An Enhanced Sequential ISAR Image Scatterer Trajectory Association Method Utilizing Modified Label Gaussian Mixture Probability Hypothesis Density Filter
Abstract
1. Introduction
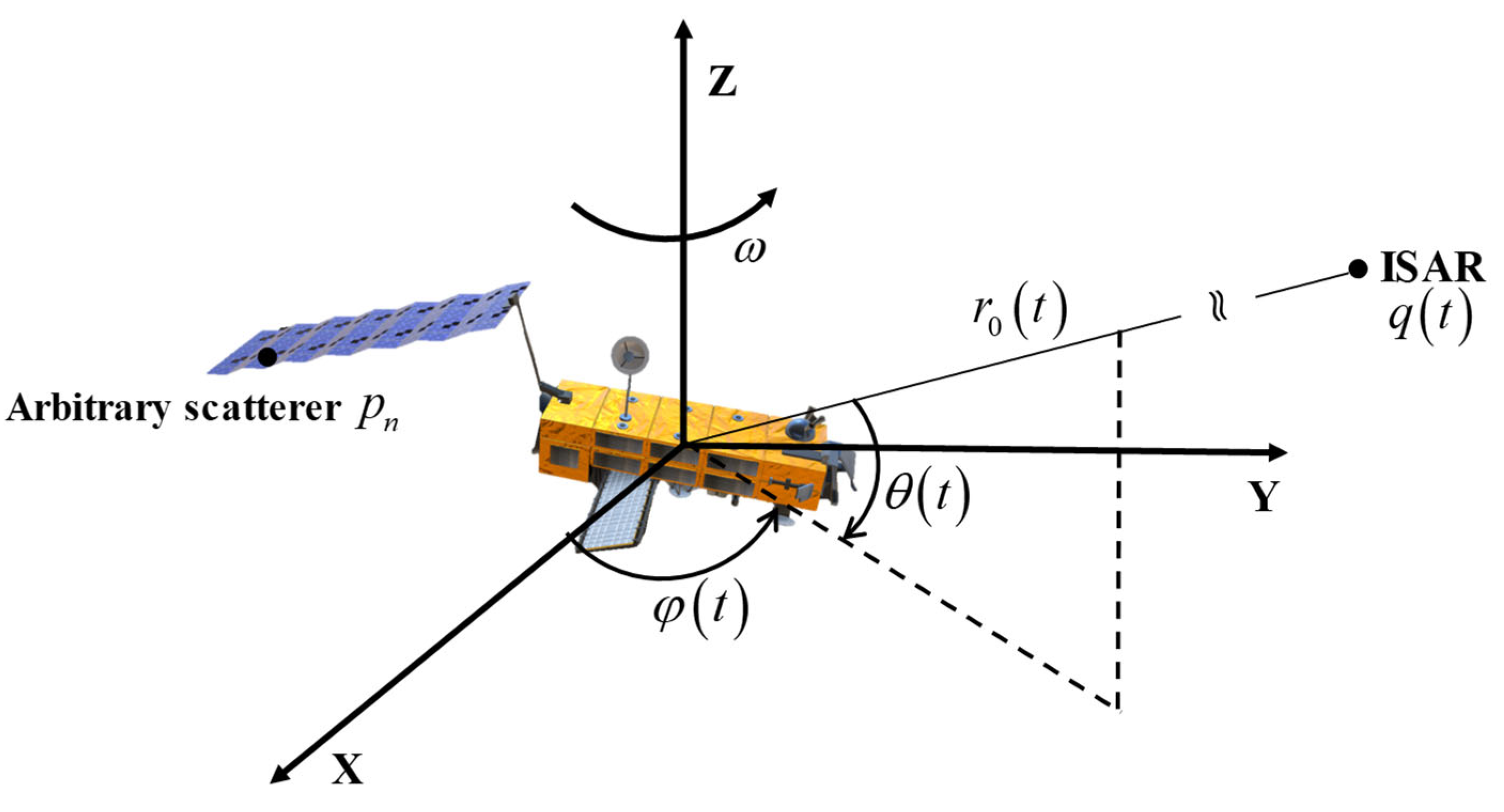
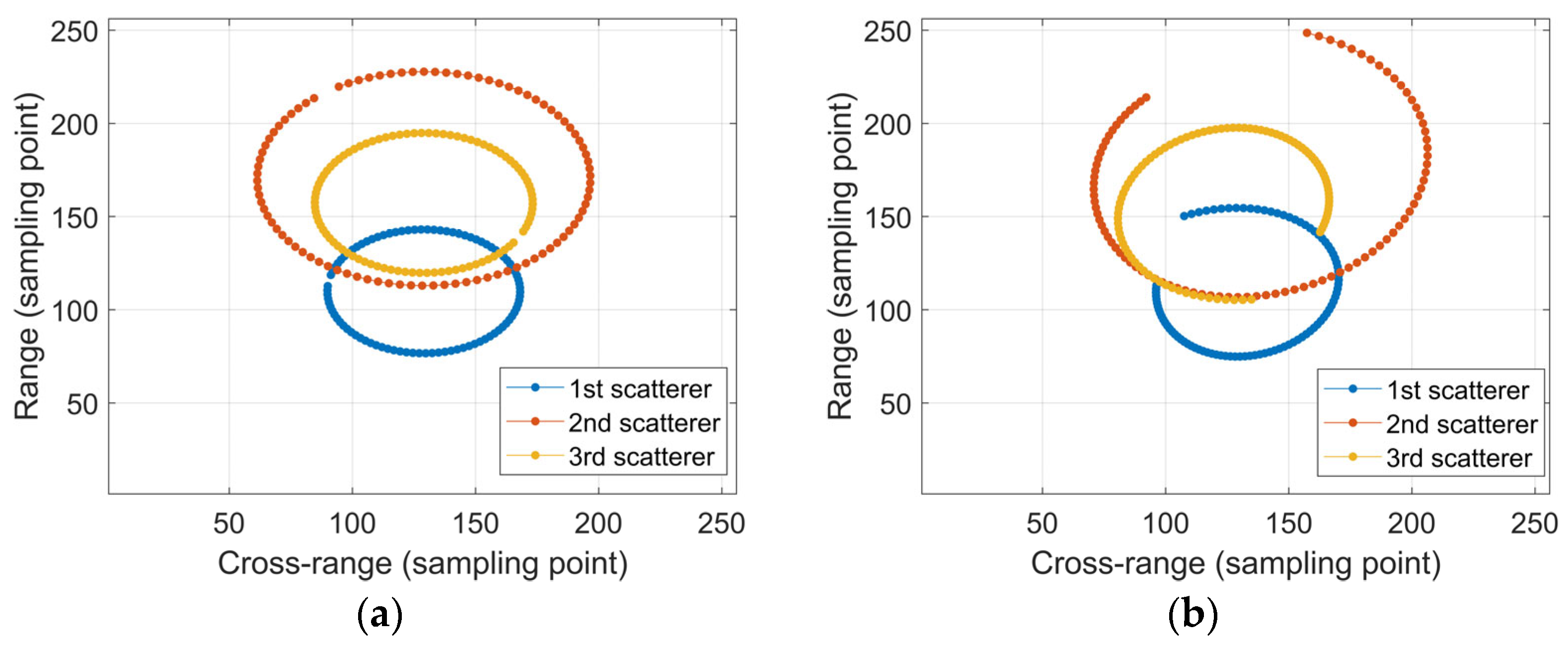
2. ISAR Imaging Model and Scatterer Trajectory Motion Characteristics Analysis
3. Optimization Model for Scatterer Trajectory Association Within the Framework of RFS
- (1)
- Prediction
- (2)
- Update
4. Methodology
4.1. Modified Label Gaussian Mixture Probability Hypothesis Density Filter-Based Trajectory Association
- (1)
- In practical scenarios, the prior PHD for a nascent target should be fixed in L-GM-PHD, which limits its practical application;
- (2)
- False alarms may persist even after pruning Gaussian components solely based on their weights;
- (3)
- The absence of an effective trajectory fusion strategy can lead to flawed trajectory associations.
