SCM-YOLO for Lightweight Small Object Detection in Remote Sensing Images
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- One-stage detection algorithms, such as the YOLO family, support feature extraction by incorporating a hierarchical structure of downsampling and upsampling [35,36]. It is typically implemented through operations such as convolution and pooling [37]. The downsampling operation loses certain spatial local information, which is insufficient for the preservation and exploitation of spatial local information.
- (2)
- In YOLO series, the Concat operation is usually used to realize feature fusion, but the Concat operation does not make flexible and efficient use of input features for feature fusion.
- (3)
- The introduction of the attention mechanism in the model can effectively improve the feature perception ability of the detector, thus improving the detection performance. However, the introduction of the attention mechanism will also lead to an additional increase in the number of parameters.
- (1)
- A small object detector, SCM-YOLO, for optical remote sensing of complex backgrounds is designed, which shows advanced performance for small objects in remote sensing complex backgrounds while balancing detection speed and resource consumption.
- (2)
- We propose the three lightweight generalized modules, SPID, CBCC, and MAGI, which improve comprehensive performance of SCM-YOLO from three aspects: local spatial information utilization, feature fusion, and global perception.
- (3)
2. Related Work
2.1. The YOLO Series Models
2.2. Attention Mechanism
2.3. Improved YOLO for Small Object Detection
3. Proposed Method
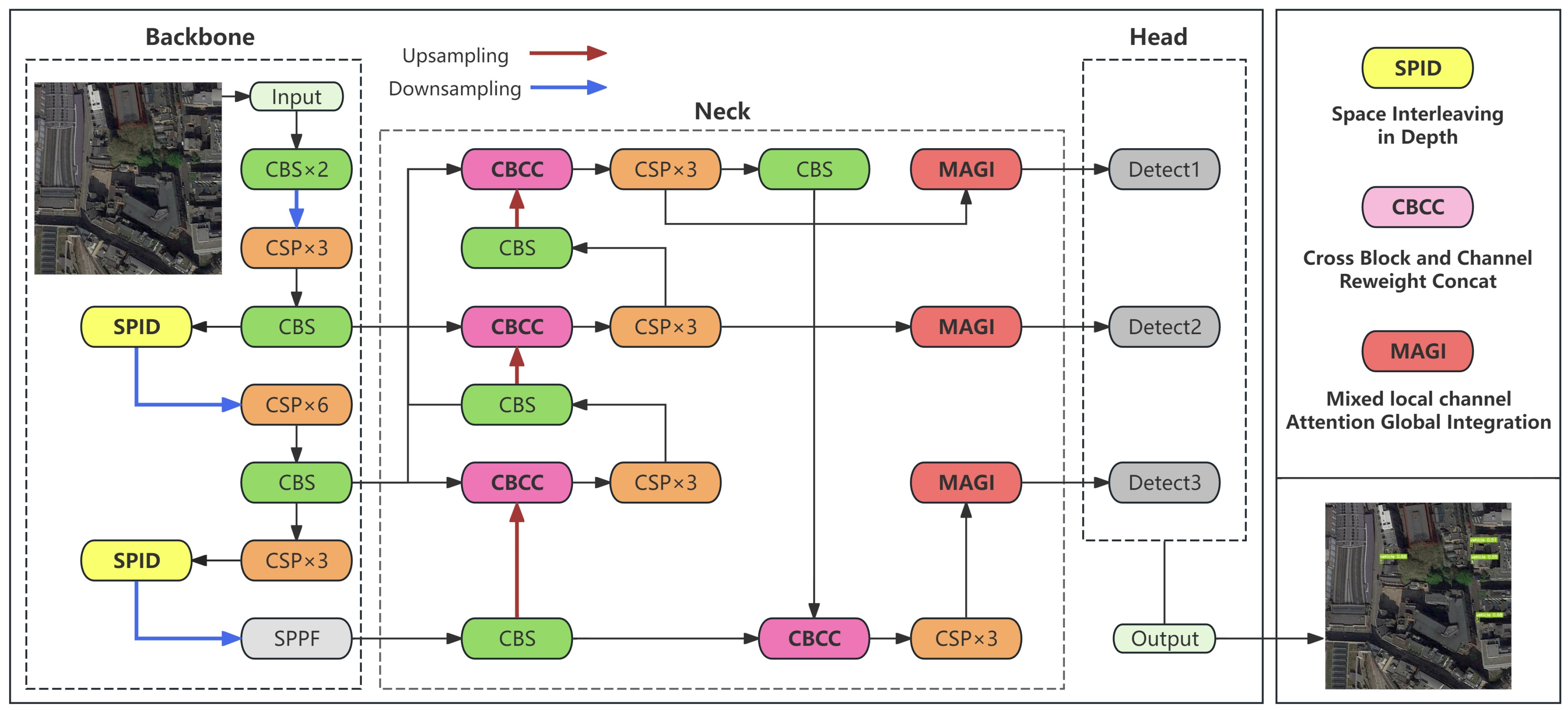
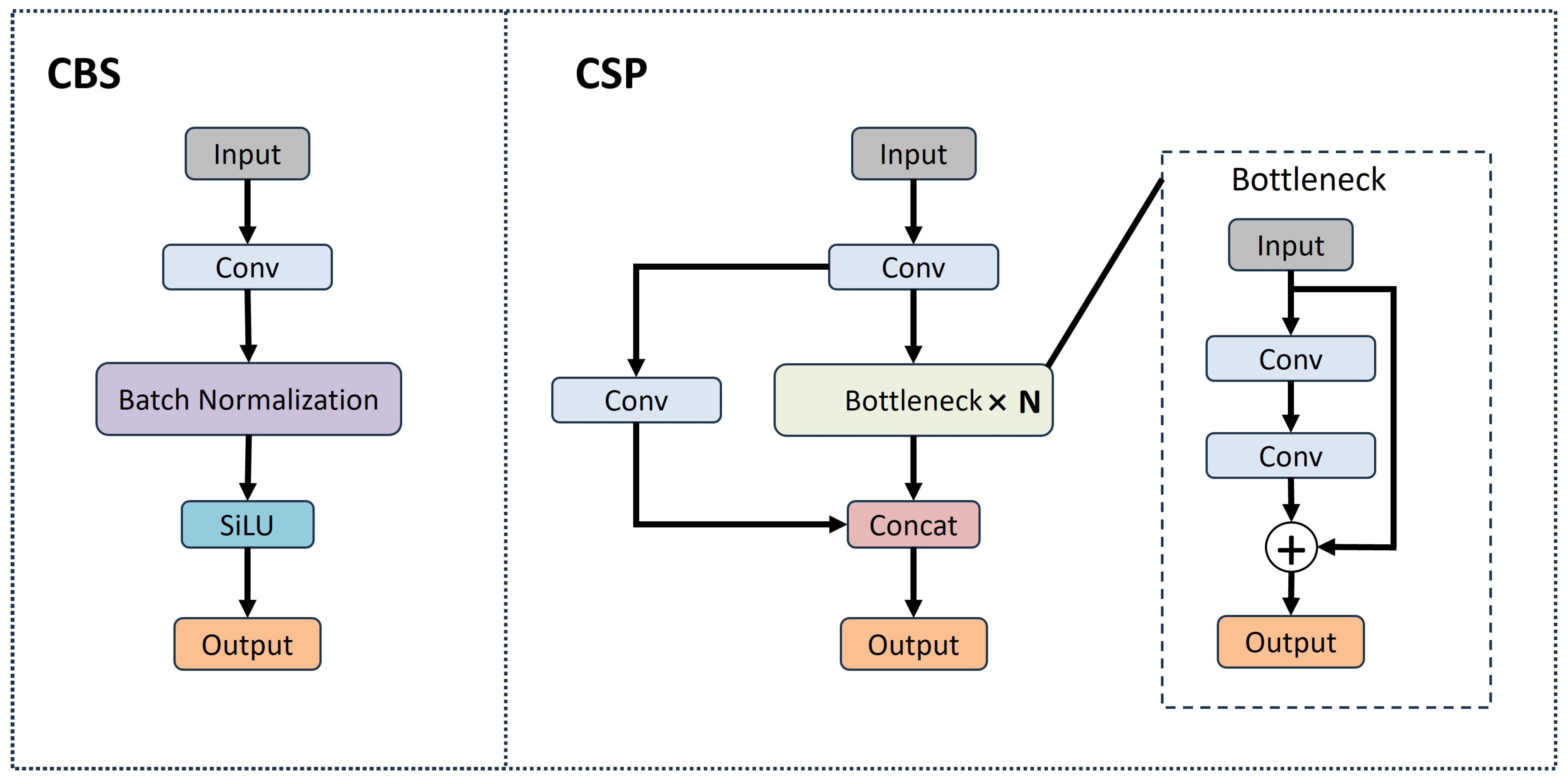
3.1. Overview of SCM-YOLO
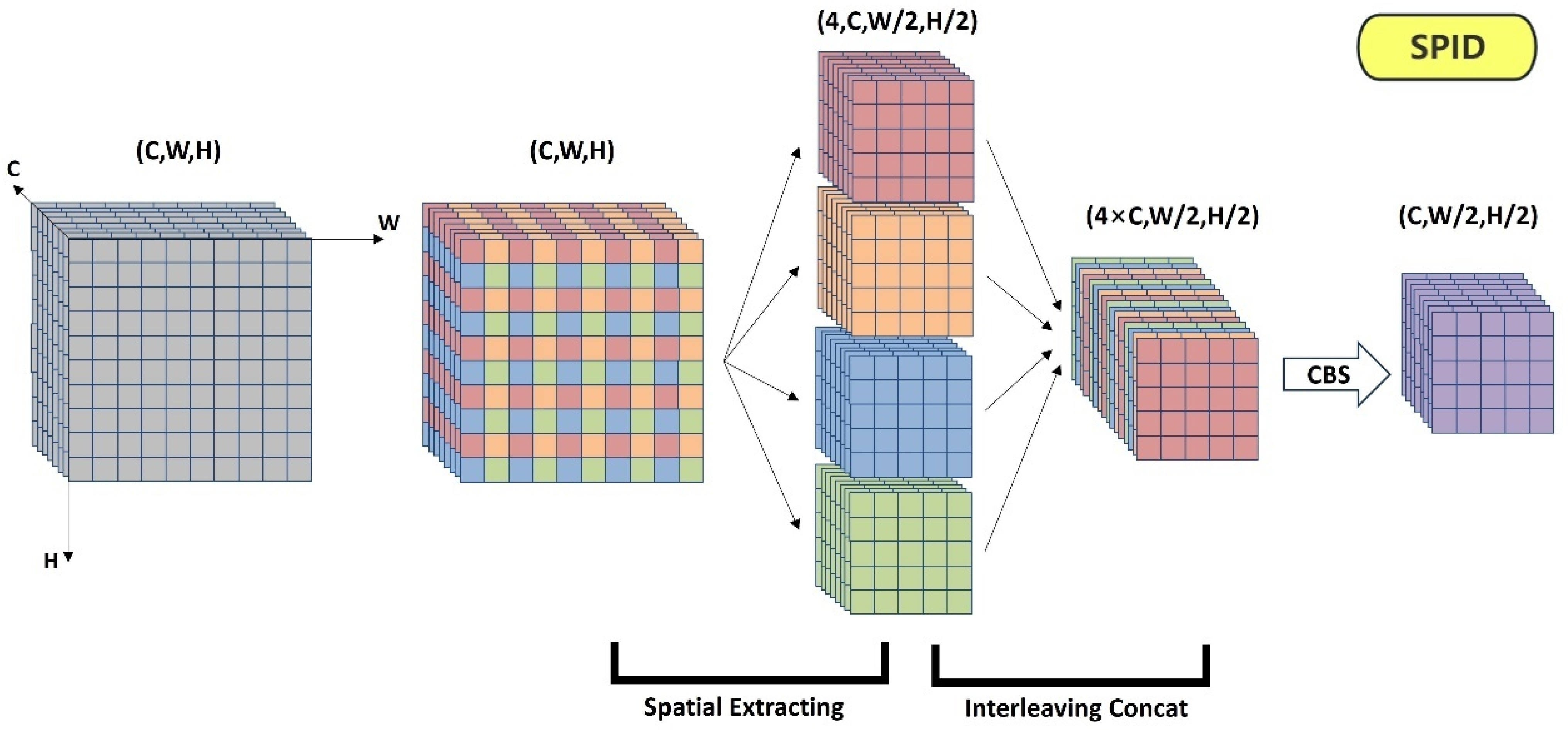
3.2. Space Interleaving in Depth (SPID) Module
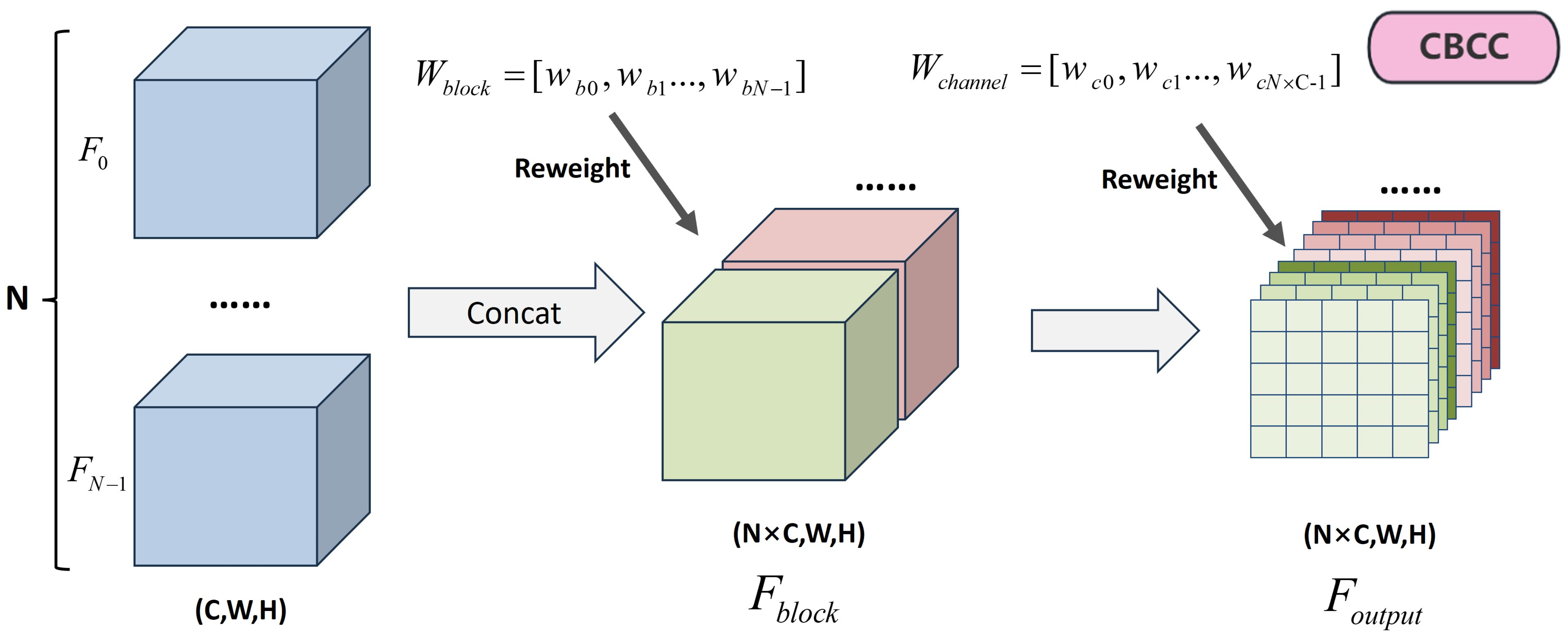
3.3. Cross Block and Channel Reweight Concat (CBCC) Module
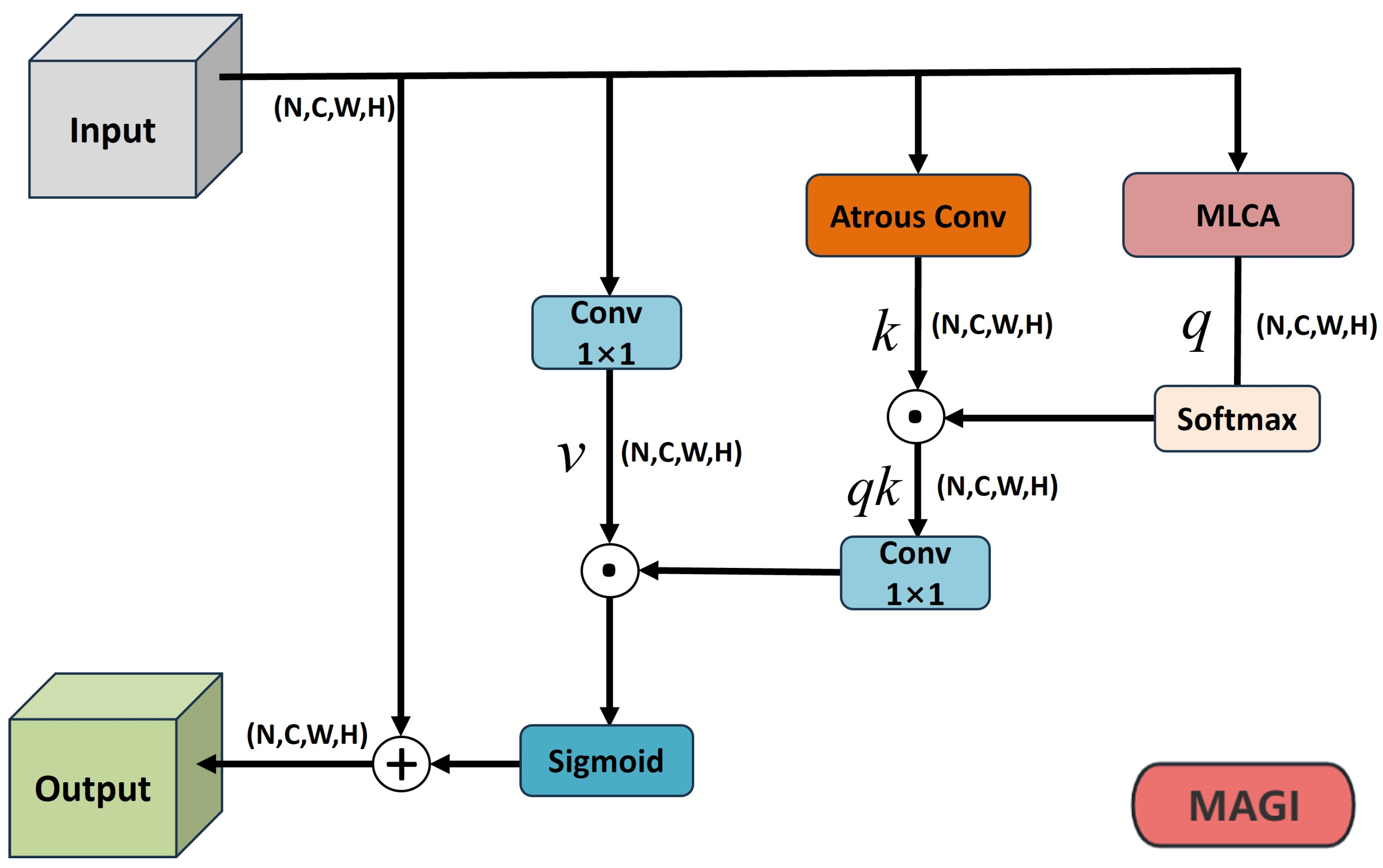
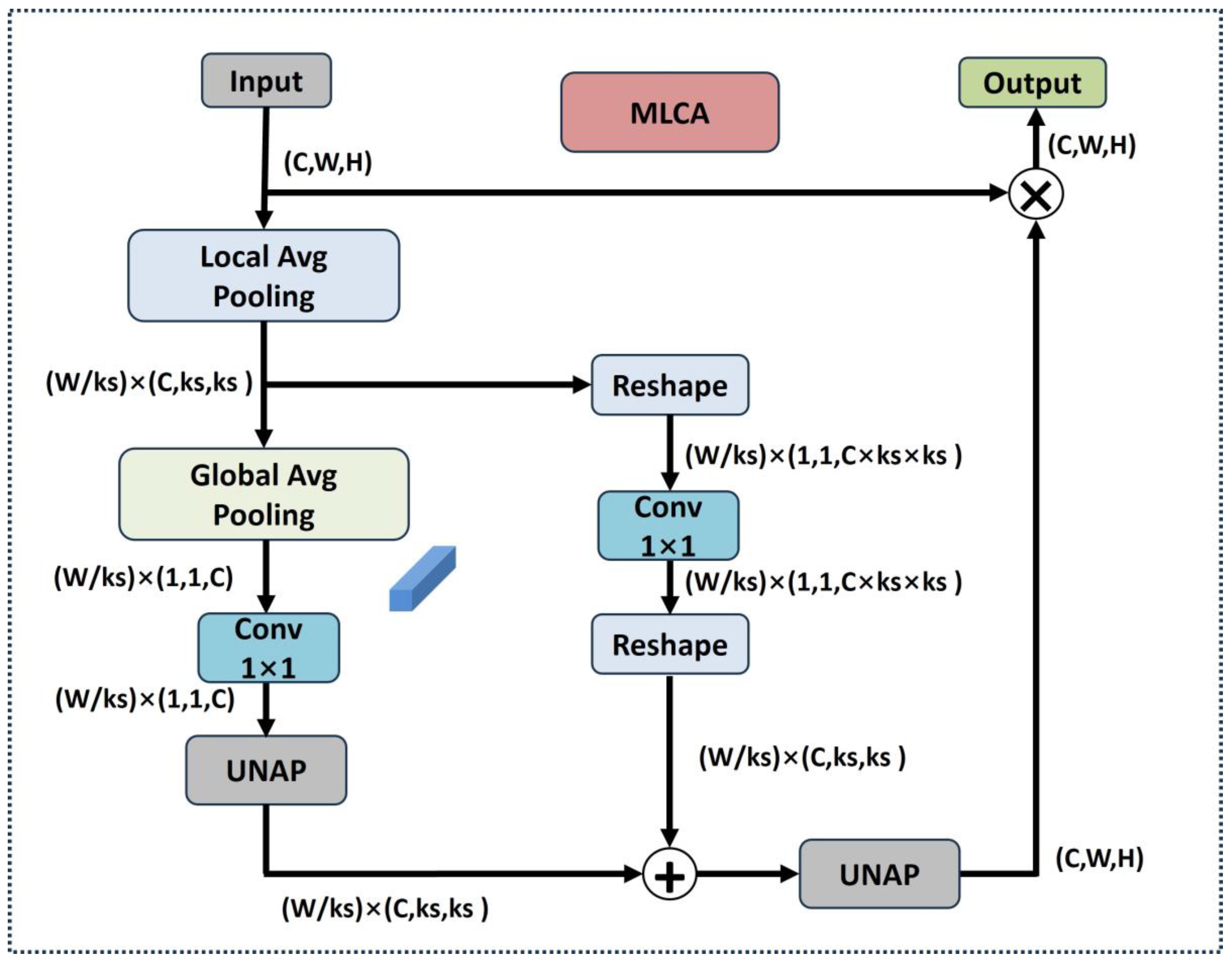
3.4. Mixed Local Channel Attention Global Integration (MAGI) Module
4. Experiment
4.1. Datasets
4.1.1. AI-TOD Dataset
4.1.2. SIMD Dataset
4.2. Experimental Evaluation Indicators
4.3. Experimental Results and Analysis
4.3.1. Ablation Test on AI-TOD
