Abstract
Sporadic E (Es) layers are irregular structures that occur at the E-layer height of the ionosphere, significantly affecting the reliability and accuracy of wireless communications, navigation, and satellite remote sensing. This study utilized the S4max data collected from the Constellation Observing System for the Meteorology, Ionosphere, and Climate (COSMIC) occultation observations from 2007 to 2016 to identify the Es layer and investigate its climatological variations. The Horizontal Wind Field model (HWM14), in conjunction with the International Geomagnetic Reference Field model (IGRF13), is used to calculate vertical ion convergence (VIC) and analyze its correlation to the Es layers. The results of this study showed that the occurrence of Es has apparent hemispheric asymmetry. In the mid- and low latitudes, Es layer activity is more intense in the summer hemispheres, with center peak altitudes of around 105 km. The summer hemisphere exhibits a semi-diurnal periodic pattern, whereas the winter hemisphere shows a weakened diurnal variation. Simulation studies indicate that VIC induced by neutral wind shear contributes to the asymmetry in Es layer activities observed between the Northern and Southern hemispheres, and the zonal wind shear plays a more critical role than the meridional wind one.
1. Introduction
Es layers are characterized by thin layers with high electron density at 90–130 km altitudes. The layers have a vertical thickness of only a few kilometers but can extend horizontally for hundreds of kilometers. The neutral wind shear that converges ions is suggested to generate the high-density layer structure. However, steep electron-density gradients significantly impact wireless communications and navigation systems. Understanding Es behaviors’ morphological characters and underlying theories is crucial for space weather investigation and further forecasting.
Over the past decades, Es behavior explorations have predominantly relied on ground-based observations [1,2], especially from ionosondes [3] and coherent/incoherent scatter radar [4,5]. Radio Occultation (RO) technology has provided a global perspective for Es variations with comparably higher spatial resolutions in recent years. Hocke et al. [6] confirmed the predominant altitude of Es layers about 90–110 km via examining Global Positioning System/Meteorology (GPS/MET) data sources. Wu et al. [7] employed GPS/CHAMP occultation measurements to investigate the global occurrence of Es and revealed the correlation to the geomagnetic inclination angle. Arras et al. [8] utilized radio occultation measurements and studied their geomagnetic influence. Meanwhile, researchers highlighted significant seasonal variations in Es occurrence using S4 indexes from COSMIC RO measurements [9,10,11,12,13], and further details on why Es layers derived from the S4 index can be found in Arames et al. [14].
Previous studies attributed the Es layer formation to the vertical convergence of metal ions due to the neutral wind shear [15,16,17,18]. The wind shear theory suggests that metal ions in the ionospheric dynamo region would converge into a thin layer because of the neutral wind dragging along the Earth’s geomagnetic field, especially in the mid-latitude regions [19,20,21,22,23,24,25]. Numerical simulations also demonstrate the high correlation between the Es happening and the vertical ion convergence rate [26]. Researchers also attributed the latitude dependence of the Es layer to the vertical shear in the zonal wind [27]. Similar attributions are reported in various other studies (e.g., [28,29] and the references therein).
Recent studies have deepened the understanding of the S4 indexes characterizing the Es layer behaviors. Tang et al. [30] pointed out that the S4 threshold 0.2 is more comparable with the ionosonde observations than the traditional 0.3, motivating a global morphological reanalysis of the Es behaviors based on occultation data. The present study uses global S4max data from FORMOSAT-3/COSMIC measurements with a threshold of 0.2 to investigate the global pattern of the Es occurrence and provide valuable information for practical applications and scientific research. Section 2 delineates the dataset and methodologies of Es layer extraction. Section 3 and Section 4 presents the examined climatological behavior and corresponding discussions [31]. Section 5 provides the conclusions.
2. Data and Methods
Six low-Earth orbit satellites with orbital inclinations of 24°, comprised in the FORMOSAT-3/COSMIC mission, were launched in April 2006 [32,33]. The GPS receiver onboard each satellite is used for radio occultation experiments. The COSMIC mission yields 2000 to 2500 RO profiles daily, characterized by high vertical resolution and a near-uniform distribution across local solar times [34]. Thus, the COSMIC satellite constellation offers the opportunity to record Es-layer observations with high spatial resolution worldwide.
