Amplitude and Phase Calibration with the Aid of Beacons in Microwave Imaging Radiometry by Aperture Synthesis: Algebraic Aspects and Algorithmic Implications
Abstract
1. Introduction
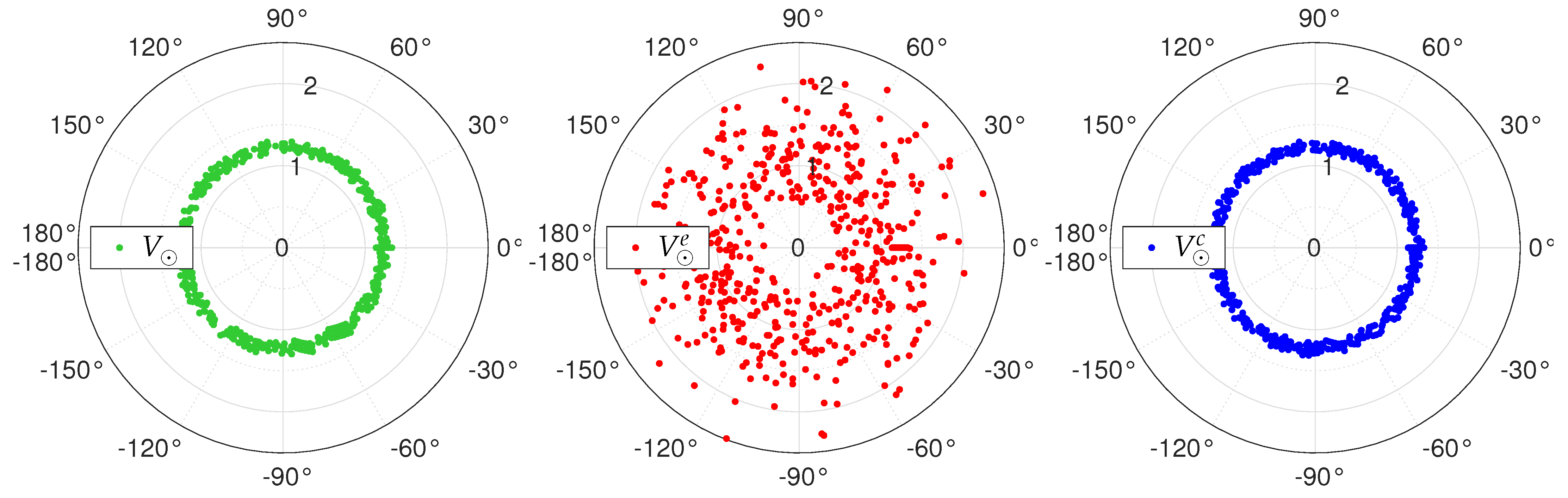
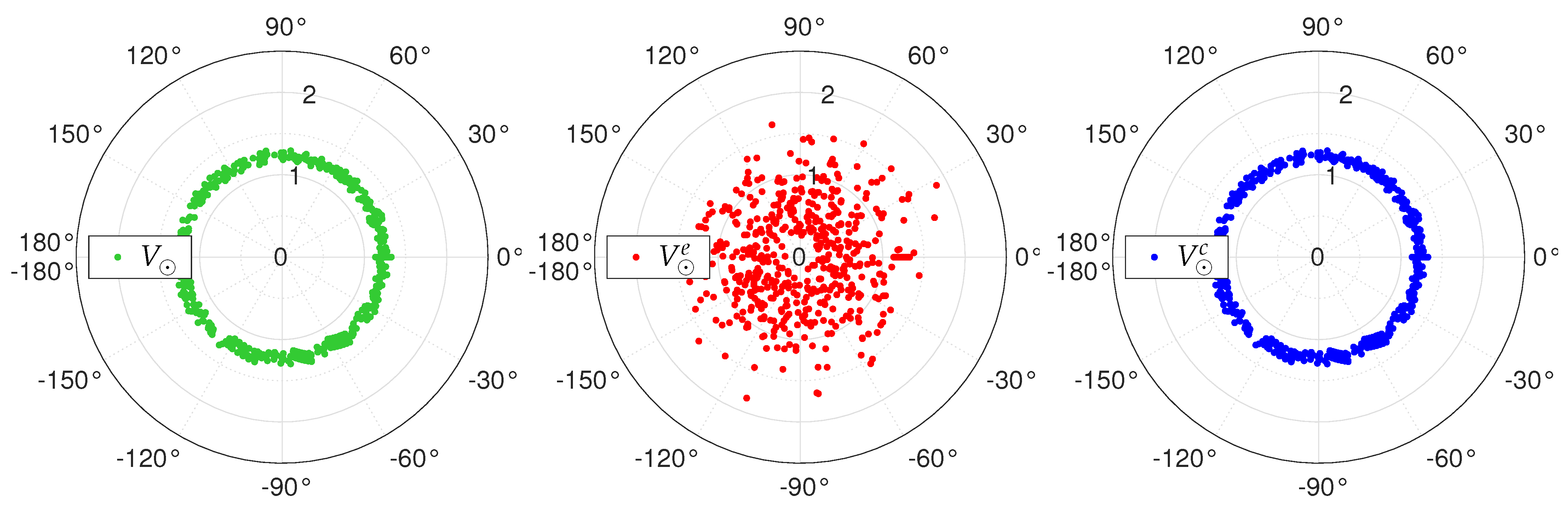
2. Theoretical Aspects
3. Aberration Operators
4. Calibration Approaches
5. Calibration Algorithms
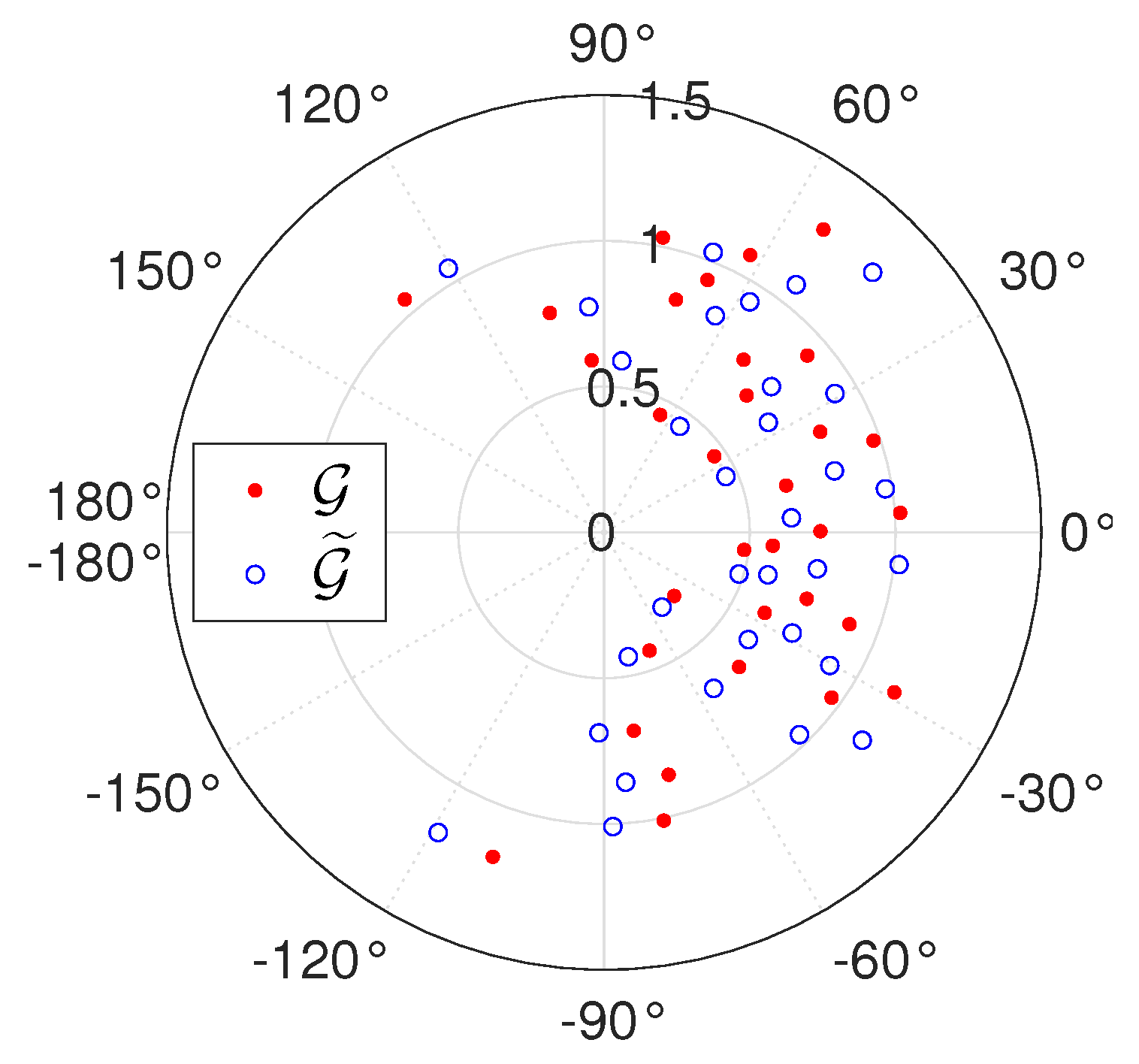
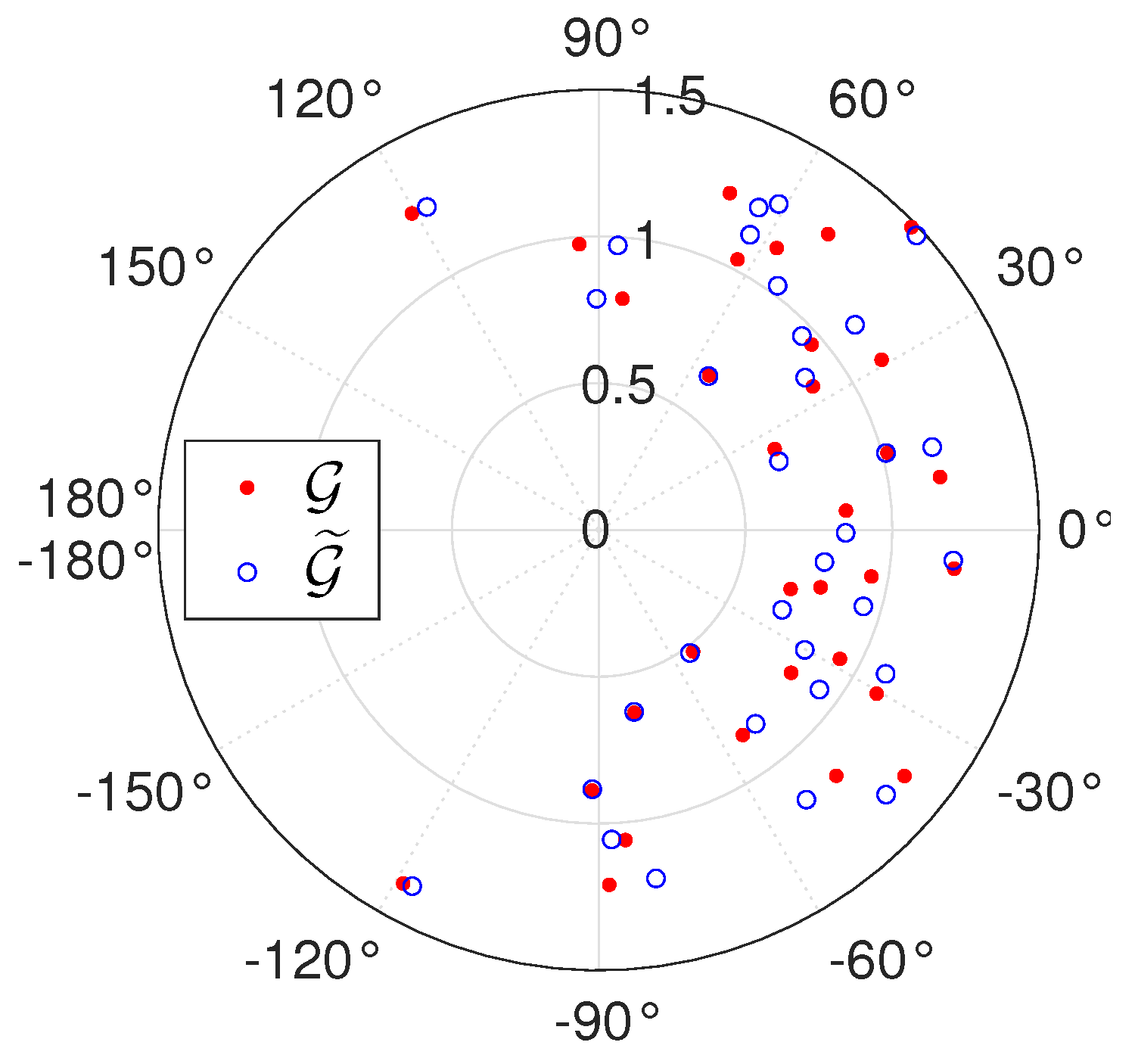
5.1. Amplitude Calibration
5.2. Phase Calibration
| Algorithm 1. Phase calibration algorithm from measured/experimental complex visibilities and expected/modeled visibilities of a beacon: the objective here is to retrieve the phase of the complex gains of every element of an antenna array, where n is a counter for the iterations and is an acceptable threshold for the norm of the correction term (in the numerical simulations presented in the next section, is set to ). |
|
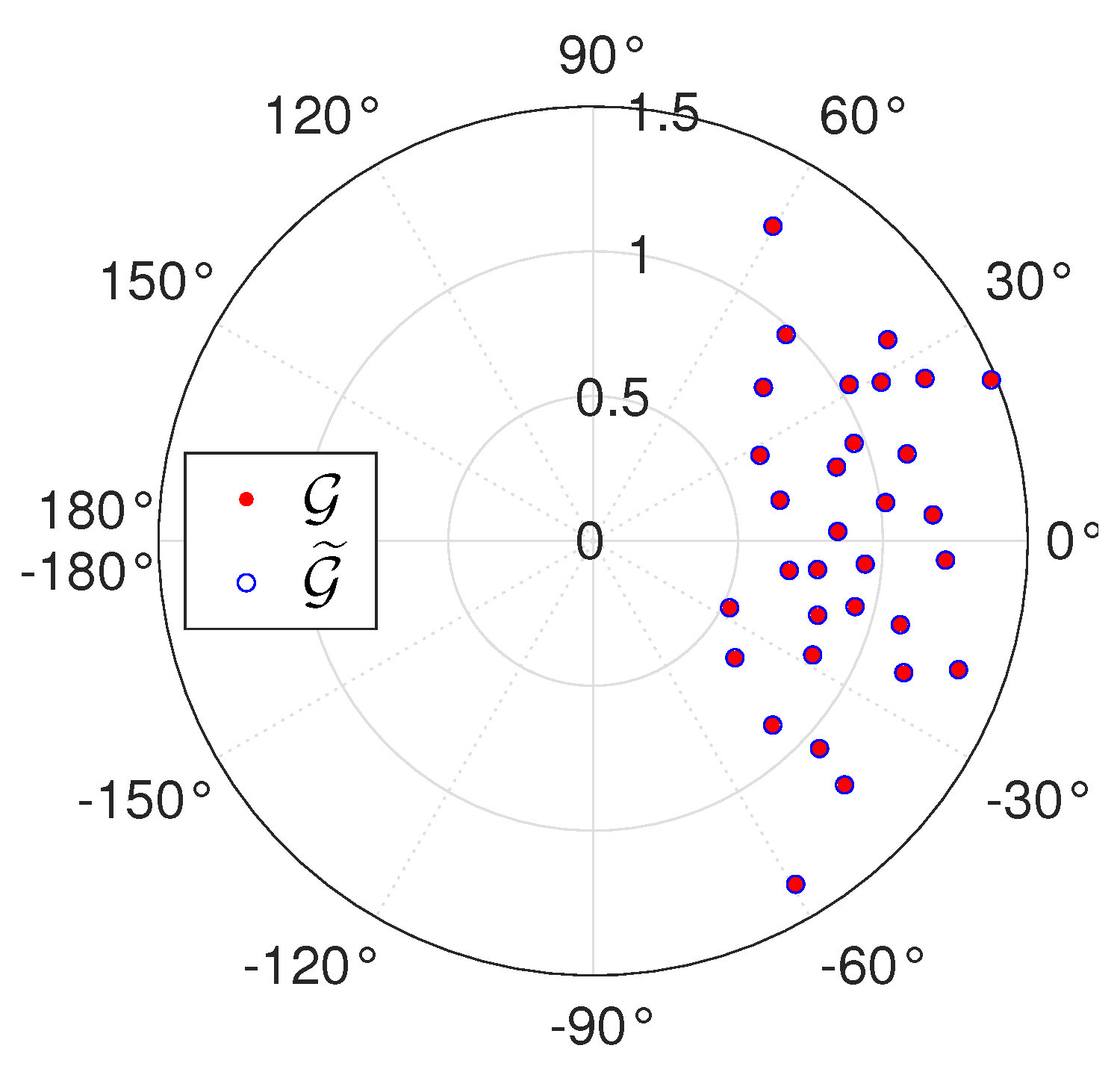
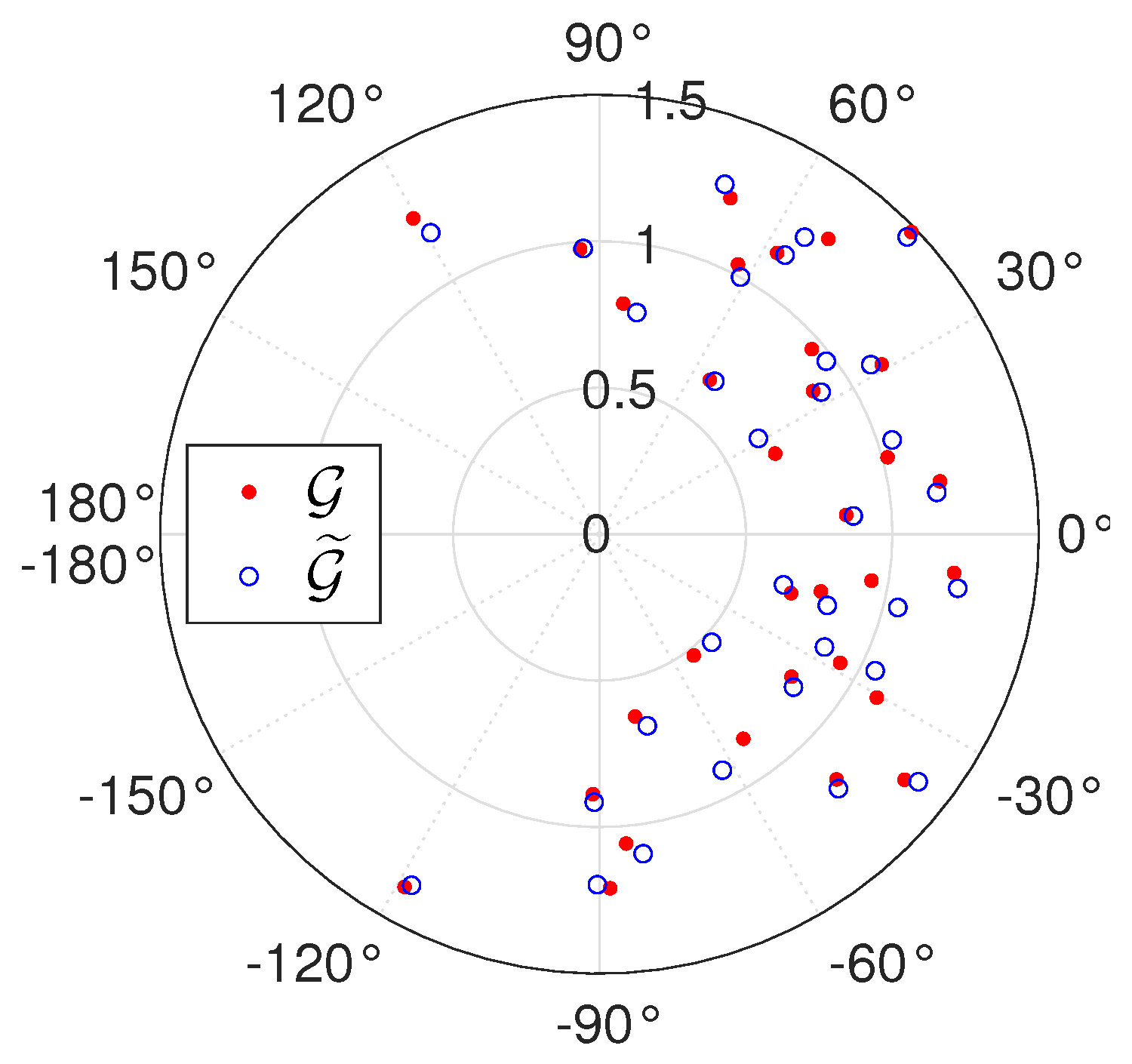
