Highlights
What are the main findings?
- A novel drone-based person detection model, PTANet, is proposed. It integrates a global adaptive feature fusion module (GAFFM), a person segmentation auxiliary branch (PSAB) during training, and a cross-modality background mask (CMBM) during inference to progressively focus on person targets while suppressing background clutter.
- The proposed PTANet consistently outperforms state-of-the-art cross-modality target detection methods on three person detection datasets and demonstrates strong potential for real-time on-board deployment.
What is the implication of the main finding?
- The proposed PTANet addresses the challenge of feature extraction caused by small target sizes and diverse poses of persons in UAV remote sensing images through an effective architecture design with minimal additional parameters and computational cost.
- The lightweight architecture and high detection accuracy greatly enhance the potential of PTANet for real-world person detection in UAV scenarios.
Abstract
Drone-based target detection using visible and thermal (RGB-T) images is critical in disaster rescue, intelligent transportation, and wildlife monitoring. However, persons typically occupy fewer pixels and exhibit more varied postures than vehicles or large animals, making them difficult to detect in unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) remote sensing images with complex backgrounds. We propose a novel progressive target-aware network (PTANet) for person detection using RGB-T images. A global adaptive feature fusion module (GAFFM) is designed to fuse the texture and thermal features of persons. A progressive focusing strategy is used. Specifically, we incorporate a person segmentation auxiliary branch (PSAB) during training to enhance target discrimination, while a cross-modality background mask (CMBM) is applied in the inference phase to suppress irrelevant background regions. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed PTANet achieves high accuracy and generalization performance, reaching 79.5%, 47.8%, and 97.3% mean average precision (mAP)@50 on three drone-based person detection benchmarks (VTUAV-det, RGBTDronePerson, and VTSaR), with only 4.72 M parameters. PTANet deployed on an embedded edge device with TensorRT acceleration and quantization achieves an inference speed of 11.177 ms (640 × 640 pixels), indicating its promising potential for real-time onboard person detection. The source code is publicly available on GitHub.
1. Introduction
Significant advances have been made in target detection in drone-based remote sensing imagery, and a wide range of practical applications have been developed in recent years, driven by the commercialization of consumer-grade unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and the rapid growth of the low-altitude economy [1]. Drone-based remote sensing imagery has advantages over satellite imagery, including lower cost, higher image resolution, and the ability to acquire imagery below clouds [2], making it feasible to detect small targets like vehicles [3,4] and persons [5]. The integration of visible and thermal (RGB-T) UAV imagery improves detection accuracy and broadens the application range. This cross-modality approach has shown substantial applicability in disaster rescue [6], intelligent transportation [7], and wildlife monitoring [8].
However, persons in UAV imagery occupy significantly smaller proportions of the scene than vehicles and large wild animals (e.g., elephants). The small size of persons poses challenges for feature extraction by detection models, resulting in more interference from complex backgrounds. In addition, since people are social and move extensively, their postures exhibit significant variability. Persons with diverse postures, such as walking, riding bicycles, and sitting, may occur in a drone-based image. Different postures lead to substantial variations in texture and shape features, which hinder effective feature extraction and consequently degrade detection performance.
With the advancement of UAV imaging technology, the improved resolution has made drone-based person detection using RGB-T images an emerging research focus. In 2023, Zhang et al. [5] developed the first drone-based person detection dataset for RGB-T images, RGBTDronePerson, and proposed a label assignment based on the Wasserstein distance. This method provides high-quality labels for pre-training and the final detection heads. It utilizes the pre-training results as prior knowledge to inform the fusion of RGB-T images, enabling the effective detection of persons in remote sensing imagery. VTSaRNet [9] achieves cross-modality feature fusion by concatenating the features of RGB-T aerial images and inputting them into a self-attention mechanism [10]. It employs Copy–Paste [11] and Mosaic [12] to increase the number of person instances and diversify image scenes, increasing detection accuracy. However, these two approaches do not fully exploit the unique characteristics of persons in UAV remote sensing imagery, focusing more on improving detection performance through label assignment and data augmentation strategies. Moreover, both methods require many model parameters and have high computational costs, limiting their applicability for real-time person detection on UAV edge devices.
This paper proposes a progressive target-aware network (PTANet) for person detection in UAV imagery. It addresses the challenges of feature extraction caused by the small size and variable postures of persons in UAV imagery and enables real-time detection using edge devices on a UAV. This method uses a progressive focusing strategy and incorporates a global adaptive feature fusion module (GAFFM), which improves the fusion of color and texture features and thermal features. A person segmentation auxiliary branch (PSAB) is utilized during training. It contains a segmentation loss function to optimize model parameters, enhancing the model’s attention to persons. A cross-modality background mask (CMBM) is used in the inference phase to suppress background information in the visible features. The PSAB and CMBM guide the model to focus on persons during training and inference, respectively, with minimal additional parameters and computational cost. The main contributions are as follows:
- We propose PTANet, a novel drone-based remote sensing model that employs a progressive target-aware strategy for person detection. A self-attention mechanism ensures that PTANet performs global adaptive fusion of RGB-T features across modalities. Moreover, it progressively increases target awareness during the training and inference stages with a minimal increase in parameters and computational cost using target perception and background suppression. PTANet enables robust discrimination of small, variably posed person targets in UAV imagery.
- We propose the GAFFM, which utilizes features from the RGB-T modalities and their element-wise summation as the query (Q), key (K), and value (V) inputs of the self-attention mechanism. The GAFFM enables the global and adaptive fusion of color and texture features and thermal features.
- We propose a progressive target-aware modeling strategy that improves the detection of persons and suppresses background interference. The PSAB is utilized during training, leveraging binary masks derived from ground-truth bounding boxes as supervision to ensure the model focuses on the persons. The CMBM is utilized in the inference phase. It focuses on the salient features of persons in thermal images and uses a band-wise index. The CMBM suppresses background noise in the visible bands, reducing false positives during detection.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 reviews recent advances in cross-modality target detection using RGB-T images and small target detection in drone-based imagery. Section 3 describes the datasets, experimental settings, and evaluation metrics, and presents the framework of the proposed PTANet and its key components. Section 4 presents performance comparisons and ablation experiments. Section 5 discusses the robustness and effectiveness of the three modules in the proposed PTANet.
2. Related Work
2.1. RGB-T Image-Based Target Detection
RGB-T images have complementary advantages under different lighting conditions, such as daytime and nighttime. Therefore, researchers have performed cross-modality fusion of RGB-T images to expand the applicability of object detection across various scenes. A straightforward and commonly used fusion strategy is to add or concatenate the two types of feature maps [13,14]. However, these methods merely aggregate or stack features from both modalities, without analyzing their strengths or interactions.
References [15,16,17,18,19] proposed illumination-aware weighted fusion strategies. An illumination perception module and a gating function were designed to assign weights adaptively to the RGB-T modalities under varying lighting conditions to improve the utilization of cross-modality information from both sources.
The difference modality features and common modality features were introduced in [20,21] to exploit the complementarity between RGB-T modalities. The difference modality features were obtained by subtracting the feature maps extracted from RGB-T branches, representing modality-specific characteristics. In contrast, the common modality features were derived by adding the same-stage feature maps from both modalities, capturing shared characteristics. This strategy enabled the model to utilize the unique and shared information of RGB-T modalities.
Some researchers have explored cross-modality fusion by incorporating self-attention mechanisms. Fang et al. [22] proposed the cross-modality fusion transformer (CFT), which concatenates feature maps from RGB-T modalities and inputs them into a transformer-based self-attention module [10]. The CFT utilizes the global modeling capability of the self-attention mechanism to enable the model to fuse the two modalities. Several studies [23,24] have investigated self-attention or cross-attention mechanisms [25] to improve the fusion of RGB-T features.
Recently, researchers have explored cross-modality target detection using RGB-T images from new perspectives. Wu et al. [3] proposed a cross-modality vehicle index based on the spectral properties of vehicles in RGB-T images. Some studies [26,27] have employed the Mamba model for cross-modality fusion of RGB-T images. -Net [28] extracted fine-grained details from visible images and broader patterns from thermal images in the frequency domain to fuse information from both modalities.
