A Dual-Branch Network of Strip Convolution and Swin Transformer for Multimodal Remote Sensing Image Registration
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
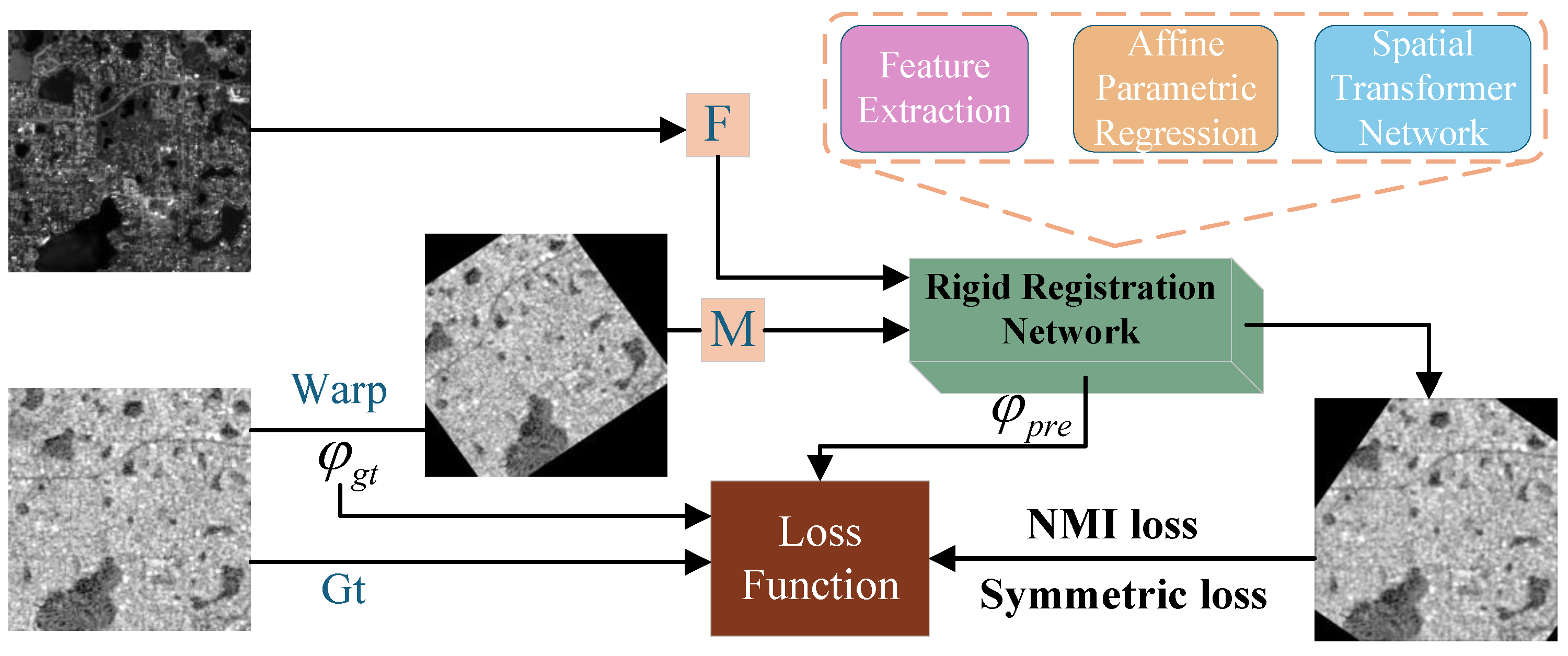
- We propose an end-to-end multimodal remote sensing image registration network that incorporates dual-branch feature extraction. This network consists of three components: feature extraction, affine parameter regression, and a spatial transformation module.
