Improving BeiDou Global Navigation Satellite System (BDS-3)-Derived Station Coordinates Using Calibrated Satellite Antennas and Station Inter-System Translation Parameters
Abstract
1. Introduction
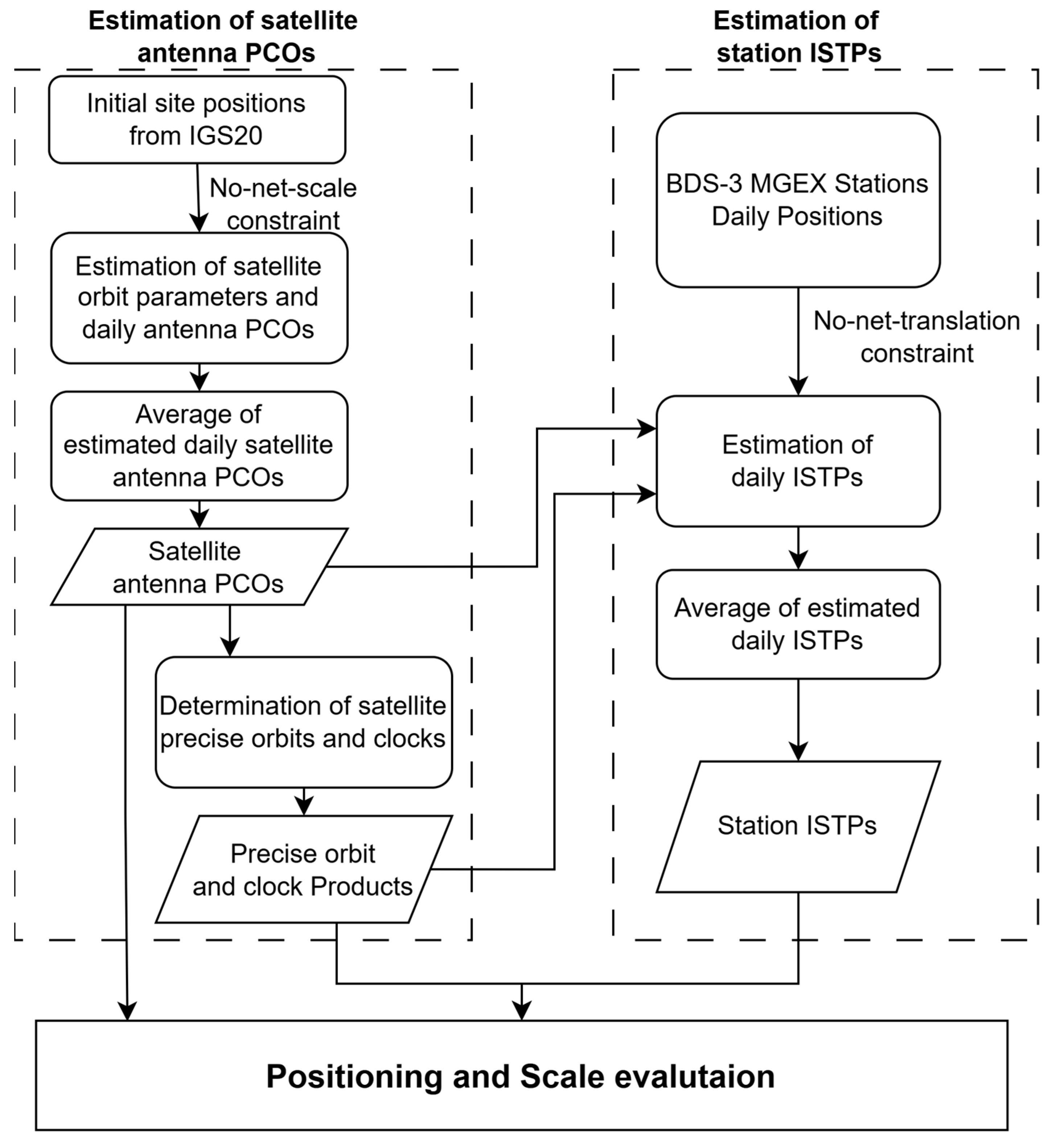
2. Methods
2.1. Estimation of Satellite Antenna PCO
2.2. Estimation of Station-Specific ISTPs
2.3. Data Collection and Processing Strategy
3. Results and Discussion
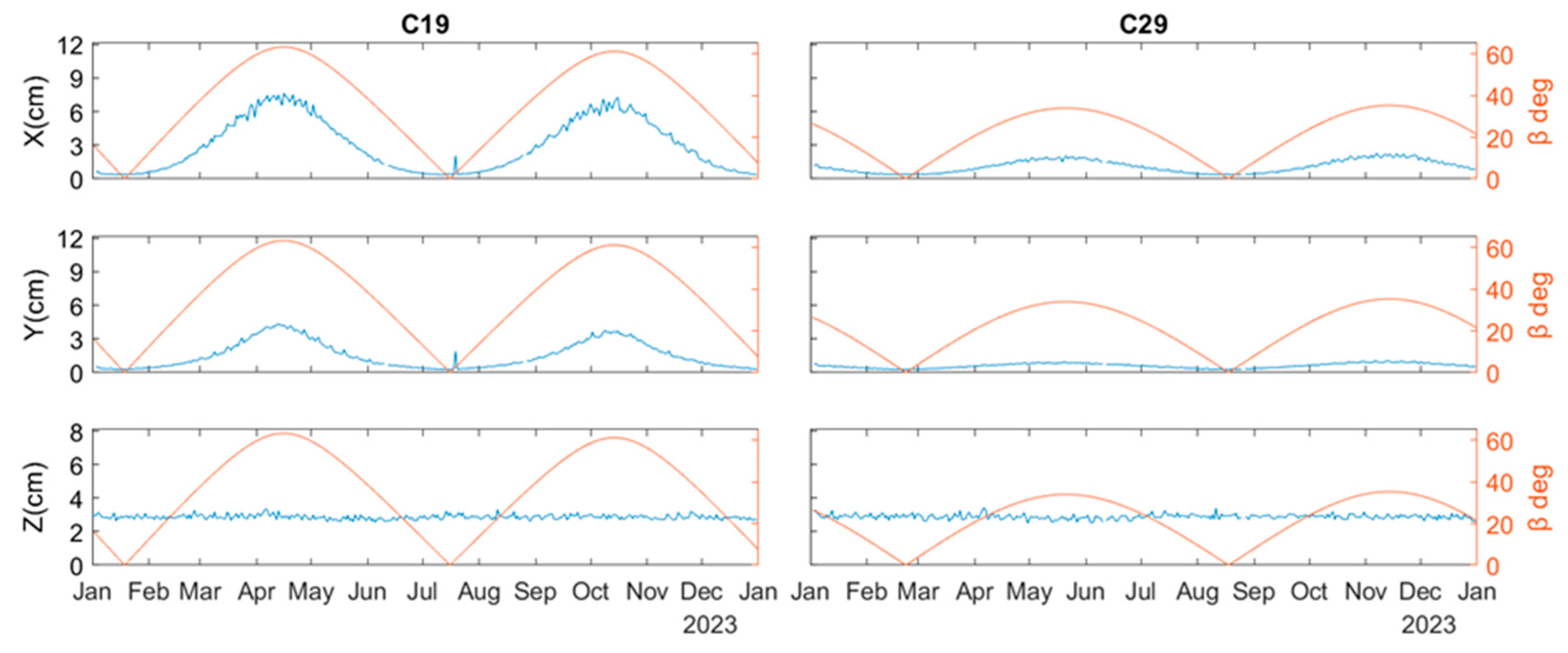
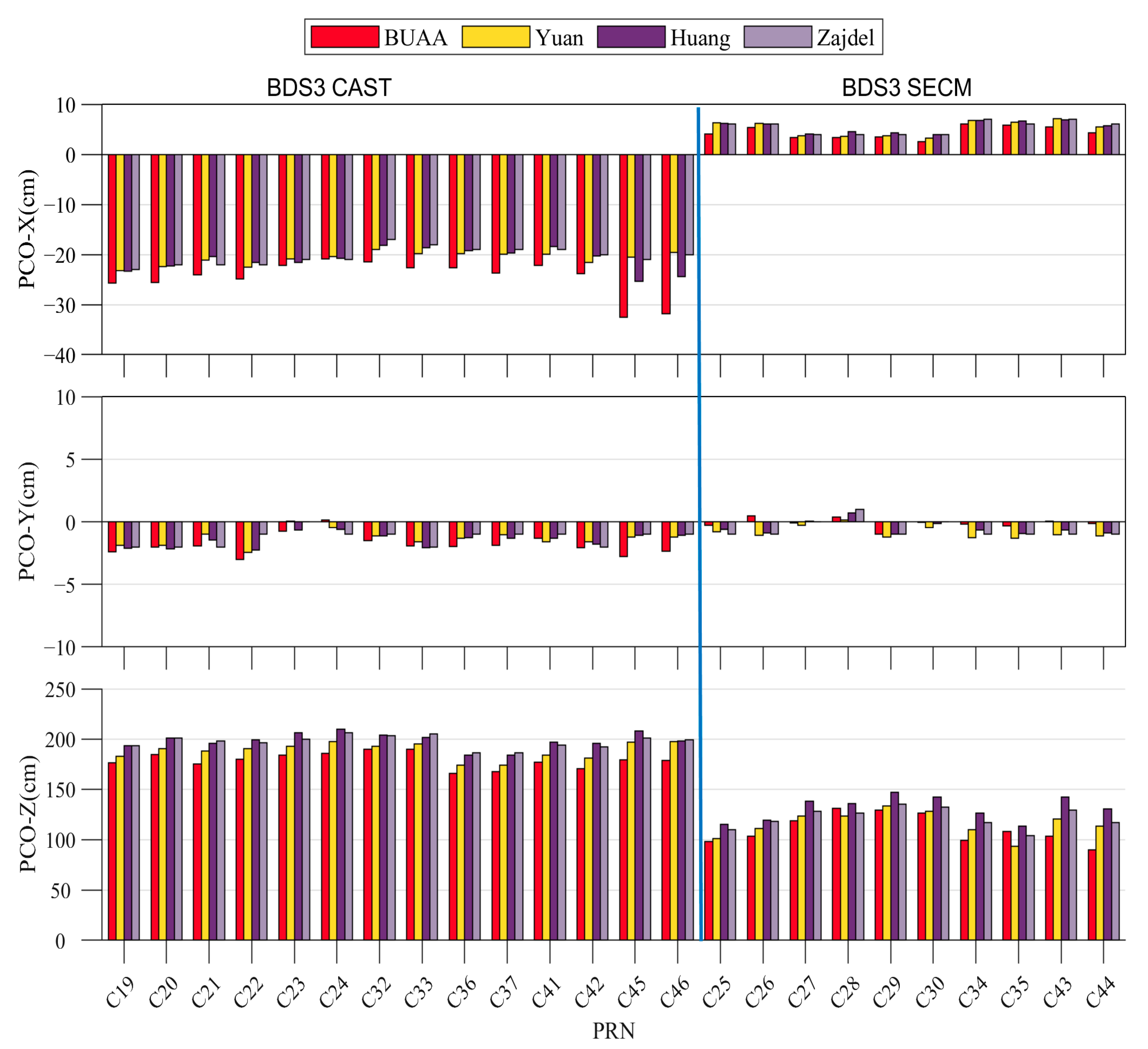
3.1. Estimation of BDS-3 MEO Satellite PCOs
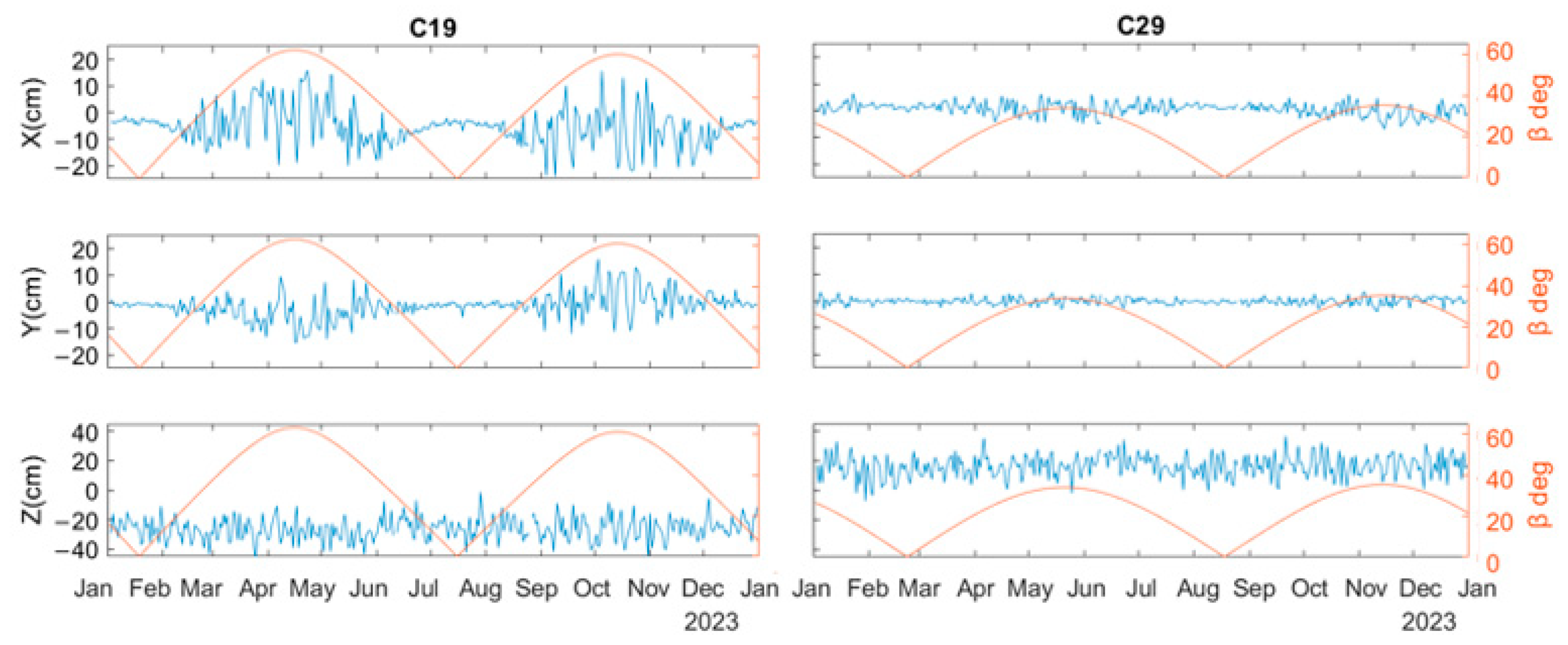
3.2. Estimation of Station-Specific ISTPs
3.3. Evaluation
3.3.1. Terrestrial Scale
3.3.2. Station Coordinates
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, Y.; Tang, J.; Montenbruck, O. Chinese Navigation Satellite Systems. In Springer Handbook of Global Navigation Satellite Systems; Teunissen, P.J.G., Montenbruck, O., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 273–304. ISBN 978-3-319-42928-1. [Google Scholar]
