Toward Automatic 3D Model Reconstruction of Building Curtain Walls from UAV Images Based on NeRF and Deep Learning
Abstract
Highlights
- A BIM model reconstruction method based on NeRF and deep learning is estab-lished.
- The overall accuracy of semantic segmentation for curtain wall point clouds is 71.8%.
- The overall dimensional error of the reconstructed BIM model is within 0.1m.
- For curtain wall reconstruction, NeRF performs better than photogrammetry.
- For semantic segmentation of curtain wall point clouds, the deep learning method is superior to the traditional method.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Image-Based 3D Model Reconstruction
2.2. Application of NeRF in the Field of Architecture
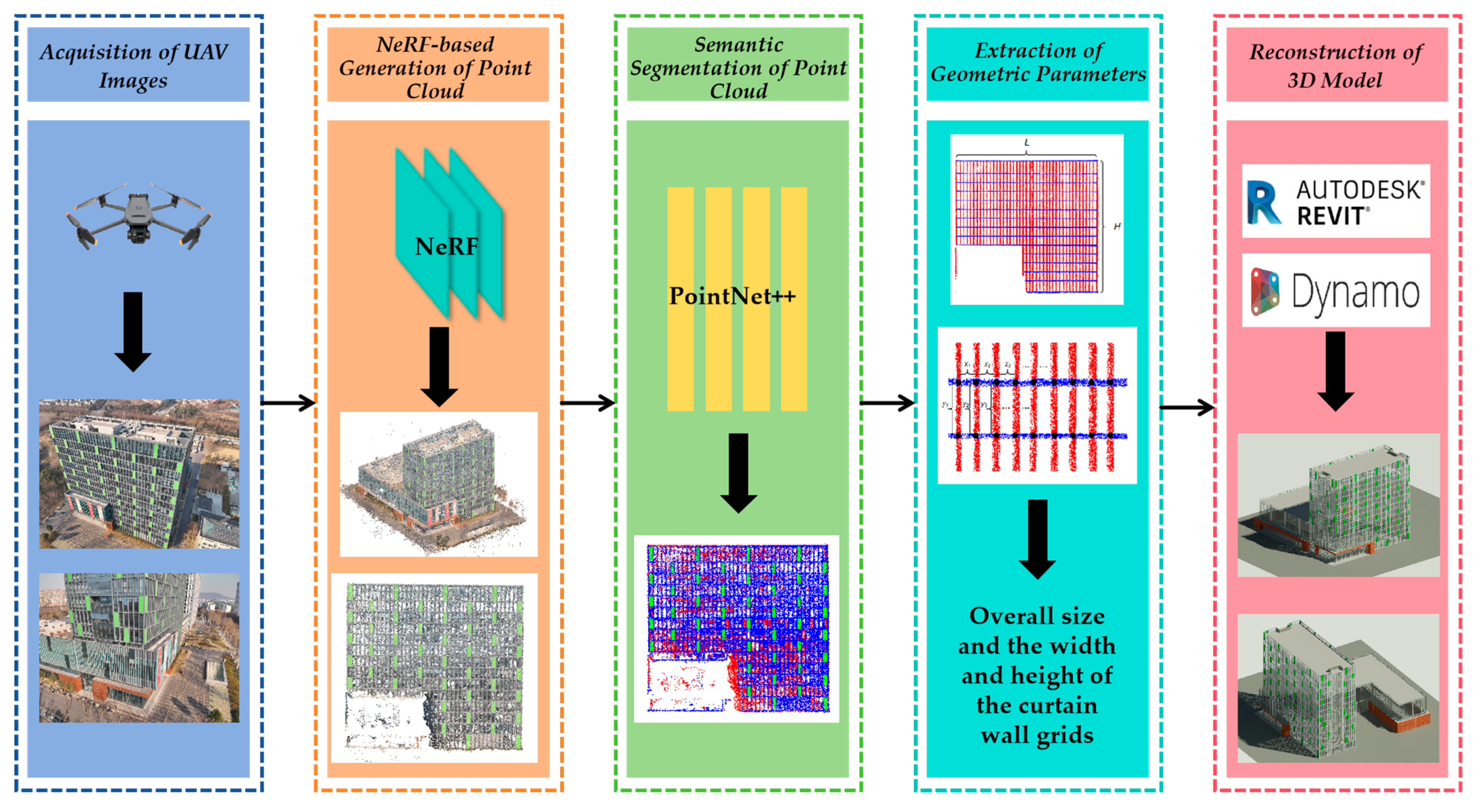
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. UAV-Based Image Acquisition
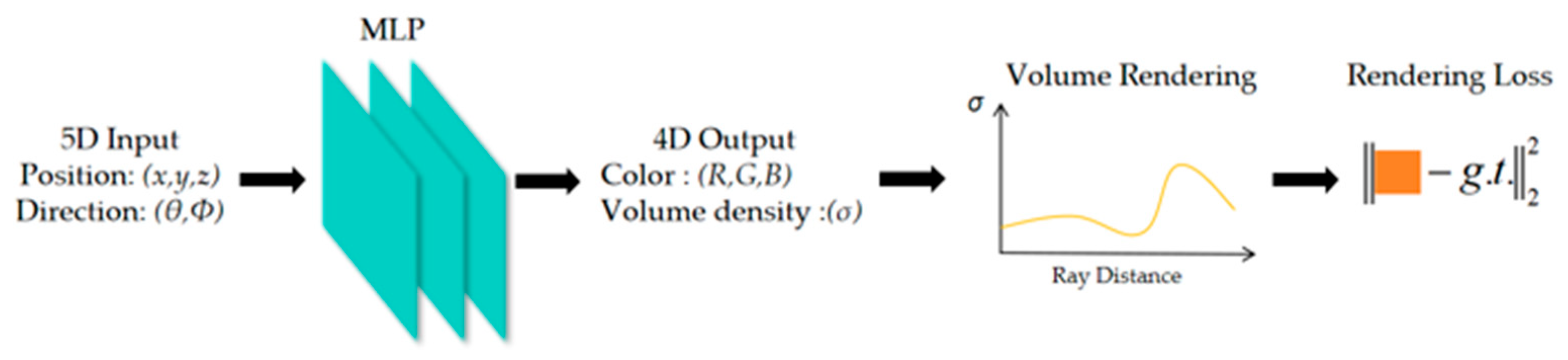
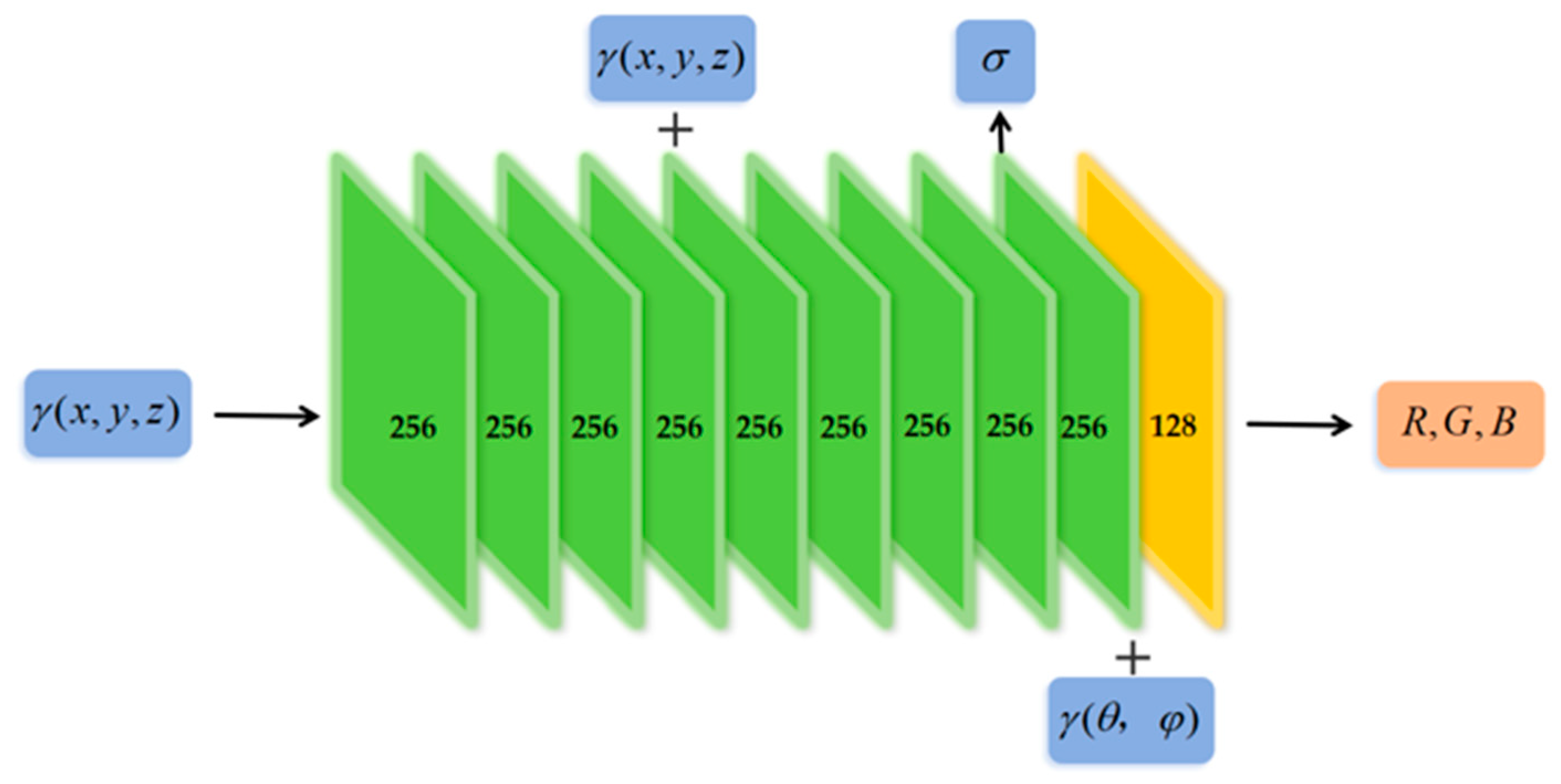
3.2. NeRF-Based Generation of Point Cloud
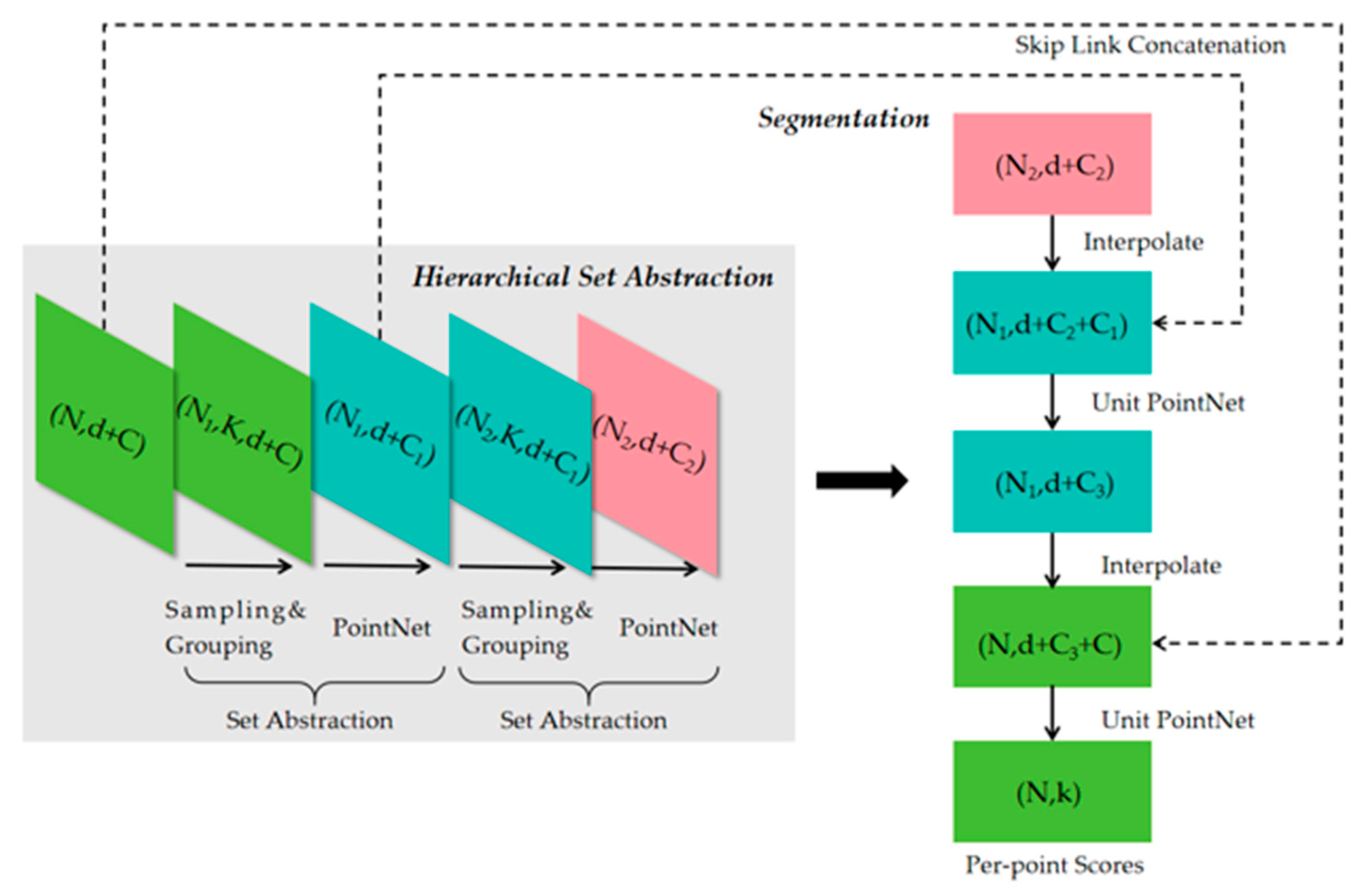
3.3. Semantic Segmentation of Point Cloud
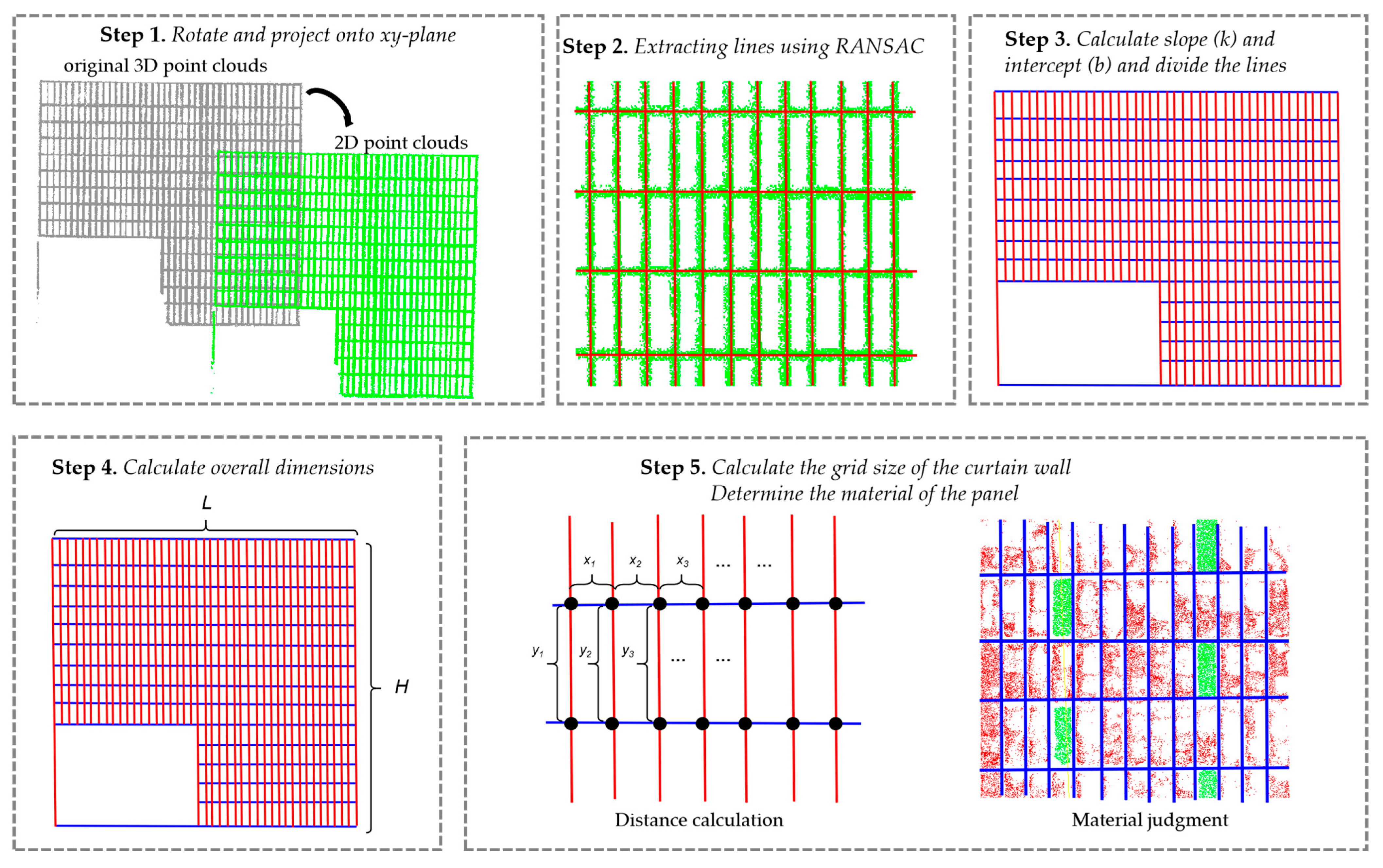
3.4. Extraction of Geometric Parameters
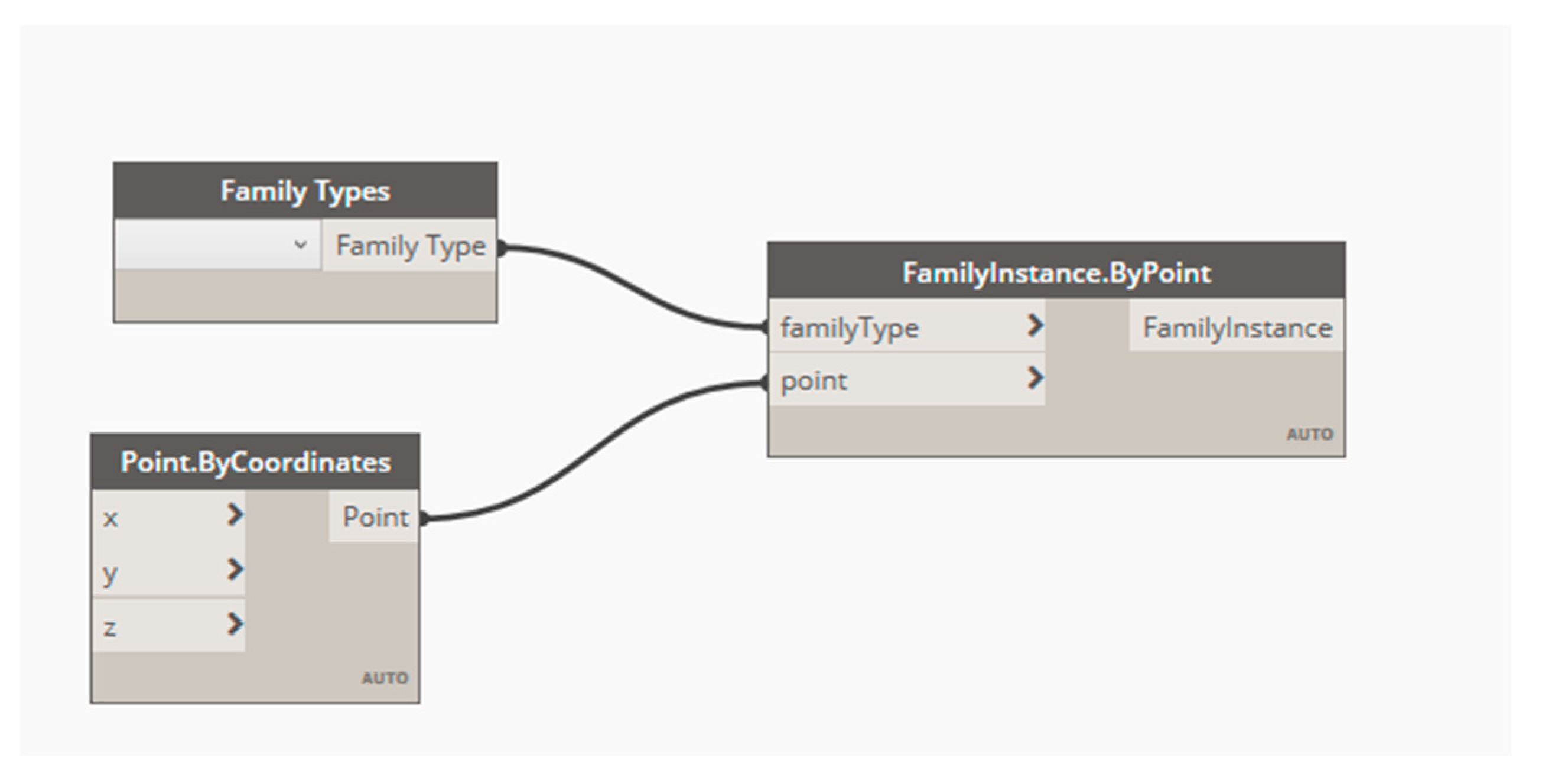
3.5. Reconstruction of BIM Model
3.6. Point Clouds Quality Assessment
3.7. Experiment
3.7.1. Basic Information of the Building
3.7.2. Image Acquisition
3.7.3. Model Parameter Settings
4. Result
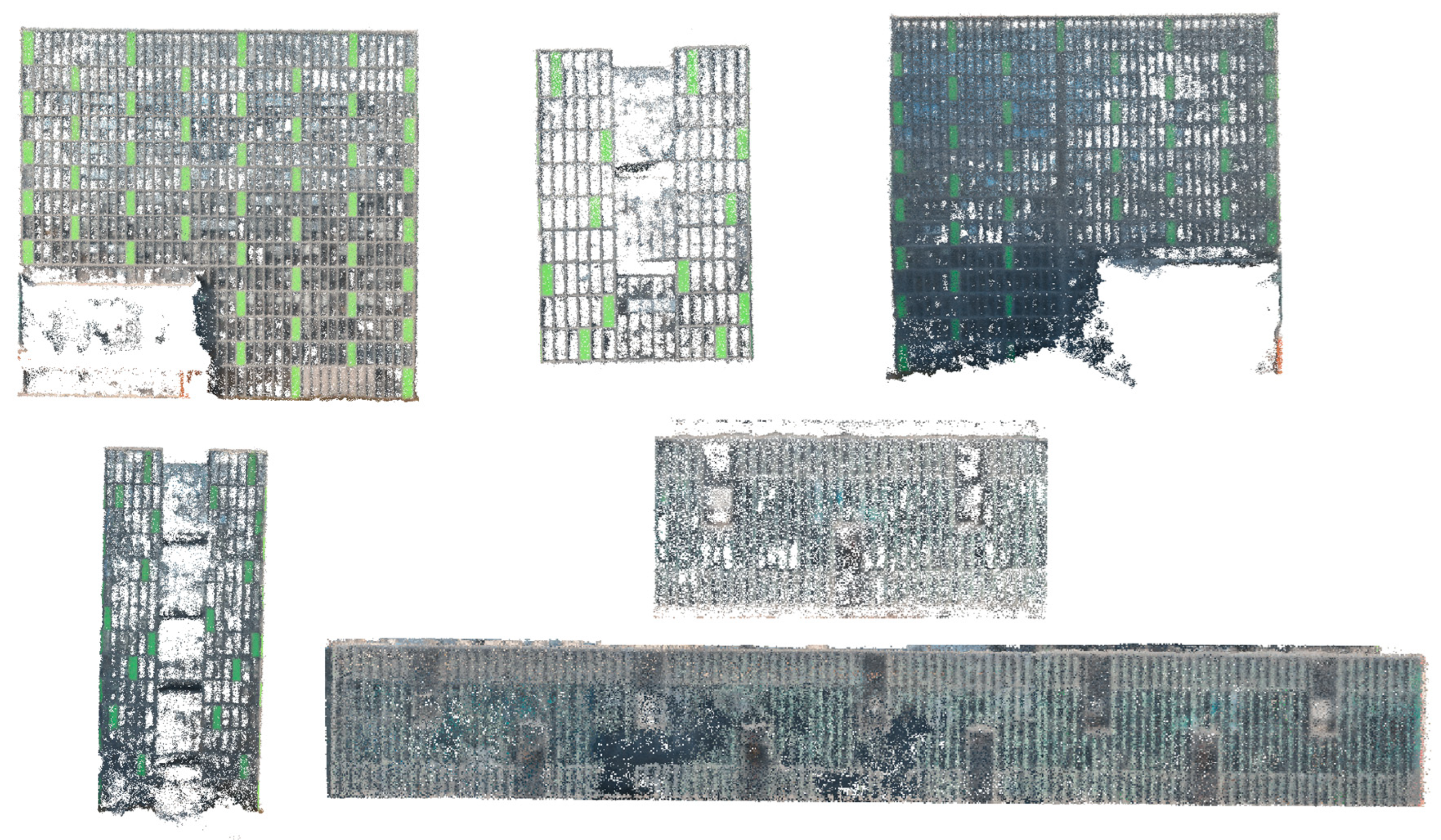
4.1. Point Clouds Obtained from NeRF
4.2. Result of Semantic Segmentation
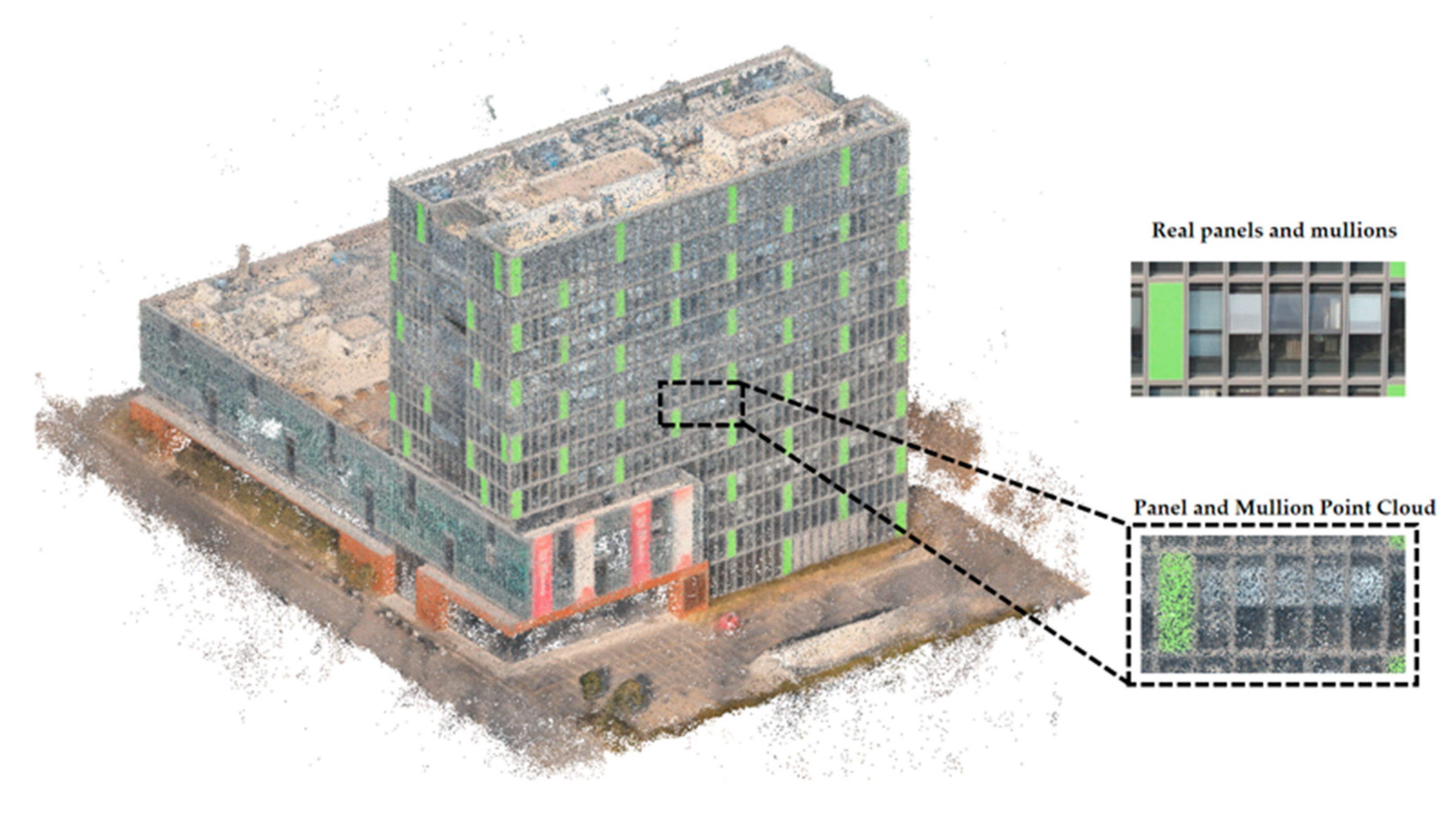
4.3. Geometric Parameters of Curtain Wall
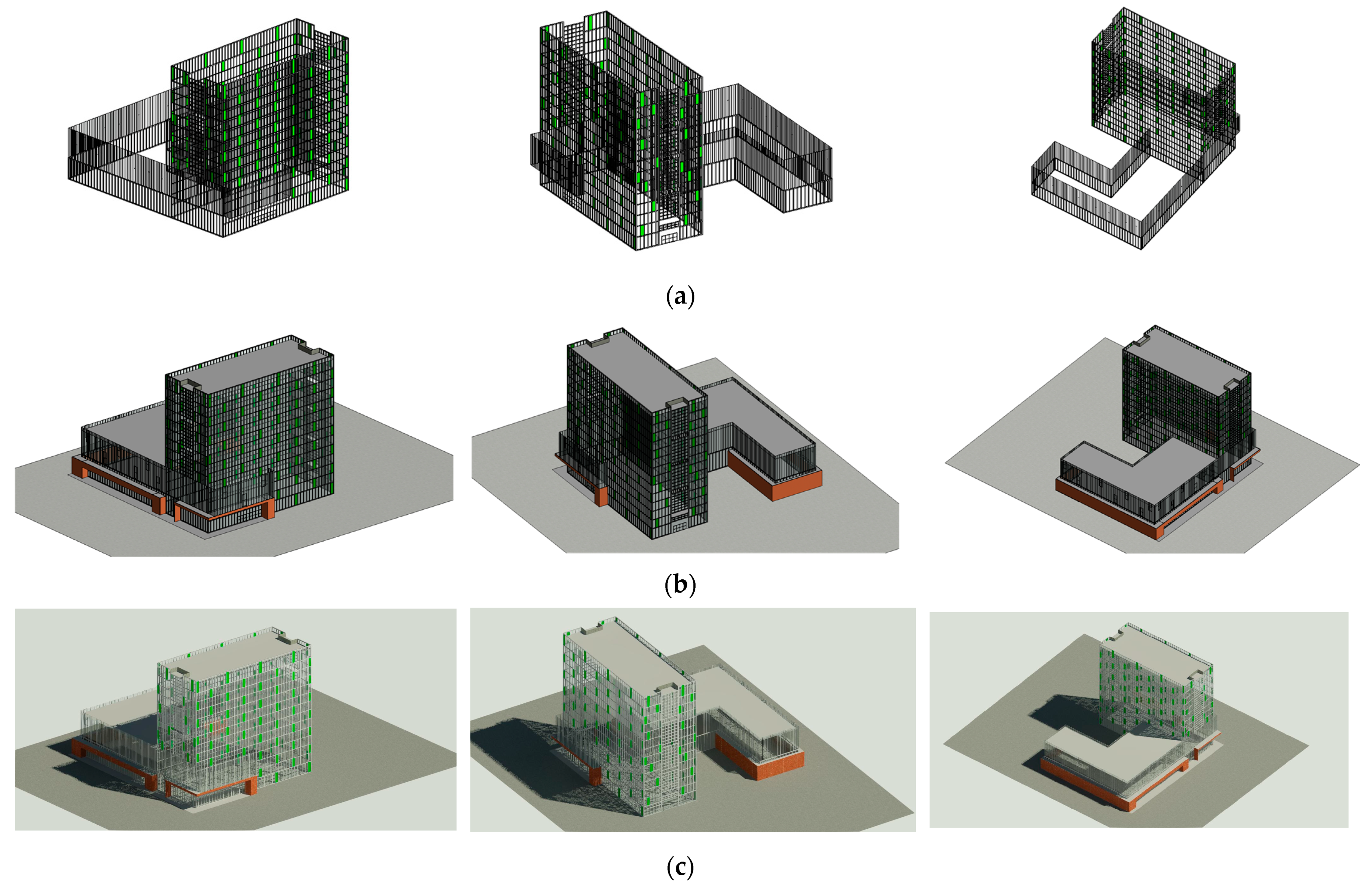
4.4. Reconstructed BIM Model
5. Discussion
5.1. Comparison of Point Cloud Quality Generated by NeRF and Photogrammetry
5.1.1. Plane Fitting Accuracy
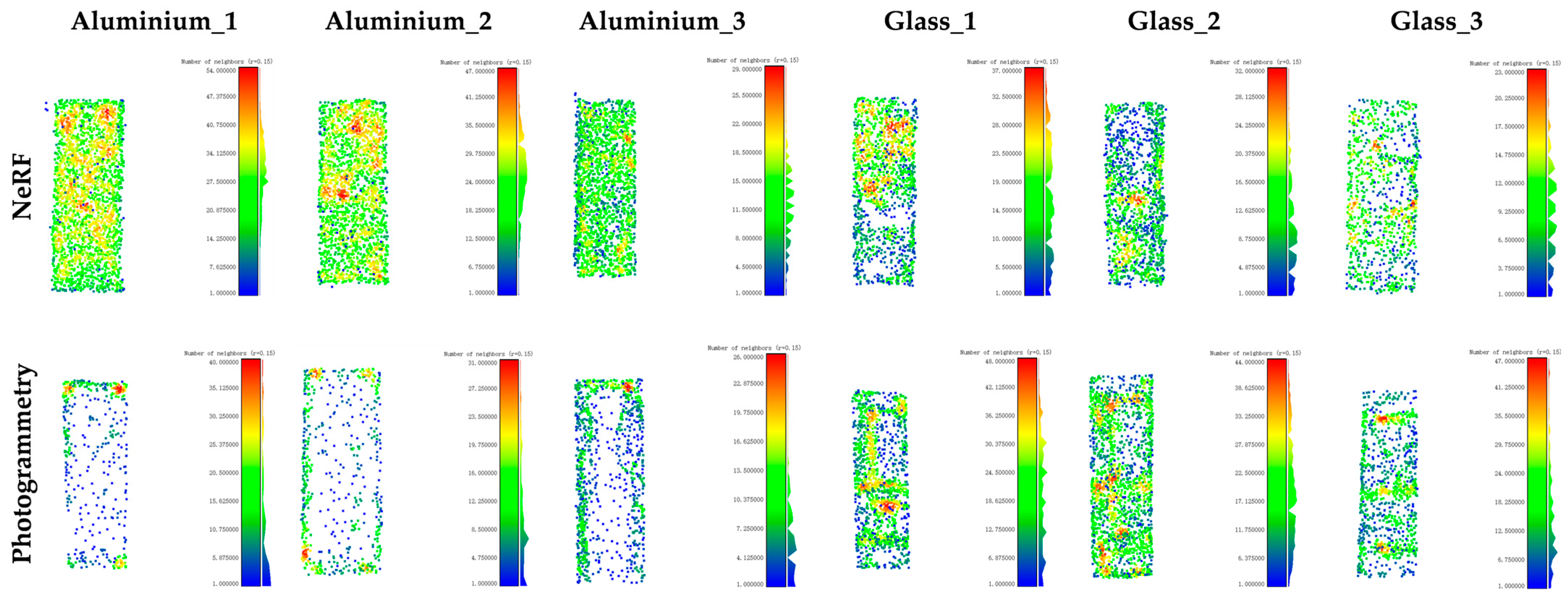
5.1.2. Point Cloud Completeness and Density Distribution
5.2. Comparison of Semantic Segmentation Between Traditional and Deep Learning Methods
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, D.; Li, Y.; Li, R.; Cheng, L.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, M.; Lee, C.H. Automatic curtain wall frame detection based on deep learning and cross-modal feature fusion. Autom. Constr. 2024, 160, 105305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Shi, J.-L.; Fu, J.-Y.; Zhang, S.-X.; Liao, T.; Yang, C.-Q.; Wu, J.-R.; He, Y.