Abstract
Pre-trained foundation models, trained on large-scale datasets, have demonstrated significant success in a variety of downstream vision tasks. Parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) methods aim to adapt these foundation models to new domains by updating only a small subset of parameters, thereby reducing computational overhead. However, the effectiveness of these PEFT methods, especially in the context of forestry remote sensing—specifically for individual tree detection—remains largely unexplored. In this work, we present a simple and efficient PEFT approach designed to transfer pre-trained transformer models to the specific tasks of tree crown detection and species classification in unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) imagery. To address the challenge of mitigating the influence of irrelevant ground targets in UAV imagery, we propose an Adaptive Salient Channel Selection (ASCS) method, which can be simply integrated into each transformer block during fine-tuning. In the proposed ASCS, task-specific channels are adaptively selected based on class-wise importance scores, where the channels most relevant to the target class are highlighted. In addition, a simple bias term is introduced to facilitate the learning of task-specific knowledge, enhancing the adaptation of the pre-trained model to the target tasks. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed ASCS fine-tuning method, which utilizes a small number of task-specific learnable parameters, significantly outperforms the latest YOLO detection framework and surpasses the state-of-the-art PEFT method in tree detection and classification tasks. These findings demonstrate that the proposed ASCS is an effective PEFT method, capable of adapting the pre-trained model’s capabilities for tree crown detection and species classification using UAV imagery.
1. Introduction
Forests, as essential renewable resources and integral components of terrestrial ecosystems, account for approximately 30% of the Earth’s land surface [1]. They play a pivotal role in soil conservation, sustainable development, and the maintenance of ecological balance [2]. At the most fundamental level, individual trees serve as the basic structural units of forests. Thus, the precise detection and identification of individual trees, as well as the accurate determination of their species, are crucial for advancing our understanding of forest ecosystem dynamics [3]. This is particularly important for biodiversity assessment [4], carbon stock estimation [5], and the implementation of forest management strategies [6].
Traditional methods for tree species inventory predominantly rely on manual field surveys. Although these methods can provide a certain level of accuracy, they are encumbered by notable drawbacks, including high costs, labor intensity, low efficiency, and limited spatial and temporal flexibility [7,8,9]. As a result, these methods are becoming increasingly inadequate for capturing the spatial patterns and dynamic changes in forest vegetation, thus proving insufficient for the demands of large-scale forest monitoring [10,11]. In contrast, satellite remote sensing technology, with its ability to rapidly collect large-scale, long-time-series data, effectively compensates for the shortcomings of traditional methods, enabling the large-scale, continuous monitoring of forest vegetation and tree species [3,12]. However, satellite remote sensing is also constrained by factors such as weather conditions (e.g., cloud cover and fog) and topographical features. Due to its high operational altitude, satellite remote sensing is more suitable for coarse monitoring of forest stands or large-scale areas. However, it faces significant limitations when applied to high-precision detection tasks at the individual tree level [13].
As an emerging low-altitude remote sensing platform, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) offer distinct advantages, including high flexibility, low cost, and ease of operation. Furthermore, UAVs can be equipped with a variety of sensors to capture various types of data, such as ultra-high-resolution, multispectral, and LiDAR data. Thus, UAVs have served as an effective tool for precise forestry applications, including canopy mapping [14], forest fire detection [15], disease monitoring [16], tree breeding [17], etc. By utilizing ultra-high-resolution remote sensing imagery, UAVs can also be employed for the accurate and rapid detection of individual tree crowns [18,19].
Early studies on individual tree crown delineation primarily relied on image processing techniques, including region growing [20,21] and watershed segmentation [22,23]. Recent years have witnessed rapid advancements in deep learning-based object detection algorithms, which have been applied to individual tree crown detection [24,25,26,27]. In individual tree crown detection, object detection methods are primarily used to identify and locate individual tree crowns, specifically to determine the bounding box and central position of the crown. For instance, Santos et al. [24] conducted experimental comparisons of three deep learning-based object detection methods—Faster R-CNN [28], YOLOv3, and RetinaNet [29]—to assess their performance in detecting Brazil nut tree (Dipteryx alata Vogel) crowns using UAV-based visible imagery. Jintasuttisak et al. [25] and Wu et al. [26] optimized and improved YOLO-based one-stage detection frameworks [30,31], achieving rapid and accurate individual tree detection on publicly available datasets, including the palm tree dataset and the dataset from the National Ecological Observatory Network (NEON). Two widely used deep learning-based methods for crown detection and delineation, DeepForest [32] and Detectree2 [27,33], are evaluated to assess their potential for detecting tree crowns in UAV-acquired RGB imagery from montane temperate deciduous forests with complex species composition in [27]. Despite the promising detection results achieved, existing studies have yet to incorporate tree species recognition into object detection.
Recently, a variety of vision grounding and detection models have been proposed [34]. Among these, Grounding-DINO [35] has emerged as a leading architecture, demonstrating exceptional performance. By leveraging the closed-set transformer-based detector DINO [36] and training on large-scale datasets, Grounding-DINO achieves a robust representation capability, establishing a new benchmark for zero-shot performance on COCO [37] and delivering impressive results without relying on any COCO-specific training data. Furthermore, Grounding-DINO optimizes end-to-end detection without requiring complex modules, showcasing its potential for application in various domains. Due to its superior performance in computer vision tasks compared to traditional detection frameworks, it is feasible to employ Grounding-DINO for detecting tree species from UAV-acquired RGB imagery. However, the model was trained on natural image samples, which leads to suboptimal performance during zero-shot inference on UAV remote sensing imagery. This limitation becomes particularly evident when multiple tree targets are present, as Grounding-DINO struggles to accurately localize the trees in UAV images with multiple species (as shown in Figure 1). According to [38,39], parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) offers a highly effective method for adapting large pre-trained models to downstream tasks by incorporating an external trainable module (e.g., Adapters [40]) or fine-tuning a subset of the parameters [41], thereby reducing the number of parameters that need to be fine-tuned. Compared to traditional full-parameter fine-tuning, PEFT achieves competitive performance while requiring an exceptionally small number of training parameters. Building upon this, the present work explores the application of PEFT to adapt Grounding-DINO for end-to-end tree crown detection and species classification using UAV imagery. To the best of our knowledge, there has been no application of large pre-trained models in individual tree crown detection and species classification using UAVs.