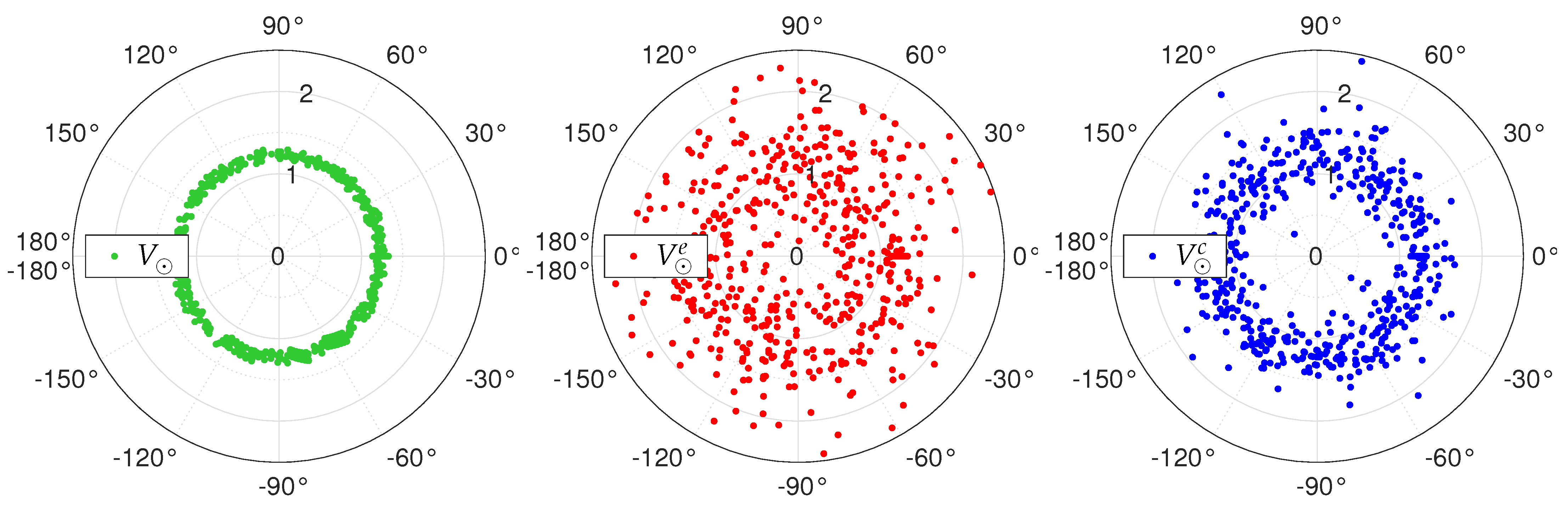
6. Numerical Simulations
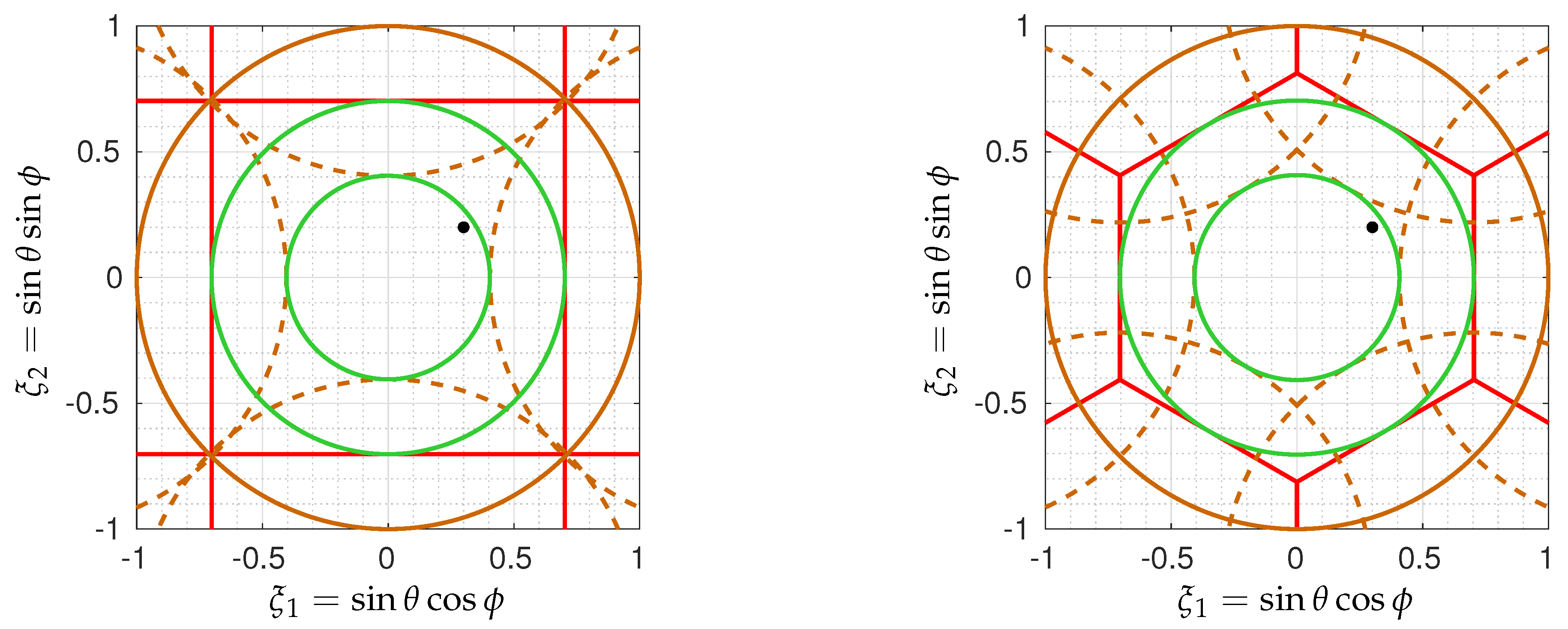
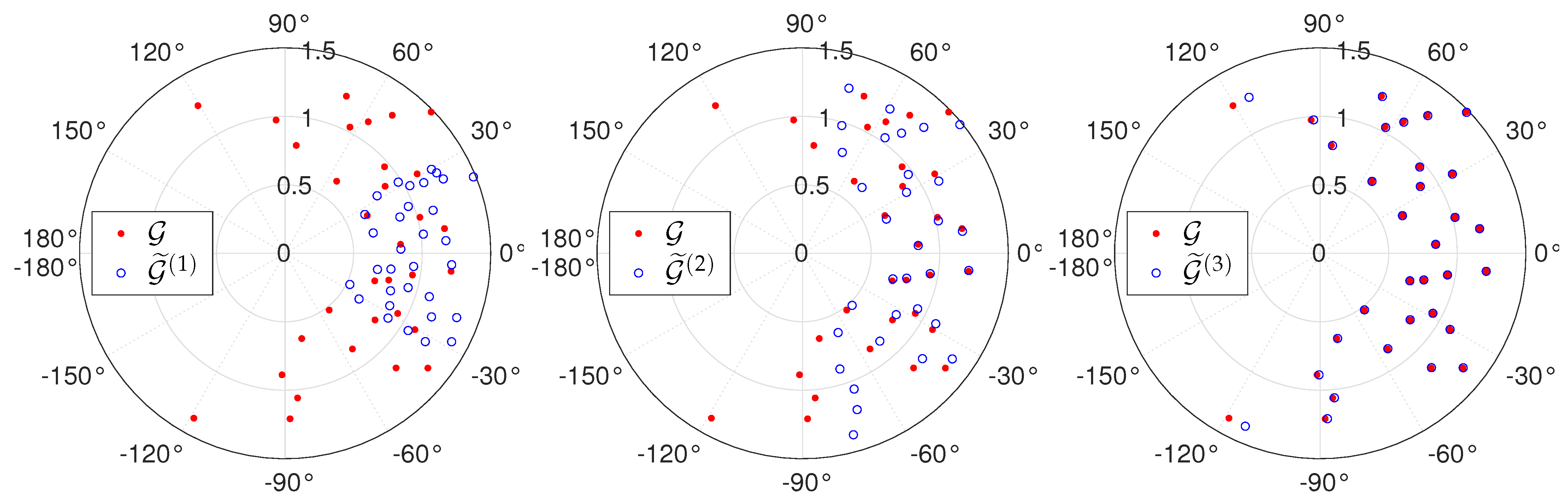
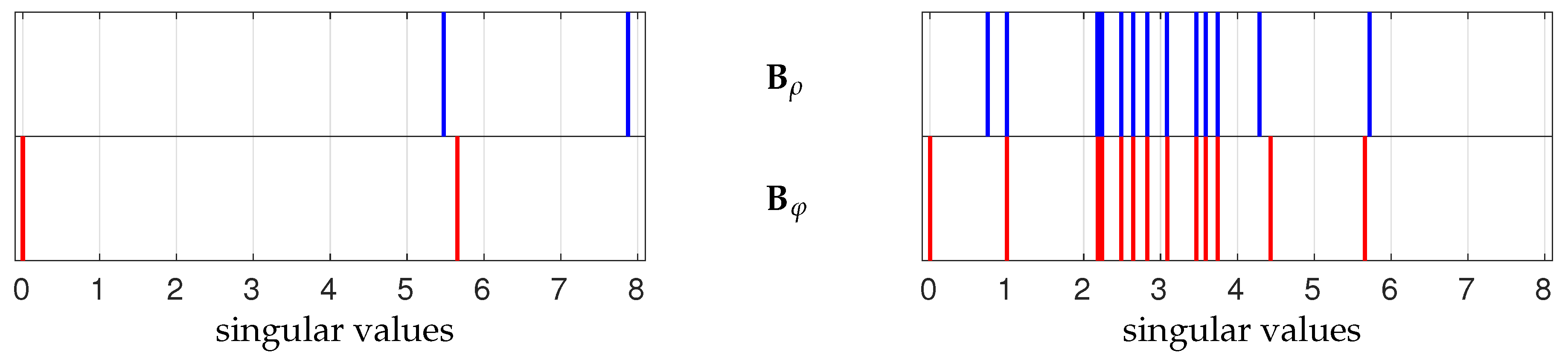
6.1. Sensitivity to Inversion Method
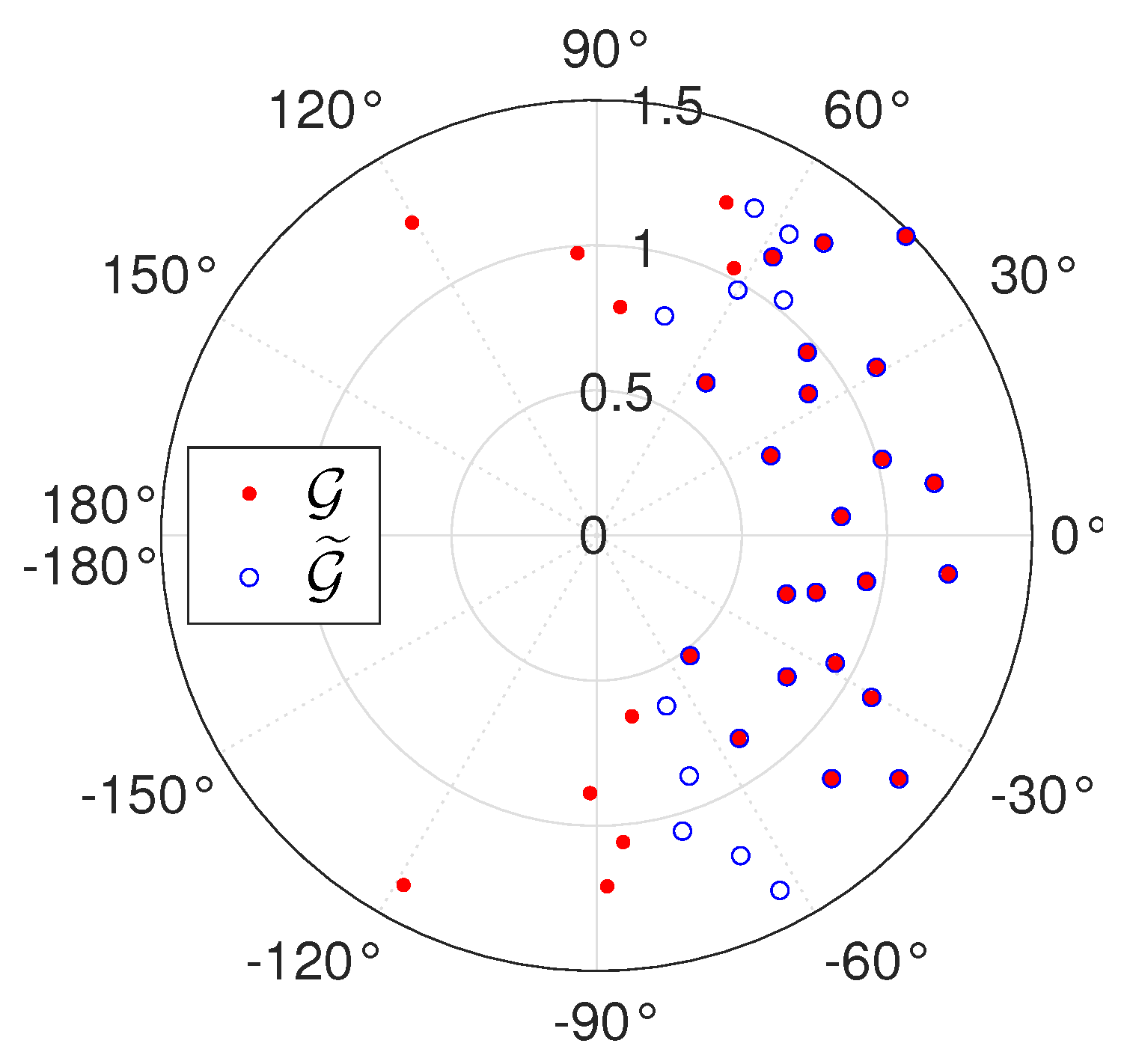
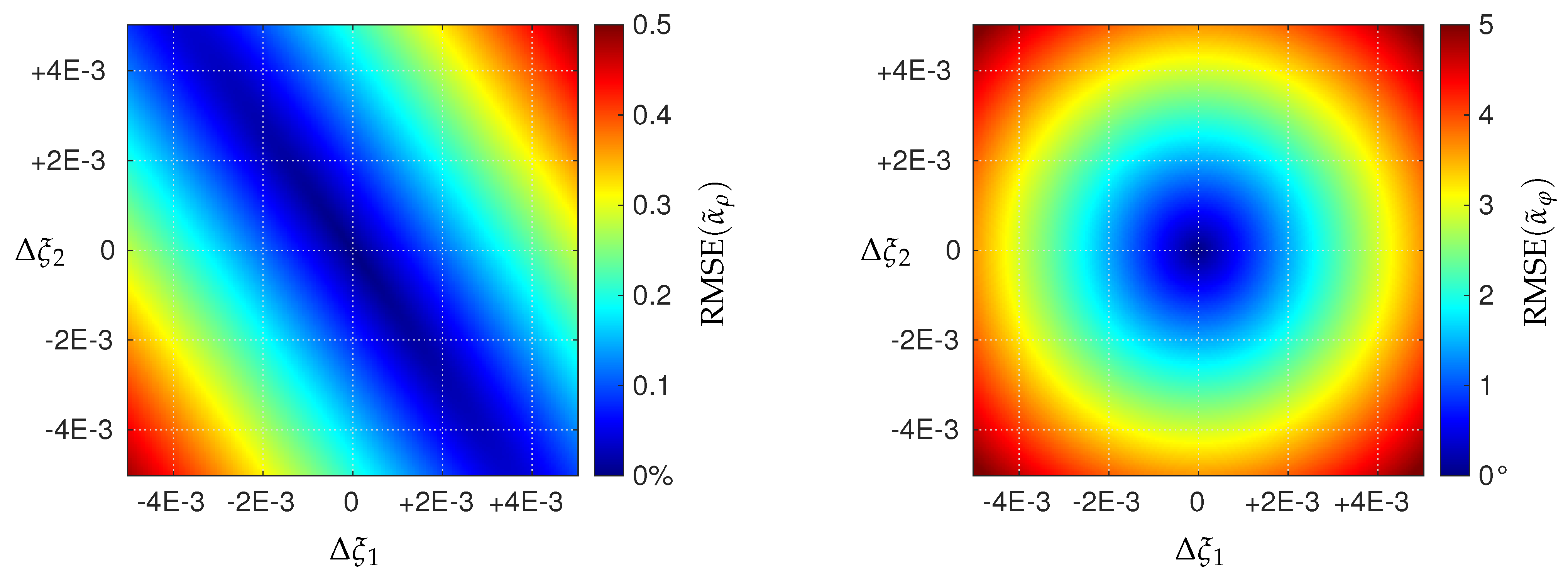
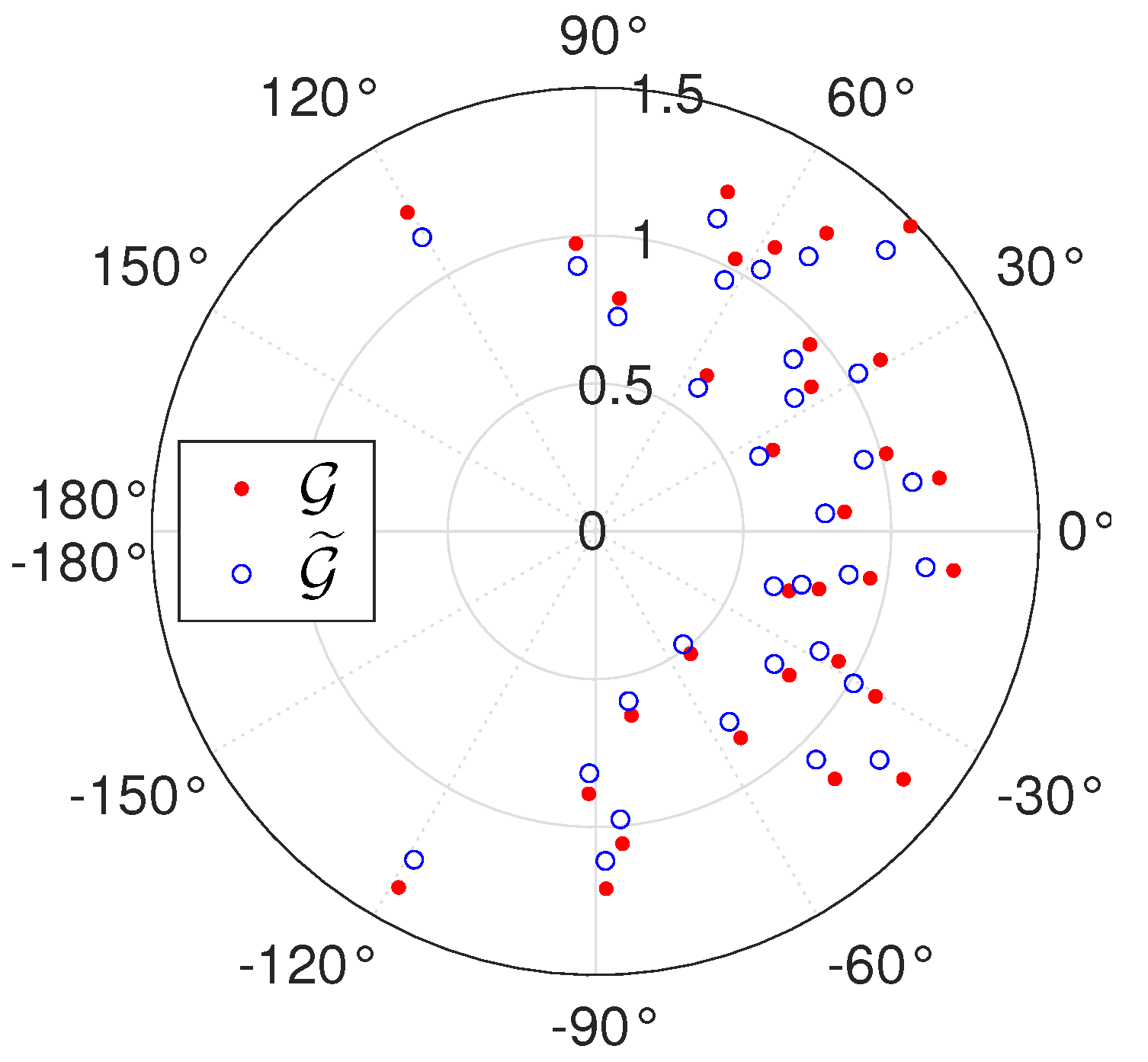
6.2. Sensitivity to Amplitude and Phase Biases
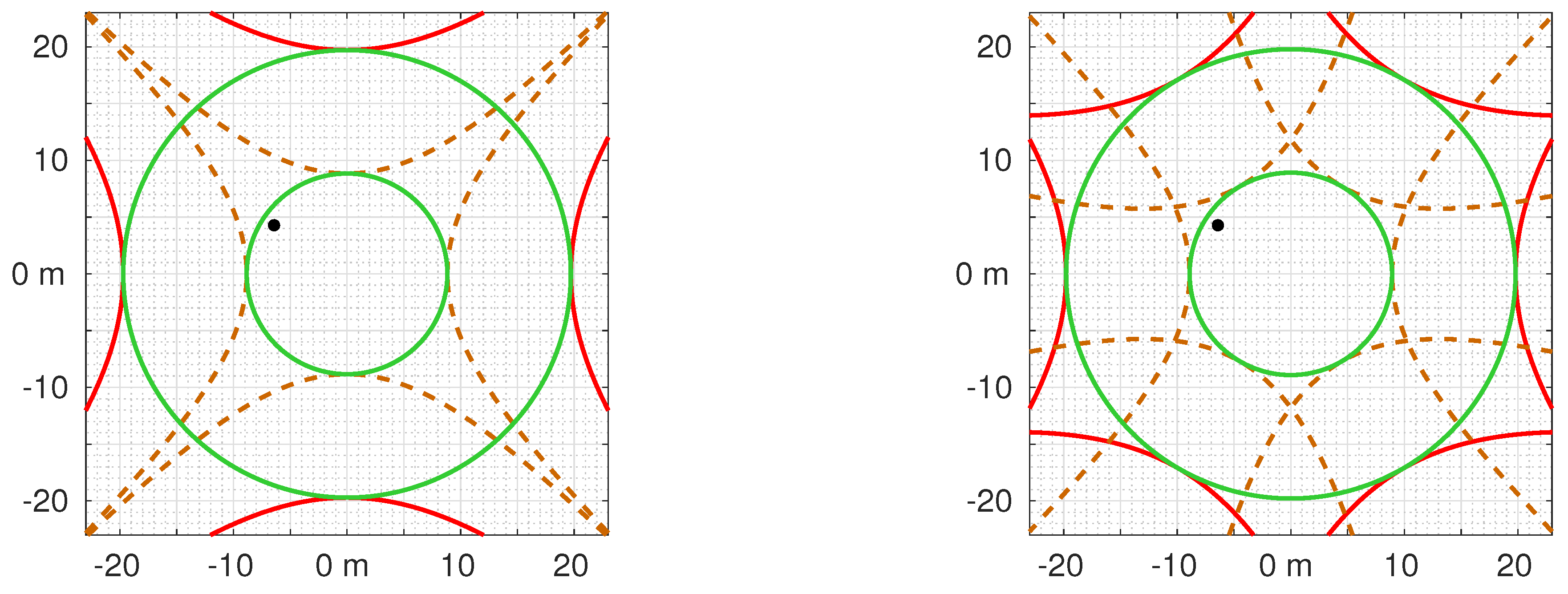
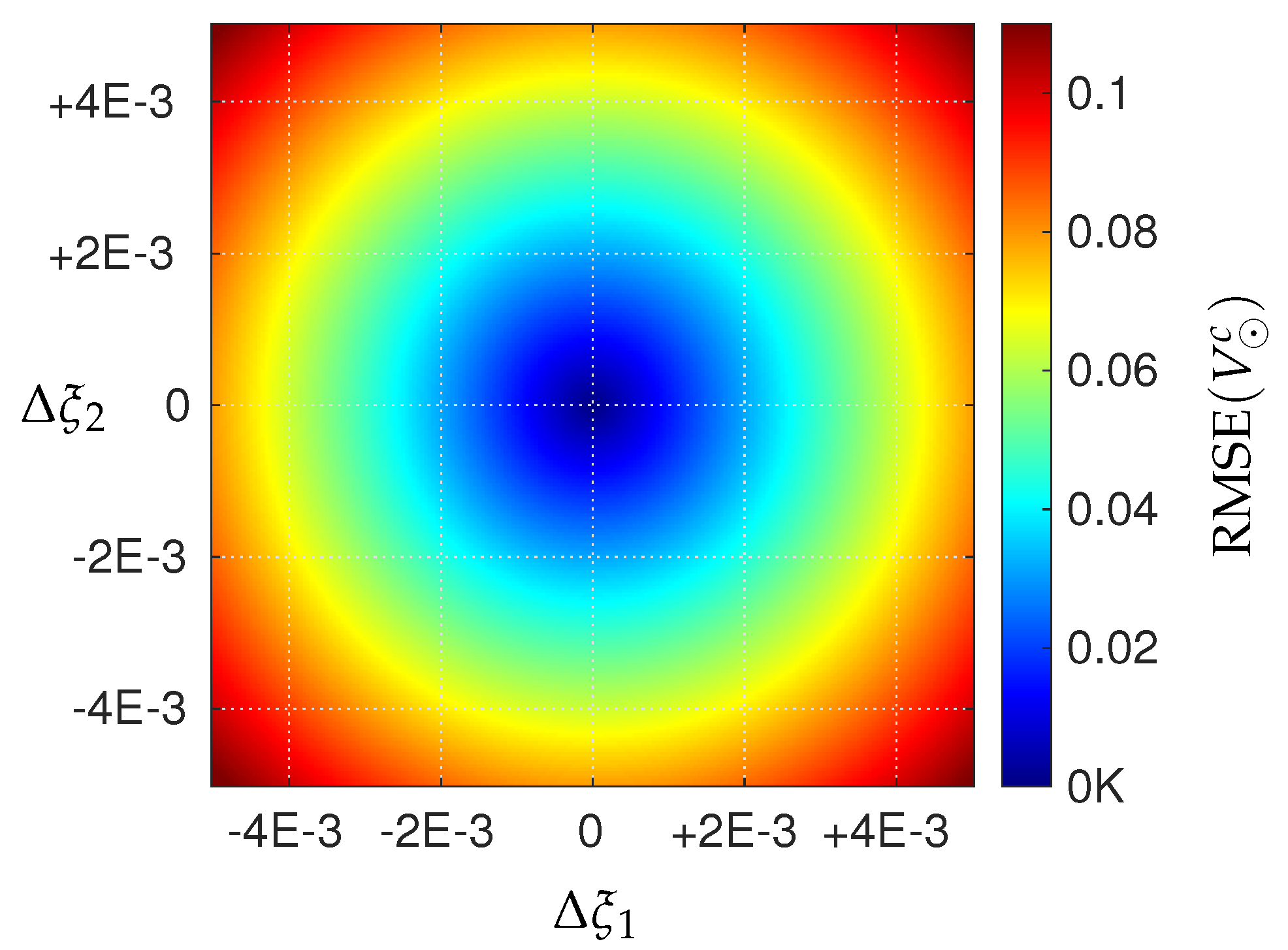
6.3. Sensitivity to Mislocation of Beacon
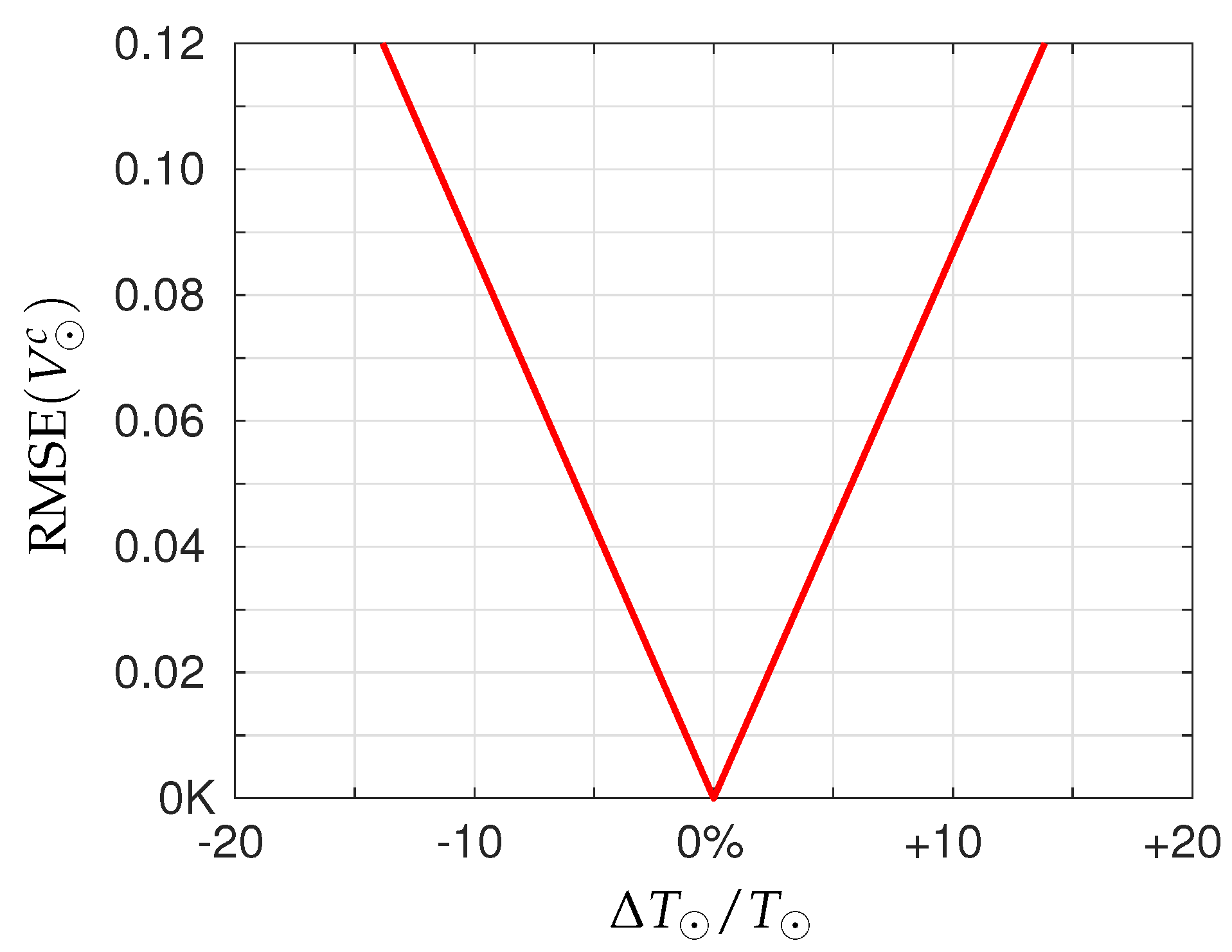
6.4. Sensitivity to Wrong Temperature of Beacon
6.5. Sensitivity to Missing Baselines
6.6. Sensitivity to Random Radiometric Noise
7. Discussion
8. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Operators Involved in Amplitude and Phase Calibration
Appendix A.1. Uniform Assignment Operator
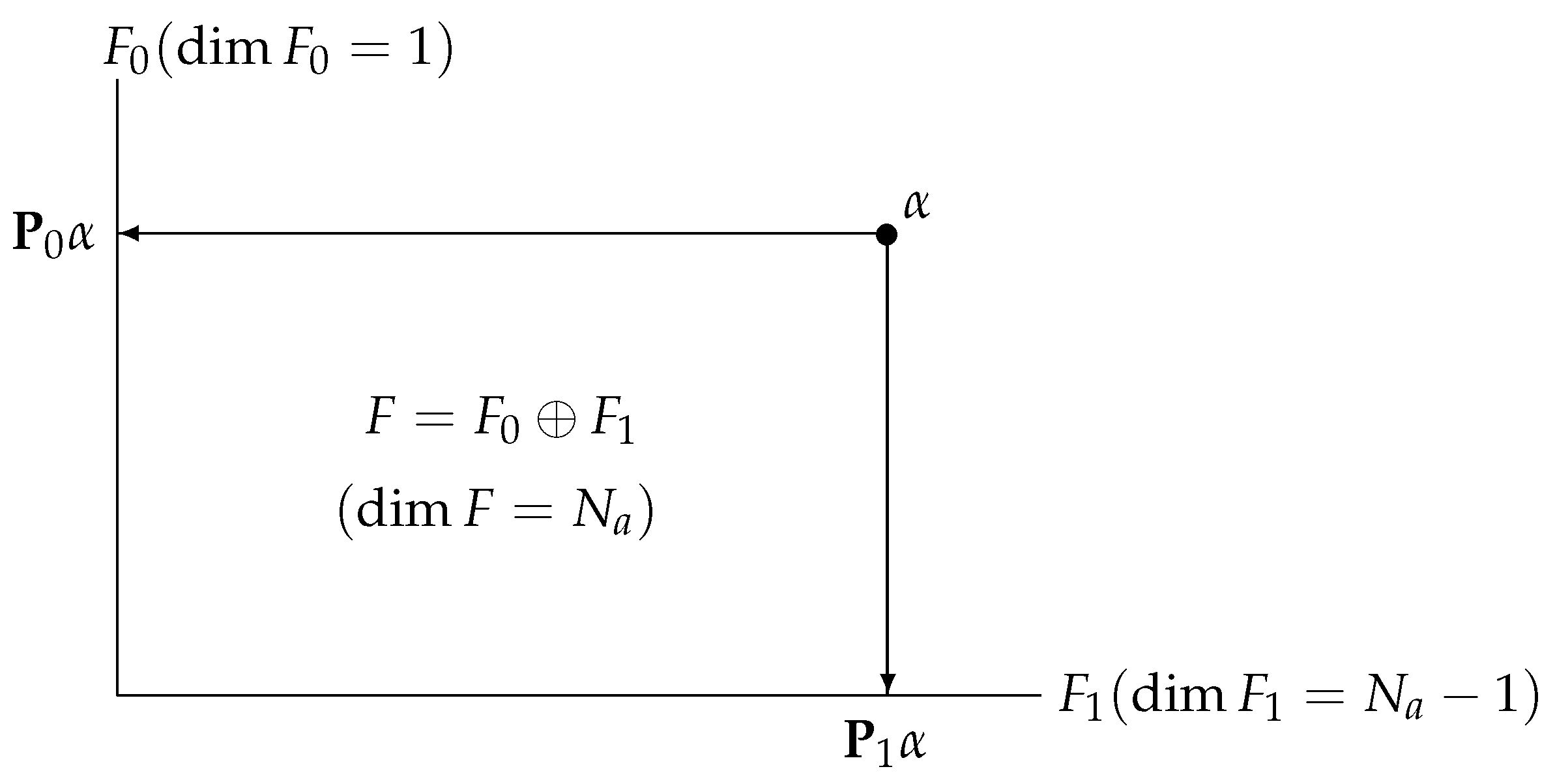
Appendix A.2. Amplitude Aberration Operator
Appendix A.3. Phase Aberration Operator