-C. An improved YOLOv10 algorithm for automated damage detection of glass curtain-walls in high-rise buildings. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 101, 111812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshabshiri, A.; Ghanim, A.; Hussien, A.; Maksoud, A.; Mushtaha, E. Integration of Building Information Modeling and Digital Twins in the Operation and Maintenance of a building lifecycle: A bibliometric analysis review. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 99, 111541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, H.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Lai, S.; Huang, G. Interactions between BIM and robotics: Towards intelligent construction engineering and management. Comput. Ind. 2025, 169, 104299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.P.; Mitoulis, S.A.; Boddice, D.; Yu, J.L.; Ninic, J. Scan-to-BIM-to-Sim: Automated reconstruction of digital and simulation models from point clouds with applications on bridges. Results Eng. 2025, 25, 104289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zou, Y.; Wang, F.; Dimyadi, J. Automated UAV image-to-BIM registration for planar and curved building façades using structure-from-motion and 3D surface unwrapping. Autom. Constr. 2025, 174, 106148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, Y.; Tran, D.Q.; Vo, K.T.D.; Jeon, J.; Park, M.; Park, S. Neural radiance fields for construction site scene representation and progress evaluation with BIM. Autom. Constr. 2025, 172, 106013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Kim, M.K. Applications of 3D point cloud data in the construction industry: A fifteen-year review from 2004 to 2018. Adv. Eng. Inf. 2019, 39, 306–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, H.Z.; Wang, Q.; Yan, Y.Z.; Huang, G.Y. Deep learning-based point cloud completion for MEP components. Autom. Constr. 2025, 175, 106218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.Z.; Song, Z.B.; Zhou, J.; Xie, D.; Lu, J.F. Camera and LiDAR Fusion for Urban Scene Reconstruction and Novel View Synthesis via Voxel-Based Neural Radiance Fields. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mildenhall, B.; Srinivasan, P.P.; Tancik, M.; Barron, J.T.; Ramamoorthi, R.; Ng, R. NeRF: Representing Scenes as Neural Radiance Fields for View Synthesis. Commun. ACM 2022, 65, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remondino, F.; Karami, A.; Yan, Z.Y.; Mazzacca, G.; Rigon, S.; Qin, R.J. A Critical Analysis of NeRF-Based 3D Reconstruction. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tancik, M.; Weber, E.; Ng, E.; Li, R.L.; Yi, B.; Kerr, J.; Wang, T.; Kristofferson, A.; Austin, J.; Salahi, K.; et al. Nerfstudio: A Modular Framework for Neural Radiance Field Development. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH Conference, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 6–10 August 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ullman, S. Interpretation of structure from motion. Proc. R. Soc. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 1979, 203, 405–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönberger, J.L.; Frahm, J.M. Structure-from-Motion Revisited. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 4104–4113. [Google Scholar]
- Snavely, N.; Seitz, S.M.; Szeliski, R. Modeling the world from Internet photo collections. Int. J. Comput. Vision 2008, 80, 189–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönberger, J.L.; Zheng, E.L.; Frahm, J.M.; Pollefeys, M. Pixelwise View Selection for Unstructured Multi-View Stereo. In Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8–16 October 2016; pp. 501–518. [Google Scholar]
- Kazhdan, M. Poisson Surface Reconstruction. In Proceedings of the Eurographics Symposium on Geometry Processing, Cagliari, Italy, 26–28 June 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Li, M.K.; Wang, H.M.; Li, P.B.; Xu, B.Q.; Hu, D.F. Context-aware depth estimation for improved 3D reconstruction of homogeneous indoor environments. Autom. Constr. 2025, 177, 106343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.D.; Zhu, Q.K.; Zhang, Q.; Du, Y.F. Deep learning-based 3D reconstruction of ancient buildings with surface damage identification and localization. Structures 2025, 73, 108383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ren, G.; Pan, Y.; Sun, J.; Wang, P.; Xu, F.; Liu, Z. Surface Reconstruction Planning with High-Quality Satellite Stereo Pairs Searching. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.Y.; Hu, L.; Yao, Y.; Shou, W.C.; Li, D.Q. Zero-reference deep learning for low-light image enhancement of underground utilities 3D reconstruction. Autom. Constr. 