Spatial–Temporal Heterogeneity of Wetlands in the Alpine Mountains of the Shule River Basin on the Northeastern Edge of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
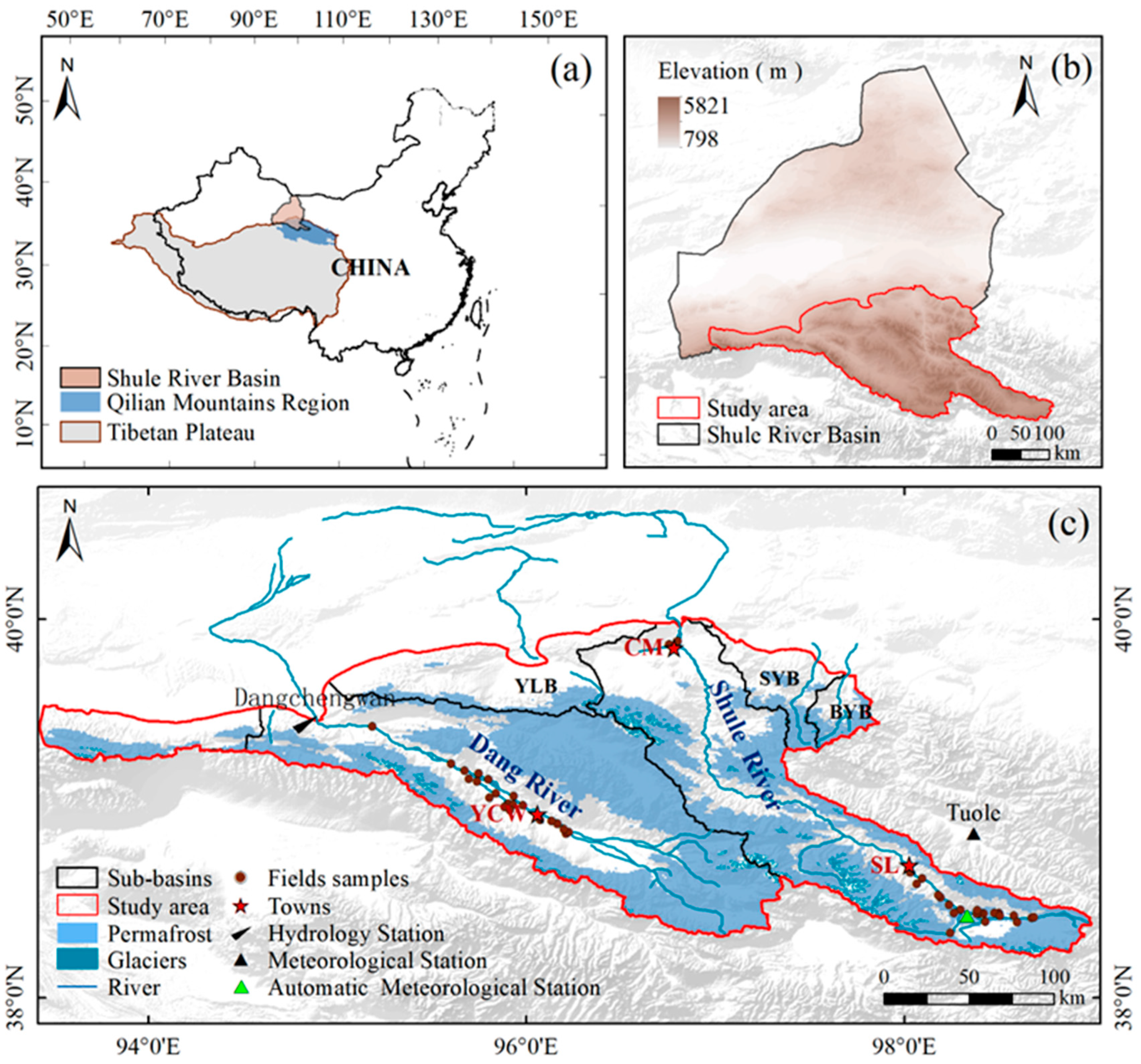
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Method
2.3.1. Land Cover Classification System and Sample Dataset
2.3.2. Feature Selection and Extraction
2.3.3. Random Forest Classification Model
2.3.4. Accuracy Assessment Methods
3. Results
3.1. Wetland Types and Classification Accuracy
3.2. Spatial Heterogeneity of Wetlands
3.3. Temporal Heterogeneity of Wetlands
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison with Products
4.2. Differing Spatial Distribution of Wetland Types
4.3. Factors Influencing Temporal Changes in Wetlands
4.4. Uncertainty Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mitsch, W.; Gosselink, J. Wetlands, 5th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, J.H. Alpine Wetlands in China; China Forestry Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2008; pp. 14–22. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, L.; Zhang, G. The dynamic evolvement and hydrological driving factors of marsh in Nenjiang River basin. Adv. Water Sci. 2013, 24, 177–183. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Q.; Sun, Z.; Pan, Z. Stream runoff formation and hydrological regulation mechanism in mountainous alpine regions: A review. Earth Sci. 2022, 47, 4196–4209. [Google Scholar]
- Werner, B.A.; Johnson, W.C.; Guntenspergen, G.R. Evidence for 20th century climate warming and wetland drying in the North American Prairie Pothole Region. Ecol. Evol. 2013, 3, 3471–3482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Shen, X.; Lü, X. Change characteristics of landscape pattern and climate in marsh areas of Northeast China during 1980–2015. Earth Environ. 2020, 48, 348–357. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.; Xuegang, C.; Yaqi, W. Dynamic change of Wetland Landscapes in the Ertix River Basin, Xinjiang during the period of 1990–2010. Arid. Zone Res. 2013, 30, 211–218. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.; Mengmeng, W.; Tao, Z.; Wenfeng, C. Progress in remote sensing monitoring of lake area, water level, and volume changes on the Tibetan Plateau. Natl. Remote Sens. Bull. 2022, 26, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Xu, X.; Fu, Y.; Li, S. Wetland Changes and Their Responses to Climate Change in the “Three-River Headwaters” Region of China since the 1990s. Energies 2014, 7, 2515–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, Q.; Niu, Z.; Hong, X.; Yang, X. Remote sensing monitoring and change analysis of wetlands in the Tibetan Plateau. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2021, 46, 230–237. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelmajeed, A.Y.A.; Juszczak, R. Challenges and Limitations of Remote Sensing Applications in Northern Peatlands: Present and Future Prospects. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Jiao, C.; Zhou, D.; Li, N. Scale issues of wetland classification and mapping using remote sensing images: A case of Honghe National Nature Reserve in Sanjiang Plain, Northeast China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2011, 21, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubert-Moy, L.; Fabre, E.; Rapinel, S. Contribution of SPOT-7 multi-temporal imagery for mapping wetland vegetation. