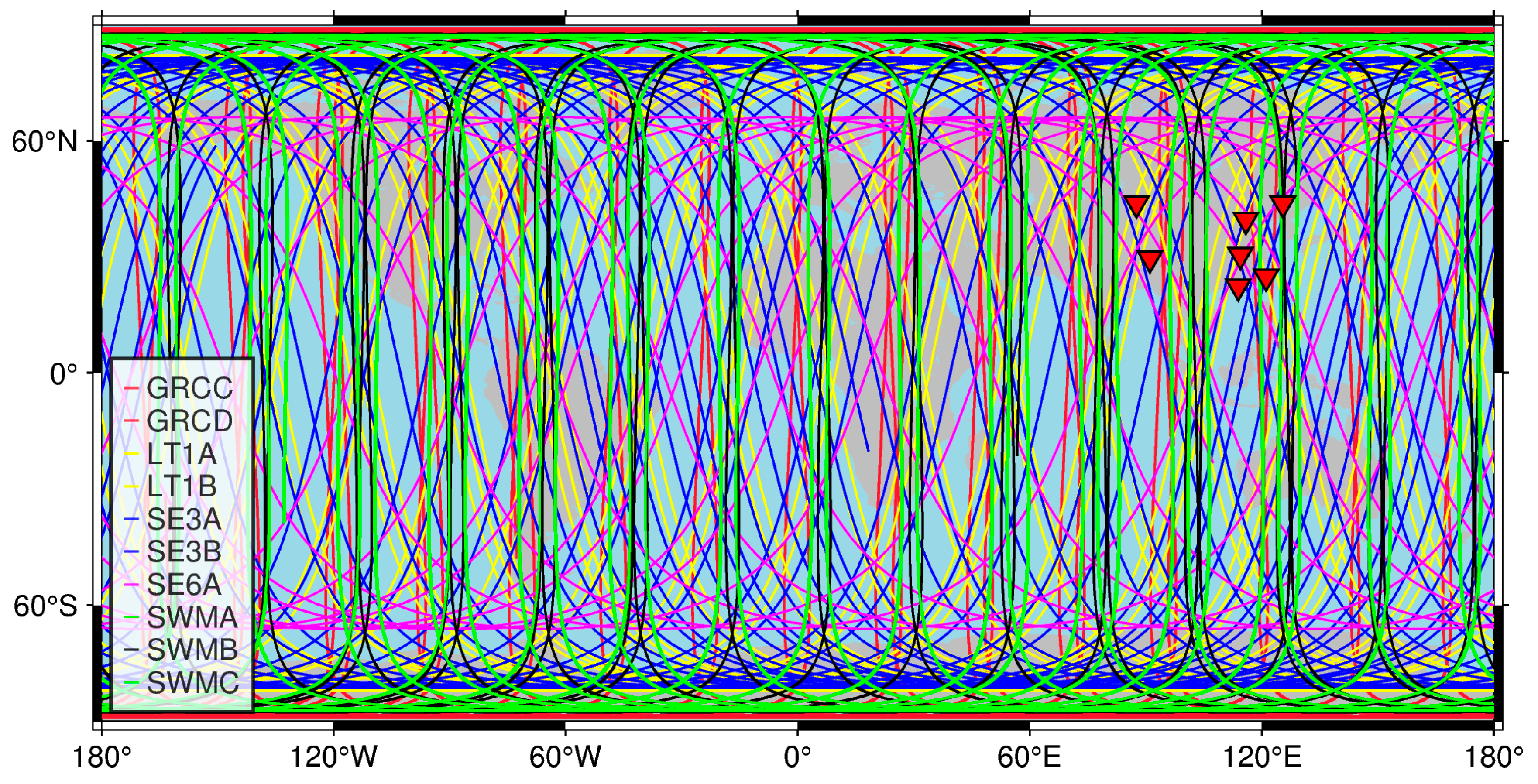

| LEO Satellite | Abbreviation | Altitude (km) | Inclination (deg) | Receiver | System | Sampling Rate | Orbit Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GRACE-C | GRCC | 490 | 89 | TriG | GPS | 10 s | Drifting orbit |
| GRACE-D | GRCD | 490 | 89 | TriG | GPS | 10 s | Drifting orbit |
| Lutan-1A | LT1A | 616 | 97.8 | Manufactured by the 704 Institute | GPS/BDS | 1 s | Sun-synchronous |
| Lutan-1B | LT1B | 616 | 97.8 | Manufactured by the 704 Institute | GPS/BDS | 1 s | Sun-synchronous |
| Sentinel-3A | SE3A | 814 | 98.65 | GPSR-G2 | GPS | 1 s | Sun-synchronous |
| Sentinel-3B | SE3B | 814 | 98.65 | GPSR-G2 | GPS | 1 s | Sun-synchronous |
| Sentinel-6A | SE6A | 1336 | 66 | PODRIX | GPS/Galileo | 1 s | Non-Sun-synchronous |
| Swarm-A | SWMA | 480 | 87.35 | GPSR-G2 | GPS | 1 s | Drifting orbit |
| Swarm-B | SWMB | 530 | 87.35 | GPSR-G2 | GPS | 1 s | Drifting orbit |
| Swarm-C | SWMC | 480 | 87.35 | GPSR-G2 | GPS | 1 s | Drifting orbit |
| Dynamic Model | GPS | LEO |
|---|---|---|
| Earth gravity field | EIGEN6C (12 × 12) with temporal–gravity field modelling | EIGEN6C (130 × 130) [36] with temporal–gravity field modelling |
