Optical Remote Sensing Ship Detection Combining Channel Shuffling and Bilinear Interpolation
Highlights
- The maritime ship targets suffer from the problem of imbalanced length-to-width ratios, which can lead to a decrease in detection accuracy.
- The sea wave background of maritime ships, as well as the similar color between ships and seawater, can blur the edge information of ships, thereby increasing the miss rate.
- To address the issue of imbalanced length-to-width ratios, this paper designs a loss function that combines position, shape, and scale information, and validates the effectiveness of the method through various experiments.
- To address the problem of ship edge information being easily confused with seawater and other background information, a feature enhancement module and an edge-gated upsampling module are designed. These modules enhance ship feature information and suppress background information, thereby reducing the miss rate.
Abstract
1. Introduction
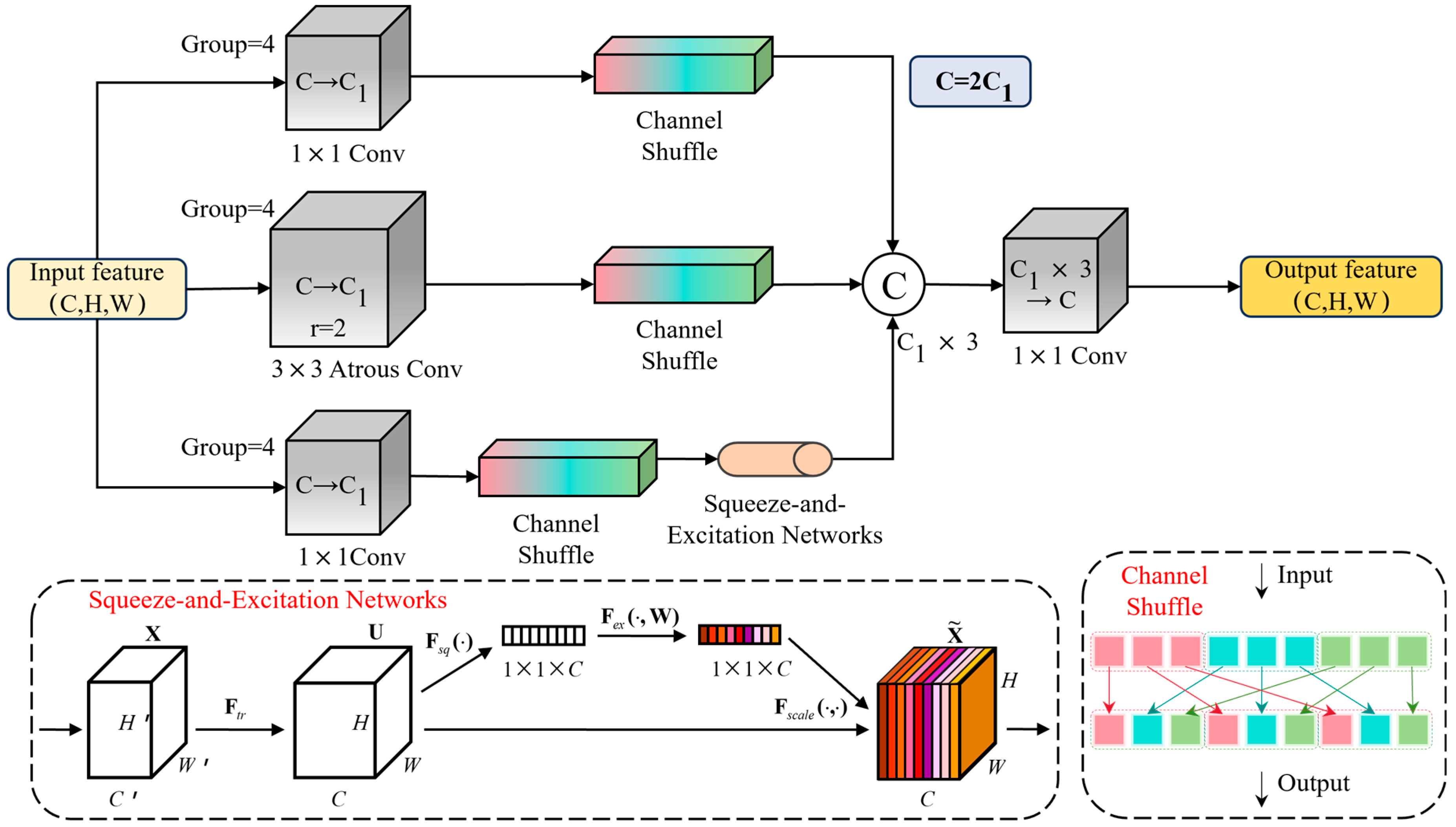
- A feature enhancement module was designed to reconstruct inter-group interactions through channel shuffling. Parallel branches capture local textures and global contexts separately, and adaptive weighting is performed in the channel dimension. This simultaneously enhances fine-grained features and long-range dependencies, achieving significant accuracy gains at the cost of a small number of parameters.
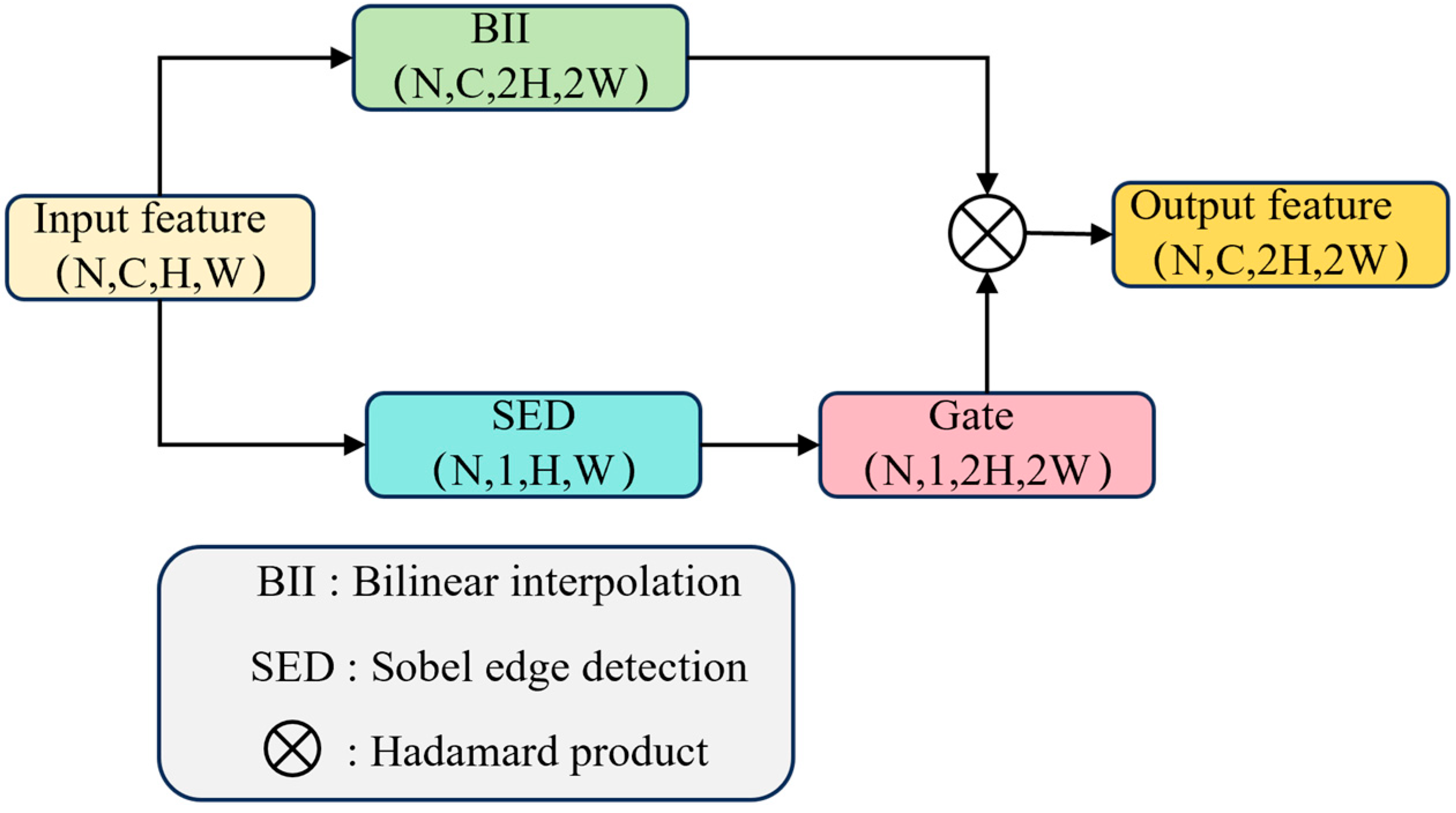
- This paper proposes the Edge-Gated Upsampler, which first generates an edge confidence map using the Sobel operator and then dynamically adjusts the edge branch weights through a temperature-learnable gating mechanism. This is done in parallel with the interpolation branch to achieve adaptive trade-offs between structural details and smooth regions, effectively enhancing the network’s ability to discriminate narrow targets.