- Zajdel, R. On the Potential Contribution of BeiDou-3 to the Realization of the Terrestrial Reference Frame Scale. GPS Solut. 2022, 26, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Lou, Y.; Dai, X.; Guo, J.; Shi, C. Impact of Solar Radiation Pressure Models on Earth Rotation Parameters Derived from BDS. GPS Solut. 2022, 26, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Fan, L.; Wei, N.; Gu, S.; Fang, X.; Jing, G.; Shi, C. Impact of Satellite Clock Modeling on the GNSS-Based Geocenter Motion Determination. J. Geod. 2024, 98, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riguzzi, F.; Devoti, R.; Pietrantonio, G. GNSS Data Provide Unexpected Insights in Hydrogeologic Processes. Bull. Geophys. Oceanogr. 2021, 62, 637–646. [Google Scholar]
- Bock, Y.; Melgar, D. Physical Applications of GPS Geodesy: A Review. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2016, 79, 106801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouba, J.; Lahaye, F.; Tétreault, P. Precise Point Positioning. In Springer Handbook of Global Navigation Satellite Systems; Teunissen, P.J.G., Montenbruck, O., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 723–751. ISBN 978-3-319-42928-1. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.; Ouyang, C.; Huang, Y.; Peng, W. Assessment of BDS-3 Global Positioning Service: Ephemeris, SPP, PPP, RTK, and New Signal. GPS Solut. 2020, 24, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, G.; Riddell, A.; Hausler, G. The International GNSS Service. In Springer Handbook of Global Navigation Satellite Systems; Teunissen, P.J.G., Montenbruck, O., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 967–982. [Google Scholar]
- Rebischung, P.; Altamimi, Z.; Métivier, L.; Collilieux, X.; Gobron, K.; Chanard, K. Analysis of the IGS Contribution to ITRF2020. J. Geod. 2024, 98, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CSNO Satellite Antenna Phase Center of BDS. Available online: http://www.beidou.gov.cn/yw/gfgg/201912/t20191209_19613.html (accessed on 26 November 2024).