2023, 152, 104930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterckx, J.; Vlaminck, M.; De Bauw, K.; Luong, H. Accurate and robust 3D reconstruction of wind turbine blade leading edges from high-resolution images. Autom. Constr. 2025, 175, 106153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dino, I.G.; Sari, A.E.; Iseri, O.K.; Akin, S.; Kalfaoglu, E.; Erdogan, B.; Kalkan, S.; Alatan, A.A. Image-based construction of building energy models using computer vision. Autom. Constr. 2020, 116, 103231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santagati, C.; Lo Turco, M.; D’Agostino, G. Populating a Library of Reusable H-Boms: Assessment of a Feasible Image Based Modeling Workflow. In Proceedings of the 26th International Symposium of ICOMOS/ISPRS-International-Scientific-Committee-on-Heritage-Documentation (CIPA) on Digital Workflows for Heritage Conservation, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 28 August–1 September 2017; pp. 627–634. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.H.; Wu, L.X.; Shen, Y.L.; Li, F.S.; Wang, Q.L.; Wang, R. Tridimensional Reconstruction Applied to Cultural Heritage with the Use of Camera-Equipped UAV and Terrestrial Laser Scanner. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 10413–10434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Gao, H. Unmanned Aerial Vehicle-Neural Radiance Field (UAV-NeRF): Learning Multiview Drone Three-Dimensional Reconstruction with Neural Radiance Field. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.; Asad, A.T.; Shabbir, K.; Sim, S.H.; Lee, J. Robust localization of shear connectors in accelerated bridge construction with neural radiance field. Autom. Constr. 2024, 168, 105843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, D.P.; Wang, W.D.; Hu, W.B.; Peng, J.; Zhao, Y.D.; Zhang, Y.K.; Wang, J. 3D reconstruction of building structures incorporating neural radiation fields and geometric constraints. Autom. Constr. 2024, 165, 105517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.M.; Lu, W.S.; Chen, J.J. Neural rendering-based semantic point cloud retrieval for indoor construction progress monitoring. Autom. Constr. 2024, 164, 105448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, D.; Guo, H.; Yue, D. 3D wireframe model reconstruction of buildings from multi-view images using neural implicit fields. Autom. Constr. 