Appendix B. Gauss–Newton Algorithm for Phase Calibration
Appendix B.1. Gauss–Newton Principle
Appendix B.2. Application to Phase Calibration
| 1 | In computer arithmetic, a multiply–accumulate (MAC) or multiply–add (MAD) operation is a common step that multiplies two numbers b and c and adds that product to an accumulator a so that the operation is summarized by the expression ; fast MAC or MAD units can greatly speed up many computations that involve the accumulation of products like those encountered in numerical linear algebra with dot products and matrix multiplications. |
| 2 | More exactly, after identifying the floating point operations in the source code of the kernel functions k_sin.c and k_cos.c, it turns out that the calculation of a sine requires 8 or 10 MACs, depending on the argument, while a cosine evaluation requires 9 or 11 MACs, depending again on the argument. |
| 3 | In linear algebra, regardless of the numerical method, when a linear system has several solutions because the null space of is not reduced to the empty set, the minimum-norm solution is obtained in the orthogonal of . Indeed, for any , by definition, so that and . The pseudo-inverse of is therefore defined by the relation . |
References
- Ulaby, F.; Moore, R.; Fung, A. Microwave Remote Sensing—Active and Passive, 1st ed.; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Bracewell, R.N.; Roberts, J.A. Aerial Smoothing in Radio Astronomy. Aust. J. Phys. 1954, 7, 615–640. [Google Scholar]
- Ryle, M.; Hewish, A. The Synthesis of Large Radio Telescopes. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1960, 120, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruf, C.S.; Swift, C.T.; Tanner, A.B.; Le Vine, D.M. Interferometric synthetic aperture microwave radiometry for the remote sensing of the Earth. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1988, 26, 597–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbella, I.; Duffo, N.; Vall-llossera, M.; Camps, A.; Torres, A. The