The S4max index is the signal-to-noise ratio of the GPS signal [35]. Arames et al. [14] found a high correlation between the S4max and Es layer occurrence. In addition, Tang et al. [30] suggested that the Es occurrence rate of S4 with a threshold of 0.2 is comparable to that of the ionosonde. Thus, this study employs the threshold of 0.2 in the S4max index to further investigate the climatological behaviors of the Es occurrence rate (EsOR).
The EsOR dependence on latitude, longitude, local time, and altitude is investigated via grid analysis. The EsOR is defined as the ratio of the Es event number to the total number of occultations observations within each grid. The grid resolutions used in this analysis are 2.5° for latitude and longitude, 1 km for altitude, and 1 h for local time. In addition, to reduce the random error, a null value will be assigned if the total RO number is less than 10 in a grid.
3. Results
Figure 1a presents the variation in monthly averaged F10.7, suggesting a relatively low solar activity period between 2007 and 2010, followed by enhanced solar activity from 2011 to 2016. Figure 1b gives the statistical results of the measurements and Es events. The yearly radio occultation experiments from 2007 to 2009 ranged in the millions but have declined to hundreds of thousands since 2010. A similar situation also happened in the number of Es events, decreasing from approximately 450,000 per year from 2007 to 2009 to around 200,000 in 2016. However, the EsOR exhibited insignificant fluctuations of around 44%, implying independence of the solar radiation. Thus, the data from 2007 to 2016 is blended in this study to describe the climatological behaviors.
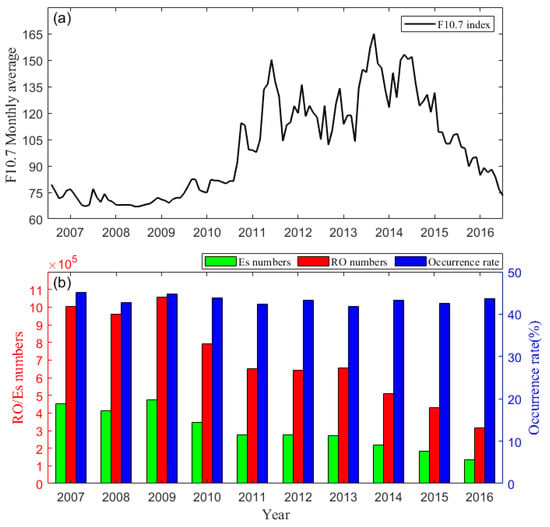
Figure 1.
(a) Monthly average of F10.7 from 2007 to 2016. (b) Statistical results for each year. Red bars for the total number of RO measurements, green for the identified number of Es events, and blue for the EsOR.
Figure 2 shows the latitude-month distribution of the RO event number for ten years. The RO event number and reliability are important for the occurrence rate study. As seen, the seasonal variation is not significant in the RO numbers except that its maximum, over 10,000 for a 10-year period, happens in the middle latitudes of two hemispheres. Meanwhile, the measurement number in the equator and polar region reaches about 5000 and 2000, respectively. Thus, the data coverage meets the requirements of this investigation.
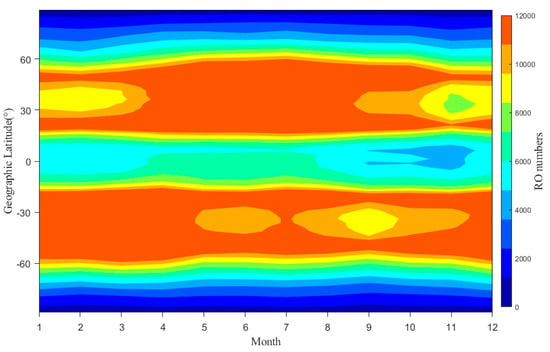
Figure 2.
Global distribution of total RO numbers by geographic latitude and month from 2007 to 2016.
Figure 3 presents the global pattern of the statistical EsOR across the four seasons. The black lines represent the contour line of geomagnetic inclination from the IGRF-13 model computation. In Figure 3a, Es events are primarily concentrated in mid-latitude regions, and the SH (Southern Hemisphere) exhibits a clear four-wave structure. The EsOR significantly decreases in high-latitude regions with geomagnetic dip angles between 60° and 80°. This reduction could be attributed to the near-vertical geomagnetic field lines, and the minimal projection of neutral winds makes the wind shear mechanism ineffective [36]. The EsOR morphology generally aligns with the contours of the geomagnetic inclination angle, with a noticeable reduction near the equator. This is consistent with Kellley [16], who suggested that the horizontal geomagnetic field in the equator region results in ineffective neutral wind shear in the ion convergence.