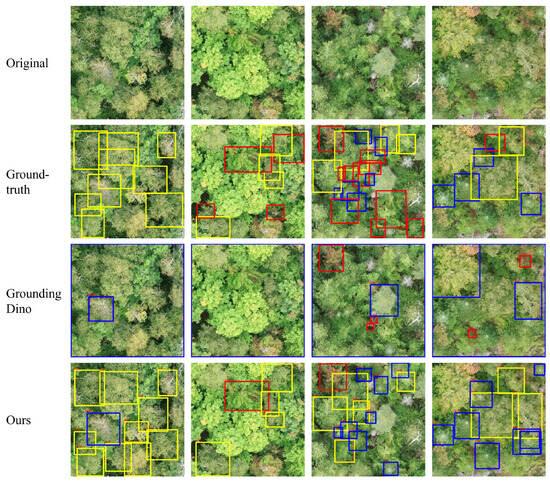

Figure 1.
Detection results using the Grounding-DINO and proposed method for images with multiple tree species. The first row shows the original images, the second row shows the ground-truth bounding boxes, the third shows the detection results using Grounding-DINO, and the fourth row shows the predictions using our proposed method. In these visualizations, yellow bounding boxes correspond to Betula papyrifera, the red bounding boxes indicate Acer rubrum, and the blue bounding boxes represent Abies balsamea.
The primary objective of this work is to propose an effective network for individual tree crown detection and tree species classification using UAV-acquired ultra-high-resolution imagery [42]. In addition, considering the unique characteristics of UAV remote sensing imagery, we propose a design of PEFT to transfer the capabilities of Grounding-DINO to tree detection and species classification in UAV imagery. The Adapter has become a widely adopted baseline for PEFT across various tasks [43]. It incorporates an MLP-like module that initially projects input features into a lower-dimensional space via a nonlinear transformation, followed by a projection back to the original feature dimensions. This design has proven effective for efficient adaptation in diverse contexts. In contrast to the Adapter, which directly inserts trainable modules into transformer blocks, LoRA optimizes a low-rank decomposition matrix with reduced intrinsic dimensions, projecting the query and key features [44]. However, these two PEFT methods were originally designed for fine-tuning language models in downstream NLP tasks, which may render them inadequate for computer vision tasks. Building upon the PEFT method, specifically VPT [45], which adapts transformer models for downstream vision tasks, this paper introduces a simple and efficient PEFT approach tailored for transferring pre-trained transformer models to the specific tasks of tree crown detection and species identification in UAV imagery. Our method introduces a small number of task-specific learnable parameters while keeping the entire backbone frozen. Specifically, to effectively mitigate the influence of irrelevant ground targets in UAV imagery and emphasize the tree target, we introduce an Adaptive Salient Channel Selection (ASCS) module into each transformer block during fine-tuning. In the proposed ASCS, task-specific channels are adaptively selected based on a class-wise L2 norm importance score, which serves as the criterion for evaluating channel saliency. This approach is inspired by classic pruning techniques, where channels most pertinent to specific tree species are highlighted. Subsequently, a simple bias term is incorporated to facilitate adaptation, resulting in fewer parameters compared to the Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP) in the common Adapter Our main contributions can be summarized as follows:
- We propose an end-to-end approach for tree crown detection and species classification, leveraging a pre-trained vision model, which addresses the limitations of current open-set object detection models in the task of tree detection and species classification using UAV imagery.
- We propose a simple and effective PEFT approach, namely, ASCS, for adapting Grounding-DINO, which facilitates the model’s effective adaptation to both tree detection and tree species classification tasks using UAV imagery.
- We propose a task-specific channel selection to emphasize the most salient channel maps, wherein the channels most relevant to specific tree species are highlighted.
- Experiments were conducted on a multi-species dataset acquired via UAV, characterized by a relatively small number of image samples. The results demonstrate that the proposed method significantly outperforms the latest YOLO detection framework and surpasses the current state-of-the-art PEFT methods.
2. Materials
Study Area and Dataset
The study area is a mixed temperate forest located in Quebec, Canada, specifically within the research station of Université de Montréal in Saint-Hippolyte (45°59′17.34″ N/ 74°0′20.75″ W). The site is characterized by diverse topography, including hills, cliffs, and valleys, which contribute to a variety of forest types and environmental conditions within the area. Predominantly covered by unmanaged mixed temperate forest, the site features an array of deciduous and evergreen tree species, along with a small bog and numerous lakes. The most prevalent canopy-forming tree species include Betula papyrifera Marshall, Acer rubrum L., Populus grandidentata Michaux, and Acer saccharum Marshall [46].
The imagery was captured using a DJI Phantom 4 RTK UAV (DJI Science and Technology Co., Ltd., Shenzhen, China), which is equipped with a real-time kinematic (RTK) GNSS receiver integrated with an inertial measurement unit (IMU) and camera [46]. The UAV operated at an altitude of 60 m above the canopy. To ensure a consistent distance between the UAV and the canopy throughout the study area, DJI’s Terrain Follow mode was employed, utilizing a 1-meter LiDAR-derived digital surface model as a reference. The aerial imagery was processed using Agisoft Metashape Professional v.1.7.5 to generate orthomosaics through structure-from-motion (SfM) photogrammetry. The resulting orthomosaics achieved a ground sampling distance ranging from 1.81 to 2.02 cm. The collected images were annotated using ArcGIS Pro v.2.9, where the identified points were utilized to generate polygons delineating individual tree crowns. Each crown was classified according to the designations established during the field survey. The dataset encompasses 14 distinct categories and includes the segmentation and annotation of 23,000 tree crowns. For the purpose of this study, we selected the data acquired on 2 September 2021, and converted the original polygon annotations into a format suitable for object detection. Given that the original annotations were in a geographic coordinate system, we transformed them into COCO-format bounding box annotations for object detection, as depicted in Figure 2.
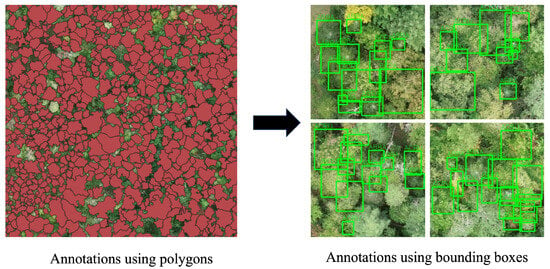
Figure 2.
On the left, the original images are displayed with polygon annotations, while on the right, the selected images are shown with bounding boxes converted to the COCO format.