Visibility Function in Interferometric Aperture Synthesis Radiometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 1677–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anterrieu, É. A Resolving Matrix Approach for Synthetic Aperture Imaging Radiometers. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 1649–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, A.R.; Moran, J.W.; Swenson, G.W. Interferometry and Synthesis in Radio Astronomy, 3rd ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Barré, H.; Duesmann, B.; Kerr, Y.H. SMOS: The Mission and the System. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiot, T.; Goldstein, C. Impact of calibration on the performance of a total power radiometer. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience And Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS 2007), Barcelona, Spain, 23–28 July 2007. [Google Scholar]
- McMullan, K.D.; Brown, M.A.; Martín-Neira, M.; Rits, W.; Ekholm, S.; Lemanczyk, J. SMOS: The Payload. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 594–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, F.; Camps, A.; Bara, J.; Corbella, I.; Ferrero, R. On-board phase and modulus calibration of large aperture synthesis radiometers: Study applied to MIRAS. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1996, 34, 1000–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Maghraby, A.K.S.; Grubisic, A.; Colombo, C.; Tatnall, A. A novel interferometric microwave radiometer concept using satellite formation flight for geostationary atmospheric sounding. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 3487–3498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, R. Types of NDB. Radio User 2016, 11, 48–49. [Google Scholar]
- El Maghraby, A.K.S.; Park, H.; Camps, A.; Grubisic, A.; Colombo, C.; Tatnall, A. Phase and Baseline Calibration for Microwave Interferometric Radiometers Using Beacons. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 5242–5253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.B.; Carilli, C.L.; Perley, R.A. (Eds.) Synthesis Imaging in Radio Astronomy II. In ASP Conference Series; The University of New Mexico: Albuquerque, NM, USA, 1999; Volume 180. [Google Scholar]
- Sostronek, M.; Matejcek, M.; Baráni, Z. Design and Implementation of Output Circuitry for Millimeter-wave Direct Detection Radiometer. Sci. Mil. 2023, 18, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE 521-2019; IEEE Standard Letter Designations for Radar-Frequency Bands. IEEE Standards Association: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020.
- European Communications Office. The Protection of the Earth Exploration-Satellite Service (passive) in the 1400–1427 MHz Band. In Proceedings of the Minutes of the 44th Meeting of the Electronic Communications Committee, Dublin, Ireland, 28 February–3 March 2017. Available online: https://docdb.cept.org/ (accessed on 16 March 2025).