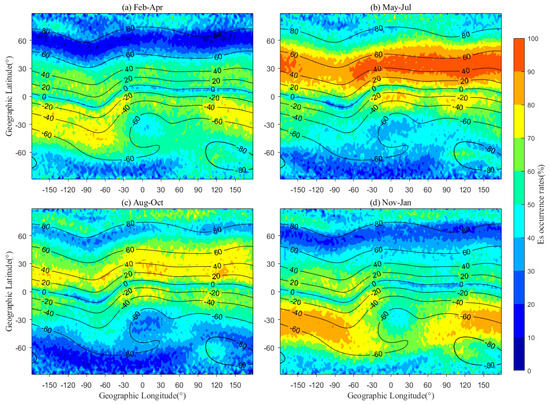
Figure 3.
Global distributions of EsOR. (a) is for the spring situation, which contains the months of February–April, (b) for summer with May–July, (c) for autumn with August–October, and (d) for winter, which contains November–January. Black lines are the contour lines of geomagnetic inclination.
Figure 3b,c illustrates a significant increase in EsOR over the NH (Northern Hemisphere) middle latitude region, contrasting with a weak pattern in SH. Meanwhile, Figure 3c displays a significant four-wave structure in NH. In Figure 3d, EsOR is significantly present in SH, with the peak value smaller than the NH one in Figure 3b. The decrease in the SAA (South Atlantic Anomaly) region and its surroundings is due to the lower geomagnetic strength and inclination [37]. Previous studies have suggested that the ion convergence in the polar region is due to the plasma drift (E×B) and gravity waves [38,39] instead of vertical wind shear. Figure 3b,d reveals a significant enhancement of EsOR in the polar region (higher than 80°), especially in NH. These findings indicate that the EsOR is strongest in the summer hemispheres, with Earth’s geomagnetic field and neutral winds playing a crucial role in shaping its global distributions and seasonal evolutions.
Figure 4 depicts the monthly average values of EsOR as a function of altitude and geomagnetic latitudes, with rows from top to bottom denoting the situations from spring to winter. As shown in spring (Figure 4a–c), the maximum value of EsOR occurs primarily around 30°S in February, and it emerges symmetrically between the NH and SH by April. During summer (the second row), the maximum value is mainly observed in the NH mid-latitudes. As the season transitions into autumn and winter, the maximum EsOR gradually shifts back to the SH. Thus, these patterns suggest a significant seasonal variation. Meanwhile, the Es layer is also observed in the polar regions of two hemispheres, with EsOR hovering at approximately 65%. The Es layer predominantly occurs in the summer hemisphere and appears between the 95 and 120 km altitude bracket, with a peak reaching 95%. In the winter hemisphere, the Es layer is predominantly detected within the 100 to 115 km altitude range, with the peak reduced to 85%. Although the summer hemisphere exhibits a higher Es occurrence rate, the latitude range of Es distribution in the winter hemisphere is more extensive, consistent with previous studies [12,37].
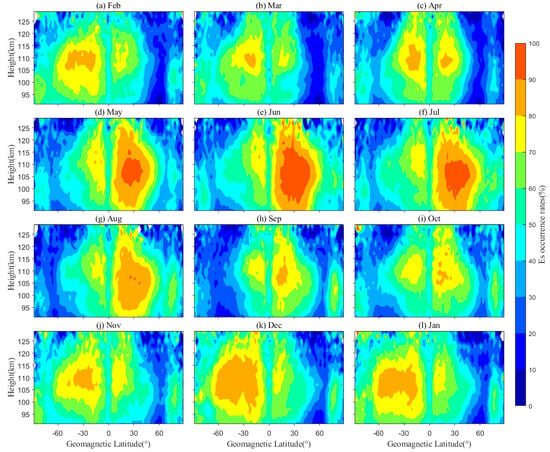
Figure 4.
The monthly average of EsOR as a function of altitude and geomagnetic latitude. (a–l) represents the months from January to December, respectively.