To align with the requirements of the deep learning model and accommodate hardware limitations, the orthophoto was cropped into a series of patches, each resized to a fixed resolution of 1024 × 1024 pixels, as illustrated in Figure 3. To assess the transferability of the pre-trained model to a dataset with a limited number of image samples, we selected 300 images representing three tree species: Abies balsamea, Betula papyrifera, and Acer rubrum, which had the highest number of annotations. For classification purposes, we use the English names of these species: Pinaceae (Abies balsamea), Betulaceae (Betula papyrifera), and Red Maple (Acer rubrum). The number of annotated detection boxes and the corresponding image counts for each species in the dataset are presented in Figure 4. Specifically, Red Maple has the highest number of detection boxes, totaling 1045 across 247 images. Betulaceae follows closely, with 1003 detection boxes spread over 256 images. Pinaceae has the fewest, with only 562 detection boxes appearing in 156 images. These statistics reflect the distribution characteristics of the three tree species within the dataset. It is important to note that a single image may contain multiple species, which adds an additional layer of complexity to the detection task.
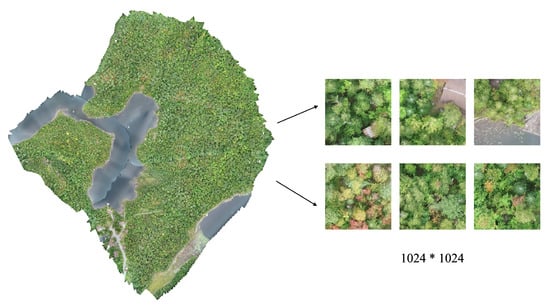
Figure 3.
On the left is the original orthophoto captured by UAV, while on the right are the cropped image patches prepared for model input.
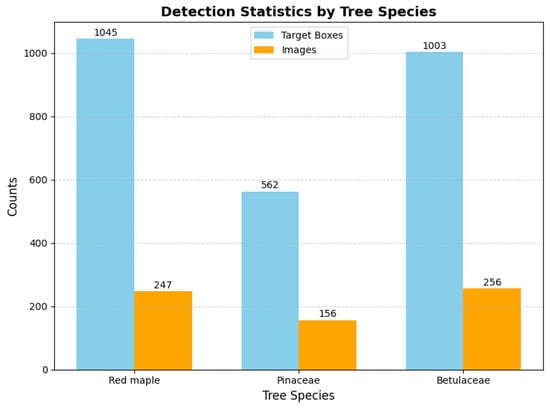
Figure 4.
Statistics for corresponding image and bounding boxes of three selected species.
3. Methods
Our method is built upon the Grounding-DINO object detection framework, an open-set object detection approach designed to enhance detection accuracy by leveraging language prompts to guide visual feature extraction. For image feature extraction, Grounding-DINO utilizes the Swin Transformer as its backbone, which effectively captures both spatial and contextual information through a layer-wise local-window-based attention mechanism, as well as a shifted-window attention mechanism. The proposed PEFT method, ASCS, is introduced at each transformer block within the Swin Transformer backbone during the fine-tuning process. Unlike conventional PEFT methods, such as the widely used Adapter, which employs down-projection, ReLU, and up-projection (illustrated in Figure 5a), our proposed module draws inspiration from classic pruning techniques. This approach introduces a small set of task-specific learnable parameters while keeping the entire backbone frozen. In ASCS, task-specific channels are adaptively selected based on a class-wise L2 norm importance score, which serves as the criterion for assessing channel saliency. This allows for the identification of channels most relevant to specific tree species. A simple bias term is then incorporated to facilitate adaptation (shown in Figure 5b), resulting in fewer parameters compared to the Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP) used in conventional Adapter methods.
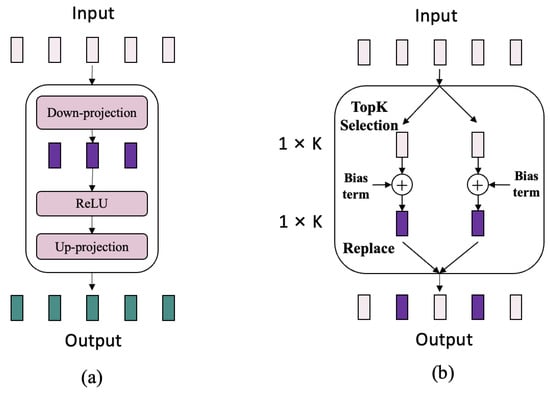
Figure 5.
Comparison between the Adapter and proposed PEFT, where (a) shows the Adapter, and (b) shows the proposed method.
3.1. Swin Transformer
In recent years, Vision Transformer (ViT) networks [47] have demonstrated exceptional performance in capturing feature correlations, rapidly emerging as a dominant model in the field of natural language processing. Unlike traditional CNNs, which aggregate local features into global representations through stacked convolution-pooling layers, ViT leverages the attention mechanism to more effectively learn global features. Building upon ViT, Swin Transformer constrains attention computation within local windows to reduce computational complexity [48]. To preserve global contextual information, Swin Transformer introduces the shifted-window mechanism, facilitating interactions between adjacent windows. The architecture of the Swin Transformer (Swin-T model), depicted in Figure 6a, is composed of four distinct stages. Specifically, stage 1 comprises two Swin Transformer blocks and a Linear Embedding layer; stage 2 includes six Swin Transformer blocks and a Patch Merging module; stages 3 and 4 share an identical structure, each consisting of two Swin Transformer blocks and a Patch Merging module. The Swin Transformer block improves feature extraction efficiency by replacing the multi-head self-attention (MSA) module with a shifted-window mechanism. After employing the moving-window grouping strategy, the calculation between two consecutive Swin Transformer blocks (shown in Figure 6b), and , at the i-th stage can be expressed as follows:
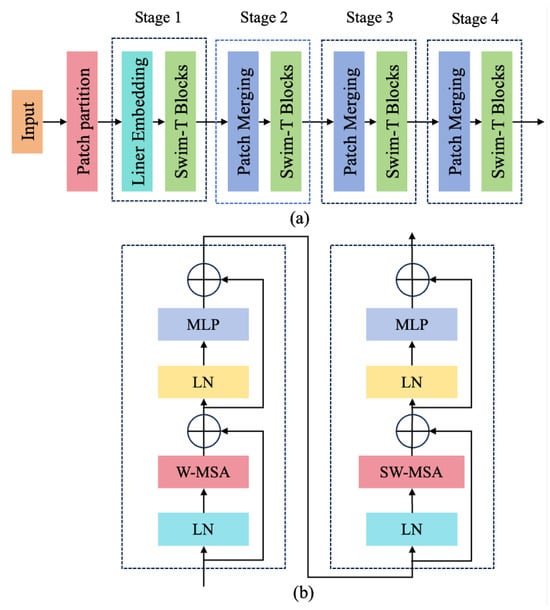
Figure 6.
Structure of Swin Transformer. (a) Architecture of Swin-T; (b) two successive Swin-T Blocks.