- Xia, F.; Ye, S.; Chen, D.; Wu, J.; Wang, C.; Sun, W. Estimation of Antenna Phase Center Offsets for BeiDou IGSO and MEO Satellites. GPS Solut. 2020, 24, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.; Guo, J.; Zhao, Q. Phase Center Corrections for BDS IGSO and MEO Satellites in IGb14 and IGSR3 Frame. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.Y.; Massmann, F.-H.; Yu, Y.; Reigber, C. Satellite Antenna Phase Center Offsets and Scale Errors in GPS Solutions. J. Geod. 2003, 76, 668–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G. Estimation of Antenna Phase Center Offset for BDS IGSO and MEO Satellites. GPS Solut. 2018, 22, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Song, S.; He, L.; Chen, Q.; Jiao, W.; Zhou, W.; Jiao, G.; Zhao, H.; Yang, Y. Estimation of Antenna Phase Center Offsets for BDS-3 Satellites with the Metadata and Receiver Antenna Calibrations. J. Geod. 2023, 97, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Li, X.; Yao, Y.; Huang, S.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, K. Estimation of Phase Center Corrections for BDS Satellites Aligned to the IGS20 Frame. GPS Solut. 2024, 28, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villiger, A.; Dach, R.; Schaer, S.; Prange, L.; Zimmermann, F.; Kuhlmann, H.; Wuebbena, G.; Schmitz, M.; Beutler, G.; Jaggi, A. GNSS Scale Determination Using Calibrated Receiver and Galileo Satellite Antenna Patterns. J. Geod. 2020, 94, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaer, S.; Meindl, M. Consideration of Station-Specific Intersystem Translation Parameters at CODE. In Proceedings of the EUREF 2011 Symposium, Chisinau, Moldova, 25–28 May 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zajdel, R.; Sośnica, K.; Dach, R.; Bury, G.; Prange, L.; Jäggi, A. Network Effects and Handling of the Geocenter Motion in Multi-GNSS Processing. JGR Solid Earth 2019, 124, 5970–5989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebischung, P.; Schmid, R. IGS14/Igs14.Atx: A New Framework for the IGS Products. In Proceedings of the American Geophysical Union, Fall Meeting 2016, San Francisco, CA, USA, 12–16 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Dach, R.; Selmke, I.; Villiger, A.; Arnold, D.; Prange, L.; Schaer, S.; Sidorov, D.; Stebler, P.; Jäggi, A.; Hugentobler, U. Review of Recent GNSS Modelling Improvements Based on CODEs Repro3 Contribution. Adv. Space Res. 2021, 68, 1263–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villiger, A.; Dach, R. International GNSS Service: Technical Report 2019. 2020. Available online: https://igs.org/igs-2019-technical-report-is-now-available/ (accessed on 1 October 2024).
- Schmid, R.; Steigenberger, P.; Gendt, G.; Ge, M.; Rothacher, M. Generation of a Consistent Absolute Phase-Center Correction Model for GPS Receiver and Satellite Antennas. J. Geod. 2007, 81, 781–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothacher, M.; Schmid, R. ANTEX: The Antenna Exchange Format, Version 1.4. Available online: https://files.igs.org/pub/data/format/antex14.txt (accessed on 1 October 2024).
- Shi, C.; Guo, S.; Fan, L.; Gu, S.; Fang, X.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, T.; Li, Z.; Li, M.; Li, W.; et al. GSTAR: An Innovative Software Platform for Processing Space Geodetic Data at the Observation Level. Satell. Navig. 2023, 4, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Guo, J.; Wang, C.; Lyu, Y.; Xu, X.; Yang, C.; Li, J. Precise Orbit Determination for BDS Satellites. Satell Navig. 2022, 3, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenbruck, O.; Steigenberger, P.; Prange, L.; Deng, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Perosanz, F.; Romero, I.; Noll, C.; Stürze, A.; Weber, G.; et al. The Multi-GNSS Experiment (MGEX) of the International GNSS Service (IGS)–Achievements, Prospects and Challenges. Adv. Space Res. 2017, 59, 1671–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steigenberger, P.; Fritsche, M.; Dach, R.; Schmid, R.; Montenbruck, O.; Uhlemann, M.; Prange, L. Estimation of Satellite Antenna Phase Center Offsets for Galileo. J. Geod. 2016, 90, 773–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, D.; Meindl, M.; Beutler, G.; Dach, R.; Schaer, S.; Lutz, S.; Prange, L.; Sośnica, K.; Mervart, L.; Jäggi, A. CODE’s New Solar Radiation Pressure Model for GNSS Orbit Determination. J. Geod. 2015, 89, 775–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlis, N.; Kenyon, S.; Factor, J.; Holmes, S. Earth gravitational model 2008. In SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts 2008; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Houston, TX, USA, 2008; pp. 761–763. [Google Scholar]
- Standish, E.M. JPL planetary and lunar ephemerides. IOM 1998, 312, F-98-048. [Google Scholar]
- Lyard, F.; Lefevre, F.; Letellier, T.; Francis, O. Modelling the global ocean tides: Modern insights from FES2004. Ocean. Dyn. 2006, 56, 394–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, G. IERS Conventions (2010). 2010. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Gerard-Petit/publication/235112142_IERS_conventions_2010/links/09e41510fd516c4924000000/IERS-conventions-2010.pdf (accessed on 1 October 2024).