Figure 5 is similar to Figure 4 but for the EsOR distribution functioning geomagnetic latitude and local time. In spring cases of Figure 5a–c, EsOR in NH exhibits diurnal variations, with the peak occurring around 18 LT (Local Time) in low latitudes. As a contrast in the NH summer of Figure 5d–g, EsOR peaks at around 9 LT and 19 LT in mid-latitudes, i.e., exhibiting an apparent semi-diurnal variation. With the arrival of autumn and winter, EsOR reverts to the diurnal variation again, where the peak occurs around 18 LT only. In SH, EsOR also converts between semi-diurnal and diurnal variations. However, the semi-diurnal variations primarily occur in SH winter and exhibit smaller amplitudes than in NH summer. These seasonal phenomena are similar to the findings of Arras et al. [8], who attribute them to the movement of the solar subpoint. Notably, the four-wave structure in Figure 3 disappears in Figure 5, due to the zonal average for each local time.
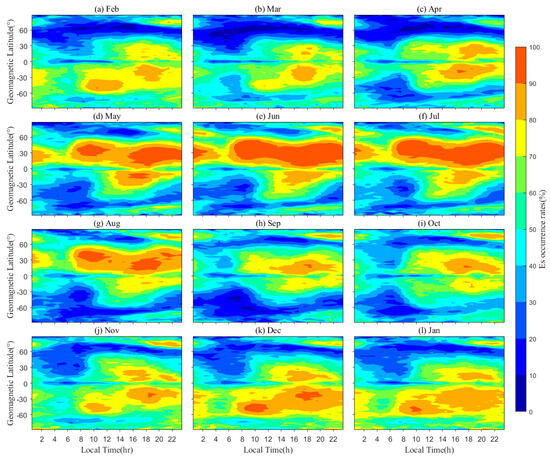
Figure 5.
Similar to Figure 4, but for the monthly average functioning geomagnetic latitude and local time.
Figure 6 illustrates the characteristic distribution of EsOR as a function of altitude and local time across different latitude bands in NH over various seasons. As shown in Figure 6, EsOR typically exhibits diurnal variations in high-latitude regions, with the peak occurring at ~21 LT. Within the latitude range of 15°–60°N, the peak EsOR exceeds 90% during summer and displays semi-diurnal variations, with the peaks observed at around 7 LT and 19 LT. In contrast, EsOR mainly displays diurnal variations in mid- and low-latitude bands during other seasons, and the peak occurs at around 18 LT, which differs from polar regions. Figure 7 is similar to Figure 6 but for different latitude bands in SH. The maximum EsOR in SH occurs between 15°S and 30°S during winter, with the peak magnitude reaching about 90%. The semi-diurnal pattern in EsOR extends from low latitudes to mid- and high latitudes, with peak occurrences typically observed at around 10 LT and 18 LT. The EsOR predominantly displays diurnal variations during other seasons with comparably lower amplitudes, especially in autumn. The diurnal peak is around 17 LT in the low- and mid-latitudes, while it turns to 20 LT in the polar region. In most cases, significant peaks of EsOR in the mid-latitude regions of both hemispheres occur at approximately 105 km. In contrast, peaks in the SH high-latitude regions are observed at 95 km, while the NH peak in high-latitude regions occurs at 100 km.
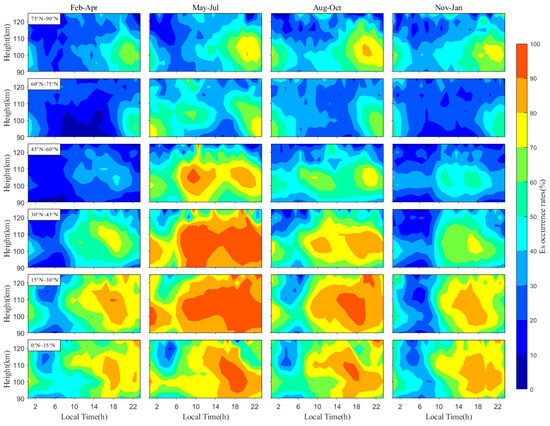
Figure 6.
Seasonal variation in EsOR at different geomagnetic latitude bands in NH functioning altitude and local time. The columns from left to right denote spring, summer, autumn, and winter, respectively.