Here, and denote the outputs of the window-based multi-head self-attention (W-MSA) and MLP modules, respectively. The and represents the outputs of the shifted-window multi-head self-attention (SW-MSA) and MLP modules, respectively. The W-MSA and SW-MSA are key components in the Swin Transformer, which are configured for both standard and shifted window attention. LN denotes the layer normalization operation.
3.2. Adaptive Salient Channel Selection Fine-Tuning
As illustrated in Figure 7, we introduce an innovative feature adaptation method, Adaptive Salient Channel Selection (ASCS), designed to enhance feature representation while reducing computational overhead. This method adaptively selects key channels relevant to the tree targets, and incorporates a learnable bias to facilitate the transition from the pre-trained model to our specific detection task. We integrate the ASCS into each W-MSA and SW-MSA module within every Swin Transformer block to effectively capture both low-level details and high-level semantic information. In the proposed ASCS, channel selection is determined based on the importance score of each channel’s feature map, with the L2 norm employed to compute the importance score. Specifically, given an input feature , where is the sample number of each category, N is the number of tokens, and C is the number of dimensions of the channels. To ensure category-specific feature activation, we first partition the input feature maps into M class-specific subsets based on their category labels:
where represents the features of the m-th category. For each category m, we compute the L2 norm of all samples and tokens N across each channel i to derive its channel-wise importance:
where denotes the feature value at the b-th sample, n-th token, and i-th channel for class m. This step ensures that the channel importance for each category is solely determined by its own samples, thereby mitigating bias caused by class imbalance. The importance score vector for the m-th category is then constructed as
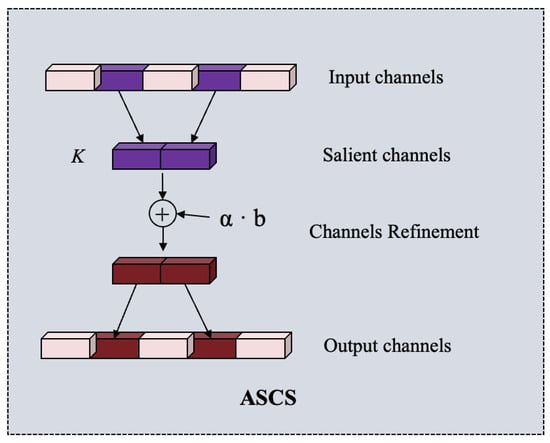
Figure 7.
Structure of the proposed ASCS.
To identify the most salient channels, we compute the average of across all categories, obtaining the importance score for the l-th layer:
After obtaining the importance score vector , we select the top K values of and derive the corresponding indices as , where at the l-th layer. Subsequently, the salient channels at each transformer block can be obtained. As demonstrated in [49], fine-tuning bias terms has been shown to be an effective way of adapting pre-trained transformer-based models to downstream tasks with minimal computational cost, requiring only a small portion of the model parameters to be fine-tuned. Inspired by this, we incorporate an additive bias term into the selected salient channels to enhance the transferability of the pre-trained transformer model to our detection task. Also, to help in aligning the model better with the task-specific features or distributions, a scaling factor is introduced to adjust the bias term, i.e.,
Here, denotes the selected channels, while the bias term b is a learnable parameter initialized to zero and optimized during training. The scaling factor is a constant parameter that scales the bias term. The refined channels are subsequently reintegrated into their original positions, with only the selected K channels being fine-tuned during training while other channels are kept frozen. The key strength of ACSC lies in its ability to perform channel selection based on the L2 norm of each channel’s feature map. This criterion ensures that the channels most essential for the task—those that contain the most informative features—are prioritized. By incorporating both bias term fine-tuning and channel selection, the ACSC method offers a highly flexible and adaptive approach for identifying and refining the most crucial channels within feature maps. This strategy enables the model to concentrate on the most relevant features for the corresponding tree species while dynamically adjusting the weights and biases of these selected channels to optimize their contribution to the final representation. As a result, only the selected K channels, along with their corresponding bias terms, require fine-tuning, which substantially reduces the computational cost.
Considering the varying positions at which the Adapter is inserted, its impact on downstream tasks may differ [50]. To better evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed ASCS, we propose three different configurations for integrating ASCS into the Swin Transformer, shown in Figure 8. The “ASCS-MLP” configuration inserts the ASCS module after the MLP block, while the “ASCS-Attn1” places it after each MHSA and SW-MSA block, but before the MLP block. The “ASCS-Attn2” configuration positions the ASCS after each MHSA and SW-MSA block, but prior to the residual connection. In the “ASCS-MLP” setup, the ASCS module mainly influences the MLP layer by selecting and refining the input feature channels. In contrast, both “ASCS-Attn1” and “ASCS-Attn2” treat the ASCS as an attention mechanism, enhancing features derived from multi-head self-attention.
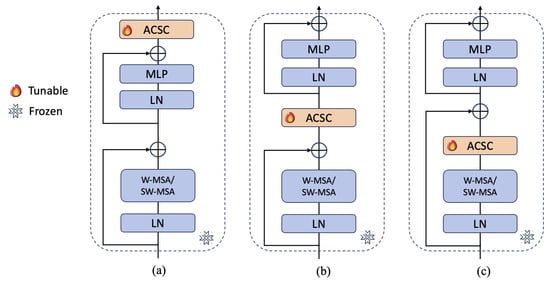
Figure 8.
Different insert position of the proposed ASCS within Swin Transformer blocks, where (a) corresponds to the ASCS-MLP configuration, (b) represents the ASCS-Attn1 configuration, and (c) illustrates the ASCS-Attn2 configuration. In all three variants, only the ASCS module is fine-tuned, while the other components of the model are kept frozen during training.
4. Experiment
4.1. Experiment Setting
All experiments are conducted on a single NVIDIA 3090 GPU with 24 GB of memory. The initial learning rate is set to 0.00005, with a linear warm-up applied during the first 30 iterations. A multi-step learning rate decay is implemented starting at epoch 15, with a decay factor of 0.1. The batch size is configured to 4. In our experiments, the scaling parameter is set to 2. Standard data augmentation techniques, including random horizontal flips, are utilized. The Swin-T backbone from Grounding-DINO is used as the base model, which is fine-tuned for 100 epochs. All 300 images are then divided into two subsets: 80% of the images are allocated to the training set, and the remaining 20% are designated as the testing set.
4.1.1. Metrics
To assess the effectiveness of the proposed method, we employ three widely recognized metrics in object detection: mean average precision (mAP), AP50, and AP75. AP50 is determined using a single intersection over union (IoU) threshold of 0.5, while AP75 is evaluated at an IoU threshold of 0.75. The mAP is computed by averaging the precision across multiple IoU thresholds, providing a comprehensive assessment of model performance.