| N-body gravitation | JPL DE405 | JPL DE405 |
| Solid Earth and pole tides | IERS conventions 2010 | IERS conventions 2010 [37] |
| Ocean tides | FES 2014b | FES 2014b [38] |
| Relativity effect | IERS conventions 2010 | IERS conventions 2010 |
| Solar radiation pressure | 7-parameter ECOM-2 model [39] | Macro-model [40] |
| Earth radiation pressure | Macro-model | Not applied |
| Atmospheric density | Not applied | DTM13 [41] |
| Observation Model | |
|---|---|
| GPS observations | Undifferenced ionosphere-free dual-frequency pseudorange and carrier-phase combination |
| Sampling rate | 30 s |
| Arc length | 24 h |
| Elevation cut-off | Ground stations: 7° LEO satellites: 1° |
| GPS satellite antenna | Phase center offset (PCO) and phase center variation (PCV) with igs14_2196.atx |
| LEO satellite antenna | In-orbit calibrated PCO and PCV correction [42] |
| Attitude model | GPS: Refer to [43] LEO: Quaternion products |
| Phase windup | Modelled [44] |
| Estimated Parameters | |
| GPS orbit | Position and velocity at initial epoch |
| GPS clock | Epoch-wise parameter estimated as white noise |
| LEO orbit | Position and velocity at initial epoch |