- Rodriguez-Solano, C.J.; Hugentobler, U.; Steigenberger, P.; Lutz, S. Impact of Earth radiation pressure on GPS position estimates. J. Geod. 2012, 86, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steigenberger, P.; Thoelert, S.; Montenbruck, O. GNSS Satellite Transmit Power and Its Impact on Orbit Determination. J. Geod. 2018, 92, 609–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saastamoinen, J. Atmospheric correction for the troposphere and stratosphere in radio ranging satellites. Use Artif. Satell. Geod. 1972, 15, 247–251. [Google Scholar]
- Boehm, J.; Werl, B.; Schuh, H. Troposphere mapping functions for GPS and very long baseline interferometry from European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts operational analysis data. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2006, 111, B02406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagler, K.; Schindelegger, M.; Böhm, J.; Krásná, H.; Nilsson, T. GPT2: Empirical slant delay model for radio space geodetic techniques. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 1069–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, M.; Gendt, G.; Dick, G.; Zhang, F.P. Improving Carrier-Phase Ambiguity Resolution in Global GPS Network Solutions. J. Geod. 2005, 79, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prange, L.; Orliac, E.; Dach, R. Others CODE’s Five-System Orbit and Clock Solution—The Challenges of Multi-GNSS Data Analysis. J. Geod. 2016, 91, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Xu, X.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, J. Precise Orbit Determination for Quad-Constellation Satellites at Wuhan University: Strategy, Result Validation, and Comparison. J. Geod. 2016, 90, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Items | Strategy |
|---|---|
| Constellation | BDS-3 MEO satellites GPS |
| Observation | Undifferenced ionosphere-free linear combination of code and phase measurements on BDS-3 B1I/B3I and GPS L1 C/A/L2 P(Y) |
| Time span | 1 January 2023~31 December 2023 |
| Sample rate | 300 s |
| Session length | 24 h |
| Cutoff elevation | 7° |
| Earth gravity | Earth Gravitational Model 2008 (EGM2008) (12 × 12) (Pavlis et al., 2008 [31]) |