4.1.2. Comparative Experiments
We compare our method with the state-of-art PEFT methods: Full fine-tuning, FIXED, BITFIT, NORM-TUNING, LoRA, VPT, EVP2, SCT, and Adapter. Full fine-tuning involves training the entire model, updating all network parameters, including weights and biases from the pre-trained model. In contrast, the FIXED method freezes all parameters of the backbone, leaving them unchanged during training. The BITFIT method [49] updates only the bias terms, providing a simplified fine-tuning strategy that adapts the model to a specific task without modifying other parameters. This approach typically reduces computational resources and is especially useful for tasks with limited parameters. NORM-TUNING [51] focuses on fine-tuning the normalization layers, such as batch normalization, optimizing the model’s performance for downstream tasks while leaving other parameters frozen. The LoRA method [44] introduces low-rank matrices into the transformer module of the Swin Transformer, enabling efficient updates to network parameters. VPT [45] is a visual prompting technique that integrates visual prompts with tokens and feeds them into the backbone network, making it particularly effective for tasks like object detection and image classification. EVP2 [50] is an explicit visual prompting method that combines high-frequency and patch embedding features for feature adjustment. The SCT method [52] offers a simple baseline for parameter-efficient fine-tuning by adaptively selecting and refining the most salient channels in the model, focusing on task-specific needs rather than updating all parameters. Lastly, the Adapter method [40] injects additional MLP modules into each transformer layer, enhancing the model’s expressive capacity and offering strong adaptability and scalability within the realm of PEFT. We directly use the publicly available implementations of these methods to generate experimental results. To ensure a fair comparison between different methods, all the experimental settings are kept the same during the experiments. The experimental results are shown in Table 1 and Figure 9.

Table 1.
Quantitative results using different PEFT methods for tree detection and species classification.
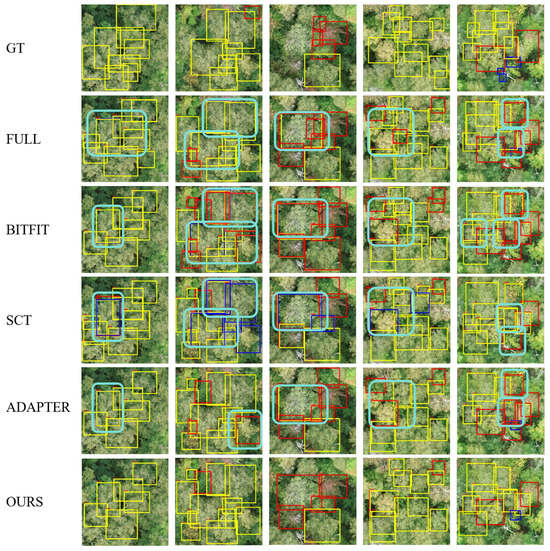
Figure 9.
Comparison of visualization results of different methods. The yellow bounding boxes correspond to Betulaceae, the red bounding boxes indicate Red Maple, and the blue bounding boxes represent Pinaceae. The light blue bold-bordered boxes indicate false detections.
From Table 1, the proposed method demonstrates notable advantages compared with other PEFT methods. Specifically, our model achieves improvements of 0.7, 0.2, and 2.1 in mAP, AP50, and AP75, respectively, over the classical PEFT method Adapter. While the mAP gain may appear modest, the substantial AP75 improvement (+2.1) directly reflects enhanced precision in delineating tree crown boundaries, which is critical for forestry applications. Compared to full fine-tuning (FULL, 100% parameters), our method attains nearly the same AP50 (60.6 vs. 60.7) with only 0.28% of the parameters, validating its ability to retain core performance under extreme parameter constraints. Additionally, while VPT is a PEFT approach tailored for vision tasks, our method surpasses it across all metrics, with increases of 0.6, 1.9, and 0.7 in mAP, AP50, and AP75, respectively. The proposed method also outperforms SCT by 1.5 in mAP, demonstrating superior robustness in complex backgrounds. Beyond detection performance, our approach exhibits exceptional parameter efficiency. By tuning merely 0.28% of the parameters (15× fewer than Adapter); this significantly reduces the memory footprint—a critical advantage for resource-constrained devices like drones processing high-resolution imagery. This lightweight design not only mitigates GPU memory overflow risks but also supports sustainable deployment through efficient multi-task scalability. The results highlight a balanced trade-off between efficiency and accuracy, positioning ACSC as a practical solution for real-world forestry monitoring systems.
Figure 9 illustrates the qualitative outcomes of crown detection across the various methods. As shown in the figure, the light blue bold-bordered area in the first column indicates false detections, particularly evident with the SCT method. This region should have been identified as Betulaceae, yet three different colored detection boxes appear, suggesting that the SCT method struggles to distinguish features between Red Maple and Pinaceae. The identification of “false detections” in this study is based on a visual comparative analysis of multi-method results. By overlaying detection boxes from baseline methods and our approach onto the original images, predictions that significantly deviate from ground truth are manually annotated as error cases. Although similar issues exist with other methods, the overlap of yellow and blue detection boxes makes errors less apparent, especially for the FULL method, which exhibits a broader range of false positives. In the second column, the central section of the ground truth contains only Betulaceae species, but the first three methods incorrectly identify multiple areas as target species. In the third column, the top-left region does not belong to any of the three species; however, other methods label at least two species there, while our approach yields superior results. Additionally, on the right side of this column, both BITFIT and SCT show varying degrees of false detection. Similar to the third column, in the fourth column, our method achieves the lowest false detection rate in the left area, outperforming others. In the fifth column, the top-right region on the right side of the ground truth does not belong to any species, yet all other methods display false detections there. In other regions, some methods also misclassify Betulaceae as Red Maple. It is evident that our method excels in reducing false detections, particularly in complex scenarios with blurred species boundaries.
To further validate the effectiveness of the proposed method, we present heatmaps, which are generated by aggregating the model’s feature responses to target regions, incorporating spatial weighting decay and Gaussian smoothing to highlight attention distribution in important areas (as illustrated in Figure 10). In the Betulaceae prediction results (first and second rows), the SCT and Adapter methods exhibit significant false detections, erroneously identifying other species as Betulaceae. In contrast, our method consistently identifies the target species with precision. Regarding the Pinaceae detection outcomes (third row), while the SCT method shows local missed detections in the third column, the Adapter method incorrectly classifies different species as Pinaceae. Conversely, our approach accurately identifies the correct species. Notably, in the detection of Red Maple within the final two rows, our method continues to precisely pinpoint the correct species, underscoring its robustness and effectiveness.