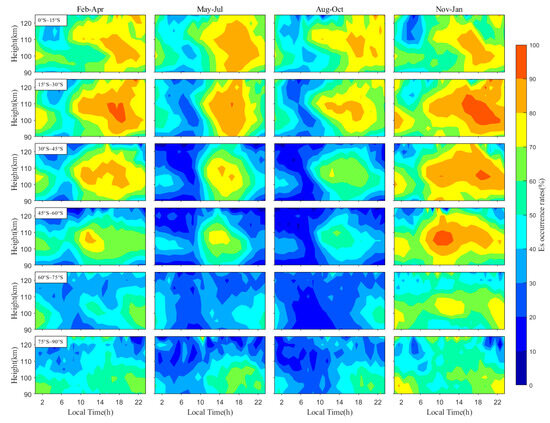
Figure 7.
Similar to Figure 6. but for the situation in SH.
Figure 8 compares the geomagnetic latitude, altitude, and magnitude of EsOR in NH and SH under 9 LT and 19 LT conditions, respectively. As shown in Figure 8(a1), the farthest latitude in NH of 9 LT occurs around 30° in summer, while it extends to about 50° in SH in winter. Figure 8(a2) is similar to Figure 8(a1) but for 19 LT situation. Compared to the ones in Figure 8(a1), the farthest latitude is equatorward moving in both hemispheres that it becomes ~25° in NH and about 35° in SH, respectively. The hemisphere comparison of the EsOR peak altitude is given in Figure 8(b1,b2). The peak altitude in 9 and 19 LT conditions experiences significant seasonal variation. Specifically, the peak altitude is much lower when the latitude is higher, e.g., in NH, the peak altitude is lowest in June and highest in December, while it is converted in SH. In addition, the peak altitude is generally higher at 9 LT than at 19 LT. Figure 8(c1,c2) illustrates the seasonal variations in the peak magnitude of EsOR in both hemispheres. Both 9 LT and 19 LT situations exhibit significant seasonal variations. For detail, the peak EsOR is higher in summer, lower in winter in NH, and reversed in SH. Furthermore, the seasonal variation is more pronounced at 9 LT than at 19 LT, even though the average magnitude is higher at 19 LT.
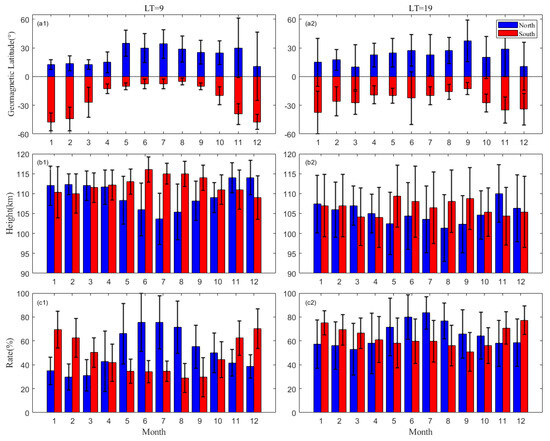
Figure 8.
Seasonal variation in the EsOR peak. Left and right columns denote the situation of 9 LT (a1,b1,c1) and 19 LT (a2,b2,c2), respectively. The rows from top to bottom represent the seasonal variation in the peak of geomagnetic latitude (a1,a2), the peak height (b1,b2), and the peak rate (c1,c2), respectively.
4. Discussion
The wind shear theory is employed in this study to explain the Es climatological behaviors. The vertical ion drift of is firstly carried out based on the well-known empirical models, including the models of HWM version 14 and IGRF-13 [26], and the formula, as presented by Mathews [1], can be articulated as follows:
where represents the geomagnetic inclination calculated from the IGRF-13 model [40]. and denote the zonal and meridional wind, respectively, computed by the HWM-14 model [41]. is the ratio of ion-neutral collision frequency (), to the ion gyrofrequency (), i.e., .
Secondly, the vertical ion convergence (VIC) is derived from the gradient computation along the altitude. Since only positive VIC contributes to the formation of the Es layer, the calculation for VIC is presented as described by Luo et al. [12]:
where is altitude. Notably, the altitude range concentrated in this work is within 105–115 km.