- A logarithmic-power composite transformation of the IoU between the predicted box and the ground-truth box is introduced to construct the R-IoU-Focal Loss. This maps the regression difficulty to exponential weights, enabling the network to focus on narrow targets with low IoU. In the complex maritime ship detection task, this loss significantly improves localization accuracy and robustness, providing a new optimization paradigm for the detection of narrow and low-contrast targets.
2. Relate Work
2.1. Imaging Technology for Remote Sensing Ship Detection
2.1.1. Optical Remote Sensing Ship Detection
2.1.2. SAR Remote Sensing Ship Detection
2.1.3. Infrared Remote Sensing Ship Detection
2.2. Application of YOLO in Remote Sensing Ship Detection
2.3. Feature Enhancement Strategies in Complex Scenarios
3. Materials and Methods
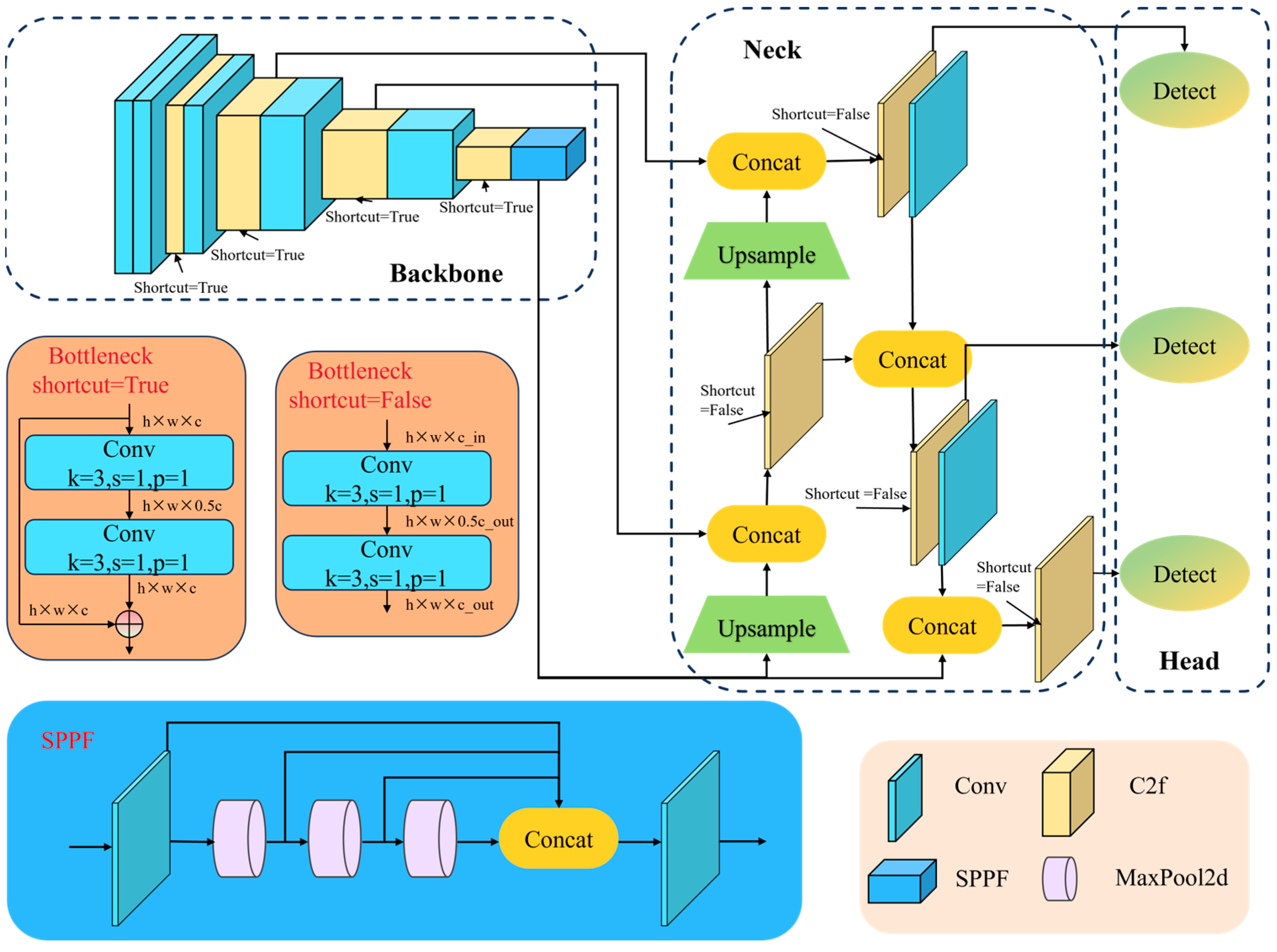
3.1. Network Architecture of YOLOv8
3.2. Network Architecture of CSBI-YOLO
3.3. GS-FEM
3.4. EGU
3.5. R-IoU-Focal Loss Function
4. Experimental Results
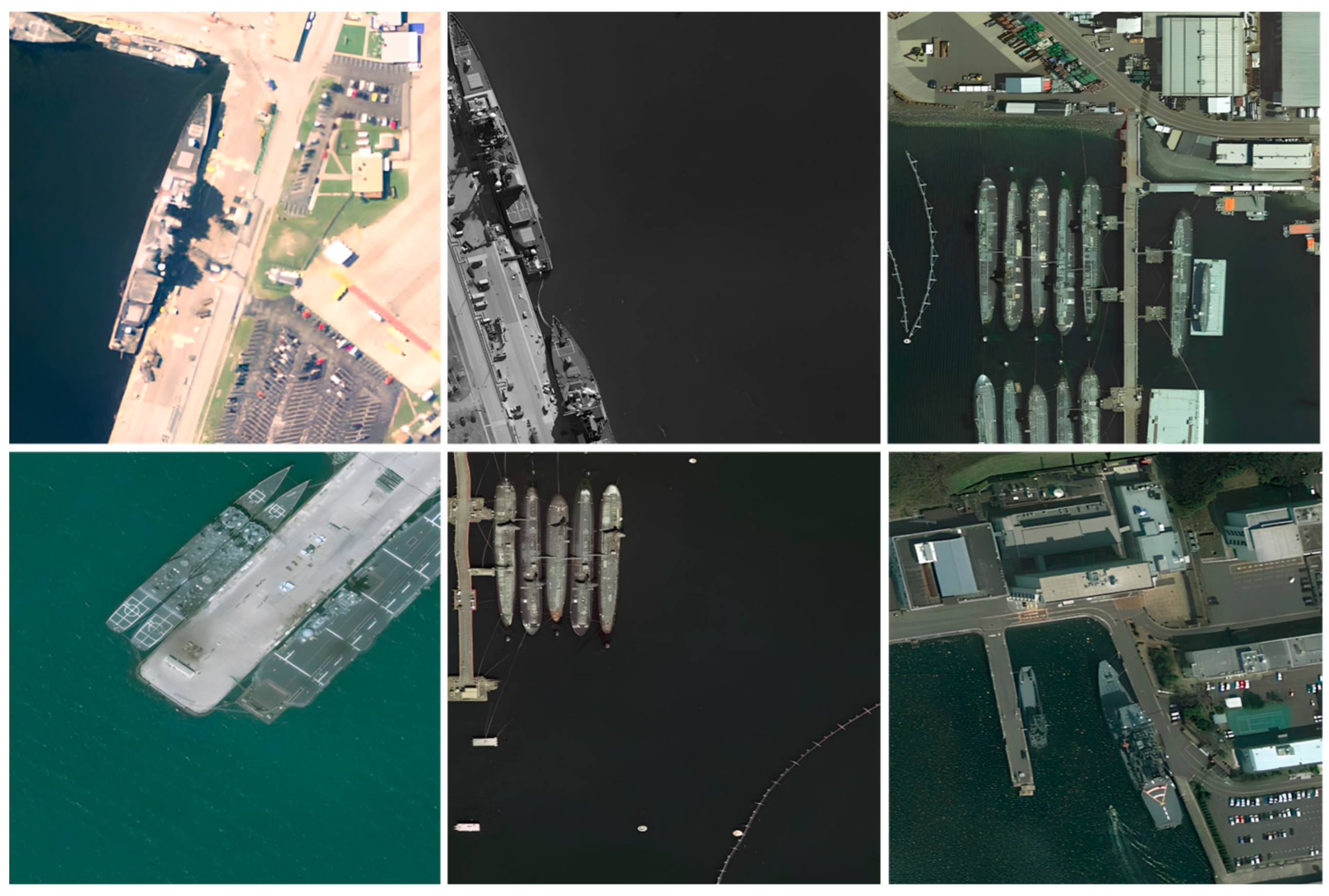
4.1. DataSet
4.2. Experimental Setup
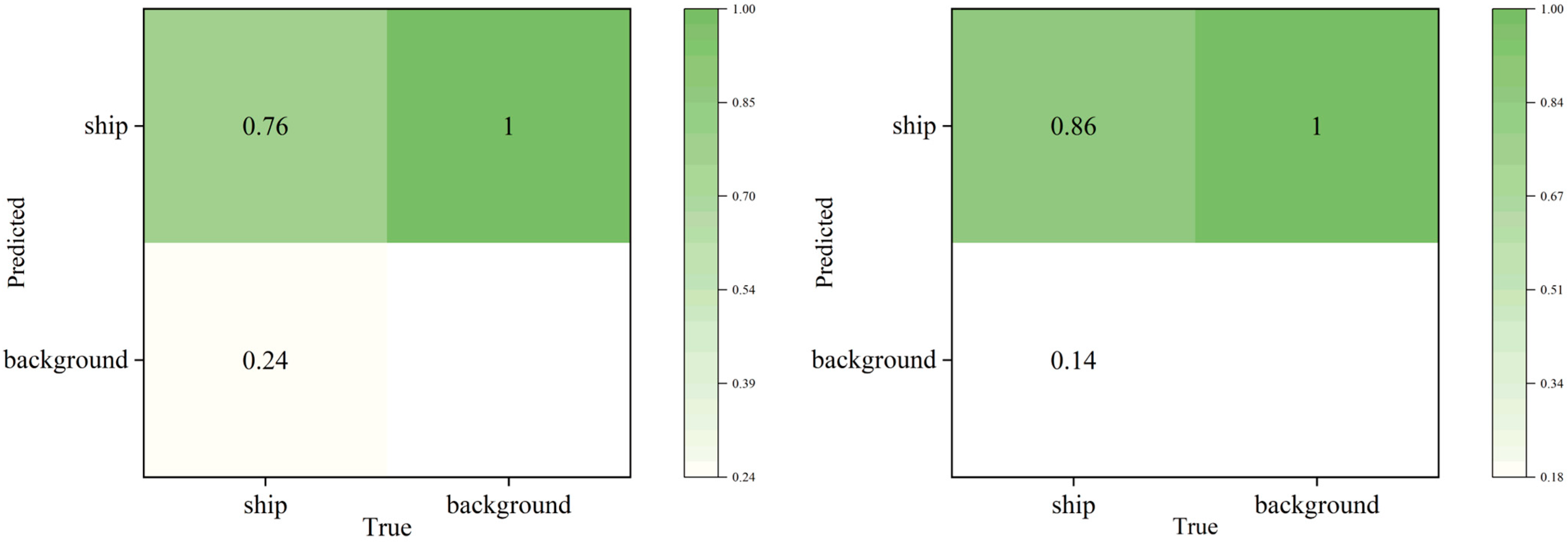
4.3. Evaluation Metric
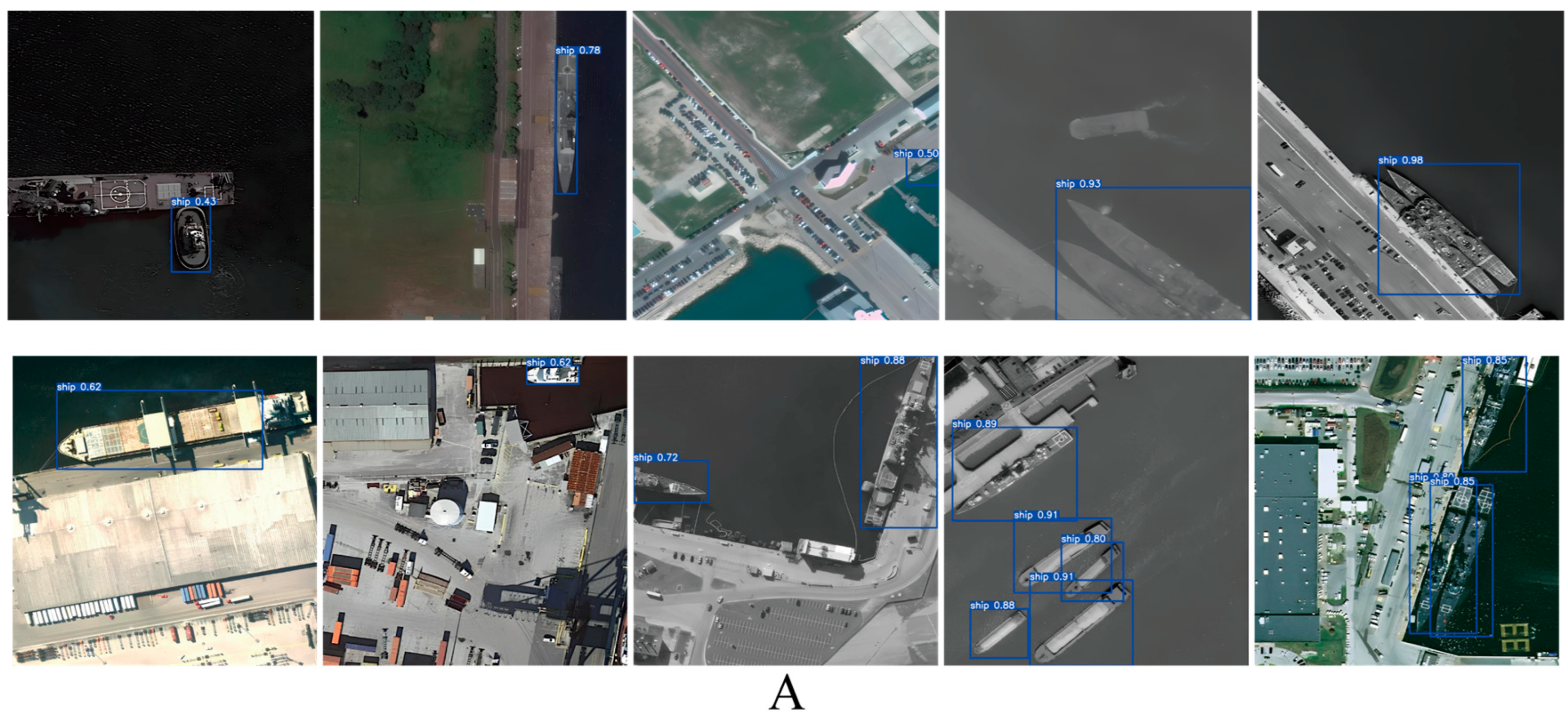
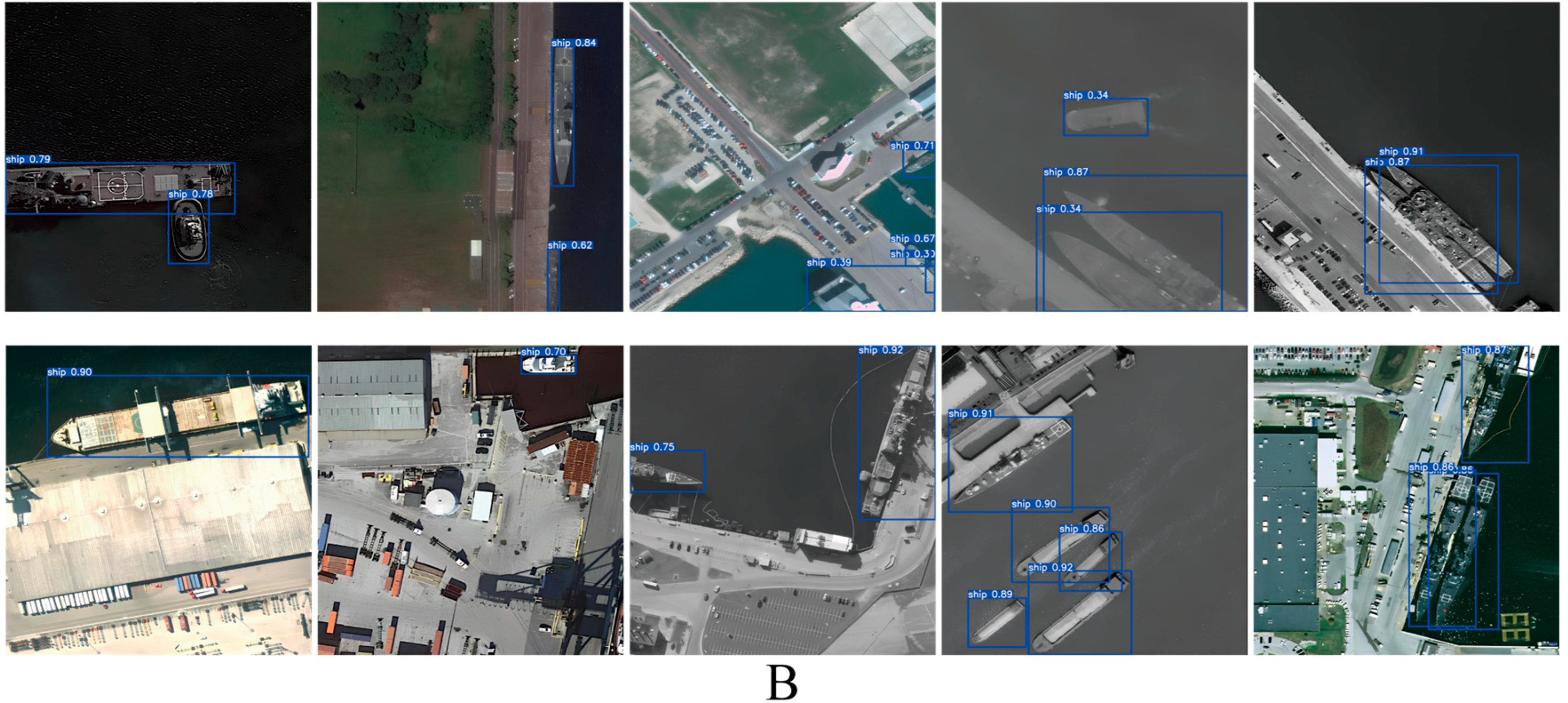
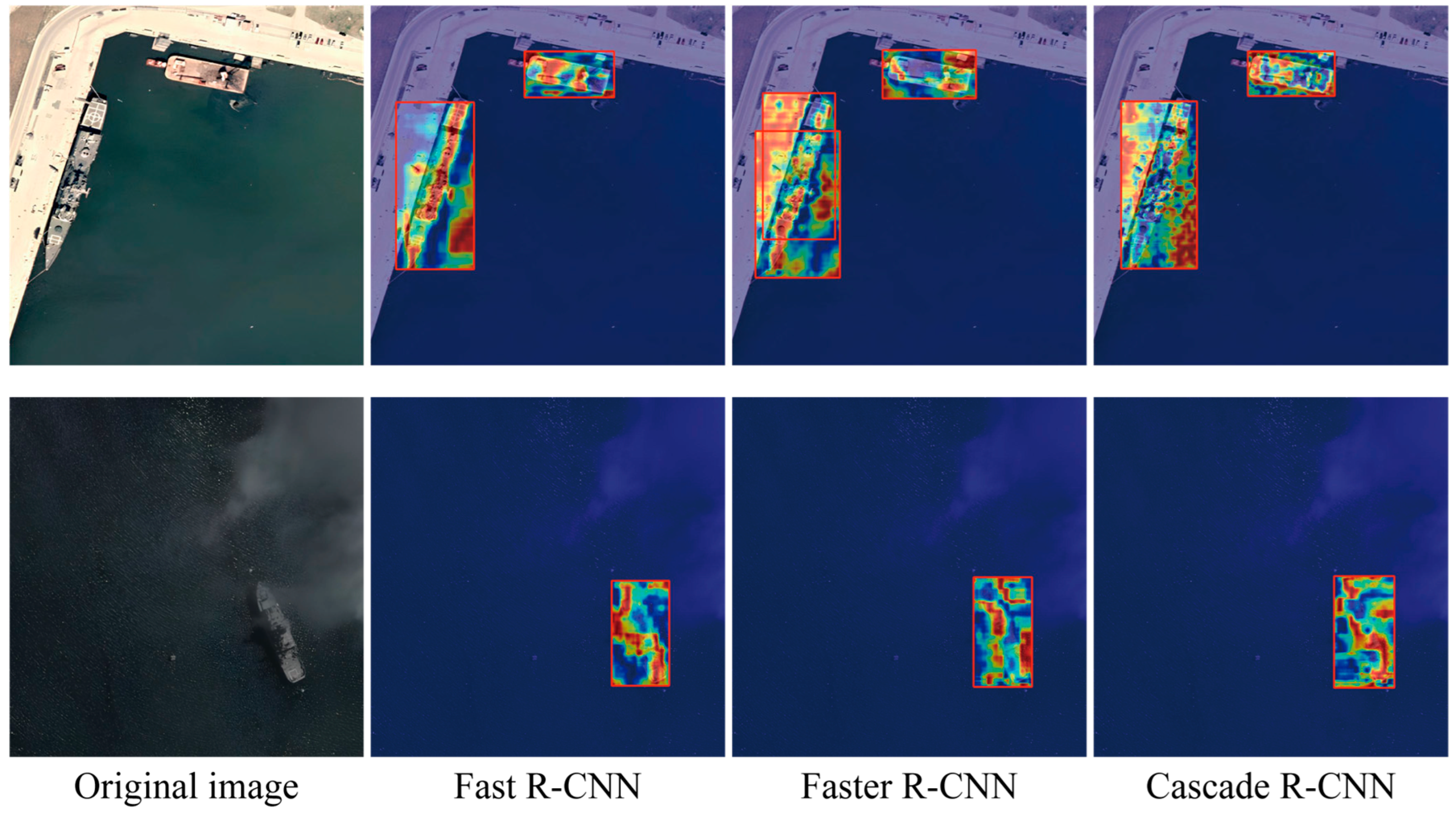
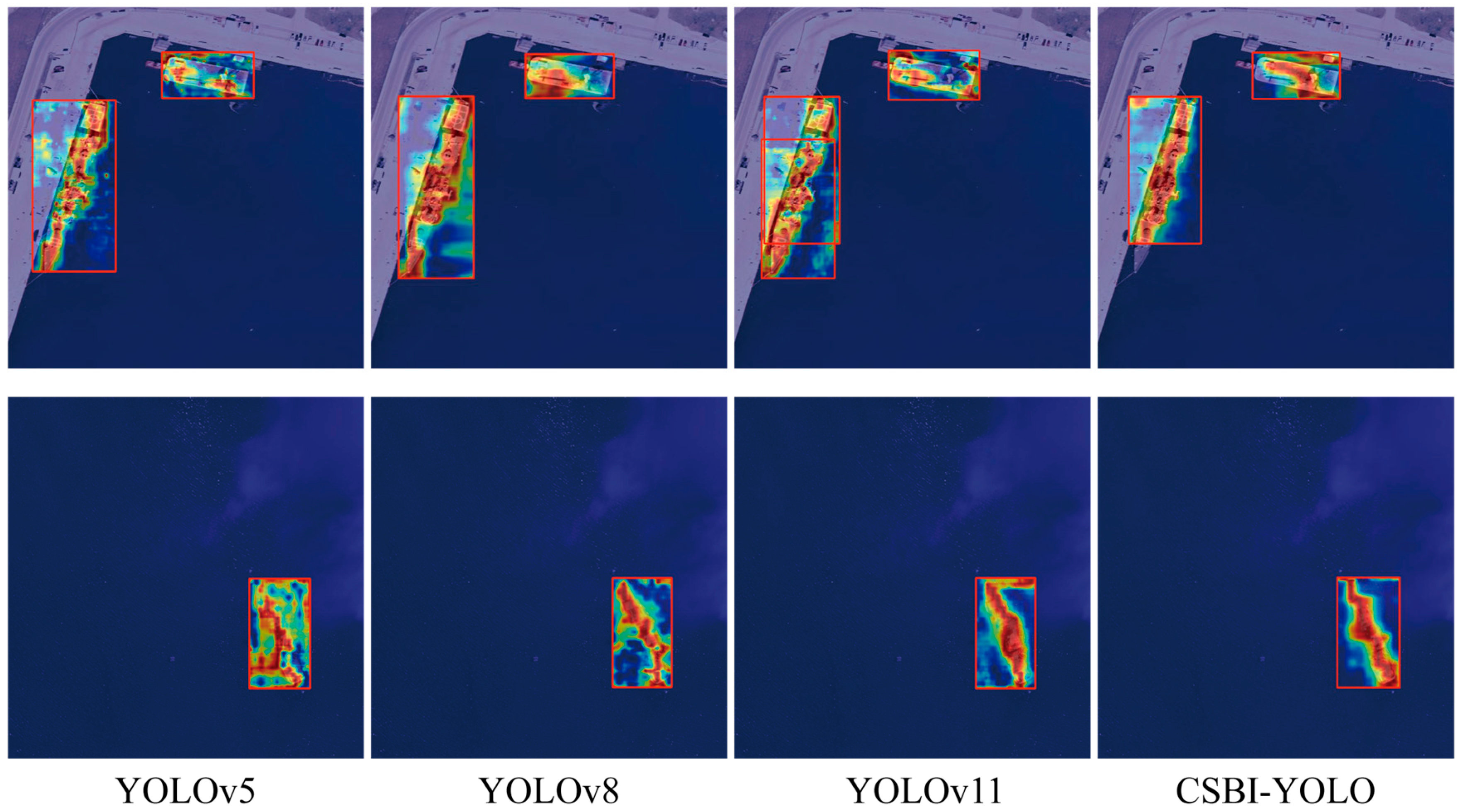
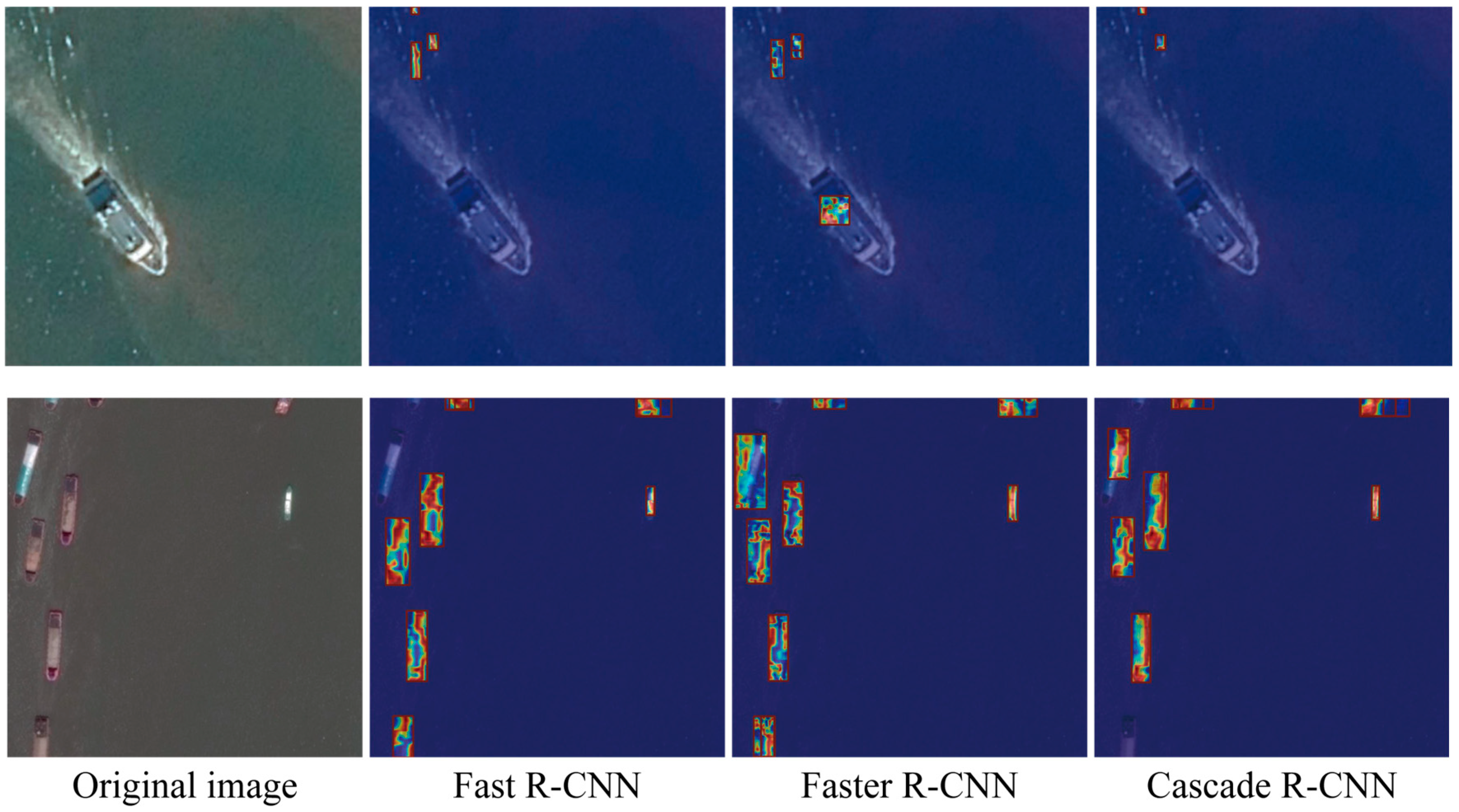
4.4. Results and Analysis
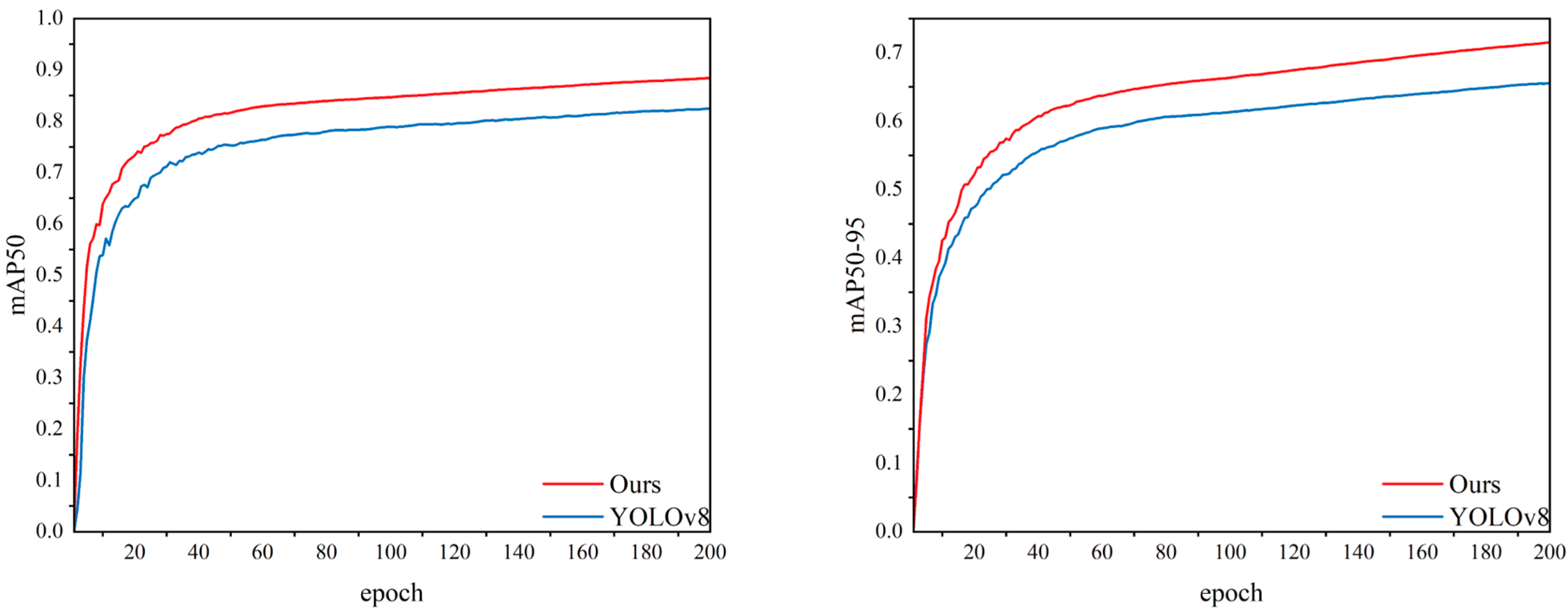
4.4.1. Comparison Experiment
4.4.2. Generalization Experiment
4.4.3. Ablation Experiment
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, H.; Chen, M. A Decade of Monitoring On-Road Vehicle Emissions Using Remote Sensing Technology. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2025, 130, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y. Application of Remote Sensing Technology in Smart City Construction and Planning. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2023, 2608, 012052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, D.; Li, L.; Ning, R.; Yu, S.; Gao, N. Application of Remote Sensing Technology in Water Quality Monitoring: From Traditional Approaches to Artificial Intelligence. Water Res. 2024, 267, 122546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsan, S.A.H.; Khan, M.A.; Ghadi, Y.Y. Editorial on the Advances, Innovations and Applications of UAV Technology for Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casagli, N.; Intrieri, E.; Tofani, V.; Gigli, G.; Raspini, F. Landslide Detection, Monitoring and Prediction with Remote-Sensing Techniques. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battison, R.; Prober, S.M.; Zdunic, K.; Jackson, T.D.; Fischer, F.J.; Jucker, T. Tracking Tree Demography and Forest Dynamics at Scale Using Remote Sensing. New Phytol. 2024, 244, 2251–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Li, H.; Xiao, Q.; Yu, P.; Ding, Z.; Wang, Z.; Xie, S. Fighting against Forest Fire: A Lightweight Real-Time Detection Approach for Forest Fire Based on Synthetic Images. Expert Syst. Appl. 2025, 262, 125620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yar, H.; Ullah, F.U.M.; Khan, Z.A.; Kim, M.J.; Baik, S.W. EFNet-CSM: EfficientNet with a Modified Attention Mechanism for Effective Fire Detection. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2025, 329, 114353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Chen, S.; Liu, G.; Yang, L.; Yuan, Q.; Cai, Y.; Chen, L. Dual-Perspective Safety Driver Secondary Task Detection Method Based on Swin-Transformer and Cross-Attention. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2025, 65, 103320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, H.; Imani, M.; Chen, R.; Imani, F. Vision Language Model for Interpretable and Fine-Grained Detection of Safety Compliance in Diverse Workplaces. Expert Syst. Appl. 2025, 265, 125769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girshick, R.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; Malik, J. Region-Based Convolutional Networks for Accurate Object Detection and Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 38, 142–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollar, P.; Girshick, R. Mask R-CNN. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2020, 42, 386–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You Only Look Once: Unified, Real-Time Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLO9000: Better, Faster, Stronger. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 6517–6525. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLOv3: An Incremental Improvement 2018. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02767. [Google Scholar]