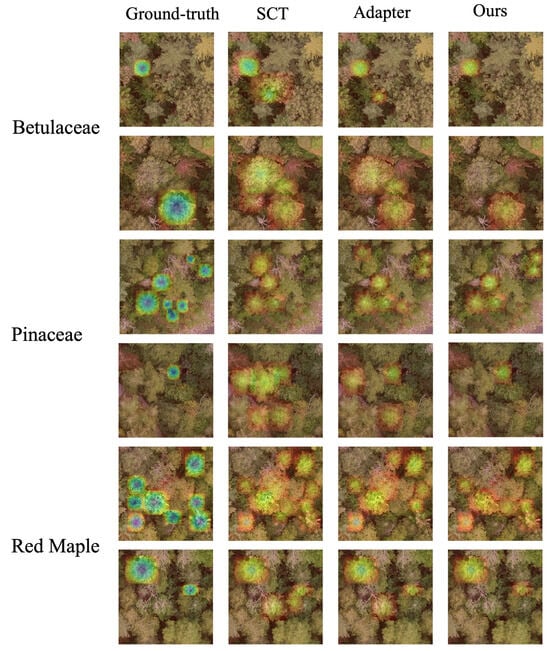
Figure 10.
Comparison of heatmap visualization using different methods (with single species shown).
We also conducted experiments comparing the proposed method with the YOLO series and DETR detection model framework, and the results are presented in Table 2. As shown in the table, the proposed PEFT method demonstrates a significant advantage compared to the latest YOLO models, achieving an AP50 of 60.6. The YOLO models’ results for AP50 are as follows: YOLOv8X: 18.0; YOLOv10: 22.6; YOLOv11: 21.2; and DETR: 57.5. These results highlight the promising potential of fine-tuning large pre-trained models for tree detection tasks, as it leverages the powerful representation capabilities of these models through PEFT. It is important to note that YOLO models (including YOLOv8 and YOLOv10/11) and DETR operate as closed-set detectors, which are optimized for predefined categories and lack inherent adaptability to unseen classes. In contrast, the proposed PEFT method bridges this gap by leveraging the open-set representation power of Grounding-DINO while fine-tuning it for domain-specific closed-set tasks, thereby achieving superior performance in both accuracy and adaptability. Furthermore, directly applying the original Grounding-DINO yields a low AP50 of only 2.4 in our tree detection with multi-species task, whereas the proposed method successfully transfers the detection capabilities of Grounding-DINO to our tree detection and species classification tasks through the use of PEFT.

Table 2.
Experiment results. The table compares different object detection methods based on AP50.
4.2. Ablation Studies
To evaluate the effectiveness of the individual components of the proposed method, we also conducted ablation studies, and the results are presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
Performance using different model designs.
The effectiveness of channel selection and bias term.We first evaluate the performance of the channel selection combined with the Adapter operation, where the bias term is replaced with the traditional Adapter module. As shown in the table, this configuration performs worse than the proposed method, with a 1.2 decrease in mAP and a 0.8 decrease in AP50. These results demonstrate that the bias term plays a crucial role in effectively transferring the pre-trained model to our detection task. Next, we test the use of a bias term, where the bias term is applied to all channels without utilizing channel selection based on importance scores. The results further highlight the critical role of channel selection in the proposed method. By refining the most relevant channels according to the importance scores, channel selection significantly enhances the model’s representation of tree targets. We also investigate the impact of keeping the bias term either frozen or tuned during training, as shown in Table 4. The results reveal a 1.3 decrease in mAP when the bias term is frozen, compared to when it is tuned. This indicates that the bias term is not merely a fixed parameter, but a crucial component that significantly enhances the model’s ability to capture key features, thereby improving both performance and detection accuracy. The findings show that the superiority of the proposed method that combine the channel selection and bias term lies in its ability to focus on the most relevant channels for our detection task, followed by precise bias adjustments. This combination not only improves the model’s focus on task-specific features but also reduces interference from irrelevant channels, allowing the model to more effectively capture the key characteristics needed for the task.

Table 4.
Comparison of mAP, AP50, and AP75 under different biases.
ACSC position. We conducted experiments to assess the influence of the position of the ACSC module within the Swin Transformer block. Three configurations were tested: “ASCS-MLP”, “ASCS-Attn1”, and “ASCS-Attn2”. As shown in Table 5, the ASCS-Attn2 configuration achieved the best performance, suggesting that placing the ACSC module immediately before the LayerNorm layer, following the W-MSA/SW-MSA operation, results in the most effective enhancement of feature channels. This configuration allows the ACSC module to function as an attention mechanism, enhancing the output features from the W-MSA and SW-MSA blocks. In this way, it enables the model to better focus on relevant information, leading to improved accuracy in subsequent classification tasks. The results confirm that this positioning optimizes the effectiveness of the ACSC module, thereby significantly enhancing overall model performance.

Table 5.
Comparison of mAP, AP50, and AP75 based on different ACSC positions.
Value of K. The parameter K, representing the number of selected channels, is evaluated by comparing different values (6, 12, 24, 36), as shown in Figure 11. Since the first layer of the Swin-T backbone contains 96 channels, K must be smaller than this number. The experimental results indicate that K = 24 achieves the highest performance. However, due to increased parameter counts compared to K = 12, we select K = 12 as the optimal balance between performance and computational efficiency. Notably, the channel selection module is inserted across all four stages of Swin-T (stages 1–4), requiring adaptive channel allocation for hierarchical feature learning: shallow layers (stages 1–2) prioritize retaining low-level details, while deeper layers (stages 3–4) focus on filtering high-level semantic features. When K approaches the total channel number (K = 36), redundant feature selection reduces computational efficiency across layers, whereas an excessively small K (K = 6) simultaneously weakens feature representation in both shallow and deep layers. Selecting K = 12 preserves core features uniformly across stages, validating the generalizability of the empirical threshold of 1/8 of the total channels. Despite a slight increase in computational cost from global insertion, the unified K = 12 configuration ensures consistent feature selection across stages, ultimately achieving a dynamic balance between performance and efficiency in multi-stage tasks.
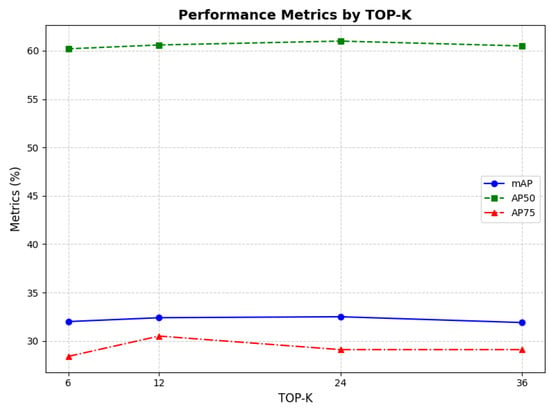
Figure 11.