| SRP | Seven parameters of the CODE model without prior model for the GPS |
| Atmospheric drag | Piece-wise drag coefficients estimated per revolution for LEOs |
| Empirical acceleration | Periodical acceleration terms (sine and cosine) in the along-track and cross-track components estimated per revolution for LEOs |
| Receiver clock | Epoch-wise parameter estimated as white noise for both LEOs and ground stations |
| Station coordinate | Highly constrained |
| Tropospheric delay | For each ground station, piece-wise constant zenith delays for 1 h intervals, piece-wise constant horizontal gradients for 24 h intervals |
| Ambiguity | Ambiguity fixed for ground stations and LEO satellites |
| Schemes | Baseline Selection | Common View Time (min) | Ambiguity Threshold (Cycle) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | LL/LG/LL + LG | 10 | 0.15 |
| S2 | LL/LG | 5/10/15 | 0.15 |
| S3 | LL/LG | 5 | 0.15/0.2 |
| S4 | GRD/LL + LG | 5 | 0.2 |
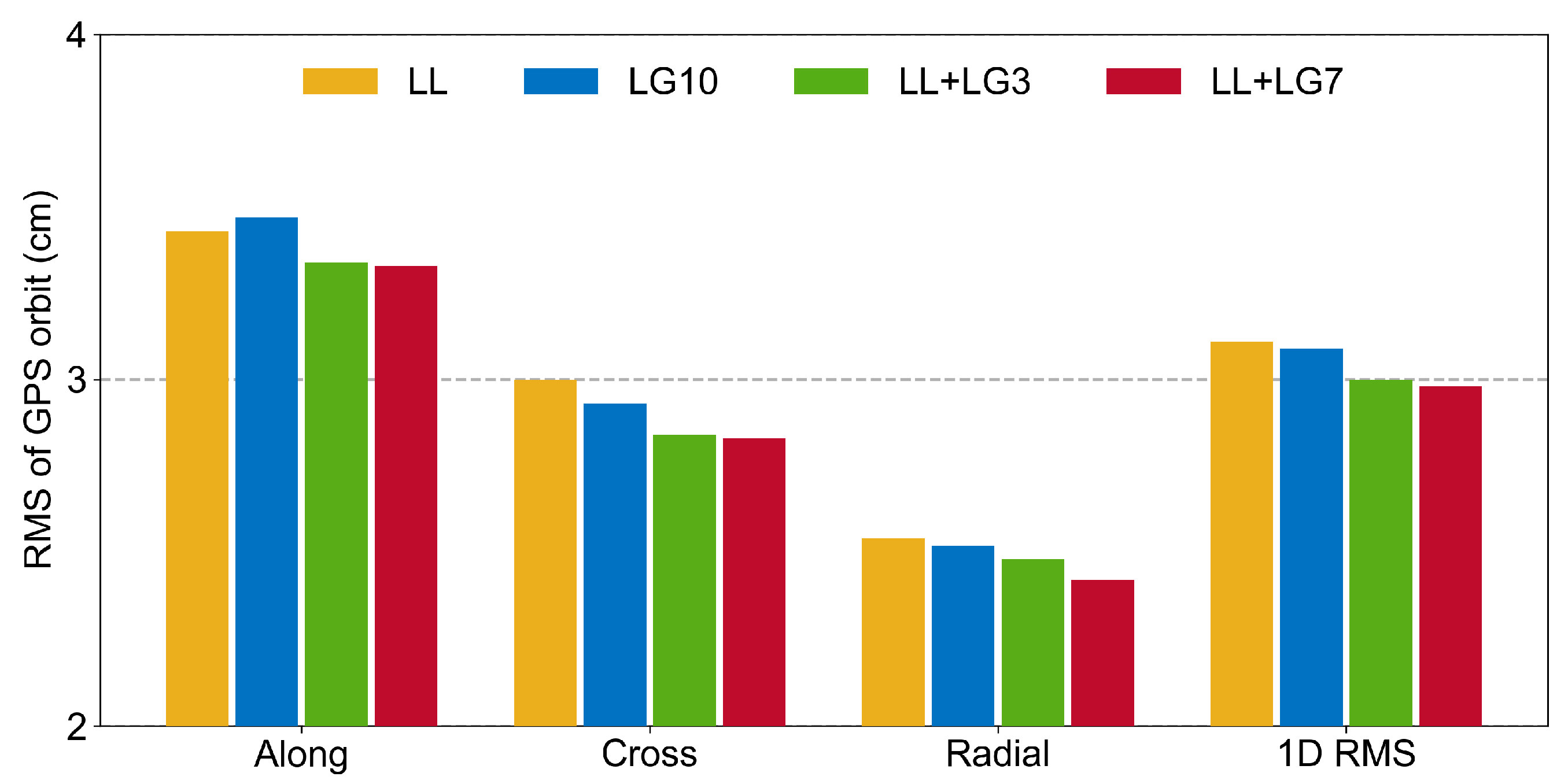
| Schemes | Along | Cross | Radial | 1D RMS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LL | 3.43 | 3.00 | 2.54 | 3.11 |
| LG10 | 3.47 | 2.93 | 2.52 | 3.09 |
| LL + LG3 | 3.34 | 2.84 | 2.48 | 3.00 |