However, current research on target detection using drone-based RGB-T images has primarily focused on relatively large rigid objects, such as vehicles, while person detection has mostly relied on vehicle-mounted or surveillance images. Therefore, exploring real-time person detection using drone-based RGB-T images is both necessary and meaningful.
2.2. Small Target Detection in UAV Remote Sensing Images
Small targets like persons and vehicles occupy a small proportion of pixels in drone-based imagery, posing significant challenges for detection models. Previous studies have addressed these challenges from various perspectives, including designing specialized loss functions, enhancing small target features, improving model architectures, and developing custom datasets.
In the method proposed by Wang et al. [29], bounding boxes are represented as 2D Gaussian distributions, and the normalized Wasserstein distance is employed as a loss function to quantify the difference between predictions and the ground truth. Chen et al. [30] developed a novel loss function called RSDS, which assigns sample weights, ensures overlap between predicted and ground-truth boxes, and improves dense target detection.
In addition, researchers have investigated methods to improve feature representation capabilities of small targets in remote sensing imagery. Yang et al. [31] proposed a plug-and-play strip convolution module called PConv, which employs four directional strip convolutions for feature extraction of small targets in thermal infrared images. This design expands the receptive field and determines the Gaussian distribution of small target pixels. To enhance the representation of small targets in remote sensing images, FFCA-YOLO [32] adopts several modules, including FEM for feature enhancement, FFM for feature fusion, and SCAM for incorporating spatial context. Liu et al. [33] enhanced the detection performance for small objects in UAV-based remote sensing images by extracting scale-invariant features and introducing adversarial learning.
Some researchers have designed specialized network architectures for detection of small targets in remote sensing imagery. In the transformer prediction head YOLO (TPH-YOLOv5) method [34], a small target detection head is added to the shallow layers of the feature maps to reduce spatial information loss for small targets in deeper layers. To better detect small targets, Yu et al. [35] designed a novel adaptive region proposal network that progressively propagates attention to suppress most irrelevant background regions. RemDet [36] effectively addresses the challenges of detecting small and densely distributed objects in UAV-based remote sensing images by incorporating the GatedFFN (Gated Feed-Forward Network) module, the CED (Context-Enhanced Downsample) module, and the ChannelC2f module, while also achieving fast real-time inference speed.
Several datasets have been developed to advance research in detection of small targets in remote sensing imagery. These include visible image [37,38,39], thermal image [8], and cross-modality (RGB-T) image [5,7,40,41] datasets. Yao et al. [42] proposed a synthetic multimodal UAV remote sensing dataset. The dataset comprises six modalities, including images and text, and is suitable for a variety of downstream tasks such as object detection, object segmentation, and image retrieval.
While most existing studies on drone-based small object detection concentrate on handling multi-scale targets, they often neglect the difficulties caused by pose variations in feature extraction. Our proposed PTANet explicitly tackles this problem and provides an effective solution.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Datasets
3.1.1. VTUAV-det
The VTUAV-det dataset was constructed by extracting 1 frame for every 50 frames from the VTUAV dataset [43]. It was captured by a DJI Matrice 300 RTK with a Zenmuse H20T camera made in China. The thermal images had a spectral range of 8–14 µm, and the UAV operated at altitudes ranging from 5 to 20 m. This dataset includes 11,392 training image pairs and 5378 testing pairs. It includes scenes captured during daytime and nighttime and under various weather conditions and viewing angles (nadir and oblique). Moreover, the person targets in this dataset exhibit diverse poses, such as walking, riding, and sitting. To improve training efficiency, the RGB-T images originally sized at 1920 × 1080 were downsampled to 640 × 360.
3.1.2. RGBTDronePerson
RGBTDronePerson [5] was the first large-scale drone-based visible–thermal dataset designed for person detection. The data were captured at flight altitudes of 50 to 80 m and imaging angles from 45° to 60° using a DJI Mavic 2 Enterprise Advanced made in China. It includes 4900 training and 1225 testing image pairs, all at a resolution of 640 × 512. It covers daytime and nighttime scenes in different seasons in Wuhan, China. Three categories of person targets are annotated in the dataset: person, rider, and crowd. Moreover, more than 90% of the person targets in this dataset have a size smaller than 32 × 32 pixels.
3.1.3. VTSaR
The VTSaR dataset was developed by Zhang et al. [6]. It was collected using a custom-built UAV platform equipped with RGB-T cameras. The dataset contains 4800 training image pairs and 533 testing pairs. The images have a resolution of 640 × 480 pixels. The image pairs cover diverse environments, such as urban areas, oceans, coastlines, and forests, and were captured under various lighting conditions, flight altitudes, viewing angles, and environmental settings. The dataset includes person targets with diverse postures, such as standing and walking. Furthermore, RGB-T images are strictly aligned to ensure pixel-level registration.
3.2. Implementation Details and Evaluation Metrics
3.2.1. Implementation Details
The proposed PTANet is based on the YOLOv8n framework [44], and all experiments were conducted on four NVIDIA RTX A5000 GPUs made in USA. PTANet was trained for 400 epochs on the VTUAV-det, RGBTDronePerson, and VTSaR datasets, with a batch size of 64. The initial learning rate was 0.005, and a warm-up period of 3 epochs was used. We used stochastic gradient descent (SGD) [45] as the optimizer. The confidence thresholds for suppressing low-confidence background bounding boxes during inference were 0.25, 0.25, and 0.03 for VTUAV-det, RGBTDronePerson, and VTSaR, respectively. The intersection over union (IoU) thresholds for non-maximum suppression (NMS) [46] were 0.5, 0.3, and 0.45, respectively. We introduced a new hyperparameter, , to adjust the loss weight for PSAB and set its default value to 1.0. All other hyperparameters had the default settings of YOLOv8n.
3.2.2. Evaluation Metrics
The mean average precision at an IoU threshold of 0.5 (mAP50) was used to evaluate model detection accuracy. Model size and computational complexity were evaluated based on parameter count (Params) and floating-point operations (GFLOPs). The inference time for a single image on the NVIDIA Jetson Orin NX was used as an indicator of onboard performance to assess the deployment efficiency of the model on resource-constrained edge platforms such as UAVs.
The Grad-CAM technique [47] was employed in the ablation study to visualize the prediction results using heatmaps.
3.3. Overall Framework
The detection strategy of the proposed PTANet for drone-based imagery is illustrated in Figure 1. The intermediate target heatmaps at different stages depict the model’s focus on the persons highlighted by the yellow rectangles while suppressing the background clutter in the red rectangles. It is achieved by color, texture, and thermal feature fusion, target-aware enhancement, and background suppression, ensuring the accurate detection of persons in UAV images.
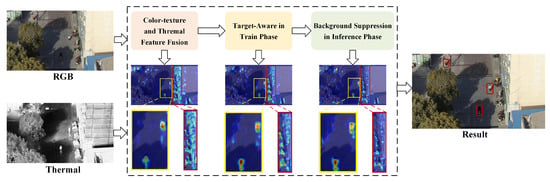
Figure 1.
Detection strategy of the proposed PTANet. The input consists of paired RGB-T images, and the output is the detection results for the visible image. The heatmaps illustrate the model’s focus at different stages. Yellow bounding boxes indicate persons, while red bounding boxes denote background clutter.
The overall structure of PTANet is depicted in Figure 2. The RGB-T images are independently processed using dual-stream backbone networks to extract modality-specific features. The GAFFM employs a self-attention mechanism to fuse globally and adaptively the color and texture features and the thermal features. A progressive target-aware strategy ensures the focus on the target and background suppression. The PSAB is incorporated into the neck during the training stage. Binary mask ground truths are used to supervise the segmentation and ensure the model concentrates on regions with persons. The CMBM is utilized during the inference stage. It is generated using an exponential index and adaptive thresholding based on the thermal image and the red channel of the visible image. This mask suppresses complex background clutter in visible images prior to fusion. Notably, the PSAB and CMBM modules have relatively few additional parameters, making PTANet well-suited for deployment on UAVs and other edge devices with limited computational resources.