| N-body gravity | Sun, moon, and planets with coordinates from Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) Development Ephemerides (DE405) ephemeris (Standish, 1998 [32]) |
| Ocean tide | Finite Element Solution 2004 (FEL2004) tide model (Lyard et al., 2006 [33]) |
| Tide forces and relativistic effects | Models refer to IERS conventions 2010 (Petit & Luzum, 2010 [34]) |
| Earth radiation pressure | Models refer to Rodriguez-Solano et al. (2012b) [35] |
| Antenna thrust | Models refer to [36] |
| Solar radiation pressure (SRP) | Seven-parameter ECOM2 for BDS and GPS satellites |
| Satellite antenna calibrations | BDS-3: initial values are from igs20_2247.atx while corrections are estimated as constants. GPS: igs20_2247.atx |
| Receiver antenna calibrations | igs20_2247.atx |
| Station coordinate | Tightly constrained to IGS daily solutions |
| Troposphere delay | Priori value using GPT2 and Saastamoinen model (Saastamoinen, 1972 [37]) with VMF1 mapping function (Boehm et al., 2006 [38]; Lagler et al., 2013 [39]); residual wet ZPD is estimated as 1 h constant and horizontal gradients are estimated as 24 h constants. |
| Ambiguity | Double-differenced ambiguity resolution [40] |
| Antenna | Radome | Antenna | Radome |
|---|---|---|---|
| ASH700936D_M | SCIS | SEPCHOKE_B3E6 | SPKE |
| ASH701945B_M | SCIS | TPSCR.G3 | SCIS |
| ASH701945C_M | NONE | TPSCR.G5 | TPSH |
| ASH701945E_M | SCIS | TRM115000.00 | NONE |
| JAVRINGANT_DM | NONE | TRM55971.00 | NONE |
| LEIAR20 | LEIM | TRM57971.00 | NONE |
| LEIAR20 | NONE | TRM59800.00 | NONE |
| LEIAR25.R3 | LEIT | TRM59800.00 | SCIS |
| LEIAR25.R4 | LEIT | TRM59800.00 | SCIT |
| LEIAR25.R4 | NONE | TRM59800.80 | SCIT |
| Manu. | PRN | SVN | X | Y | Z |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAST | C19 | C201 | −25.7 | −2.4 | 176.0 |
| CAST | C20 | C202 | −25.6 | −2.0 | 184.6 |
| CAST | C21 | C206 | −24.1 | −1.9 | 174.8 |
| CAST | C22 | C205 | −24.9 | −3.0 | 179.8 |
| CAST | C23 | C209 | −22.2 | −0.7 | 183.7 |
| CAST | C24 | C210 | −20.9 | 0.1 | 185.8 |
| CAST | C32 | C213 | −21.5 | −1.5 | 189.7 |
| CAST | C33 | C214 | −22.7 | −1.9 | 189.7 |