- (2)
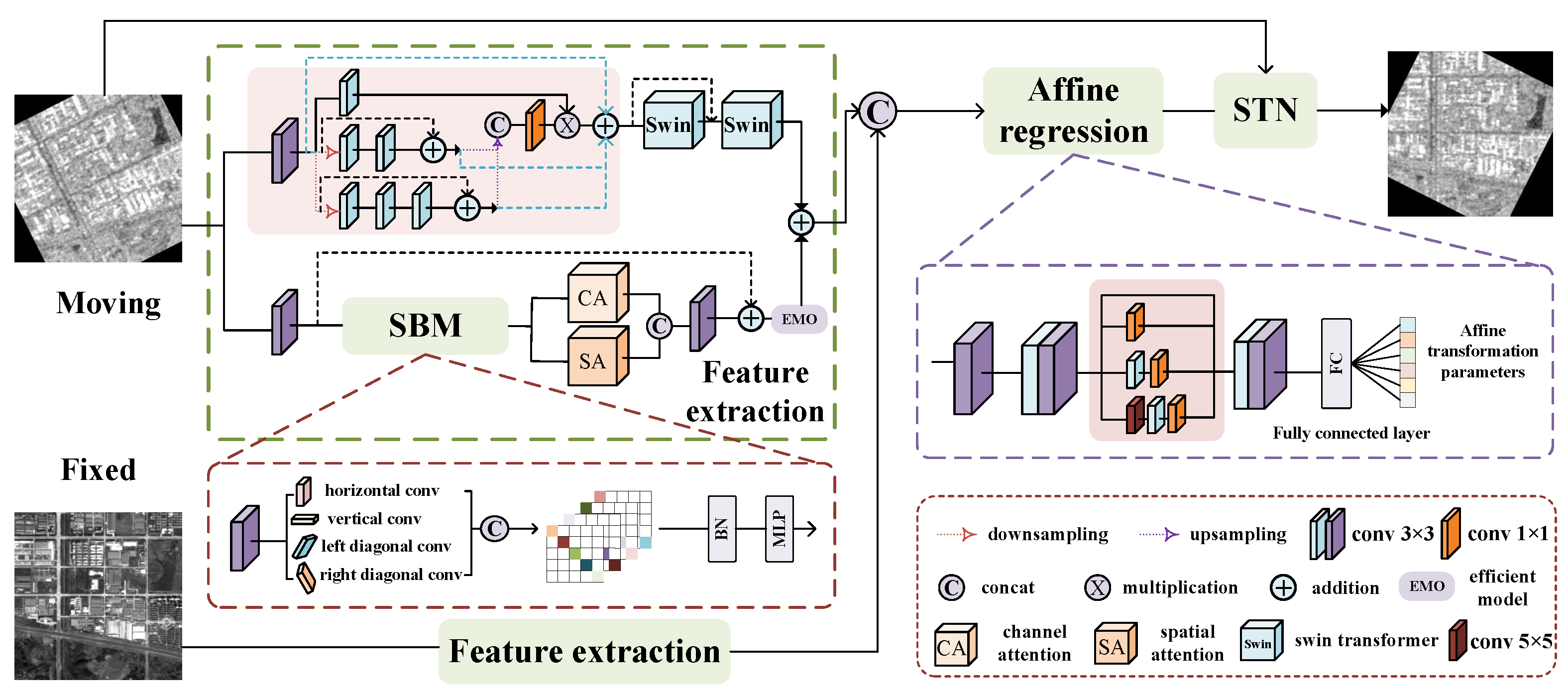
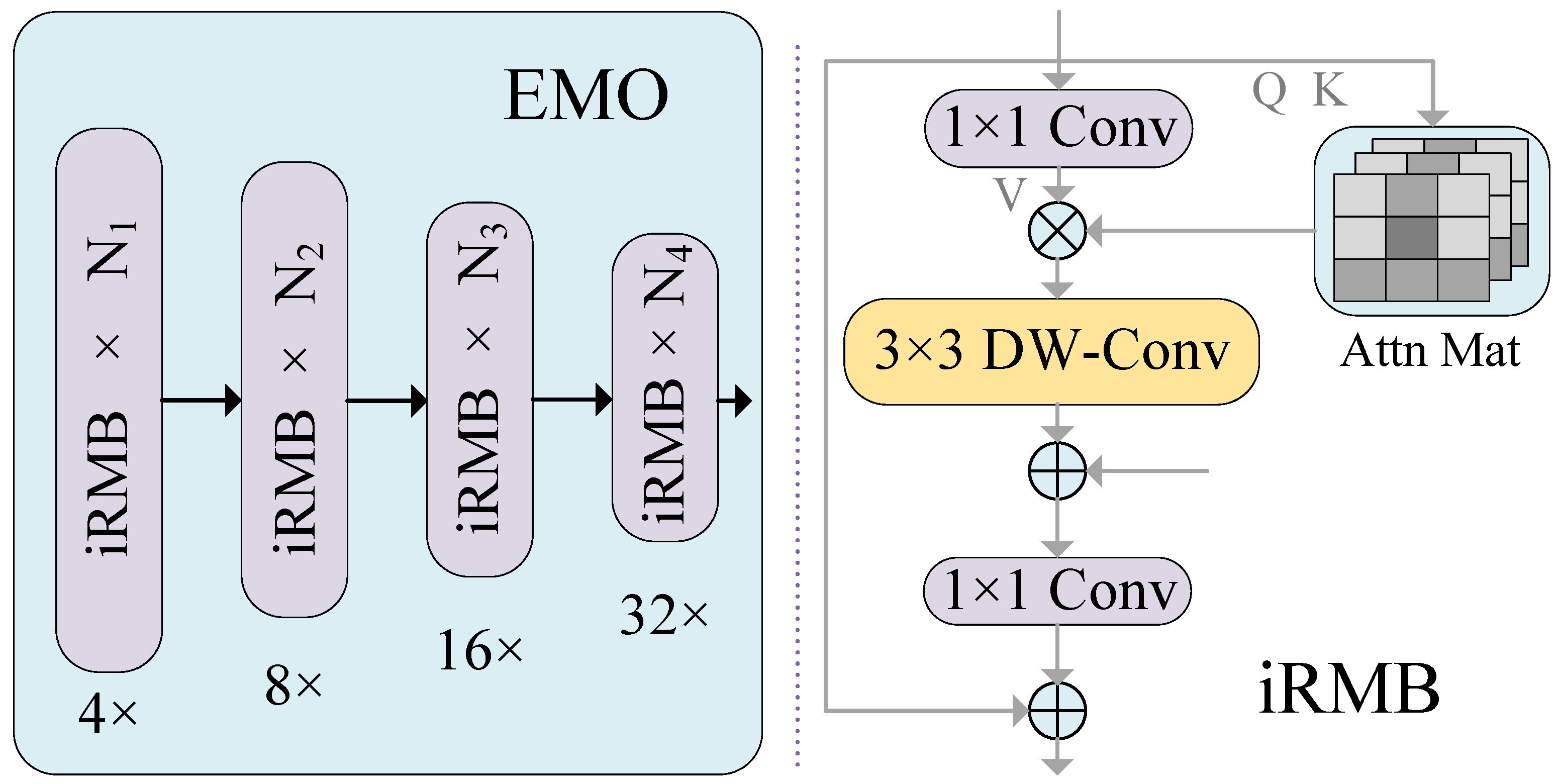
- In our dual-branch feature extraction module, the upper branch is designed for multi-scale feature extraction, allowing it to account for information across various scales and levels. It employs the Swin Transformer self-attention mechanism to model long-range dependencies within the image. In the lower branch, we introduce a module that integrates strip convolution blocks, batch normalization (BN), and multilayer perceptron (MLP). We define this module as the SBM module, which aims to capture remote contextual information from four different directions. Additionally, we combine channel and spatial attention modules to minimize irrelevant feature interference.