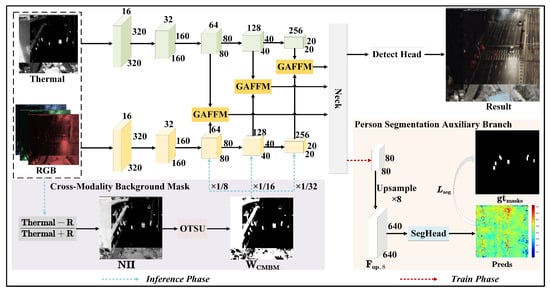
Figure 2.
Structure of PTANet. The red dashed arrows denote the person segmentation auxiliary branch, which is implemented during the training phase. The blue dashed arrows represent the cross-modality background mask, which is only used during the inference phase. GAFFM indicates the proposed global adaptive feature fusion module.
3.4. Global Adaptive Feature Fusion Module
As illustrated in Figure 3, existing transformer-based methods for fusing RGB-T features [9,22,23] typically concatenate the features from both modalities and use vector encoding and positional embedding to generate the Q, K, and V vectors for the self-attention mechanism. In contrast to these conventional approaches, the proposed GAFFM adopts a modality injection strategy: the query vector Q is generated from the visible features, while the key vector K is derived from the thermal features. This design maximizes the preservation of color–texture information from the visible modality and thermal radiation characteristics from the thermal modality, thereby enabling more comprehensive representation of both common and specific features when computing the similarity between Q and K. Moreover, in the self-attention computation, the value vector V serves as a reference baseline. Therefore, we consider it appropriate to generate the value vector by summing the visible and thermal features. Figure 4 depicts the structure of the GAFFM module.
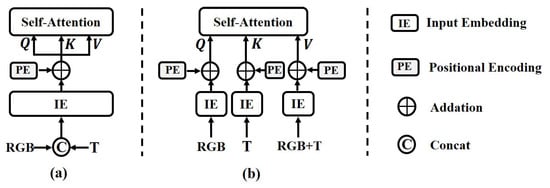
Figure 3.
Comparison of (a) traditional transformer-based fusion methods and (b) our method.
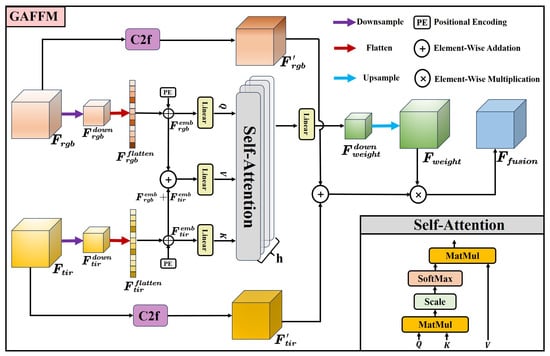
Figure 4.
Structure of the GAFFM. The inputs are visible features and thermal features , and the output is their fused feature obtained via the GAFFM module.
Firstly, the modality-specific features extracted by the dual-branch backbone from RGB-T images are downsampled to a spatial resolution of (B, C, 8, 8) to reduce the computational burden.
Subsequently, the downsampled feature maps are flattened and then reshaped by transposing their final two dimensions to prepare for self-attention computation.
Learnable positional embeddings are added to the flattened feature sequences to preserve the two-dimensional spatial information of targets in the image.
Next, the encoded feature sequences are linearly projected to generate the Q, K, and V vectors required for computing cross-modal global attention weights.
A multi-head attention mechanism is employed during the computation of cross-modal global attention weights, where h denotes the number of attention heads. This study used h = 8.
The cross-modal global attention weights of the Q, K, and V vectors are computed as follows.
The global adaptive fusion attention weights are obtained by upsampling the linearly projected attention weights to the same spatial resolution as the original input feature maps of both modalities. The final fused feature is obtained by performing element-wise multiplication between and the sum of the modality-specific features processed by the C2f module.
where ⊙ denotes element-wise multiplication along the corresponding channels and C2f refers to a feature extraction module used in the backbone network of YOLOv8.
Algorithm 1 outlines the computational process of the GAFFM module for cross-modality global adaptive feature fusion.
| Algorithm 1: Global adaptive feature fusion module. |
Input: RGB features , TIR features . 5. Computing the cross-modal global attention weights using Equation (11). 6. Upsampling , and computing the final fused features using Equation (12). Output: The fused features produced by the GAFFM. |
3.5. Person Segmentation Auxiliary Branch
Figure 5 shows the size distribution of ground-truth bounding boxes for persons in three UAV remote sensing datasets: VTUAV-det [5], RGBTDronePerson [5], and VTSaR [6]. We followed the MS-COCO dataset [48] definition of small targets. Targets with a width and height of less than 32 pixels were considered small. The proportions of small person targets in VTUAV-det, RGBTDronePerson, and VTSaR were 53.87%, 94.06%, and 86.03%, respectively. The high percentage of small targets significantly limits the discriminative features the model can learn, posing considerable challenges for detecting small targets in UAV imagery.
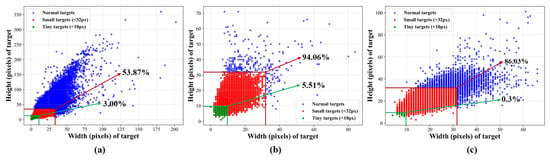
Figure 5.
Statistics of person sizes in three drone-based datasets: (a) VTUAV-det, (b) RGBTDronePerson, and (c) VTSaR datasets. Green dots indicate persons smaller than 10 × 10 pixels, red dots represent persons larger than 10 × 10 but smaller than 32 × 32 pixels, and blue dots correspond to persons larger than 32 × 32 pixels.
Therefore, we used a progressive target-aware approach and introduced the PSAB during the training phase. It optimizes the model parameters by calculating the loss between the predicted segmentation results and the ground-truth binary masks of persons. This strategy enables the trained model to focus on persons in UAV imagery. Figure 6 depicts the structure of the PSAB.
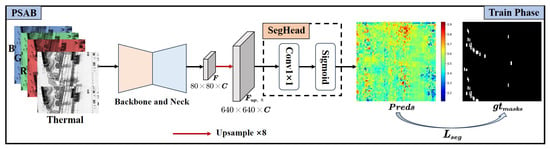
Figure 6.
Structure of the PSAB. The red arrow indicates the upsampling operation.
Inspired by several classic lightweight semantic segmentation networks [49,50], we used an upsampling operation for deep feature maps in the decoder. The 80 × 80 feature map from the model’s neck layer was upsampled eight times using nearest-neighbor interpolation, resulting in minimal computational overhead while preserving the semantic information of the deep feature map. The height H and width W of the upsampled feature map are 640, which matches the size of the model’s input image. This process is expressed in Equation (13):
A lightweight segmentation head SegHead is designed at the detection stage to perform segmentation prediction on the upsampled feature map . The proposed segmentation head SegHead consists of a 1 × 1 convolution followed by a Sigmoid activation function to minimize parameters and computational cost. The segmentation head SegHead and the segmentation prediction result Preds are defined in Equations (14) and (15), respectively:
The 1 × 1 convolution receives the same number of input channels as and outputs a feature map with channels equal to the number of target categories (i.e., “person”, “rider”, and “crowd” in the RGBTDronePerson dataset). Thus, one segmentation map is generated for each category. The Sigmoid function, which is commonly used in segmentation tasks, is employed as the activation function to constrain the pixel values in the predicted segmentation maps to the range of (0, 1), making it suitable for loss computation against binary mask ground truths.
The loss function for the PSAB includes the binary cross-entropy (BCE) loss [51] and the Dice loss [52]. The ground-truth binary mask is generated by assigning a value of 1 to the pixels inside the annotated bounding boxes of the person targets and 0 elsewhere (Equation (16)):
For single-class targets, the ground-truth label is represented by a single-channel binary mask, while for multi-class scenarios, a multi-channel binary mask is used, where each channel corresponds to a specific target category. The original images and the binary mask are shown in Figure 7.

Figure 7.
Original image (a) and target binary mask (b).
Finally, the overall loss function of the proposed PTANet can be formulated as follows:
where and represent the bounding box regression loss and classification loss, respectively. = denotes the loss from the PSAB. The terms , , are the weighting coefficients for the loss components.