| CAST | C36 | C218 | −22.6 | −2.0 | 165.5 |
| CAST | C37 | C219 | −23.7 | −1.9 | 167.2 |
| CAST | C41 | C227 | −22.1 | −1.3 | 176.9 |
| CAST | C42 | C228 | −23.8 | −2.1 | 170.3 |
| CAST | C45 | C223 | −32.6 | −2.8 | 179.4 |
| CAST | C46 | C222 | −31.8 | −2.4 | 178.8 |
| SECM-A | C25 | C212 | 4.1 | −0.3 | 98.2 |
| SECM-A | C26 | C211 | 5.4 | 0.5 | 103.4 |
| SECM-A | C27 | C203 | 3.3 | −0.1 | 118.4 |
| SECM-A | C28 | C204 | 3.3 | 0.4 | 130.9 |
| SECM-A | C29 | C207 | 3.5 | −1.0 | 128.9 |
| SECM-A | C30 | C208 | 2.6 | 0.0 | 126.0 |
| SECM-A | C34 | C216 | 6.0 | −0.2 | 99.3 |
| SECM-A | C35 | C215 | 5.9 | −0.3 | 107.9 |
| SECM-B | C43 | C226 | 5.4 | 0.1 | 103.5 |
| SECM-B | C44 | C225 | 4.3 | −0.2 | 89.8 |
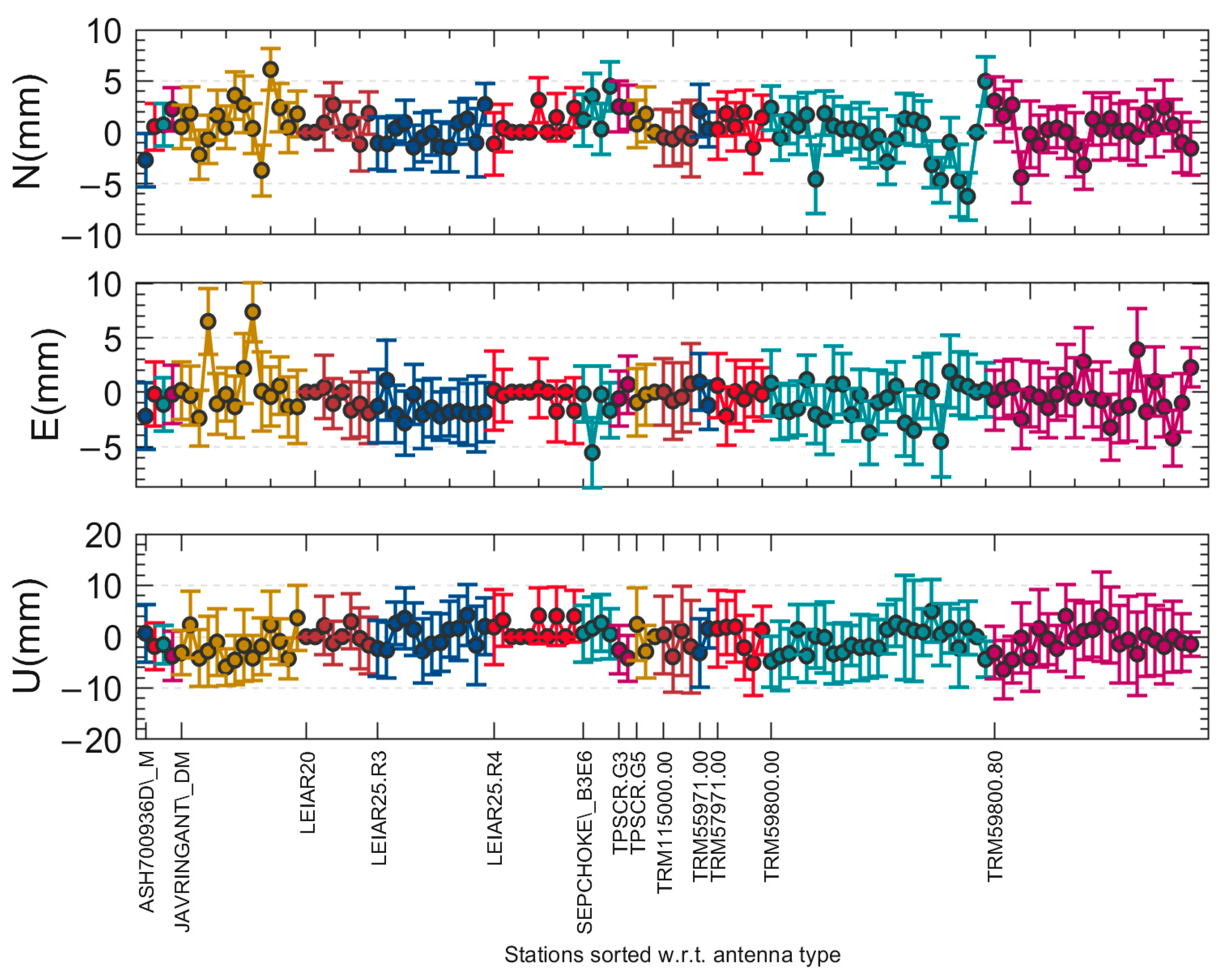
| Antenna Type | Station Number | N | E | U |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASH700936D_M | 1 | −2.7 ± 2.6 | −2.2 ± 3.0 | 0.7 ± 5.6 |
| ASH701945B_M | 1 | 0.5 ± 2.3 | −0.2 ± 3.0 | −1.9 ± 4.5 |
| ASH701945C_M | 1 | 0.7 ± 2.1 | −1.1 ± 2.5 | −1.5 ± 3.8 |
| ASH701945E_M | 1 | 2.3 ± 2.1 | −0.2 ± 2.7 | −3.7 ± 4.8 |
| JAVRINGANT_DM | 1 | 1.1 ± 2.4 | 0.6 ± 2.9 | −1.9 ± 5.5 |
| LEIAR20 | 14 | 0.7 ± 1.4 | −0.7 ± 1.7 | 0.2 ± 3.3 |
| LEIAR25.R3 | 8 | −0.2 ± 2.3 | −1.6 ± 2.9 | 0.4 ± 5.8 |
| LEIAR25.R4 | 13 | 0.6 ± 1.2 | −0.3 ± 1.5 | 1.7 ± 2.9 |
| SEPCHOKE_B3E6 | 10 | 2.4 ± 2.4 | −1.9 ± 2.7 | 1.4 ± 5.5 |
| TPSCR.G3 | 4 | 2.5 ± 2.3 | 0.1 ± 2.6 | −3.4 ± 4.6 |
| TPSCR.G5 | 2 | 0.9 ± 1.7 | −0.4 ± 2.0 | −0.2 ± 4.1 |
| TRM115000.00 | 3 | −0.5 ± 3.0 | −0.1 ± 3.4 | −1.1 ± 8.0 |
| TRM55971.00 | 4 | 1.2 ± 2.1 | −0.1 ± 2.4 | −0.8 ± 5.2 |
| TRM57971.00 | 2 | 0.8 ± 2.4 | −0.4 ± 2.7 | −0.1 ± 6.2 |
| TRM59800.00 | 6 | −0.5 ± 2.3 | −0.8 ± 2.7 | −0.7 ± 5.6 |
| TRM59800.80 | 25 | 0.1 ± 2.6 | −0.4 ± 3.0 | −0.8 ± 6.4 |
| Mean | -- | 0.6 ± 2.2 | −0.6 ± 2.6 | −0.7 ± 5.1 |
| Solutions | Satellite Products | Satellite PCOs | Station ISTPs |
|---|---|---|---|
| CODE-IGS | Precise products from CODE | igs20.atx | - |
| WHU-IGS | Precise products from WHU | igs20.atx | - |
| BUAA-IGS | Reprocessed using igs20.atx | igs20.atx | - |
| BUAA-EST | Reprocessed using the estimated PCOs | Values of this study | - |
