Gully Extraction in Northeast China’s Black Soil Region: A Multi-CNN Comparison with Texture-Enhanced Remote Sensing
Highlights
- A GLCM-based texture enhancement method with a 5 × 5 window and 32 gray levels improves boundary detection in high-resolution imagery, boosting U-Net accuracy by 1.54% for erosion gully extraction.
- Among DeepLabv3+, U-Net, and U-Net++, U-Net achieves the highest performance (90.27% accuracy with texture features), excelling in capturing elongated gully structures while reducing false positives.
- The texture-fused U-Net framework enables scalable, automated gully monitoring in Northeast China’s black soil region, aiding timely soil erosion assessment without relying on DEM data.
- Enhanced extraction accuracy supports sustainable land management and policy decisions for conserving fertile black soils, mitigating threats to agricultural productivity and food security.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
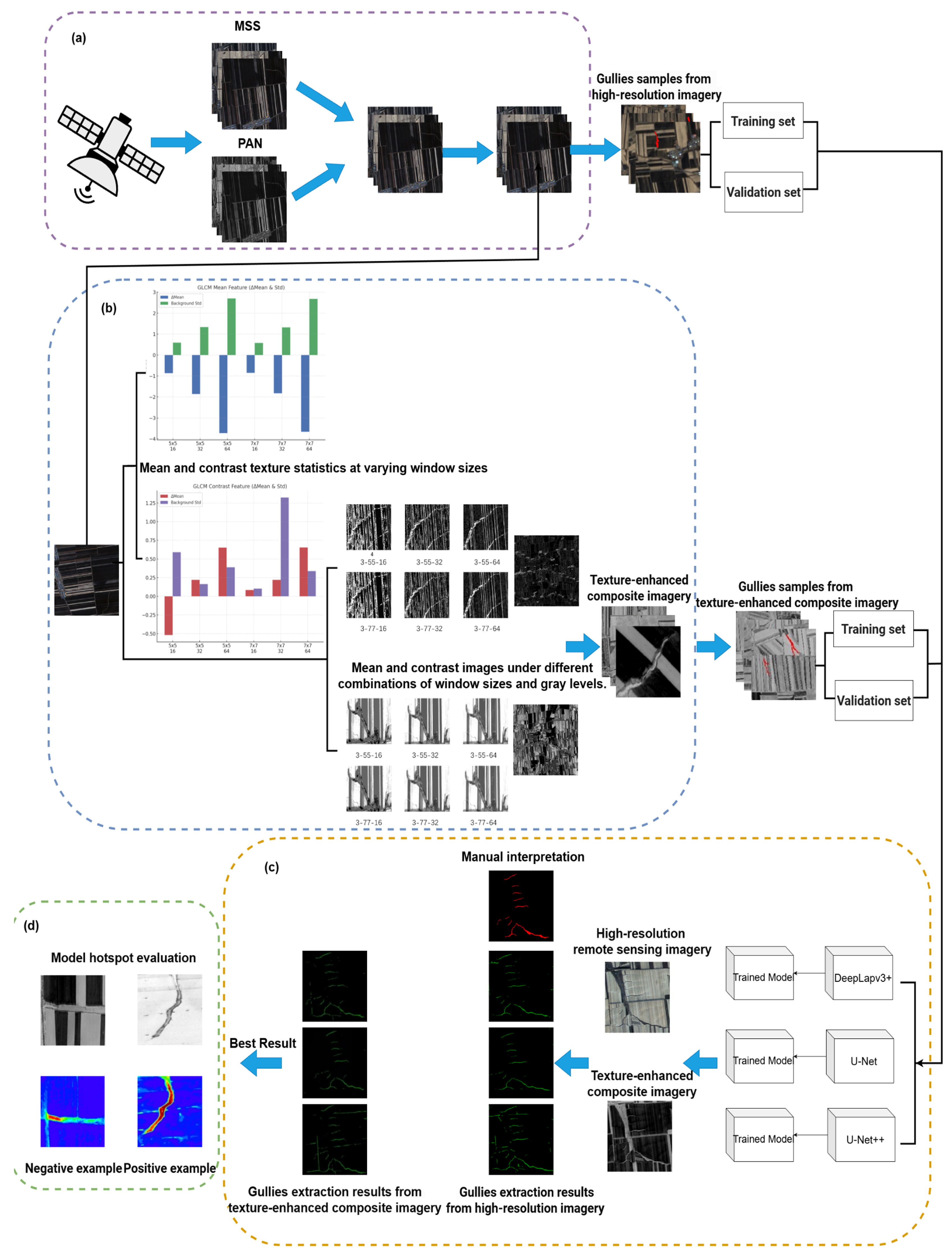
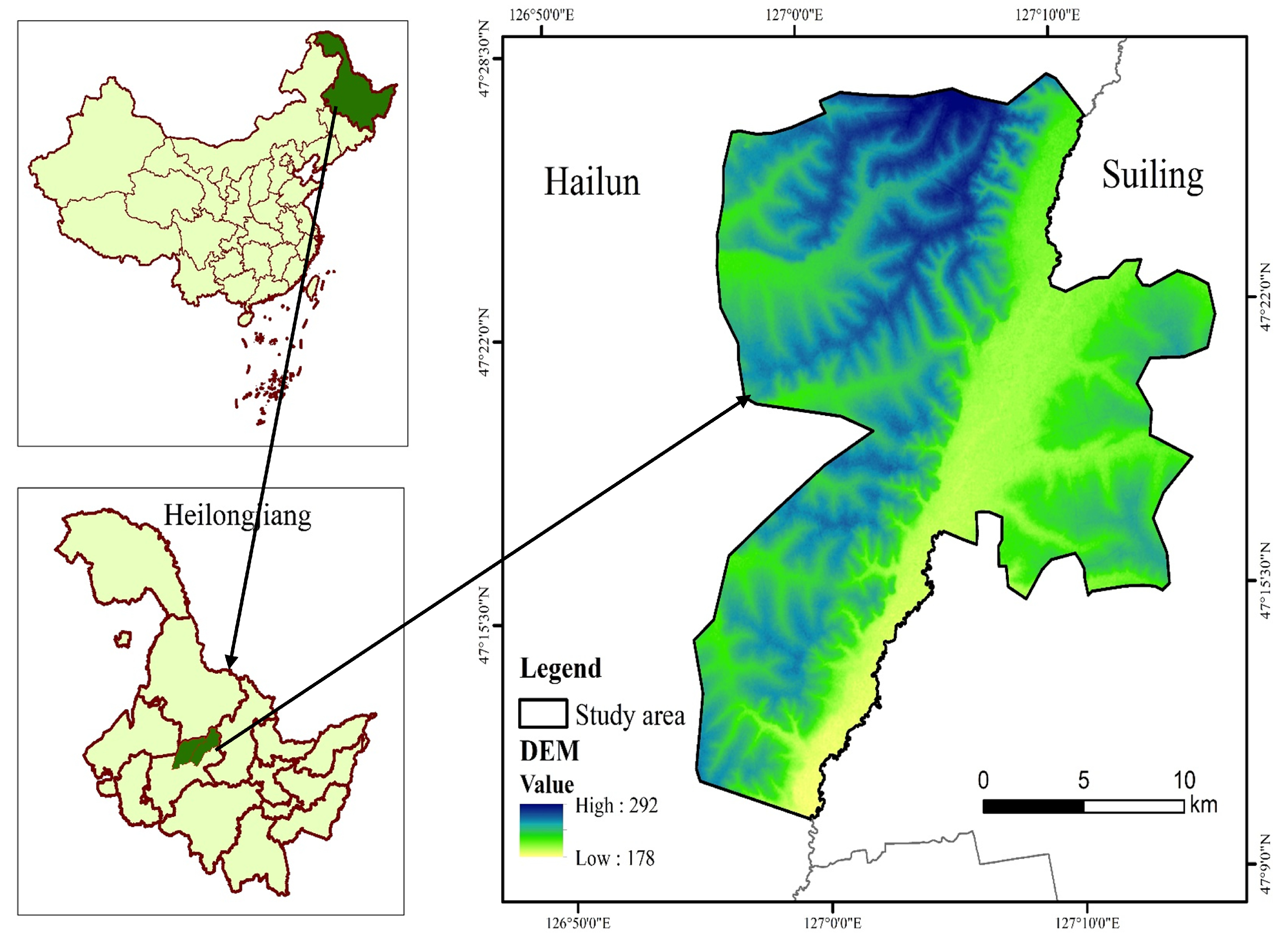
2.1. Study Area and Data Source
2.1.1. Study Area
2.1.2. Data Source and Preprocessing
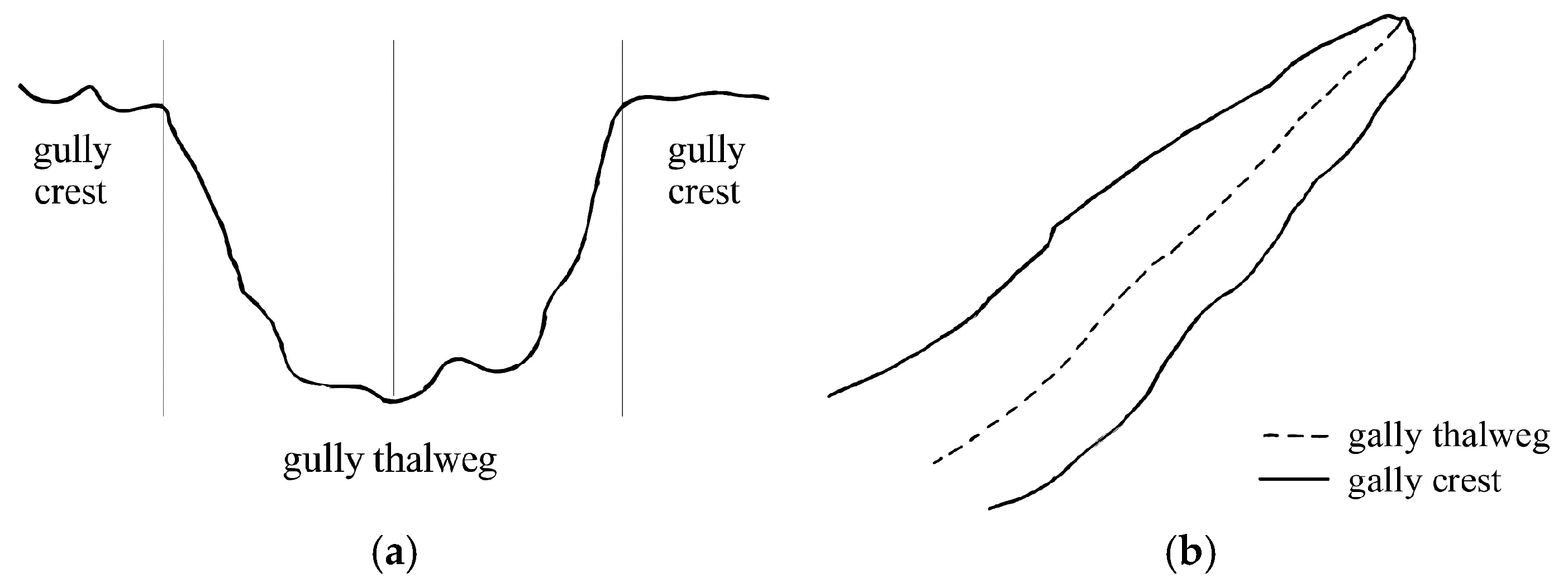
2.2. Texture Feature Extraction of Gray-Level Co-Occurrence Matrix Images
2.2.1. Texture Feature Extraction