- (1)
- Prediction
| Algorithm 1. Prediction Procedure of ML-GM-PHD Filtering Algorithm. |
| Input: and with ranging from 1 to , , and with ranging from 1 to , , , and 1: Set the number of the Gaussian components of the prediction PHD with 2: For 3: 4: End for 5: For 6: |
| 7: End for Output: , , , with ranging from 1 to |
- (2)
- Update
| Algorithm 2. Update Process of ML-GM-PHD Filtering Algorithm. |
| Input: , , , with ranging from 1 to , , and 1: For let 2: 3: End for 4: For let 5: 6: 7: 8: 9: End for 10: For 11: for let 12: 13: 14: 15: 16: end for 17: for let 18: 19: end for 20: End for Output: , , and with ranging from 1 to |
- (3)
- Prune and merge
- (4)
- Scatterer state extraction
4.2. Trajectory Integration and Management
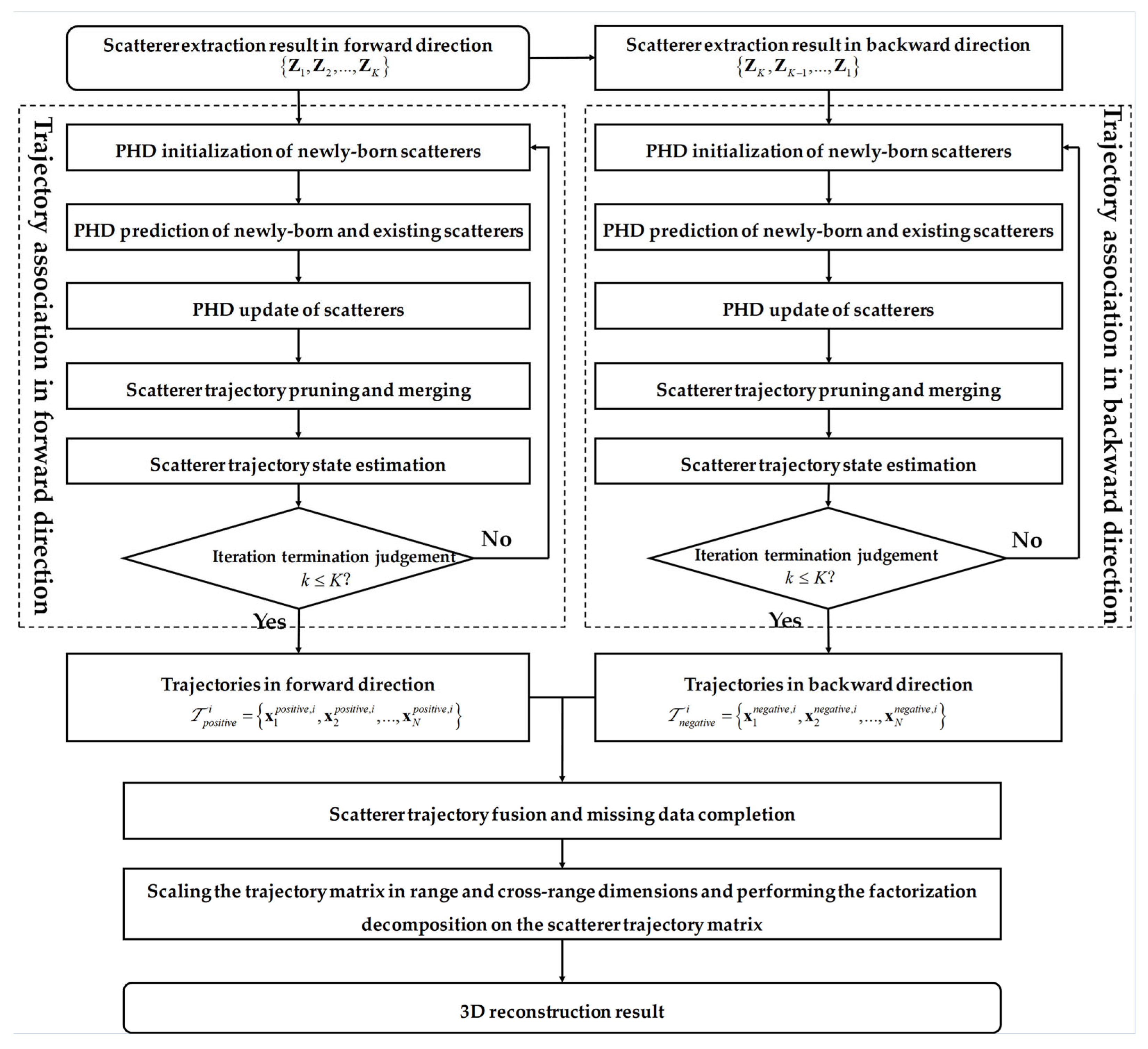
4.3. Algorithm Summation
- Step (1):
- Input the scatterer extraction results of the image sequence in forward and backward directions.