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 53, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niculescu, S.; Lardeux, C.; Grigoras, I.; Hanganu, J.; David, L. Synergy Between LiDAR, RADARSAT-2, and Spot-5 Images for the Detection and Mapping of Wetland Vegetation in the Danube Delta. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 3651–3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Zhu, B.; Gan, H.; Xia, Z.; Wang, K.; Yue, Y.; Li, R. Wetland change in Wangning during 2002 and 2013. In Proceedings of the 19th National Symposium on Remote Sensing of China—Remote Sensing of the Environment, Xian, China, 20–23 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Bo, Z.; Leng, Z. Current status and prospect of researches on wetland monitoring based on remote sensing. Prog. Geogr. 2007, 26, 33–43. [Google Scholar]
- Mahdianpari, M.; Salehi, B.; Mohammadimanesh, F.; Homayouni, S.; Gill, E. The First Wetland Inventory Map of Newfoundland at a Spatial Resolution of 10 m Using Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 Data on the Google Earth Engine Cloud Computing Platform. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapinel, S.; Mony, C.; Lecoq, L.; Clement, B.; Thomas, A.; Hubert-Moy, L. Evaluation of Sentinel-2 time-series for mapping floodplain grassland plant communities. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 223, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Wang, Z.; Mao, D.; Ren, C.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y. Rapid, robust, and automated mapping of tidal flats in China using time series Sentinel-2 images and Google Earth Engine. Remote Sens. Environ. 2021, 255, 112285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, A.; Flood, N.; Danaher, T. Comparing Landsat water index methods for automated water classification in eastern Australia. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 175, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, L.; Sun, W.; Yang, G.; Ren, G.; Liu, Y. A Hierarchical Classification Framework of Satellite Multispectral/Hyperspectral Images for Mapping Coastal Wetlands. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, R.W.; Naz, I.; Shu, H.; Yan, J.; Quddoos, A.; Tariq, A.; Davis, J.B.; Al-Saif, A.M.; Soufan, W. Multi-temporal image analysis of wetland dynamics using machine learning algorithms. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 371, 123123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutler, A.; Cutler, D.; Stevens, J. Random Forests. In Ensemble Machine Learning; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; Volume 45, pp. 157–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gislason, P.O.; Benediktsson, J.A.; Sveinsson, J.R. Random Forests for land cover classification. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2006, 27, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, A.; Muñoz-Carpena, R.; Kennedy, R.E.; Murcia, C. Wetland Landscape Spatio-Temporal Degradation Dynamics Using the New Google Earth Engine Cloud-Based Platform: Opportunities for Non-Specialists in Remote Sensing. Trans. Asabe 2016, 59, 1333–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farda, N.M.; IOP. Multi-temporal Land Use Mapping of Coastal Wetlands Area using Machine Learning in Google Earth Engine. In Proceedings of the 5th Geoinformation Science Symposium (GSS) on Bridging Geospatial Industries and Scientific Research, Univ Gadjah Mada, Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 27–28 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Zhengyang, H.; Liqiang, Z.; Ying, Q.; Guoqing, Z.; Jintai, L.; Jingwen, L.; Ke, H. Long-term spatio-temporal changes of wetlands in Tibetan Plateau and their response to climate change. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2023, 121, 103351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, Z.; Nie, Y.; Rai, M.K. A novel Landsat-based automated mapping of marsh wetland in the headwaters of the Brahmaputra, Ganges and Indus Rivers, southwestern Tibetan Plateau. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 103, 102481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Sun, J.; Blanchette, M.; Rousseau, A.N.; Xu, Y.J.; Hu, B.; Zhang, G. Wetland mitigation functions on hydrological droughts: From drought characteristics to propagation of meteorological droughts to hydrological droughts. J. Hydrol. 2023, 617, 128971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.X.; An, B.; Shu, M.L.; Yang, X.J. Nest-site selection, reproductive ecology and shifts within core-use areas of Black-necked Cranes at the northern limit of the Tibetan Plateau. PeerJ 2017, 5, e2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, H.; Zhou, J.; Tai, S.; Wang, X. Variation of Runoff and Runoff Components of the Upper Shule River in the Northeastern Qinghai–Tibet Plateau under Climate Change. Water 2021, 13, 3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Y.; Hu, X.; Xiao, S.; Wen, J.; Wang, G.; Zou, S.; La, C.; Song, J. Study on climate change in mountainous region of Shulehe River Basin in past 50 years and its effect to mountainous runoff. Plateau Meteorol. 2012, 31, 1636–1644. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Chen, J.; Wu, H.; Zhang, S.; Gao, M.; Qin, H. Comparative study of evapotranspiration in an alpine meadow in the upper reach of Shulehe River Basin. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2013, 33, 97–103. [Google Scholar]
- Shiyin, L.; Wanqin, G.; Junli, X. The Second Glacier Inventory Dataset of China (Version 1.0) (2006–2011); National Tibetan Plateau/Third Pole Environment Data Center: Bejing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y. Distribution patterns of permafrost in the upper area of Shule River with the application of GIS technique. J. China Univ. Min. Technol. 2010, 1, 32–39. [Google Scholar]
- Youhua, R.; Xin, L. The Mean Annual Ground Temperature (MAGT) and Permafrost Thermal Stability Dataset over Tibetan Plateau for 2005–2015; National Tibetan Plateau/Third Pole Environment Data Center: Bejing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Zhao, K. Records of Mires in China, 2nd ed.; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2023; pp. 540–549. [Google Scholar]
- Hongxia, Z.; Chengzhang, Z.; Yufang, W. Landscape pattern evolution and its influencing factors of alpine wetland in Yanchi Bay. Arid. Zone Res. 2021, 38, 1771–1781. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, X. Wetlands and Wetland in China; Hebei Science & Technology Press: Shijiazhuang, China, 2008; pp. 187–203. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, D.; Cheng, J.; Xiong, L. Digital Extraction of Surface Hydrological Elements from DEM Data in the Wetland Area of a Flood Plain. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2008, 28, 776–781. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 24708-2009; Wetland Classification. National Standards of People’s Republic of China: Bejing, China, 2009.