2025, 174, 106145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermann, M.; Kwak, H.; Ruf, B.; Weinmann, M. Leveraging Neural Radiance Fields for Large-Scale 3D Reconstruction from Aerial Imagery. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Qin, R.J.; Chen, X.Y. Unmanned Aerial Vehicle for Remote Sensing Applications-A Review. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, T.; Hu, P.C.; Sang, L.Z. Research on route planning of aerial photography of UAV in highway greening monitoring. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Power Electronics and Control Engineering (ISPECE), Xi’an, China, 28–30 December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, R.Y.; Yang, F.; Dong, Z.H. Path Planning of Unmanned Air Vehicles Relay Communication Based on Lowest Power Loss. In Proceedings of the 9th Asia Conference on Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering (ACMAE), Singapore, 29–31 December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.L.; Xin, B.; Chen, J.; Fang, H.; Zhu, Y.G.; Gao, G.Q.; Dou, L.H. Path Planning of Messenger UAV in Air-ground Coordination. In Proceedings of the 20th World Congress of the International-Federation-of-Automatic-Control (IFAC), Toulouse, France, 9–14 July 2017; pp. 8045–8051. [Google Scholar]
- Yusof, H.; Ahmad, M.A.; Abdullah, A.M.T. Historical Building Inspection using the Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (Uav). Int. J. Sustain. Constr. Eng. Technol. 2020, 11, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.F.; Ruan, Z.M.; Li, L. Application of Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Oblique Photography in 3D Modeling of Crag. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Digital Image Processing (ICDIP), Shanghai, China, 11–14 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, H.; Wang, Q.; Huang, L.; Zhang, M. Enhancing point cloud semantic segmentation of building interiors through diffusion-based scene-level synthesis. Autom. Constr. 2025, 178, 106390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, H.Z.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, M.Y.; Xue, Y.T.; Lu, L. 2D-3D fusion approach for improved point cloud segmentation. Autom. Constr. 2025, 177, 106336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.; Bischof, L. Seeded Region Growing. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1994, 16, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.K.; Murty, M.N.; Flynn, P.J. Data clustering: A review. ACM Comput. Surv. 1999, 31, 264–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.R.; Su, H.; Mo, K.C.; Guibas, L.J. PointNet: Deep Learning on Point Sets for 3D Classification and Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 30th IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 77–85. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, H.; Wang, Q.; Su, Y.; Fang, H.; Cheng, J.C.P.; Zhang, M. A point cloud dataset and deep learning method for semantic segmentation of underground garages. Copmut.-Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2025, 40, 3726–3749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.R.; Yi, L.; Su, H.; Guibas, L.J. PointNet plus plus: Deep Hierarchical Feature Learning on Point Sets in a Metric Space. In Proceedings of the 31st Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Fischler, M.A.; Bolles, R.C. Random sample consensus: A paradigm for model-fitting with applications to image-analysis and automated cartography. Commun. ACM 1981, 24, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Bu, R.; Sun, M.; Wu, W.; Di, X.; Chen, B. PointCNN: Convolution On X-Transformed Points. In Proceedings of the 32nd Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), Montreal, QC, Canada, 2–8 December 2018. [Google Scholar]
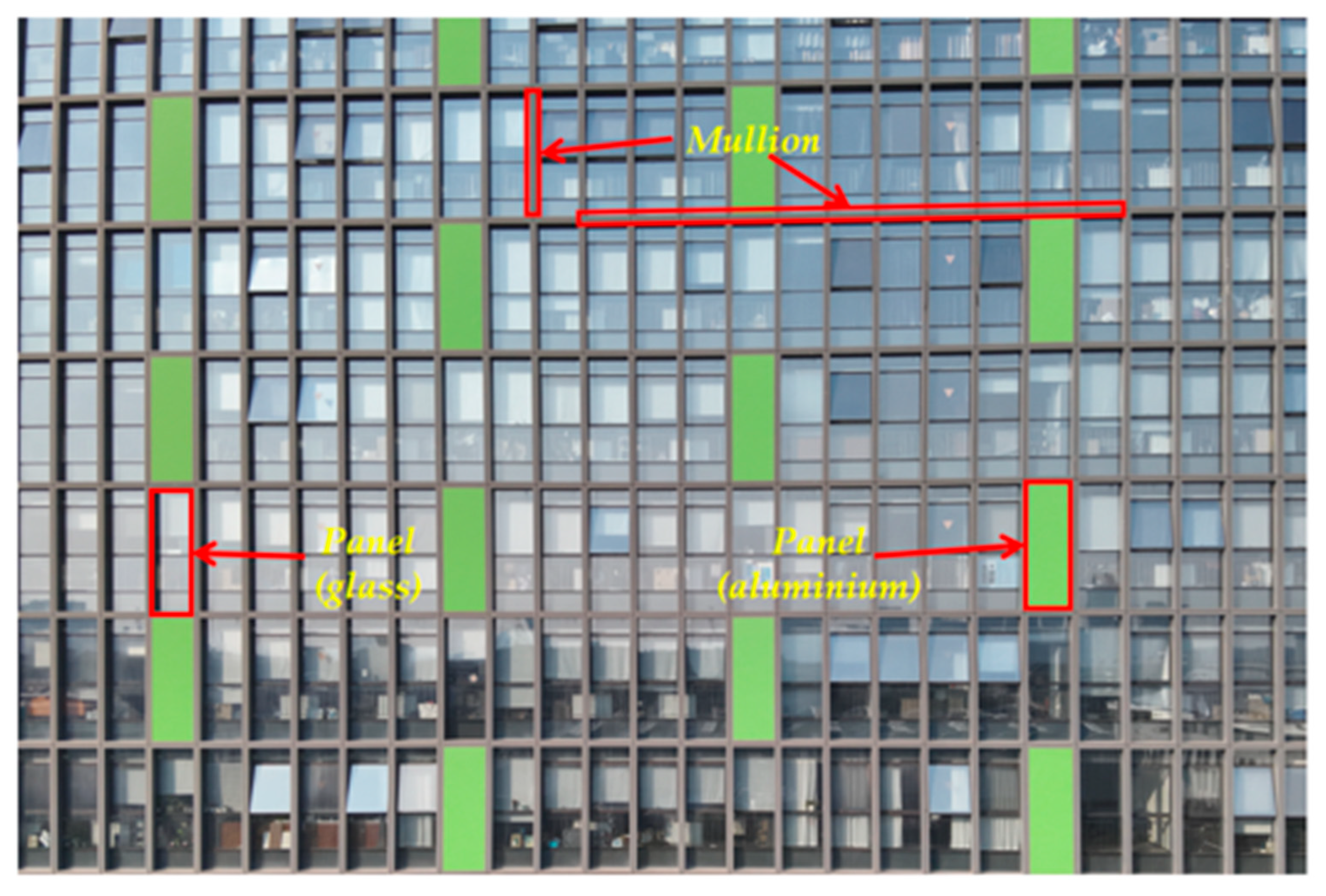


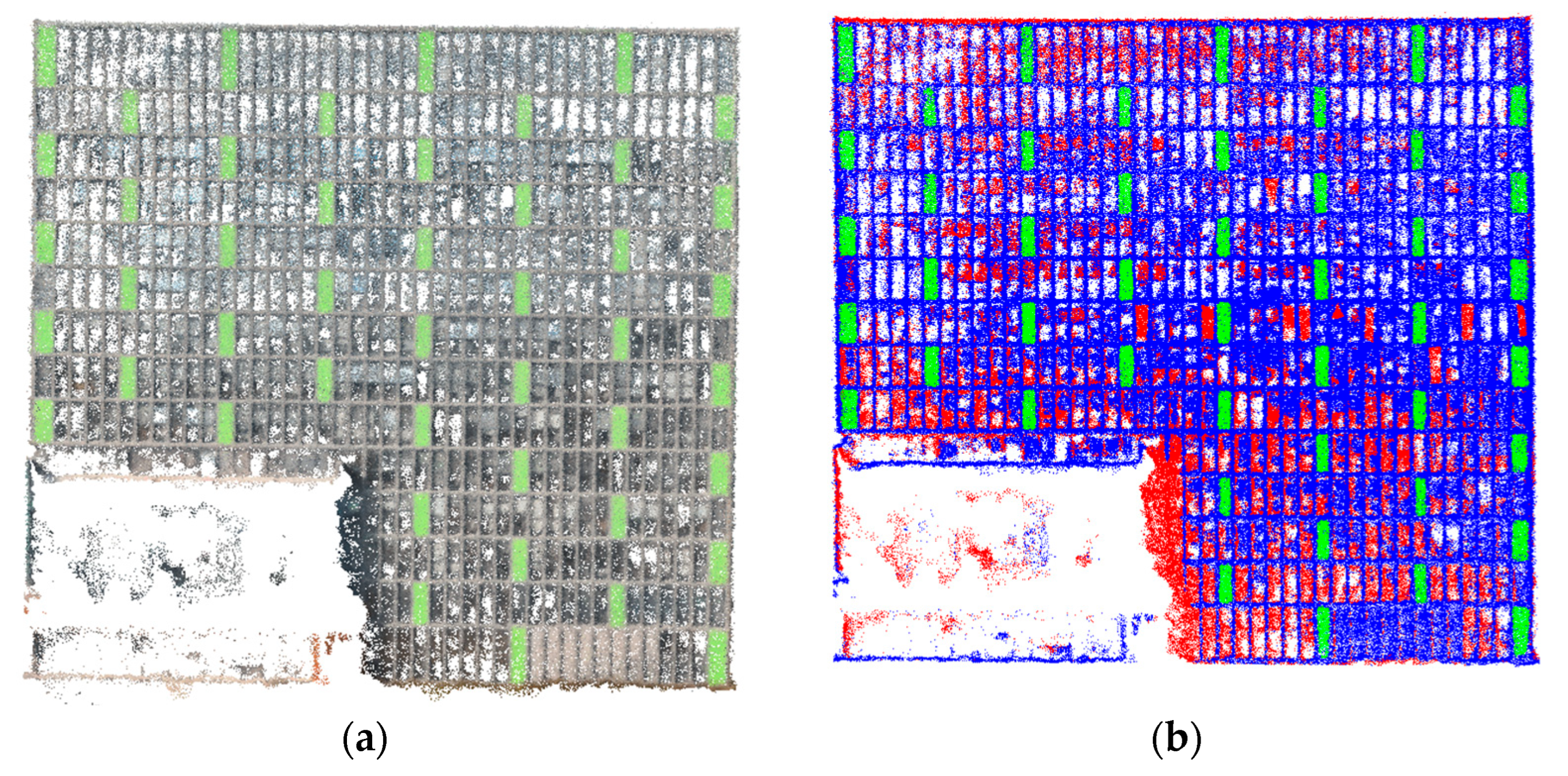
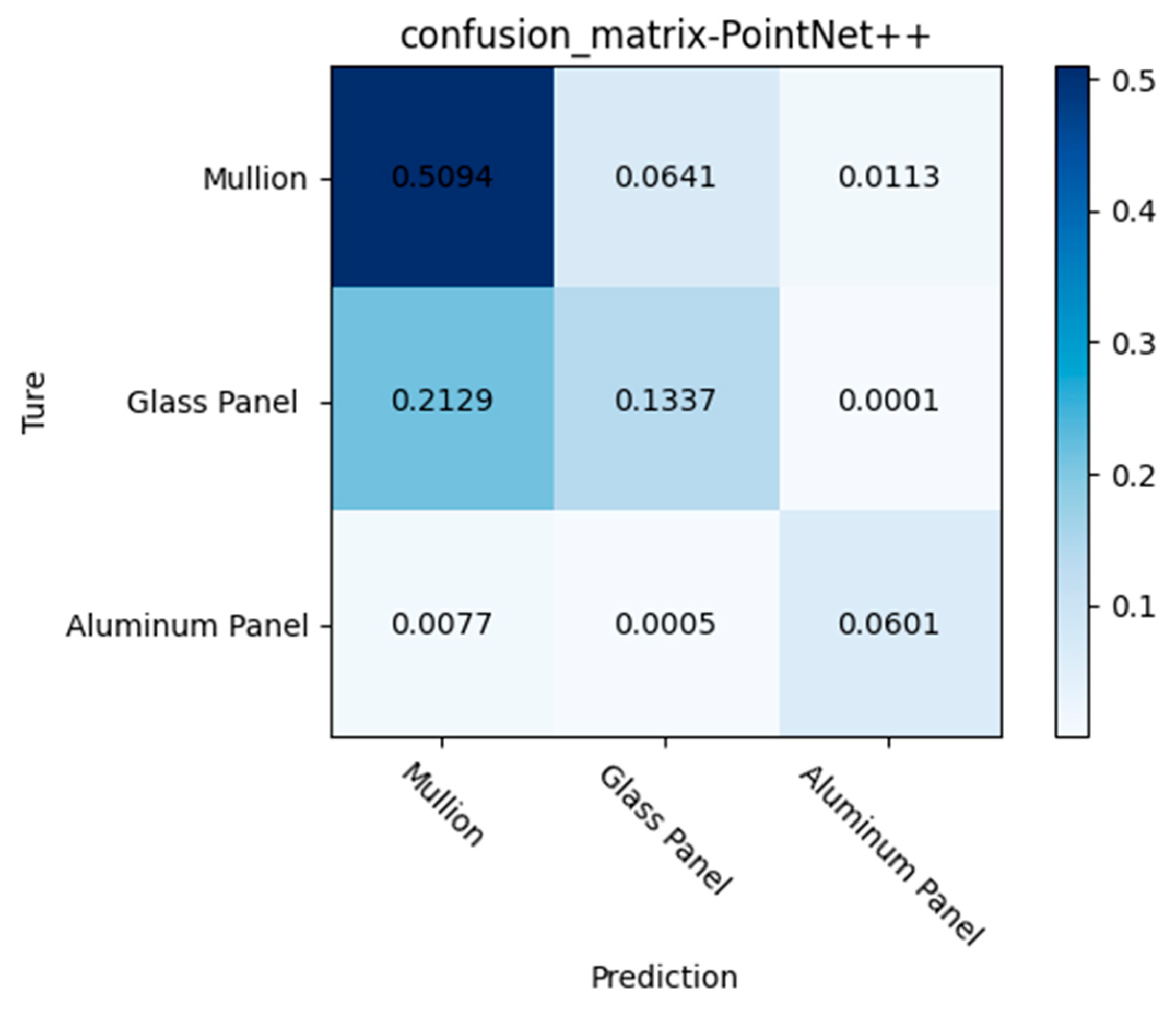
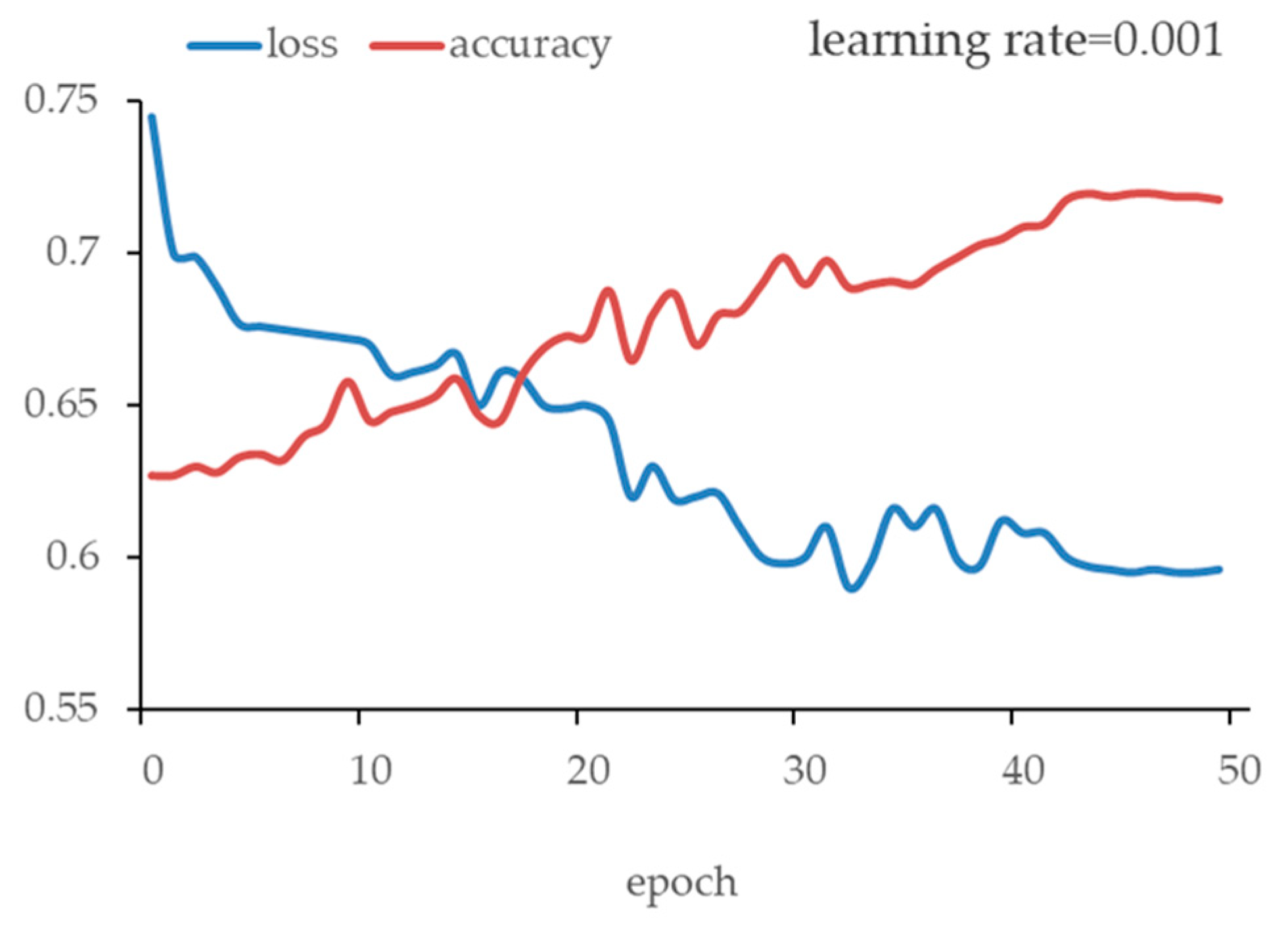

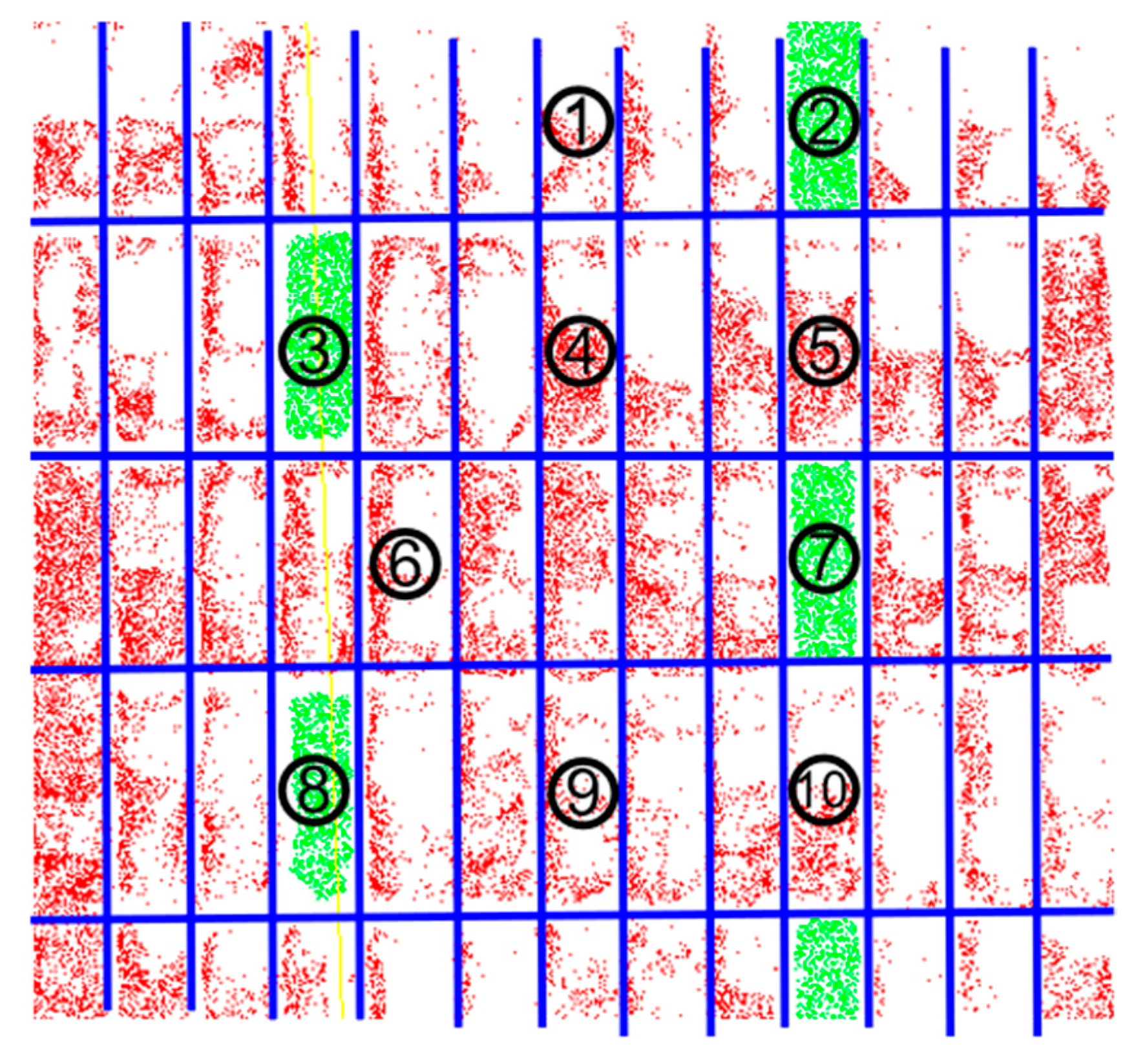
| Researcher | Method | Application Scenarios | Semantic Information |
|---|---|---|---|
| Jeon et al. [7] | NeRF, BIM | Construction site progress monitoring | Yes |
| Dong et al. [30] | SRecon-NeRF | Indoor construction progress monitoring | Yes |
| Chen et al. [10] | Voxel-Based NeRF | Reconstruction of urban scenes. | No |
| Cui et al. [29] | NeRFusion | Reconstruction of complex architectural scenes | No |
| Fan et al. [31] | Edge-NeRF | Extraction of 3D wireframe models | No |
| Lee et al. [28] | Nerfacto | Recognition of prefabricated bridge components | No |
| Ours | NeRF (Nerfacto), Semantic segmentation, BIM | Curtain walls O&M | Yes |