- (3)
- We design convolutional kernels of varying sizes in parallel within the affine parameter regression network to enhance the adaptability of the network to a diverse range of features. This approach increases the flexibility of the model and generalizability across different input images.
- (4)
- We conduct extensive experiments on three datasets, panchromatic–multispectral, SAR–optical, and infrared–optical, with different scales of rigid transformations. Compared to the most advanced multimodal remote sensing image registration methods, our experiments demonstrate strong performance, validating the effectiveness of our network in image registration.
2. Related Works
2.1. Based on Traditional Registration Method
2.2. Based on Learning Registration Method
3. Method
3.1. The Overview of Network Framework
3.2. Feature Extraction Module
3.2.1. The Upper Branch Feature Extraction
3.2.2. The Lower Branch Feature Extraction
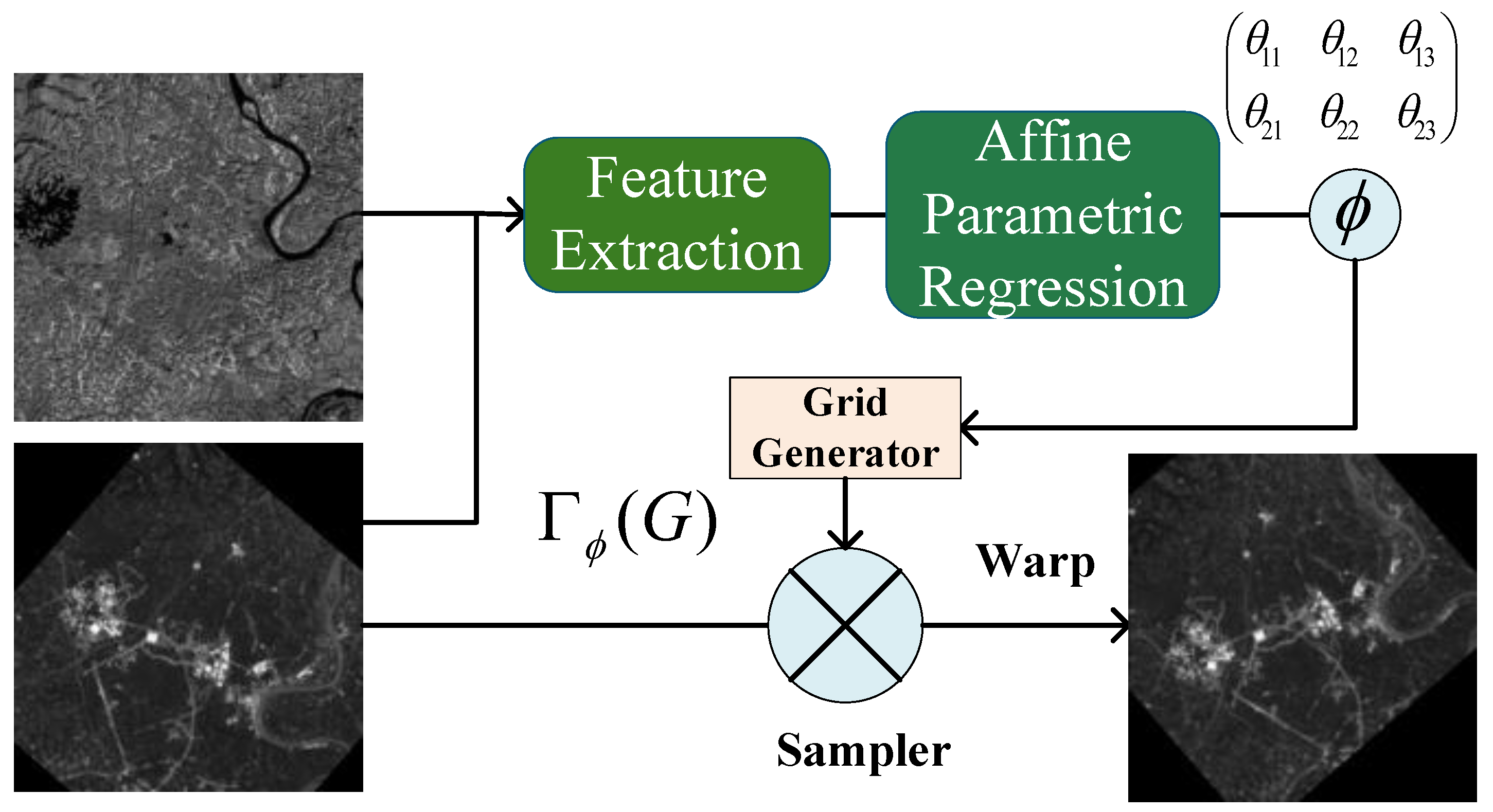
3.3. Affine Parameter Regression Module
3.4. Spatial Transformer Network (STN)
3.5. Loss Function
4. Experiments
4.1. Dataset
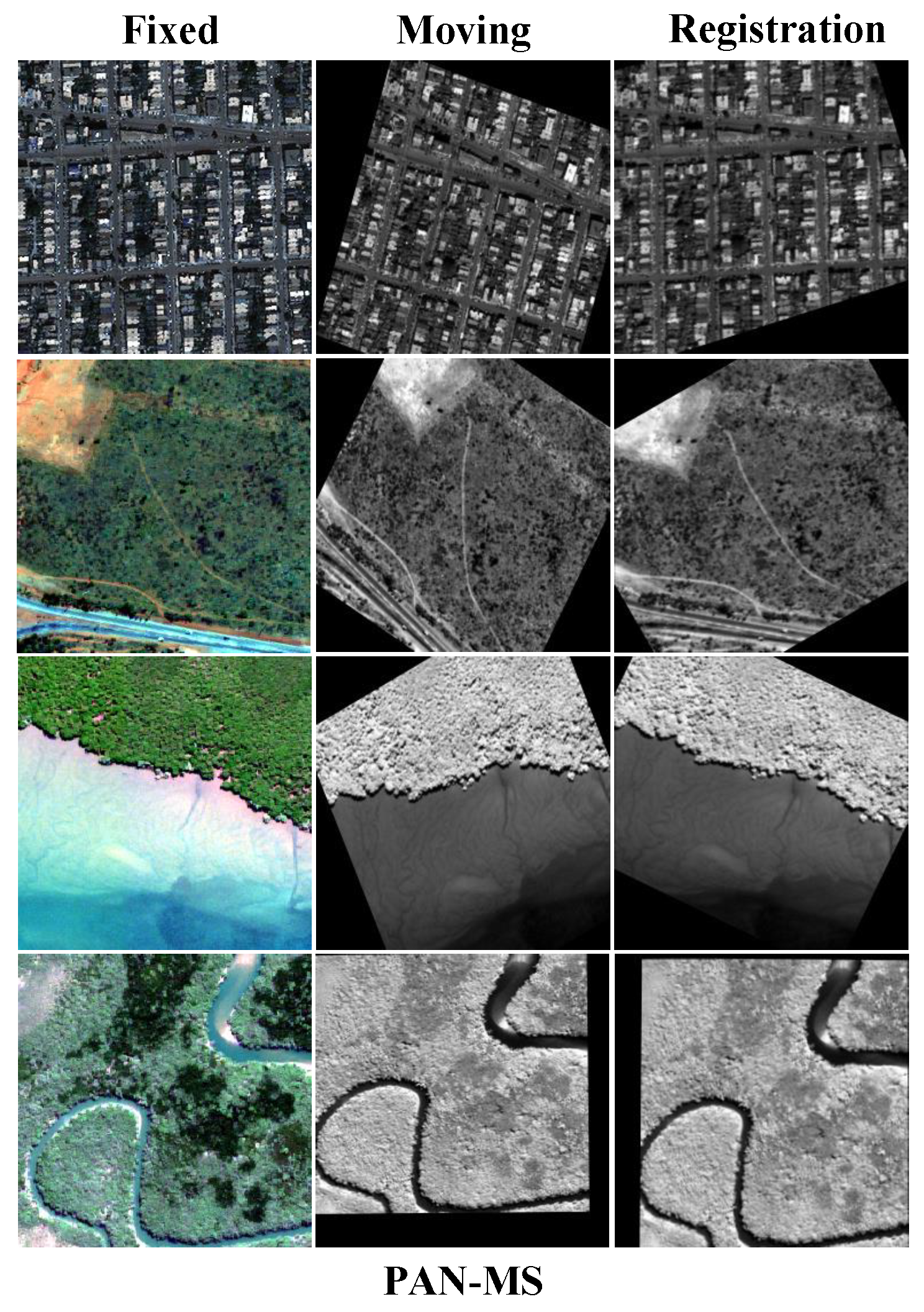
4.1.1. PAN-MS
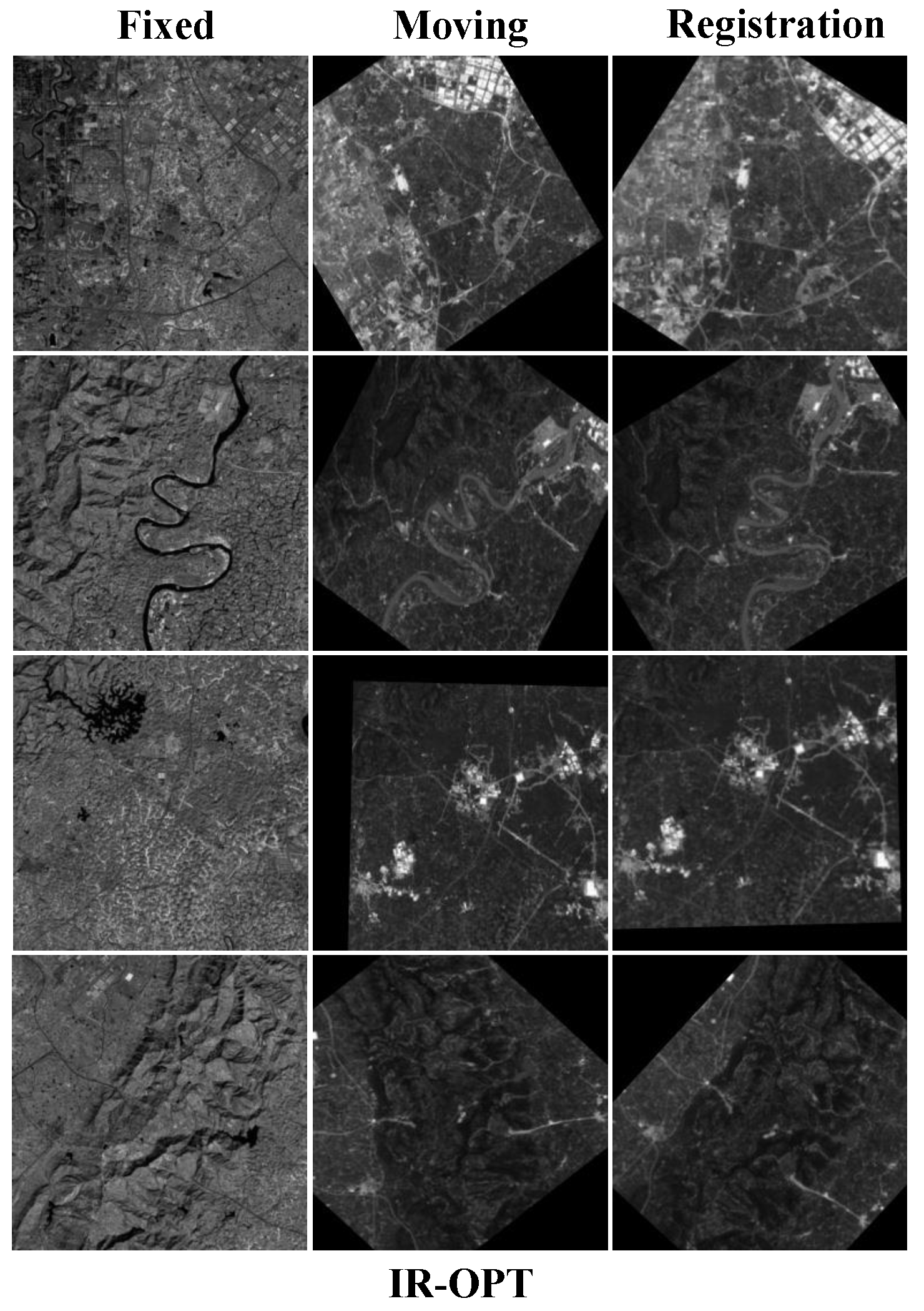
4.1.2. IR-OPT
4.1.3. SAR-OPT
4.2. Implementation Details
4.3. Evaluation Metrics
4.4. Experimental Results and Analysis
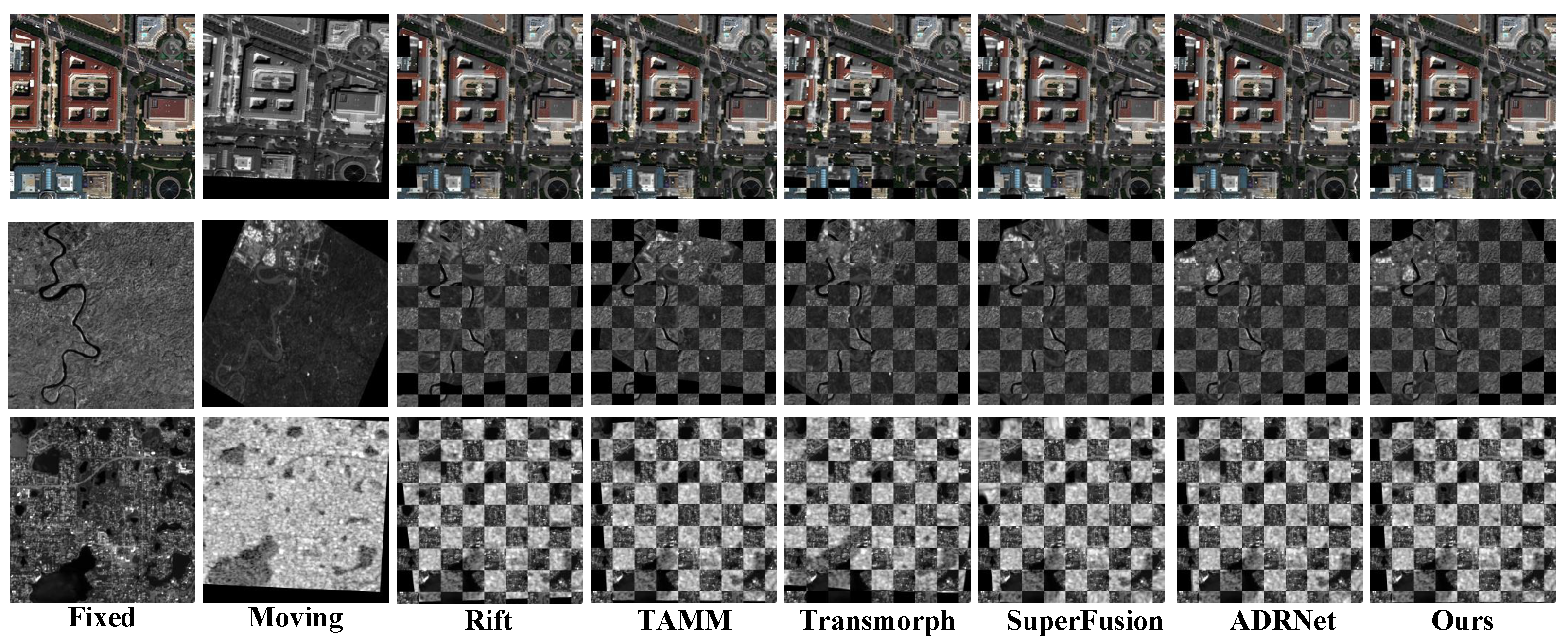
4.4.1. Qualitative Comparisons
4.4.2. Quantitative Comparisons
4.4.3. Further Result Analysis
4.5. Ablation Study
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiang, X.; Ma, J.; Xiao, G.; Shao, Z.; Guo, X. A review of multimodal image matching: Methods and applications. Inf. Fusion 2021, 73, 22–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Zhu, R.; Sun, X.; Li, X.; Xiang, D. Optical and SAR Image Registration Based on Pseudo-SAR Image Generation Strategy. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y. Review of pixel-level remote sensing image fusion based on deep learning. Inf. Fusion 2023, 90, 36–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Jin, K.; Zuo, B.; Yang, J. A novel change detection method combined with registration for SAR images. Remote Sens. Lett. 2019, 10, 669–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J. RFM-GAN: Robust feature matching with GAN-based neighborhood representation for agricultural remote sensing image registration. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2023, 20, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Zhou, L.; Pu, S.; Fan, J.; Ye, Y. Advances and challenges in multimodal remote sensing image registration. IEEE J. Miniaturization Air Space Syst. 2023, 4, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.; Shen, H.; Bai, J.; Li, X. Advances and opportunities in remote sensing image geometric registration: A systematic review of state-of-the-art approaches and future research directions. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2021, 9, 120–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, F.; Collignon, A.; Vandermeulen, D.; Marchal, G.; Suetens, P. Multimodality image registration by maximization of mutual information. IEEE Trans. Med Imaging 1997, 16, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarvaiya, J.N.; Patnaik, S.; Bombaywala, S. Image registration by template matching using normalized cross-correlation. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Advances in Computing, Control, and Telecommunication Technologies, Bangalore, India, 28–29 December 2009; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 819–822. [Google Scholar]
- Lowe, D.G. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2004, 60, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rublee, E.; Rabaud, V.; Konolige, K.; Bradski, G. ORB: An efficient alternative to SIFT or SURF. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision, Barcelona, Spain, 6–13 November 2011; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 2564–2571. [Google Scholar]
- Bay, H. Surf: Speeded up robust features. In Computer Vision—ECCV; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Xu, F.; Liu, F.; Tong, Y.; Lyu, X.; Zhou, J. Semantic segmentation of remote sensing images by interactive representation refinement and geometric prior-guided inference. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 62, 5400318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Bi, G.; Wang, X.; Nie, T.; Huang, L. Radiation-Variation Insensitive Coarse-to-Fine Image Registration for Infrared and Visible Remote Sensing Based on Zero-Shot Learning. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Zhao, R.; Pan, B.; Zou, Z.; Shi, Z. Unsupervised multimodal remote sensing image registration via domain adaptation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5626211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, F.; Liu, F.; Lyu, X.; Tong, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, J. A synergistical attention model for semantic segmentation of remote sensing images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5400916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Mu, K.; Liu, H. A Multi-Hierarchy Flow Field Prediction Network for multimodal remote sensing image registration. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2025, 18, 5232–5243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, L.H.; Marcos, D.; Lobry, S.; Tuia, D.; Schmitt, M. A deep learning framework for matching of SAR and optical imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 169, 166–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Ye, Y.; Tang, T.; Nan, K.; Qin, Y. Robust matching for SAR and optical images using multiscale convolutional gradient features. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 19, 4017605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Han, L.; Ding, M.; Liu, Z.; Cao, H. Remote sensing image registration based on deep learning regression model. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2020, 19, 8002905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Tang, T.; Zhu, B.; Yang, C.; Li, B.; Hao, S. A multiscale framework with unsupervised learning for remote sensing image registration. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5622215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaderberg, M.; Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A.; Kavukcuoglu, K. Spatial transformer networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2015, 28, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar]
- Shadaydeh, M.; Sziranyi, T. An improved mutual information similarity measure for registration of multi-modal remote sensing images. In Proceedings of the Image and Signal Processing for Remote Sensing XXI, Toulouse, France, 21–23 September 2015; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2015; Volume 9643, pp. 146–152. [Google Scholar]
- Sedaghat, A.; Mokhtarzade, M.; Ebadi, H. Uniform robust scale-invariant feature matching for optical remote sensing images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 4516–4527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellinger, F.; Delon, J.; Gousseau, Y.; Michel, J.; Tupin, F. SAR-SIFT: A SIFT-like algorithm for SAR images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 53, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Shen, L. Hopc: A novel similarity metric based on geometric structural properties for multi-modal remote sensing image matching. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2016, 3, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, C.; Li, W.; Tao, R.; Du, Q. MS-HLMO: Multiscale histogram of local main orientation for remote sensing image registration. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5626714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hu, Q.; Ai, M. RIFT: Multi-modal image matching based on radiation-variation insensitive feature transform. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 29, 3296–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Quan, D.; Liang, X.; Ning, M.; Guo, Y.; Jiao, L. A deep learning framework for remote sensing image registration. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2018, 145, 148–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, B.; Tang, J. ADRNet: Affine and Deformable Registration Networks for Multimodal Remote Sensing Images. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isola, P.; Zhu, J.Y.; Zhou, T.; Efros, A.A. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1125–1134. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.Y.; Park, T.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A. Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2223–2232. [Google Scholar]