2.2.2. Principal Component Analysis
2.2.3. Setting the Sliding Window Sizes and Gray Levels
2.3. Sample Set Construction
2.4. Convolutional Neural Networks
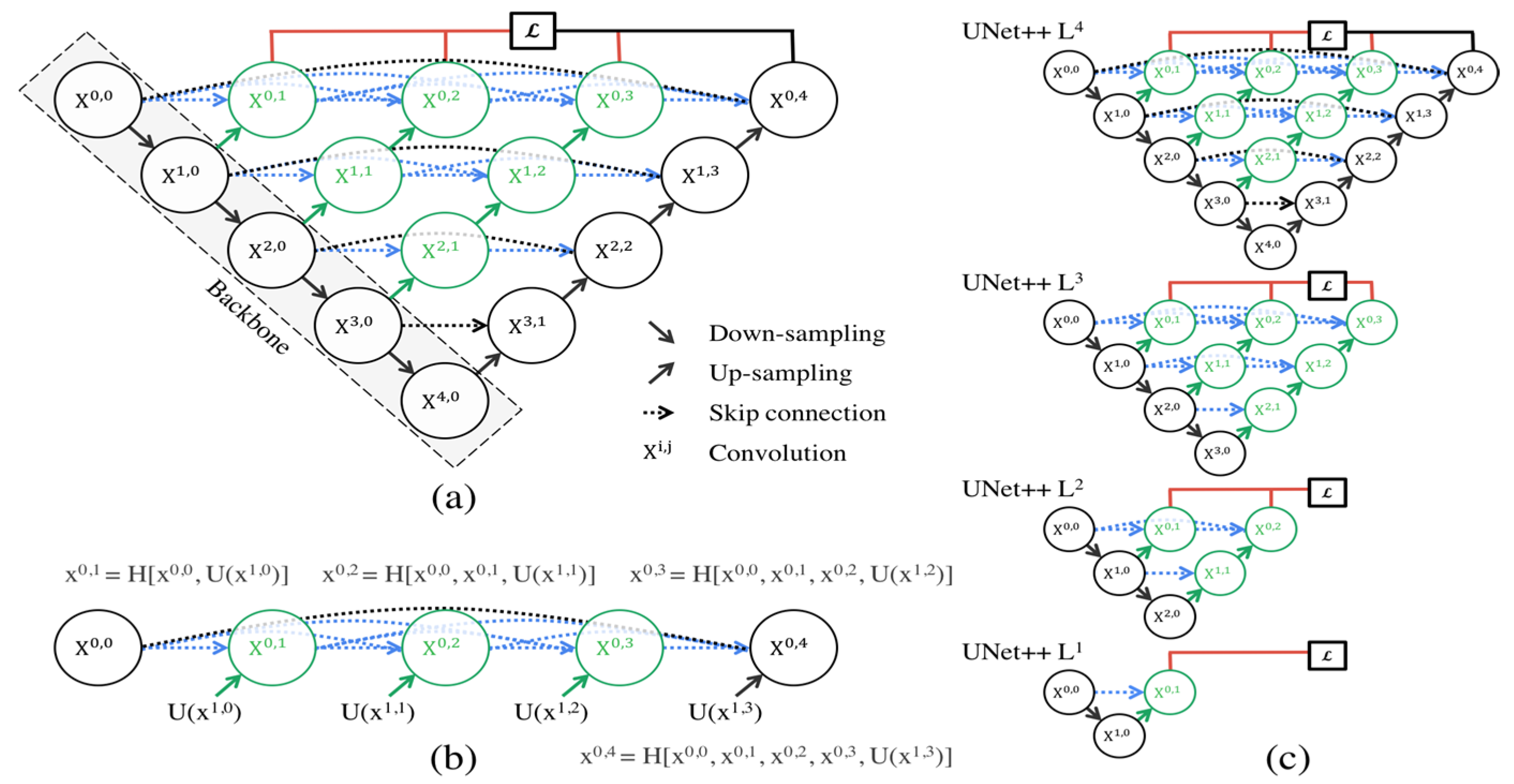
2.4.1. U-Net Network
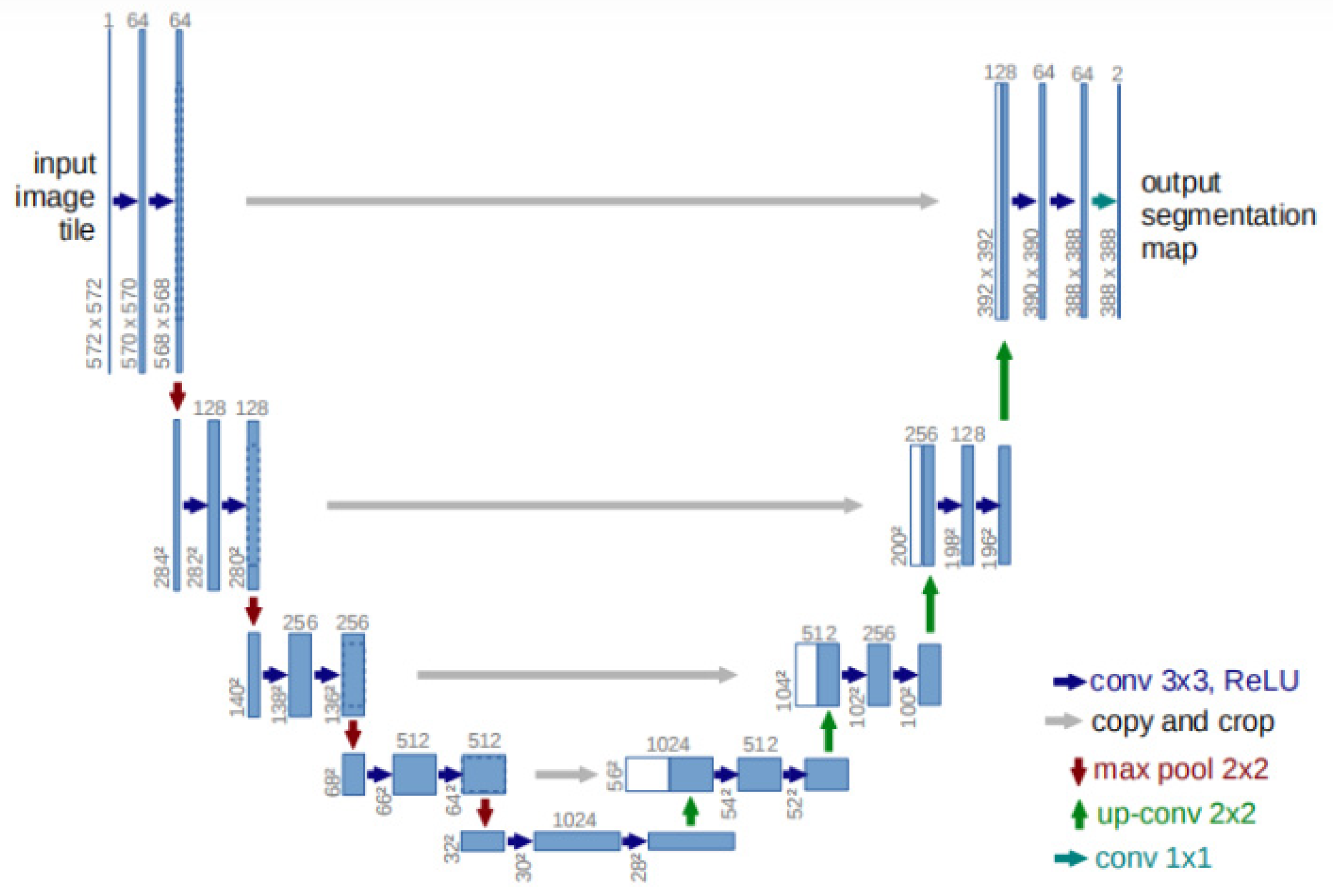
2.4.2. U-Net++ Network
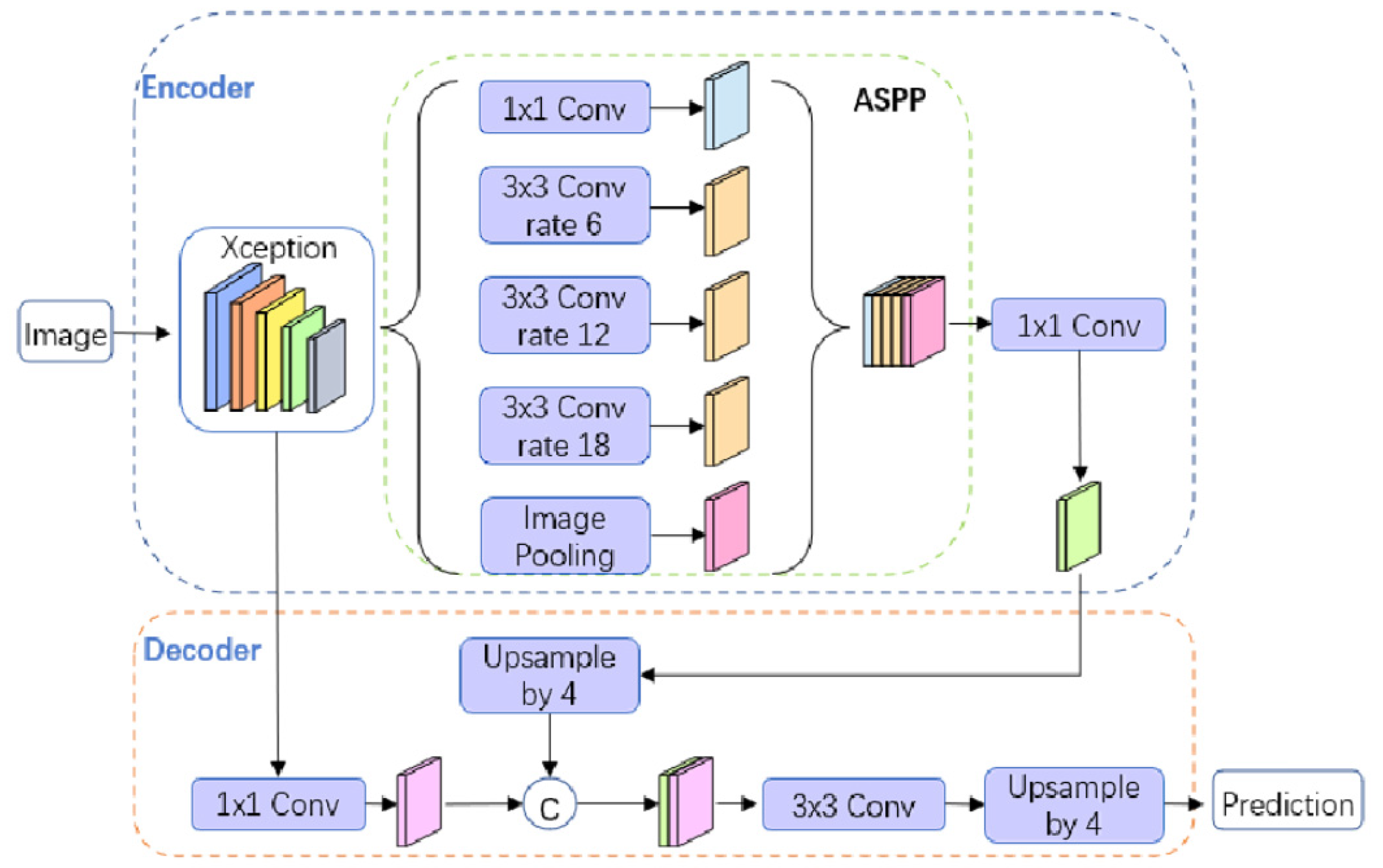
2.4.3. DeepLabv3+ Network
2.4.4. Model Training Settings
2.5. Accuracy Evaluation
- TP—Number of samples correctly predicted as positive;
- TN—Number of samples correctly predicted as negative;
- FP—Number of samples incorrectly predicted as positive;
- FN—Number of samples incorrectly predicted as negative.