3.6. Cross-Modality Background Mask
The CMBM is applied during the inference phase to improve the model’s focus on small person targets in UAV imagery and to mitigate interference from complex background features from the visible branch. The CMBM utilizes prior knowledge regarding the thermal features of persons and uses a spectral index. It suppresses background features in the visible branch features, minimizing noisy background information from visible images during fusion. Figure 8 depicts the structure of the CMBM.
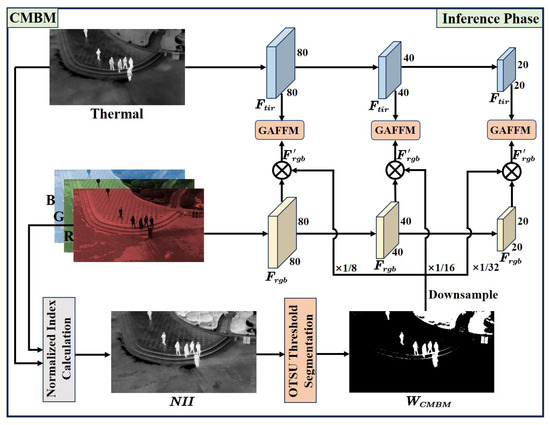
Figure 8.
Structure of the CMBM. The thermal image and the red band of the visible image are used as input to generate , which is downsampled to the spatial resolution of the visible branch feature map and element-wise multiplied with it to produce the final visible branch feature .
During model inference, the single-band thermal image and the red channel of the visible image are used to compute an index using an exponential function (Figure 8), resulting in a single-channel normalized grayscale image, referred to as the normalized index image (NII) (Equation (18)):
Automatic thresholding of the NII using the OTSU method [53] is used to generate the (Equation (19)):
Pixels with values above the threshold are assigned a value of 1 in the binary mask, and those below the threshold are assigned 0.
Subsequently, the is downsampled by factors of 8, 16, and 32 to match the resolutions of the final three backbone stages. The downsampled is element-wise multiplied with the visible branch feature maps during the inference phase to create the final visible branch features (Equation (20)):
The CMBM suppresses background clutter in the features extracted by the visible branch during the inference phase, further enhancing the model’s focus on small persons based on the optimization provided by the GAFFM and PSAB during the training phase.
4. Results
The proposed PTANet was extensively evaluated against advanced single-modality and visible–thermal cross-modality fusion-based target detection models on three UAV-based remote sensing datasets to validate its effectiveness. The single-modality detectors include the one-stage models YOLOv8n [44], YOLOv5n [54], and SSD512 [55] and the two-stage model Faster-RCNN [56]. We compared against several advanced cross-modality fusion-based methods, including TINet [17], which utilizes illumination-aware and differential/common modality features; SuperYOLO* (without the super-resolution branch) [57] and TFDet [58], which utilize attention-based fusion strategies; CFT [22], a transformer-based model; QFDet [5], which contains label quality-aware mechanisms; QFDet’ [5], which is a variant of QFDet, utilizing P2-P6 feature maps for detection; and VTSaRNet [9], which incorporates person-specific data augmentation.
4.1. On VTUAV-det
Table 1 presents the quantitative evaluation results for the proposed PTANet and other single-modality and cross-modality visible–thermal target detection models on the VTUAV-det dataset. The proposed PTANet achieved the best detection performance with an mAP50 of 79.5%, outperforming the second-best method, SuperYOLO*, by a margin of 3.05%.

Table 1.
Performance comparison of different methods on VTUAV-det dataset. Bold values indicate results of the proposed method.
For single-modality models, the detection results based on thermal images were generally superior to those based on visible images. This finding confirms that small person targets are more distinctive in thermal imagery due to the relatively simpler background. Among the single-modality methods, YOLOv8n achieved the highest detection accuracy of 73.5% for thermal images. However, this performance was 6.0% lower than that of the proposed PTANet. This result demonstrates the necessity and effectiveness of the proposed GAFFM for cross-modality feature fusion.
Among the cross-modality fusion methods based on RGB-T images, the CFT model, which has a transformer architecture for feature fusion, achieved a detection accuracy of 76%. However, it had the highest parameter count and computational cost of all methods. In contrast, the proposed PTANet achieved a higher detection accuracy of 79.5%, with only 4.72 million parameters and 29.2 GFLOPs. This result demonstrates the effectiveness of the proposed PSAB and CMBM, which were designed to detect small person targets in drone-based imagery. These two modules enable the model to focus on small person targets during training and inference, improving the detection rate while reducing false positives.
As illustrated in Figure 9, the first column includes challenging RGB-T images from the VTUAV-det dataset annotated ground-truth boxes of person targets. The following columns present predictions by CFT, SuperYOLO*, and PTANet, respectively, offering a qualitative comparison of these cross-modality fusion-based detectors.

Figure 9.
Visualization results of different models on VTUAV-det. (a) Ground truth; (b) CFT; (c) SuperYOLO*; and (d) PTANet. Ground-truth targets are shown in red, undetected targets in yellow, and false alarms in blue. Scene types are labeled as ST (small targets), WI (low-light conditions), and CB (cluttered backgrounds).
The proposed PTANet achieved higher accuracy than CFT and SuperYOLO* in detecting persons that appear small in UAV imagery. The targets include people distant from the UAV camera and small individuals such as children. The results verify that the PSAB module effectively guides the network to focus on small person targets in drone-based imagery during training.
CFT and SuperYOLO* mistook street lamps in thermal images as persons in low-light conditions and nighttime scenes. In the second row of Figure 9, PTANet detected persons in low-illumination scenarios while significantly reducing false positives. This result demonstrates that the proposed GAFFM improved the fusion of features from RGB-T modalities, enhancing detection robustness in challenging lighting conditions.
From the third and fourth rows in Figure 9, it can be observed that low vegetation along roadsides or persons holding umbrellas in daytime visible images with complex backgrounds often resulted in false positives and missed detections by other models. In contrast, PTANet did not exhibit these issues due to the CMBM, which suppresses complex background information in the visible modality.
4.2. On RGBTDronePerson
Table 2 presents the quantitative evaluation results of the proposed PTANet and single-modality and visible–thermal cross-modality target detection models on the RGBTDronePerson dataset.

Table 2.
Performance comparison of different methods on RGBTDronePerson dataset. Bold values indicate results of the proposed method.
The detection accuracy of PTANet was lower on the RGBTDronePerson dataset than on the VTUAV-det dataset, which can be attributed to two factors. First, as illustrated in Figure 5, 94.06% of person targets in the RGBTDronePerson dataset have widths and heights smaller than 32 pixels. Furthermore, 5.51% of the targets have both dimensions smaller than 10 pixels. In contrast, the proportions of very small targets in the VTUAV-det and VTSaR datasets are only 3.00% and 0.3%, respectively. Since PTANet utilizes three detection heads corresponding to feature maps with 1/8, 1/16, and 1/32 of the input resolution, a target of 10 × 10 pixels in the original image occupies less than one pixel on the deepest feature map, making it extremely difficult to detect. Consequently, the recall rate for these very small person targets is significantly lower. In addition, as shown in Figure 10, the VTUAV-det and VTSaR datasets provide pre-aligned visible and thermal images, so the annotations of the same person target exhibit minimal positional deviation between the two modalities. In contrast, because the visible and thermal images in the RGBTDronePerson dataset had different resolutions, the visible images were cropped to match the thermal ones, resulting in a large spatial misalignment between the two modalities, particularly for small person targets. Furthermore, all annotations in the dataset are based on the thermal images, causing many ground-truth bounding boxes to be misaligned with the targets in the visible images. Therefore, we obtained significantly lower detection accuracy when using the visible modality, as reflected in Table 2.
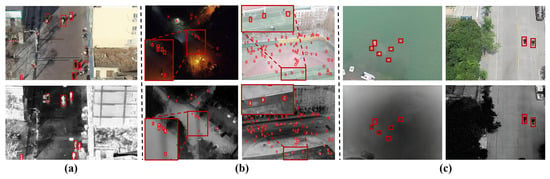
Figure 10.