- Du, W.L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, H.; Zhao, J.; Shao, Z.; Tian, X. A Semi-Supervised Image-to-Image Translation Framework for SAR–Optical Image Matching. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 19, 4516305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Liu, J.; Fan, X.; Liu, R. Unsupervised Misaligned Infrared and Visible Image Fusion via Cross-Modality Image Generation and Registration. In Proceedings of the Thirty-First International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, IJCAI-22, Vienna, Austria, 23–29 July 2022; pp. 3508–3515. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, K.; Gao, L.; Hong, D.; Zhang, B.; Chanussot, J. NonRegSRNet: A nonrigid registration hyperspectral super-resolution network. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2021, 60, 5520216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Deng, Y.; Ma, Y.; Huang, J.; Ma, J. SuperFusion: A versatile image registration and fusion network with semantic awareness. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2022, 9, 2121–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Quan, D.; Wang, S.; Lv, C.; Cao, X.; Chanussot, J.; Li, Y.; Jiao, L. A unified deep learning network for remote sensing image registration and change detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 62, 5101216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; He, J.; Liu, H. EMOST: A dual-branch hybrid network for medical image fusion via efficient model module and sparse transformer. Comput. Biol. Med. 2024, 179, 108771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Song, R.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, K. MCT-Net: Multi-hierarchical cross transformer for hyperspectral and multispectral image fusion. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2023, 264, 110362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhai, Y.; Tang, Y.; Wang, Y. Context-Guided Spatial Feature Reconstruction for Efficient Semantic Segmentation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.06228. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Liu, L.; Xue, Z.; Zhang, B.; Jiang, Z.; Huang, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C. Rethinking mobile block for efficient attention-based models. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 2–3 October 2023; IEEE Computer Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2023; pp. 1389–1400. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 27 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, S.Y.; Hu, J.; Sheng, Z.; Shen, H.L. Iterative deep homography estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 1879–1888. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Han, L.; Ding, M.; Cao, H. Multimodal image fusion framework for end-to-end remote sensing image registration. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5607214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Xiong, Y.; Shao, F.; Shen, H.; Sun, W.; Yang, G.; Yuan, Q.; Fu, R.; Zhang, H. A large-scale benchmark data set for evaluating pansharpening performance: Overview and implementation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2020, 9, 18–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahapatra, D.; Ge, Z.; Sedai, S.; Chakravorty, R. Joint registration and segmentation of xray images using generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the Machine Learning in Medical Imaging: 9th International Workshop, MLMI 2018, Held in Conjunction with MICCAI 2018, Granada, Spain, 16 September 2018; Proceedings 9. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 73–80. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, X.; Yang, J.; Wang, L.; Xue, Z.; Wang, Q.; Shen, D. Deep learning based inter-modality image registration supervised by intra-modality similarity. In Proceedings of the Machine Learning in Medical Imaging: 9th International Workshop, MLMI 2018, Held in Conjunction with MICCAI 2018, Granada, Spain, 16 September 2018; Proceedings 9. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 55–63. [Google Scholar]
- DeTone, D.; Malisiewicz, T.; Rabinovich, A. Deep image homography estimation. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1606.03798. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, L.; Zhou, J.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Ding, L.; Shen, L.; Wang, S. A robust registration method for UAV thermal infrared and visible images taken by dual-cameras. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2022, 192, 189–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Frey, E.C.; He, Y.; Segars, W.P.; Li, Y.; Du, Y. Transmorph: Transformer for unsupervised medical image registration. Med Image Anal. 2022, 82, 102615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Method | RE↓ | MI↑ | NCC↑ | ↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIFT | 11.5427 | 0.5943 | 0.8476 | 15.6192 |
| RIFT | 49.9124 | 0.5056 | 0.4663 | 37.9398 |
| TWMM | 45.0727 | 0.5265 | 0.5081 | 36.8204 |
| TransMorph | 45.3599 | 0.5465 | 0.5058 | - |
| SuperFusion | 43.1178 | 0.4377 | 0.5243 | - |
| 6.7682 | 0.6726 | 0.9601 | 0.5172 | |
| ADRNet | 5.3717 | 0.6800 | 0.9613 | - |