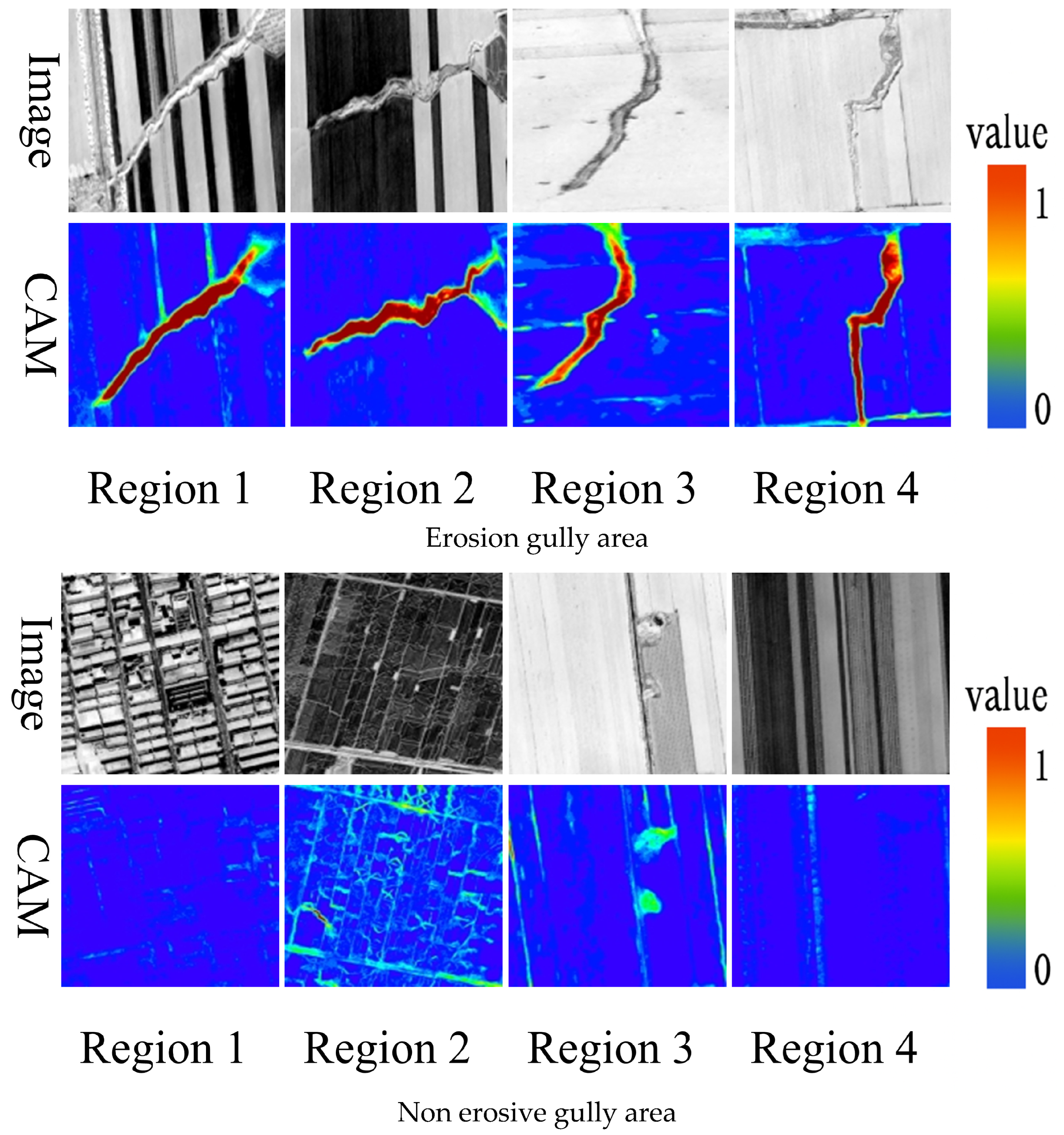
2.6. Visualization and Interpretation of Model Decisions Based on Class Activation Mapping
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Optimization and Analysis of Texture Feature Parameters
3.1.1. Band Statistical Analysis and Principal Component Analysis
3.1.2. Determination of Optimal GLCM Parameter Combination
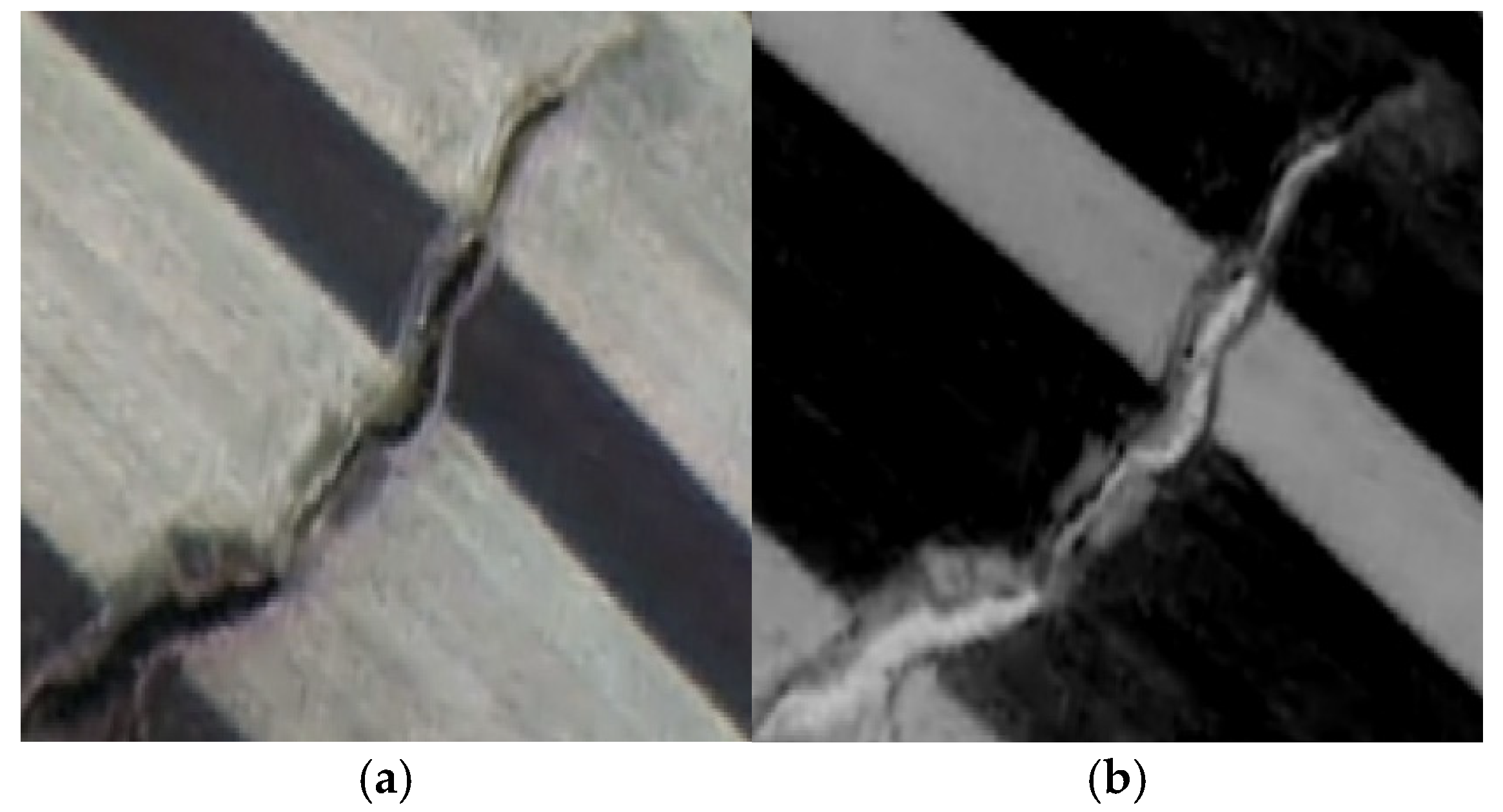
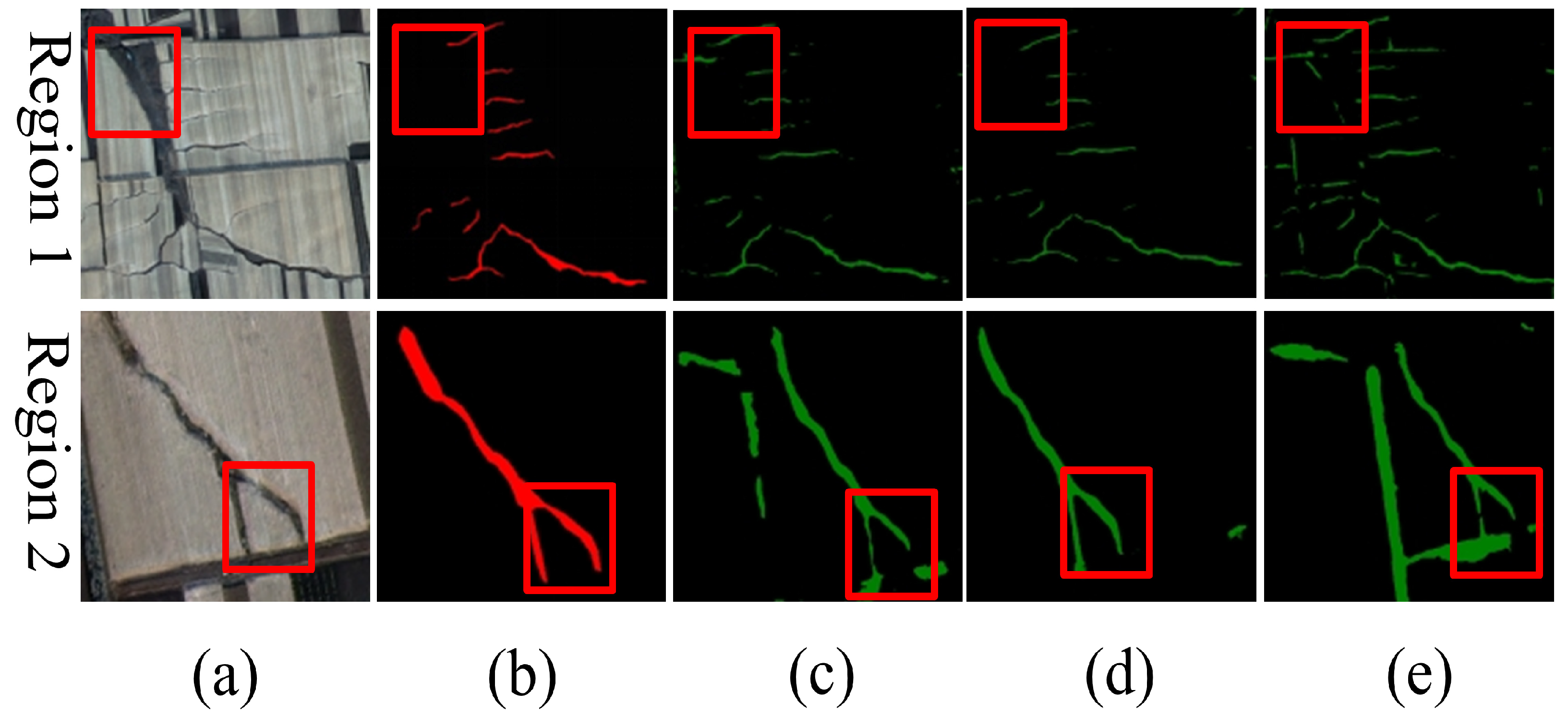
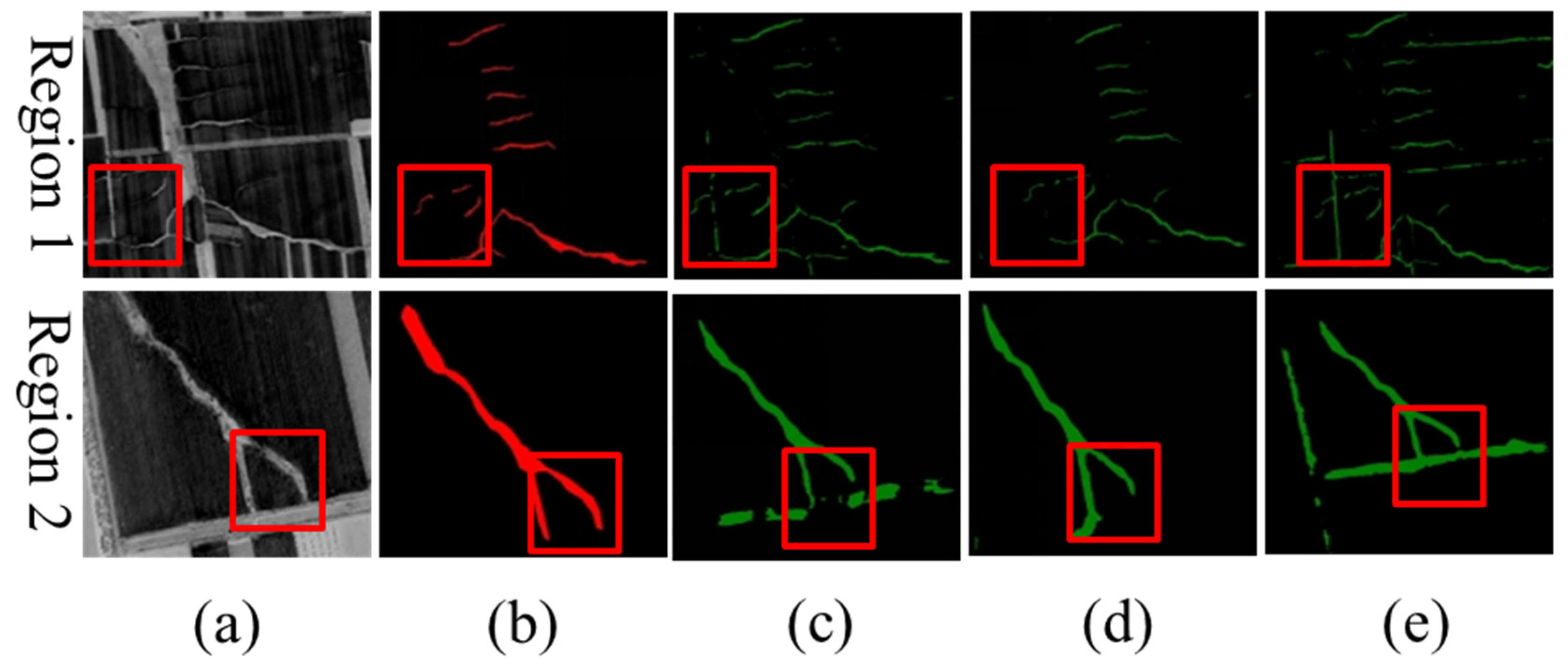
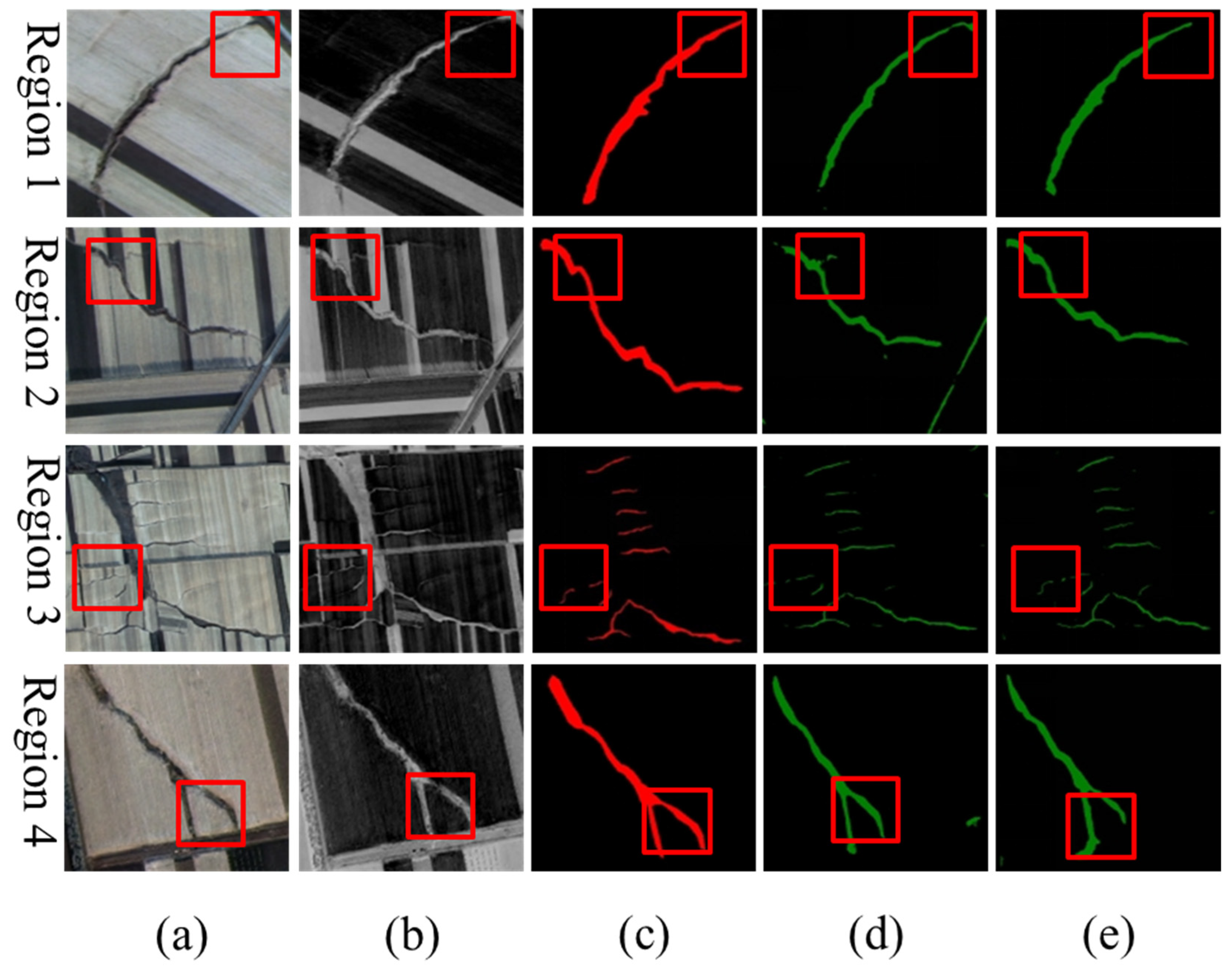
3.2. Comparison Between Texture-Enhanced Composite Imagery and Original Imagery
3.3. Comparison Between Multiple CNNs Based on Original Imagery
3.4. Comparison Between Multiple CNNs Based on Texture-Enhanced Composite Imagery
3.5. Comparison Between Results Based on Different Inputs
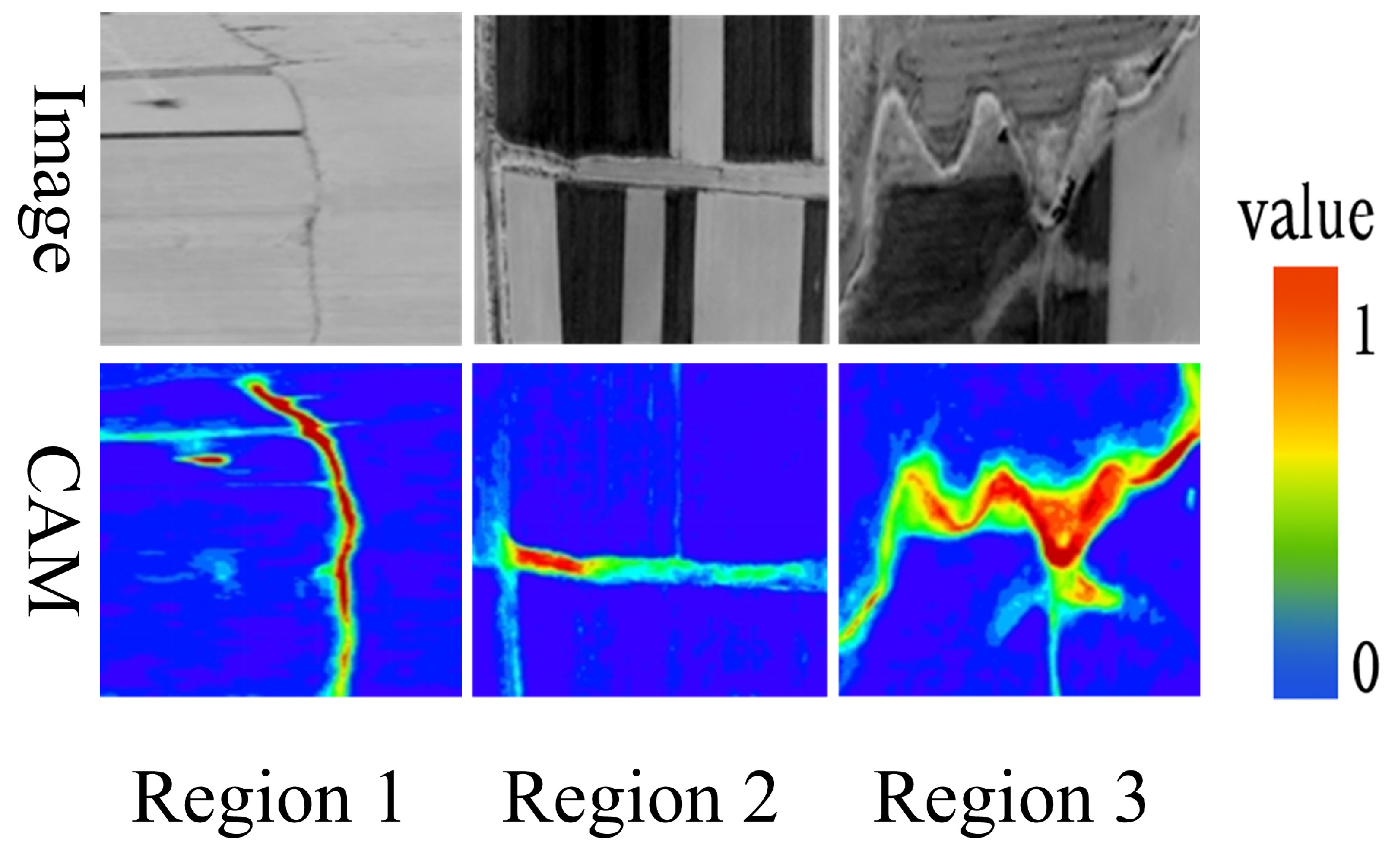
3.6. Analysis of Class Activation Maps and Error
4. Discussion
4.1. Research Overview and Key Findings
4.2. Mechanisms of CNN Models for Erosion Gully Extraction
4.3. Innovation of the GLCM-CNN Integration Method and Its Practical Application Value
4.4. Research Limitations and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Yu, Y.; Zang, D.; Dai, X.; Zheng, S. Cropland zoning based on district and county scales in the black soil region of northeastern China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 3341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Ran, D.; Tan, D.; Liao, X. Spatiotemporal evolution of cropland in Northeast China’s black soil region over the past 40 years at the county scale. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2024, 7, 1332595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Sun, H.; Yang, J.; Zhang, S.; Fu, H.; Wang, N.; Liu, Q. Quantitative evaluation of gully erosion using multitemporal UAV data in the southern black soil region of Northeast China: A case study. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Li, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Liang, A.; Zhang, Y.; Wen, X.; Hu, W.; Zhou, Y. Temporal and spatial distribution and development of permanent gully in cropland in the rolling hill region (phaeozems area) of northeast China. Catena 2024, 235, 107625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Wu, Y.; Qin, W.; Guo, Q.; Yin, Z.; Duan, X. The gully erosion rates in the black soil region of northeastern China: Induced by different processes and indicated by different indexes. Catena 2019, 182, 104146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinsey-Henderson, A.; Hawdon, A.; Bartley, R.; Wilkinson, S.N.; Lowe, T. Applying a hand-held laser scanner to monitoring gully erosion: Workflow and evaluation. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, J.; Li, Z.; Ke, L.; Li, Q.; Fan, J.; Wang, X. Research on soil erosion based on remote sensing technology: A review. Agriculture 2025, 15, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Zhang, B.; Wang, C.; Liu, M.; Wang, X. Erosion gully networks extraction based on InSAR refined digital elevation model and relative elevation algorithm—A case study in Huangfuchuan Basin, Northern Loess Plateau, China. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, C.; Long, Y.; Pang, G.; Shen, H.; Wang, L.; Yang, Q. Comparative analysis of gully morphology extraction suitability using unmanned aerial vehicle and Google Earth imagery. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Qin, F. Deep segmentation and classification of complex crops using multi-feature satellite imagery. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 200, 107249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slimane, A.B.; Raclot, D.; Rebai, H.; Le Bissonnais, Y.; Planchon, O.; Bouksila, F. Combining field monitoring and aerial imagery to evaluate the role of gully erosion in a Mediterranean catchment (Tunisia). Catena 2018, 170, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahabi, H.; Jarihani, B.; Tavakkoli Piralilou, S.; Chittleborough, D.; Avand, M.; Ghorbanzadeh, O. A semi-automated object-based gully networks detection using different machine learning models: A case study of Bowen Catchment, Queensland, Australia. Sensors 2019, 19, 4893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, T. Verifying the effects of the grey level co-occurrence matrix and topographic–hydrologic features on automatic gully extraction in Dexiang Town, Bayan County, China. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Z.; Liu, Y. Study on multi-scale window determination for GLCM texture description in high-resolution remote sensing image geo-analysis supported by GIS and domain knowledge. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moya, L.; Zakeri, H.; Yamazaki, F.; Liu, W.; Mas, E.; Koshimura, S. 3D gray level co-occurrence matrix and its application to identifying collapsed buildings. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 149, 14–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.; Wang, J.F.; Guangpei, C.; Yunrong, L.V.; Chen, Y. Convolu-tional neural network for the semantic segmentation of remote sensing images. Mob. Netw. Appl. 2021, 26, 200–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, D.; Liu, M.; Jia, J. CNN and transformer fusion for remote sensing image semantic segmentation. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Miao, F. Building extraction from remote sensing images using deep residual U-Net. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2022, 55, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Meng, X.; Zhang, G.; Zang, D.; Han, Y.; Ai, H.; Liu, H. Remote sensing image segmentation of gully erosion in a typical black soil area in Northeast China based on improved DeepLabV3+ model. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 84, 102929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 801–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diakogiannis, F.I.; Waldner, F.; Caccetta, P.; Wu, C. ResUNet-a: A deep learning framework for semantic segmentation of remotely sensed data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 162, 94–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, Y.; Ai, J.; Shu, Z.; Xia, J.; Xia, Y. Semantic segmentation of UAV remote sensing images based on edge feature fusing and multi-level upsampling integrated with Deeplabv3+. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0279097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, C.; Li, J.; Fan, W.; Du, J.; Zhong, B. Adaboost-like end-to-end multiple lightweight U-Nets for road extraction from optical remote sensing images. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2021, 100, 102341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Ma, T.; Wang, Z.; Cachim, P.; Qin, M. Pavement crack detection and segmentation using nested U-Net with residual attention mechanism. Comput.-Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2025, 40, 4076–4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Jin, J.; Dong, F.; Zhang, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y. Gully erosion susceptibility prediction using high-resolution data: Evaluation, comparison, and improvement of multiple machine learning models. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javidan, N.; Kavian, A.; Conoscenti, C.; Jafarian, Z.; Kalehhouei, M.; Javidan, R. Development of risk maps for flood, landslide, and soil erosion using machine learning model. Nat. Hazards 2024, 120, 11987–12010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lana, J.C.; Castro, P.D.T.A.; Lana, C.E. Assessing gully erosion susceptibility and its conditioning factors in southeastern Brazil using machine learning algorithms and bivariate statistical methods: A regional approach. Geomorphology 2022, 402, 108159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanh, B.N.; Van Phong, T.; Trinh, P.T.; Costache, R.; Amiri, M.; Nguyen, D.D.; Van Le, H.; Prakash, I.; Pham, B.T. Prediction of coastal erosion susceptible areas of Quang Nam Province, Vietnam using machine learning models. Earth Sci. Inform. 