| The Number of Points | Mullion | Glass Panel | Aluminum Panel | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training set | 2,295,934 | 1,029,146 | 150,648 | 3,475,728 |
| Testing set | 540,282 | 320,291 | 63,148 | 923,721 |
| Dataset | OA | mAcc | Mullion IoU | Glass Panel IoU | Aluminum Panel IoU | mIoU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NeRF point cloud | 0.718 | 0.700 | 0.626 | 0.425 | 0.732 | 0.594 |
| Building Part | Dimensions | Ground-Truth | Measured by Proposed Method | Discrepancy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main Building | Height (m) | 57.60 | 57.53 | 0.07 |
| Length (m) | 62.50 | 62.42 | 0.08 | |
| Width (m) | 25.80 | 25.75 | 0.05 | |
| Curtain Wall Grid (m × m) | 5.62 × 1.43, 3.96 × 1.43, 4.95 × 1.43 | 5.70 × 1.48, 3.90 × 1.48, 5.00 × 1.48 | 0.08, 0.06, 0.05 | |
| Podium | Height (m) | 19.50 | 19.52 | 0.02 |
| Length (m) | 62.50 | 62.42 | 0.08 | |
| Width (m) | 80.50, 18.80, 34.20 | 80.43, 18.84, 34.15 | 0.07, 0.04, 0.05 | |
| Curtain Wall Grid (m × m) | 11.18 × 0.86 | 11.12 × 0.80 | 0.06 |
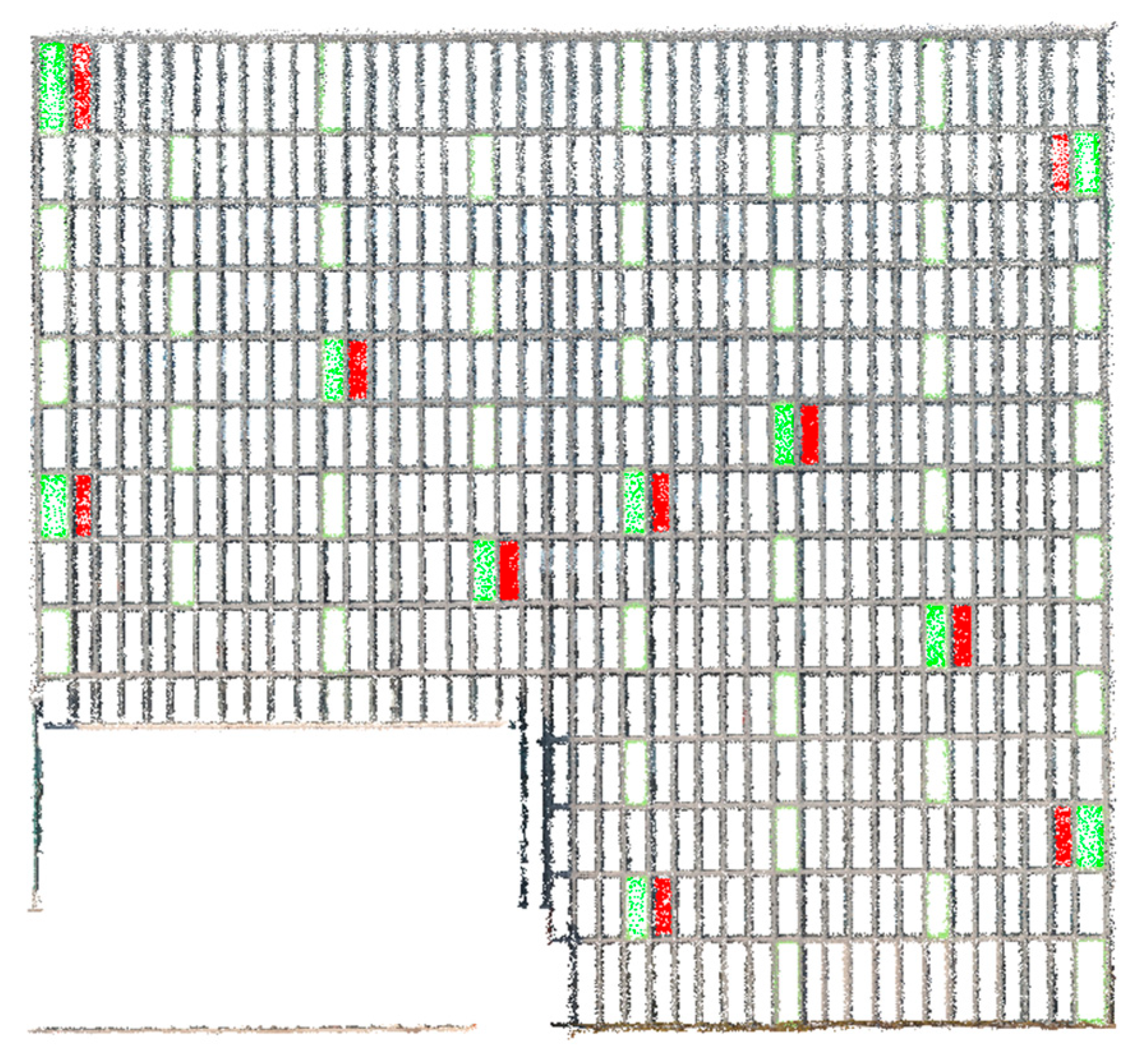
| Panel No. | Proportion of Points Classified as Glass Panel (%) | Proportion of Points Classified as Aluminum Panel (%) | Material Classification |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 23.2 | 0 | Glass |
| 2 | 0 | 93.6 | Aluminum |
| 3 | 0 | 94.1 | Aluminum |
| 4 | 52.6 | 0.4 | Glass |
| 5 | 66.5 | 0.1 | Glass |
| 6 | 30.1 | 0 | Glass |
| 7 | 0.1 | 96.5 | Aluminum |
| 8 | 0 | 88.3 | Aluminum |
| 9 | 36.8 | 0 | Glass |
| 10 | 52.6 | 0.1 | Glass |
| Material | NeRF | Photogrammetry | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| STD | RMSE | MAE | STD | RMSE | MAE | |
| Aluminium_1 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.06 |
| Aluminium_2 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.14 | 0.11 | 0.08 |
| Aluminium_3 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.17 | 0.13 | 0.10 |
| Aluminium_4 | 0.16 | 0.14 | 0.08 | 0.27 | 0.22 | 0.16 |
| Aluminium_5 | 0.20 | 0.16 | 0.12 | 0.49 | 0.36 | 0.33 |
| Aluminium_6 | 0.23 | 0.19 | 0.13 | 0.26 | 0.21 | 0.16 |
| Aluminium_7 | 0.20 | 0.16 | 0.12 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.04 |
| Aluminium_8 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.07 |
| Aluminium_9 | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0.10 | 0.08 | 0.05 |
| Aluminium_10 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.04 |