Annotated visible and thermal person targets on different datasets. (a) VTUAV-det. (b) RGBDronePerson. (c) VTSaR. Red squares indicate person targets.
In contrast, when the thermal modality was used for detection, YOLOv5n and SSD achieved detection accuracies of 45.9% and 42.3%, respectively, which were higher than those of some cross-modality fusion-based target detection methods. Among the cross-modality methods, the proposed PTANet achieved the highest mAP50 of 47.8%, outperforming the second-best method, QFDet’, by 1.08%. Notably, PTANet achieved this with approximately one-tenth of the parameters and a computational cost comparable to QFDet’.
Unlike TINet and CFT, which are primarily designed for person detection in vehicle-mounted or surveillance imagery, the proposed PTANet was developed for detecting small person targets in drone-based images. The GAFFM can capture global features in both modalities and adaptively fuses the color and texture features and the thermal features. In addition, the progressive target-aware strategy uses the PSAB during training and the CMBM during inference to focus on person targets and reduce background interference. As a result, PTANet outperformed other cross-modal detection methods on the RGBTDronePerson dataset, whose images have very small person targets.
As illustrated in Figure 11, the first column includes challenging RGB-T images from the RGBTDronePerson dataset annotated ground-truth boxes of person targets. The following columns present predictions by the YOLOv5n model on thermal images, the QFDet’ model, and PTANet, respectively, offering a qualitative comparison of these single- and cross-modality fusion-based detectors.
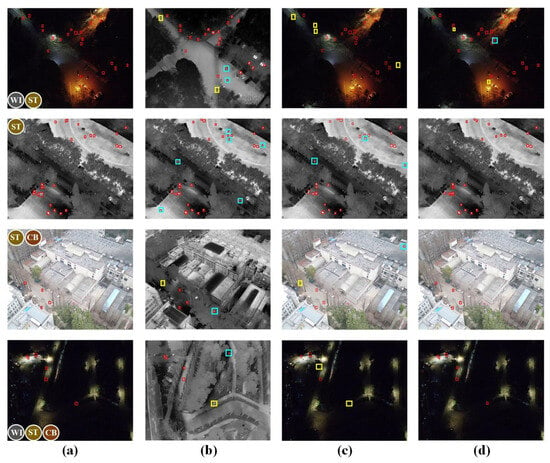
Figure 11.
Visualization results of different models on RGBTDronePerson. (a) Ground truth; (b) YOLOv5n (thermal); (c) QFDet’; and (d) PTANet. Ground-truth targets are shown in red, undetected targets in yellow, and false alarms in blue. Scene types are labeled as ST (small targets), WI (low-light conditions), and CB (cluttered backgrounds).
As shown in the second column of Figure 11, since the YOLOv5n model utilizes only the thermal modality for detection, it lacks the texture and color information provided by the visible spectrum, resulting in a large number of false positives. The third column shows the results of the QFDet’ model. It mistook a concrete cone on the rooftop as a person target during the daytime and failed to detect person targets partially occluded by tree foliage. QFDet’ also failed to detect person targets in low-illumination areas, such as roads without street lights. In contrast, the proposed PTANet achieved superior detection performance, benefiting from its specially designed modules that address challenges in drone-based person detection: GAFFM, PSAB, and CMBM.
4.3. On VTSaR
As shown in Table 3, PTANet achieved a superior mAP50 of 97.3% on the VTSaR dataset, surpassing all single- and cross-modality models. It outperformed the second-best method, SuperYOLO*, by 0.31% on this dataset.

Table 3.
Performance comparison of different methods on VTSaR dataset. Bold values indicate results of the proposed method.
Among single-modality images, the YOLOv8n model achieved the highest detection accuracy of 96.2% on the visible modality, which was 1.1% lower than the final detection result of the proposed PTANet. This finding highlights the necessity and effectiveness of the GAFFM. Since the targets in both modalities of the VTSaR dataset are well aligned and annotated, most multimodal detection methods based on feature fusion achieved similar detection accuracies. However, the proposed PTANet uses a progressive target-focusing strategy by the PSAB during training and the CMBM during inference. These components progressively enhance the model’s focus on small person targets in drone-based imagery and ensure background suppression. As a result, PTANet exhibited superior detection accuracy while significantly reducing the parameter count and computational cost compared to other fusion-based approaches.
As illustrated in Figure 12, the first column includes challenging RGB-T images from the VTSaR dataset annotated ground-truth boxes of person targets. The following columns present predictions by TFDet, SuperYOLO*, and PTANet, respectively, offering a qualitative comparison of these cross-modality fusion-based detectors.
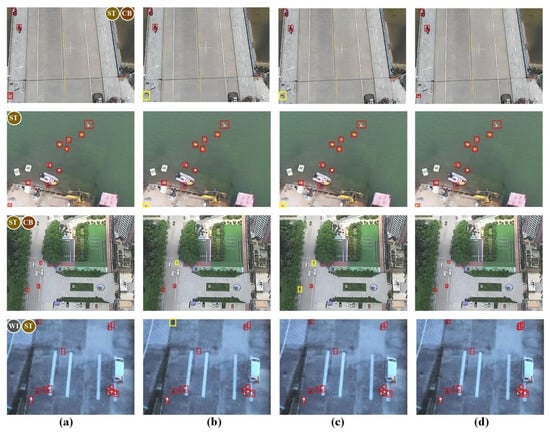

Figure 12.
Visualization results of different models on VTSaR. (a) Ground truth; (b) TFDet; (c) SuperYOLO*; and (d) PTANet. Ground-truth targets are shown in red and undetected targets in yellow. Scene types are labeled as ST (small targets), WI (low-light conditions), and CB (cluttered backgrounds).
PTANet showed fewer missed detections of small person targets than TFDet and SuperYOLO* under challenging conditions, such as complex backgrounds and low illumination. The number of yellow bounding boxes is significantly lower in the fourth column than in the second and third columns. This result demonstrates the effectiveness of the proposed PSAB and CMBM in progressively focusing on small person targets in drone-based images.
4.4. On Small Person Targets
To quantitatively evaluate the detection performance of PTANet on small person targets (with sizes smaller than 32 × 32), we report the corresponding mAP50 and mAP50:95 results across the three datasets in Table 4.

Table 4.
Performance of PTANet on small person targets.
As shown in Table 4, the proposed PTANet achieves high detection accuracy on small person targets across the three datasets, which demonstrates the robustness and effectiveness of our method. Furthermore, to make the results more convincing, we provide the PR curves of PTANet on the three datasets in Figure 13.
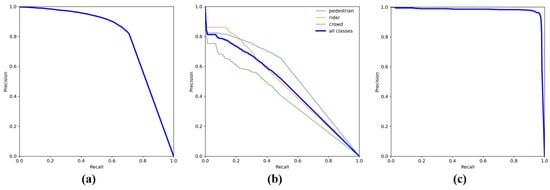
Figure 13.
Precison–Recall (PR) curves of PTANet for person detection on three datasets. (a) VTUAV-det. (b) RGBTDronePerson. (c) VTSaR.
In future work, we will conduct comparisons with state-of-the-art methods on the mAP50:95 metric for small person detection so as to more convincingly validate the effectiveness of our proposed approach.
4.5. On Different Postures of Persons
Unlike vehicle targets, person targets are non-rigid and often exhibit diverse postures (e.g., walking, riding, and sitting), which makes it more challenging for the model to learn their features effectively. While one of PTANet’s main motivations is to mitigate negative impacts from variations in person postures (e.g., walking, riding, and sitting), our current dataset does not provide explicit posture annotations. Therefore, we cannot provide quantitative posture-specific metrics. To partially address this, we present detection heatmaps in Figure 14, which visually demonstrate that PTANet robustly detects targets across different postures. These visualizations support the claim that the proposed feature extraction mechanism effectively handles posture variations in UAV-based RGB-T detection scenarios.