- Shengyun, C.; Wenjie, L.; Xiang, Q.; Yushuo, L.; Tongzuo, Z.; Kelong, C.; Fengzu, H.; Jiawen, R.; Dahe, Q. Response characteristics of vegetation and soil environment to permafrost degradation in the upstream regions of the Shule River Basin. Environ. Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 045406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Sun, X.; Liu, Z. Object-Oriented Coastline Classification and Extraction from Remote Sensing Imagery; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2014; Volume 9158. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Ding, J.; Li, Y.; Niu, Z. Extraction of water information based on China-made GF-1 remote sense image. Resour. Sci. 2015, 37, 1166–1172. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; Kobayashi, H.; Wang, C.; Shen, M.; Chen, J.; Matsushita, B.; Tang, Y.; Kim, Y.; Bret-Harte, M.S.; Zona, D.; et al. A semi-analytical snow-free vegetation index for improving estimation of plant phenology in tundra and grassland ecosystems. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 228, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, H.; Chong, H.; He, L.; Qingsheng, L.; Gaohuan, L.; Zhenchao, Z.; Chenchen, Z. Land-cover classification of random forest based on Sentinel-2A image feature optimization. Resour. Sci. 2019, 41, 992–1001. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Sheng, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, J. Permafrost in source areas of Shule River in Qilian Mountains. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2009, 64, 571–580. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Liao, A.; Cao, X.; Chen, L.; Chen, X.; He, C.; Han, G.; Peng, S.; Lu, M.; et al. Global land cover mapping at 30 m resolution: A POK-based operational approach. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 103, 7–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, L.; Chen, X.; Gao, Y.; Xie, S.; Mi, J. GLC_FCS30: Global land-cover product with fine classification system at 30 m using time-series Landsat imagery. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 2753–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanaga, D.; Van De Kerchove, R.; De Keersmaecker, W.; Souverijns, N.; Brockmann, C.; Quast, R.; Wevers, J.; Grosu, A.; Paccini, A.; Vergnaud, S.; et al. ESA WorldCover 10 m 2020 v100. 2021. Available online: https://zenodo.org/records/5571936 (accessed on 1 January 2020).