| Material | NeRF | Photogrammetry | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| STD | RMSE | MAE | STD | RMSE | MAE | |
| Glass_1 | 0.25 | 0.20 | 0.16 | 0.27 | 0.21 | 0.18 |
| Glass_2 | 0.36 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.27 | 0.21 | 0.17 |
| Glass_3 | 0.30 | 0.24 | 0.19 | 0.22 | 0.17 | 0.14 |
| Glass_4 | 0.22 | 0.18 | 0.14 | 0.18 | 0.14 | 0.11 |
| Glass_5 | 0.29 | 0.22 | 0.18 | 0.31 | 0.24 | 0.19 |
| Glass_6 | 0.29 | 0.23 | 0.18 | 0.21 | 0.16 | 0.13 |
| Glass_7 | 0.34 | 0.26 | 0.22 | 0.20 | 0.15 | 0.12 |
| Glass_8 | 0.20 | 0.17 | 0.12 | 0.20 | 0.16 | 0.12 |
| Glass_9 | 0.23 | 0.19 | 0.14 | 0.20 | 0.15 | 0.13 |
| Glass_10 | 0.29 | 0.23 | 0.19 | 0.24 | 0.18 | 0.15 |
| Dataset | Method | OA | mAcc | Mullion IoU | Glass Panel IoU | Aluminum Panel IoU | mIoU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NeRF | PointNet++ | 0.718 | 0.700 | 0.626 | 0.425 | 0.732 | 0.594 |
| Photogrammetry | PointNet++ | 0.736 | 0.745 | 0.569 | 0.585 | 0.699 | 0.617 |
| NeRF | Traditional method | 0.563 | 0.656 | 0.273 | 0.436 | 0.566 | 0.425 |
| Photogrammetry | Traditional method | 0.533 | 0.643 | 0.155 | 0.490 | 0.432 | 0.359 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Wang, Q.; Yue, H.; Nie, X. Toward Automatic 3D Model Reconstruction of Building Curtain Walls from UAV Images Based on NeRF and Deep Learning. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 3368. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17193368
Li Z, Wang Q, Yue H, Nie X. Toward Automatic 3D Model Reconstruction of Building Curtain Walls from UAV Images Based on NeRF and Deep Learning. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(19):3368. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17193368
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zeyu, Qian Wang, Hongzhe Yue, and Xiang Nie. 2025. "Toward Automatic 3D Model Reconstruction of Building Curtain Walls from UAV Images Based on NeRF and Deep Learning" Remote Sensing 17, no. 19: 3368. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17193368
APA StyleLi, Z., Wang, Q., Yue, H., & Nie, X. (2025). Toward Automatic 3D Model Reconstruction of Building Curtain Walls from UAV Images Based on NeRF and Deep Learning. Remote Sensing, 17(19), 3368. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17193368