| BUAA-EST-ISTP | Reprocessed using the estimated PCOs | Values of this study | Values of this study |
| Solutions | Satellite products | Satellite PCOs | Station ISTPs |
| CODE-IGS | Precise products from CODE | igs20.atx | - |
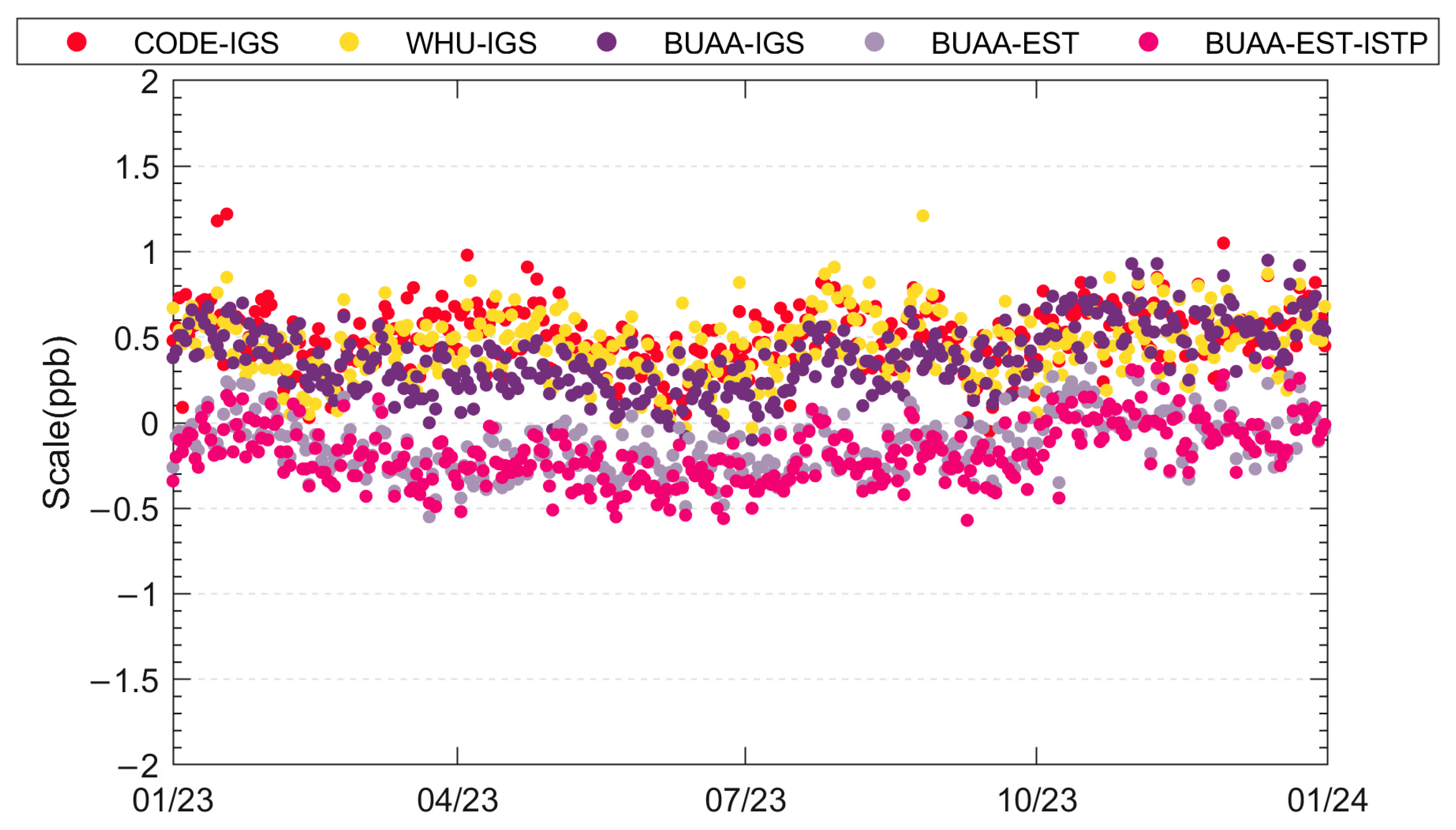
| Solution | Scale (ppb) |
|---|---|
| CODE-IGS | 0.51 ± 0.18 |
| WHU-IGS | 0.46 ± 0.18 |
| BUAA-IGS | 0.38 ± 0.20 |
| BUAA-EST | −0.12 ± 0.17 |
| BUAA-EST-ISTP | −0.18 ± 0.17 |
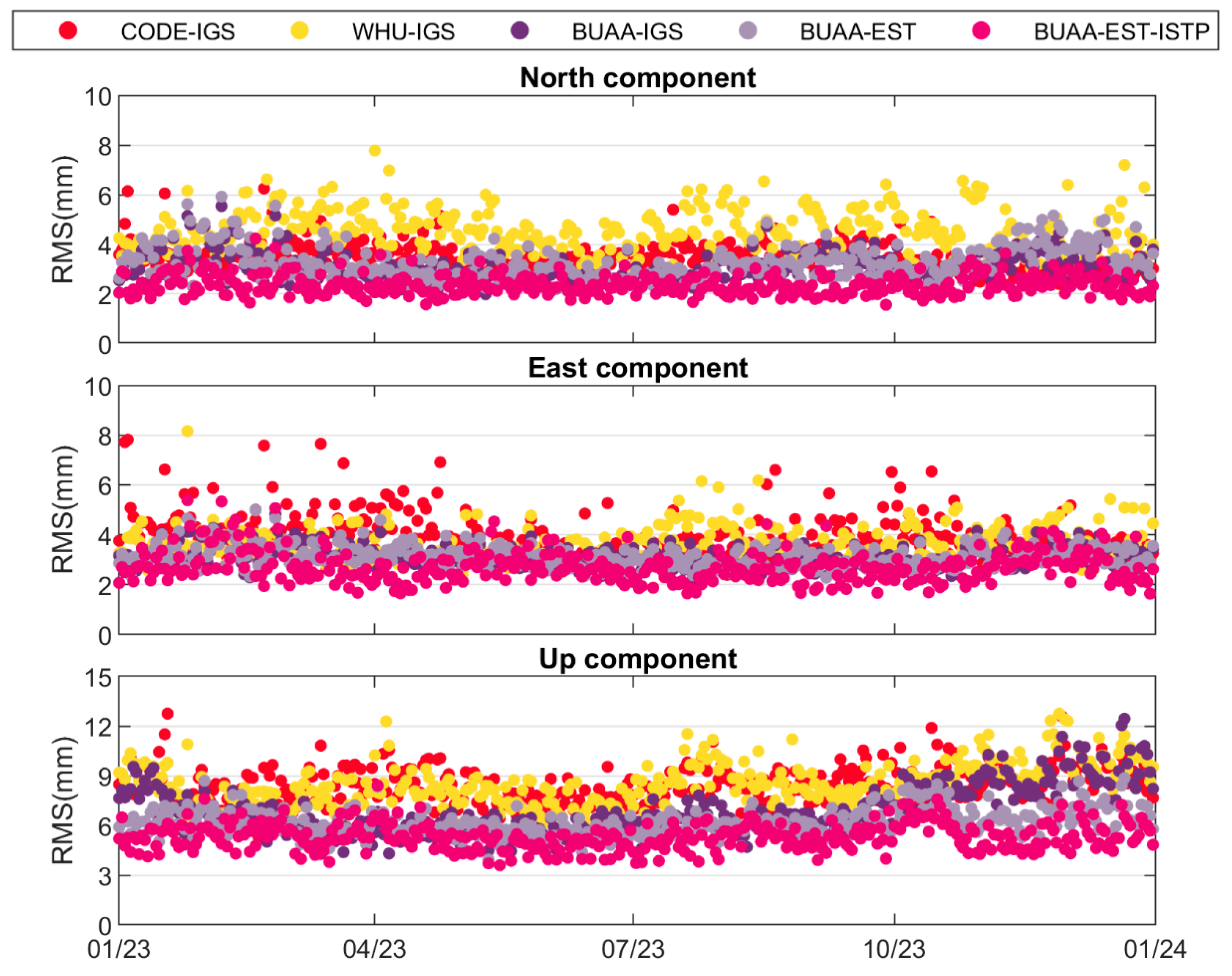
| Solution | Without Helmert Transformation(mm) | With Helmert Transformation(mm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | E | U | N | E | U | |
| CODE-IGS | 3.4 | 3.9 | 8.5 | 3.1 | 3.4 | 7.3 |
| WHU-IGS | 4.5 | 3.6 | 8.5 | 3.3 | 3.1 | 6.9 |
| BUAA-IGS | 3.0 | 3.1 | 7.0 | 2.8 | 2.9 | 6.0 |
| BUAA-EST | 3.2 | 3.1 | 6.2 | 2.8 | 2.8 | 5.7 |
| BUAA-EST-ISTP | 2.3 | 2.7 | 5.2 | 2.3 | 2.4 | 5.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, T.; Guo, S.; Fan, L.; Shi, C. Improving BeiDou Global Navigation Satellite System (BDS-3)-Derived Station Coordinates Using Calibrated Satellite Antennas and Station Inter-System Translation Parameters. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17030510
Zhang T, Guo S, Fan L, Shi C. Improving BeiDou Global Navigation Satellite System (BDS-3)-Derived Station Coordinates Using Calibrated Satellite Antennas and Station Inter-System Translation Parameters. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(3):510. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17030510
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Tao, Shiwei Guo, Lei Fan, and Chuang Shi. 2025. "Improving BeiDou Global Navigation Satellite System (BDS-3)-Derived Station Coordinates Using Calibrated Satellite Antennas and Station Inter-System Translation Parameters" Remote Sensing 17, no. 3: 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17030510
APA StyleZhang, T., Guo, S., Fan, L., & Shi, C. (2025). Improving BeiDou Global Navigation Satellite System (BDS-3)-Derived Station Coordinates Using Calibrated Satellite Antennas and Station Inter-System Translation Parameters. Remote Sensing, 17(3), 510. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17030510