| LL + LG7 | 3.33 | 2.83 | 2.42 | 2.98 |
| Schemes | Along | Cross | Radial | 1D RMS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LL-5 | 3.38 | 2.95 | 2.50 | 3.07 |
| LL-10 | 3.43 | 3.00 | 2.54 | 3.11 |
| LL-15 | 3.50 | 3.05 | 2.59 | 3.17 |
| LG-5 | 3.45 | 2.91 | 2.51 | 3.07 |
| LG-10 | 3.47 | 2.93 | 2.52 | 3.09 |
| LG-15 | 3.45 | 2.95 | 2.52 | 3.10 |
| Schemes | Along | Cross | Radial | 1D RMS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LL 0.15 | 3.38 | 2.95 | 2.50 | 3.07 |
| LL 0.20 | 3.38 | 2.94 | 2.50 | 3.07 |
| LG 0.15 | 3.45 | 2.91 | 2.51 | 3.08 |
| LG 0.20 | 3.42 | 2.88 | 2.50 | 3.05 |
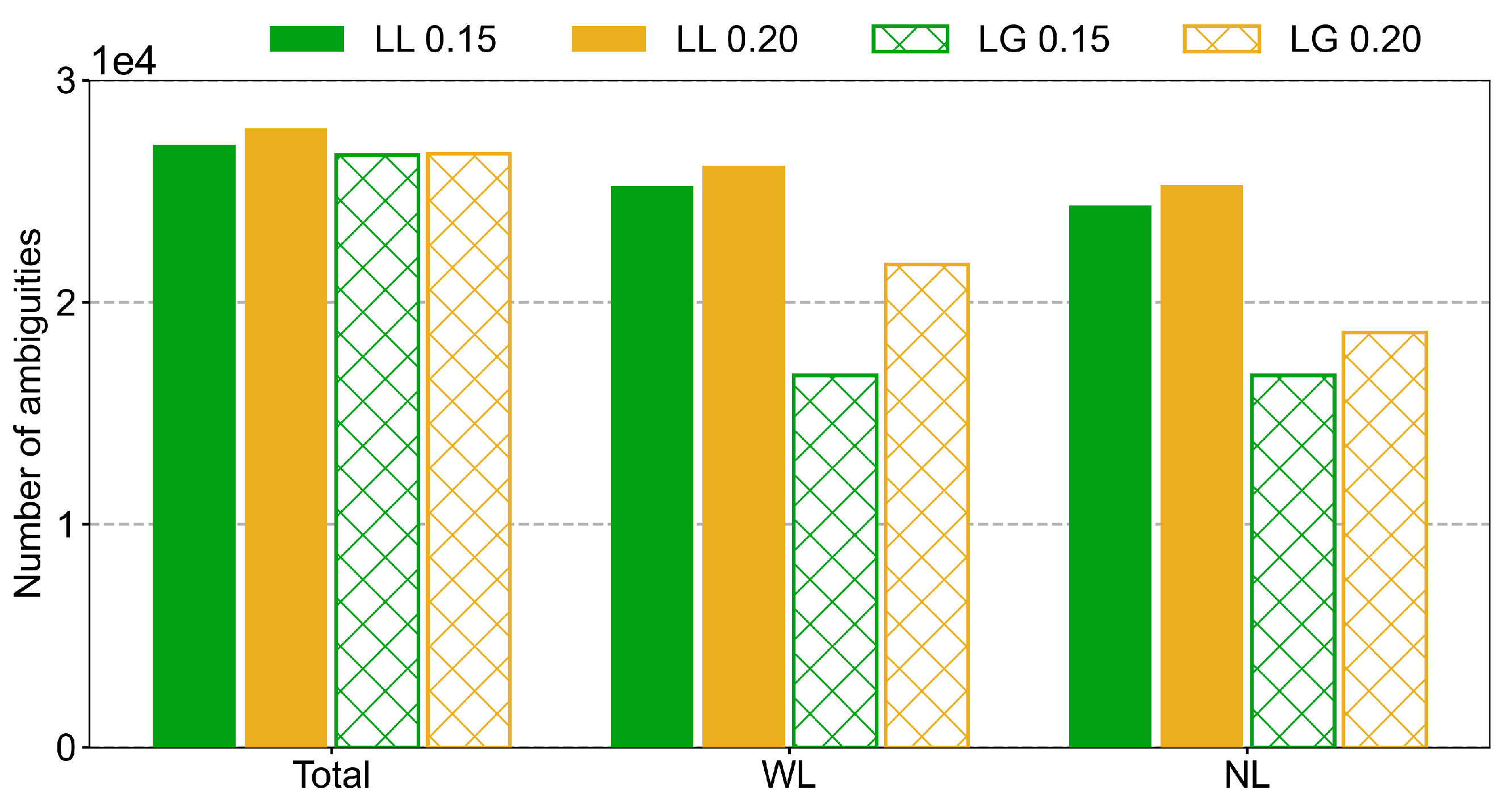
| Schemes | Total | WL | NL | WL Fixing Rate | NL Fixing Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LL 0.15 | 27,093 | 25,221 | 24,361 | 93.09% | 96.59% |
| LL 0.20 | 27,834 | 26,138 | 25,290 | 93.91% | 96.76% |
| LG 0.15 | 26,632 | 19,862 | 16,711 | 74.22% | 83.78% |
| LG 0.20 | 26,677 | 21,712 | 18,644 | 80.96% | 85.61% |
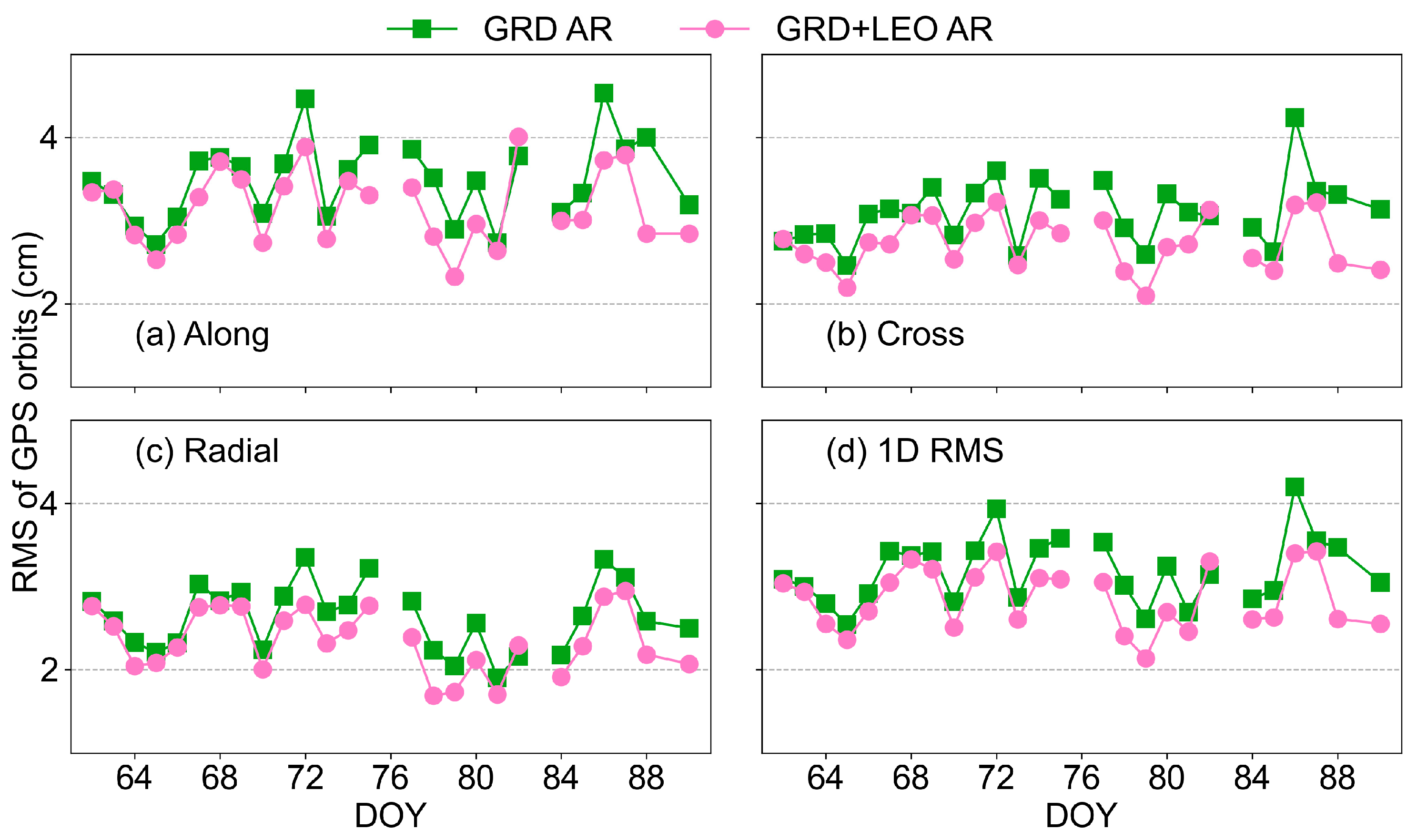
| Schemes | Along | Cross | Radial | 1D RMS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GRD | 3.56 | 3.13 | 2.65 | 3.24 |
| GRD + LEO | 3.23 | 2.74 | 2.36 | 2.89 |
| Improvement | 9.3% | 12.5% | 10.9% | 10.8% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Guo, J.; Li, J.; Xu, S.; Zhao, Q. Ambiguity Resolution Strategy for GPS/LEO Integrated Orbit Determination Based on Regional Ground Stations. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1590. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091590
Liu X, Guo J, Li J, Xu S, Zhao Q. Ambiguity Resolution Strategy for GPS/LEO Integrated Orbit Determination Based on Regional Ground Stations. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(9):1590. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091590
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xiao, Jing Guo, Junqiang Li, Shengyi Xu, and Qile Zhao. 2025. "Ambiguity Resolution Strategy for GPS/LEO Integrated Orbit Determination Based on Regional Ground Stations" Remote Sensing 17, no. 9: 1590. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091590
APA StyleLiu, X., Guo, J., Li, J., Xu, S., & Zhao, Q. (2025). Ambiguity Resolution Strategy for GPS/LEO Integrated Orbit Determination Based on Regional Ground Stations. Remote Sensing, 17(9), 1590. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17091590