Comparison of mAP, AP50, and AP75 based on different values.
Scaling factor . As shown in Table 6, the ablation study on the scaling factor reveals its critical impact on model performance. When = 2, the model achieves peak values in both AP50 (60.6) and AP75 (30.5), whereas = 3 leads to a significant performance drop in AP50, indicating that excessively large scaling factors may destabilize feature distributions. This aligns with the design goal of the channel selection mechanism: by adjusting the bias term (Equation (9)), controls the enhancement intensity of feature channels. The optimal value = 2 is empirically determined through validation set comparisons of values (0.5–3), balancing feature adaptability and computational efficiency. Notably, AP75 exhibits higher sensitivity to variations compared to AP50, likely due to the stronger dependency of high-level semantic features on bias adjustments. Although the performance difference between = 0.5 and = 1 is minimal, the general superiority of = 2 suggests better compatibility with multi-stage feature learning requirements. Combined with the global insertion strategy of the ACSC module (stages 1–4), = 2 effectively preserves low-level details in shallow layers while enhancing the representation of complex semantics in deeper layers, achieving dynamic equilibrium across hierarchical tasks. This analysis underscores the importance of for model robustness and provides theoretical guidance for parameter selection in downstream tasks.

Table 6.
Comparison of mAP, AP50, and AP75 based on different values of .
5. Discussion and Conclusions
In this study, we investigate the potential of pre-trained transformer models for tree detection and species classification using UAV imagery. Motivated by PEFT techniques, we propose a simple yet effective method for transferring pre-trained transformer models to our specific task. To tackle the challenge of minimizing the influence of irrelevant ground targets in UAV imagery, we introduce the ASCS method, which can be seamlessly integrated into each transformer block during fine-tuning. In the ASCS approach, task-specific channels are adaptively selected based on class-wise importance scores, ensuring that the most relevant channels for the target class are emphasized. Additionally, a bias term is incorporated to facilitate the learning of task-specific knowledge, further enhancing the adaptation of the pre-trained model to the target task. Experiments were conducted on a multi-species dataset captured using UAVs, which is characterized by a limited number of image samples. The results indicate that the proposed method substantially outperforms the most recent YOLO detection framework and exceeds the performance of current state-of-the-art PEFT approaches. These findings highlight the potential of leveraging pre-trained models for tree detection in UAV imagery through the use of PEFT. Future research will focus on expanding the method to address a broader range of species present in the images.
Author Contributions
Software, J.Z.; Writing—original draft, J.Z.; Writing—review & editing, F.L. and X.F.; Supervision, X.F.; Project administration, F.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Key Laboratory of Natural Resources Monitoring and Supervision in Southern Hilly Region, Ministry of Natural Resources, Changsha, China (grant number: NRMSSHR2023Y07).
Data Availability Statement
The raw dataset can be available at https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8148479, accessed on 29 March 2025.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Wenhua, L. Degradation and restoration of forest ecosystems in China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2004, 201, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, L.; Zohner, C.M.; Reich, P.B.; Liang, J.; De Miguel, S.; Nabuurs, G.J.; Renner, S.S.; van den Hoogen, J.; Araza, A.; Herold, M.; et al. Integrated global assessment of the natural forest carbon potential. Nature 2023, 624, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassnacht, F.E.; Latifi, H.; Stereńczak, K.; Modzelewska, A.; Lefsky, M.; Waser, L.T.; Straub, C.; Ghosh, A. Review of studies on tree species classification from remotely sensed data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 186, 64–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corona, P.; Chirici, G.; McRoberts, R.E.; Winter, S.; Barbati, A. Contribution of large-scale forest inventories to biodiversity assessment and monitoring. For. Ecol. Manag. 2011, 262, 2061–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Birdsey, R.A.; Fang, J.; Houghton, R.; Kauppi, P.E.; Kurz, W.A.; Phillips, O.L.; Shvidenko, A.; Lewis, S.L.; Canadell, J.G.; et al. A large and persistent carbon sink in the world’s forests. Science 2011, 333, 988–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santopuoli, G.; Vizzarri, M.; Spina, P.; Maesano, M.; Mugnozza, G.S.; Lasserre, B. How individual tree characteristics and forest management influence occurrence and richness of tree-related microhabitats in Mediterranean mountain forests. For. Ecol. Manag. 2022, 503, 119780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomppo, E.; Olsson, H.; Ståhl, G.; Nilsson, M.; Hagner, O.; Katila, M. Combining national forest inventory field plots and remote sensing data for forest databases. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 1982–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senf, C.; Seidl, R.; Hostert, P. Remote sensing of forest insect disturbances: Current state and future directions. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 60, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Wang, L.; Fan, X.; Bo, W.; Yang, X.; Tjahjadi, T. Semi-FCMNet: Semi-supervised learning for forest cover mapping from satellite imagery via ensemble self-training and perturbation. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayet, N. Forest Health Monitoring using Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Techniques. In Spatial Modeling in Forest Resources Management: Rural Livelihood and Sustainable Development; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 239–257. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, P. Forest fire and degradation assessment using satellite remote sensing and geographic information system. In Satellite Remote Sensing and GIS Applications in Agricultural Meteorology; World Meteorological Organisation: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003; Volume 361, pp. 361–400. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Chen, G.; Potter, C.; Meentemeyer, R.K. Integrating multi-sensor remote sensing and species distribution modeling to map the spread of emerging forest disease and tree mortality. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 231, 111238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, W.; Liu, J.; Fan, X.; Tjahjadi, T.; Ye, Q.; Fu, L. BASNet: Burned area segmentation network for real-time detection of damage maps in remote sensing images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, C.; Fan, X.; Tjahjadi, T.; Guan, H.; Fu, L.; Ye, Q.; Wang, R. Vision foundation model guided multi-modal fusion network for remote sensing semantic segmentation. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fan, X.; Yang, X.; Tjahjadi, T.; Wang, Y. Semi-supervised learning for forest fire segmentation using UAV imagery. Forests 2022, 13, 1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, J.P.; Watt, M.S.; Pearse, G.D.; Heaphy, M.; Dungey, H.S. Assessing very high resolution UAV imagery for monitoring forest health during a simulated disease outbreak. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 131, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, C.; Zhong, W.; Luan, Q.; Wu, C. UAV-driven GWAS analysis of canopy temperature and new shoots genetics in slash pine. Industrial Crops Prod. 2024, 212, 118330. [Google Scholar]