4.3.2. Comparison Experiments on AI-TOD
4.3.3. Comparison Experiments on SIMD
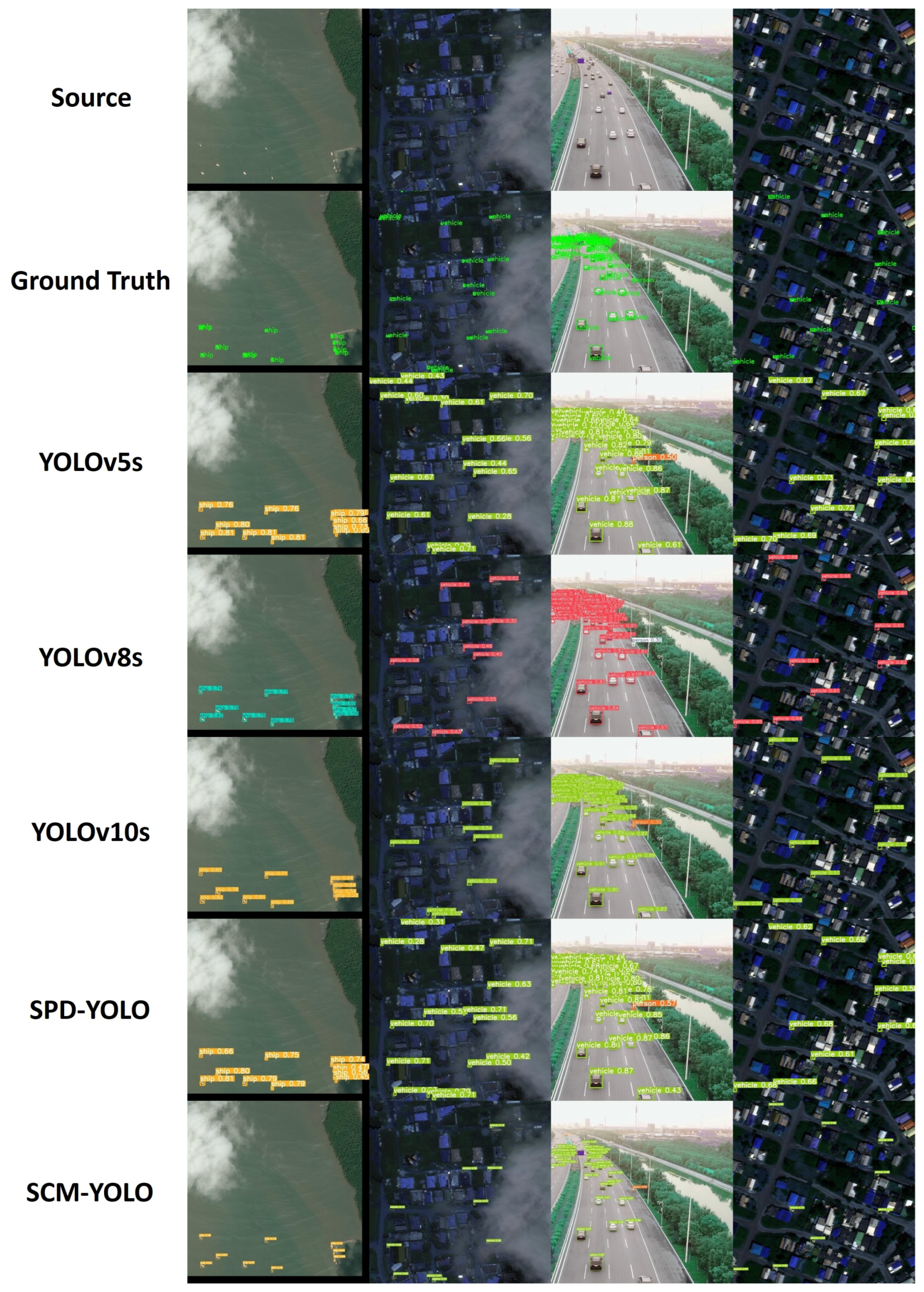
4.4. SCM-YOLO in Challenging Scenarios
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- In comparison with the SPID and CBCC modules, the MAGI module proposed in this paper introduces the largest number of parameters and exerts the greatest influence on the model size. In the domain of object detection, the incorporation of an attention mechanism has been shown to enhance the model’s detection capability while concomitantly increasing the number of model parameters. A significant number of researchers are exploring more efficient and lightweight designs for the attention mechanism. In our future research, we also plan to design or introduce more lightweight attention mechanisms to improve the model’s global perceptual ability. Furthermore, we will continue to explore more efficient ways of utilizing attention mechanisms than the MAGI module.
- (2)
- The method only improves the retention and fusion of spatial local information in the feature enhancement part, and the detection ability of the model can be further improved by introducing more comprehensive feature enhancement means.