Figure 9 illustrates the zonal mean of simulated VIC as a function of month and latitude at 9 LT and 19 LT in the units 10−3 s−1. The maximum VIC under 9 LT and 19 LT conditions occurs in the summer hemisphere, i.e., in NH from May to August, while in SH, it spans from December to February. In addition, the VIC is minimized in the winter hemisphere. These features are aligned with the EsOR characteristics in Figure 8(a1,a2). However, the peak VIC value at 19 LT is smaller than at 9 LT, which is opposite in Figure 8(c1,c2), suggesting other factors play important roles as well (e.g., the electron density). This is consistent with the results of Yeh et al. [35].
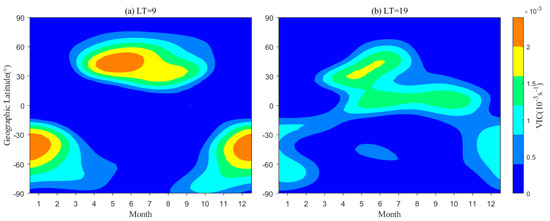
Figure 9.
The zonal mean of VIC within the altitude of 105 to 115 km from simulation as a function of geographic latitude and month at (a) 9 LT and (b) 19 LT, respectively.
Figure 10 and Figure 11 further display the contributions from meridional and zonal winds, respectively, to the VIC. The calculations are expressed as follows:
where and denote the VIC component from meridional and zonal wind, respectively. As shown, both the meridional and zonal wind-associated VIC components exhibit significant seasonal and latitudinal variation at 9 LT and 19 LT. However, the meridional wind-associated VIC component peaks at latitudes lower than ~30° in two hemispheres with peak values of S−1 and S−1 in Figure 10a,b, respectively. Meanwhile, the maximum zonal wind-associated VIC component in Figure 11 occurs at middle latitudes of the summer hemisphere, and the magnitudes both reach about S−1 in Figure 11a,b, respectively. These comparisons suggest that the vertical wind shear from the zonal wind is more critical than meridional wind in modulating the Es layer behaviors.
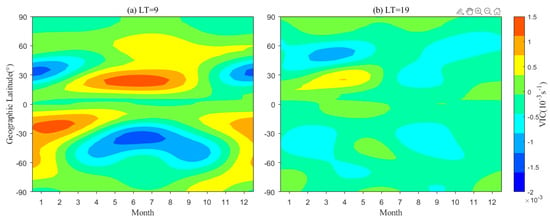
Figure 10.
Meridional wind contribution to VIC. (a,b) denotes the situations of 9 LT and 19 LT, respectively.
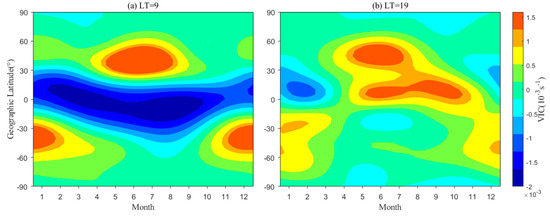
Figure 11.
Similar to Figure 10, but for zonal wind.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we performed a statistical analysis of the Es layer behaviors using S4max data from FORMOSAT-3/COSMIC radio occultation experiments. The results show that the EsOR in the summer hemisphere mid-latitude areas is 2–3 times greater than in the winter hemisphere. Additionally, the geomagnetic field controls the EsOR, significantly reducing it in the SAA region and at the geomagnetic equator.
The Es layer predominantly appears in the mid–low latitudes (10°–60°) of the summer hemisphere, with altitudes ranging from 95 km to 120 km. In the summer hemisphere, the peak altitude is 115 km, contrasting with the winter hemisphere, where it decreases to around 105 km. The EsOR is generally higher in the nighttime than the daytime, suggesting a significant diurnal variation, except for mid-latitudes in the summer hemisphere, where it displays an apparent semidiurnal evolution.
This study employs wind shear theory to explore the EsOR global pattern. Our findings suggest a strong correlation between vertical ion convergence and neutral wind shear, reproducing EsOR’s seasonal and latitudinal behaviors. Moreover, the zonal wind is more dominant in ion convergence than the meridional wind.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.R.; methodology, H.R.; validation, H.R., and X.Q.; formal analysis, X.Q.; data curation, X.Q.; investigation, X.Q.; resources, H.R.; writing—original draft preparation, X.Q.; writing—review & editing, H.R.; visualization, X.Q.; supervision, H.R., X.G., X.W. and X.Z.; project administration, H.R.; funding acquisition, H.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key R&D Program of China (2022YFF0503702), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42074186), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20220451), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2023M731757), and the Key Laboratory of Geospace Environment, Chinese Academy of Sciences, University of Science and Technology of China.