- Bochkovskiy, A.; Wang, C.-Y.; Liao, H.-Y.M. YOLOv4: Optimal Speed and Accuracy of Object Detection 2020. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.10934. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Li, L.; Jiang, H.; Weng, K.; Geng, Y.; Li, L.; Ke, Z.; Li, Q.; Cheng, M.; Nie, W.; et al. YOLOv6: A Single-Stage Object Detection Framework for Industrial Applications 2022. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2209.02976. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Bochkovskiy, A.; Liao, H.-Y.M. YOLOv7: Trainable Bag-of-Freebies Sets New State-of-the-Art for Real-Time Object Detectors. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 7464–7475. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Shao, F.; Chu, W.; Dai, J.; Zhang, H. An Improved YOLOv8-Based Lightweight Attention Mechanism for Cross-Scale Feature Fusion. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, W.; Xia, S.; Kuzmin, S.; Gerasimov, I.; Cheng, X. RTFVE-YOLOv9: Real-Time Fruit Volume Estimation Model Integrating YOLOv9 and Binocular Stereo Vision. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2025, 236, 110401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Chen, J.; Lv, B.; Peng, L. Lightweight Marine Biodetection Model Based on Improved YOLOv10. Alex. Eng. J. 2025, 119, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Shao, F.; Yang, C.; Dai, J.; Xue, J.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, T. ACLC-Detection: A Network for Remote Sensing Image Detection Based on Attention Mechanism and Lightweight Convolution. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Chen, S.; You, Z.; Tang, J. FSENet: Feature Suppression and Enhancement Network for Tiny Object Detection. Pattern Recognit. 2025, 162, 111425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Wu, X.; Shi, J.; Su, Y.; Shi, B. Enhancing Real-Time Detection Transformer for Small Floating Targets. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2025, 161, 112038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Luo, F.; Wu, P.; Tan, J.; Wang, L.; Niu, Q.; Li, H.; Wang, P. An Improved YOLO Network for Small Target Insects Detection in Tomato Fields. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2025, 239, 110915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, T.; Chen, G.; Zhu, K.; Tan, X.; Wang, J.; Guo, W.; Wang, Q.; Luo, X.; Zhang, X. BFA-YOLO: A Balanced Multiscale Object Detection Network for Building Façade Elements Detection. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2025, 65, 103289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Zhang, M.; Wu, L.; Yu, D.; Li, J.; Fan, F.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y. Lightweight SAR Ship Detection Network Based on Transformer and Feature Enhancement. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 4845–4858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Hu, T.; Xu, S.; Xu, H.; Song, L.; Sun, Z. PPDM-YOLO: A Lightweight Algorithm for SAR Ship Image Target Detection in Complex Environments. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2025, 18, 22690–22705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Han, D.; Han, B.; Huang, X. YOLO-HPSD: A High-Precision Ship Target Detection Model Based on YOLOv10. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0321863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Leng, X.; Luo, R.; Sun, Z.; Ji, K.; Kuang, G. YOLO-RC: SAR Ship Detection Guided by Characteristics of Range-Compressed Domain. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 18834–18851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Mei, S. Large Convolution Kernel Network With Edge Self-Attention for Oriented SAR Ship Detection. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2025, 18, 2867–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yan, F.; Liu, Y.; Shen, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, K. A Multi-Scale Rotated Ship Targets Detection Network for Remote Sensing Images in Complex Scenarios. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Fang, W. Incorporating Estimated Depth Maps and Multi-Modal Pretraining to Improve Salient Object Detection in Optical Remote Sensing Images. Expert Syst. Appl. 2025, 298, 129624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, N.; Wang, J.; Shi, H.; Zhang, Z.; Han, Y. Degradation-Removed Multiscale Fusion for Low-Light Salient Object Detection. Pattern Recognit. 2024, 155, 110650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinoth, K.; Sasikumar, P. Lightweight Object Detection in Low Light: Pixel-Wise Depth Refinement and TensorRT Optimization. Results Eng. 2024, 23, 102510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, H.; Tao, Q.; Liu, D. Low-Light Object Detection via Adaptive Enhancement and Dynamic Feature Fusion. Alex. Eng. J. 2025, 126, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Huang, W.; Hu, T.; Duan, X.; Yu, J.; Huang, J.; Wei, J. Efficient Network Architecture for Target Detection in Challenging Low-Light Environments. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2025, 142, 109967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolie, H.F.; Ren, J.; Elyan, E. DICAM: Deep Inception and Channel-Wise Attention Modules for Underwater Image Enhancement. Neurocomputing 2024, 584, 127585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, J.; Bo, Y.; Wang, J. ISTD-DETR: A Deep Learning Algorithm Based on DETR and Super-Resolution for Infrared Small Target Detection. Neurocomputing 2025, 621, 129289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, G.-S.; Bai, X.; Ding, J.; Zhu, Z.; Belongie, S.; Luo, J.; Datcu, M.; Pelillo, M.; Zhang, L. DOTA: A Large-Scale Dataset for Object Detection in Aerial Images. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 3974–3983. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R. Fast R-CNN. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1504.08083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Vasconcelos, N. Cascade R-CNN: Delving into High Quality Object Detection. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1712.00726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






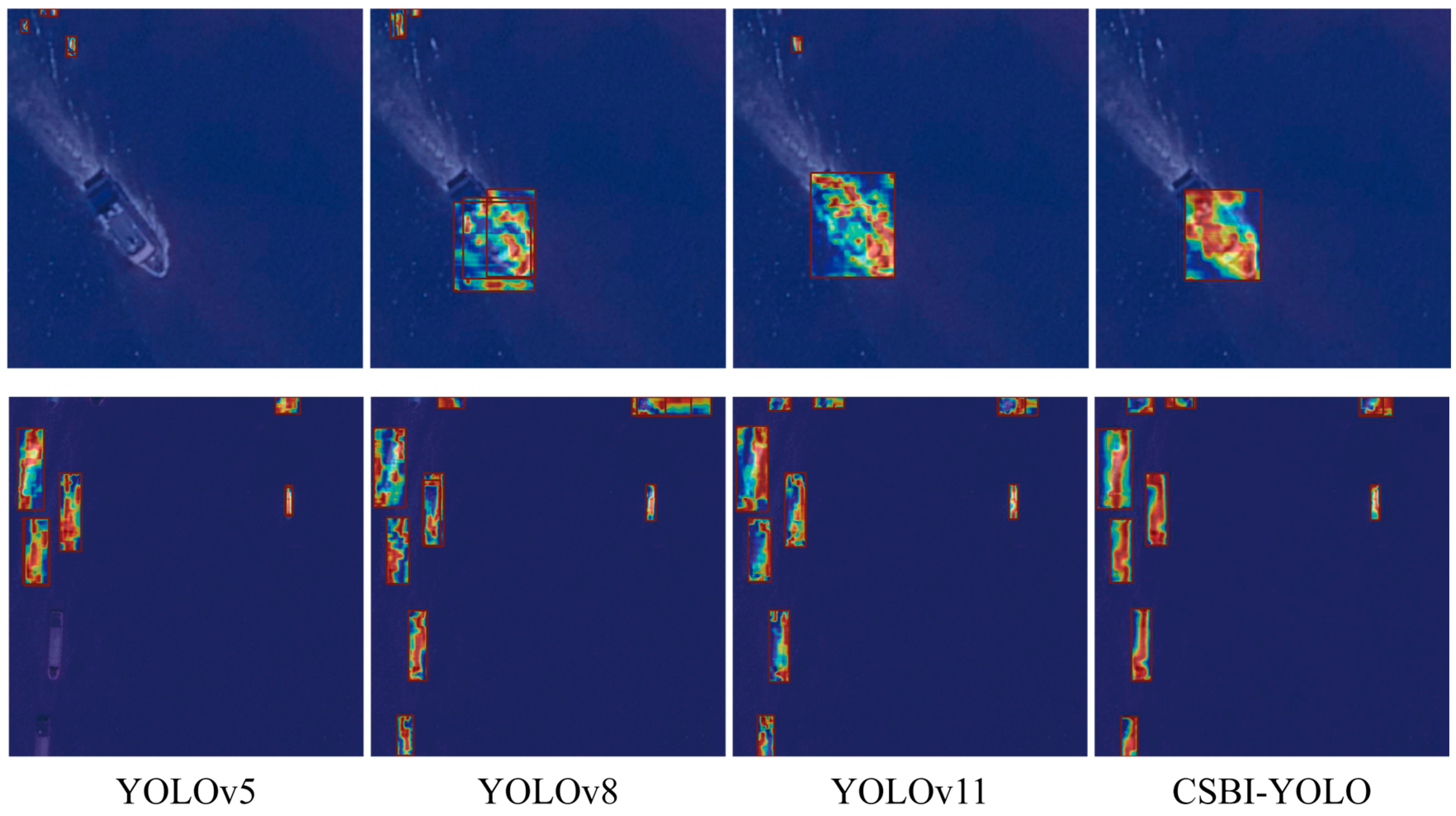
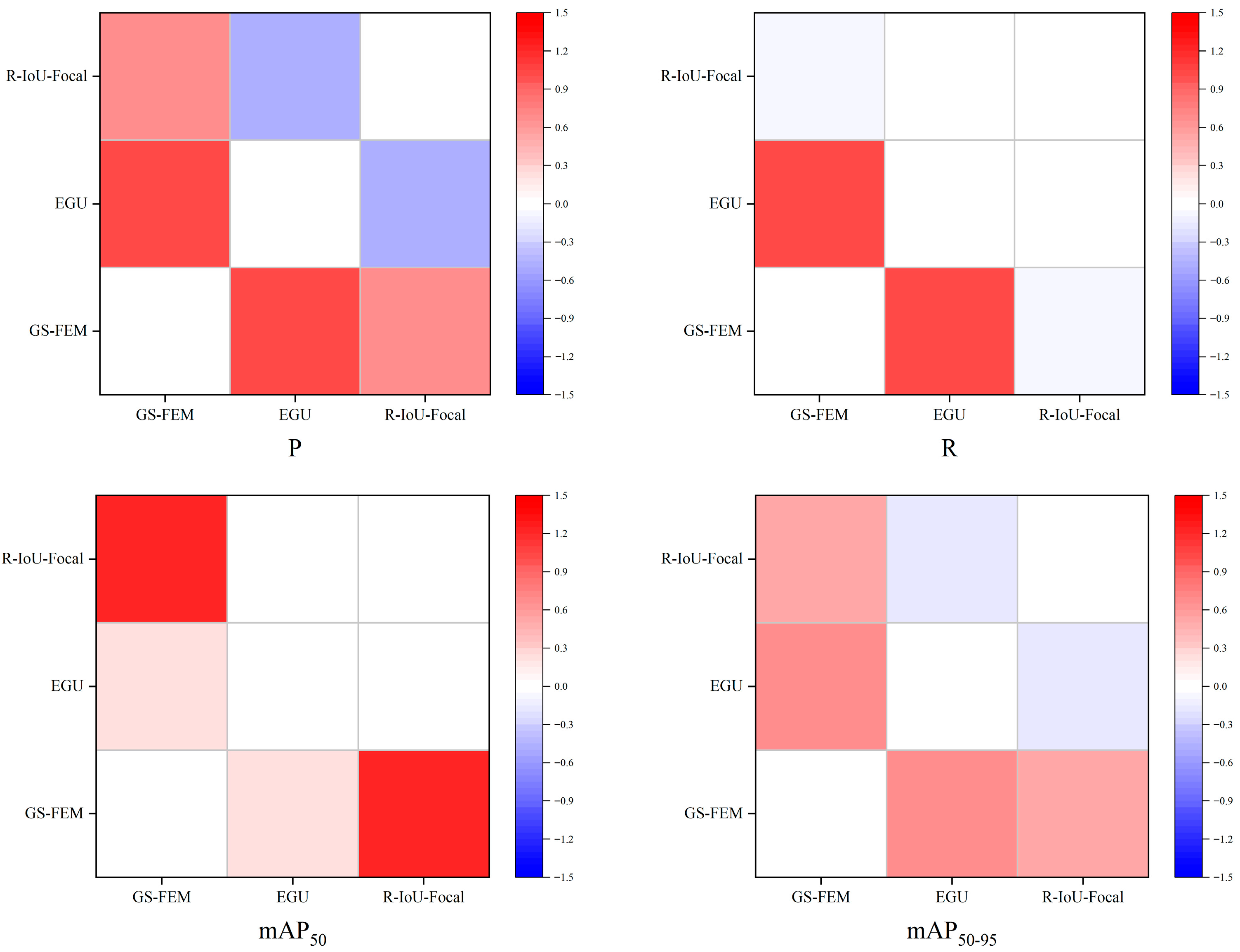