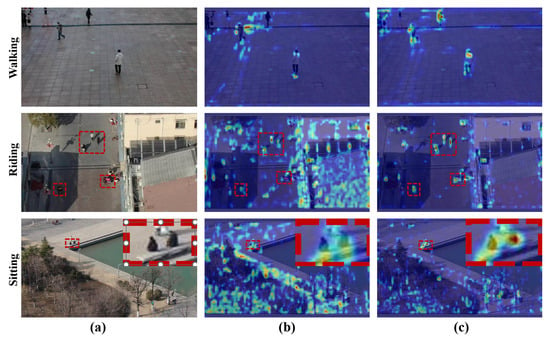
Figure 14.
Detection heatmaps for different postures of person. (a) Original images. (b) Heatmaps for the baseline model. (c) Heatmaps for the PTANet.
As shown in Figure 14, compared with the baseline model, the proposed PTANet demonstrates higher attention to person targets with varying postures in UAV-based remote sensing images and is less affected by background interference. This indicates that our model effectively mitigates the feature extraction challenges caused by variations in person target postures.
4.6. Statistical Significance Analysis
To assess the robustness of the reported improvements, we conducted three runs of each method with different random seeds and calculated the mean and standard deviation of key metrics. The results are shown in Table 5.

Table 5.
Statistical tests for PTANet.
As shown in Table 5, we repeated the key experiment with three different random seeds (0, 1, 2). The mAP50 scores obtained were 79.5%, 79.3% and 79.2%. The mean performance is 79.33% (±0.15% std), with a 95% confidence interval [78.95%, 79.71%]. These results show that the reported improvement is consistent across different seeds.
4.7. Deployment on Jetson Orin NX
The trained PTANet model with optimal weights was deployed on the Jetson Orin NX edge device to evaluate its performance on edge devices such as UAVs. The Jetson Orin NX board and its specifications are illustrated in Figure 15.
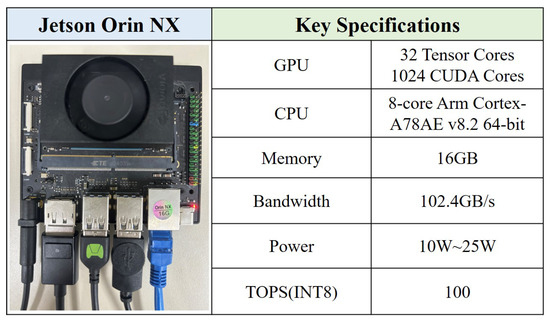
Figure 15.
Jetson Orin NX board and its hardware specifications.
We used the MAXN best performance mode on the board and TensorRT quantization tools to accelerate the model and perform FP16 and INT8 quantization. Table 6 presents the model sizes before and after quantization and the inference speed on the Jetson Orin NX for a single image with a size of 640 × 640.

Table 6.
Performance of PTANet on Jetson Orin NX.
The model size on the Jetson Orin NX edge device was 21.8 MB, and the inference time for a single 640 × 640 image was 16.707 ms before quantization. After applying FP16 quantization using TensorRT, the model size was reduced to 13.1 MB, and the inference time decreased to 12.539 ms. After quantization of the model parameters to INT8, the model size decreased to 8.4 MB, and the inference time for a single 640 × 640 image was 11.177 ms, corresponding to approximately 90 inferences per second. The proposed PTANet can achieve real-time person detection on edge devices, such as UAVs, for video streams at 30 fps or 60 fps with a resolution of 640 × 640.
4.8. Ablation Study
4.8.1. Quantitative Analysis
Table 7 presents the ablation results on the VTUAV-det and RGBTDronePerson datasets, illustrating the effectiveness of the GAFFM, PSAB, and CMBM when added individually or in pairs to the baseline. In the table, ✔ indicates that the corresponding module has been added.

Table 7.
Results of ablation study for modules in PTANet.
The baseline model achieved detection accuracies (mAP50) of 78.4% and 44.9% on the VTUAV-det and RGBTDronePerson datasets, respectively. After adding the GAFFM, PSAB, and CMBM modules, the detection accuracies on the VTUAV-det dataset improved to 78.9%, 78.5%, and 78.6%, corresponding to increases of 0.5%, 0.1%, and 0.2% over the baseline. On the RGBTDronePerson dataset, the detection accuracies increased to 45.1%, 45.1%, and 45.7%, representing improvements of 0.2%, 0.2%, and 0.8%, respectively. The effectiveness of the three modules is confirmed through their contribution to improved detection of small and variably posed persons in UAV images.
The pairwise combinations of modules resulted in greater improvements than the addition of a single module, except for the combination of the PSAB and CMBM on the VTUAV-det dataset, where the detection accuracy remained unchanged. This finding demonstrates the complementarity and compatibility among the proposed modules.
The baseline model with all three modules had an mAP50 of 79.5% on the VTUAV-det dataset, outperforming all pairwise combinations and providing a 1.1% improvement over the baseline. On the RGBTDronePerson dataset, the model’s mAP50 was 47.8%, surpassing all pairwise combinations and showing a 2.9% improvement over the baseline. The proposed PTANet had only 4.72 million parameters, which is only 0.64 million parameters more than the baseline’s 4.08 million. This result shows that the modules are lightweight and effective, making real-time person detection on UAVs and other edge devices feasible.
4.8.2. Qualitative Analysis
Figure 16 shows the heatmaps of prediction results before and after adding the modules individually on the VTUAV-det dataset.
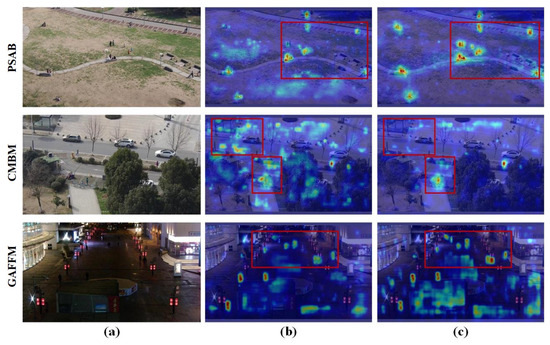
Figure 16.
Heatmaps of prediction results before and after adding modules. (a) Original images. (b) Heatmaps for the baseline model. (c) Heatmaps for the model after adding the modules.
After adding the PSAB to the baseline model, the network focused significantly more on the person targets in the red boxes. This result demonstrates that the PSAB improved the model’s focus on small person targets, validating the module’s effectiveness. After incorporating the CMBM into the baseline, the model’s attention to the complex background areas inside the red boxes decreased significantly, lowering the false positive rate caused by confusing background objects with person targets. After adding the GAFFM to the baseline, the model’s attention to person targets in low-illumination scenarios (highlighted by the red boxes) improved, indicating high detection performance under low-light conditions and confirming the module’s effectiveness.
However, as shown in the third row of Figure 16, the GAFFM sometimes enhances irrelevant background regions. This occurs because the GAFFM is a global adaptive feature fusion module designed to emphasize object features, and weak background responses are an inevitable side effect of attention mechanisms. To address this, our method adopts a progressive target-aware strategy: after the GAFFM, the PSAB and CMBM modules are applied to further concentrate on small person targets while effectively suppressing background interference in the visible branch feature maps.
5. Discussion
In this section, we provide a thorough discussion of the robustness and effectiveness of the three modules in the proposed PTANet.
5.1. Sensitivity Analysis of GAFFM and Its Variants
To validate the effectiveness and robustness of the proposed GAFFM module, we conducted a series of comparative experiments as follows.
Add: Adding visible and thermal features as input to the self-attention mechanism.
Concat: Concatenating visible and thermal features followed by dimensionality reduction before feeding them into the self-attention mechanism.
Swapping Q and K sources: We tested generating Q from thermal features and K from visible features while keeping V unchanged.
Symmetric cross-attention: Instead of using a directed Q/K assignment, we allowed both visible and thermal features to serve as queries, keys, and values simultaneously, enforcing a fully symmetric interaction.
Multi-scale tokens: During training, we downsampled the GAFFM input feature maps at different resolutions (80 × 80, 40 × 40, and 20 × 20) into a consistent set of multi-scale tokens (32 × 32, 16 × 16, and 8 × 8). This setting attempts to retain more contextual information from large-scale feature maps while still benefiting from multi-level tokenization.
The results are shown in Table 8.

Table 8.