- Diez, Y.; Kentsch, S.; Fukuda, M.; Caceres, M.L.L.; Moritake, K.; Cabezas, M. Deep learning in forestry using uav-acquired rgb data: A practical review. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, N.; Pádua, L.; Marques, P.; Silva, N.; Peres, E.; Sousa, J.J. Forestry remote sensing from unmanned aerial vehicles: A review focusing on the data, processing and potentialities. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Grybas, H.; Congalton, R.G. Individual tree crown delineation from UAS imagery based on region growing and growth space considerations. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safonova, A.; Hamad, Y.; Dmitriev, E.; Georgiev, G.; Trenkin, V.; Georgieva, M.; Dimitrov, S.; Iliev, M. Individual tree crown delineation for the species classification and assessment of vital status of forest stands from UAV images. Drones 2021, 5, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Li, X.; Chen, C. Individual tree crown detection and delineation from very-high-resolution UAV images based on bias field and marker-controlled watershed segmentation algorithms. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2018, 11, 2253–2262. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Gong, P.; Biging, G.S. Individual tree-crown delineation and treetop detection in high-spatial-resolution aerial imagery. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2004, 70, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.A.d.; Marcato Junior, J.; Araújo, M.S.; Di Martini, D.R.; Tetila, E.C.; Siqueira, H.L.; Aoki, C.; Eltner, A.; Matsubara, E.T.; Pistori, H.; et al. Assessment of CNN-based methods for individual tree detection on images captured by RGB cameras attached to UAVs. Sensors 2019, 19, 3595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jintasuttisak, T.; Edirisinghe, E.; Elbattay, A. Deep neural network based date palm tree detection in drone imagery. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 192, 106560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Fan, X.; Qu, H.; Yang, X.; Tjahjadi, T. TCDNet: Tree crown detection from UAV optical images using uncertainty-aware one-stage network. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Y.; Wang, Q.; Iio, A. Tree crown detection and delineation in a temperate deciduous forest from UAV RGB imagery using deep learning approaches: Effects of spatial resolution and species characteristics. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T. Focal Loss for Dense Object Detection. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1708.02002. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.Y.; Yeh, I.H.; Mark Liao, H.Y. Yolov9: Learning what you want to learn using programmable gradient information. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 26–27 March 2025; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2025; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.; Chen, H.; Liu, L.; Chen, K.; Lin, Z.; Han, J.; Ding, G. YOLOv10: Real-Time End-to-End Object Detection. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2405.14458. [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein, B.G.; Marconi, S.; Aubry-Kientz, M.; Vincent, G.; Senyondo, H.; White, E.P. DeepForest: A Python package for RGB deep learning tree crown delineation. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2020, 11, 1743–1751. [Google Scholar]
- Ball, J.G.; Hickman, S.H.; Jackson, T.D.; Koay, X.J.; Hirst, J.; Jay, W.; Archer, M.; Aubry-Kientz, M.; Vincent, G.; Coomes, D.A. Accurate delineation of individual tree crowns in tropical forests from aerial RGB imagery using Mask R-CNN. Remote Sens. Ecol. Conserv. 2023, 9, 641–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Sun, A.; Jing, W.; Zhou, J.T. Temporal sentence grounding in videos: A survey and future directions. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 10443–10465. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Zeng, Z.; Ren, T.; Li, F.; Zhang, H.; Yang, J.; Jiang, Q.; Li, C.; Yang, J.; Su, H.; et al. Grounding dino: Marrying dino with grounded pre-training for open-set object detection. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 26–27 March 2025; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2025; pp. 38–55. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Li, F.; Liu, S.; Zhang, L.; Su, H.; Zhu, J.; Ni, L.M.; Shum, H.Y. Dino: Detr with improved denoising anchor boxes for end-to-end object detection. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.03605. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2014: 13th European Conference, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; Proceedings, Part V 13. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 740–755. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Z.; Yang, H.; So, A.M.C.; Lam, W.; Bing, L.; Collier, N. On the effectiveness of parameter-efficient fine-tuning. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Washington, DC, USA, 7–14 February 2023; Volume 37, pp. 12799–12807. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Xie, H.; Qin, S.Z.J.; Tao, X.; Wang, F.L. Parameter-efficient fine-tuning methods for pretrained language models: A critical review and assessment. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2312.12148. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.O.; Sax, A.; Zamir, A.; Guibas, L.; Malik, J. Side-tuning: A baseline for network adaptation via additive side networks. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Proceedings, Part III 16. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 698–714. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, H.; Gan, C.; Zhu, L.; Han, S. Tinytl: Reduce memory, not parameters for efficient on-device learning. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 11285–11297. [Google Scholar]
- Beloiu, M.; Heinzmann, L.; Rehush, N.; Gessler, A.; Griess, V.C. Individual tree-crown detection and species identification in heterogeneous forests using aerial RGB imagery and deep learning. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houlsby, N.; Giurgiu, A.; Jastrzebski, S.; Morrone, B.; De Laroussilhe, Q.; Gesmundo, A.; Attariyan, M.; Gelly, S. Parameter-efficient transfer learning for NLP. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; PMLR: Birmingham, UK, 2019; pp. 2790–2799. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, E.J.; Shen, Y.; Wallis, P.; Allen-Zhu, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Chen, W. Lora: Low-rank adaptation of large language models. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.09685. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, M.; Tang, L.; Chen, B.C.; Cardie, C.; Belongie, S.; Hariharan, B.; Lim, S.N. Visual prompt tuning. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 709–727. [Google Scholar]
- Cloutier, M.; Germain, M.; Laliberté, E. Influence of temperate forest autumn leaf phenology on segmentation of tree species from UAV imagery using deep learning. Remote Sens. Environ. 2024, 311, 114283. [Google Scholar]
- Alexey, D. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin Transformer: Hierarchical Vision Transformer using Shifted Windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar]
- Zaken, E.B.; Ravfogel, S.; Goldberg, Y. Bitfit: Simple parameter-efficient fine-tuning for transformer-based masked language-models. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.10199. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Shen, X.; Pun, C.M.; Cun, X. Explicit visual prompting for universal foreground segmentations. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.18476. [Google Scholar]
- Giannou, A.; Rajput, S.; Papailiopoulos, D. The expressive power of tuning only the Norm layers. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.07937. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.H.; Wang, P.; Zhao, Y.; Luo, H.; Wang, F.; Shou, M.Z. Sct: A simple baseline for parameter-efficient fine-tuning via salient channels. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2024, 132, 731–749. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).