- Gong, P.; Wang, J.; Huang, H. Stable classification with limited samples in global land cover mapping: Theory and experiments. Sci. Bull. 2024, 69, 1862–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Feng, M.; Jiang, H.; Wang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, Y. Assessing Consistency of Five Global Land Cover Data Sets in China. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 8739–8759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Xu, X.; Jiang, X.; Mo, Y.; Cui, H.; Zhu, S.; Wu, H. Evaluation of six global high-resolution global land cover products over China. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2024, 17, 2301673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.-J.; Zhang, Y.-B.; Wang, Y.-M.; Yang, H.-R.; Ma, Z.-B.; Dong, W.-T.; Yang, J.-C.; Dabuxilite; Wuliji. Spermatophyte diversity and flora in wetland of Yanchiwan National Nature Reserve in Gansu. J. Gansu Agric. Univ. 2018, 53, 18–126. [Google Scholar]
- Comber, A.; Fisher, P.; Wadsworth, R. Integrating land-cover data with different ontologies: Identifying change from inconsistency. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2004, 18, 691–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-W.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, L.; Wu, X.-D.; Yue, G.-Y.; Zou, D.-F.; Nan, Z.-T.; Liu, G.-Y.; Pang, Q.-Q.; Fang, H.-B.; et al. Mapping the vegetation distribution of the permafrost zone on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J. Mt. Sci. 2016, 13, 1035–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, D.; Zhao, L.; Liu, G.; Du, E.; Hu, G.; Li, Z.; Wu, T.; Wu, X.; Chen, J. Vegetation Mapping in the Permafrost Region: A Case Study on the Central Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L. Typical alpine wetland system changes on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau in recent 40 years. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2007, 62, 481–491. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.-W.; Li, S.-N.; Wei, W.; Song, X.-J. Research progress on alpine wetland changes and driving forces in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau during the last three decades. Chin. J. Ecol. 2019, 38, 856. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Ding, Y.; Li, J.; Shangguan, D.; Zhang, Y. Glaciers in Response to Recent Climate Warming in Western China. Quat. Sci. 2006, 26, 762–771. [Google Scholar]
- Meiping, S.U.N.; Shiyin, L.I.U.; Xiaojun, Y.A.O.; Wanqin, G.U.O.; Junli, X.U. Glacier changes in the Qilian Mountains in the past half century: Based on the revised First and Second Chinese Glacier Inventory. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2015, 70, 1402–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhao, Q.; Wu, J.; Ding, Y.; Qin, J.; Wei, H.; Zeng, D. Quantitative simulation of the runoff components and its variation characteristics in the upstream of the Shule River. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2019, 41, 907–917. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Z.; Guojie, H.; Defu, Z.; Xiaodong, W.; Lu, M.; Zhe, S.; Liming, Y.; Huayun, Z.; Shibo, L. Permafrost changes and its effects on hydrological processes on Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. (Chin. Version) 2019, 34, 1233–1246. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Z.; Lyu, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, M.; Zhang, K.; Lyu, Y. Spatial and Temporal Changes of Wetlands on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau from the 1970s to 2010s. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2018, 28, 935–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgenson, M.T.; Shur, Y.L.; Pullman, E.R. Abrupt increase in permafrost degradation in Arctic Alaska. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, P.S.A.; Goetz, S.J. Satellite observations of high northern latitude vegetation productivity changes between 1982 and 2008: Ecological variability and regional differences. Environ. Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 045501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.-Y.; Jin, H.-J.; Iwahana, G.; Marchenko, S.S.; Luo, D.-L.; Li, X.-Y.; Liang, S.-H. Impacts of climate-induced permafrost degradation on vegetation: A review. Adv. Clim. Change Res. 2021, 12, 29–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, M.-J.; Gao, J.-L.; Ge, J.; Li, Y.-C.; Liu, J.; Yin, J.-P.; Feng, Q.-S.; Liang, T.-G. An analysis of dynamic changes and their driving factors in marsh wetlands in the eastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Acta Prataculturae Sin. 2020, 29, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Warner, T.; Wang, Y.; Bai, J.; Bao, A. Mapping glacial lakes partially obscured by mountain shadows for time series and regional mapping applications. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 40, 615–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.-G.; Jing, Y.-H.; Zhang, D.-Q.; Zhang, B. An overview and the outlook for wetland ecosystems in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau under climate change. Adv. Clim. Change Res. 2024, 20, 509. [Google Scholar]