Performance comparison of GAFFM variants.
As shown in Table 8, compared to two typical transformer-based fusion approaches, Add and Concat, GAFFM consistently outperforms these baselines in terms of mAP50, mAP50:95. Swapping Q and K results in only a minor difference in mAP50 (+0.1%), indicating that the model is relatively robust to this modification. Symmetric cross-attention slightly improves mAP50 (78.9% → 79.2%) but significantly increases GFLOPs (29.2 → 42.1), indicating higher computational cost without substantial gain. Multi-scale tokenization further improves performance (mAP50: 79.3%, mAP50:95: 40.8%) with only a minor increase in parameters and computation. These results confirm that our directed GAFFM design achieves a good balance between accuracy and efficiency, while multi-scale tokenization offers additional potential for future work.
5.2. Robustness of Target Mask Generation in the PSAB Module
To investigate the effect of mask quality, we implemented several variants of the PSAB mask: (1) Boundary relaxation/erosion: enlarging or shrinking the ground-truth bounding box by one tenth of its original width and height, respectively, to generate the corresponding ground-truth masks. (2) Gaussian center heatmap: a circular ground-truth mask generated by placing a 2D Gaussian distribution at the bounding box center. Figure 17 presents target masks generated using different strategies.
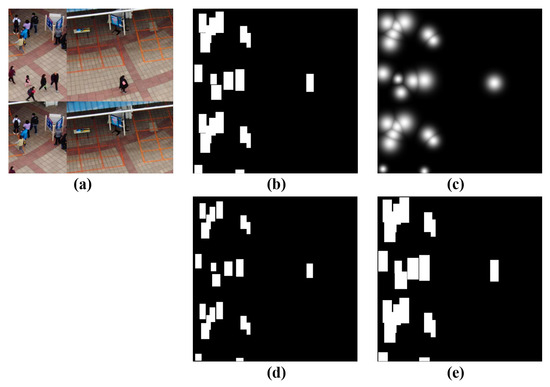
Figure 17.
Examples of target masks generated by different approaches. (a) Original image. (b) Box-driven mask. (c) Gaussian center heatmap. (d) Boundary erosion. (e) Boundary relaxation.
As shown in Figure 17, compared with the box-driven approach, the Gaussian-based center heatmap mask introduces less background information but inevitably loses the shape characteristics of the person targets. In contrast, the boundary relaxation or erosion strategies are extensions of the box-driven method, introducing either more or less background information depending on the scaling direction.
To further evaluate the impact of different target mask generation strategies, we performed comparative experiments on the VTUAV-det dataset, with the results summarized in Table 9.

Table 9.
Performance using different forms of target masks on the VTUAV-det dataset.
As shown in Table 9, using a Gaussian center heatmap to generate target masks leads to lower performance than our box-driven design, since the shape information of the person targets is largely lost. For boundary relaxation, the ground-truth boxes are expanded by one tenth in both height and width, which introduces excessive background information and thus degrades detection accuracy. Boundary erosion, in contrast, shrinks the ground-truth boxes by one tenth, reducing background noise but inevitably discarding part of the target information. Although boundary erosion slightly improves mAP50, its mAP50:95 remains lower than that of the box-driven mask. Therefore, we keep the box-driven mask as the default design in our framework due to its superior balance between accuracy and stability.
In addition, the designed PSAB is only involved during the training phase. The masks generated from ground-truth bounding boxes are solely used to guide parameter optimization at this stage. During inference, all parameters remain fixed, and no ground-truth bounding boxes are required. Therefore, the proposed PTANet is completely independent of ground-truth information in the inference phase.
5.3. Quantitative Analysis of CMBM Robustness Under Different Conditions
To quantify the CMBM’s behavior under realistic conditions, we conducted targeted inference experiments: morphological post-processing (opening/closing), local (windowed) Otsu thresholding, RGB channel switching (R/G/B), and simulated registration errors (thermal image translated by +4 pixels). The results are summarized in Table 10 below.

Table 10.
Performance of CMBM under perturbations and alignment errors.
These results indicate that morphological post-processing and adaptive thresholding can effectively maintain accuracy under local lighting or thermal saturation, with negligible latency overhead (0.5 ms/frame). RGB channel switching does not significantly affect the index calculation, demonstrating robustness to visible band variations. Small misregistration (4 px shift) only causes a minor drop (0.1 mAP50), suggesting that the CMBM is tolerant to modest alignment errors. Overall, these findings confirm that the proposed CMBM is efficient and robust in realistic UAV deployment scenarios.
6. Conclusions
This paper proposed PTANet, a progressive target-aware network for person detection in UAV imagery. It addresses the challenges of detecting persons with varied postures and covering a small number of pixels in UAV images, which complicate feature extraction. The model utilizes the GAFFM to improve the fusion of color and texture features from visible images and thermal features from thermal images, increasing the detection rates of persons under low-light conditions. PTANet utilizes the PSAB during training and the CMBM during inference to enhance model attention progressively on persons by focusing on the targets and suppressing background information. Unlike other cross-modality person detection models designed for vehicle-mounted or surveillance applications, PTANet is tailored to the characteristics of person targets in a UAV. It achieved superior detection performance on three UAV remote sensing datasets: VTUAV-det, RGBTDronePerson, and VTSaR. PTANet provided the highest detection accuracy with the lowest parameter count and computational complexity among comparable RGB-T fusion methods, making it more suitable for onboard real-time deployment. Moreover, after acceleration and INT8 quantization using TensorRT on the Jetson Orin NX platform, PTANet achieved an inference time of 11.177 ms for a 640 × 640 image, demonstrating its efficiency for real-time onboard person detection.
Although the proposed PTANet provided excellent performance, several areas require improvement. Directions for future research include improving the detection performance for very small targets in the RGBTDronePerson dataset, developing more effective fusion strategies for cases with strong misalignment between RGB-T modalities, and extending the proposed framework to multi-class detection and broader remote sensing applications to further evaluate its generalization ability.
Author Contributions
Z.H. and B.Z. created and designed the framework. Z.H. performed the algorithm on Pytorch. Z.H., B.Z., Y.W., Y.J. and Q.Z. wrote the paper. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China under Grant 2021YFA0715203, the Science and Disruptive Technology Program, AIRCAS, under Grant 2024-AIRCAS-SDTP-12, and the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants 62001455 and 41871245.