| 6.4662 | 0.6819 | 0.9695 | 0.4300 |
| Method | RE↓ | MI↑ | NCC↑ | ↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIFT | 28.9698 | 0.3355 | 0.4048 | 98.2099 |
| RIFT | 27.4187 | 0.5182 | 0.5124 | 87.4960 |
| TWMM | 24.8630 | 0.5363 | 0.5378 | 82.5501 |
| TransMorph | 24.3016 | 0.4924 | 0.5005 | - |
| SuperFusion | 23.3576 | 0.5478 | 0.6381 | - |
| 4.6481 | 0.6742 | 0.9406 | 0.5581 | |
| ADRNet | 3.6888 | 0.7260 | 0.9598 | - |
| 3.5301 | 0.7305 | 0.9623 | 0.2586 |
| Method | RE↓ | MI↑ | NCC↑ | ↓ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIFT | 36.1812 | 0.2885 | 0.6193 | 356.0067 |
| RIFT | 35.5640 | 0.4421 | 0.6591 | 206.2428 |
| TWMM | 34.8395 | 0.4640 | 0.7273 | 90.1855 |
| TransMorph | 35.6048 | 0.4038 | 0.6891 | - |
| SuperFusion | 39.6567 | 0.3756 | 0.6758 | - |
| 9.5703 | 0.4503 | 0.8406 | 1.2129 | |
| ADRNet | 8.9019 | 0.4814 | 0.9541 | - |
| Ours | 8.6391 | 0.4842 | 0.9550 | 0.9397 |
| Method | SIFT | RIFT | TWMM | TransMorph | SuperFusion | ADRNet | Ours | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Params (M) | - | - | - | 31.10 | 1.96 | 22.77 | 75.51 | 22.15 |
| Flops (G) | - | - | - | 11.12 | 7.32 | 26.90 | 245.33 | 33.23 |
| Test time (s) | 0.0421 | 0.175 | 15.1 | 0.023 | 0.160 | 0.203 | 0.313 | 0.227 |
| Method | RE (SAR/OPT) ↓ | ↓ | Flops (G) |
|---|---|---|---|
| w/o | 10.8353/14.6769 | 1.5701 | 30.0412 |
| w/o | 10.6707/11.7660 | 1.5947 | 32.4949 |
| w/o | 9.9812/8.7278 | 1.4563 | 32.7049 |
| w/o | 9.5335/8.6891 | 1.2668 | 32.9430 |
| w/o | 9.2471/9.0489 | 1.1936 | 30.1435 |
| Ours | 8.6391/8.4939 | 0.9397 | 33.2373 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mu, K.; Wang, W.; Liu, H.; Liang, L.; Zhang, S. A Dual-Branch Network of Strip Convolution and Swin Transformer for Multimodal Remote Sensing Image Registration. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1071. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17061071
Mu K, Wang W, Liu H, Liang L, Zhang S. A Dual-Branch Network of Strip Convolution and Swin Transformer for Multimodal Remote Sensing Image Registration. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(6):1071. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17061071
Chicago/Turabian StyleMu, Kunpeng, Wenqing Wang, Han Liu, Lili Liang, and Shuang Zhang. 2025. "A Dual-Branch Network of Strip Convolution and Swin Transformer for Multimodal Remote Sensing Image Registration" Remote Sensing 17, no. 6: 1071. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17061071
APA StyleMu, K., Wang, W., Liu, H., Liang, L., & Zhang, S. (2025). A Dual-Branch Network of Strip Convolution and Swin Transformer for Multimodal Remote Sensing Image Registration. Remote Sensing, 17(6), 1071. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17061071