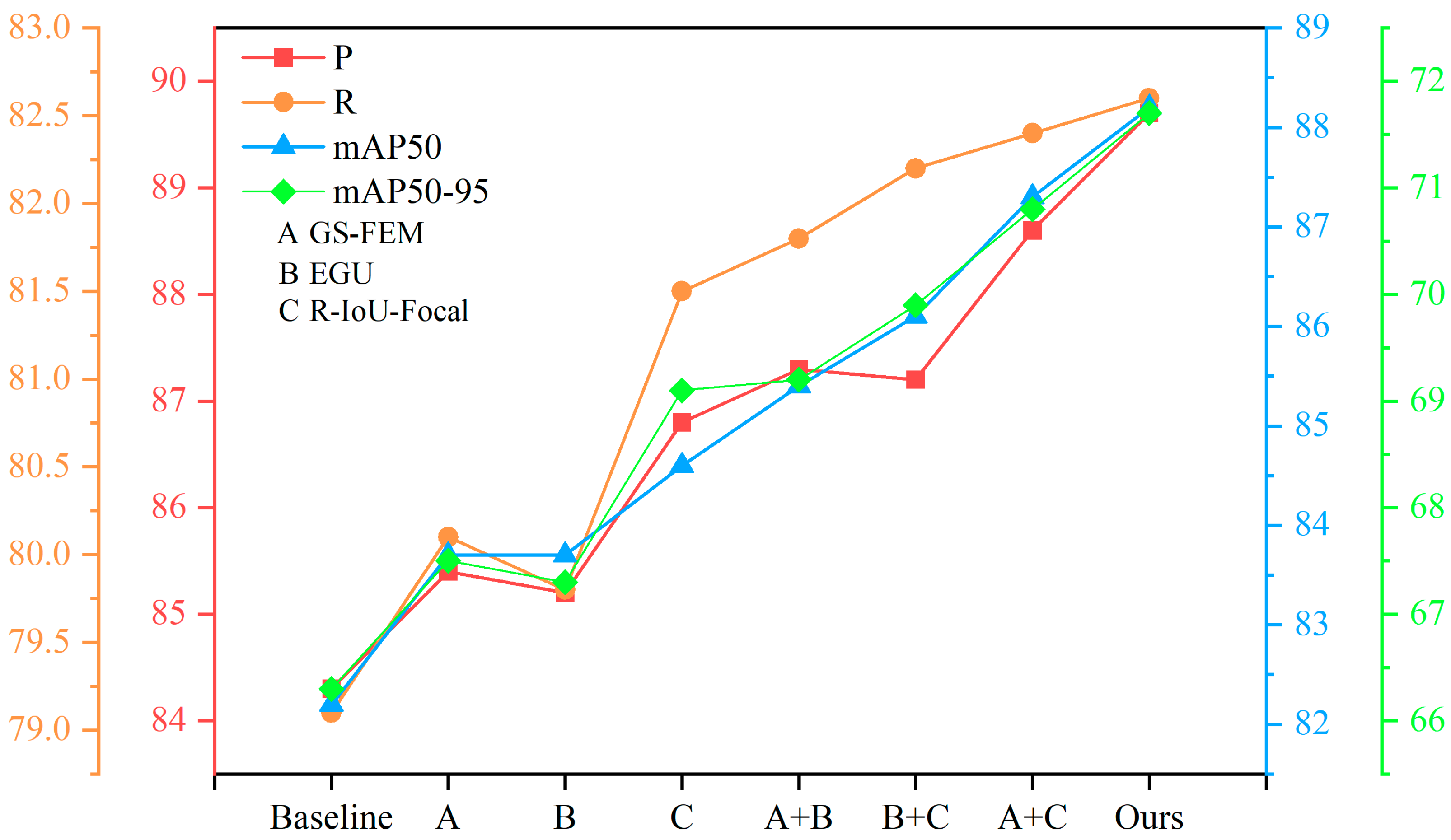

| Parameter | Configuration |
|---|---|
| CPU model | Intel Core i7-9700k |
| GPU model | NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090Ti |
| Operating system | Ubuntu 18.04 LTS 64-bits |
| Deep learning frame | PyTorch 1.9.1 |
| GPU accelerator | CUDA 10.2 |
| Integrated development environment | PyCharm 2024.03 |
| Scripting language | Python 3.8 |
| Neural network accelerator | CUDNN 7.6.5 |
| Parameter | Configuration |
|---|---|
| Neural network optimizer | SGD |
| Learning rate | 0.001 |
| Training epochs | 200 |
| Momentum | 0.937 |
| Batch size | 32 |
| Weight decay | 0.0005 |
| Method | Param. | FLOPS | P | R | mAP50 | mAP50–95 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fast R-CNN | 48.5 | 85.7 | 74.8 | 72.2 | 77.5 | 62.6 |
| Faster R-CNN | 42.3 | 64.1 | 77.4 | 75.2 | 76.1 | 63.4 |
| Cascade R-CNN | 44.6 | 75.2 | 79.8 | 74.6 | 80.4 | 63.3 |
| YOLOv5 | 7.5 | 16.8 | 83.5 | 76.6 | 81.1 | 62.8 |
| YOLOv8 | 11.2 | 28.4 | 84.3 | 79.1 | 82.2 | 66.3 |
| YOLOv11 | 9.6 | 22.1 | 86.5 | 78.4 | 85.6 | 67.2 |
| DEMNet | 2.1 | 4.5 | 88.1 | 77.5 | 86.4 | 70.3 |
| CSBI-YOLO | 13.3 | 30.7 | 89.7 | 82.6 | 88.2 | 71.7 |
| Method | Param. | FLOPS | P | R | mAP50 | mAP50–95 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fast R-CNN | 48.5 | 85.7 | 85.9 | 83.7 | 85.1 | 56.2 |
| Faster R-CNN | 42.3 | 64.1 | 82.9 | 84.4 | 85.9 | 57.1 |
| Cascade R-CNN | 44.6 | 75.2 | 82.6 | 80.8 | 85.5 | 56.4 |
| YOLOv5 | 7.5 | 16.8 | 87.3 | 81.9 | 86.4 | 56.5 |
| YOLOv8 | 11.2 | 28.4 | 85.1 | 87.4 | 86.6 | 61.7 |
| YOLOv11 | 9.6 | 22.1 | 86.8 | 86.4 | 86.9 | 60.9 |
| DEMNet | 2.1 | 4.5 | 90.1 | 85.6 | 85.2 | 61.3 |
| CSBI-YOLO | 13.3 | 30.7 | 90.5 | 84.1 | 87.9 | 62.7 |
| Mobile | GS-FEM | EGU | R-IoU-Focal | Param. | FLOPS | P | R | mAP50 | mAP50–95 | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv8 | -- | -- | -- | 11.2 | 28.4 | 84.3 | 79.1 | 82.2 | 66.3 | 106 |
| √ | -- | -- | 13.2 | 30.7 | 85.4 | 80.1 | 83.7 | 67.5 | 95 | |
| -- | √ | -- | 11.3 | 28.4 | 85.2 | 79.8 | 83.7 | 67.3 | 104 | |
| -- | -- | √ | 11.2 | 28.4 | 86.8 | 81.5 | 84.6 | 69.1 | 106 | |
| √ | √ | -- | 13.3 | 30.7 | 87.3 | 81.8 | 85.4 | 69.2 | 94 | |