- Step (2):
- Performing the ML-GM-PHD filtering processing along the forward and backward directions, respectively. In the ML-GM-PHD filtering processing, PHD initialization of newly born scatterers, PHD prediction, PHD update, scatterer trajectory pruning and merging, scatterer trajectory state estimation are sequentially performed on the input scatterer extraction results. Associated trajectories in forward direction and backward direction can be obtained after the iteration processing.
- Step (3):
- Performing the scatterer trajectory fusion processing and estimating the missing points. Consequently, complete scatterer trajectory matrix is obtained.
- Step (4):
- Scaling the scatterer trajectory matrix in range dimension and cross-range dimension.
- Step (5):
- Performing the factorization decomposition on the scatterer trajectory matrix to obtain the 3D reconstruction result.
5. Experimental Results and Analysis
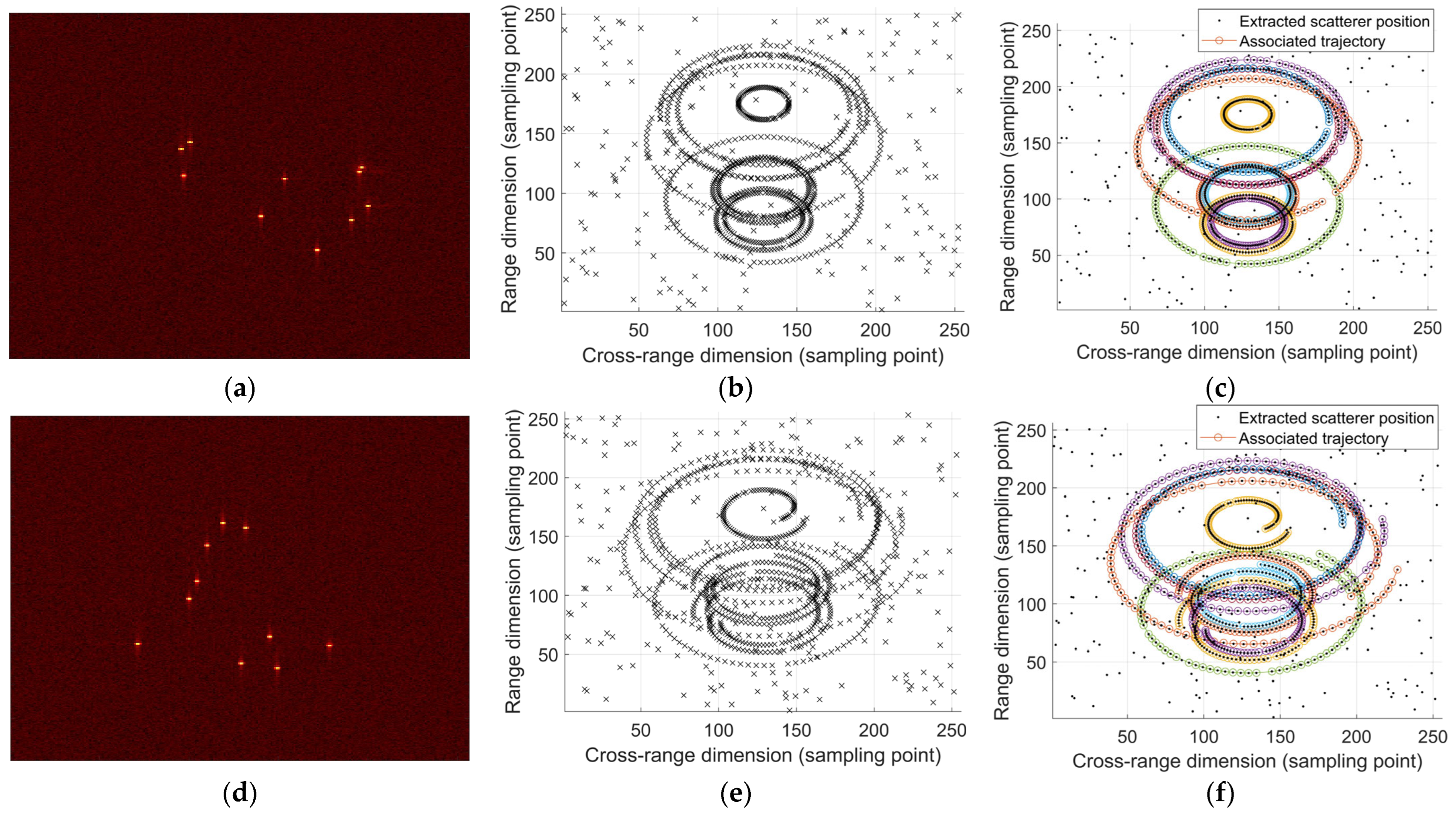
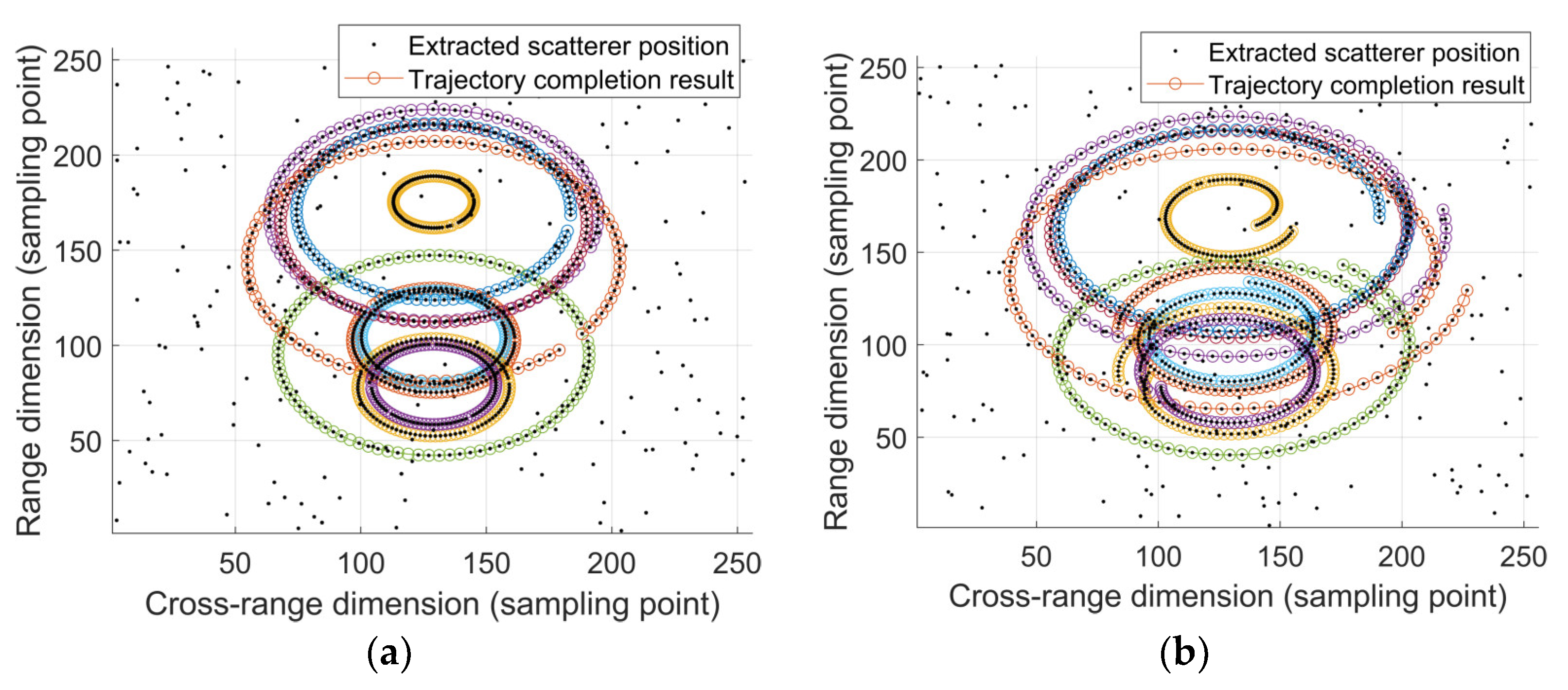
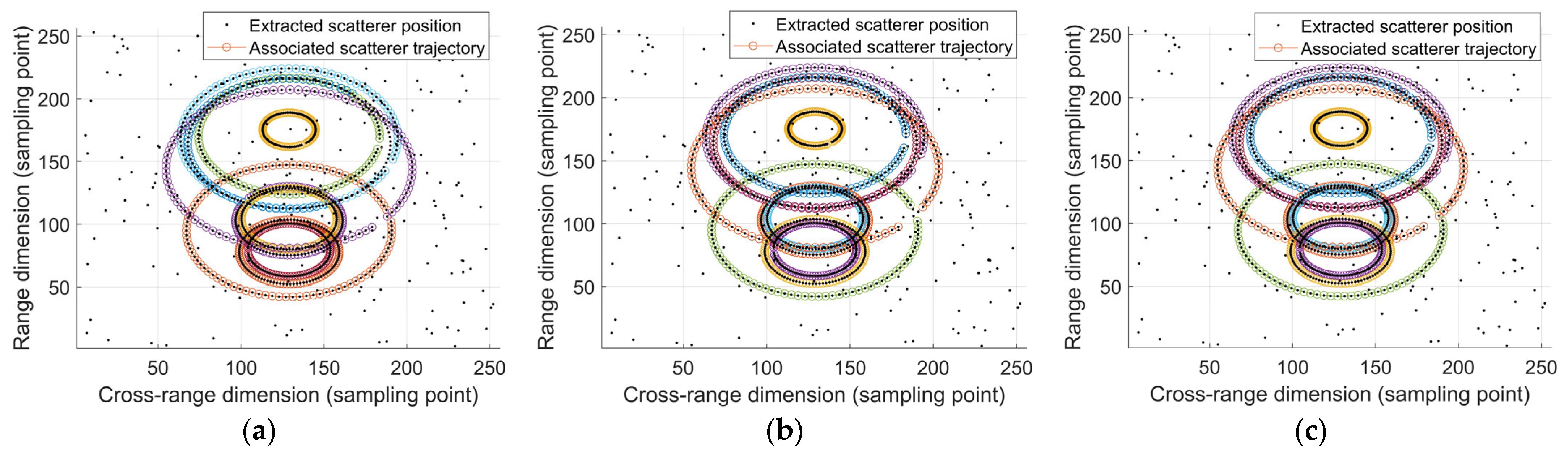
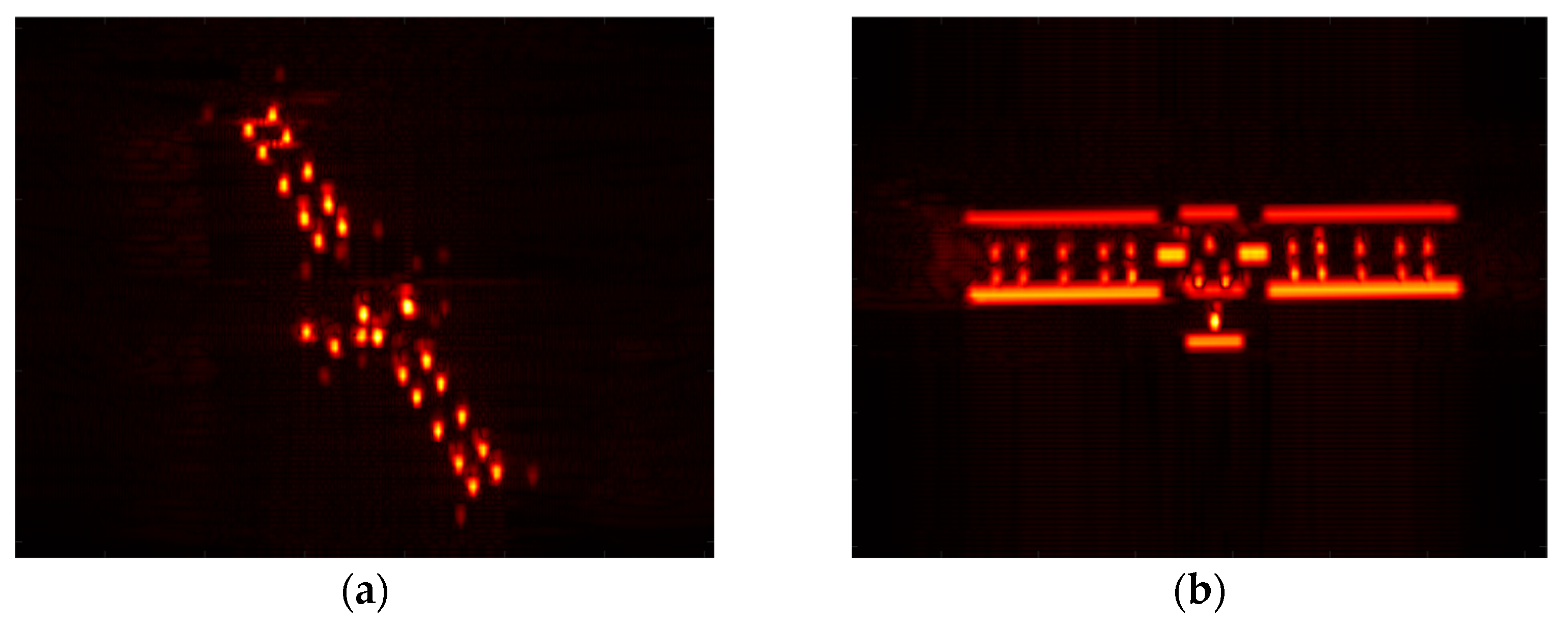
5.1. Effectiveness Analysis
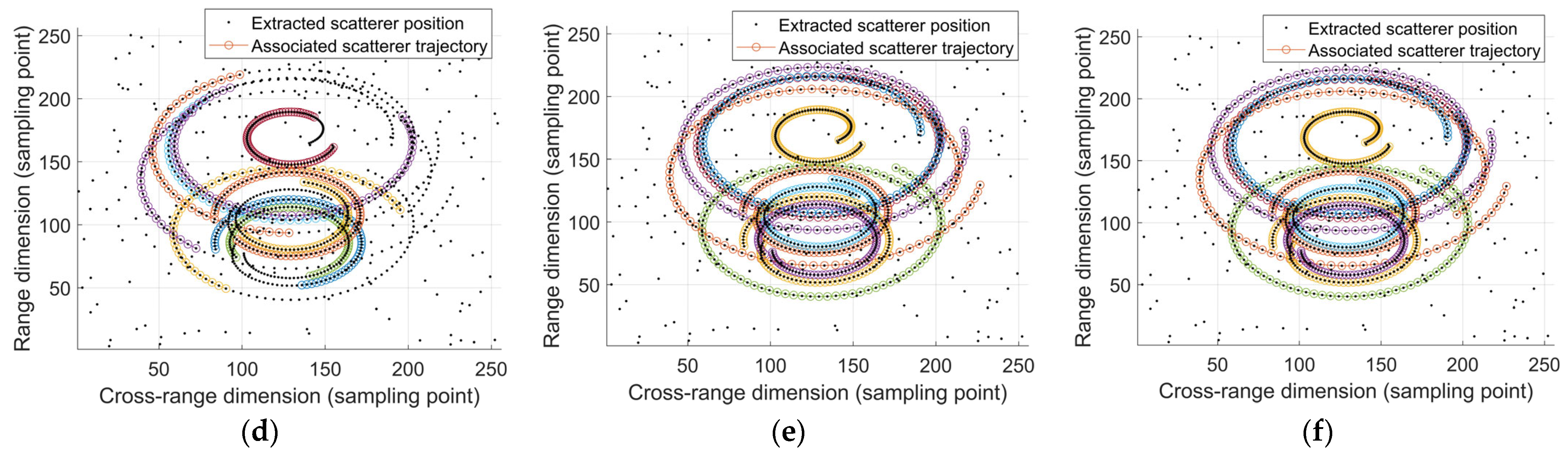
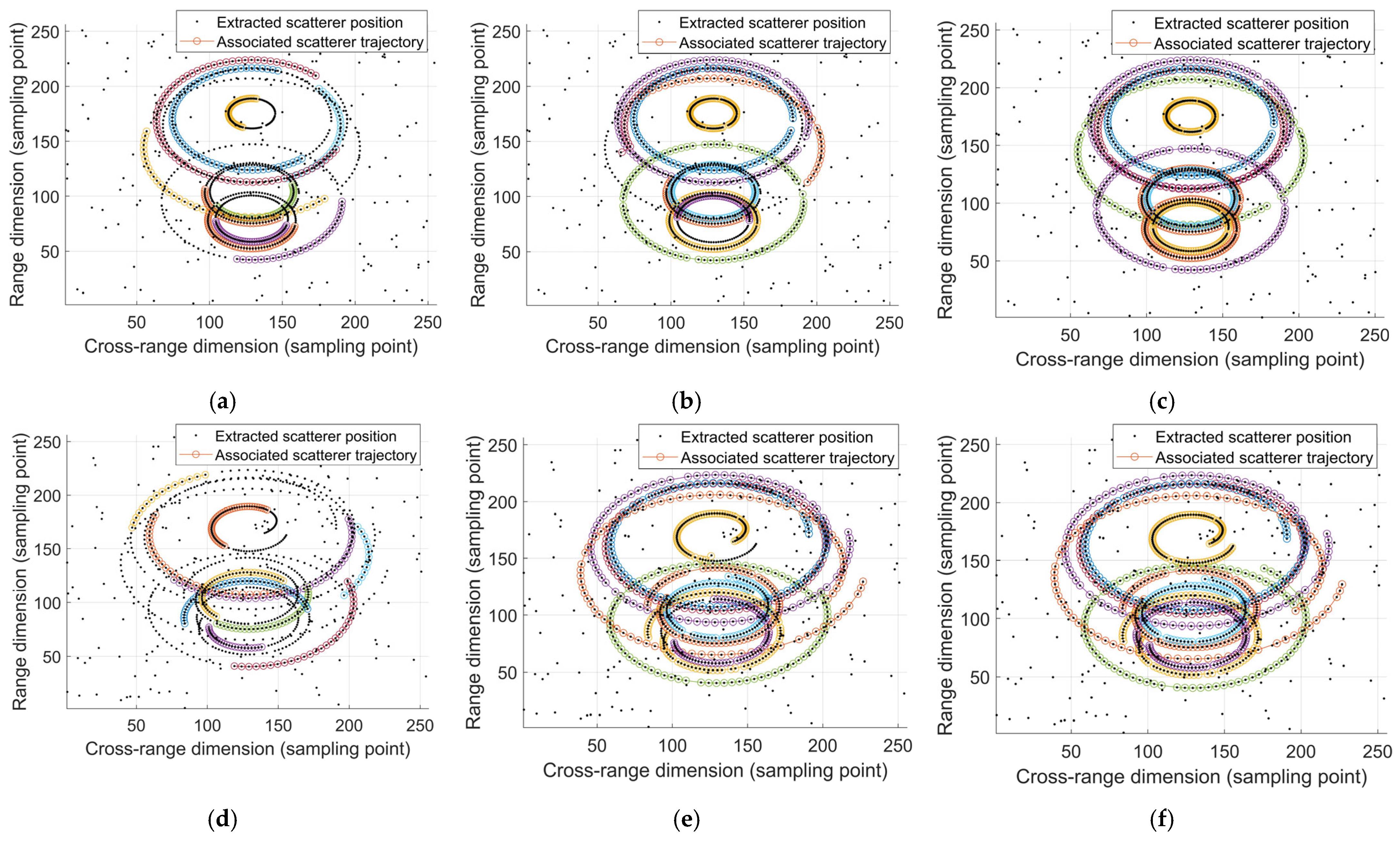
5.2. Performance Comparison and Analysis
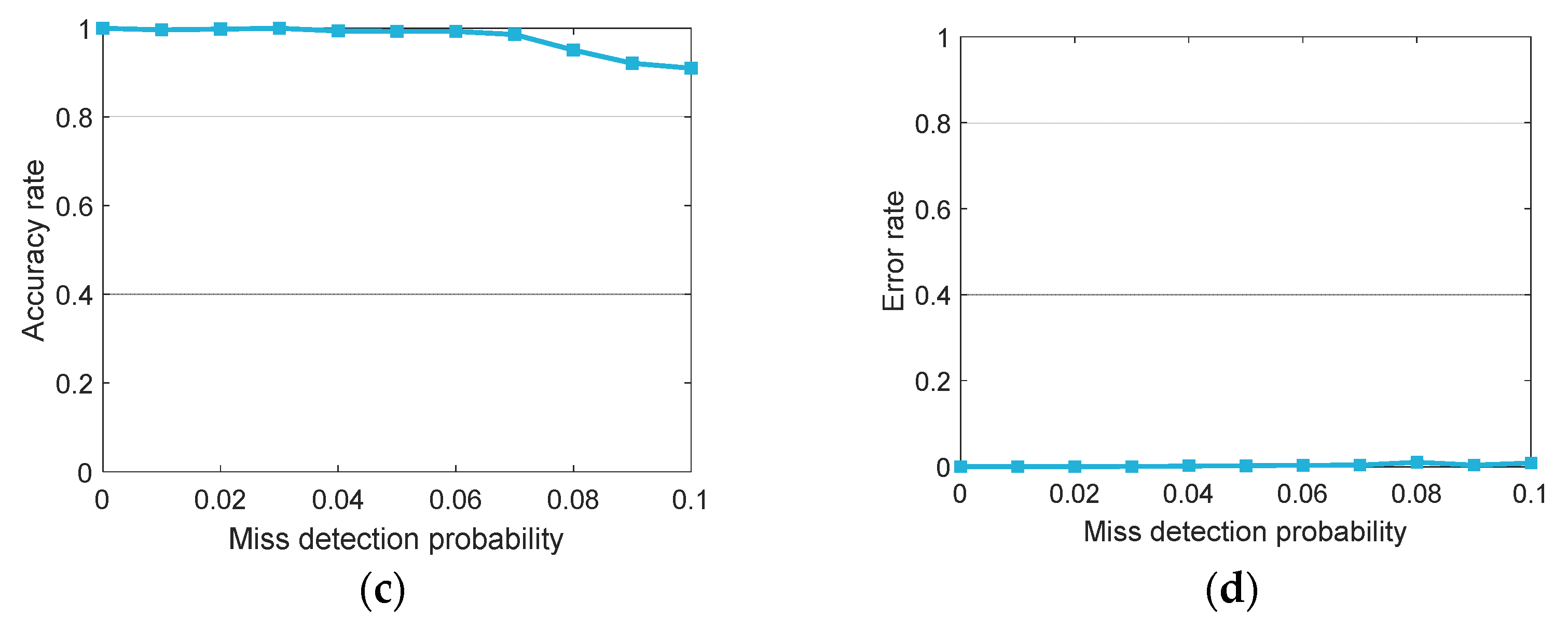
5.3. Algorithm Robustness Analysis
5.4. Experimental Results on Electromagnetical Data
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gong, R.; Wang, L.; Wu, B.; Zhang, G.; Zhu, D. Optimal Space-Borne ISAR Imaging of Space Objects with Co-Maximization of Doppler Spread and Spacecraft Component Area. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, J.; Su, J.; Luo, H. Spatial Feature-Based ISAR Image Registration for Space Targets. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, Y. Unblurring ISAR Imaging for Maneuvering Target Based on UFGAN. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anger, S.; Jirousek, M.; Dill, S.; Peichl, M. Inverse Synthetic Aperture Radar Imaging of Space Targets Using Wideband Pseudo-Noise Signals with Low Peak-to-Average Power Ratio. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Jiang, W.; Tian, B. ISAR Image matching and 3D reconstruction based on improved SIFT Method. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Electronic Engineering and Informatics, Nanjing, China, 8–10 November 2019; pp. 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Bie, B.; Sun, G.-C.; Xing, M.; Pascazio, V. ISAR Image Matching and Three-Dimensional Scattering Imaging Based on Extracted Dominant Scatterers. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, G.; Su, F.; Yang, H.; Fu, S. ISAR Image Scattering Center Association Based on Speeded-up Robust Features. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 79, 5065–5082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Guo, B.F.; Shang, C.X. 3D Reconstruction of Target Geometry Based on 2D Data of Inverse Synthetic Aperture Radar Images. J. Electron. Informa. Tech. 2013, 35, 2475–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Xu, F.; Jin, Y.Q. Three-Dimensional Reconstruction from a Multiview Sequence of Sparse ISAR Imaging of a Space Target. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, R.; Liu, L.; Bai, X.; Zhou, F. A New Scatterer Trajectory Association Method for ISAR Image Sequence Utilizing Multiple Hypothesis Tracking Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5103213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhou, F.; Bai, X.R. Method for Scatterer Trajectory Association of Sequential ISAR Images Based on Markov Chain Monte Carlo Algorithm. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2018, 12, 1535–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.; Wei, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Yuan, C. New Method of Scatterers Association and 3D Reconstruction Based on Multi-Hypothesis Tracking. J. Beijing Uni. Aeronaut. Astronaut. 2016, 42, 1219–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhou, F.; Bai, X.R.; Paisley, J.; Ji, H. A Modified EM Algorithm for ISAR Scatterer Trajectory Matrix Completion. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 3953–3962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhou, F.; Bai, X.R.; Tao, M.L.; Zhang, Z.J. Joint Cross-Range Scaling and 3D Geometry Reconstruction of ISAR Targets Based on Factorization Method. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2016, 25, 1740–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, S.; Li, M.; Hou, Y.; Yu, J. 3D Target reconstruction based on the ISAR image sequence. In Proceedings of the 12th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, Aachen, Germany, 4–7 June 2018; pp. 1142–1146. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, D.; Xing, M.; Xia, X.-G.; Sun, G.-C.; Fu, J.; Su, T. A Multi-Perspective 3D Reconstruction Method with Single Perspective Instantaneous Target Attitude Estimation. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Jiang, L.; Yang, Q.; Ren, X.; Wang, Z. High Precision Cross-Range Scaling and 3D Geometry Reconstruction of ISAR Targets Based on Geometrical Analysis. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 132415–132423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Liu, Y.; Wu, L.; Xu, S.; Chen, Z. Three-Dimensional Reconstruction Using ISAR Sequences. In Proceedings of the 8th International Symposium on Multispectral Image Processing and Pattern Recognition, Wuhan, China, 26–27 October 2013; p. 8919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xing, C.; Xie, P.; Cao, Y. Target Three-Dimensional Reconstruction from the Multi-view Radar Image Sequence. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 36722–36735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhou, Z.B.; Zhou, F.; Shi, X. A New 3-D Geometry Reconstruction Method of Space Target Utilizing the Scatterer Energy Accumulation of ISAR Image Sequence. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2020, 58, 8345–8357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Liu, L.; Du, R.; Zhou, F. Three-Dimensional Geometry Reconstruction Method for Slowly Rotating Space Targets utilizing ISAR Image Sequence. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Jin, X.; Liu, L.; Zhou, F. Three-Dimensional Geometry Reconstruction Method from Multi-View ISAR Images Utilizing Deep Learning. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahler, R.P.S. Multitarget Bayes Filtering via First-order Multitarget Moments. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2003, 39, 1152–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, B.N.; Vo, B.T.; Phung, D. Labeled Random Finite Sets and the Bayes Multi-Target Tracking Filter. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2014, 62, 6554–6567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesar, H.D.; Abrishami Moghaddam, H.; Safari, A.; Eftekhari-Yazdi, P. Multiple Sperm Tracking in Microscopic Videos Using Modified GM-PHD filter. Mach. Vis. Appl. 2018, 29, 433–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, B.N.; Ma, W.K. The Gaussian Mixture Probability Hypothesis Density Filter. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2006, 54, 4091–4104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahler, R. PHD Filters of Higher Order in Target Number. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2007, 43, 1523–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, B.N.; Singh, S.; Doucet, A. Random Finite Sets and Sequential Monte Carlo Methods in Multi-Target Tracking. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Radar, Adelaide, SA, Australia, 3–5 September 2003; pp. 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, B.N.; Singh, S.; Doucet, A. Sequential Monte Carlo Implementation of the PHD Filter for Multi-Target Tracking. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference of Information Fusion, Cairns, QLD, Australia, 8–11 July 2003; pp. 792–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panta, K.; Clark, D.E.; Vo, B.N. Data Association and Track Management for the Gaussian Mixture Probability Hypothesis Density Filter. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2009, 45, 1003–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, D.E.; Panta, K.; Vo, B.N. The GM-PHD Filter Multiple Target Tracker. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Information Fusion, Florence, Italy, 10–13 July 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H. A "Current" Statistical Model and Adaptive Tracking Algorithm for Maneuvering Targets. Acta Aeronaut. Astronaut. Sin. 1983, 4, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Bi, G. Fast ISAR Cross-Range Scaling Using Modified Newton Method. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2018, 54, 1355–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Q. Rotation Parameters Estimation and Cross-Range Scaling Research for Range Instantaneous Doppler ISAR Images. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 7010–7020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameters | Values | |
|---|---|---|
| Elliptical Trajectories | Non-Elliptical Trajectories | |
| Total observation time (second) | 92 | 92 |
| Image frame number | 92 | 92 |
| Range of the variation of the azimuth angle of the radar LOS (degree) | [0, 360] * | [0, 360] * |
| The pitch angle of the radar LOS (degree) | 45 | 45 |
| Rotation angular velocity (degree/s) | 0 | 0.6 |
| Pitch angle of the spin axis of the space target (degree) | 0 | 10 |
| Azimuth angle of the spin axis of the space target (degree) | 0 | 5 |
| Trajectory Type | Number of Real Scatterers | Number of Correctly Associated Scatterers | Number of Incorrectly Associated Scatterers | Accuracy Rate | Error Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elliptical trajectories | 882 | 882 | 0 | 100% | 0 |
| Non-elliptical trajectories | 879 | 879 | 0 | 100% | 0 |
| Trajectory Type | Elliptical Trajectories | Non-Elliptical Trajectories | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of real scatterers | 920 | 920 | ||||
| Algorithm | MCMCDA | L-GM-PHD | Proposed algorithm | MCMCDA | L-GM-PHD | Proposed algorithm |
| Number of correctly associated scatterers | 891 | 909 | 920 | 553 | 907 | 920 |