- Anterrieu, É.; Cabot, F.; Kerr, Y.H.; Amiot, T.; Valat, D.; Lestarquit, L. Synchronization of Radio Signals for the Unconnected L-Band Interferometer Demonstrator (ULID). In Proceedings of the IEEE International Geoscience And Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS 2021), Brussels, Belgium, 12–16 July 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Hagen, J.B.; Farley, D.T. Digital-Correlation Techniques in Radio Science. Radio Sci. 1973, 8, 775–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, H. Coherence theory of radio-astronomical measurements. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1967, 15, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swenson, G.W.; Mathur, N.C. The interferometer in radio astronomy. Proc. IEEE 1968, 56, 2114–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J.L. Array antennas: New applications for an old technique. IEEE Spectr. 1964, 1, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijnholds, S.J.; van der Tol, S.; Nijboer, R.; van der Veen, A.-J. Calibration challenges for future radio telescopes. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2010, 27, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grobler, T.L.; Nunhokee, C.D.; Smirnov, O.M.; van Zyl, A.J.; de Bruyn, A.G. Calibration artefacts in radio interferometry–I. Ghost sources in Westerbork Synthesis Radio Telescope data. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 439, 4030–4047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijnholds, S.J.; Grobler, T.L.; Smirnov, O.M. Calibration artefacts in radio interferometry–II. Ghost patterns for irregular arrays. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 457, 2331–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grobler, T.L.; Stewart, A.J.; Wijnholds, S.J.; Kenyon, J.S.; Smirnov, O.M. Calibration artefacts in radio interferometry–III. Phase-only calibration and primary beam correction. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2016, 461, 2975–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anterrieu, É.; Lafuma, P.; Jeannin, N. An Algebraic Comparison of Synthetic Aperture Interferometry and Digital Beam Forming in Imaging Radiometry. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Cittert, P.H. Die Wahrscheinliche Schwingungsverteilung in Einer von Einer Lichtquelle Direkt Oder Mittels Einer Linse Beleuchteten Ebene. Physica 1934, 1, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zernike, F. The Concept of Degree of Coherence and its Application to Optical Problems. Physica 1934, 5, 785–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anterrieu, É.; Yu, L.; Jeannin, N. A Comprehensive Comparison of Far-Field and Near-Field Imaging Radiometry in Synthetic Aperture Interferometry. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvan, K.T.; Janaswamy, R. Fraunhofer and Fresnel Distances: Unified Derivation for Aperture Antennas. IEEE Antennas Propag. Mag. 2017, 59, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, P.C. Rank-Deficient and Discrete Ill-Posed Problems, 1st ed.; Society for Industrial & Applied Mathematics: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Picard, B.; Anterrieu, E. Comparizon of regularized inversion methods in synthetic aperture imaging radiometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodberlet, M.A. Improved Image Reconstruction Techniques for Synthetic Aperture Radiometers. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 1362–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penrose, R. A generalized inverse for matrices. Math. Proc. Camb. Philos. Soc. 1955, 51, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, P.C. The Truncated SVD as a Method for Regularization. BIT Numer. Math. 1987, 27, 534–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smithies, F. The Eigen-Values and Singular Values of Integral Equations. Proc. Lond. Math. Soc. 1938, 43, 255–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornwell, T.J.; Wilkinson, P.N. A new method for making maps with unstable radio interferometers. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1981, 196, 1067–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lannes, A. Phase and Amplitude Calibration in Aperture Synthesis. Algebraic Structures. Inverse Probl. 1991, 7, 261–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patnaik, A.R.; Browne, I.W.A.; Wilkinson, P.N.; Wrobel, J.M. Interferometer phase calibration sources–I. The region 35° ≤ δ ≤ 75°. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1992, 254, 655–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, I.W.A.; Patnaik, A.R.; Wilkinson, P.N.; Wrobel, J.M. Interferometer phase calibration sources–II. The region 0° ≤ δ ≤ 20°. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1998, 293, 257–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, P.N.; Browne, I.W.A.; Patnaik, A.R.; Wrobel, J.M.; Sorathia, B. Interferometer phase calibration sources–III. The regions 20° ≤ δ ≤ 35° and 75° ≤ δ ≤ 90°. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1998, 300, 790–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, T.J.; Readhead, A.C.S. Image Formation by Self-Calibration in Radio Astronomy. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 1984, 22, 97–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Neira, M.; Ribǿ, S.; Martín-Polegre, A.J. Polarimetric Mode of MIRAS. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 1755–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayle, F.; Wigneron, J.-P.; Kerr, Y.H.; Waldteufel, P.; Anterrieu, E.; Orlhac, J.-C.; Chanzy, A.; Marloie, O.; Bernardini, M.; Sobjaerg, S.; et al. Two-dimensional synthetic aperture images over a land surface scene. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 710–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Fur, G.; Robin, G.; Adnet, N.; Duchesne, L.; Belot, D.; Feat, L.; Elis, K.; Bellion, A.; Contreres, R. Implementation of a VHF Spherical Near-Field Measurement Facility at CNES. In Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the Antenna Measurement Techniques Association (AMTA 2016), Austin, TX, USA, 30 October–3 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatnagar, S.; Cornwell, T.J.; Golap, K.; Uson, J.M. Correcting direction-dependent gains in the deconvolution of radio interferometric images. Astron. Astrophys. 2008, 487, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjorck, A. Numerical Methods for Least Squares Problems, 1st ed.; Society for Industrial & Applied Mathematics: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Hestenes, M.R.; Stiefel, E. Methods of Conjugate Gradients for Solving Linear Systems. J. Res. Natl. Bur. Stand. 1952, 49, 409–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parhami, B. Computer Arithmetic: Algorithms and Hardware Designs, 3rd ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrmann, D.R. Estimation of sensor gain and phase. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1994, 42, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nocedal, J.; Wright, S. Numerical Optimization, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Higham, N.J. Accuracy and Stability of Numerical Algorithms, 2nd ed.; Society for Industrial & Applied Mathematics: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Lannes, A. Integer ambiguity resolution in phase closure imaging. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2001, 18, 1046–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marron, J.C.; Sanchez, P.P.; Sullivan, R.C. Unwrapping algorithm for least-squares phase recovery from the modulo 2π bispectrum. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 1990, 7, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornwell, T.J. The applications of closure phase to astronomical imaging. Science 1989, 245, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, P.J.; Ronchetti, E.M. Robust Statistics, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Camps, A.; Corbella, I.; Bará, J.; Torres, F. Radiometric sensitivity computation in aperture synthesis interferometric radiometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracewell, R. The Fourier Transform and Its Applications, 3rd ed.; McGraw-Hill: New-York City, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenceau, J. Geometry and the visual brain. J. Physiol. 2003, 97, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.R. An Introduction to Error Analysis: The Study of Uncertainties in Physical Measurements, 2nd ed.; University Science Books: New-York City, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Anjum, R.L.; Mumford, S. Causation in Science and the Methods of Scientific Discovery, 1st ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lannes, A. Remarkable algebraic structures of phase-closure imaging and their algorithmic implications in aperture synthesis. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 1990, 7, 500–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, S. A First Course in Calculus, 5th ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
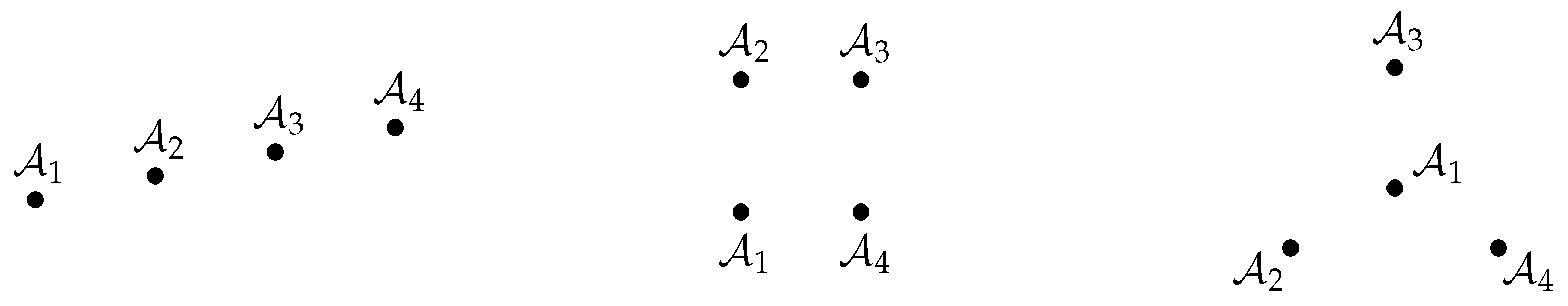









| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||||||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||||||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||||||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||||||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||||||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anterrieu, E. Amplitude and Phase Calibration with the Aid of Beacons in Microwave Imaging Radiometry by Aperture Synthesis: Algebraic Aspects and Algorithmic Implications. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1098. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17061098
Anterrieu E. Amplitude and Phase Calibration with the Aid of Beacons in Microwave Imaging Radiometry by Aperture Synthesis: Algebraic Aspects and Algorithmic Implications. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(6):1098. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17061098
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnterrieu, Eric. 2025. "Amplitude and Phase Calibration with the Aid of Beacons in Microwave Imaging Radiometry by Aperture Synthesis: Algebraic Aspects and Algorithmic Implications" Remote Sensing 17, no. 6: 1098. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17061098
APA StyleAnterrieu, E. (2025). Amplitude and Phase Calibration with the Aid of Beacons in Microwave Imaging Radiometry by Aperture Synthesis: Algebraic Aspects and Algorithmic Implications. Remote Sensing, 17(6), 1098. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17061098