| -- | √ | √ | 11.3 | 28.4 | 87.2 | 82.2 | 86.1 | 69.9 | 104 | |
| √ | -- | √ | 13.2 | 30.7 | 88.6 | 82.4 | 87.3 | 70.8 | 95 | |
| √ | √ | √ | 13.3 | 30.7 | 89.7 | 82.6 | 88.2 | 71.7 | 94 |
| Mobile | Branch One | Branch Two | Branch Three | Branch Four | Param. | mAP50 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ■ | ○ | ■ | ○ | ■ | ○ | ■ | ○ | |||
| GS-FEM | √ | -- | √ | -- | √ | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| √ | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | ↓ 85% | ↓ 72% | |
| -- | √ | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | ↓ 86% | ↓ 79% | |
| √ | -- | √ | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | ↓ 61% | ↓ 55% | |
| √ | -- | -- | √ | -- | -- | -- | -- | ↓ 62% | ↓ 63% | |
| √ | -- | √ | -- | -- | √ | -- | -- | ↓ 6% | ↓ 8% | |
| √ | -- | √ | -- | √ | -- | √-- | -- | ↑ 23% | ↑ 4% | |
| √ | -- | √ | -- | √ | -- | -- | √ | ↑ 22% | ↑ 3% | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, S.; Shao, F.; Xue, J.; Dai, J.; Chu, W.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, T. Optical Remote Sensing Ship Detection Combining Channel Shuffling and Bilinear Interpolation. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 3828. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17233828
Liu S, Shao F, Xue J, Dai J, Chu W, Liu Q, Zhang T. Optical Remote Sensing Ship Detection Combining Channel Shuffling and Bilinear Interpolation. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(23):3828. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17233828
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Shaodong, Faming Shao, Jinhong Xue, Juying Dai, Weijun Chu, Qing Liu, and Tao Zhang. 2025. "Optical Remote Sensing Ship Detection Combining Channel Shuffling and Bilinear Interpolation" Remote Sensing 17, no. 23: 3828. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17233828
APA StyleLiu, S., Shao, F., Xue, J., Dai, J., Chu, W., Liu, Q., & Zhang, T. (2025). Optical Remote Sensing Ship Detection Combining Channel Shuffling and Bilinear Interpolation. Remote Sensing, 17(23), 3828. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17233828