- (3)
- The method has only been validated on the AI-TOD and SIMD remote sensing small object datasets. Its performance should be further validated on a wider range of remote sensing small object datasets.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Božić-Štulić, D.; Marušić, Ž.; Gotovac, S. Deep learning approach in aerial imagery for supporting land search and rescue missions. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2019, 127, 1256–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, S.; Shin, I.-K.; Moon, J.; Kang, J.; Choi, S.-I. Road traffic monitoring from UAV images using deep learning networks. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimoni, M.; Haelterman, R.; Perneel, C. Hypersectral imaging for military and security applications: Combining myriad processing and sensing techniques. IEEE Geosci. Remote. Sens. Mag. 2019, 7, 101–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhuang, Y.; Dong, S.; Gao, P.; Dong, H.; Chen, H.; Chen, L.; Li, L. Hierarchical disentangling network for building extraction from very high resolution optical remote sensing imagery. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Wan, G.; Cheng, G.; Meng, L.; Han, J. Object detection in optical remote sensing images: A survey and a new benchmark. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 159, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Gu, T.; Guan, H.; Li, D.; Jin, S. Vehicle detection from high-resolution remote sensing imagery using convolutional capsule networks. IEEE Geosci. Remote. Sens. Lett. 2019, 16, 1894–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Gong, J.; Hu, J.; Zhi, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Bao, G. Feature-enhanced CenterNet for small object detection in remote sensing images. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Han, J. A survey on object detection in optical remote sensing images. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 117, 11–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, Q.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, B.; Wu, Y.; Pu, S.; Li, Z. Lightweight oriented object detection using multiscale context and enhanced channel attention in remote sensing images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote. Sens. 2021, 14, 5786–5795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girshick, R.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; Malik, J. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 580–587. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R. Fast r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1440–1448. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLO9000: Better, faster, stronger. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 7263–7271. [Google Scholar]
- Farhadi, A.; Redmon, J. Yolov3: An incremental improvement. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Bochkovskiy, A.; Wang, C.-Y.; Liao, H.-Y.M. Yolov4: Optimal speed and accuracy of object detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.10934. [Google Scholar]
- Jocher, G.; Stoken, A.; Chaurasia, A.; Borovec, J.; Kwon, Y.; Michael, K.; Changyu, L.; Fang, J.; Skalski, P.; Hogan, A.; et al. YOLOv5. Available online: https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5 (accessed on 27 August 2024).