Data Availability Statement
The amplitude scintillation index S4max data are provided by the COSMIC Data Analysis and Archival Center (CDAAC, https://data.cosmic.ucar.edu/gnss-ro/, accessed on 7 February 2023).
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Lihui Qiu for the helpful guidance about VIC simulations.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Mathews, J. Sporadic E: Current views and recent progress. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 1998, 60, 413–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resende, L.C.; Arras, C.; Batista, I.S.; Denardini, C.M.; Bertollotto, T.O.; Moro, J. Study of sporadic E layers based on GPS radio occultation measurements and digisonde data over the Brazilian region. In Annales Geophysicae; Copernicus Publications: Göttingen, Germany, 2018; pp. 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leighton, H.; Shapley, A.; Smith, E. The occurrence of sporadic E during the IGY. In Ionospheric Sporadic; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1962; pp. 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, F.; Doles, J., III. Velocity shear and the E × B instability. J. Geophys. Res. 1975, 80, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farley, D. Theory of equatorial electrojet plasma waves-new developments and current status. J. Atmos. Terr. Phys. 1985, 47, 729–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hocke, K.; Tsuda, T. Gravity waves and ionospheric irregularities over tropical convection zones observed by GPS/MET radio occultation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2001, 28, 2815–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.L.; Ao, C.O.; Hajj, G.A.; de La Torre Juarez, M.; Mannucci, A.J. Sporadic E morphology from GPS-CHAMP radio occultation. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2005, 110, A01306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arras, C.; Wickert, J.; Beyerle, G.; Heise, S.; Schmidt, T.; Jacobi, C. A global climatology of ionospheric irregularities derived from GPS radio occultation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L14809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.-H.; Wang, C.; Wu, K.; Chen, K.; Tzeng, K.; Su, C.-L.; Feng, W.; Plane, J. Morphology of sporadic E layer retrieved from COSMIC GPS radio occultation measurements: Wind shear theory examination. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2014, 119, 2117–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Schreiner, W.S.; Pedatella, N.M.; Kuo, Y.H. Characterizing GPS radio occultation loss of lock due to ionospheric weather. Space Weather 2016, 14, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Tang, Q.; Song, X.; Qing, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Gu, X.; Ni, B.; Zhao, Z. A statistical analysis of sporadic E layer occurrence in the midlatitude China region. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2017, 122, 3617–3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Liu, H.; Xu, X. Sporadic E morphology based on COSMIC radio occultation data and its relationship with wind shear theory. Earth Planets Space 2021, 73, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Luo, J.; Wang, H.; Liu, H.; Hu, T. Morphology of sporadic E layers derived from Fengyun-3C GPS radio occultation measurements. Earth Planets Space 2022, 74, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seif, A.; Liu, J.Y.; Mannucci, A.J.; Carter, B.A.; Norman, R.; Caton, R.G.; Tsunoda, R.T. A study of daytime L-band scintillation in association with sporadic E along the magnetic dip equator. Radio Sci. 2017, 52, 1570–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schunk, R.W.; Nagy, A.F. Ionospheres: Physics, Plasma Physics, and Chemistry; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, M.C. The Earth’s Ionosphere: Plasma Physics and Electrodynamics; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, T.; Wang, J.; Cai, X.; Sojka, J.; Rice, D.; Oberheide, J.; Criddle, N. Investigation of the seasonal and local time variations of the high-altitude sporadic Na layer (Nas) formation and the associated midlatitude descending E layer (Es) in lower E region. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2014, 119, 5985–5999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Yuan, T.; Eccles, J.V. A numerical investigation on tidal and gravity wave contributions to the summer time Na variations in the midlatitude E region. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2017, 122, 10577–10595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehead, J. The formation of the sporadic-E layer in the temperate zones. J. Atmos. Terr. Phys. 1961, 20, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehead, J. Production and prediction of sporadic E. Rev. Geophys. 