2024, 17, 401–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phinzi, K.; Ngetar, N.S.; Le Roux, J.J. Predictive machine learning for gully susceptibility modeling with geo-environmental covariates: Main drivers, model performance, and computational efficiency. Nat. Hazards 2024, 120, 8239–8272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkahtani, M.; Mallick, J.; Alqadhi, S.; Sarif, M.N.; Fatahalla Mohamed Ahmed, M.; Abdo, H.G. Interpretation of Bayesian-optimized deep learning models for enhancing soil erosion susceptibility prediction and management: A case study of Eastern India. Geocarto Int. 2024, 39, 2367611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Q.; Qin, K.; Li, Z.; Zhang, H.; Xu, K.; Xia, G.S. A multiple-instance densely-connected ConvNet for aerial scene classification. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 29, 4911–4926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, G. EANet: Edge-aware network for the extraction of buildings from aerial images. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.B.; Zhang, X.Y.; Wang, Y.X.; Sui, Y.Y.; Zhang, S.L.; Herbert, S.J.; Ding, G. Soil degradation: A problem threatening the sustainable development of agriculture in Northeast China. Plant Soil Environ. 2010, 56, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Ma, L.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, A.; Li, G.; Wang, J.; Wu, D.; Wu, W.; Du, Z. Conservation tillage for 17 years alters the molecular composition of organic matter in soil profile. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 762, 143116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, S.; Cruse, R.M.; Zhang, X. Gully erosion control practices in Northeast China: A review. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharati, M.H.; Liu, J.J.; MacGregor, J.F. Image texture analysis: Methods and comparisons. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2004, 72, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianconi, F.; Fernández, A.; Smeraldi, F.; Pascoletti, G. Colour and texture descriptors for visual recognition: A historical overview. J. Imaging 2021, 7, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alçin Ö, F.; Siuly, S.; Bajaj, V.; Guo, Y.; Şengu, A.; Zhang, Y. Multi-category EEG signal classification developing time-frequency texture features based Fisher Vector encoding method. Neurocomputing 2016, 218, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Cui, J.; Wang, W.; Lin, C. A study for texture feature extraction of high-resolution satellite images based on a direction measure and gray level co-occurrence matrix fusion algorithm. Sensors 2017, 17, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sill, M.; Saadati, M.; Benner, A. Applying stability selection to consistently estimate sparse principal components in high-dimensional molecular data. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 2683–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Ye, Q.; Zhang, F.; Yang, G.; Zhu, W.; Yang, Z. Double L 2, p-norm based PCA for feature extraction. Inf. Sci. 2021, 573, 345–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwokoma, F.; Foreman, J.; Akujuobi, C.M. Effective data reduction using discriminative feature selection based on principal component analysis. Mach. Learn. Knowl. Extr. 2024, 6, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall-Beyer, M. Practical guidelines for choosing GLCM textures to use in landscape classification tasks over a range of moderate spatial scales. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 1312–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Song, L.; Su, X.; Li, J.; Zheng, J.; Zhu, X.; Ren, L.; Wang, W.; Li, X. Optimizing window size and directional parameters of GLCM texture features for estimating rice AGB based on UAVs multispectral imagery. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1284235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brynjolfsson, P.; Nilsson, D.; Torheim, T.; Asklund, T.; Karlsson, C.T.; Trygg, J.; Nyholm, T.; Garpebring, A. Haralick texture features from apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) MRI images depend on imaging and pre-processing parameters. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clausi, D.A. An analysis of co-occurrence texture statistics as a function of grey level quantization. Can. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 28, 45–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, H.; Lucieer, A.; Williams, R. Texture-based classification of sub- Antarctic vegetation communities on Heard Island. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2010, 12, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balling, J.; Reiche, J.; Herold, M. How textural features can improve SAR-based tropical forest disturbance mapping. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2023, 122, 103492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuvo, M.B.; Ahommed, R.; Reza, S.; Hashem, M.M.A. CNL-UNet: A novel lightweight deep learning architecture for multimodal biomedical image segmentation with false output suppression. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2021, 70, 102959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, T.; Zhang, C.; Wang, X.; Song, Y.; Liu, D.; Huang, H.; Cai, W. Towards bi-directional skip connections in encoder-decoder architectures and beyond. Med. Image Anal. 2022, 78, 102420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Duan, M.; Yang, L.; Feng, W.; Ding, L.; Jiang, L. An improved U-Net image segmentation method and its application for metallic grain size statistics. Materials 2022, 15, 4417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2015, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Rahman Siddiquee, M.M.; Tajbakhsh, N.; Liang, J. UNet++: A nested U-Net architecture for medical image segmentation. In Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis and Multimodal Learning for Clinical Decision Support; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Bai, X.; Wang, J.; Li, G.; Li, J.; Lv, Z. Image semantic segmentation approach based on DeepLabV3 plus network with an attention mechanism. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 127, 107260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, X.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, M. Sh-DeepLabv3+: An improved semantic segmentation lightweight network for corn straw cover form plot classification. Agriculture 2024, 14, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X. Research on Iris Segmentation Method Based on Improved DeepLab-V3+ Structure. Master’s Thesis, Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.; Bengio, Y.; Courville, A. Deep Learning; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Khosla, A.; Lapedriza, A.; Oliva, A.; Torralba, A. Learning deep features for discriminative localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2921–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Zhu, M.; Stanković, L.; Ji, H. Self-matching CAM: A novel accurate visual explanation of CNNs for SAR image interpretation. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.B.; Rodriguez, J.J.; Gmitro, A.F. Effect of gray-level re-quantization on co-occurrence based texture analysis. In Proceedings of the 2008 15th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, San Diego, CA, USA, 12–15 October 2008; pp. 585–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gu, M. Classification methods for hyperspectral remote sensing images with weak texture features. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2024, 17, 101019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yang, J.