- Li, C.; Li, L.; Jiang, H.; Weng, K.; Geng, Y.; Li, L.; Ke, Z.; Li, Q.; Cheng, M.; Nie, W. YOLOv6: A single-stage object detection framework for industrial applications. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2209.02976. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Bochkovskiy, A.; Liao, H.-Y.M. YOLOv7: Trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 7464–7475. [Google Scholar]
- Joher, G.; Chaurasia, A.; Qiu, J. YOLOv8. Available online: https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics (accessed on 27 August 2024).
- Wang, C.-Y.; Yeh, I.-H.; Liao, H.-Y.M. Yolov9: Learning what you want to learn using programmable gradient information. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.13616. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.; Chen, H.; Liu, L.; Chen, K.; Lin, Z.; Han, J.; Ding, G. Yolov10: Real-time end-to-end object detection. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.14458. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Andreetto, M.; Adam, H. MobileNets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L.-C. Mobilenetv2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 4510–4520. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.; Sandler, M.; Chu, G.; Chen, L.-C.; Chen, B.; Tan, M.; Wang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Pang, R.; Vasudevan, V. Searching for mobilenetv3. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 1314–1324. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, X.; Zhang, B.; Xu, R. Moga: Searching beyond mobilenetv3. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2020—2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Barcelona, Spain, 4–8 May 2020; pp. 4042–4046. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kweon, I.S. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, B.; Zhu, P.; Li, P.; Zuo, W.; Hu, Q. ECA-Net: Efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 11534–11542. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, D.; Lu, R.; Shen, S.; Xu, T.; Lang, X.; Ren, Z. Mixed local channel attention for object detection. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 123, 106442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Girshick, R.; Gupta, A.; He, K. Non-local neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7794–7803. [Google Scholar]
- Merget, D.; Rock, M.; Rigoll, G. Robust facial landmark detection via a fully-convolutional local-global context network. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 781–790. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Xu, J.; Lin, S.; Wei, F.; Hu, H. Gcnet: Non-local networks meet squeeze-excitation networks and beyond. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27–28 October 2019; pp. 0–0. [Google Scholar]
- Han, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, J.; Chiu, C.-C.; Qin, J.; Gulati, A.; Pang, R.; Wu, Y. Contextnet: Improving convolutional neural networks for automatic speech recognition with global context. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.03191. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2117–2125. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Qi, L.; Qin, H.; Shi, J.; Jia, J. Path aggregation network for instance segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 8759–8768. [Google Scholar]
- LeCun, Y.; Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y.; Haffner, P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE 1998, 86, 2278–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunkara, R.; Luo, T. No More Strided Convolutions or Pooling: A New CNN Building Block for Low-Resolution Images and Small Objects. In Proceedings of the Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases: European Conference, ECML PKDD 2022, Grenoble, France, 19–23 September 2022; pp. 443–459. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.; Pang, R.; Le, Q.V. Efficientdet: Scalable and efficient object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 10781–10790. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Hu, C.; Luo, S.; Luo, Y.; Chen, C.W. Learning to aggregate multi-scale context for instance segmentation in remote sensing images. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2111.11057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Yang, W.; Guo, H.; Zhang, R.; Xia, G.-S. Tiny object detection in aerial images. In Proceedings of the 2020 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Milan, Italy, 10–15 January 2021; pp. 3791–3798. [Google Scholar]
- Haroon, M.; Shahzad, M.; Fraz, M.M. Multisized object detection using spaceborne optical imagery. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 3032–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioffe, S. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1502.03167. [Google Scholar]