1970, 8, 65–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehead, J. Recent work on mid-latitude and equatorial sporadic-E. J. Atmos. Terr. Phys. 1989, 51, 401–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macleod, M.A. Sporadic E theory. I. Collision-geomagnetic equilibrium. J. Atmos. Sci. 1966, 23, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nygren, T.; Jalonen, L.; Oksman, J.; Turunen, T. The role of electric field and neutral wind direction in the formation of sporadic E-layers. J. Atmosheric Terr. Phys. 1984, 46, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldoupis, C.; Pancheva, D. Planetary waves and midlatitude sporadic E layers: Strong experimental evidence for a close relationship. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2002, 107, SIA 3-1–SIA 3-6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, Y.; Arras, C.; Andoh, S.; Miyoshi, Y.; Shinagawa, H.; Harding, B.; Englert, C.; Immel, T.; Sobhkhiz-Miandehi, S.; Stolle, C. Examining the wind shear theory of sporadic E with ICON/MIGHTI winds and COSMIC-2 radio occultation data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2021GL096202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinagawa, H.; Miyoshi, Y.; Jin, H.; Fujiwara, H. Global distribution of neutral wind shear associated with sporadic E layers derived from GAIA. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2017, 122, 4450–4465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Yu, T.; Yan, X.; Sun, Y.Y.; Zuo, X.; Yang, N.; Wang, J.; Qi, Y. Altitudinal and latitudinal variations in ionospheric sporadic-E layer obtained from FORMOSAT-3/COSMIC radio occultation. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2021, 126, e2021JA029454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, C.; Tang, Q.; Li, Z.; Song, Y.; Qing, H.; Ni, B.; Zhao, Z. The seasonal distribution of sporadic E layers observed from radio occultation measurements and its relation with wind shear measured by TIMED/TIDI. Adv. Space Res. 2018, 62, 426–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, W.H.; Liu, J.Y.; Huang, C.Y.; Chen, S.P. Explanation of the sporadic-E layer formation by comparing FORMOSAT-3/COSMIC data with meteor and wind shear information. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 4568–4579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, F.; Zou, F. Comparative study of ionospheric sporadic E occurrence rates using SNRnstd and S4 derived from GPS radio occultation. GPS Solut. 2023, 27, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Xue, X.; Scott, C.J.; Yue, X.; Dou, X. An empirical model of the ionospheric sporadic E layer based on GNSS radio occultation data. Space Weather 2022, 20, e2022SW003113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiner, W.; Rocken, C.; Sokolovskiy, S.; Syndergaard, S.; Hunt, D. Estimates of the precision of GPS radio occultations from the COSMIC/FORMOSAT-3 mission. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L04808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthes, R.; Schreiner, W. Six new satellites watch the atmosphere over Earth’s equator. EOS 2019, 100, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthes, R.A.; Bernhardt, P.; Chen, Y.; Cucurull, L.; Dymond, K.; Ector, D.; Healy, S.; Ho, S.-P.; Hunt, D.; Kuo, Y.-H. The COSMIC/FORMOSAT-3 mission: Early results. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2008, 89, 313–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, W.H.; Huang, C.Y.; Hsiao, T.Y.; Chiu, T.C.; Lin, C.H.; Liou, Y.A. Amplitude morphology of GPS radio occultation data for sporadic-E layers. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 2012, 117, A11304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldoupis, C. Midlatitude sporadic E. A typical paradigm of atmosphere-ionosphere coupling. Space Sci. Rev. 2012, 168, 441–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Xue, X.; Yue, X.A.; Yang, C.; Yu, C.; Dou, X.; Ning, B.; Hu, L. The global climatology of the intensity of the ionospheric sporadic E layer. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 4139–4151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkwood, S.; Nilsson, H. High-latitude sporadic-E and other thin layers–the role of magnetospheric electric fields. Space Sci. Rev. 2000, 91, 579–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDougall, J.; Plane, J.; Jayachandran, P. Polar cap sporadic-E: Part 2, modeling. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2000, 62, 1169–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alken, P.; Thébault, E.; Beggan, C.D.; Amit, H.; Aubert, J.; Baerenzung, J.; Bondar, T.; Brown, W.; Califf, S.; Chambodut, A. International geomagnetic reference field: The thirteenth generation. Earth Planets Space 2021, 73, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Xiong, C.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, Y. Vertical gradients of neutral winds observed by ICON and estimated by the Horizontal Wind Model during the geomagnetic storm on August 26−28, 2021. Earth Planet. Phys. 2024, 9, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).