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Fan, J.; Ke, L.; Wang, X. Gully-ERFNet: A novel lightweight deep learning model for extracting erosion gullies in the black soil region of Northeast China. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2025, 18, 2494074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Su, L.; Zhou, L.; Tian, Y.; Fan, H. Assessment of gully erosion susceptibility using different DEM-derived topographic factors in the black soil region of Northeast China. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2023, 11, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Fan, H.; Wang, Y. Gully erosion susceptibility assessment using three machine learning models in the black soil region of Northeast China. Catena 2024, 245, 108275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Jin, J.; Li, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y. A Multi-Scale Content-Structure Feature Extraction Network Applied to Gully Extraction. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristic | Basic Stats | Min | Max | Mean | Std |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Band:1 | 0 | 2.8280 | 1.6254 | 1.4853 |
| Band:2 | 0 | 2.8840 | 1.5715 | 1.4906 | |
| Band:3 | 0 | 2.8360 | 2.0417 | 1.8462 | |
| Contrast | Band:1 | 0 | 109.0000 | 0.1059 | 0.2804 |
| Band:2 | 0 | 118.0000 | 0.1050 | 0.2823 | |
| Band:3 | 0 | 159.0000 | 0.1346 | 0.3849 |
| Characteristic | Principal Components | Band 1 | Band 2 | Band 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Eig.1 | 0.4198 | 0.4271 | 0.5315 |
| Eig.2 | 0.6210 | 0.3783 | −0.0211 | |
| Eig.3 | 0.5434 | −0.2102 | −0.7087 | |
| Contrast | Eig.1 | 4.9500 | 5.0200 | 5.0300 |
| Eig.2 | 7.1000 | 2.3400 | −4.2500 | |
| Eig.3 | 4.7400 | −7.5500 | −1.4000 |
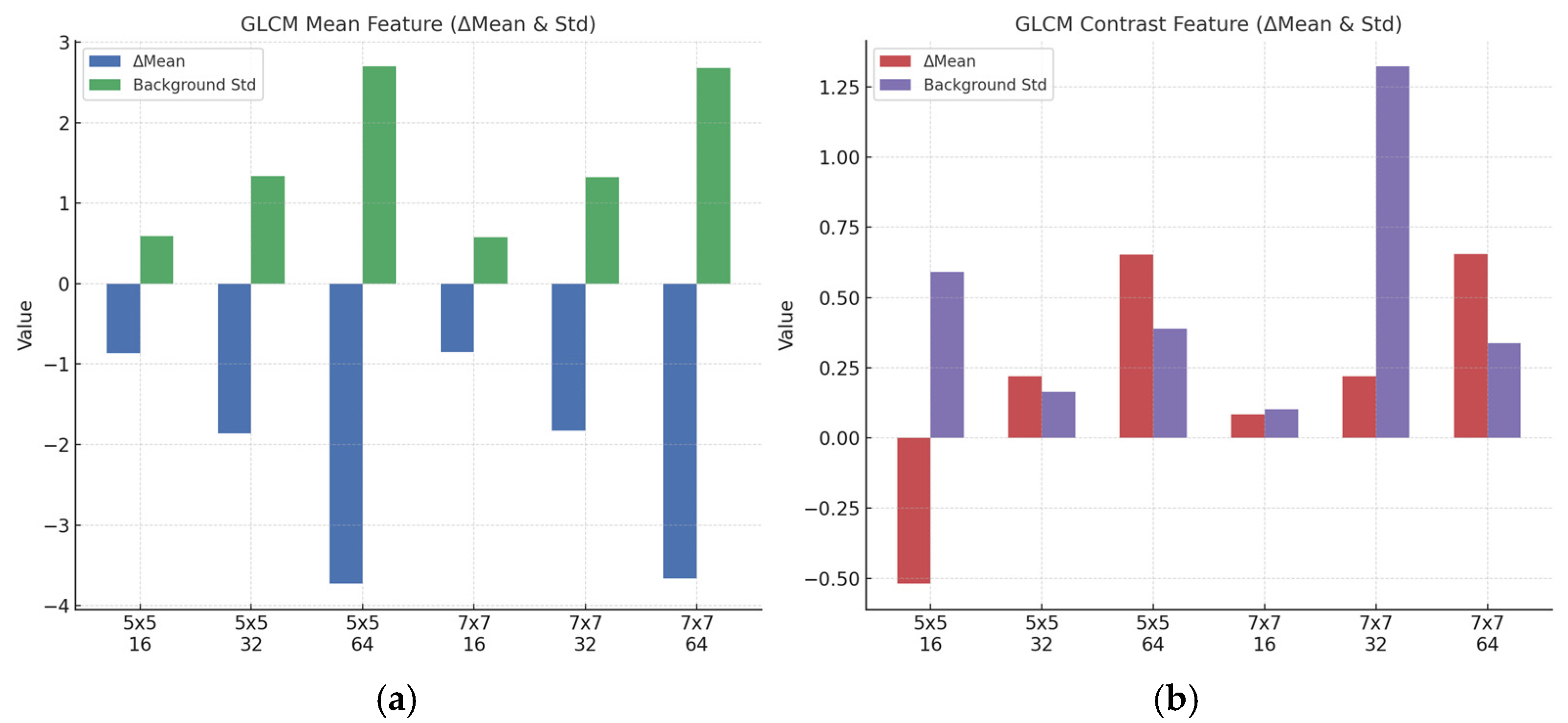
| Window Size | Gray Levels | ΔMean (Mean) | Std (Mean) | ΔMean (Contrast) | Std (Contrast) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 × 5 | 16 | −0.8657 | 0.5905 | −0.5186 | 0.5905 |
| 5 × 5 | 32 | −1.8602 | 1.3374 | 0.2195 | 0.1639 |
| 5 × 5 | 64 | −3.7273 | 2.7040 | 0.6519 | 0.3896 |
| 7 × 7 | 16 | −0.8492 | 0.5806 | 0.0842 | 0.1011 |
| 7 × 7 | 32 | −1.8281 | 1.3239 | 0.2204 | 1.3239 |
| 7 × 7 | 64 | −3.6636 | 2.6804 | 0.6550 | 0.3383 |
| Model | Acc (%) | AP (%) | IoU (%) | Loss |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DeepLabv3+ | 84.94 | 86.94 | 78.25 | 0.020 |
| U-Net | 88.73 | 89.49 | 82.50 | 0.014 |
| U-Net++ | 75.92 | 76.88 | 68.75 | 0.033 |
| Model | Acc (%) | AP (%) | IoU (%) | Loss |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DeepLabv3+ | 84.21 | 87.96 | 79.32 | 0.025 |
| U-Net | 90.27 | 90.87 | 84.16 | 0.011 |
| U-Net++ | 80.94 | 84.45 | 73.50 | 0.026 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, J.; Yang, J.; Xu, X.; Ke, L. Gully Extraction in Northeast China’s Black Soil Region: A Multi-CNN Comparison with Texture-Enhanced Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 3792. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17233792
Yu J, Yang J, Xu X, Ke L. Gully Extraction in Northeast China’s Black Soil Region: A Multi-CNN Comparison with Texture-Enhanced Remote Sensing. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(23):3792. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17233792
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Jiaxin, Jiuchun Yang, Xiaoyan Xu, and Liwei Ke. 2025. "Gully Extraction in Northeast China’s Black Soil Region: A Multi-CNN Comparison with Texture-Enhanced Remote Sensing" Remote Sensing 17, no. 23: 3792. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17233792
APA StyleYu, J., Yang, J., Xu, X., & Ke, L. (2025). Gully Extraction in Northeast China’s Black Soil Region: A Multi-CNN Comparison with Texture-Enhanced Remote Sensing. Remote Sensing, 17(23), 3792. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17233792