- Misra, D. Mish: A self regularized non-monotonic activation function. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1908.08681. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 37, 1904–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.-Y.; Liao, H.-Y.M.; Wu, Y.-H.; Chen, P.-Y.; Hsieh, J.-W.; Yeh, I.-H. CSPNet: A new backbone that can enhance learning capability of CNN. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 390–391. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, M. YOLOv5, YOLOv8 and YOLOv10: The Go-To Detectors for Real-time Vision. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.02988. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Lyu, S.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Q. TPH-YOLOv5: Improved YOLOv5 Based on Transformer Prediction Head for Object Detection on Drone-captured Scenarios. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Yang, W.; Wang, L.; Chen, D.; Wei, F.; KeZiErBieKe, H.; Liao, Y. FE-YOLOv5: Feature enhancement network based on YOLOv5 for small object detection. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2023, 90, 103752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, B. A-YOLO: Small object vehicle detection based on improved YOLOv5. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Intelligent Traffic Systems and Smart City (ITSSC 2023), Xi’an, China, 10–12 November 2024; pp. 208–216. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.-F.; Ren, W.; Zhang, Z.; Jia, Z.; Wang, L.; Tan, T. Focal and efficient IOU loss for accurate bounding box regression. Neurocomputing 2022, 506, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.L.; Yu, T.; Gao, P.; Wang, F.; Yuan, R.Y. Yolo-tla: An Efficient and Lightweight Small Object Detection Model based on YOLOv5. J. Real-Time Image Process. 2024, 21, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Q.; Pan, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, H.; Wei, H.; Liu, C. SOD-YOLO: Small-Object-Detection Algorithm Based on Improved YOLOv8 for UAV Images. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, D.; Lu, R.; Wang, S.; Shen, S.; Xu, T.; Lang, X. Yolo-hr: Improved yolov5 for object detection in high-resolution optical remote sensing images. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Dong, Y. YOLO-SE: Improved YOLOv8 for remote sensing object detection and recognition. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 12977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Wu, Y. Improved YOLO-V3 with DenseNet for multi-scale remote sensing object detection. Sensors 2020, 20, 4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Koltun, V. Multi-scale context aggregation by dilated convolutions. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1511.07122. [Google Scholar]



| SPID | CBCC | MAGI | mAP50 (%) | mAP50-95 (%) | Para (M) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| × | × | × | 60.680 | 25.395 | 5.407 |
| √ | × | × | 61.621 | 25.380 | 5.699 |
| × | √ | × | 62.005 | 26.383 | 5.446 |
| × | × | √ | 62.216 | 25.263 | 7.346 |
| √ | √ | × | 63.025 | 26.522 | 5.765 |
| √ | × | √ | 63.302 | 26.562 | 7.665 |
| × | √ | √ | 63.523 | 26.493 | 7.384 |
| √ | √ | √ | 64.053 | 27.283 | 7.895 |
| Model | mAP50 (%) | mAP50-95 (%) | Recall (%) | Precision (%) | Para (M) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv5s | 58.567 | 23.352 | 57.518 | 71.527 | 7.023 |
| YOLOv8s | 58.760 | 26.910 | 55.823 | 67.176 | 11.172 |
| YOLOv10s | 50.020 | 22.930 | 48.850 | 62.009 | 8.071 |
| SPD-YOLO | 58.090 | 23.220 | 59.031 | 67.392 | 8.536 |
| SCM-YOLO | 64.053 | 27.283 | 60.046 | 73.443 | 7.895 |
| Model | GFLOPs | Para (M) | FPS (s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv5s | 15.8 | 7.023 | 136 |
| YOLOv8s | 28.5 | 11.172 | 133 |
| YOLOv10s | 24.5 | 8.071 | 96 |
| SPD-YOLO | 33.1 | 8.536 | 138 |
| SCM-YOLO | 42.7 | 7.895 | 78 |
| Model | mAP50 (%) | mAP50-95 (%) | Recall (%) | Precision (%) | Para (M) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv5s | 81.450 | 64.784 | 78.347 | 80.754 | 7.061 |
| YOLOv8s | 82.213 | 64.928 | 81.670 | 77.628 | 11.141 |
| YOLOv10s | 81.061 | 64.859 | 78.386 | 76.714 | 8.077 |
| SPD-YOLO | 82.081 | 64.055 | 80.317 | 76.543 | 8.596 |
| SCM-YOLO | 83.158 | 65.402 | 81.866 | 78.735 | 7.690 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiang, H.; Hao, W.; Xie, M.; Tang, Q.; Shi, H.; Zhao, Y.; Han, X. SCM-YOLO for Lightweight Small Object Detection in Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17020249
Qiang H, Hao W, Xie M, Tang Q, Shi H, Zhao Y, Han X. SCM-YOLO for Lightweight Small Object Detection in Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(2):249. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17020249
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiang, Hao, Wei Hao, Meilin Xie, Qiang Tang, Heng Shi, Yixin Zhao, and Xiaoteng Han. 2025. "SCM-YOLO for Lightweight Small Object Detection in Remote Sensing Images" Remote Sensing 17, no. 2: 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17020249
APA StyleQiang, H., Hao, W., Xie, M., Tang, Q., Shi, H., Zhao, Y., & Han, X. (2025). SCM-YOLO for Lightweight Small Object Detection in Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sensing, 17(2), 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17020249