Data Availability Statement
The codes are available at https://github.com/Hzp1231/PTANet, accessed on 1 October 2025.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Huang, X. The small-drone revolution is coming—Scientists need to ensure it will be safe. Nature 2025, 637, 29–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bing, Z. Current Status and Future Prospects of Remote Sensing. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2017, 32, 774–784. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Guan, X.; Zhao, B.; Ni, L.; Huang, M. Vehicle detection based on adaptive multimodal feature fusion and cross-modal vehicle index using RGB-T images. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 8166–8177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Li, T.; Peng, D. Aerial image object detection based on RGB-Infrared multi-branch progressive fusion. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 5402714. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, C.; Yang, W.; He, G.; Yu, H.; Yu, L.; Xia, G.S. Drone-based RGBT tiny person detection. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2023, 204, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Feng, Y.; Wang, N.; Lu, G.; Mei, S. Aerial Person Detection for Search and Rescue: Survey and Benchmarks. J. Remote Sens. 2025, 2025, 0474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Cao, B.; Zhu, P.; Hu, Q. Drone-based RGB-infrared cross-modality vehicle detection via uncertainty-aware learning. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2022, 32, 6700–6713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondi, E.; Jain, R.; Aggrawal, P.; Anand, S.; Hannaford, R.; Kapoor, A.; Piavis, J.; Shah, S.; Joppa, L.; Dilkina, B.; et al. BIRDSAI: A dataset for detection and tracking in aerial thermal infrared videos. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Snowmass Village, CO, USA, 1–5 March 2020; pp. 1747–1756. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Feng, Y.; Wang, N.; Lu, G.; Mei, S. Transformer-based Person Detection in Paired RGB-T Aerial Images with VTSaR Dataset. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2025, 18, 5082–5099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Ghiasi, G.; Cui, Y.; Srinivas, A.; Qian, R.; Lin, T.Y.; Cubuk, E.D.; Le, Q.V.; Zoph, B. Simple copy-paste is a strong data augmentation method for instance segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Virtual, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 2918–2928. [Google Scholar]
- Bochkovskiy, A.; Wang, C.Y.; Liao, H.Y.M. Yolov4: Optimal speed and accuracy of object detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.10934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, J.; Fischer, V.; Herman, M.; Behnke, S. Multispectral pedestrian detection using deep fusion convolutional neural Networks. In Proceedings of the ESANN, Bruges, Belgium, 27–29 April 2016; Volume 587, pp. 509–514. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, S.; Metaxas, D.N. Multispectral deep neural networks for pedestrian detection. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1611.02644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, D.; Cao, Y.; Yang, J.; Cao, Y.; Yang, M.Y. Fusion of multispectral data through illumination-aware deep neural networks for pedestrian detection. Inf. Fusion 2019, 50, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Cheng, T.Y.; Dai, Z.; Tran, V.; Trigoni, N.; Markham, A. Illumination-Aware Hallucination-Based Domain Adaptation for Thermal Pedestrian Detection. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 25, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, H.; He, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, W. Illumination-guided RGBT object detection with inter-and intra-modality fusion. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 2508013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Qian, Y.; Zhu, H.; Wang, C.; Yang, M. BAANet: Learning bi-directional adaptive attention gates for multispectral pedestrian detection. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 23–27 May 2022; pp. 2920–2926. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, R.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Yao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Song, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhao, Y. PedDet: Adaptive Spectral Optimization for Multimodal Pedestrian Detection. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.14063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qingyun, F.; Zhaokui, W. Cross-modality attentive feature fusion for object detection in multispectral remote sensing imagery. Pattern Recognit. 2022, 130, 108786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Chen, L.; Cao, X. Improving multispectral pedestrian detection by addressing modality imbalance problems. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 787–803. [Google Scholar]
- Qingyun, F.; Dapeng, H.; Zhaokui, W. Cross-modality fusion transformer for multispectral object detection. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.00273. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, M.; Wei, X. C 2 former: Calibrated and complementary transformer for rgb-infrared object detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5403712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, S.; Wang, S.; Ma, H. Cross Teaching-Enhanced Multi-Spectral Remote Sensing Object Detection with Transformer. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 18, 2401–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheini, M.; Ren, X.; May, J. Cross-attention is all you need: Adapting pretrained transformers for machine translation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.08771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Hu, Q.; Yao, Y.; Yang, K.; Chen, P. CFMW: Cross-modality Fusion Mamba for Multispectral Object Detection under Adverse Weather Conditions. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.16302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Ma, X.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, Y. COMO: Cross-Mamba Interaction and Offset-Guided Fusion for Multimodal Object Detection. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2412.18076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Wang, D.; Hu, Z.; Li, S.; Ni, W.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Q. FD2-Net: Frequency-Driven Feature Decomposition Network for Infrared-Visible Object Detection. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2412.09258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, C.; Yang, W.; Yu, L. A normalized Gaussian Wasserstein distance for tiny object detection. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.13389. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Zeng, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, J.; Chang, Y.; Wang, F. RSDS: A Specialized Loss Calculation Method for Dense Small Object Detection in Remote Sensing Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 4211817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liu, S.; Wu, J.; Su, X.; Hai, N.; Huang, X. Pinwheel-shaped Convolution and Scale-based Dynamic Loss for Infrared Small Target Detection. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2412.16986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ye, M.; Zhu, G.; Liu, Y.; Guo, P.; Yan, J. FFCA-YOLO for small object detection in remote sensing images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5611215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Yao, L.; Zhang, C.; Wu, T.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, X.; Zhou, J. Boost UAV-based Object Detection via Scale-Invariant Feature Disentanglement and Adversarial Learning. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 5622113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Lyu, S.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Q. TPH-YOLOv5: Improved YOLOv5 based on transformer prediction head for object detection on drone-captured scenarios. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 2778–2788. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Zhang, K.; Wang, X.; Wang, N.; Gao, X. An Adaptive Region Proposal Network with Progressive Attention Propagation for Tiny Person Detection from UAV Images. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2023, 34, 4392–4406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhao, R.; Wang, Z.; Xu, H.; Zhu, X. Remdet: Rethinking efficient model design for uav object detection. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 25 February–4 March 2025; Volume 39, pp. 4643–4651. [Google Scholar]
- Akshatha, K.; Karunakar, A.; Shenoy, S.; Dhareshwar, C.V.; Johnson, D.G. Manipal-UAV person detection dataset: A step towards benchmarking dataset and algorithms for small object detection. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2023, 195, 77–89. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Yang, W.; Guo, H.; Zhang, R.; Xia, G.S. Tiny object detection in aerial images. In Proceedings of the 2020 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Milan, Italy, 10–15 January 2021; pp. 3791–3798. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, P.; Wen, L.; Bian, X.; Ling, H.; Hu, Q. Vision meets drones: A challenge. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.07437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razakarivony, S.; Jurie, F. Vehicle detection in aerial imagery: A small target detection benchmark. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2016, 34, 187–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, X.; Xiao, C.; An, W.; Li, R.; He, X.; Li, B.; Cao, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Hu, M. Visible-thermal tiny object detection: A benchmark dataset and baselines. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2025, 47, 6088–6096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, L.; Liu, F.; Xu, S.; Zhang, C.; Ma, X.; Jiang, J.; Wang, Z.; Di, S.; Zhou, J. UEMM-Air: Make Unmanned Aerial Vehicles Perform More Multi-modal Tasks. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.06230. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Zhao, J.; Wang, D.; Lu, H.; Ruan, X. Visible-thermal UAV tracking: A large-scale benchmark and new baseline. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 8886–8895. [Google Scholar]
- Jocher, G.; Qiu, J.; Chaurasia, A. Ultralytics YOLO (Version 8.0.0). 2023. Available online: https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/tree/main/ultralytics/cfg/models/v8 (accessed on 1 October 2025).
- Robbins, H.; Monro, S. A stochastic approximation method. Ann. Math. Stat. 1951, 22, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neubeck, A.; Van Gool, L. Efficient non-maximum suppression. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR’06), Hong Kong, China, 20–24 August 2006; Volume 3, pp. 850–855. [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-cam: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 618–626. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 740–755. [Google Scholar]
- Emara, T.; Abd El Munim, H.E.; Abbas, H.M. LiteSeg: A Novel Lightweight ConvNet for Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2019 Digital Image Computing: Techniques and Applications (DICTA), Perth, WA, Australia, 2–4 December 2019; Volume 10. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, Y.; Pan, H.; Sun, W.; Jia, Y. Deep dual-resolution networks for real-time and accurate semantic segmentation of road scenes. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2101.06085. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Sheng, Z.; Shen, H.L. FocusNet: Classifying better by focusing on confusing classes. Pattern Recognit. 2022, 129, 108709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milletari, F.; Navab, N.; Ahmadi, S.A. V-net: Fully convolutional neural networks for volumetric medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2016 Fourth International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), Stanford, CA, USA, 25–28 October 2016; pp. 565–571. [Google Scholar]
- Otsu, N. A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. Automatica 1975, 11, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jocher, G.; Stoken, A.; Borovec, J.; Changyu, L.; Hogan, A.; Diaconu, L.; Poznanski, J.; Yu, L.; Rai, P.; Ferriday, R. ultralytics/yolov5: v3.0. Zenodo. 2020. Available online: https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2020zndo...3983579J/abstract (accessed on 1 October 2025).
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.Y.; Berg, A.C. Ssd: Single shot multibox detector. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. In Proceedings of the Neural Information Processing Systems, New Orleans, LA, USA, 10–16 December 2015; Volume 28. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Lei, J.; Xie, W.; Fang, Z.; Li, Y.; Du, Q. SuperYOLO: Super resolution assisted object detection in multimodal remote sensing imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5605415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Ying, J.; Sheng, Z.; Yu, H.; Li, C.; Shen, H.L. Tfdet: Target-aware fusion for rgb-t pedestrian detection. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2024, 36, 13276–13290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).