| Number of incorrectly associated scatterers | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Accuracy rate (%) | 96.85 | 98.8 | 100 | 60.11 | 98.59 | 100 |
| Error rate (%) | 0.11 | 0 | 0 | 0.11 | 0 | 0 |
| Trajectory Type | Elliptical Trajectories | Non-Elliptical Trajectories | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of real scatterers | 886 | 868 | ||||
| Method | MCMCDA | L-GM-PHD | Proposed algorithm | MCMCDA | L-GM-PHD | Proposed algorithm |
| Number of correctly associated scatterers | 448 | 696 | 886 | 317 | 805 | 868 |
| Number of incorrectly associated scatterers | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 |
| Accuracy rate (%) | 50.56 | 78.56 | 100 | 36.52 | 92.74 | 100 |
| Error rate (%) | 0 | 0.11 | 0 | 0 | 0.23 | 0.12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, L.; Zhou, Z.; Li, C.; Zhou, F. An Enhanced Sequential ISAR Image Scatterer Trajectory Association Method Utilizing Modified Label Gaussian Mixture Probability Hypothesis Density Filter. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17030354
Liu L, Zhou Z, Li C, Zhou F. An Enhanced Sequential ISAR Image Scatterer Trajectory Association Method Utilizing Modified Label Gaussian Mixture Probability Hypothesis Density Filter. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(3):354. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17030354
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Lei, Zuobang Zhou, Cheng Li, and Feng Zhou. 2025. "An Enhanced Sequential ISAR Image Scatterer Trajectory Association Method Utilizing Modified Label Gaussian Mixture Probability Hypothesis Density Filter" Remote Sensing 17, no. 3: 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17030354
APA StyleLiu, L., Zhou, Z., Li, C., & Zhou, F. (2025). An Enhanced Sequential ISAR Image Scatterer Trajectory Association Method Utilizing Modified Label Gaussian Mixture Probability Hypothesis Density Filter. Remote Sensing, 17(3), 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17030354