- Kassawmar, T.; Eckert, S.; Hurni, K.; Zeleke, G.; Hurni, H. Reducing landscape heterogeneity for improved land use and land cover (LULC) classification across the large and complex Ethiopian highlands. Geocarto Int. 2018, 33, 53–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Land Cover Types | Description | Digital Camera | UAV | High-Resolution Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| marsh | Freshwater marshes with dominant aquatic and marshy herb communities dominated by Najadacea, Zannichelliaceae, and Triglochin maritimum, shallow water depth |  |  |  |
| swamp meadow | The soil is developed under an excessively humid environment, the water depth is shallow, and plants such as Blysmus sinocompressus, and Kobresia littledalei |  |  |  |
| natural grassland | Various types of grassland mainly growing herbaceous plants with a coverage of more than 5%, including shrubland grassland mainly grazing and sparsely forested grassland with a canopy of less than 10% |  |  |  |
| bare land | Soil cover, vegetation coverage below 5% of the land |  |  |  |
| glacier | Land that is covered by glaciers and snow all year round |  |  |  |
| river and lake water body | Naturally formed rivers and waterlogged areas and land below the perennial water level |  |  |  |
| Wetland Types | Elevation/m | Location |
|---|---|---|
| river and lake water body, swamp meadow | 2020 | 96.80°E, 39.88°N |
| river and lake water body, swamp meadow | 2061 | 96.76°E, 39.86°N |
| river and lake water body | 2620 | 95.11°E, 39.44°N |
| swamp meadow | 3839 | 98.31°E, 38.46°N |
| marsh | 3850 | 98.43°E, 38.45°N |
| river and lake water body | 3856 | 98.40°E, 38.46°N |
| marsh | 3904 | 98.55°E, 38.46°N |
| Class | Variable | Description and Equation |
|---|---|---|
| Spectral bands | Band | Band1, Band2, Band3, Band4, Band5, Band7 (TM) |
| Band2, Band3, Band4, Band5, Band6, Band7 (OLI) | ||
| Spectral index | Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) | NDWI = (GREEN − NIR)/(GREEN + NIR) |
| Modified Soil adjusted Vegetation Index (MSAVI) | ||
| Shadow Water Index (SWI) [45] | SWI = BLUE + GREEN − NIR | |
| Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) | NDVI = (NIR − RED)/(NIR + RED) | |
| Redness Index (RI) | RI = (RED − GREEN)/(RED + GREEN) | |
| Normalized Difference Greenness Index (NDGI) [46] | NDGI = (0.65GREEN + 0.35NIR − RED)/(0.65GREEN + 0.35NIR + RED) | |
| Difference Vegetation Index (DVI) | DVI = NIR − RED | |
| Ratio Vegetation Index (RVI) | RVI = NIR/RED | |
| Transformed Vegetation Index (TVI) | ||
| Wetness Index (WI) | Tasseled Cap Wetness | |
| Brightness Index (BI) | Tasseled Cap Brightness | |
| Green Index (GI) | Tasseled Cap Greenness | |
| Texture | GLCM | ASM, IDM, SAVG, SVAR |
| Topography | Elevation | DEM |
| Slope | DEM |
| Landcover | River and Lake Water Body | Swamp Meadow | Marsh | Natural Grassland | Bare Land | Glacier |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| User accuracy | 97.2% | 91.3% | 93.4% | 95.0% | 94.57% | 99.16% |
| Producer accuracy | 96.6% | 90.8% | 93.9% | 96.5% | 93.72% | 96.19% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tai, S.; Shangguan, D.; Wu, J.; Wang, R.; Li, D. Spatial–Temporal Heterogeneity of Wetlands in the Alpine Mountains of the Shule River Basin on the Northeastern Edge of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 976. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17060976
Tai S, Shangguan D, Wu J, Wang R, Li D. Spatial–Temporal Heterogeneity of Wetlands in the Alpine Mountains of the Shule River Basin on the Northeastern Edge of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(6):976. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17060976
Chicago/Turabian StyleTai, Shuya, Donghui Shangguan, Jinkui Wu, Rongjun Wang, and Da Li. 2025. "Spatial–Temporal Heterogeneity of Wetlands in the Alpine Mountains of the Shule River Basin on the Northeastern Edge of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau" Remote Sensing 17, no. 6: 976. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17060976
APA StyleTai, S., Shangguan, D., Wu, J., Wang, R., & Li, D. (2025). Spatial–Temporal Heterogeneity of Wetlands in the Alpine Mountains of the Shule River Basin on the Northeastern Edge of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Remote Sensing, 17(6), 976. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17060976






